What to take for a yeast infection while pregnant
Answers to 6 burning questions about yeast infection during pregnancy | Your Pregnancy Matters
×
What can we help you find?Refine your search: Find a Doctor Search Conditions & Treatments Find a Location
Appointment New Patient Appointment
or Call214-645-8300
MedBlog
Your Pregnancy Matters
September 20, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M. D. Obstetrics and Gynecology
Vaginal candidiasis, also known as a yeast infection, can be a real pain. The itching, burning, and discharge can be especially worrisome during pregnancy.
In most cases, though, vaginal yeast infections and most treatment options pose minimal risk to the patient or pregnancy.
After bacterial vaginal infections, yeast infections are the second most common cause of vaginal inflammation, and 75% of women will have at least one in their lifetime. Common symptoms can include redness, itching, or irritation on the external genital area (vulva), an increase in white or tan vaginal discharge, and a burning sensation during urination or intercourse.
There are a range of over-the-counter and prescription treatments, and an Ob/Gyn or gynecologist can help you choose the safest, most effective option during pregnancy.
I’ve invited Meredith McClure, M.D., a UT Southwestern gynecologist, to answer the top questions pregnant and breastfeeding patients ask about yeast infection treatment and prevention.
Meredith McClure, M.D.Q: How common are yeast infections during pregnancy?
A: Studies have found that 20%-30% of women develop a yeast infection during pregnancy. An increase in the hormone estrogen creates a more hospitable climate for yeast to colonize the vagina because it binds to the protein factor H on the surface of the cells that cause vulvovaginal candidiasis.
Some women are more likely to develop yeast infections due to their genetics. Mutations of several genes can interfere with the immune system’s ability to defend against candida yeast, resulting in recurring infections for some people. This inherited predisposition is called familial candidiasis.
This inherited predisposition is called familial candidiasis.
Q: Can a yeast infection harm my pregnancy?
A: No. A yeast infection won’t affect your developing baby – that’s why we don’t treat yeast infections that don’t have symptoms. However, most symptomatic yeast infections get worse when left untreated. This means more itching, redness, and inflammation. If the skin becomes cracked or torn from repeated scratching, a skin infection can result. In rare cases, an untreated yeast infection can lead to fatigue, oral thrush, or digestive problems.
Q: Do yeast infections appear throughout pregnancy?
A: Yeast infections can occur any time, but they are most common during the second trimester. Talk with your doctor if you notice signs of a yeast infection while pregnant, even if you have had one before. Some more serious infections have similar symptoms, so your doctor will perform a simple fungal culture swap in the office to check for the presence of yeast.
Q: What treatment options are available?
Talk with your doctor about the safest and most effective options for treating yeast infections during pregnancy.A: Topical creams or vaginal suppositories are the recommended yeast infection treatment options during pregnancy or while breastfeeding. Over-the-counter medications such as Miconazole, Clotrimazole, and Terconazole have been shown to eliminate a yeast infection safely and effectively. They are usually applied for three to seven days. It is important to finish the entire course of medication to prevent the infection from coming back. Studies have demonstrated these medications are safe to use during pregnancy.
The oral medication Diflucan (fluconazole) is not recommended for most patients during pregnancy. Though taking a single pill is simpler, quicker, and less messy, some studies suggest fluconazole carries a slightly increased risk of miscarriage, birth defects, or stillbirth, especially at high doses taken over long periods of time.
While the increase is small – approximately 12 incidents per 10,000 births – the convenience of single-pill treatment might not outweigh the risk. However, in the event you have already taken or need to take fluconazole while pregnant, the additional risk at a normal dose is unlikely to pose any problems for your baby.
Q: Are yeast infection treatments safe while breastfeeding?
A: Yeast infections are less common among breastfeeding patients because estrogen levels drop dramatically in the postpartum period, making it hard for yeast to thrive. But if they occur, fluconazole may be taken by women who are breastfeeding as the levels secreted into breast milk are small.
