Is not eating a sign of pregnancy
Pregnancy - signs and symptoms
Significant hormonal changes take place during pregnancy. These trigger a variety of symptoms. Some women experience many of the symptoms of pregnancy, while others may have only a few.
Symptoms of early pregnancy include missed periods, breast changes, tiredness, frequent urination, and nausea and vomiting (morning sickness). However, these symptoms may be caused by other factors and do not necessarily mean that you are pregnant, so if you suspect you are pregnant take a home pregnancy test and see your GP.
A wide range of changes can occur in your body in the later stages of pregnancy, including backache, headache, leg cramps or varicose veins, itch or tingling, constipation, haemorrhoids or indigestion, vaginitis or vaginal discharge, or mood changes or depression.
If you have any concerns don’t hesitate to talk to your GP. See your GP right away if you experience symptoms like vaginal bleeding or breaking waters, chronic pain, high temperature, severe headaches or vision loss.
The signs of early pregnancy can include:
- missed period
- nausea and vomiting (often called ‘morning’ sickness, but it can occur at any time)
- breast tenderness and enlargement
- fatigue
- passing urine more frequently than usual, particularly at night
- cravings for some foods, distaste for foods you usually like, and a sour or metallic taste that persists even when you’re not eating (dysgeusia).
Many of the signs of pregnancy, such as a missed period (amenorrhoea), nausea (morning sickness) or tiredness can also be caused by stress or illness, so if you think you are pregnant take a home pregnancy test (urine test) or see your GP, who will administer a urine test, blood test or ultrasound scan.
Missed period
Missing a period is often the first sign of possible pregnancy. However, some women experience light bleeding around the time of their expected period.
Nausea and vomiting
‘Morning’ sickness is a condition that affects more than half of all pregnant women. The symptoms include nausea and vomiting, and loss of appetite. Many women with morning sickness don’t just get symptoms in the morning but experience them throughout the whole day.
The symptoms include nausea and vomiting, and loss of appetite. Many women with morning sickness don’t just get symptoms in the morning but experience them throughout the whole day.
Morning sickness usually begins around the fourth to sixth week of pregnancy and may settle by week 12, although it can continue for longer or return at around 32 weeks.
Breast changes
During pregnancy, the breasts become fuller, swollen and tender. These changes are similar to those you may have noticed in the few days before your period. During pregnancy, the skin around the nipple becomes darker and the veins in the breast become more obvious.
Fatigue
Overwhelming tiredness is common in early pregnancy. This is most likely caused by the massive increase in the sex hormone progesterone. Progesterone is needed to maintain the pregnancy and help the baby to grow, but it also slows your metabolism.
Try to get some more sleep or rest when you can during this early stage. Your energy levels will probably rise again by around the fourth month of pregnancy when the placenta is well established.
Your energy levels will probably rise again by around the fourth month of pregnancy when the placenta is well established.
Tiredness during pregnancy can also be caused by anaemia, which is most commonly caused by iron deficiency. Eating iron-rich foods is important in the prevention of iron deficiency anaemia during pregnancy. Medical treatment of anaemia in pregnancy usually involves taking iron tablets. Sometimes an iron infusion (iron medicine given by a drip) is needed. This needs a hospital admission but only takes a few hours. Some iron infusions can be given by your GP.
Frequent urination
Pregnancy causes an increase in levels of body fluids and greater kidney efficiency. The swelling uterus also presses against the bladder. As a result, most women start experiencing more frequent urination within the first few weeks of becoming pregnant.
Food cravings
Cravings for certain foods are very common in pregnancy, especially for foods that provide energy and calcium, such as milk and other dairy products. You may also notice a sudden distaste for foods you previously liked.
You may also notice a sudden distaste for foods you previously liked.
Some women even develop an unusual taste for non-food items such as soil or paper. This is called ‘pica’ and may indicate a nutrient deficiency. Please speak to your GP or midwife if this develops.
Other symptoms of pregnancy
Many of these symptoms may also be indicative of other conditions. If in doubt, see your GP.
