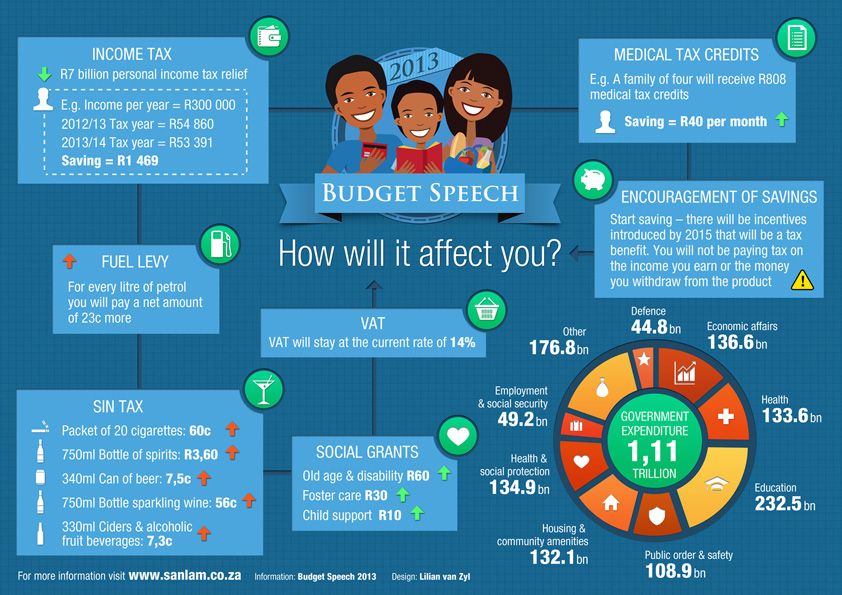
What the baby looks like
Pictures of Fetal Development Month-by-Month
Reviewed by Amita Shroff, MD on February 24, 2021
You're pregnant. Congratulations! Are you curious how big your developing baby is, what your baby looks like as it grows inside you, and when you'll feel it move? Take a peek inside the womb to see how a baby develops from month to month.
Fertilization happens when a sperm meets and penetrates an egg. It's also called conception. At this moment, the genetic makeup is complete, including the sex of the baby. Within about three days after conception, the fertilized egg is dividing very fast into many cells. It passes through the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it attaches to the uterine wall. The placenta, which will nourish the baby, also starts to form.
At this point the baby is developing the structures that will eventually form their face and neck. The heart and blood vessels continue to develop. And the lungs, stomach, and liver start to develop. A home pregnancy test would show positive.
The baby is now a little over half an inch in size. Eyelids and ears are forming, and you can see the tip of the nose. The arms and legs are well formed. The fingers and toes grow longer and more distinct.
The baby measures about 2 inches and starts to make its own movements. You may start to feel the top of your uterus above your pubic bone. Your doctor may hear the baby's heartbeat with special instruments. The sex organs of the baby should start to become clear.
The baby now measures about 4.3 to 4.6 inches and weighs about 3.5 ounces. You should be able to feel the top of your uterus about 3 inches below your belly button. The baby's eyes can blink and the heart and blood vessels are fully formed. The baby's fingers and toes have fingerprints.
The baby weighs about 10 ounces and is a little more than 6 inches long. Your uterus should be at the level of your belly button. The baby can suck a thumb, yawn, stretch, and make faces. Soon -- if you haven't already -- you'll feel your baby move, which is called "quickening. "
"
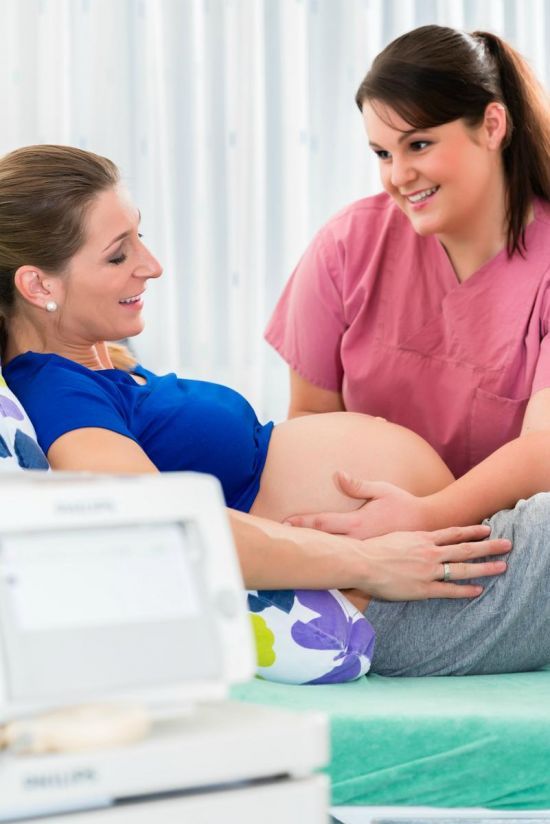
An ultrasound is usually done for all pregnant women at 20 weeks. During this ultrasound, the doctor will make sure that the placenta is healthy and attached normally and that your baby is growing properly. You can see the baby's heartbeat and movement of its body, arms, and legs on the ultrasound. You can usually find out whether it's a boy or a girl at 20 weeks.
