What week is ectopic pregnancy detected
Ectopic pregnancy - NHS
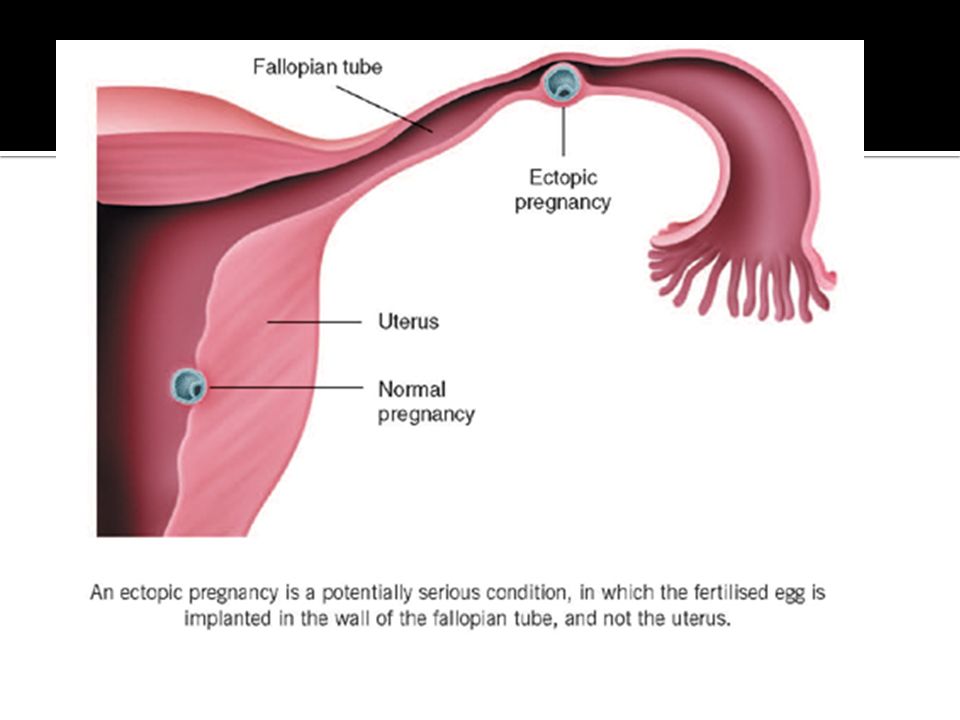
An ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilised egg implants itself outside of the womb, usually in one of the fallopian tubes.
The fallopian tubes are the tubes connecting the ovaries to the womb. If an egg gets stuck in them, it won't develop into a baby and your health may be at risk if the pregnancy continues.
Unfortunately, it's not possible to save the pregnancy. It usually has to be removed using medicine or an operation.
In the UK, around 1 in every 90 pregnancies is ectopic. This is around 11,000 pregnancies a year.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy doesn't always cause symptoms and may only be detected during a routine pregnancy scan.
If you do have symptoms, they tend to develop between the 4th and 12th week of pregnancy.
Symptoms can include a combination of:
- a missed period and other signs of pregnancy
- tummy pain low down on one side
- vaginal bleeding or a brown watery discharge
- pain in the tip of your shoulder
- discomfort when peeing or pooing
But these symptoms aren't necessarily a sign of a serious problem. They can sometimes be caused by other problems, such as a stomach bug.
Read more about the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy.
When to get medical advice
Contact your GP or call NHS 111 if you have a combination of any of the above symptoms and you might be pregnant – even if you haven't had a positive pregnancy test.
An ectopic pregnancy can be serious, so it's important to get advice right away.
Your GP will ask about your symptoms and you'll usually need to do a pregnancy test to determine if you could have an ectopic pregnancy.
You may be referred to a specialist early pregnancy clinic for further assessment, where an ultrasound scan and blood tests may be carried out to confirm the diagnosis.
Read more about ectopic pregnancy tests.
When to get emergency help
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest accident and emergency (A&E) department immediately if you experience a combination of:
- a sharp, sudden and intense pain in your tummy
- feeling very dizzy or fainting
- feeling sick
- looking very pale
These symptoms could mean that your fallopian tube has split open (ruptured).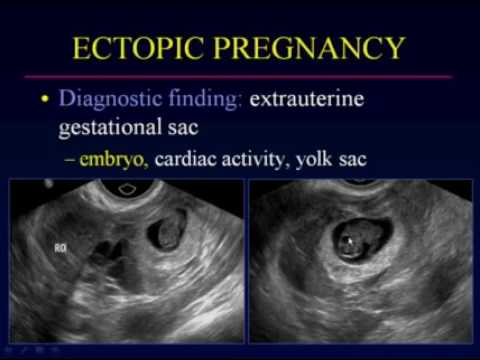 This is very serious and surgery to repair the fallopian tube needs to be carried out as soon as possible.
This is very serious and surgery to repair the fallopian tube needs to be carried out as soon as possible.
A rupture can be life threatening, but fortunately they're uncommon and treatable, if dealt with quickly. Deaths from ruptures are extremely rare in the UK.
How an ectopic pregnancy is treated
There are 3 main treatments for an ectopic pregnancy:
- expectant management – you're carefully monitored and 1 of the treatments below is used if the fertilised egg doesn't dissolve by itself
- medicine – an injection of a powerful medicine called methotrexate is used to stop the pregnancy growing
- surgery – keyhole surgery (laparoscopy) is performed under general anaesthetic to remove the fertilised egg, usually along with the affected fallopian tube
You'll be told about the benefits and risks of each option. In many cases, a particular treatment will be recommended based on your symptoms and the results of the tests you have.