- backache
- breathlessness
- constipation
- haemorrhoids (piles)
- headaches
- heartburn and indigestion
- itchy skin
- leg cramps
- mood changes (such as unexplained crying)
- tingling and numbness in your hands
- vaginal discharge
- vaginitis
- varicose veins and leg oedema (swelling).
Backache
Back pain during pregnancy can affect more than 1 in 3 women. This is usually due to loosening of ligaments and change in posture due to the growing pregnancy.
You can help reduce back pain during pregnancy by wearing flat heeled shoes, using chairs with good back support, avoiding lifting heavy objects, and doing gentle exercise. Exercising in water can reduce back pain in pregnancy, and physiotherapy and acupuncture may also help.
Exercising in water can reduce back pain in pregnancy, and physiotherapy and acupuncture may also help.
Breathlessness
At the onset of pregnancy the hormone progesterone increases your lung capacity. This enables you to carry more oxygen to your baby and get rid of waste products such as the carbon dioxide that you both produce. At each breath you breathe more deeply and the amount of air you inhale (and exhale) increases significantly. This can make you feel short of breath.
In addition, as pregnancy approaches term, the pressure of the enlarging uterus and baby on your diaphragm can make your breathing feel more laboured.
Contact your doctor or midwife if you experience sudden onset of breathlessness associated with any of the following:
- pain
- palpitations (heart pounding)
- extreme tiredness
- exercise.
Constipation
Constipation refers to infrequent, hard bowel movements that are difficult to pass. Constipation is a common problem in pregnancy that may be caused by pregnancy hormones slowing your gastrointestinal movement, or by the pressure of your growing uterus on your rectum.
If you experience constipation during pregnancy, you are advised to:
- drink plenty of water every day.
- increase your dietary fibre (such as bran, wheat and fresh fruit and vegetables).
- do gentle, low impact exercise such as swimming, walking or yoga.
Don't take over-the-counter laxatives without first consulting your midwife or GP. If changes to your diet and lifestyle don't make a difference then your GP or midwife can prescribe a laxative that is safe to use in pregnancy.
Haemorrhoids (piles)
You may develop haemorrhoids (also known as piles) as a result of straining from constipation or the pressure of your baby’s head. Be reassured, symptoms usually resolve on their own soon after birth.
If you have bleeding from haemorrhoids, itching, discomfort or pain it is recommended that you:
- Alleviate or prevent constipation by increasing your daily water and fibre intake.
- Sit in warm salty water for about 15 minutes, especially after a bowel motion.

- Apply haemorrhoid cream.
If the bleeding or pain continues, talk with your GP (doctor) or midwife.
Headaches
Contact your GP or midwife if you have a headache during pregnancy that is not relieved by paracetamol (such as Panadol), especially in the second half of pregnancy.
A persistent headache can be associated with pre-eclampsia – a condition that can affect your kidneys and thus increase blood pressure and decrease blood flow to your baby.
Heartburn and indigestion
Heartburn, reflux or indigestion is the pain and discomfort associated with acid from the stomach entering and ‘burning’ the oesophagus.
Indigestion is more common during pregnancy due to the pressure of the enlarging uterus on the organs of the abdomen and the action of the hormone progesterone that relaxes the muscle between the oesophagus and stomach.
If you are experiencing heartburn, reflux or indigestion, it is recommended that you:
- Eat small and more frequent meals.

- Avoid eating just before going to bed.
- Sleep with extra pillows so your head is raised.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing.
- Avoid any food or fluid that aggravates symptoms – such as fatty foods (including fried foods, fatty meats and pastry), spicy foods (including curry and chilli), alcohol and caffeine (including tea, coffee, chocolate and cola).
- Consult your doctor before taking antacids.
If these strategies do not relieve your symptoms, please consult your GP, who may prescribe a medication that will safely reduce the secretion of acid.
Itchy skin
Widespread itching over the body is not common in pregnancy but it can be very distressing, interfering with sleep and enjoyment of pregnancy. Dry skin and eczema are the most common causes but sometimes there may be no apparent cause for the itching. In rare cases, where the palms of the hands and soles of the feet are itchy, it may be due to serious liver disease – a blood test can be done to check for this.
