What to expect after early miscarriage
Miscarriage - What happens - NHS
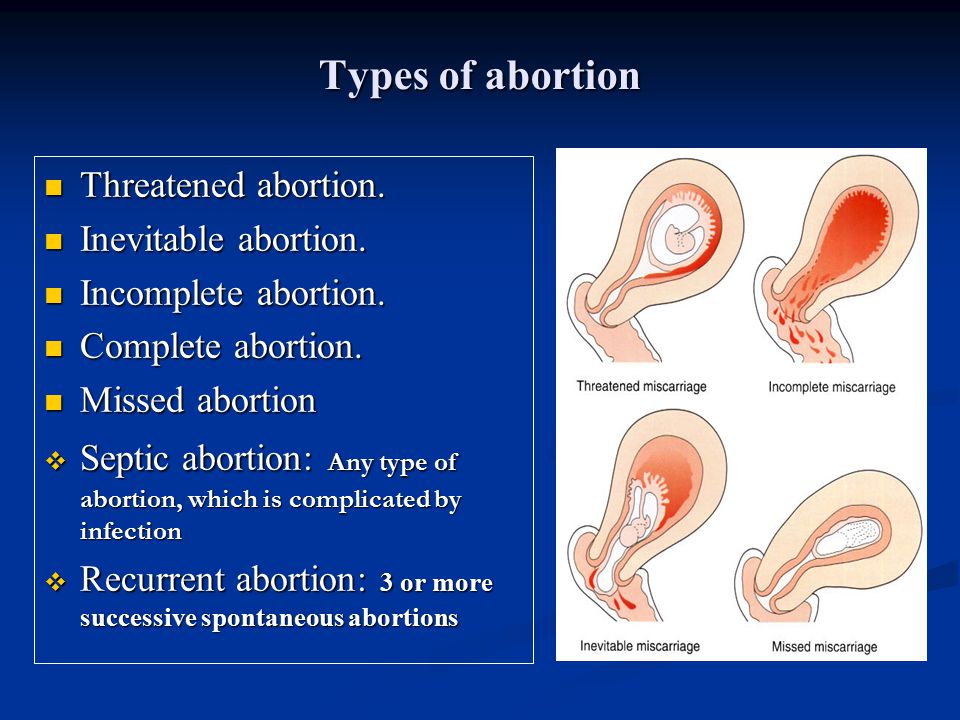
If there's no pregnancy tissue left in your womb, no treatment is required.
However, if there's still some pregnancy tissue in your womb, your options are:
- expectant management – wait for the tissue to pass out of your womb naturally
- medical management – take medicine that causes the tissue to pass out of your womb
- surgical management – have the tissue surgically removed
The risk of complications is very small for all these options. It's important to discuss them all with the doctor in charge of your care.
Expectant management
If you have a miscarriage in your first trimester, you may choose to wait 7 to 14 days after a miscarriage for the tissue to pass out naturally. This is called expectant management.
If the pain and bleeding have lessened or stopped completely during this time, this usually means the miscarriage has finished. You should be advised to take a home pregnancy test after 3 weeks.
If the test shows you're still pregnant, you may need to have further tests.
If the pain and bleeding have not started within 7 to 14 days or are continuing or getting worse, this could mean the miscarriage has not begun or has not finished. In this case, you should be offered another scan.
After this scan, you may decide to either continue waiting for the miscarriage to occur naturally, or have drug treatment or surgery. If you choose to continue to wait, your healthcare professional should check your condition again up to 14 days later.
Contact your hospital immediately if the bleeding becomes particularly heavy, you develop a high temperature (fever) or you experience severe pain.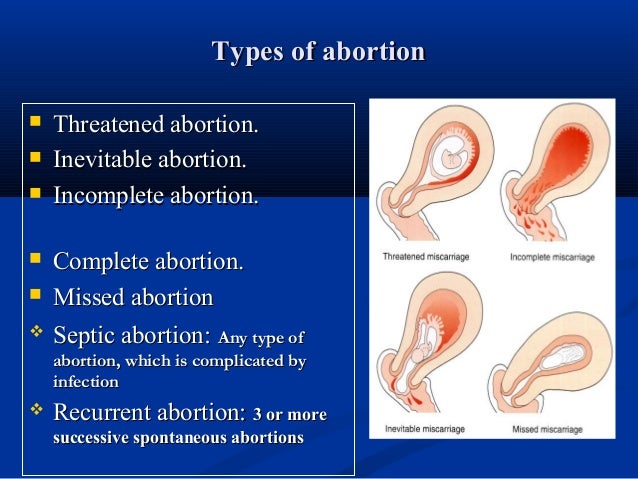
Medicine
You may choose to have medicine to remove the tissue if you do not want to wait, or if it does not pass out naturally within 2 weeks. This involves taking tablets that cause the cervix to open, allowing the tissue to pass out.