Shown here is a 2D ultrasound (inset) contrasted with a 4D ultrasound, both at 20 weeks.
The baby weighs about 1.4 pounds now and responds to sounds by moving or increasing their pulse. You may notice jerking motions if they hiccup. With the inner ear fully developed, the baby may be able to sense being upside down in the womb.
The baby weighs about 2 pounds, 6 ounces, and changes position often at this point in pregnancy. If you had to deliver prematurely now, there is a good chance the baby would survive. Ask your doctor about preterm labor warning signs. Now is the time to register for birthing classes. Birthing classes prepare you for many aspects of childbirth, including labor and delivery and taking care of your newborn.
Birthing classes prepare you for many aspects of childbirth, including labor and delivery and taking care of your newborn.
The baby weighs almost 4 pounds and is moving around often. The baby's skin has fewer wrinkles as a layer of fat starts to form under the skin. Between now and delivery, your baby will gain up to half their birth weight. Ask your doctor how to do a fetal movement chart. Think about breastfeeding. You may notice a yellowish fluid leaking from your breasts. That is colostrum, and it happens to get your breasts ready for making milk. Most women go to the doctor every two weeks at this stage of pregnancy.
Babies differ in size, depending on many factors, such as gender, the number of babies being carried, and size of the parents. So your baby's overall rate of growth is as important as the actual size. On average, a baby at this stage is about 18.5 inches and weighs close to 6 pounds. The brain has been developing rapidly. Lungs are nearly fully developed. The head is usually positioned down into the pelvis by now. Your baby is considered at 'term' when they are 37 weeks. They are an early term baby if born between 37-39 weeks, at term, if they're 39-40 weeks and late term if they're 41-42 weeks.
The head is usually positioned down into the pelvis by now. Your baby is considered at 'term' when they are 37 weeks. They are an early term baby if born between 37-39 weeks, at term, if they're 39-40 weeks and late term if they're 41-42 weeks.
A mother's due date marks the end of their 40th week. The delivery date is calculated using the first day of their last period. Based on this, pregnancy can last between 38 and 42 weeks with a full-term delivery happening around 40 weeks. Some post-term pregnancies -- those lasting more than 42 weeks -- are not really late. The due date may just not be accurate. For safety reasons, most babies are delivered by 42 weeks. Sometimes the doctor may need to induce labor.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
(1) Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake – All rights reserved.
(2) Dr. David M. Phillips / Visuals Unlimited / Getty Images
(3) 3D4Medical.com / Getty Images
(4) Copyright © Scott Camazine / Phototake -- All rights reserved.
(5) Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake – All rights reserved.
(6) Nestle / Petit Format / Photo Researchers, Inc.
(7) © Lennart Nilsson Photography AB. All rights reserved worldwide.
(8) a) Dr.Benoit/Mona Lisa. Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake -- All rights reserved. b)Vincenzo Lombardo / Photographer's Choice / Getty Images
(9) Dr. Benoit/Mona Lisa. Copyright © LookatSciences / Phototake -- All rights reserved.
(10) © Lennart Nilsson Photography AB. All rights reserved worldwide.
(11) Jose Manuel Gelpi Diaz / iStockphoto
(12) © Lennart Nilsson Photography AB. All rights reserved worldwide.