In many cases, a particular treatment will be recommended based on your symptoms and the results of the tests you have.
Some treatments may reduce your chances of being able to conceive naturally in the future, although most women will still be able to get pregnant. Talk to your doctor about this.
Read more about treating an ectopic pregnancy.
Help and support after an ectopic pregnancy
Losing a pregnancy can be devastating, and many women feel the same sense of grief as if they had lost a family member or partner.
It's not uncommon for these feelings to last several months, although they usually improve with time. Make sure you give yourself and your partner time to grieve.
If you or your partner are struggling to come to terms with your loss, you may benefit from professional support or counselling. Speak to your GP about this.
Speak to your GP about this.
Support groups for people who have been affected by loss of a pregnancy can also help.
These include:
- The Ectopic Pregnancy Trust
- Ectopic Pregnancy Foundation
- Miscarriage Association
- Cruse Bereavement Care
Read more about dealing with loss and find bereavement support services in your area.
Trying for another baby
You may want to try for another baby when you and your partner feel physically and emotionally ready.
You'll probably be advised to wait until you've had at least 2 periods after treatment before trying again to allow yourself to recover.
If you were treated with methotrexate, it's usually recommended that you wait at least 3 months because the medicine could harm your baby if you become pregnant during this time.
Most women who have had an ectopic pregnancy will be able to get pregnant again, even if they've had a fallopian tube removed. Occasionally, it may be necessary to use fertility treatment such as IVF.
The chances of having another ectopic pregnancy are higher if you've had one before, but the risk is still small.
If you do become pregnant again, it's a good idea to let your GP know as soon as possible so early scans can be carried out to check everything is OK.
What can cause an ectopic pregnancy?
In many cases, it's not clear why a woman has an ectopic pregnancy. Sometimes it happens when there's a problem with the fallopian tubes, such as them being narrow or blocked.
The following are all associated with an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy:
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) – inflammation of the female reproductive system, usually caused by a sexually transmitted infection (STI)
- previous ectopic pregnancy – the risk of having another ectopic pregnancy is around 10%
- previous surgery on your fallopian tubes – such as an unsuccessful female sterilisation procedure
- fertility treatment, such as IVF – taking medicine to stimulate ovulation (the release of an egg) can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy
- becoming pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) or intrauterine system (IUS) for contraception – it's rare to get pregnant while using these, but if you do you're more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy
- smoking
- increasing age – the risk is highest for pregnant women aged over 35
You can't always prevent an ectopic pregnancy, but you can reduce your risk by using a condom when not trying for a baby to protect yourself against STIs, and by stopping smoking if you smoke.
Page last reviewed: 23 August 2022
Next review due: 23 August 2025
Ectopic pregnancy - Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis
A pelvic exam can help your doctor identify areas of pain, tenderness, or a mass in the fallopian tube or ovary. However, your doctor can't diagnose an ectopic pregnancy by examining you. You'll need blood tests and an ultrasound.
Pregnancy test
Your doctor will order the human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) blood test to confirm that you're pregnant. Levels of this hormone increase during pregnancy. This blood test may be repeated every few days until ultrasound testing can confirm or rule out an ectopic pregnancy — usually about five to six weeks after conception.
Ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasound
During a transvaginal ultrasound, you lie on an exam table while a health care provider or a medical technician puts a wandlike device, known as a transducer, into the vagina.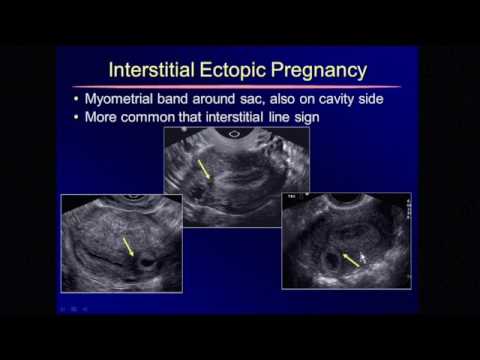 Sound waves from the transducer create images of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Sound waves from the transducer create images of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes.
A transvaginal ultrasound allows your doctor to see the exact location of your pregnancy. For this test, a wandlike device is placed into your vagina. It uses sound waves to create images of your uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes, and sends the pictures to a nearby monitor.
Abdominal ultrasound, in which an ultrasound wand is moved over your belly, may be used to confirm your pregnancy or evaluate for internal bleeding.
Other blood tests
A complete blood count will be done to check for anemia or other signs of blood loss. If you're diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy, your doctor may also order tests to check your blood type in case you need a transfusion.
More Information
- Ultrasound
Treatment
A fertilized egg can't develop normally outside the uterus. To prevent life-threatening complications, the ectopic tissue needs to be removed. Depending on your symptoms and when the ectopic pregnancy is discovered, this may be done using medication, laparoscopic surgery or abdominal surgery.
Depending on your symptoms and when the ectopic pregnancy is discovered, this may be done using medication, laparoscopic surgery or abdominal surgery.
Medication
An early ectopic pregnancy without unstable bleeding is most often treated with a medication called methotrexate, which stops cell growth and dissolves existing cells. The medication is given by injection. It's very important that the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is certain before receiving this treatment.
