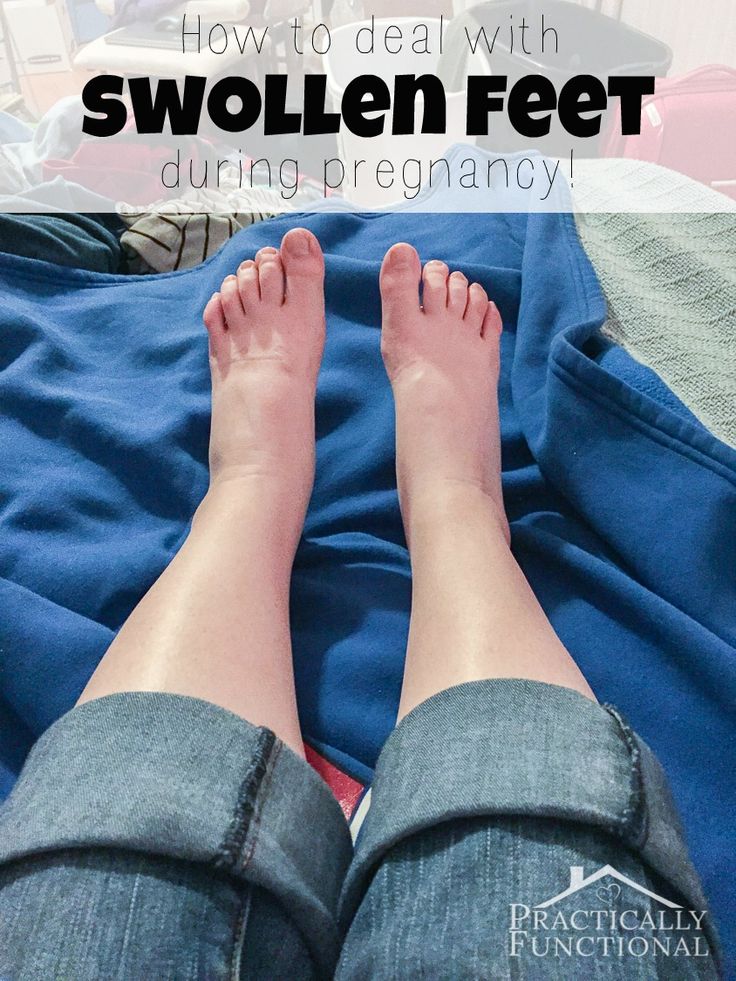
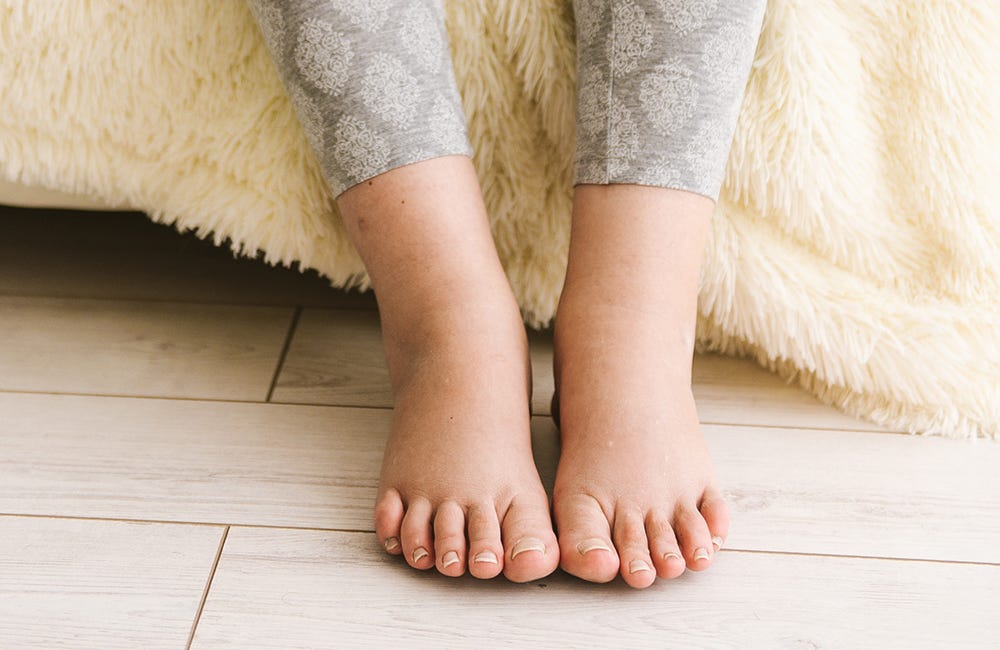
How to help swelling in feet during pregnancy
Swollen ankles, feet and fingers in pregnancy
It's normal to get some swelling in pregnancy, particularly in your legs, ankles, feet and fingers.