An itchy rash in the later part of pregnancy is thought to be caused by the body’s reaction to the stretching of the skin. This is called PUPPS. Itching can be controlled by using moisturisers and antihistamines. Ask your doctor or midwife what antihistamines are safe in pregnancy.
Leg cramps
Leg cramps occur due to a build-up of acids that cause involuntary contractions of the affected muscles. They are experienced by up to half of pregnant women, usually at night. Leg cramps are more likely in the second and third trimesters.
If you experience leg cramps, it is recommended that during an episode you:
- Walk around.
- Stretch and massage the affected muscle(s) to disperse the build-up of acids.
- Apply a warm pack to the affected muscle(s).
If you find cramps troublesome, discuss with your GP or midwife the option of taking magnesium lactate or citrate morning and evening.
Mood changes
Some newly pregnant women experience mood changes such as irritability. Other pregnant women experience feelings of elation. It is thought that the pregnancy hormones influence chemicals in the brain, causing mood changes.
Other pregnant women experience feelings of elation. It is thought that the pregnancy hormones influence chemicals in the brain, causing mood changes.
During pregnancy, 1 in 10 women experience depression. Depression is treatable, so if you are feeling depressed or ‘down’ during pregnancy it is extremely important to get help early. Please contact your GP (doctor), midwife or maternal and child health nurse as soon as possible.
Tingling and numbness in your hands (carpal tunnel syndrome)
Carpal tunnel syndrome – tingling and numbness in your hands – affects up to 60 per cent of women during pregnancy. It is caused by compression of the median nerve due to an increase in the tissue fluids during pregnancy.
Carpal tunnel syndrome may be mild, intermittently painful, or severe, which may cause partial paralysis of the thumb or loss of sensation. Symptoms usually resolve on their own soon after birth.
If you are experiencing tingling and numbness in your hands, inform your doctor or midwife. In very severe cases, your doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections or surgical treatment.
In very severe cases, your doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections or surgical treatment.
Vaginal discharge
An increase in vaginal discharge is a common change during pregnancy. If it is associated with itchiness, pain, a bad odour or pain on passing urine then it may be due to an infection. Seek treatment from your GP.
Vaginitis
Vaginitis is inflammation of the vagina, and is a distressing complaint for many women. It is more frequent during pregnancy. Some causes of vaginitis include vaginal thrush, bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis and chlamydia. See your GP for diagnosis and treatment
Varicose veins and leg oedema (swelling)
Varicose veins of the legs are very common in pregnancy due to a combination of factors, including increased volume of circulating blood during pregnancy, and pressure of the pregnant uterus on the larger veins. This increased pressure on the veins can also result in swelling of the legs (oedema) that can cause pain, feelings of heaviness, cramps (especially at night) and other unusual sensations.
If you have varicose veins, it is recommended that you:
- Wear support stockings.
- Avoid standing for long periods.
- Exercise gently and regularly (walking or swimming).
- Lie down to rest with feet elevated, when you can.
- Try massaging your legs.
- Tell your doctor or midwife at your next pregnancy visit.
It is recommended that you contact your hospital or carer if you are worried or if you have any of the following during pregnancy:
- vaginal bleeding
- less movement of your baby than usual
- severe stomach pain
- pain that doesn’t go away
- leaking amniotic fluid (that is, if your waters break)
- a high temperature
- vomiting that will not stop
- a headache that will not go away
- vision loss or blurred vision
- widespread itching of the skin
- sudden swelling of face, hands and feet.
Read more about problems that can occur during pregnancy.
Where to get help
- In an emergency, call 000 for an ambulance
- Your GP (doctor)
- Midwife
- Obstetrician
- Your maternity hospital
- Your maternal and child health nurse
- Pharmacist
- Sexual Health Victoria Tel. 1800 013 952
- Sexual Health Victoria - Our Clinics
Appetite Loss During Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, and Advice
Many women experience appetite loss during pregnancy.
You may occasionally find food unappealing, or you may feel hungry but can’t bring yourself to eat.
If you’re dealing with these symptoms, you may want to know possible reasons for your appetite loss, tips for treating it, and when to see a health professional.
This article explains all you need to know about appetite loss during pregnancy.
It’s normal for your appetite to fluctuate, especially as your body undergoes numerous changes during pregnancy.
If you lose your appetite, you may experience a general disinterest in all foods or a lack of desire to eat. Keep in mind that appetite loss differs from an aversion to a few specific foods, which is also fairly common during pregnancy.
Keep in mind that appetite loss differs from an aversion to a few specific foods, which is also fairly common during pregnancy.
Several factors may cause appetite loss during pregnancy, such as the following.
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are common during pregnancy, especially during the first trimester — though some women may experience these symptoms throughout their pregnancy (1).
Both mild and extreme cases of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy can significantly affect food intake and appetite.
Research has shown that fluctuations in the hormones leptin and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) during pregnancy may lead to decreased appetite and more nausea and vomiting (2).
A study in 2,270 pregnant women demonstrated that among women with moderate or severe nausea and vomiting, 42% and 70% reported a reduced level of food intake in early pregnancy, respectively (3).
If you’re experiencing appetite loss due to nausea and vomiting, try to avoid fatty or spicy foods, drink fluids separately from your meals, and eat small, more frequent meals.
You may more easily tolerate dry, salty snacks like pretzels and crackers, as well as bland foods like baked chicken breast.
However, you may need to see a health professional if you experience more serious cases of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy.
Mental health conditions
Various mental health conditions, including anxiety and depression, may affect your appetite.
In fact, pregnant women may be more prone to mental health issues due to various physical and biochemical changes. In particular, depression may lead to altered eating habits, including decreased appetite and a reduced intake of nutrient-dense foods (4, 5).
In a study in 94 pregnant women, 51% of those diagnosed with depression had poor dietary intake, which increased to 71% after 6 months (6).
What’s more, depression during pregnancy is linked to a decreased appetite for healthy foods, an increased appetite for unhealthy foods, and lower intakes of important nutrients like folate, fatty acids, iron, and zinc. This may negatively affect fetal and maternal health (7).
This may negatively affect fetal and maternal health (7).
Mental health disorders commonly go undiagnosed during pregnancy due to the shame that some pregnant women feel talking about them. If you’re experiencing symptoms of depression or anxiety, it’s important to consult a trusted health professional.
Medications
Certain medications that are safe to use during pregnancy may cause side effects like decreased appetite.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like Zoloft and Prozac are sometimes prescribed to pregnant women diagnosed with depression or anxiety (8).
SSRIs can cause decreased appetite. In fact, some pregnant women have reported a complete loss of appetite, early fullness, and weight loss after starting fluoxetine (Prozac) for depression (9, 10).
Olanzapine and buprenorphine are other drugs that may lead to decreased appetite (11, 12).
Disordered eating
Some pregnant women may experience eating disorders, including anorexia and bulimia. Experts estimate that the prevalence of disordered eating in pregnant women is 0.6–27.8% (13).
Experts estimate that the prevalence of disordered eating in pregnant women is 0.6–27.8% (13).
Disordered eating can lead to changes in appetite, a phobia of weight gain, and decreased food intake (14, 15).
If you’re pregnant and have an eating disorder, ask your healthcare provider for treatment options.
Other potential causes
Pregnant women may also experience appetite loss due to medical conditions like tumors, delayed stomach emptying, heartburn, and Addison’s disease (16, 17, 18, 19).
Furthermore, high levels of stress may affect maternal health and cause a loss of appetite (20).
Additionally, pregnancy-related changes to taste and smell, nutrient deficiencies in vitamin B12 and iron, and general discomfort from carrying a baby may cause appetite loss in some pregnant women (21, 22, 23, 24, 25).
summaryNausea and vomiting are some of the most common causes of appetite loss during pregnancy, though there are numerous other factors.

If you’re experiencing appetite loss, you may wonder how to get your eating back on track.
Foods to prioritize
There are a few foods you can prioritize even if you feel you can’t eat whole meals. These will help ensure adequate nutrient intake for you and your baby.
Many of the following foods are simple to make, small in portion size, filling, and easy on your stomach.
- Protein-rich snacks: hard-boiled eggs, Greek yogurt, roasted chickpeas, cheese and crackers, and sliced chicken, turkey, or ham served cold
- Bland, fiber-packed veggies: sweet potatoes, green beans, baby carrots (steamed or raw), and raw spinach salad
- Sweet, simple bites: fresh berries, oatmeal, dried fruit, and cold dairy products like plain cottage cheese
- Bland grains/starches: quinoa, brown rice, pasta, macaroni and cheese, and baked or mashed potato
- Soup: chicken noodle soup and chicken rice soup
- Liquids: simple broths and healthy smoothies
Other strategies
If your appetite loss is linked to nausea or vomiting, try eating small, more frequent meals, avoiding spicy and fatty foods, and supplementing with ginger and thiamine. If acupuncture is an option for you, it may also help (26).
If acupuncture is an option for you, it may also help (26).
Severe nausea and vomiting may require different treatment methods, including medications and intravenous (IV) fluids (27).
If you have nutrient deficiencies linked to appetite loss, you may need high-dose supplements to restore normal levels. Any supplements should be prescribed and monitored by a medical professional (24, 25).
You can also consult your healthcare provider for individualized treatment.
summaryIf you’re experiencing appetite loss during pregnancy, you should prioritize bland, filling foods that are rich in nutrients.
If you’re experiencing occasional appetite loss or a loss of appetite for specific foods, there’s usually no need to worry as long as you’re consuming enough nutrients on a daily basis.
For example, if you’re eating nutrient-dense meals consistently and your weight gain is appropriate to promote fetal growth, occasional appetite loss should not be a concern.
Additionally, some pregnant women may lose their appetite for specific foods, including highly fragrant foods and meat. Yet, this is a relatively common occurrence and not typically a cause for concern.
However, if you’re regularly skipping meals or lose your appetite for more than a day, you should contact your healthcare provider for advice.
This is because it’s crucial to get enough nutrients to support your health, as well as the health of your growing baby.
Potential complications related to poor intake during pregnancy
Undernutrition can lead to many pregnancy-related complications, including poor fetal growth, low birth weight, and maternal weight loss. It’s also associated with lower mental function and behavioral problems in children (29, 30, 31).
Both macronutrients and micronutrients are essential to sustain a healthy pregnancy.
Pregnant women with chronically poor appetites run a risk of anemia, fetal growth abnormalities, and preterm birth (32, 33).
summaryChronic appetite loss during pregnancy can lead to undernutrition, which can cause many adverse health effects in both you and your baby.
As your body adjusts to pregnancy, you may find certain foods unappealing or experience a loss of appetite. Sometimes, you can’t bring yourself to eat even if you’re hungry.
Keep in mind that appetite loss is fairly common and often linked to other symptoms like nausea and vomiting. You may find that your appetite fluctuates, which is perfectly normal.
If you lose your appetite but still feel hungry, you can try eating small servings of bland, simple foods that are filling, rich in nutrients, and easy on your stomach.
If you experience chronic or long-lasting appetite loss, consult a health professional.
First signs of pregnancy before delay, early symptoms
Significant hormonal changes occur during pregnancy. This causes a number of symptoms. Some women experience pregnancy symptoms right away, while others may only have a few. About the first signs of pregnancy at an early stage and when exactly the initial signs of pregnancy appear are described in the article.
About the first signs of pregnancy at an early stage and when exactly the initial signs of pregnancy appear are described in the article.
At what time do the first signs of pregnancy appear
The answer to the question of when the first signs of pregnancy appear is rather ambiguous, because some women do not feel any signs at all during the first few weeks. At what week do the first signs of pregnancy appear in others? When do the first signs of pregnancy appear after conception? Symptoms of very early pregnancy (such as breast tenderness) may appear before a missed period, as early as six to seven days after conception, while other early signs of pregnancy (such as spotting) may appear about a week after ovulation. We will tell you more about the first signs of pregnancy before menstruation and when the signs of pregnancy appear.
What are the earliest signs of pregnancy?
The first signs of pregnancy in the early stages:
- delayed menstruation - 29%;
- nausea - 25%;
- mood swings - from 14 to 23%;
- breast changes - 17%;
- pain in the lower abdomen - 15%;
- depression - 15%;
- fatigue, drowsiness - 13%
- decrease in immunity - 6%;
- the first signs of pregnancy - discharge or implantation bleeding - only 3%.

Physiological first signs of pregnancy
What are the very first symptoms of pregnancy?
The most common physiological signs of pregnancy include:
- Tender and enlarged breasts. Signs of pregnancy in the first days after conception include breast changes (1-2 weeks after conception). The area around the nipples, called the areola, may also darken.
- Drowsiness and fatigue. Fatigue is also among the signs of pregnancy in the first days after conception. During early pregnancy, levels of the hormone progesterone rise dramatically, which can cause drowsiness.
- Nausea with vomiting. When do these signs of pregnancy appear? Morning sickness, which can appear at any time of the day or night, often appears between the second and eighth weeks after conception.
- Dizziness and fainting .
 This may be due to dilation of blood vessels, lowering blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
This may be due to dilation of blood vessels, lowering blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
- Spasms. Some women experience symptoms of pregnancy in the early days, such as mild uterine cramps.
- Headaches and back pains. Many pregnant women complain of frequent headaches, while others experience back pain.
- Insomnia - another first sign of pregnancy before the test. Causes can include stress, physical discomfort, and hormonal changes.
- Change in taste preferences. Like most other symptoms of pregnancy, these eating habits can be attributed to hormonal changes.
- Temperature. Early signs of pregnancy include fever (37-37.5).
- Delayed menstruation. How long does it take for the first signs of pregnancy to appear? If you are of childbearing age and a week or more has passed without your expected period, you may be pregnant.
 However, this symptom can be misleading if you have an irregular menstrual cycle.
However, this symptom can be misleading if you have an irregular menstrual cycle.
- Bloody discharge - the first signs of pregnancy . This bleeding, known as implantation bleeding, occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus, approximately 10 to 14 days after conception.
- Bloating, heartburn. Hormonal changes can cause problems with the stomach and esophagus - these are common signs of pregnancy at 2 weeks.
- Constipation . Hormonal changes cause the digestive system to slow down, which can lead to constipation (signs of pregnancy after a delay).
- Frequent urination. You may urinate more than usual, which is a common sign of pregnancy at 5 weeks. During pregnancy, the amount of blood in the body increases, causing the kidneys to process excess fluid that enters the bladder.
- Runny nose.
 The appearance of this symptom is associated with excessive production of the hormone estrogen.
The appearance of this symptom is associated with excessive production of the hormone estrogen.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases. This is a sign of pregnancy after ovulation.
- Increased salivation. Also associated with hormonal changes.
- Sense of smell enhancement . Signs of pregnancy in the first two weeks may cause sensitivity to certain smells and the sense of taste may change.
Emotional first signs of pregnancy
The first signs of pregnancy before the delay (the earliest signs of pregnancy) include psycho-emotional symptoms.
- Mood swings.
- Irritability.
- Vulnerability, tearfulness.
- Capriciousness.
- Depression.
These are all emotional signs of early pregnancy that many women report. They describe feelings of heightened emotion or even bouts of crying, which are associated with rapid changes in hormone levels in the body. Also, signs of pregnancy at week 4 can make you feel PMS-style cranky. In addition, about 15% of women suffer from depression or anxiety during pregnancy. And after childbirth, these conditions suffer even more. In this case, it is better to seek help from a doctor.
Also, signs of pregnancy at week 4 can make you feel PMS-style cranky. In addition, about 15% of women suffer from depression or anxiety during pregnancy. And after childbirth, these conditions suffer even more. In this case, it is better to seek help from a doctor.
Do everything you can to improve your mood: get plenty of rest, eat well, get enough sleep, do things you love, and pamper yourself.
However, be aware that mood swings can be caused by a number of conditions other than pregnancy.
Influence of early pregnancy on daily routine
Early signs of pregnancy, mainly those that bring discomfort, can cause a change in daily routine. Here are some tips on what you can do with some of them:
- In case of toxicosis, avoid too hot or too cold food - this provokes an attack of vomiting. Eat often - at least 5-6 times a day, but in small portions.
- For nausea or vomiting, try ginger, chamomile, or vitamin B6.
- Drink plenty of water, in small sips between meals, to replenish lost fluids.
 Teas, juices, fruit drinks are also suitable.
Teas, juices, fruit drinks are also suitable. - For back pain, wear shoes or shoe insoles designed for pregnant women and avoid high heels. Sleep on a firm mattress.
- For chest discomfort, wear a special bra that supports enlarged breasts.
- For constipation, eat more fiber-rich foods such as wheat bran and fresh vegetables and fruits.
- If you suffer from headaches and mood swings, try stress reduction techniques such as yoga or meditation.
- Be outdoors more often, at least half an hour a day. This helps to reduce the symptoms of toxicosis, calm the nervous system.
- Maintain your daily physical activity for as long as it is convenient for you to perform certain activities.
- Eat a balanced diet with enough proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
Important! All these tips are advisory in nature, be sure to consult your doctor if you encounter discomfort.
What to do if you notice early signs of pregnancy
To make sure the signs of pregnancy are accurate, you can use the following methods to diagnose early pregnancy:
- Donate blood for hCG.
 This method can be used a few days after conception. This type of pregnancy test is done using a small sample of blood that is analyzed in a hospital. It determines whether there is a pregnancy hormone in your body and in what quantity. Its accuracy is 99%.
This method can be used a few days after conception. This type of pregnancy test is done using a small sample of blood that is analyzed in a hospital. It determines whether there is a pregnancy hormone in your body and in what quantity. Its accuracy is 99%. - Use a test strip. It can be used at home from the first days of delay. To determine pregnancy, dip the reagent area of the test strip into the urine. Accuracy: 99%. You can buy Evitest or HomeTest test strips in our pharmacy.
- Use jet or electronic test. They can be used at home a few days before your expected period. You need to remove its protective cap, substitute the test under the stream of urine for 10 seconds, and after 3-5 minutes get the result. Accuracy: 97%. In our pharmacy you can buy Evitest or Alpe inkjet tests.
- Get your first ultrasound. You can use this method at 3-4 weeks from the start of a missed period.
 At this time, ultrasound will show the very fact of uterine pregnancy, and the place of attachment of the fetal egg is also determined. Accuracy: 100%.
At this time, ultrasound will show the very fact of uterine pregnancy, and the place of attachment of the fetal egg is also determined. Accuracy: 100%.
Help Doc.ua: you can make an appointment with a gynecologist on the website.
First signs of pregnancy | Kotex®
Although pregnancy tests and ultrasound are the only ways to accurately determine pregnancy, there are a number of signs and symptoms to watch out for. The first signs of pregnancy include not only the absence of a period, but may also include fatigue, sensitivity to smells, and morning sickness. It is worth remembering that these are POSSIBLE signs of pregnancy, they can appear in both pregnant and non-pregnant women and are associated with ovulation and menstruation.
When do symptoms appear?
Oddly enough, the first week of pregnancy is determined by the date of the last menstruation.
Your last period counts as the first week of pregnancy, even if you haven't actually been pregnant yet. The estimated due date is calculated from the first day of your last period.
The estimated due date is calculated from the first day of your last period.
Taking a home pregnancy test is the cheapest and easiest way to find out if you are pregnant. Remember that home pregnancy tests measure the level of a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the urine, and there is usually less of it in the urine than in the blood.
The test gives the most accurate results from the moment of missed menstruation.
The menstrual cycle is considered delayed if the menstruation did not begin within 5 or more days after the day of their expected start.
However, it is worth remembering that even the day after the expected delay, more than a third of women have such home tests come back negative, and if you test too early, the result can be negative, even if you are already pregnant. You can do another test at home after a couple of days to get a more accurate result.
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy
If you are pregnant for the first time, then you may not notice these first signs of pregnancy or confuse them with symptoms of impending menstruation.
It is not worth spending long hours looking for answers on the forums in experiences, in any case, your research will not change what has already happened or has not happened, but mood and sleep can thoroughly spoil.
Slight lower abdominal pain and spotting
Absence of menstruation
Fatigue
Nausea
Breast swelling
Frequent urination
Constipation
Vertigo on motion
Mood swings
Temperature changes
High blood pressure
Pain and slight bleeding
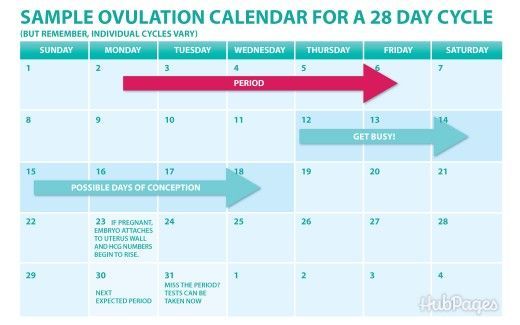
From weeks 1 to 4, changes in a woman's body are still happening at the cellular level. A fertilized egg creates a group of cells filled with fluid, which is called a blastocyst, which, after pregnancy, will have to turn into organs and body parts of the fetus.
Approximately 10-14 days after conception (4 weeks), the blastocyst attaches itself to the endometrium lining the uterine wall. This process can cause some bleeding, which can be confused with light menstruation.
This process can cause some bleeding, which can be confused with light menstruation.
Here are some signs of such bleeding:
-
color can be red, pink or brown
-
bleeding: usually comparable to normal menstruation, usually lighter
-
painful sensations
-
usually lasts about three days
No period
After the blastocyst attaches to the walls of the uterus, the body begins to produce a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin, which tells the body that it is time to stop releasing eggs from the ovaries every month. Most often, after conception, menstruation disappears at 4 weeks of pregnancy.
If you're late, it's worth taking a home pregnancy test, especially if you have irregular periods.
Fatigue
Fatigue may appear at any time during pregnancy. During pregnancy, progesterone levels rise, and this hormone can make you feel sleepy. If you feel tired, then make sure you get enough sleep.
During pregnancy, progesterone levels rise, and this hormone can make you feel sleepy. If you feel tired, then make sure you get enough sleep.
Morning sickness and vomiting
Nausea and morning vomiting usually develop between 4 and 6 weeks of gestation. In fact, such symptoms can occur not only in the morning, but in general at any time of the day. This symptom is typical for the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. If you often feel sick, then you need to make sure that you drink enough water to avoid dehydration.
Breast swelling and tenderness
Breast changes may begin at 4-6 weeks of gestation. They are also associated with changes in hormone levels. Most often, the breast swells somewhat and becomes more sensitive than usual. Usually these symptoms disappear in the future, when the body gets used to the changed hormonal background.
Frequent urination
During pregnancy, blood flow increases and this causes the kidneys to process more fluid than usual, which can cause frequent urination even in the early stages of pregnancy.
Constipation and bloating
This symptom is similar to the typical menstrual symptom and is also caused by hormonal changes, which can slow down the digestive processes, which causes bloating and constipation.
High blood pressure and dizziness during pregnancy
Most often in the early stages of pregnancy in women, blood pressure drops, which can cause a feeling of dizziness due to vasodilation of the brain. High blood pressure in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy usually means that there are some health problems that occur along with pregnancy. Such a symptom may have been present unnoticed prior to pregnancy, or it may have developed during the process. In such cases, it is especially important to monitor your blood pressure and consult your doctor.
Mood swings
Since estrogen and progesterone levels are elevated during pregnancy, this can cause changes in your emotional background and you may become more sensitive than usual.