After the injection, your doctor will order another HCG test to determine how well treatment is working, and if you need more medication.
Laparoscopic procedures
Salpingostomy and salpingectomy are two laparoscopic surgeries used to treat some ectopic pregnancies. In these procedure, a small incision is made in the abdomen, near or in the navel. Next, your doctor uses a thin tube equipped with a camera lens and light (laparoscope) to view the tubal area.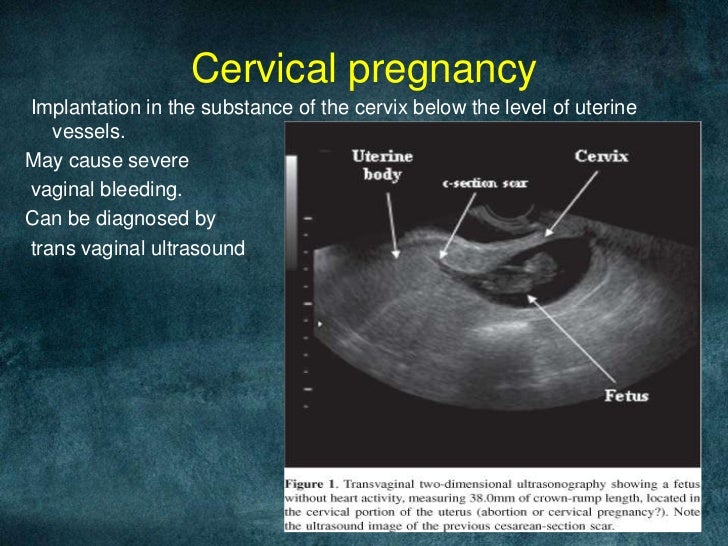
In a salpingostomy, the ectopic pregnancy is removed and the tube left to heal on its own. In a salpingectomy, the ectopic pregnancy and the tube are both removed.
Which procedure you have depends on the amount of bleeding and damage and whether the tube has ruptured. Also a factor is whether your other fallopian tube is normal or shows signs of prior damage.
Emergency surgery
If the ectopic pregnancy is causing heavy bleeding, you might need emergency surgery. This can be done laparoscopically or through an abdominal incision (laparotomy). In some cases, the fallopian tube can be saved. Typically, however, a ruptured tube must be removed.
Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free, and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips and current health topics, like COVID-19, plus expertise on managing health.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which
information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with
other information we have about you.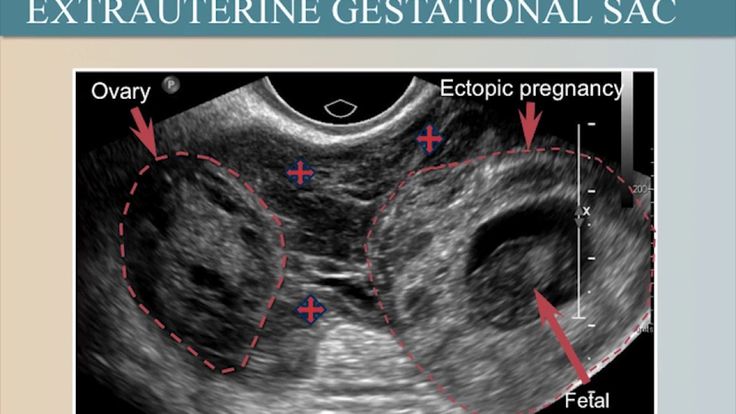 If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could
include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected
health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health
information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of
privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on
the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could
include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected
health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health
information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of
privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on
the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Coping and support
Losing a pregnancy is devastating, even if you've only known about it for a short time. Recognize the loss, and give yourself time to grieve. Talk about your feelings and allow yourself to experience them fully.
Rely on your partner, loved ones and friends for support. You might also seek the help of a support group, grief counselor or other mental health provider.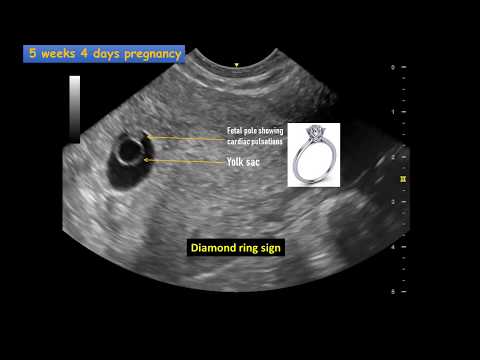
Many women who have an ectopic pregnancy go on to have a future, healthy pregnancy. The female body normally has two fallopian tubes. If one is damaged or removed, an egg may join with a sperm in the other tube and then travel to the uterus.
If both fallopian tubes have been injured or removed, in vitro fertilization (IVF) might still be an option. With this procedure, mature eggs are fertilized in a lab and then implanted into the uterus.
If you've had an ectopic pregnancy, your risk of having another one is increased. If you wish to try to get pregnant again, it's very important to see your doctor regularly. Early blood tests are recommended for all women who've had an ectopic pregnancy. Blood tests and ultrasound testing can alert your doctor if another ectopic pregnancy is developing.
Preparing for your appointment
Call your doctor's office if you have light vaginal bleeding or slight abdominal pain. The doctor might recommend an office visit or immediate medical care.