It is possible for a breastfeeding mother and baby to pass thrush, a fungal infection that typically grows in the mouth and throat, back and forth between nipple and mouth. If that happens, both must be treated to stop the infection. Thrush is usually minor and is often caused by the same fungus – and treated with a 7- to 14-day course of the same antifungal medicines – as a yeast infection in the vagina.
Q: What steps can reduce the risk of yeast infection?
A: During pregnancy and otherwise, take the following precautions:
- Wipe front to back after using the toilet.
- Avoid using scented tampons, pads, and pantyliners.
- Change tampons, pads, and pantyliners often.
- Avoid very hot baths and hot tubs.
- Wear underwear with a cotton lining to promote airflow.
- Do not douche, which removes healthy vaginal bacteria that prevent infection.
- Wear loose fitting clothing.
- Manage your blood sugar if you have diabetes or gestational diabetes.
- Remove wet workout clothes and swimsuits as soon as possible after activities.
If you’re pregnant and notice signs of a yeast infection, discuss treatment options with your doctor so you can eliminate these disruptive symptoms. To request an appointment, call 214-645-8300 or request online.
More in: Your Pregnancy Matters
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Shivani Patel, M.
 D.
D.
November 22, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
November 15, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
November 7, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.
 D.
D.
October 11, 2022
Prevention; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
October 4, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Meitra Doty, M.
 D.
D.
September 27, 2022
Men's Health; Women's Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Yair Lotan, M.D.
September 6, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
August 29, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Patricia Santiago-Munoz, M.
 D.
D.
August 23, 2022
More Articles
Yeast Infections During Pregnancy: What To Do
Written by Camille Peri
Reviewed by Dan Brennan, MD on August 09, 2022
In this Article
- What is a Yeast Infection During Pregnancy?
- Symptoms of a Yeast Infection During Pregnancy
- Causes of a Yeast Infection During Pregnancy
- Treating a Yeast Infection During Pregnancy
- Preventing a Yeast Infection During Pregnancy:
What is a Yeast Infection During Pregnancy?
Yeast infections (also known as candidiasis) are common in women, especially when you're pregnant. Increased estrogen in your pregnant body can throw off the normal balance of yeast and bacteria in your vagina. This may let the yeast overgrow. Most yeast infections during pregnancy result from the fungus candida albicans. Two other kinds of yeast that can also cause them are candida glabrata and candida tropicalis.
Most yeast infections during pregnancy result from the fungus candida albicans. Two other kinds of yeast that can also cause them are candida glabrata and candida tropicalis.
Yeast infections aren't pleasant, but they won't hurt you or your baby. And they can be safely treated, usually with a topical cream.
Symptoms of a Yeast Infection During Pregnancy
You might notice:
- Itching
- Burning
- Redness or swelling in your vulva, the area outside your vagina.
- Thick, white vaginal discharge that looks like cottage cheese.
Causes of a Yeast Infection During Pregnancy
- Taking antibiotics, which can cause that can change the balance of yeast and bacteria in your vagina.
- Diabetes that isn’t well controlled
- Conditions like HIV or medications, like corticosteroids that make it harder for your immune system to work well.
- If your sexual partner has a yeast infection, it can be passed to you during vaginal sex.

Treating a Yeast Infection During Pregnancy
It's safe to treat a yeast infection with over-the-counter (OTC) vaginal creams or suppositories that contain miconazole or clotrimazole.
Don’t take an oral fluconazole tablet to treat a yeast infection during pregnancy. It may cause birth defects.
If you think you have a yeast infection, call your doctor before using over-the-counter medications to treat it.
Preventing a Yeast Infection During Pregnancy:
- Wear cotton underwear and pantyhose with a cotton crotch to keep your vaginal area dry and let it "breathe."
- Always wipe from front to back after you go to the bathroom.
- Don't douche. It can upset the balance in your vagina. In late pregnancy, it may also cause your water to break.
- Avoid tight pants and pantyhose.
- Change out of a wet swimsuit or sweats immediately. This keeps the genital area dry.
- Avoid toilet paper, feminine sprays, bubble bath, and sanitary pads that are scented.

- Keep good control of your blood sugar if you have diabetes.
- Eat yogurt with live cultures; some research suggests this can help.
Ecofucin for the treatment of thrush during pregnancy.
Thrush is a disease of the vaginal and vulvar mucosa caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida, which affects 35% of women during pregnancy 1 .
At risk for the occurrence of a recurrent form of thrush are those pregnant women who have already had episodes of thrush in their anamnesis the level of estrogens rises, in connection with which glycogen accumulates in the vaginal mucosa - a nutrient medium for yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida.
Lactobacilli are the predominant microorganisms in the vaginal microflora of a healthy woman. A normal concentration of lactobacilli provides the necessary acidity in the vagina, which inhibits the growth of fungi. Lactobacilli also participate in the formation of local immunity
In addition, during thrush, the vaginal microflora is disturbed - the number of lactobacilli decreases sharply. These changes lead to the growth and reproduction of pathogenic fungi of the genus Candida, which leads to an increase in the number of manifestations of acute and recurrent forms of thrush.
These changes lead to the growth and reproduction of pathogenic fungi of the genus Candida, which leads to an increase in the number of manifestations of acute and recurrent forms of thrush.
Symptoms of thrush in a pregnant woman:
- itching and burning in the vulva and/or vagina, swelling and irritation in the vulva
- vaginal discharge with a "curdled character" and occasional foul odor
- pain during and after intercourse
- urination disorder and pain
The appearance of at least one of the symptoms is a reason for an unscheduled visit to the doctor.
Why is it important to diagnose and treat thrush in a pregnant woman in time?
Some women are asymptomatic carriers of yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida and experience neither discomfort nor manifestations of the disease throughout the entire period of pregnancy 2
A pregnant woman with thrush (including an asymptomatic carrier) is a source of infection for her unborn child. Infection from mother to child occurs in 75-80% of cases 3 . Infection of a newborn occurs when passing through the birth canal (the skin of the child comes into contact with the infected mucous membranes of the mother's birth canal). In newborns, candidiasis is manifested by lesions of the mucous membranes and skin 2 , which can lead to negative consequences. For premature babies, infection with fungi of the genus Candida is especially dangerous 2 .
Infection from mother to child occurs in 75-80% of cases 3 . Infection of a newborn occurs when passing through the birth canal (the skin of the child comes into contact with the infected mucous membranes of the mother's birth canal). In newborns, candidiasis is manifested by lesions of the mucous membranes and skin 2 , which can lead to negative consequences. For premature babies, infection with fungi of the genus Candida is especially dangerous 2 .
Timely and effective treatment of thrush in a pregnant woman is an important task
Treatment of thrush
Safety and efficacy are the main criteria for choosing a drug in the treatment of thrush in pregnant women
The earlier a pregnant woman is diagnosed and treated for thrush, the less the risk of negative consequences and complications for the course of pregnancy and for the health of the mother and her unborn child. In the treatment of thrush, experts recommend an integrated approach to therapy.
It is important to follow the recommendations of a specialist, following the prescribed dosage and regimen.
Comprehensive treatment should be aimed at solving two problems: eliminating the cause of thrush (fungi of the genus Candida) and restoring the vaginal microflora. It is important to know that not all drugs are approved for use during pregnancy. For example, most oral (systemic) drugs and some topical drugs for treating thrush are contraindicated during pregnancy.
Ecofucin
® in the treatment of thrush in pregnancyEcofucin
® is allowed at all stages of pregnancy and lactation 4
Natamycin
- practically not absorbed into the blood and has no systemic effect
- has a fungicidal effect - causes fungal cell death
- resistance to it does not develop
- does not inhibit the growth of natural microflora
+
Prebiotic 5
- actively fermented by the normal microflora of the vagina, stimulating the growth of lactobacilli 6
- causes restoration of the vaginal microflora, stimulates local immunity 6
The active substance 7 of Ecofucin ® eliminates the cause of thrush, and the prebiotic 5 in Ecofucin ® promotes the restoration of the vaginal microflora and strengthens local immunity 6 .
Efficacy and safety of the drug Ecofucin has been proven by clinical studies
Ecofucin promotes faster recovery of patients with thrush.
More details
For pregnant women
Moscow 40 patients
For non-pregnant women
St. Petersburg 36 patients
Clinical cure occurred significantly earlier in the group of patients who used Ecofucin.
Kuzmin V.N., Bogdanova M.N. Ecofucin® is the first drug for the eradication of Candida fungi with the effect of stimulating the growth of lactobacilli in pregnant women. breast cancer. 2020; one; 28-33
Ecofucin helps to increase the number of own lactobacilli in the vagina and reduce the risk of recurrence of thrush.
More details
For pregnant women
Moscow 40 patients
For non-pregnant women
St. Petersburg 36 patients
Clinical cure occurred significantly earlier in the group of patients who used Ecofucin.
Kuzmin V.N., Bogdanova M.N. Ecofucin® is the first drug for the eradication of Candida fungi with the effect of stimulating the growth of lactobacilli in pregnant women. breast cancer. 2020; one; 28-33
Dosage and Administration
The regimen for the use of Ecofucin ® in a pregnant woman is prescribed by the attending physician individually.
Additional conditions for effective treatment of thrush are: giving up bad habits, a carbohydrate-restricted diet, wearing underwear made from natural fabrics, etc.
It is important to consult a gynecologist in a timely manner and exclude self-medication.
1. Tikhomirov A.L., Sarsania S.I. Features of candidal vulvovaginitis in pregnant women at the present stage. // Farmateka No. 9, 2009, p. 64-70.
2. Prilepskaya V.N., Mirzabalaeva A.K., Kira E.F., Gomberg M.A., Apolikhina I.A., Bairamova G.R. Federal clinical guidelines "Urogenital candidiasis". // 2013.
3. Kupert A.F., Akudovich N.V., Khoroshikh O.V., Vereshchagina S.A., Khmel T.V. Features of the clinic and treatment of vaginal candidiasis in pregnant women, depending on the type of fungi of the genus Candida. // Gynecology. v. 05, N 5b, 2003.
4. Instructions for use of the drug Ecofucin ® .
5. Excipient, lactulose.
6. Dikovskiy A.V., Dorozhko O.V., Rudoy B.A. Pharmaceutical composition of antimycotics and prebiotics and a method for the treatment of candidal vaginitis. // International publication WO 2010/039054 A1.
7. Active ingredient, natamycin.
treatment, symptoms, which suppositories and preparations can be used
A woman who is impatiently waiting for the birth of a baby, as a rule, is very attentive to her health. The slightest infection can have a fatal effect on the development of a child. However, there are ailments that pregnant women are particularly susceptible to. One of these diseases is thrush.
Causes of thrush in pregnancy
Vaginal candidiasis, or thrush, is three times more common in pregnant women than in non-pregnant women. The thing is that the body of the future mother is being rebuilt, the hormonal status is changing, her immunity is decreasing.
Physiological decrease in immunity is an important condition for the possibility of bearing a fetus and the course of pregnancy. Thus, more favorable conditions are created for the reproduction of the fungus of the genus Candida in the body, which cause inflammation. AT 95% of cases the cause lies in the action of Candida albicans.
Additional risk factors for the development of vaginal thrush are the wearing of synthetic underwear, violations of the rules of intimate hygiene.
The growth of own lactobacilli is promoted by lactulose, which is part of the vaginal suppositories of the drug Ecofucin® . Lactulose is a nutrient substrate only for its own lactobacilli, but not for fungi of the genus Candida. Therefore, the use of drug Ecofucin® is not only the treatment of thrush, but also the prevention of its recurrence. Normalization of the vaginal microflora contributes to the physiological course of pregnancy and childbirth, the birth of healthy children, in which the sterile organism is populated with physiological flora. And this creates a reliable and strong immunity in the baby from the first days of life!
Therefore, the use of drug Ecofucin® is not only the treatment of thrush, but also the prevention of its recurrence. Normalization of the vaginal microflora contributes to the physiological course of pregnancy and childbirth, the birth of healthy children, in which the sterile organism is populated with physiological flora. And this creates a reliable and strong immunity in the baby from the first days of life!
This is described in detail in a clinical study, which was conducted on the basis of the city clinical hospital №315 named after. O.M. Filatov in Moscow.
More
CONTRAINDICATIONS. CONSULT A SPECIALIST
Symptoms of thrush in pregnancy
Symptoms of candidiasis in pregnancy are no different from symptoms of the same disease at any other time in life. Severe itching, discomfort, burning sensation in the vulva, which increases during intercourse and after urination, are the most common signs of thrush. If abundant curdled discharge is added to them, and sometimes with an unpleasant sour smell, this is a serious reason to consult a doctor.
Sometimes thrush is manifested by swelling and redness of the mucous membranes of the external genitalia.
Forms of thrush in pregnant women
In clinical practice, there are several forms of candidiasis in pregnant women. Each of them has its own characteristics.
Carriage. In this case, there are no symptoms, but according to the data of a gynecological smear on the microflora, fungi are detected. If during pregnancy a large number of lactobacilli are found in the microbiome, then this is a reason for careful monitoring by a doctor.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis. It is characterized by a vivid clinical picture: itching, burning, a large amount of curdled discharge with a sour smell. In some cases, there may be swelling of the external genital organs, pain during urination and sexual intercourse.
In addition, thrush during pregnancy can be acute, when the inflammation occurs for the first time, the symptoms are pronounced. In the absence of treatment or the action of other predisposing factors, the acute form can turn into a chronic relapsing one. Outside of exacerbations, there are no symptoms, but with a relapse, the clinical picture is similar to the acute form.
In the absence of treatment or the action of other predisposing factors, the acute form can turn into a chronic relapsing one. Outside of exacerbations, there are no symptoms, but with a relapse, the clinical picture is similar to the acute form.
Persistent thrush. It is characterized by constant symptoms of pathology, although with active treatment there is an improvement in the condition.
Treatment of thrush in pregnancy
Treatment of thrush in pregnancy should be under medical supervision. The use of a number of drugs during the period of bearing a child is prohibited, as they affect the course of pregnancy and the development of the fetus. Many pills that can be used without problems by ordinary women are contraindicated for expectant mothers, but candles carry a much lower risk to the health of the baby.
IMPORTANT
Why women suffering from candidiasis during pregnancy and lactation should consider using Ecofucin® :
✓ allowed from the 1st trimester of pregnancy and during breastfeeding;
✓ natamycin — the active ingredient of the drug Ecofucin ® helps to eliminate the cause of thrush - fungi of the genus Candida;
✓ the preparation contains lactulose, which is a prebiotic that helps to increase the number of lactobacilli and restore the normal microflora of the vagina;
✓ Timely and effective treatment of thrush in pregnancy is especially important.
Read more
CONTRAINDICATIONS. CONSULT A SPECIALIST
Diagnosis
Symptoms of vulvovaginal candidiasis are similar to those of other diseases. Therefore, the diagnosis is aimed at identifying the cause of the symptoms. To do this, the doctor finds out when the symptoms appeared, what preceded them, how long they persist. After the interview, they proceed to the inspection. These data are sufficient to make a preliminary diagnosis, however, to confirm it, it is necessary to conduct laboratory examination methods:
- a gynecological smear for microflora allows to assess the qualitative and quantitative indicators of microflora, to identify possible inflammatory reactions and dysbacteriosis;
- PCR diagnostics allows you to detect fungal DNA in vaginal discharge and make a differential diagnosis, that is, to distinguish one disease from another.
Based on the results of the examination, a treatment plan is drawn up, taking into account the duration of pregnancy and the severity of the problem.
Modern methods of treatment of thrush in pregnant women
Treatment tactics should take into account the physiological characteristics of the body of a pregnant woman and a developing fetus. Systemic drugs, which are often the drugs of choice in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis in women, are prohibited during pregnancy. Therefore, the tactics of treatment also depend on the trimester of pregnancy.
First trimester
The first trimester is very important for the development of a healthy baby. During this period, the choice of means for treatment is especially limited, but this does not mean that taking medications should be delayed.
If you wait to start therapy from the second trimester, there is a risk of getting complications. In the first trimester, natamycin and, accordingly, drugs that have it as the main active ingredient can be used to treat thrush. With the rest of the funds, it is better to wait until the second trimester.
These drugs include Primafungin, Pimafucin, etc.
And you should also review your diet, exclude from it sugary foods containing a large amount of carbohydrates, which promote the growth and reproduction of Candida fungi.
IMPORTANT
Natamycin is the main active ingredient in Ecofucin® . Natamycin is practically not absorbed into the blood and does not have a systemic effect, contributing to the safety of use:
✓ has a fungicidal effect - causes the death of the fungus of the genus Candida;
✓ fungi practically do not develop resistance to natamycin.
Prebiotic lactulose, which is part of Ecofucin ® , is actively fermented by the normal microflora of the vagina, stimulating the growth of lactobacilli, and causes the restoration of the microflora of the vagina, stimulating local immunity.
Where to buy
CONTRAINDICATIONS. CONSULT A SPECIALIST
Second trimester
In the second trimester, the gynecologist has to choose drugs for treatment based on the benefit-risk ratio. At such times, more effective means are allowed, based on substances such as clotrimazole, itraconazole and others. Sometimes drugs based on metronidazole are prescribed.
At such times, more effective means are allowed, based on substances such as clotrimazole, itraconazole and others. Sometimes drugs based on metronidazole are prescribed.
In the second trimester, the choice of drugs is much wider, because the protective mechanisms of the fetus have already been formed. The doctor can prescribe Candide B6, Irunin, Primafungin, Pimafucin, etc.
Third trimester
If in the early stages doctors are limited in the choice of pharmacological drugs, then in the later stages the list of drugs is significantly expanded. During this period, it is especially important to get rid of the disease, because infection with Candida fungi from mother to child occurs in 75-80% of cases during childbirth.
After the examination, the doctor may prescribe Sertoconazole, Econazole, Clotrimazole, etc.
Can suppositories be used
then expectant mothers are allowed to use candles. But you should consult a doctor of choice, as some suppositories are allowed in certain trimesters.
It is important to remember that pregnant women should not use suppositories for thrush containing metronidazole or fluconazole as an active ingredient, as well as nystatin, without consulting a doctor.
Natamycin is considered one of the common drugs for the treatment of thrush in pregnant women. It underlies a number of drugs. Its target is the structural elements of fungi, not enzymes, so the formation of drug resistance to it rarely occurs.
Can I use
tabletsMost oral medications are contraindicated during pregnancy. Gynecologists recommend giving preference to local therapy: suppositories, creams and ointments.
Effective folk remedies
For obvious reasons, gynecologists do not advocate the treatment of thrush during pregnancy with folk remedies. Their effectiveness is sometimes questionable, and the risk is great, both for the mother and for the baby.
During pregnancy, thrush is sometimes treated with douching with a decoction of chamomile, calendula, oak bark, St.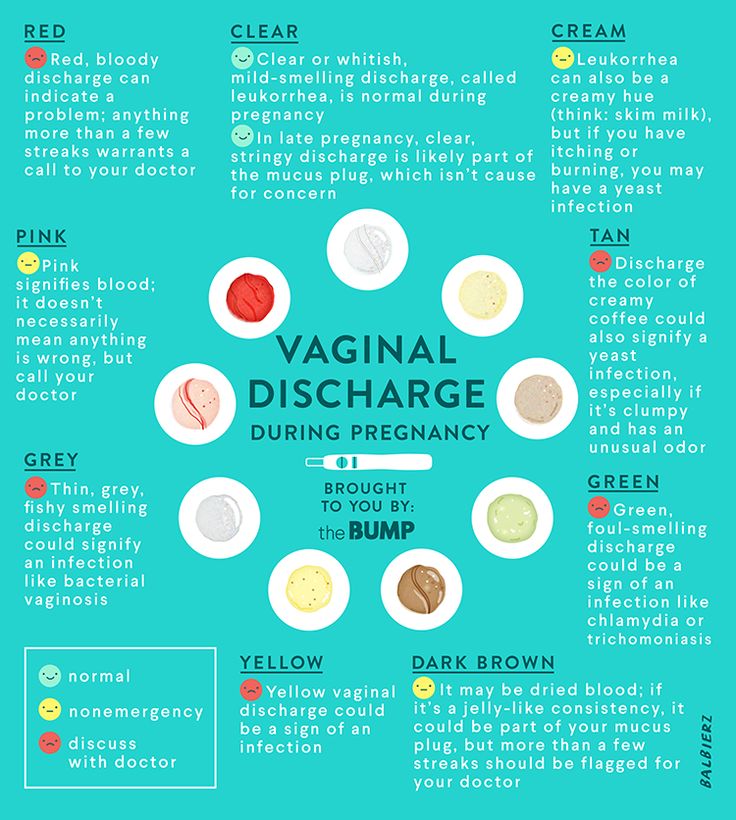 John's wort and sage. But it is worth remembering that they are not safe either. In addition, practice shows that such treatment does not eliminate the fungus that caused the disease and most often aggravates the violation of the vaginal microflora.
John's wort and sage. But it is worth remembering that they are not safe either. In addition, practice shows that such treatment does not eliminate the fungus that caused the disease and most often aggravates the violation of the vaginal microflora.
What is not recommended for use in the treatment
Most pharmacological agents that act on Candida fungi are either contraindicated for pregnant women or have restrictions in use at specific stages of pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to remember that what you used to treat thrush before pregnancy should not be taken out of habit during the period of expectation of the child.
Photo: MART PRODUCTION, pexels.comNutrition for thrush in pregnant women
It is necessary to review the diet. It is recommended to avoid spicy and fried foods, sweet, starchy foods. It is also necessary to exclude products that contain hidden sugars, for example, mayonnaise, ketchup, flavors for cooking first and second courses, etc.
Carbohydrates are an excellent breeding ground for Candida.
Fermented products or those that can cause these processes in the intestines, as well as those containing artificial dyes, are prohibited.
Why is thrush coming back? How to avoid it?
One of the reasons for the development of recurrence of thrush or exacerbation of candidiasis is the situation when the number of lactobacilli is reduced in the vagina, resulting in a state of dysbiosis and this creates excellent conditions for the development of fungi of the genus Candida. When the number of own lactobacilli is restored, the risk of developing a recurrence of thrush is significantly reduced. It is important to increase the number of own lactobacilli, whose genetic structure is not alien. Their growth should be gradual.
Prevention of thrush in pregnant women at home
In addition to the general rules for the prevention of thrush (hygiene, proper nutrition, avoidance of synthetic underwear), pregnant women should regularly visit an obstetrician-gynecologist. In the first trimester, it is recommended to make an appointment once a month, in the second - once every 2-3 weeks, and in the third - once every 7-10 days.
In the first trimester, it is recommended to make an appointment once a month, in the second - once every 2-3 weeks, and in the third - once every 7-10 days.
With constant monitoring in the antenatal clinic during pregnancy and timely correct treatment, if thrush is detected, the risk of passing it on to the unborn baby will be extremely small.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to use baking soda for thrush in pregnant women?
Baking soda is considered relatively safe and is often used in alternative and even evidence-based medicine. However, it is forbidden to use it during pregnancy. Symptoms of thrush are also characteristic of a number of other diseases that require a completely different treatment.
The use of soda can blur the clinical picture and give false hope of recovery. However, the underlying disease progresses and this leads to complications, sometimes fatal. Self-treatment of thrush during pregnancy is unacceptable.