It's often worse at the end of the day and further into your pregnancy.
Swelling that comes on gradually is not usually harmful to you or your baby, but it can be uncomfortable.
A sudden increase in swelling can be a sign of pre-eclampsia, a condition that needs to be monitored as soon as possible.
Non-urgent advice: Call your midwife, GP or labour ward immediately if you have:
- a sudden increase in swelling in your face, hands or feet
- a very bad headache
- problems with your vision, such as blurring or flashing lights in your eyes
- severe pain just below your ribs
- vomiting with any of these symptoms
These could be symptoms of pre-eclampsia, which can lead to serious complications if it's not monitored and treated.
Normal pregnancy swelling
Swelling is caused by your body holding more water than usual when you're pregnant.
Throughout the day the extra water tends to gather in the lowest parts of the body, especially if the weather is hot or you have been standing a lot.
The pressure of your growing womb can also affect the blood flow in your legs. This can cause fluid to build up in your legs, ankles and feet.
What can help to reduce swelling
Try to:
- avoid standing for long periods
- wear comfortable shoes and socks – avoid tight straps or anything that might pinch if your feet swell
- try to rest with your feet up as much as you can
- drink plenty of water – this helps your body get rid of excess water
- exercise – try to take regular walks during the day or doing foot exercises
Foot exercises
You can do foot exercises sitting or standing. They improve blood circulation, reduce swelling in the ankles, and prevent cramp in the calf muscles:
They improve blood circulation, reduce swelling in the ankles, and prevent cramp in the calf muscles:
- bend and stretch your foot up and down 30 times
- rotate each foot in a circle 8 times one way and 8 times the other way
Get more tips on exercising in pregnancy.
Page last reviewed: 10 March 2021
Next review due: 10 March 2024
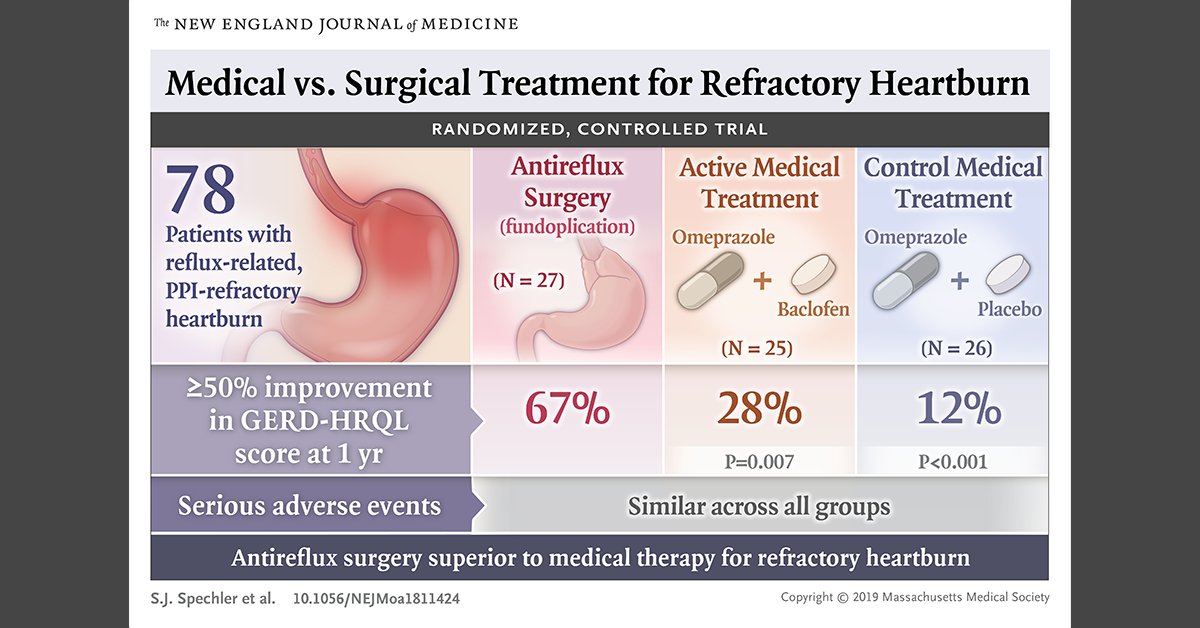
5 ways to manage swollen legs and feet during pregnancy | Your Pregnancy Matters
×
What can we help you find?Refine your search: Find a Doctor Search Conditions & Treatments Find a Location
Appointment New Patient Appointment
or Call214-645-8300
MedBlog
Your Pregnancy Matters
September 14, 2021
Your Pregnancy Matters
Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M. D. Obstetrics and Gynecology
D. Obstetrics and Gynecology
Of all the body parts you expect to get bigger during pregnancy, feet might not be at the top of your list. But most pregnant women experience swelling in their lower legs and feet.