However, emergency medical help is needed if you develop these warning signs or symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy:
- Severe abdominal or pelvic pain accompanied by vaginal bleeding
- Extreme lightheadedness
- Fainting
Call 911 (or your local emergency number) or go to the hospital if you have the above symptoms.
What you can do
It can be helpful to jot down your questions for the doctor before your visit. Here are some questions you might want to ask your doctor:
- What kinds of tests do I need?
- What are the treatment options?
- What are my chances of having a healthy pregnancy in the future?
- How long should I wait before trying to become pregnant again?
- Will I need to follow any special precautions if I become pregnant again?
In addition to your prepared questions, don't hesitate to ask questions anytime you don't understand something. Ask a loved one or friend to come with you, if possible. Sometimes it can be difficult to remember all of the information provided, especially in an emergency situation.
Sometimes it can be difficult to remember all of the information provided, especially in an emergency situation.
What to expect from your doctor
If you don't require emergency treatment and haven't yet been diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy, your doctor will talk to you about medical history and symptoms. You'll be asked many questions about your menstrual cycle, fertility and overall health.
Menstruation
- When was your last period?
- Did you notice anything unusual about it?
Pregnancy
- Could you be pregnant?
- Have you taken a pregnancy test? If so, was the test positive?
- Have you been pregnant before? If so, what was the outcome of each pregnancy?
- Have you ever had fertility treatments?
- Do you plan to become pregnant in the future?
Symptoms
- Are you in pain? If so, where does it hurt?
- Do you have vaginal bleeding? If so, is it more or less than your typical period?
- Are you lightheaded or dizzy?
Health history
- Have you ever had reproductive surgery, including getting your tubes tied (or a reversal)?
- Have you had a sexually transmitted infection?
- Are you being treated for any other medical conditions?
- What medications do you take?
By Mayo Clinic Staff
Related
Associated Procedures
Products & Services
Ectopic pregnancy - early signs, first manifestations
home
Articles
Signs of an ectopic pregnancy.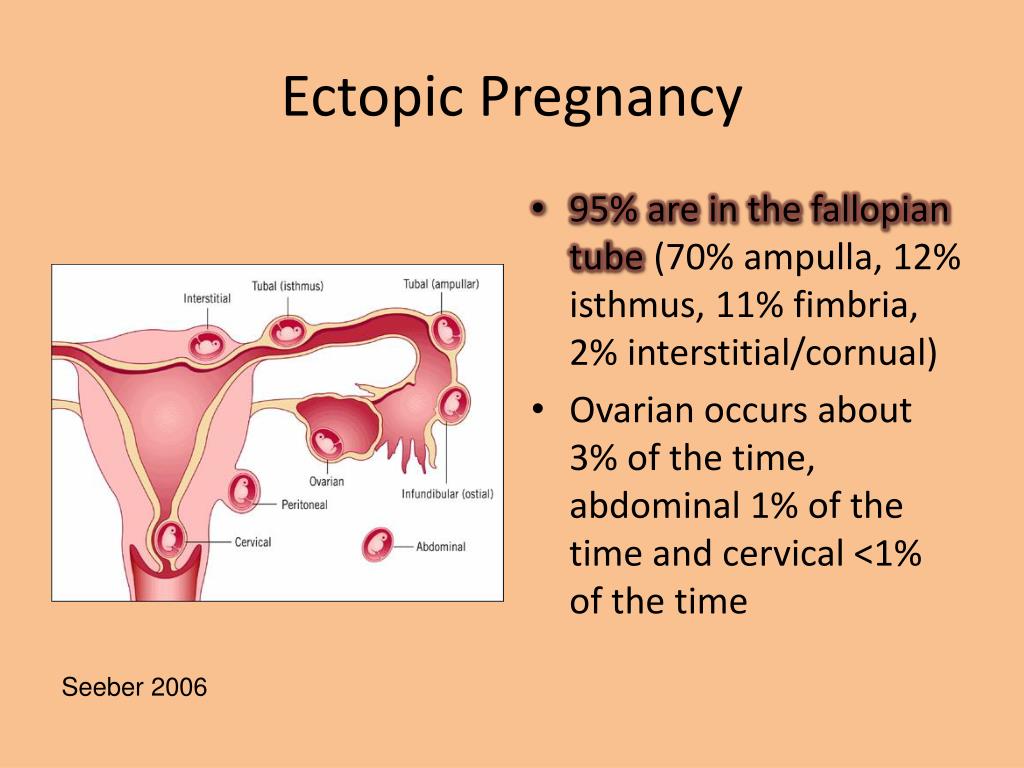 How not to miss the pathology
How not to miss the pathology
August 06, 2019
Ectopic or ectopic pregnancy is an atypical course of pregnancy in which implantation and development of the fetal egg occur outside the uterus, for example, in the abdominal cavity, ovary, cervix, fallopian tube.
According to the latest statistics, ectopic pregnancy accounts for approximately 2% of all pregnancies. At the same time, tubal ectopic pregnancy is most often diagnosed.
Ectopic pregnancy threatens with serious complications - rupture of the fetal egg and peritonitis, recurrence of ectopic pregnancy, infertility. Often it is a threat to a woman's life and, as statistics show, in 3% of all cases it ends in death. Therefore, it is very important to be able to recognize the first signs of an ectopic pregnancy in time.