In most cases, you'll be offered tablets called pessaries that are inserted directly into your vagina, where they dissolve.
The tablets usually begin to work within a few hours. You'll experience symptoms similar to a heavy period, such as cramping and heavy vaginal bleeding. You may also experience vaginal bleeding for up to 3 weeks.
In most units, you'll be sent home for the miscarriage to complete. This is safe, but ring your hospital if the bleeding becomes very heavy.
You should be advised to take a home pregnancy test 3 weeks after taking this medicine. If the pregnancy test shows you're still pregnant, you may need to have further tests.
If the pregnancy test shows you're still pregnant, you may need to have further tests.
You may be advised to contact your healthcare professional to discuss your options if bleeding has not started within 24 hours of taking the medicine.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery is used to remove any remaining pregnancy tissue. You may be advised to have immediate surgery if:
- you experience continuous heavy bleeding
- there's evidence the pregnancy tissue has become infected
- medicine or waiting for the tissue to pass out naturally has been unsuccessful
Surgery involves removing any remaining tissue in your womb with a suction device. You should be offered a choice of general anaesthetic or local anaesthetic if both are suitable.
After a miscarriage
A miscarriage can be very upsetting, and you and your partner may need counselling or support. You may also have questions about trying for another baby and what happens to the miscarried foetus.
You may also have questions about trying for another baby and what happens to the miscarried foetus.
For more information, read what happens after a miscarriage.
Page last reviewed: 09 March 2022
Next review due: 09 March 2025
What Happens After a Miscarriage? An Ob-Gyn Discusses the Options.
Miscarriage, the loss of a pregnancy that’s in the uterus, is common. It happens in about 1 in 10 women who know they’re pregnant. But many people don’t know what to expect afterward.
The vast majority of miscarriages happen in the first trimester, before 13 weeks of pregnancy. Most occur before 10 weeks. In this article, I’ll discuss the treatment options for first-trimester miscarriage, also called early pregnancy loss. Second-trimester miscarriage usually requires different treatments.
Here’s what to know about care and recovery.
There are three main treatments for early pregnancy loss. The goal for all three is to remove any pregnancy tissue left in the uterus. There are two nonsurgical treatments: expectant management (letting the tissue pass on its own) and medication. The third treatment is a surgical procedure called dilation and curettage (also known as D&C or suction curettage).
The goal for all three is to remove any pregnancy tissue left in the uterus. There are two nonsurgical treatments: expectant management (letting the tissue pass on its own) and medication. The third treatment is a surgical procedure called dilation and curettage (also known as D&C or suction curettage).
In many cases, patients can choose the option they prefer.
Expectant management is giving your body time to pass the tissue on its own. This doesn’t involve medication or surgery. Some women choose this because it’s the most natural option, but it is more unpredictable than other treatments.
Most women pass the tissue within 2 weeks of a miscarriage diagnosis, but it can take longer. If it takes too long, your ob-gyn may recommend medication to start the process. (Once the process starts and cramping and bleeding begin, most of the tissue passes within a few hours. More on that below.)
Sometimes, the body doesn’t pass all the tissue.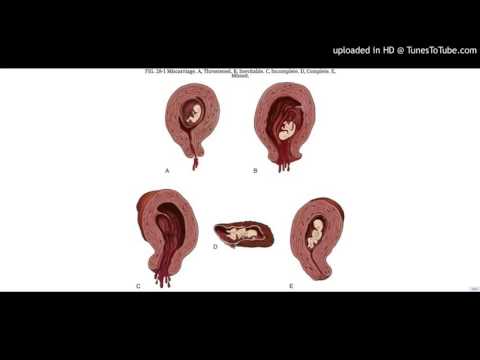 When this happens, another treatment is recommended, usually a D&C. Expectant management is most likely to work when you already have some bleeding and cramping. This means your body has begun the process of passing the tissue.
When this happens, another treatment is recommended, usually a D&C. Expectant management is most likely to work when you already have some bleeding and cramping. This means your body has begun the process of passing the tissue.
Medication works faster and is more predictable. Some women choose medication that helps their body remove any leftover tissue. These drugs are absorbed through the cheek in the mouth or through the vagina. Cramping or bleeding usually starts within a few hours. Most women pass the tissue within 48 hours and don’t need any other treatment. (Some women may still not pass all the tissue and may need a surgical procedure.)
Medication gives you more control over the timing of the tissue passing. And it’s often quicker than waiting for the tissue to pass on its own.
Some women like to take the medication in the morning, so the process doesn’t start overnight. And some women like to have a support person, such as a friend or family member, with them when they take the medication.