If your ankles appear puffy and your shoes don’t feel quite right, you’re not imagining things. The additional fluid and blood your body creates to support healthy fetal growth also slows down blood circulation. That can cause blood to accumulate in your lower extremities, causing swelling.
During pregnancy, you also produce more relaxin, a hormone that helps your tendons, ligaments, joints, and muscles – you guessed it – relax.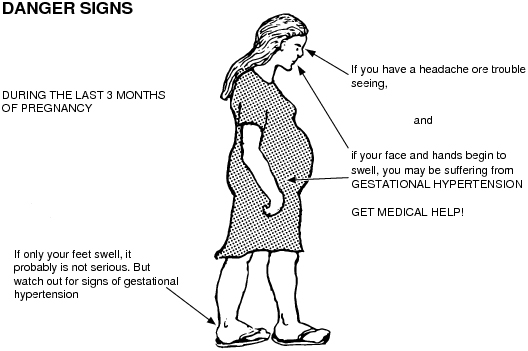 While relaxin helps your pelvis open to give birth, it also loosens the tendons and ligaments in your feet.
While relaxin helps your pelvis open to give birth, it also loosens the tendons and ligaments in your feet.
The combination of extra weight and hormones during pregnancy can cause your feet not only to widen but also flatten and lengthen. Leg or ankle swelling likely will decrease a week or two after your baby is born, but your feet may never be the same again.
Studies have shown that pregnancy can cause a permanent decrease in your arch and increase in foot length – typically only after a woman’s first pregnancy.
While more research is needed to determine whether these structural changes can be prevented, there are a few things you can do throughout your pregnancy to reduce swelling and feel more comfortable.
Coping with swollen legs and feet during pregnancy
1. Wear compression socks
Wearing 15-20mmHG compression socks that end at your knee can help alleviate achiness. The socks gradually increase pressure in your legs and move some of the excess fluid back into your blood vessels and the rest of your body.
Avoid socks with a tight band at the top. The tightness might worsen swelling by blocking blood return. That can increase your risk of developing a blood clot – which is already five times higher during pregnancy. You don’t need to purchase medical-grade socks, but you can find a good pair of compression socks for $10-$20.
Compression socks also can prevent the formation of new varicose veins, which occur in 15% of pregnant women for the same reason that causes swelling. The risk doubles after your first pregnancy and is four times higher in women over 35. These veins start out as little bumps under your skin; the socks squeeze them just enough to prevent backward blood flow and bulging. Existing varicose veins aren’t likely to shrink, but compression socks can reduce the pain and discomfort they cause.
2. Rest efficiently
You can easily improve blood circulation during downtime and sleep:
- Elevate your legs above heart level while reading, watching TV, or doing other seated activities.
 The simple change in body position decreases pressure on your veins, which no longer have to work against gravity to send blood to your heart. Use cushions for comfort and elevate in 15- to 20-minute intervals a few times a day.
The simple change in body position decreases pressure on your veins, which no longer have to work against gravity to send blood to your heart. Use cushions for comfort and elevate in 15- to 20-minute intervals a few times a day. - Sleep on your left side. While you can safely sleep on either side during pregnancy, the left side is often recommended to avoid putting pressure on the inferior vena cava, a large vein that carries blood from your lower extremities to your heart.
3. Get your feet wet
Immersing your feet and ankles in cool water for 20 minutes a few times a week can minimize swelling, whether you use a pool, bathtub, or even a large bowl. Bonus: It’s also a great way to deal with the Texas heat if you’re pregnant during the summer.
Be sure the water temperature is moderate and not ice cold. Cooler temperatures cause the smaller blood vessels close to your skin to constrict, which reduces blood flow to and swelling within the affected area. Water that is too cold can have the opposite effect. Whether you stand and sway or sit and dangle your feet, water therapy is a great way to relieve stress and pain.
Water that is too cold can have the opposite effect. Whether you stand and sway or sit and dangle your feet, water therapy is a great way to relieve stress and pain.
Related reading: Water immersion during labor
4. Invest in supportive shoes that fit.
Unsupportive and uncomfortable shoes can cause even more leg and foot pain, plus backaches. Even if your feet return to their pre-pregnancy size, you’ll feel more comfortable in shoes that fit your feet and support your additional body weight. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends wearing shoes that:
- Have a low heel but are not flat
- Provide good arch support, such as athletic shoes
Many patients prefer shoes that have mesh, which allow their feet to breathe, and can easily slip on and off to limit bending over while pregnant. More shoe brands are merging comfort and style, so even the most fashionable patients will have no problem finding footwear they feel good about wearing.
5. Visit a podiatrist or pedicurist.
Another reason to wear shoes that fit: Stress from tight shoes can cause ingrown toenails, and so can infrequent nail trimming. In the first two trimesters you probably won’t have any difficulty trimming your toenails. But once you reach the third trimester, it might get more challenging.
Try propping up your feet on a stool or ask your partner to help trim your toenails. Nail salon gift cards are a great item to add to your baby shower (or sprinkle!) registry, too.
Seeing a podiatrist is another option to prevent or treat painful foot conditions, such as ingrown toenail, bunions, or plantar warts.
When swelling becomes serious
While gradual swelling in your lower and upper extremities is normal, sudden or severe swelling in your face, hands, or feet might be a symptom of preeclampsia. This pregnancy complication involves very high blood pressure.
If you have preeclampsia, you may need to stay in the hospital until you give birth. Delivery is the only way to “treat” preeclampsia. Left untreated, the condition can cause seizures, kidney or liver damage, and in rare cases, death.
Delivery is the only way to “treat” preeclampsia. Left untreated, the condition can cause seizures, kidney or liver damage, and in rare cases, death.
Related reading: Postpartum hypertension: When a new mom's blood pressure is too high
Talk with your doctor about foot and leg swelling, as well as any other pregnancy symptoms. The more we know about your current condition, the more we can help reduce your risk of future complications.
While we can’t fully prevent foot and leg swelling, we can recommend ways to reduce your risk, such as:
- Regular exercise
- Good-quality sleep
- A healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
Discomfort during pregnancy is to be expected, but our goal is to partner with you to minimize it – as well as the risk of more serious conditions.
To discuss your pregnancy concerns or symptoms with an expert, call 214-645-8300 or request an appointment online.
More in: Your Pregnancy Matters
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Shivani Patel, M.
 D.
D.
November 22, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
November 15, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
November 7, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.
 D.
D.
October 11, 2022
Prevention; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
October 4, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Meitra Doty, M.
 D.
D.
September 27, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
September 20, 2022
Men's Health; Women's Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Yair Lotan, M.
 D.
D.
September 6, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
August 29, 2022
More Articles
Edema during pregnancy
Edema during pregnancy- Phlebology Center >
- Pregnancy and varicose veins >
- Edema during pregnancy
Article content:
- Pregnancy and edema
- Why does swelling occur during pregnancy?
- When does edema occur during pregnancy?
- What factors can affect the appearance of edema during pregnancy
- What can be done to get rid of edema during pregnancy?
- Questions from patients about edema and pregnancy
Pregnancy and Edema
Swelling during pregnancy is normal because the body produces approximately 50% more blood and body fluids to meet the needs of a developing baby.
Edema during pregnancy
Edema during pregnancy occurs on the hands, face, legs, ankles and feet.
Why does swelling occur during pregnancy?
This extra fluid retention is needed to soften the body, allowing it to expand as the baby develops. The extra fluid also helps prepare the pelvic joints and tissues for reopening for childbirth. Additional fluids make up approximately 25% of a woman's weight gain during pregnancy.
When does swelling occur during pregnancy?
Swelling can appear at any stage of pregnancy, but it usually starts around the fifth month and may worsen while you are in the third trimester.
What factors can affect the appearance of edema during pregnancy
The following factors can also affect edema during pregnancy:
- Varicose disease
- Summer heat
- Standing for a long time
- Prolonged physical activity
- Low potassium diet
- High caffeine intake
- High sodium intake
Moderate swelling occurs during normal pregnancy, however, if you feel a sudden swelling of the hands and face, this may be a sign of preeclampsia.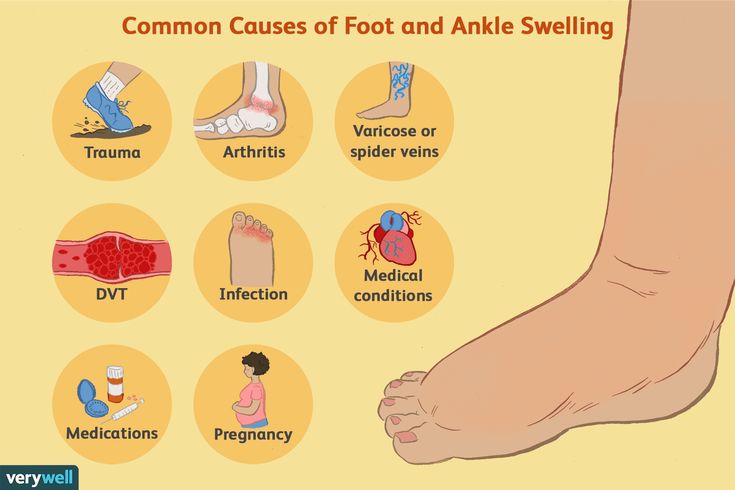
Pregnancy and thrombosis
Severe swelling of the distal lower extremities may be due to thrombosis. In these cases of sudden swelling, it is important to see a doctor immediately.
What can I do to get rid of swelling during pregnancy?
Swelling during pregnancy can be reduced by eating high potassium foods such as bananas, dried apricots, prunes and limiting caffeine intake.
Here are some more helpful tips for managing swelling during pregnancy:
- Avoid prolonged standing.
- Minimize your time outside in hot weather.
- Rest with your legs elevated.
- Wear comfortable shoes, avoiding high heels if possible.
- Wear special compression stockings or stockings.
Pregnancy Compression Stockings
- Avoid clothing that is tight around your wrists or ankles.
- Relax or take a dip in the pool.
- Use cold compresses on swollen areas.

- Drink water that stimulates the kidneys and helps reduce water retention.
- Minimize sodium (salt) intake and avoid adding salt to food.
Pregnancy Swelling Prevention
These simple guidelines will help reduce swelling during pregnancy and make this period more comfortable and safe.
Questions from patients about edema and pregnancy
What to do with swelling of the legs during pregnancy?
Edema during pregnancy is most often a physiological phenomenon, but often a sign of serious clinical situations. It is important to tell your doctor, a gynecologist, about the edema that bothers you. It makes sense to consult a phlebologist in order to exclude the pathology of the veins of the lower extremities.
How to deal with swelling during pregnancy?
Combating edema during pregnancy will help adhere to a certain regimen, indicated above.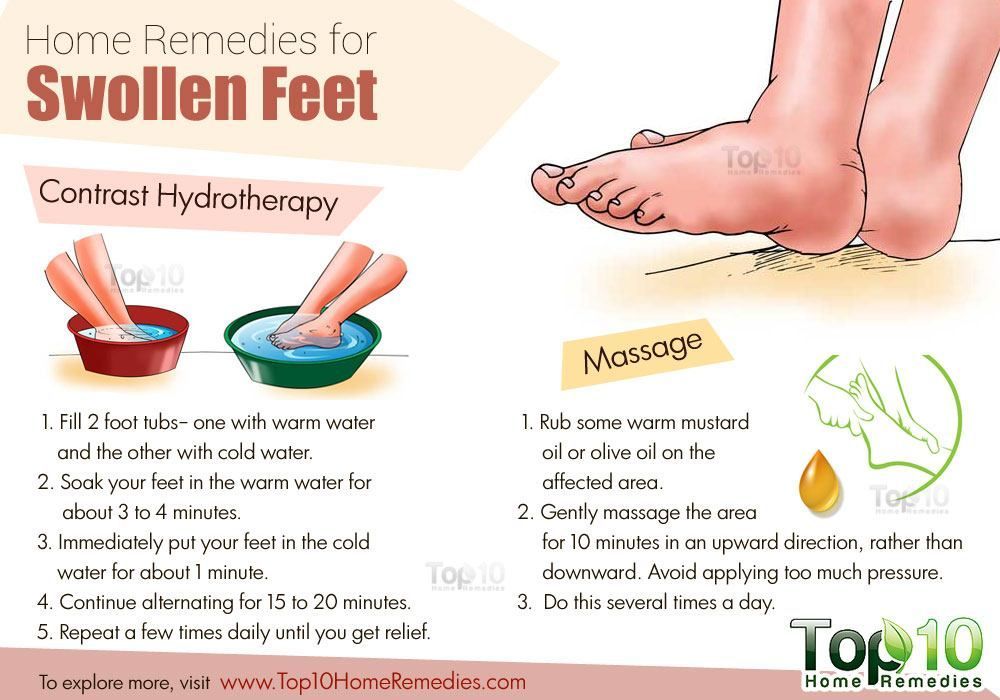 It is also necessary to follow the recommendations of your obstetrician-gynecologist and phlebologist.
It is also necessary to follow the recommendations of your obstetrician-gynecologist and phlebologist.
Can swelling be avoided during pregnancy?
It is almost impossible to completely avoid swelling during pregnancy. You should pay attention to the regimen and follow the recommendations of your doctor. Also, it is useful to pay attention to the dynamics of edema, its symmetry. If in doubt, voice them to the doctor.
Which doctor should I go to if swelling occurs during pregnancy?
If edema occurs during pregnancy, you need to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist, as well as a phlebologist.
Are swelling during pregnancy dangerous?
Physiological swelling is inevitable during pregnancy. However, swelling should be kept under control and if in doubt seek medical attention.
Edema in pregnancy, edema of pregnancy
Edema in pregnant women is mainly divided into generalized (widespread) and local (local).
Edema is a symptom that occurs in various conditions of the body, characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in the tissues and / or cavities of the body.
Accumulation and stagnation of fluid in tissues is the release of fluid from a vessel or cell into the intercellular space.
With generalized edema, fluid can accumulate not only in the tissues, but also in the cavities - abdominal, pleural, pericardial. Such edema in pregnant women is rare. More often, swelling is local, for example, they affect the nasal mucosa, the so-called rhinitis of pregnant women) and even the inner ear (feeling of stuffy ears). With swelling of the legs during pregnancy, pressing a finger on the lower leg causes the formation of a hole that does not smooth out for a minute, or even a few.
 For example, in the Leningrad blockade or in concentration camps, the vast majority of people had such edema.
For example, in the Leningrad blockade or in concentration camps, the vast majority of people had such edema. It must be understood that the very fact of pregnancy and the presence of sources of progesterone provokes the appearance of edema. First, the corpus luteum, then the placenta, produce progesterone, the hormone of the second phase of the menstrual cycle. By itself, progesterone contributes to the accumulation of fluid in the tissues.
Some women have swelling in the second phase of the menstrual cycle - they have a high sensitivity of the receptors even to the small level of progesterone that the corpus luteum produces. At the end of pregnancy, progesterone provides fluid accumulation in the extravascular (interstitial) space. The accumulation of fluid during physiological pregnancy usually ranges from 1-2 kg., But it can be up to 4 kg.
Part of the edema can compensate for excessive blood loss during childbirth and is the supply of fluid that will enter the bloodstream if necessary. Parturient women with moderate edema can tolerate blood loss more easily and recover faster.
What to do about edema during pregnancy (general recommendations)
- Urinalysis in the 3rd trimester should be checked every 2 weeks. It is necessary to ensure that there is no protein in the urine, and the level of leukocytes does not rise above "5".
- Almost all edemas are treated with contrast procedures, a contrast shower, and, best of all, a bath followed by dousing with cold water or a font.
 This improves the functioning of peripheral capillaries and enhances the outflow of fluid from the intercellular space.
This improves the functioning of peripheral capillaries and enhances the outflow of fluid from the intercellular space. - Never limit fluids and eliminate salt from the diet.
- Diaphragmatic breathing (abdominal breathing) allows you to increase the flow of lymph and its return to the venous bed.
Causes of edema in pregnant women and help in case of their occurrence
| Lymphostasis | Asymmetric edema (e.g. swelling of one leg). Physical therapy, compression stockings, osteopathic consultation, bandage can help. Diaphragmatic breathing. |
| Varicose veins | The deep veins of the lower extremities and the veins of the small pelvis suffer. Help is the same. Phlebologist, hematologist consultation. |
| Swelling due to incorrect position | Swelling of the fingers during pregnancy in the morning ! with a decrease in mobility during sleep (usually a month before delivery). Swelling of the legs from habit of sitting cross-legged or on a chair with a hard edge. Help - Rest against the door jamb, make several circular movements in the shoulder joints. Swelling of the legs from habit of sitting cross-legged or on a chair with a hard edge. Help - Rest against the door jamb, make several circular movements in the shoulder joints. |
| Nutritional edema | With a sharp decrease in protein in the diet, after 2-3 weeks, Braxton Higgs contractions may become more frequent. It is necessary to introduce vegetable and / or proteins into the diet. See Nutrition for pregnant women. |
| Nasal swelling | Often associated with sleep disturbance. Help - visiting the bathhouse, yoga breathing practices, aromatherapy - Breathing oil, inhalation of lemon peel, bird cherry branches, Rhinorin, homeopathic preparations - Fleming's ointment, Euphorbium compositum nazentropfen C. |
| Edema associated with impaired salt metabolism: | Increased consumption of clean water in the morning. Cucumbers - as a source of mineral salts. Raw beets in the form of salad or diluted juice - as a source of potassium. Mineral water, fruit drinks, dried fruit compote. Decrease in the diet of dairy products and, especially, milk. Diet for edema during pregnancy, using buckwheat with vegetables. (see "Unloading diet"). Mineral water, fruit drinks, dried fruit compote. Decrease in the diet of dairy products and, especially, milk. Diet for edema during pregnancy, using buckwheat with vegetables. (see "Unloading diet"). |
Which conditions are accompanied by edema in pregnant women
There are threatening conditions during pregnancy, which can also be accompanied by edema. The most formidable are preeclampsia and eclampsia . This condition is not always accompanied by significant swelling, but they can accompany it. For control, it is necessary to take a urine test in the 3rd trimester every 10-14 days and control blood pressure every 3-5 days.
The appearance and increase in the level of protein in the urine, the increase in blood pressure, and in some cases the development of edema require careful observation by an obstetrician-gynecologist and, often, hospitalization in the pregnancy pathology department. Preeclampsia goes away only after childbirth, you can try to restrain its development with the help of treatment, but this condition does not reverse.