Further in the article, we will analyze in detail at what time an ectopic pregnancy can manifest itself, its signs in early and late terms, as well as on ultrasound.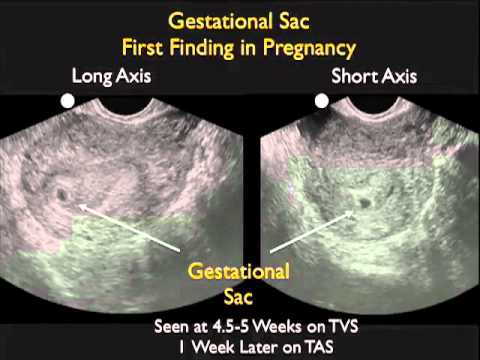
How an ectopic pregnancy manifests itself: the first signs
Given all of the above, it is very important to know how an ectopic pregnancy manifests itself. Timely diagnosis of this pathology will help to avoid complications, and in some cases even save the life of a woman.
In the early stages, women can often ignore unusual symptoms and believe that this is how a normal pregnancy should proceed.
Indeed, as the ovum develops, even with an ectopic pregnancy, a woman may show signs of a normal pregnancy, namely:
- Absence of menses
- Increase in basal body temperature
- Breast engorgement
- Nausea, vomiting
However, along with these symptoms, the first signs of an ectopic pregnancy appear, which should alert. So how does an ectopic pregnancy manifest itself?
The following symptoms may indicate an atypical pregnancy:
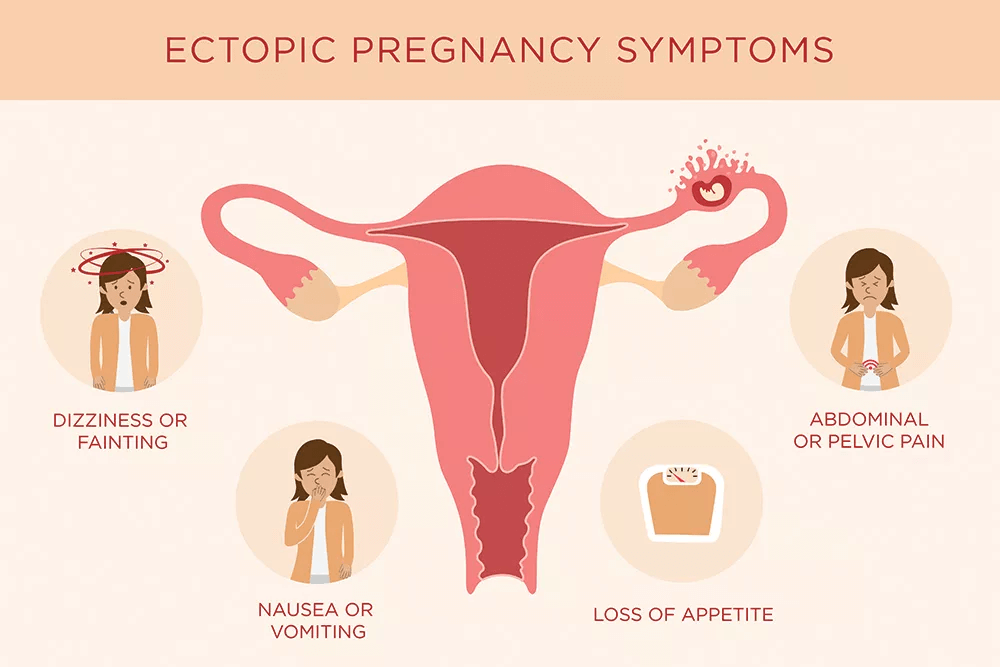
- Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen, aching, pulling pains in the location of the fetal egg, or in the lower abdomen, mainly on one side - the very first signs of an ectopic pregnancy.
 Pain may increase during urination or defecation.
Pain may increase during urination or defecation. - Scanty bloody, spotting discharge that usually lasts a long time. In rare cases, uterine bleeding, or profuse spotting, resembling menstruation, is observed.
- With severe blood loss in the early stages, signs of shock may occur, namely, pale skin, tachycardia, drop in blood pressure, loss of consciousness.
How long can an ectopic pregnancy appear
The timing when the first signs of an ectopic pregnancy appear is individual in each case. In some women, an ectopic pregnancy can be asymptomatic right up to the development of complications, while in others, adverse symptoms can be noticed already from the first weeks of pregnancy.