You’ll have a similar experience whether the tissue passes on its own or you take medication. You’ll have bleeding and cramping that are heavier than your normal period. The pregnancy tissue may look like large blood clots, or it may look white or gray. It does not look like a baby. The process can be painful, and ob-gyns may prescribe medication to help with this discomfort. Your ob-gyn may also suggest over-the-counter pain medication. Talk with your ob-gyn about pain relief options.
Most of the tissue passes within 2 to 4 hours after the cramping and bleeding start. Cramping usually stops within a day. Light bleeding or spotting can go on for 4 to 6 weeks. Two weeks after the tissue passes, your ob-gyn may do an ultrasound exam or other tests to make sure all the tissue has passed.
A D&C is the most predictable treatment. During a D&C, your ob-gyn passes a small tool through the cervix and into the uterus to remove the tissue. Some women choose this option because they want a faster, more certain treatment. And if you’re already bleeding heavily, it’s the safest option.
Some women choose this option because they want a faster, more certain treatment. And if you’re already bleeding heavily, it’s the safest option.
Some ob-gyns do D&Cs in an operating room using general anesthesia, which means you’ll be asleep. Some offer a form of pain relief called sedation, where you will be awake but comfortable. Others do the procedure in a normal exam room, with an injection of drugs that block pain in a specific area. Women often have some bleeding and intense cramping during a D&C. They usually have little discomfort afterward.
Light spotting or bleeding can last up to a month. An antibiotic is prescribed to prevent infection. Other complications are rare, and most women don’t need any follow-up appointments.
Whichever option you choose, call your ob-gyn if you have very heavy bleeding, a fever, or feel unwell. Dangerous bleeding and infection are a risk of all treatments, but these problems are rare. Call your ob-gyn right away if you have any of these symptoms:
-
Your bleeding soaks through more than two large pads in an hour for 2 hours or more.
 This much bleeding is dangerous and needs immediate care.
This much bleeding is dangerous and needs immediate care. -
You have a temperature higher than 100 °F.
-
You have chills, severe pain, or any other symptoms that concern you.
Physical recovery is usually quick. Most women resume their regular activities a day or two after they pass the tissue or have a D&C. For some, nausea and other pregnancy symptoms stop before their ob-gyn diagnoses a miscarriage. For others, these symptoms go away a few days after the tissue passes.
To keep your infection risk low, don’t put anything into your vagina for a week—no douching (which is never a good idea at any time), vaginal sex, tampons, or menstrual cups. You can use pads to absorb the bleeding. Most women have their first period about 2 weeks after any spotting or light bleeding ends, which is usually about 2 to 3 months after you pass the tissue or have a D&C.
People have different emotional reactions. Some women feel sadness or grief. Others may feel relief. Some may feel a mixture of emotions. All these feelings are normal, and it’s important to allow yourself time to process them.
Some women feel sadness or grief. Others may feel relief. Some may feel a mixture of emotions. All these feelings are normal, and it’s important to allow yourself time to process them.
Talking about these feelings with friends, family, your ob-gyn, or a mental health professional can help. If you feel depressed or are thinking of hurting yourself, tell your ob-gyn or another doctor right away. Support groups and resources, such as Share Pregnancy & Infant Loss Support, may be helpful too.
Miscarriage isn’t your fault. Women often worry that they somehow caused their miscarriage. This is not the case. Physical activity, stress, and sex don’t cause miscarriages. Most happen because the pregnancy wasn’t developing normally. Often, the egg or sperm develops with more or fewer chromosomes than normal, which can lead to miscarriage. This is a random event that you cannot control.
Most women can have a healthy pregnancy after a miscarriage. Talk with your ob-gyn if you have concerns. Your ob-gyn can help ease your fears, answer any questions, and talk about preparing for your next pregnancy.
Talk with your ob-gyn if you have concerns. Your ob-gyn can help ease your fears, answer any questions, and talk about preparing for your next pregnancy.
Published: June 2022
Last reviewed: June 2022
Copyright 2023 by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. All rights reserved. Read copyright and permissions information.
This information is designed as an educational aid for the public. It offers current information and opinions related to women's health. It is not intended as a statement of the standard of care. It does not explain all of the proper treatments or methods of care. It is not a substitute for the advice of a physician. Read ACOG’s complete disclaimer.
When can you get pregnant after a miscarriage - the opinion of geneticists
No matter how scary it sounds, miscarriages are common. One in four women experience this condition while trying to get pregnant. In most cases, the failed mother does not even know about the irreversible changes that have occurred in her body, since they occur before the conception became known. Couples who know about the misfortune that happened are interested in when it is possible to become pregnant after a miscarriage, and what conditions must be observed in order to endure and give birth to a healthy baby.
Couples who know about the misfortune that happened are interested in when it is possible to become pregnant after a miscarriage, and what conditions must be observed in order to endure and give birth to a healthy baby.