(13) © Yoav Levy / Phototake -- All rights reserved.
SOURCES:
American Academy of Family Physicians.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: "How Your Baby Grows During Pregnancy."
KidsHealth.org: "Pregnancy Calendar."
March of Dimes: "Prenatal Care – Ultrasound."
US Department of Health and Human Services Office of Women’s Health: "Pregnancy: Breast Changes."
© 2021 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. View privacy policy and trust info
All rights reserved. View privacy policy and trust info
7 Things That Influence What Your Baby Will Look Like
One of the most common questions in an expecting mother’s mind is what her unborn baby will look like. From the moment we realize we’re pregnant until the day our baby is in our arms, most mothers will spend countless hours daydreaming about who their little one will resemble. Most babies will look more like mom, more like dad, or a curiously even combination of the two. On the other hand, some babies come out looking like no one expected!
There are a great number of factors that go into what your unborn baby will look like. Here are some of the most common things that can influence how your baby will look when they finally make their grand debut.
DNA
Everyone knows that DNA is what determines your baby’s appearance. But DNA is a very complex subject. Everything from hair color, eye color, height, and weight to the placement of dimples or freckles can be dictated by you or your partner’s (or both!) DNA.![]() And while, in most cases, dominant genes win the DNA fight, every now and then, a recessive gene will come out of nowhere and surprise everyone!
And while, in most cases, dominant genes win the DNA fight, every now and then, a recessive gene will come out of nowhere and surprise everyone!
Alcohol
While some studies show that a tiny amount of alcohol every now and then may be okay for women during pregnancy, there is a chance that any alcohol consumption could result in Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. This syndrome can cause a developing fetus to be born with unique facial appearances such as very small eyes or thin lips. It can also affect a child’s cognitive and developmental abilities.
Healthy Habits
Moms who make poor exercise and food choices while pregnant may affect whether their child will be born at a healthy weight. Studies show that obese moms are more likely to give birth to babies who later also become obese. From the moment you realize you’re pregnant (and even before!), make sure you are making healthy, nutritious food choices. And don’t skip that exercise!
Supplements
Prenatal vitamins are important for a great number of reasons. But one supplement, in particular, can affect the baby’s appearance more than others. Folate is critical in helping to form your baby’s spine. A folate deficiency can result in spina bifida.
But one supplement, in particular, can affect the baby’s appearance more than others. Folate is critical in helping to form your baby’s spine. A folate deficiency can result in spina bifida.
Caffeine
Studies have shown that excessive caffeine consumption may affect a baby’s birth weight, producing a newborn that is smaller and slimmer than normal at birth. It is best to limit your caffeine consumption to the equivalent of one cup of coffee a day or less.
Traveling
Extensive airline travel can expose a pregnant mama to unhealthy levels of radiation. As you can imagine, radiation is not recommended for a developing fetus and can potentially affect your baby’s appearance. Periodic travel during pregnancy is considered safe for most women, however.
Family History
Your family’s history can play a part in how your baby looks. Like recessive genes, some inherited genes may lay “dormant” or “skip” generations and suddenly pop up to surprise families when they least expect it!
While there’s no way to tell exactly what your baby will look like before he or she is born, these are some of the ways that may influence their appearance. As a mom of two myself, I was surprised to find that my daughter came out looking exactly like my husband but had my personality. On the other hand, my son was my mini-me with his daddy’s infectious wit and charm. One of the best things about parenthood, I think, is being surprised by the wonderful little human beings you and your partner have created. They change so much every day, so be sure to savor every moment!
As a mom of two myself, I was surprised to find that my daughter came out looking exactly like my husband but had my personality. On the other hand, my son was my mini-me with his daddy’s infectious wit and charm. One of the best things about parenthood, I think, is being surprised by the wonderful little human beings you and your partner have created. They change so much every day, so be sure to savor every moment!
Child development by week | Regional Perinatal Center
Expectant mothers are always curious about how the fetus develops at a time when it is awaited with such impatience. Let's talk and look at the photos and pictures of how the fetus grows and develops week by week.
What does the puffer do for 9 whole months in mom's tummy? What does he feel, see and hear?
Let's start the story about the development of the fetus by weeks from the very beginning - from the moment of fertilization. A fetus up to 8 weeks old is called embryo , this occurs before the formation of all organ systems.
Embryo development: 1st week
The egg is fertilized and begins to actively split. The ovum travels to the uterus, getting rid of the membrane along the way.
On the 6th-8th days, implantation of eggs is carried out - implantation into the uterus. The egg settles on the surface of the uterine mucosa and, using the chorionic villi, attaches to the uterine mucosa.
Embryo development: 2-3 weeks
Picture of embryo development at 3 weeks.
The embryo is actively developing, starting to separate from the membranes. At this stage, the beginnings of the muscular, skeletal and nervous systems are formed. Therefore, this period of pregnancy is considered important.
Embryo development: 4–7 weeks
Fetal development by week in pictures: week 4
Fetal development by week photo: week 4
Photo of an embryo before the 6th week of pregnancy.
The heart, head, arms, legs and tail are formed in the embryo :) . Gill slit is defined. The length of the embryo at the fifth week reaches 6 mm.
Fetal development by week photo: week 5
At the 7th week, the rudiments of the eyes, stomach and chest are determined, and fingers appear on the handles. The baby already has a sense organ - the vestibular apparatus. The length of the embryo is up to 12 mm.
Fetal development: 8th week
Fetal development by week photo: week 7-8
The face of the fetus can be identified, the mouth, nose, and auricles can be distinguished. The head of the embryo is large and its length corresponds to the length of the body; the fetal body is formed. All significant, but not yet fully formed, elements of the baby's body already exist. The nervous system, muscles, skeleton continue to improve.
Fetal development in the photo already sensitive arms and legs: week 8
The fetus developed skin sensitivity in the mouth (preparation for the sucking reflex), and later in the face and palms.
At this stage of pregnancy, the genitals are already visible. Gill slits die. The fruit reaches 20 mm in length.
Fetal development: 9–10 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 9
Fingers and toes already with nails. The fetus begins to move in the pregnant woman's stomach, but the mother does not feel it yet. With a special stethoscope, you can hear the baby's heartbeat. Muscles continue to develop.
Weekly development of the fetus photo: week 10
The entire surface of the fetal body is sensitive and the baby develops tactile sensations with pleasure, touching his own body, the walls of the fetal bladder and the umbilical cord. It is very curious to observe this on ultrasound. By the way, the baby first moves away from the ultrasound sensor (of course, because it is cold and unusual!), And then puts his hands and heels trying to touch the sensor.
It's amazing when a mother puts her hand to her stomach, the baby tries to master the world and tries to touch with his pen "from the back".
The development of the fetus: 11–14 weeks
Development of the fetus in the photo of the legs: weeks 11
The baby, legs and eyelids are formed, and the genitals become distinguishable (you can find out the gender (you can find out the gender child). The fetus begins to swallow, and if something is not to its taste, for example, if something bitter got into the amniotic fluid (mother ate something), then the baby will begin to frown and stick out his tongue, making less swallowing movements.
Fruit skin appears translucent.
Fruit development: Week 12
Photo of the fetus 12 weeks per 3D Uzi
buds are responsible for production for production urine. Blood forms inside the bones. And hairs begin to grow on the head. The skin turns pink, the ears and other parts of the body, including the face, are already visible. Imagine, a child can already open his mouth and blink, as well as make grasping movements. The fetus begins to actively push in the mother's tummy. The sex of the fetus can be determined by ultrasound. Baby sucks his thumb, becomes more energetic. Pseudo-feces are formed in the intestines of the fetus - meconium , kidneys begin to work. During this period, the brain develops very actively. The auditory ossicles become stiff and now they are able to conduct sounds, the baby hears his mother - heartbeat, breathing, voice. The lungs at this stage of fetal development are so developed that the baby can survive in the artificial conditions of the intensive care unit. Lungs continue to develop. Now the baby is already falling asleep and waking up. Downy hairs appear on the skin, the skin becomes wrinkled and covered with grease. The cartilage of the ears and nose is still soft. Lips and mouth become more sensitive. The eyes develop, open slightly and can perceive light and squint from direct sunlight. In girls, the labia majora do not yet cover the small ones, and in boys, the testicles have not yet descended into the scrotum. Fetal weight reaches 900–1200 g, and the length is 350 mm. 9 out of 10 children born at this term survive. The lungs are now adapted to breathe normal air. Breathing is rhythmic and body temperature is controlled by the CNS. The baby can cry and responds to external sounds. Child opens eyes while awake and closes during sleep. The skin becomes thicker, smoother and pinkish. Starting from this period, the fetus will actively gain weight and grow rapidly. Almost all babies born prematurely at this time are viable. The weight of the fetus reaches 2500 g, and the length is 450 mm. The fetus reacts to a light source. Muscle tone increases and the baby can turn and raise his head. On which, the hairs become silky. The child develops a grasping reflex. The lungs are fully developed. The fetus is quite developed, prepared for birth and considered mature. The baby perfectly mastered the movements of his mother , knows when she is calm, excited, upset and reacts to this with her movements. During the intrauterine period, the fetus gets used to moving in space, which is why babies love it so much when they are carried in their arms or rolled in a stroller. For a baby, this is a completely natural state, so he will calm down and fall asleep when he is shaken. The nails protrude beyond the tips of the fingers, the cartilages of the ears and nose are elastic. In boys, the testicles have descended into the scrotum, and in girls, the large labia cover the small ones. The weight of the fetus reaches 3200-3600 g, and the length is 480-520 mm. After the birth, the baby longs for touching his body, because at first he cannot feel himself - the arms and legs do not obey the child as confidently as it was in the amniotic fluid. And one more thing, the baby remembers the rhythm and sound of your heart very well . Therefore, you can comfort the baby in this way - take him in your arms, put him on the left side and your miracle will calm down, stop crying and fall asleep. And for you, finally, the time of bliss will come :) . During the ninth week, the weight of the fetus changes from 1 gram to 10 grams, the length is 30-45 mm. The back of the fetus straightens and the embryonic tail disappears. The future child becomes completely similar to a small person. The head at this stage is pressed to the chest, the neck is bent, the arms are also brought to the chest. The development of the brain, which is quite intense, is one of the main processes of this period. The heart rate at this stage is 120-150 beats per minute, the heart has two ventricles and two atria. There is a circulatory system of vessels, blood begins to flow through them. While blood circulation in the upper part of the fetus is characterized by greater intensity than in the lower. Therefore, the arms are more developed in comparison with the legs. There is an elongation of the fingers, and the membranes between them slowly disappear. By the end of the ninth week, the formation of the eye ends, they are tightly covered with eyelids. There is a closing of the facial bones, on the head it is already possible to distinguish the nose and nostrils, auricles and lobes, and the upper lip. At this stage, the fetus becomes more and more like a human face. Intensive development of internal organs leads to rounding of the tummy of the fetus. The digestive organs and the liver develop, which is important because it is responsible for hematopoiesis (the formation of new blood cells). Thus, "fetal" blood appears. At this stage in the life of the fetus, such an important event occurs as the beginning of the synthesis of hormones, which include adrenaline. Intensive growth of the adrenal glands provides this process. Also, the beginning of the synthesis of hormones is associated with the complication of the structure of the adrenal glands. All this helps the fetus to comfortably adapt to a variety of changes and extreme conditions. It is the presence of adrenaline in the body that allows it to withstand various stresses. The fetus acquires the ability to endure stress, since adrenaline provides the regulation of a special mode of "survival". At this stage, the woman may still have drowsiness, fatigue, frequent mood swings and dizziness. This week is important and significant, it is from it that the fetal stage of development begins, and the unborn child is now officially called a fetus, not an embryo. All the internal organs have already been laid, which in the future will only have to grow and develop. Experts rightly consider the tenth week to be the final one in the first critical period: from that time on, the likelihood of developing defects that may arise due to chemical factors of various nature is no longer so high. The fetus at this time is freely located in the uterine cavity, practically not touching its walls. The future baby has an intensive formation of the nervous system, the transmission of impulses by neuromuscular pathways is being established. This process leads to the emergence of intense movements. Such movements are reflex, they are active and are caused by contact with the walls of the uterus. At this time, the diaphragm is finally formed - a flat muscle designed to separate the abdominal and chest cavities. There is a further development of internal organs. The woman feels increased anxiety, she retains emotional lability. All this is a consequence of ongoing hormonal changes. The only thing to be understood is that the balance will soon be restored, which means the return of a stable good mood. The situation changes with the manifestations of toxicosis. Nausea begins to disturb less and less, and vomiting, as a rule, stops altogether. Nausea mostly in the morning. If toxicosis completely disappears, increased appetite may occur. At this time, it is important to monitor the diet and prevent a sharp increase in weight. Women in the tenth week may notice a change in the abdomen. The reason may be overeating, as well as the redistribution of subcutaneous fat and muscle relaxation due to the influence of the pregnancy hormone - progesterone. The uterus enlarges during this period, but not so much as to influence the shape of the abdomen, it reaches the size of a large apple or grapefruit. Accordingly, for others, pregnancy is still completely invisible. The fetus at the eleventh week continues intensive growth. Outwardly, it looks like this: a fairly large head, small legs pressed to the tummy, a small torso and well-developed long arms. The fetus continues to form joints and bones, muscle growth. Not only large joints develop, but also small ones. In the jaws, the rudiments of teeth are formed, on the fingers - nails. The movements of the unborn child become more and more purposeful. Loud noises and sudden movements begin to cause a response in him. Grasping and sucking reflexes develop - this can be seen in the movement of the fingers and lips. The formation of olfactory and taste buds begins. If amniotic fluid enters the nose or mouth, the fetus is able to taste it. At this stage, the formation of the iris of the eyes also takes place, which after birth will determine their color. In newborns, in most cases, the eyes are blue or blue, brown are quite rare. At this time, in most cases, vomiting and nausea, as well as intolerance to certain odors, disappear. Thus, a woman gets the opportunity to form a complete diet and start eating varied, giving preference to various healthy foods. It is advisable to eat freshly prepared food. If you follow a certain diet, you can avoid any problems at this time, the main of which is a problem with digestion. The relaxing hormone progesterone causes the bowel muscles to become lazy, leading to bloating and constipation. If even strict adherence to the diet does not help to cope with problems, you need to contact a specialist who can prescribe safe medications. As the fetus grows, blood volume also increases. As a result of such changes, a woman may experience increased sweating. At eleven weeks, the first prenatal screening is performed, which is aimed at identifying malformations. An ultrasound and biochemical study is performed. The first screening is not only aimed at identifying malformations. This examination allows you to find out the state of the chorion, the growth and degree of development of the fetus, the exact gestational age and other details. Twelfth week ends the first trimester of pregnancy. By the end of this period, the length of the fetus is 90 mm, and its weight is approximately 20 g. At this time, many significant events take place in the life of the fetus. He has an intensive development of the brain, the formation of connections between the spinal cord and the cerebral hemispheres. There is also development of the digestive tract. The liver, which at this stage is the most developed organ and occupies most of the abdominal cavity, begins to produce bile, and not only provide hematopoiesis, as it was before. It is from the twelfth week that the intestine actively grows and begins to fit into loops, which can later be seen in an adult. The first peristaltic movements occur, i.e., the contraction of the muscles of the intestine, which should in the future ensure the movement of food through it. The fetus, starting from this week, swallows amniotic fluid, and they pass through the intestines. This happens before birth. Peristaltic waves are a training of the intestinal muscles. In addition, rhythmic muscle movements occur in the fetus, which are also training and imitate breathing. The glottis is tightly closed, so amniotic fluid is not able to penetrate to the respiratory organs. The kidneys begin to function in the fetus, urine in them is collected in small portions and exits through the urethra, entering the amniotic fluid. At the twelfth week, the formation of the placenta is completed, which becomes able to function independently. The placenta is the most important organ for the fetus; through it, not only is the exchange of nutrients between the woman and the fetus. The placenta is an effective protector against internal and external toxins. Twelve weeks is rightly considered the best in pregnancy. The woman's well-being returns to normal due to the transfer of control of the process from the corpus luteum, which produced progesterone, which is the culprit of many troubles, to the placenta.
Development of the fetus for weeks: Week 14 9000 9000  Moves more coordinated.
Moves more coordinated. Fetal development: 15-18 weeks
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 15 Fetal development: 19-23 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 19
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 20  The fetus intensively gains weight, fat deposits are formed. The weight of the fetus reaches 650 g, and the length is 300 mm.
The fetus intensively gains weight, fat deposits are formed. The weight of the fetus reaches 650 g, and the length is 300 mm. Fetal development: 24-27 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 27 
Fetal development: 28-32 weeks
Fetal development: 33-37 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 36 Fetal development: 38-42 weeks
 The baby has mastered over 70 different reflex movements. Due to the subcutaneous fatty tissue, the baby's skin is pale pink. The head is covered with hairs up to 3 cm.
The baby has mastered over 70 different reflex movements. Due to the subcutaneous fatty tissue, the baby's skin is pale pink. The head is covered with hairs up to 3 cm.
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 40  Therefore, so that your baby does not feel lonely, it is advisable to carry him in your arms, press him to you while stroking his body.
Therefore, so that your baby does not feel lonely, it is advisable to carry him in your arms, press him to you while stroking his body. 9-12 weeks of pregnancy
Ninth week for the baby
 The cerebellum begins to function, the hemispheres acquire a clear outline. Since the cerebellum is responsible for the coordination of movements, in the fetus they cease to be spontaneous and become clear and active, the fetus begins to feel the movement of its own body.
The cerebellum begins to function, the hemispheres acquire a clear outline. Since the cerebellum is responsible for the coordination of movements, in the fetus they cease to be spontaneous and become clear and active, the fetus begins to feel the movement of its own body. 
Ninth week for the expectant mother
 Manifestations of toxicosis can reach their maximum. It is this period that is optimal in order to visit a gynecologist and register.
Manifestations of toxicosis can reach their maximum. It is this period that is optimal in order to visit a gynecologist and register. The tenth week for the baby
 The fetus already makes fairly clear movements with its legs, head and handles. The woman is not yet able to feel the movements of the fetus, but they are clearly visible during an ultrasound examination.
The fetus already makes fairly clear movements with its legs, head and handles. The woman is not yet able to feel the movements of the fetus, but they are clearly visible during an ultrasound examination. The tenth week for the expectant mother
 It is necessary to exclude overeating and the use of high-calorie foods. For a woman in position, this is harmful and can cause shortness of breath, swelling, deterioration of well-being. Excess weight is the reason for increasing the load on all body systems, which already spends a lot of energy on the development of the fetus.
It is necessary to exclude overeating and the use of high-calorie foods. For a woman in position, this is harmful and can cause shortness of breath, swelling, deterioration of well-being. Excess weight is the reason for increasing the load on all body systems, which already spends a lot of energy on the development of the fetus. Eleventh week for baby
 Such an uneven development is due to the fact that it was the upper part of the body that received the bulk of the nutrients and the proportion of oxygen throughout the entire previous period, in which such vital organs as the heart and brain are located.
Such an uneven development is due to the fact that it was the upper part of the body that received the bulk of the nutrients and the proportion of oxygen throughout the entire previous period, in which such vital organs as the heart and brain are located.  The final color of the iris is formed by five months. It depends on the accumulated melanin pigment located in the iris. Genetic inheritance determines the amount of this pigment.
The final color of the iris is formed by five months. It depends on the accumulated melanin pigment located in the iris. Genetic inheritance determines the amount of this pigment. Eleventh week for the expectant mother
 Increased kidney function leads to more frequent urination. If there is no discomfort and pain with frequent urination, there is no reason to worry. Otherwise, you will also need to pay a visit to a specialist. Discomfort and pain can be symptoms of inflammation of the bladder, i.e. cystitis syndromes.
Increased kidney function leads to more frequent urination. If there is no discomfort and pain with frequent urination, there is no reason to worry. Otherwise, you will also need to pay a visit to a specialist. Discomfort and pain can be symptoms of inflammation of the bladder, i.e. cystitis syndromes. Twelfth week for the baby
 If we consider the structure of the brain, it resembles a smaller version of the brain of an adult. During all the first months, only erythrocytes were in the blood of the fetus, but at the twelfth week, leukocytes, which are the body's defenders and belong to the immune system, are added to them.
If we consider the structure of the brain, it resembles a smaller version of the brain of an adult. During all the first months, only erythrocytes were in the blood of the fetus, but at the twelfth week, leukocytes, which are the body's defenders and belong to the immune system, are added to them. 
Twelfth week for the mother-to-be