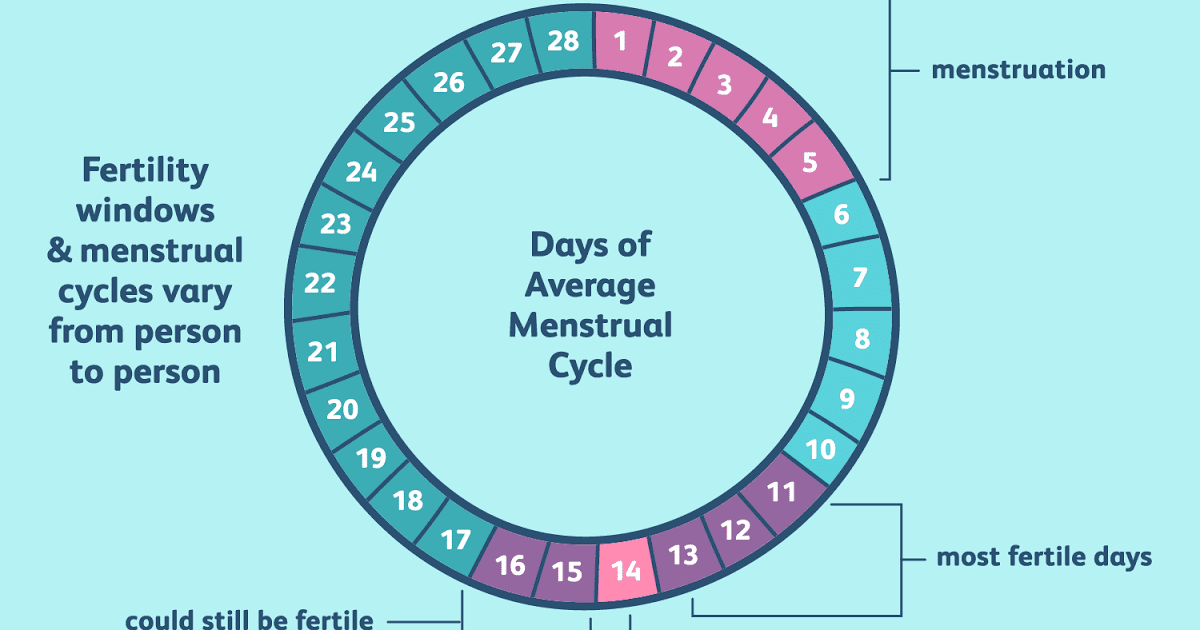
Usually, the first signs appear with an increase in the size of the fetal egg. Therefore, at what time an ectopic pregnancy appears can be established using ultrasound. Usually, a fetal egg is visualized at a period of 4.5-5 weeks of pregnancy.
The average time for an ectopic pregnancy to appear is 3 to 8 weeks. It is during this period that the highest risk of adverse symptoms!
It is during this period that the highest risk of adverse symptoms!
What are the signs of an ectopic pregnancy at a later date
If you ignore the first signs of an ectopic pregnancy, the risk of complications increases significantly. An ectopic pregnancy can have two outcomes - abortion, or rupture of the fallopian tube, or another organ in which the fetal egg has attached.
In the first case, with an ectopic pregnancy, the signs include intense pain, pain in the posterior vaginal fornix, and bleeding. With intense bleeding, symptoms of shock may appear - a decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia, a weak rapid pulse, shallow breathing, weakness, loss of consciousness.
Signs in case of rupture of the fallopian tube resemble those of ovarian apoplexy. Life-threatening internal bleeding develops, acute, dagger pain in the lower abdomen occurs, which can radiate to the perineum and anus, symptoms of shock are expressed. This condition requires immediate hospitalization!
Signs of ectopic pregnancy on ultrasound
With such a pathology as an ectopic pregnancy, ultrasound signs can be determined at about 4. 5-5 weeks of pregnancy. Usually, ultrasound does not allow to detect a fetal egg outside the uterus, so they are guided by other signs.
5-5 weeks of pregnancy. Usually, ultrasound does not allow to detect a fetal egg outside the uterus, so they are guided by other signs.
Ectopic pregnancy findings on ultrasound include the following:
- Absence of a fertilized egg in the uterus
- The presence of an inhomogeneous mass in the area of the appendages on one side
- Abdominal fluid
Only ultrasound can confirm the diagnosis of pathological pregnancy. Therefore, you should not engage in self-diagnosis and, if the first adverse symptoms appear, immediately consult a doctor!
Ectopic pregnancy - signs, causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Ectopic pregnancy
Table of contents
- What is an ectopic pregnancy and how does it develop?
- Signs and symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
- Causes of an ectopic pregnancy
- Diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy
- Treatment of an ectopic pregnancy
- Consequences of an ectopic pregnancy
- Why is it worth contacting the Mama Papa Ya clinic?
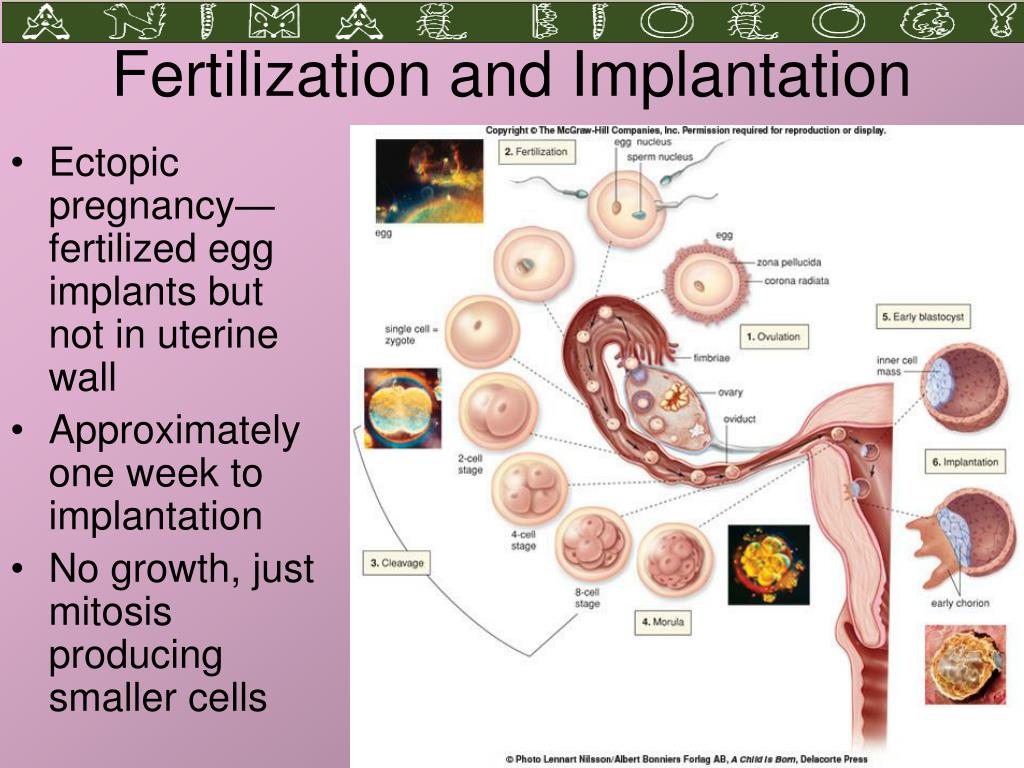
After fertilization, the egg moves sequentially along the fallopian tube with the help of cilia of the epithelium and attaches to the inner surface of the uterus. Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy occur when such implantation occurs outside the surface of the endometrium. This happens in 2% of all conceptions.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy occur when such implantation occurs outside the surface of the endometrium. This happens in 2% of all conceptions.