5 things you should know about miscarriage
Fortunately, many women who experience early and late miscarriages go further in their desire to become a mother. We offer to get acquainted with the facts that confirm the frequency of miscarriage and speak about the normal fertility of a woman in the subsequent period:
1. Very early miscarriages that occur shortly after implantation of the embryo are called chemical pregnancy. During this period, a woman may not know that she is pregnant;
2. Most miscarriages occur within the first three months after conception. After the 13-week mark and the end of the first trimester, the likelihood of spontaneous abortion decreases;
3. Miscarriages in the second trimester are rare. This is 1-5% of the number of all pregnancies. If a spontaneous abortion occurred after 20 weeks, it is customary to talk about a stillbirth;
This is 1-5% of the number of all pregnancies. If a spontaneous abortion occurred after 20 weeks, it is customary to talk about a stillbirth;
4. Trying to figure out how long it takes to get pregnant after a miscarriage, study all the possible reasons why the misfortune happened. In most situations, it is the result of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. This may be due to the action of the sperm or the egg. The second option is more likely, since the eggs are at rest, maturing in the ovaries for many years, while the sperm is constantly being renewed;
5. More than 85% of women after a late miscarriage can get pregnant again and give birth to healthy children. But many of them are in a difficult psychological state, which can create a real problem for conception. American researchers believe that it is very important to focus on self-soothing techniques, meditation, and learn to act through negative thoughts. The support of loved ones is very important during this period.
How long can you get pregnant after a miscarriage, and how long should a woman look after an accident? Each case is unique, and when a woman decides to conceive again depends on many factors. If there was a molar or ectopic pregnancy, when asked when it is possible to become pregnant after a miscarriage, doctors in most situations recommend waiting until the menstrual cycle is restored (at least one period after a miscarriage). But this is not the ultimate truth.
When can you get pregnant after a miscarriage - research, experiments, observations
How long should a woman wait to try to conceive again? Recent studies by scientists from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (USA) have shown that by trying to conceive within 3 months after an accident, couples increase the success of their attempts by 71% and subsequently give birth to healthy children. The study, which was based on the conceptual question - is it possible to get pregnant after a miscarriage immediately or should you wait - in the example of 1000 couples, it showed that timing matters.
765 couples tried to get pregnant in the first 90 days after a miscarriage and in 77% of cases they conceived and gave birth to a healthy baby. For those couples who waited longer than the specified period, only in 23% of cases a child was born. This proves - finding out how much you can get pregnant after a miscarriage, cast aside doubts - try to conceive. Scientists have proven that couples should not wait a certain period. The main thing is the psychological and physiological readiness for pregnancy.
How long before ovulation after a miscarriage
A miscarriage is usually accompanied by bleeding, but this cannot be considered a menstrual period. The discharge of blood is a sign of uterine cleansing. The first period will pass approximately two weeks after the first ovulation. Ovulation can be delayed if there is a high level of pregnancy hormone in the blood. On average, it occurs 14-20 days after the loss of the fetus. It is important not to try to conceive until the hormonal background is restored and the pregnancy hormone is close to zero.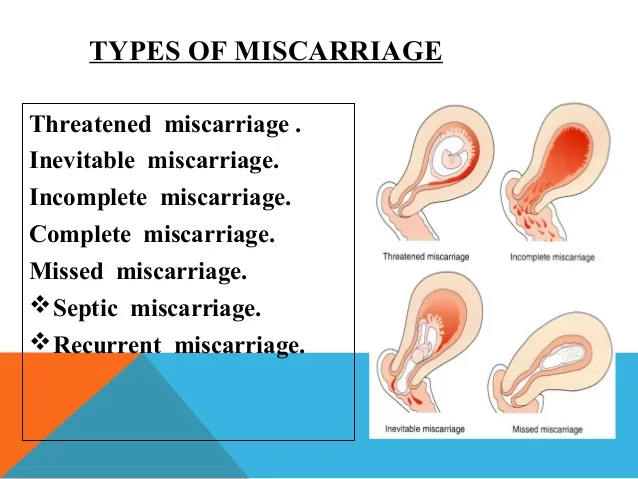
It will not be superfluous to take a pregnancy test and wait until the result is negative. This is the only way to make sure that the uterus does not contain residual effects of a failed pregnancy. In some cases, the uterus may contain foreign tissue, which can lead to fertility problems and cause abnormal bleeding. But if the level of hCG is zero, and the woman feels good, the dilemma of whether it is possible to become pregnant after a miscarriage should not worry her. The answer is obvious - yes.
If a woman has a history of two or three miscarriages in a row, this is called a recurrent miscarriage. In this case, you should contact the services of doctors for a detailed study of the situation in order to prevent its recurrence. If after the examination no serious violations are found, the chances of having healthy offspring are high.
Treatment - is cleaning required
The main goal of treatment during or after a miscarriage is to prevent bleeding and infection.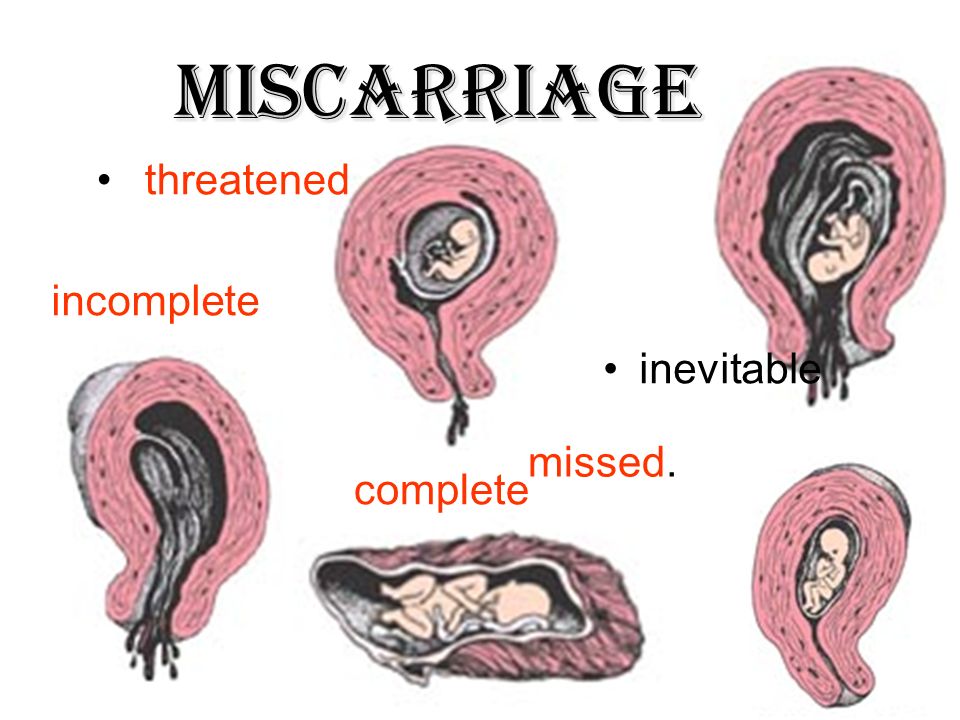 The earlier the pregnancy, the more likely it is that the body will get rid of the embryonic tissue on its own without the use of additional medical procedures. If this does not happen, the most common method to stop bleeding is cleaning (curettage, curettage, dilatation).
The earlier the pregnancy, the more likely it is that the body will get rid of the embryonic tissue on its own without the use of additional medical procedures. If this does not happen, the most common method to stop bleeding is cleaning (curettage, curettage, dilatation).
A surgical procedure is often performed after a miscarriage in the first trimester. The doctor dilates the cervix, scrapes or removes the contents. Curettage can be performed by scraping the walls of the uterus with a curette or a suction device (vacuum aspiration). When worried about when you can get pregnant after a miscarriage and curettage, study the information more carefully or ask your doctor a question.
About 50% of women who have a miscarriage do not have a curettage. If a spontaneous abortion occurred before the 10-week period, then the probability of self-cleansing of the uterus is high. If later, most likely the miscarriage will be incomplete, which requires mandatory cleaning. Also, curettage is necessary after an abortion in order to clean the uterine cavity from foreign inclusions. In any case, expectant tactics should be reasonable, you must trust the doctor's opinion.
In any case, expectant tactics should be reasonable, you must trust the doctor's opinion.
Risks after curettage
If there is no doubt when it is possible to get pregnant after a miscarriage, and the terms determined by doctors without cleaning and curettage are the minimum value, then how are things going with curettage? Does the procedure affect conception and can it cause fear of a repeated miscarriage? To figure out when you can get pregnant after a miscarriage and curettage, let's figure out what complications minimally invasive surgery can provoke.
Complications after cleansing
Cleaning, like any surgery, can cause some complications.
In the short term, these are:
- excessive bleeding shortly after surgery;
- uterine perforation;
- trauma of the cervix;
- infectious process and pain in the pelvic area.
In the long term, with a history of cleansing, it is possible:
- Development of chronic infection;
- Adhesions (tissue scarring) inside the uterus.
After the operation, the patient may experience spastic pain. You can remove them with painkillers recommended by the doctor. You can use drugs based on paracetamol (for example, Panadol) or a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory group (Brufen, Nurofen). Even with cleansing without complications, bleeding is observed for several days after the procedure. This period is different in duration for each woman. If severe bleeding develops, due to which the pad gets wet through every 30-60 minutes, you should immediately consult a doctor.
When can you get pregnant after a miscarriage and a purge - we answer questions
When asked when you can get pregnant after a miscarriage and curettage, and after how many days you can have sex, the answer is quite objective. Intimacy is available at least two weeks later, after the bleeding stops and the tissues begin to return to normal.
It is imperative to consult a doctor if you develop a fever, have vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor, abdominal and pelvic pains are gaining more intensity, bleeding is increasing. Normally, blood can flow for about two weeks after cleansing with a gradual decrease in the amount of discharge. For several days, a woman's breasts will be particularly sensitive.
Normally, blood can flow for about two weeks after cleansing with a gradual decrease in the amount of discharge. For several days, a woman's breasts will be particularly sensitive.
Surgical treatment of miscarriage does not carry a greater risk of fertility problems, in most situations it is not necessary to calculate when it is possible to become pregnant after an early miscarriage with a purge or when it is possible to conceive after a late spontaneous abortion with curettage. As soon as the body returns to normal, ovulation and the menstrual cycle are restored, a woman can begin to attempt to conceive a baby if she is emotionally ready for this. The period before conception must be devoted to restoring the body - to organize a healthy meal, use the vitamins recommended by the doctor, give up bad habits, and stabilize the rest and sleep regimen.
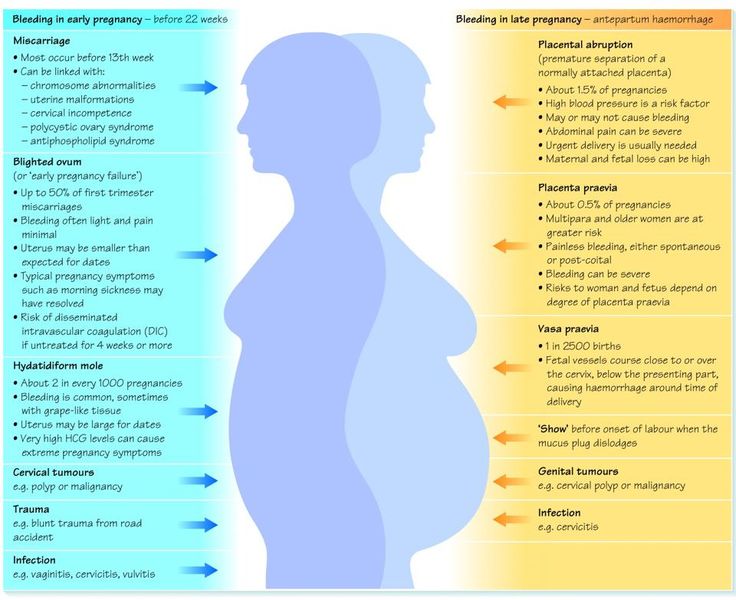
Late miscarriage - causes and consequences
The role of pregnancy in a woman's life cannot be overestimated. From the moment of conception, a woman becomes the bearer of a new life. Unfortunately, not all women are given to endure pregnancy until the final. In some cases, miscarriage occurs at a later date.
Unfortunately, not all women are given to endure pregnancy until the final. In some cases, miscarriage occurs at a later date.
What is a late miscarriage
Usually, the term "miscarriage" refers to spontaneous termination of pregnancy up to twenty-two weeks. If the fetus is lost after this period, then the term "premature birth" should be used. But quite often it is called "late miscarriage". In this case, the fetus has a chance for life if the woman seeks medical help in a timely manner and this assistance is qualified.
If the pregnancy is terminated before the twelfth week, it is called an early miscarriage. It happens in almost every fourth pregnancy. And if we take into account the data of scientific research, we can say that more than half of the fertilized eggs die on the way to the uterus, another quarter of the remaining viable ones die as a result of unsuccessful implantation.
Many women don't even know about a miscarriage because they think it's heavy menstruation after a short delay. It is necessary to determine the signs of a miscarriage in early pregnancy. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- intense pulling pains in the lower abdomen;
- profuse bleeding from the genital tract of a woman, which is accompanied by the release of massive blood clots or small parts of the fetus;
- nausea, vomiting and intestinal dyspepsia.
These signs should alert a woman and cause an immediate visit to a gynecologist. The doctor will examine the patient, perform an ultrasound scan and determine the degree of danger of this condition for the fetus. Since similar symptoms can be with an ectopic pregnancy, this disease should be ruled out immediately. The specialist will determine if the woman suffers from other diseases that could manifest similar symptoms. Then he will take emergency measures, the volume of which will depend on the identified causes of the miscarriage. With an early miscarriage, the fetus has no chance of surviving.
If the pregnancy ends spontaneously between the twelfth and twenty-second weeks, it is a late miscarriage. Threatened late miscarriage has the following symptoms:
- cramping pains resembling those during childbirth;
- uterine bleeding;
- passage of fetal fragments;
- nausea, vomiting.
Causes of miscarriage
Most miscarriages are due to genetic disorders. As you know, when an egg is fertilized by a sperm, a zygote is formed. Each sex cell (both male and female) carries a half set of chromosomes. Thus, the embryo has half of the genetic information from the father, and the other half from the mother. It is fifty percent foreign to the mother's body. If the pregnancy proceeds normally, then the woman's body starts a chain of reactions that prevent the expulsion of the fetus. In the event that gene breakdowns occur, protective factors do not work and the mother's body perceives the fetus as a foreign body, from which it tries to get rid of. As a result, an early miscarriage occurs.
As a result, an early miscarriage occurs.
Sometimes gene breakdowns are not decisive in the first trimester of pregnancy. They begin to affect at a later date, and then a late miscarriage occurs. With a late miscarriage, the fetus can be saved.
The genetic information contained in the female and male germ cells is not identical. But in the case of consanguineous marriages or a complete coincidence of genes for some other reason, the woman's body cannot cope with the tasks. Since the defense mechanisms of the fetus do not work, it is expelled from the womb and a late miscarriage occurs.
Do not forget that after fertilization there is an exchange of genes between male and female chromosomes. At this point, they may break. This will also affect the viability of the fetus and may lead to a late miscarriage.
Congenital and acquired defects in the anatomical structure of the uterus also lead to abortion and late miscarriage. The next cause of late miscarriage is isthmic-cervical insufficiency, or incompetence of the cervix. This is a condition in which the cervix loses its ability to hold the fetus inside the uterus. Late miscarriage occurs with uterine fibroids and malignant neoplasms in its wall.
This is a condition in which the cervix loses its ability to hold the fetus inside the uterus. Late miscarriage occurs with uterine fibroids and malignant neoplasms in its wall.
A separate case is an abortion during the first pregnancy. There is no doubt that every woman has the right to choose whether to leave the pregnancy or not. However, she should be aware that in many cases, cervical insufficiency develops after the first abortion, and the uterus may lose its ability to hold the fetus. The cause of fetal loss in fifteen percent of cases is problems with the umbilical cord of the embryo or placental disorders.
Some infectious diseases, such as rubella, lead to congenital anomalies in the development of the fetus, which make it unviable. The fetus dies, and the uterus begins to expel it from the cavity, which leads to a late miscarriage. The reason for termination of pregnancy may be a violation of hormonal homeostasis in the body of a pregnant woman. This happens with an imbalance of sex hormones or hypothyroidism. The presence of several fetuses in the uterine cavity, active sports, as well as excessive physical and emotional stress quite often lead to termination of pregnancy. The risk of late miscarriage decreases starting from the eighteenth week of pregnancy.
The presence of several fetuses in the uterine cavity, active sports, as well as excessive physical and emotional stress quite often lead to termination of pregnancy. The risk of late miscarriage decreases starting from the eighteenth week of pregnancy.
Late miscarriage can be caused by arterial hypertension, which is one of the signs of preeclampsia in pregnant women, and hyperglycemia in diabetes mellitus. Tobacco smoking, alcohol abuse and drug use can adversely affect pregnancy, cause disorders incompatible with the life of the fetus and provoke its death. It is impossible not to note the role of such adverse environmental factors as air pollution, the content of an excess amount of chemicals in water, ionizing radiation on the course of pregnancy and the condition of the fetus. They can also provoke a late miscarriage. It is known that quite often a late miscarriage occurs after suffering emotional upheavals, taking certain medications and injuries.
Consequences of a late miscarriage
Positive signs, although not very pleasant for a woman, that indicate that the pregnancy is proceeding normally, in the first trimester of pregnancy are malaise, as well as nausea and vomiting in the morning. If a late miscarriage has already occurred, then it can have unpleasant consequences:
If a late miscarriage has already occurred, then it can have unpleasant consequences:
- Uterine bleeding, which can be either profuse and lead to hemorrhagic shock, or insignificant over a long period of time. Sometimes parts of the ovum come off with blood clots.
- Infection of the uterus in case of fetal membranes and particles of the placenta remaining in its cavity. Fragments of an aborted pregnancy can begin to decompose and thereby cause inflammation, which can lead to the death of a woman in case of untimely and unqualified treatment.
- Infertility after late miscarriage is possible after purulent endometritis.
Methods for reducing the risk of complications after a late miscarriage
After a late miscarriage, doctors take all preventive measures to reduce the risk of complications. The choice of treatment method mainly depends on the identified pathology and can be either medical or surgical. If the late miscarriage was incomplete and either parts of the fetus or embryo, or the placenta remained in the uterine cavity, then the most effective and fastest way is to complete the miscarriage. It reduces the severity of bleeding and the intensity of pain, but, at the same time, is the most dangerous.
It reduces the severity of bleeding and the intensity of pain, but, at the same time, is the most dangerous.
During surgery, there is always a risk of perforation of the uterine wall or damage to the cervix. In this case, the woman is hospitalized, the operation is performed under general anesthesia. After the operation, she is prescribed intensive postoperative therapy.
Chances of getting pregnant after a late miscarriage
It should be understood that after a late miscarriage there is always a chance of getting pregnant again. However, it must be remembered that after a miscarriage, the probability of terminating a subsequent pregnancy increases by twenty-five percent. Its risks can be minimized only by timely full-fledged treatment. The next pregnancy must be approached carefully and responsibly.
First of all, a woman should know that she is not recommended to have sex for several weeks after a miscarriage in order to avoid infection of the uterine mucosa. Yes, and the uterus after a miscarriage should recover. The first menstruation can be expected only starting from the fifth week after a spontaneous abortion.
Yes, and the uterus after a miscarriage should recover. The first menstruation can be expected only starting from the fifth week after a spontaneous abortion.
It is worth planning a pregnancy after a late miscarriage after six months. At this time, it is necessary to contact the reproductive center to find out the reasons for the termination of pregnancy. A full examination with a spermogram is also recommended for the husband. It is also necessary, having found out the cause of the miscarriage at a later date, to undergo a course of treatment. Excellent results are obtained after spa treatment.
It is also necessary to restore the psycho-emotional balance of the spouses, give them time to realize what has happened and cope with their emotions. They may need the help of a psychologist. Sometimes women fall into a state of depression, from which they can get out after consulting a psychotherapist.
In some cases it may be necessary to consult a geneticist. Modern genetics allows not only to identify the causes of abortion, but also to predict the risks of subsequent conceptions, as well as to prevent miscarriage. You should discuss with your gynecologist the methods of contraception that are safest for a woman planning a pregnancy after a late miscarriage.
You should discuss with your gynecologist the methods of contraception that are safest for a woman planning a pregnancy after a late miscarriage.
Missed miscarriage
In some cases, an undeveloped pregnancy (empty gestational sac) is determined by ultrasound. In this case, if there is a fetal egg, there is no living embryo in it (it either developed incorrectly or lost its viability). A woman's body may not respond to these changes, and a miscarriage does not occur. The expulsion of a frozen embryo from the uterine cavity will happen one way or another, it is a matter of time. But if this happens on its own, bleeding may begin, which poses a risk to the woman's life.
In order to resolve the situation, the woman is asked to perform a curettage, or cleaning of the uterus. This procedure is performed under general anesthesia, it is done in a hospital, it lasts a few minutes. The uterine cavity is carefully, but very carefully, cleaned of the fetal egg. This helps to contract the uterus and prevent infection and bleeding. After cleaning, a woman is sometimes prescribed antibiotics.
After cleaning, a woman is sometimes prescribed antibiotics.
There is a known method of cleansing the uterus with the help of the hormonal preparation prostaglandin. It is not used so often, because the expected effect is not always observed. In this case, doctors are forced to perform surgery. In case of fetal death in late pregnancy, an artificial birth can be induced by using the hormonal drug oxytocin.
Prevention of late miscarriage
All the factors that lead to miscarriage in late pregnancy can be managed with modern methods of treatment. This greatly increases the chances of success in a subsequent pregnancy. In addition, a woman needs to take care of herself both before pregnancy and from the very beginning. The course of her pregnancy depends on the lifestyle of a woman. In order to avoid late miscarriages, you need to think a hundred times whether to terminate the first pregnancy, even if it was not planned.
You can pay too much for the dubious pleasure of smoking cigarettes or weed, drinking an alcoholic drink or walking around in thin pantyhose in winter. Also, the expectant mother should think about proper nutrition. She should eat a lot of fresh berries, fruits and vegetables, take the vitamins recommended by the doctor.
Also, the expectant mother should think about proper nutrition. She should eat a lot of fresh berries, fruits and vegetables, take the vitamins recommended by the doctor.
If you experience pain in the lower abdomen or spotting from the vagina during pregnancy, seek medical attention immediately. Indeed, in many cases, a late miscarriage that has begun can be stopped and the life of the child can be saved. In no case should you use the recommendations of casual acquaintances, girlfriends or craftsmen.
Late miscarriage can be prevented or delayed. In the latter case, the fetus retains a chance for life.
Free appointment with a reproductive specialist
until February 28, 2023
26 days left
Dear patients! Clinic "IVF Center" invites you to free reception of a reproductologist with ultrasound and preparation of a treatment plan .
Start your journey to happiness - right now!
Name *
Telephone *
E-mail *
Message *
By submitting this form, I confirm that, in accordance with the requirements of the “Federal Law on Personal Data No.