What is an ectopic pregnancy and how does it develop?
In this condition, the egg is attached not in the uterus, but in the fallopian tube, on the surface of the peritoneum or cervix. At this time, a home pregnancy test will be positive, but the fetal egg will not be able to fully develop and will inevitably die.
Early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are a medical emergency. Prompt treatment reduces a woman's risk of complications and increases her chance of having a baby in the future.
Signs and symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
When a patient develops an ectopic pregnancy, early signs are normal. Observed:
- delayed menstruation;
- breast tenderness;
- fatigue;
- nausea;
- frequent urination.
Later signs of ectopic pregnancy appear after 6 to 8 weeks of delayed menstruation:
- slight discharge of blood from the vagina;
- abdominal or pelvic pain.
With further development, the following signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy occur:
- pain in the lower abdomen, aggravated by movement; at first, it may suddenly appear on one side, and then spread to the entire pelvic area;
- severe vaginal bleeding;
- soreness during intercourse or gynecological examination;
- dizziness or fainting due to internal bleeding;
- pale skin, cold sweat, shortness of breath, weak rapid pulse, impaired consciousness (signs of shock).
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
The most common type of pathology is tubal, in which a fertilized egg develops in the fallopian tube. Causes of an ectopic pregnancy in such a case include:
- smoking: it interferes with the ability of the fallopian tube to move the fetus into the uterine cavity;
- an inflammatory disease such as gonorrhea or chlamydia that has caused scarring in the tubal cavity;
- previous fallopian tube operation;
- previous ectopic pregnancy.
Risk factors for pathology:
- woman's age over 35;
- surgery for diseases of the abdominal organs;
- multiple abortions;
- endometriosis;
- malformations of the fallopian tubes;
- pregnancy resulting from the use of an intrauterine device.
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy
At the beginning of its development, such a pregnancy proceeds as normal, and its termination resembles a spontaneous abortion. How to recognize an ectopic pregnancy? It is very difficult to do this on your own, since such a measureable sign as basal temperature during ectopic pregnancy is not informative - the schedule before the loss of the embryo is the same as during normal gestation.
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is carried out using the following methods:
- gynecological examination, revealing the absence of signs of uterine pregnancy and pathological formation, for example, in the tube;
- Ultrasound, which makes it possible to determine the pathology from 1 - 2 weeks of delayed menstruation, when a fetal egg is not found in the uterus;
- analysis for hCG with an interval of 48 hours, normally the indicator doubles during this time, with an ectopic pregnancy, its increase in the blood is not so great.

Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
The child cannot develop outside the uterus, and the spontaneous interruption of such a pathological process is dangerous for the woman's life. Therefore, the treatment of ectopic pregnancy is only surgical:
- salpingostomy - a longitudinal incision of the tube with subsequent restoration of its wall;
- salpingectomy - removal of part of the tube when it is ruptured.
Both operations can be performed laparoscopically or laparotomically.
There is also a medical method of treatment - methotrexate. It is used only in the earliest stages when the operation is impossible.
Consequences of an ectopic pregnancy
Usually the consequences of an ectopic pregnancy are relatively favorable: although a woman's ability to conceive is reduced by about 40%, she can still carry and give birth to a child. Another negative factor is the increased risk of recurrence of such a pathology.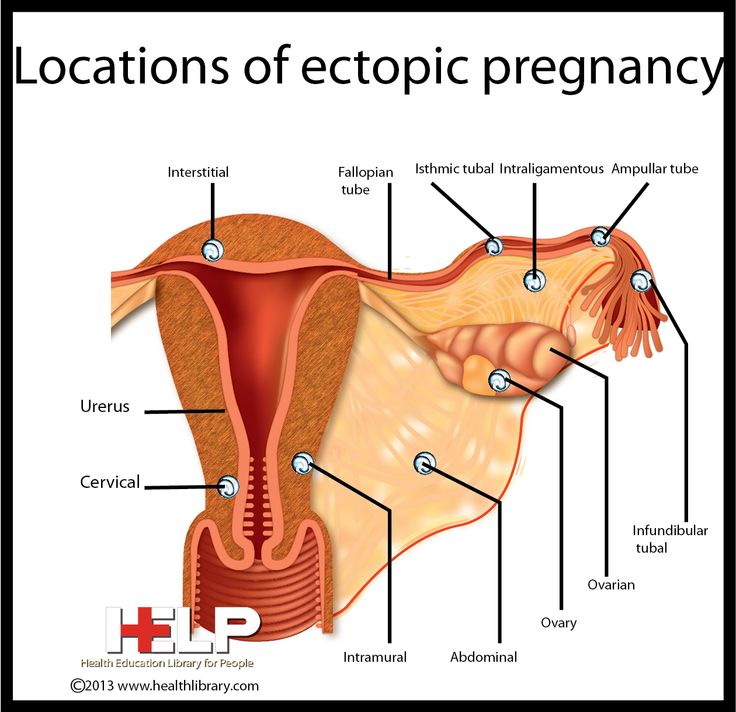
Recovery from an ectopic pregnancy occurs during the next menstrual cycle. Much more harm to a woman is brought not by physical, but by psychological trauma. Full rehabilitation requires the support of relatives, communication on appropriate forums, and sometimes individual and group psychotherapy.
The negative consequences of an ectopic pregnancy can be reduced if the causes of the disease are immediately looked for and eliminated.
Why should you visit the Mama Papa Ya clinic?
The network of medical clinics "Mama Papa Ya", whose branches are located in Moscow and other cities, offers medical services at affordable prices that will help to avoid the development of pathology or diagnose it in time:
- consultation of a qualified gynecologist on pregnancy planning;
- individual pregnancy management program “Waiting for you, baby!”;
- tests necessary for expectant mothers, including determining the level of hCG;
- gynecological ultrasound for the diagnosis of the disease at an early stage.

All consultations and procedures are carried out at a convenient time for the patient, without waiting and queues.
If you miss your period, we recommend that you take a home pregnancy test and, regardless of the results, make an appointment with a gynecologist. This can be done by calling the nearest clinic or on the website.
Reviews
Good clinic, good doctor! Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and easily explain what the essence of the problem is. If something is wrong, she talks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don't regret that I went to her.
Anna
I would like to thank the staff of the clinic Mom, Dad, me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, very friendly and cheerful staff and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish prosperity to your clinic.
Anonymous user
Today I removed a mole on my face at the dermatologist Kodareva I.A. Doctor is very thorough! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Borshchevskaya Julia is friendly, clearly fulfills her duties.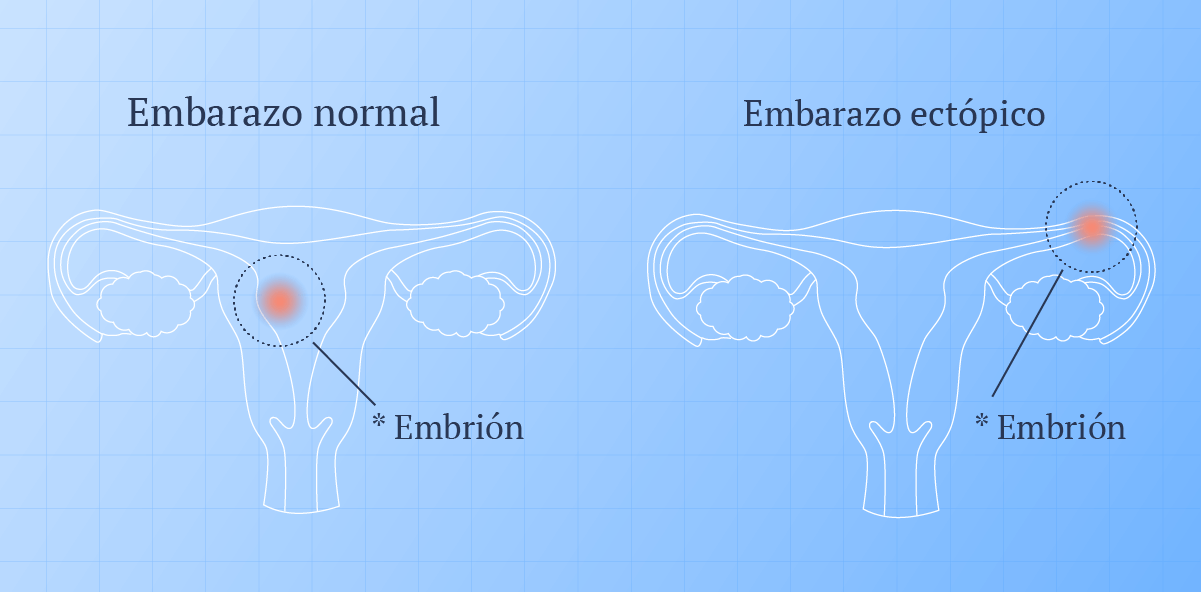
Belova E.M.
Today I was served in the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and care. We thank them very much and continue to prosper.
Anonymous
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Iratiev V.V.
Visited the clinic "Mama Papa Ya" with a child. I needed a consultation with a pediatric cardiologist. I liked the clinic. Good service doctors. We didn't stand in line, everything was the same price.
Evgeniya
I liked the first visit. I was carefully examined, additional examinations were prescribed, and good recommendations were given. I will continue the treatment further, I liked the conditions in the clinic.
Kristina
The doctor carefully examined my husband, ordered an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis.