What rash looks like pimples
Skin Bumps That Look Like Pimples but Aren’t
Skin Bumps That Look Like Pimples but Aren’t Search iconA magnifying glass. It indicates, "Click to perform a search". Chevron iconIt indicates an expandable section or menu, or sometimes previous / next navigation options.HOMEPAGEHealth
Save Article IconA bookmarkShare iconAn curved arrow pointing right.Download the app
Some spots you see may not be acne at all. kpboonjit/Shutterstock- Not all red skin spots are caused by acne.
- Many other skin conditions can result in bumps that look like normal blemishes.
- Some more serious conditions, like staph infections and skin cancer, can also look like pimples.
Spotting a new blemish can put a damper on anyone's day, but not every skin bump is a pimple.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), acne is caused by blocked pores that become infected by bacteria. There are plenty of skin conditions that mimic the look and feel of acne.
Insider consulted with dermatologists and doctors to identify a few of the most-common skin bumps that may masquerade as pimples, but are actually something totally different.
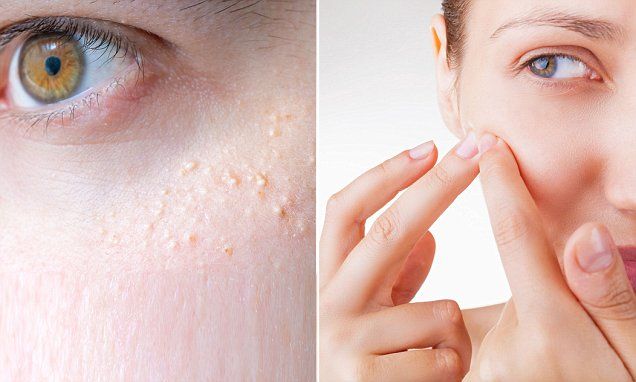
Milia can look like whiteheads.
They're not quite the same. Shutterstock
Shutterstock One type of skin lesion that can mimic a pimple is a milia. These pale, raised dots frequently appear around the eyes, but milia can also show up on other areas of the skin.
"Milia can look like whiteheads, but they are actually tiny keratin cysts that form in a pore. Since milia are encased under skin, they can sit there for months bothering you unless they are extracted," board-certified dermatologist Dr. Heather Downes told Insider.
Milia are harmless, but many people want to be rid of them for cosmetic reasons. Dermatologists typically puncture the skin with a sterile instrument and then use a tool called a comedone extractor to squeeze them out of the skin.
According to Healthline, chemical peels and topical retinoids may also be helpful in clearing away milia.
Rosacea can cause red patches and bumps on the skin.
This means the skin is very sensitive. Lipowski Milan/ShutterstockAnother condition that is frequently confused with acne is rosacea. This chronic skin condition often leads to facial redness, visible blood vessels, and bumps.
"Patients with rosacea have very sensitive skin. Their skin gets easily irritated by sunlight, cold wind, and irritating skin products. As a result, their skin can turn red and form small. temporary pink bumps and pustules that look like acne, but are actually bumps of inflammation," explained Dr. Downes.
These bumps usually occur on the forehead, nose, cheeks, or chin and can last days.
Dr. Downes advised that scrubbing or using acne medications on rosacea can inflame the skin more. It's best to see a dermatologist to treat rosacea, as there are topical medications that can keep it under control. People with rosacea should also be careful about protecting their skin from the sun.
Periorificial dermatitis can cause “breakouts” around the nose and mouth.
It can be caused by the use of steroids. Nau Nau/Shutterstock
Nau Nau/Shutterstock Periorificial dermatitis is a skin condition that causes clusters of small, itchy, and sometimes sore red bumps on the face. When the condition affects the lower half of the face, it may be known by the more specific term of perioral dermatitis.
Board-certified dermatologist Dr. Susan Bard told Insider that it most commonly presents around the nose and mouth and is usually linked to overuse of topical steroids. It can also be triggered by inhaled prescription steroid sprays used in the nose and the mouth, some toothpaste, and heavy face moisturizers.
Normally, periorificial dermatitis will go away once you stop using topical steroids or the irritating product. Sometimes dermatologists will also prescribe an oral antibiotic, such as tetracycline, or a topical antibiotic, like metronidazole.
Sometimes dermatologists will also prescribe an oral antibiotic, such as tetracycline, or a topical antibiotic, like metronidazole.
It’s easy to mistake folliculitis for body acne.
Showering after you exercise can help. ShutterstockIf you think you have body acne, you may want to make sure it's not actually folliculitis. This is a condition in which normal hair follicles become inflamed or infected, resulting in small red bumps. It most commonly occurs on the chest, back, arms, and legs.
This is a condition in which normal hair follicles become inflamed or infected, resulting in small red bumps. It most commonly occurs on the chest, back, arms, and legs.
"The bumps look like acne, but if you look closely, you will see the pattern follows hair your follicles. This condition is usually caused by bacteria but can sometimes be caused by yeast in the skin," board-certified dermatologist Dr. Jerome Potozkin told Insider.
Prevention includes showering after exercise or hot tub use to remove sweat and bacteria, as well as using gentle antibacterial soap on affected areas. Treatment options range from topical antibacterial agents and anti-yeast medicines to oral medications.
The AAD advised that if you keep your immune system healthy and stop doing whatever is causing the folliculitis, it will usually go away.
Sebaceous hyperplasia can look like large pimples.
They can appear on the scalp. Shutterstock
Shutterstock Sebaceous hyperplasia takes the form of small bumps that grow in hair follicles with enlarged sebaceous glands. Though it is technically considered a tumor, sebaceous hyperplasia is totally harmless and not cancerous.
These benign growths often appear reddish with a hint of yellow or white, Dr. Potozkin explained. They tend to be inherited and most commonly appear on the face of older adults, though they can occur at any age.
If you wish to have sebaceous hyperplasia treated, your dermatologist will likely use light electrocautery or laser vaporization to remove individual lumps.
Molluscum contagiosum can cause doughnut-shaped bumps on the skin.
They look just like pimples. Shutterstock/ LukassekThough acne pimples are caused by bacteria on the skin, similar-looking lesions can actually be caused by a viral infection.
"Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin condition that can cause doughnut-shaped pink or skin-colored bumps on the skin. When small, these may be confused with pimples," Dr. Bard told Insider.
When small, these may be confused with pimples," Dr. Bard told Insider.
According to the British Association of Dermatologists, molluscum contagiosum is caused by a pox virus and can be spread from person to person through direct contact or sharing personal items like towels or clothes.
The condition is generally harmless and usually clears by itself, though in some people this may take between six and 18 months.
Keratosis pilaris can cause small bumps on the skin.
Keratosis pilaris can be a genetic condition. ShutterstockKeratosis pilaris is a very common skin condition that causes small, hard bumps to appear on your skin like a rash.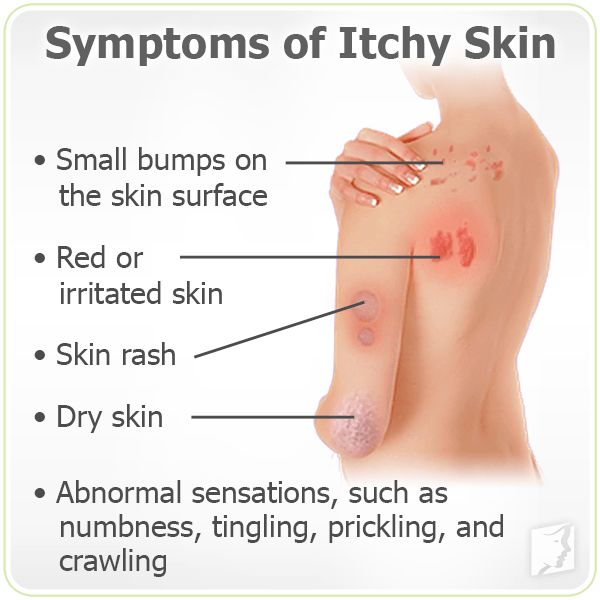 These bumps may make your skin feel like sandpaper.
These bumps may make your skin feel like sandpaper.
"Some might mistake keratosis pilaris for acne, but it's a genetic condition that occurs when the skin doesn't exfoliate normally and the keratin blocks the pores, causing these tiny bumps," Dr. Debra Jaliman, dermatologist and assistant professor of dermatology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, told Insider.
The bumps caused by keratosis pilaris are often light-colored and tend to crop up on the arms. Dr. Jaliman advised that the condition can be treated using lotions that contain keratolytic agents such as salicylic acid. Keratolytic agents cause the outer layer of the skin to loosen and shed, helping to exfoliate areas affected by keratosis pilaris.
Your pimples might be an allergic reaction.
Your makeup could be to blame. Sarah Schmalbruch/INSIDER
Sarah Schmalbruch/INSIDER Some skin products can clog pores and cause acne, but even many non-comedogenic products may cause rashes and allergic reactions that can look like acne.
"An allergic reaction could cause red bumps that may look similar to pimples. An allergic reaction tends to itch, while acne doesn't cause itching," explained Dr. Jaliman.
Dr. Jaliman advised that people with sensitive skin should avoid products with fragrance, as it's a common source of skin sensitivity and skin allergy.
Preservatives used in makeup can also cause allergic reactions, and some people may experience skin problems as a reaction to certain foods or allergens like pollen.
Chickenpox can cause a rash that looks surprisingly like acne.
Chickenpox causes a blister-like rash on the skin. ShutterstockChickenpox is a common infection that is caused by the varicella-zoster virus. Symptoms start to develop around 10 to 20 days after exposure to the virus and typically include skin bumps that look very similar to body acne.
"Chickenpox is quite commonly mistaken for acne. That is because it causes an itchy rash along with small blisters that are filled with fluid," Dr. Hardik Soni, emergency medicine physician and medical director of Ethos Spa, Skin, and Laser Center, told Insider.
If you're prone to pimples on your body, you may mistake chickenpox for just another breakout. However, the virus will usually eventually cause fever, aches, and pains.
Though the symptoms of chickenpox are usually worse in adults, the condition does normally resolve by itself in about a week without any special treatment. It may be worth visiting your doctor anyway to confirm a diagnosis and get advice for alleviating your symptoms.
Staph infections can mimic acne.
They can be painful.Staph infections are caused by staphylococcus bacteria. These germs are usually harmless and normally found on the skin of healthy people, but can cause infection if they find their way into open cuts or scratches.
Dr. Soni told Insider that staph infections often cause pimple-like boils, bumps, and redness that can be easily mistaken for acne. Unlike normal pimples, staph infections can process to pus-filled blisters or large patches of irritated skin.
Though most staph infections are minor and will clear up on their own, some can lead to life-threatening conditions such as septicemia or an infection of the inner lining of the heart. If you suspect you have a staph infection or have a skin lesion that isn't getting better, head to your doctor for a diagnosis.
If you suspect you have a staph infection or have a skin lesion that isn't getting better, head to your doctor for a diagnosis.
Monkeypox is contagious and can involve painful pus-filled lesions.
Monkeypox lesions can look different. UK HSAMonkeypox can lead to a rash that involves red spots that become filled with fluid and pus, infectious disease expert Daniel Bausch, president of the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, previously told Insider.
Patients have described monkeypox lesions as being "very painful" at most stages of their development. They can also become itchy during the crusting stage, CDC epidemiologist Andrea McCollum previously told Insider's Hilary Brueck.
As long as lesions remain on the skin, an individual can spread monkeypox via sores and bodily fluids, Insider has reported.
Early monkeypox symptoms can also be flu-like, including a fever, exhaustion, and body aches, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Some types of skin cancer can look like pimples.
You should be checked often. Joe Raedle/GettyOne of the most alarming types of acne-mimickers is a type of skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma.
"Basal cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer and is often mistaken for a pimple. Pimples usually resolve over days to weeks. If instead, it lasts several months, you should see a board-certified dermatologist as it might need to be biopsied to rule out skin cancer," Dr. Downes told Insider.
The good news is that basal cell carcinoma is considered a low-risk skin cancer. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, it is only life-threatening in exceedingly rare cases.
"The risk of it spreading in the body is close to zero. It is just locally destructive to adjacent tissues," explained Dr. Downes.
The typical treatment involves surgically removing the affected area. Even though basal cell carcinoma isn't usually an aggressive type of cancer, it can result in scarring if left untreated for too long. Get any suspicious marks or bumps checked sooner rather than later to catch skin cancer early.
Read More:
Dermatologists debunk 10 myths about washing your face
7 reasons you could be breaking out in hives and how to deal with them
10 common skin bumps and how to tell if they are a cause for concern
Read next
LoadingSomething is loading.
Thanks for signing up!
Access your favorite topics in a personalized feed while you're on the go.
Features Acne skin careMore...
Pictures, Types, Causes, and Treatment
Raised skin bumps are very common, and in most cases, they’re harmless. They can result from a number of conditions, including:
- infections
- allergic reactions
- skin disorders
- skin cancer
Skin bumps can vary in appearance and number depending on the cause. They may be the same color as your skin or a different color. They may be itchy, large, or small. Some can be hard, while others can feel soft and movable.
They may be the same color as your skin or a different color. They may be itchy, large, or small. Some can be hard, while others can feel soft and movable.
Most skin bumps do not need treatment. However, you should speak with a doctor if your bumps are causing discomfort. You should also call a doctor if you’re concerned about any changes in your bumps or in the overall condition of your skin.
Many conditions can cause raised bumps to appear on the skin. Here’s a list of 25 possible causes.
Warning: Graphic images ahead.
Acne
- commonly located on the face, neck, shoulders, chest, and upper back
- breakouts on the skin composed of blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, or deep, painful cysts and nodules
- may leave scars or darken the skin if untreated
Read the full article on acne.
Cold sore
- red, painful, fluid-filled blister that appears near the mouth and lips
- affected area will often tingle or burn before the sore is visible
- may be accompanied by mild, flu-like symptoms, such as low fever, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes
Read the full article on cold sores.
Corns and calluses
- small, round circles of thickened skin with a painful, horn-like central area of hardened tissue
- commonly found on the tops and sides of the toes and on the soles of the feet
- caused by friction and pressure
Read the full article on corns and calluses.
Skin tags
- skin growths that can become up to half an inch long
- same color as your skin or slightly darker
- most likely caused by friction
- commonly found near the neck, armpits, breasts, groin, stomach, or eyelids
Read the full article on skin tags.
Nodule
- small to medium growth that may be filled with tissue, fluid, or both
- usually wider than a pimple and may look like a firm, smooth elevation under the skin
- usually harmless, but may cause discomfort if it presses on other structures
- nodules may also be located deep inside the body where you cannot see or feel them
Read the full article on nodules.
Impetigo
- common in babies and children
- irritating rash and fluid-filled blisters that pop easily and form a honey-colored crust
- rash is often located in the area around the mouth, chin, and nose
Read the full article on impetigo.
Molluscum contagiosum
- bumps that may appear in a patch of up to 20
- small, shiny, and smooth
- flesh-colored, white, or pink
- firm and dome-shaped with a dent or dimple in the middle
Read the full article on molluscum contagiosum.
Lipoma
- soft to the touch and moves easily if prodded with your finger
- small, just under the skin, and pale or colorless
- commonly located in the neck, back, or shoulders
- only painful if it presses on a nerve
Read the full article on lipoma.
Cyst
- slow-growing bump under the skin that has a smooth surface
- can be large or small and is usually painless
- typically not a problem unless it’s infected, very large, or growing in a sensitive area
- some grow deep inside your body where you can’t see or feel them
Read the full article on cysts.
Wart
- caused by many different types of a virus called human papillomavirus (HPV)
- may be found on the skin or mucous membranes
- may occur as one wart or in groups
- contagious and may be passed to others
Read the full article on warts.
Actinic keratosis
- typically less than 2 centimeters (cm), or about the size of a pencil eraser
- thick, scaly, or crusty skin patch
- appears on parts of the body that receive a lot of sun exposure (hands, arms, face, scalp, and neck)
- usually pink in color but can have a brown, tan, or gray base
Read the full article on actinic keratosis.
Basal cell carcinoma
- raised, firm, and pale areas that may resemble a scar
- dome-like, pink or red, shiny, and pearly areas that may have a sunk-in center, like a crater
- visible blood vessels on the growth
- easy bleeding or oozing wound that doesn’t seem to heal, or heals and then reappears
Read the full article on basal cell carcinoma.
Squamous cell carcinoma
- often occurs in areas exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, such as the face, ears, and back of the hands
- scaly, reddish patch of skin that progresses to a raised bump and continues to grow
- growth that bleeds easily and doesn’t heal, or heals and then reappears
Read the full article on squamous cell carcinoma.
Melanoma
- the most serious form of skin cancer, more common in people with lighter skin tones
- mole anywhere on the body that has irregularly shaped edges, asymmetrical shape, and multiple colors
- mole that has changed color or gotten bigger over time
- usually larger than a pencil eraser
Read the full article on melanoma.
Boils
- bacterial or fungal infection of a hair follicle or oil gland
- can appear anywhere on the body but are most common on the face, neck, armpit, and buttock
- red, painful, raised bump with a yellow or white center
- may rupture and weep fluid
Read the full article on boils.
Bullae
- clear, watery, fluid-filled blister that is greater than 1 cm in size
- can be caused by friction, contact dermatitis, and other skin disorders
- if clear liquid turns milky, there might be an infection
Read the full article on bullae.
Contact dermatitis
- appears hours to days after contact with an allergen
- rash has visible borders and appears where your skin touched the irritating substance
- skin is itchy, red, scaly, or raw
- blisters that weep, ooze, or become crusty
Read the full article on contact dermatitis.
Cherry angioma
- common skin growth that can be found anywhere on the body but is most likely to be seen on the torso, arms, legs, and shoulders
- more common in people over age 30
- small, bright red circular or oval spots that may be raised or smooth and bleed if rubbed or scratched
- generally harmless but may require removal if they’re in problem areas
Read the full article on cherry angioma.
Keloids
- symptoms occur at the site of a previous injury
- lumpy or rigid area of skin that may be painful or itchy
- area is flesh-colored, pink, or red
Read the full article on keloids.
Keratosis pilaris
- common skin condition that’s most often seen on the arms and legs but might also occur on the face, buttocks, and torso
- often clears up on its own by age 30
- patches of skin that appear bumpy, slightly red, and feel rough
- may get worse in dry weather
Read the full article on keratosis pilaris.
Seborrheic keratoses
- common, harmless skin growth that is usually seen in older adults
- can be located anywhere on the body except for the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
- round, oval, dark-colored growth with a “stuck-on” appearance
- raised and bumpy with a waxy feel
Read the full article on seborrheic keratoses.
Chickenpox
- clusters of itchy, red, fluid-filled blisters in various stages of healing all over the body
- accompanied by fever, body aches, sore throat, and loss of appetite
- remains contagious until all blisters have crusted over
Read the full article on chickenpox.
MRSA (staph) infection
This condition is considered a medical emergency. Urgent care may be required.
- an infection caused by a type of Staphylococcus, or staph, bacteria that is resistant to many different antibiotics
- causes an infection when it enters through a cut or scrape on the skin
- skin infection that often looks like a spider bite, with a painful, raised, red pimple that may drain pus
- needs to be treated with powerful antibiotics and can lead to more dangerous conditions like cellulitis or blood infection
Read the full article on MRSA (staph) infection.
Scabies
- symptoms may take 4 to 6 weeks to appear
- extremely itchy rash that may be pimply, made up of tiny blisters, or scaly
- raised white or flesh-colored lines
Read the full article on scabies.
Strawberry nevus
- red or purplish raised mark, commonly located on the face, scalp, back, or chest
- appears at birth or in very young children
- gradually gets smaller or disappears as the child ages
Read the full article on strawberry nevus.
The most common causes of raised skin bumps are harmless and do not require medical treatment unless you have discomfort. Here are some of the possible reasons for raised skin bumps:
- Acne is the most common skin condition in the United States, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. It causes skin bumps that can range from very small and painless to large and painful. The bumps are usually accompanied by redness and swelling.
- Boils are infected hair follicles that look like red, raised bumps on the skin. They can be painful, but they eventually go away once they burst and release fluid.
- Bullae are raised, fluid-filled bumps that can result from friction, or conditions like contact dermatitis and chickenpox.
- Cherry angiomas are common skin growths that can form on most areas of the body. They develop when blood vessels clump together and create a raised, bright-red bump under or on the skin.

- Cold sores are red, fluid-filled bumps that form around the mouth or other areas of the face and can burst. They’re caused by a common virus called herpes simplex.
- Contact dermatitis is an allergic skin reaction that produces an itchy, red skin rash. The rash may consist of raised, red bumps that ooze, drain, or crust.
- Corns or calluses are rough, thickened areas of skin. They’re most often found on the feet and hands.
- Cysts are growths that contain fluid, air, or other substances. They develop under the skin in any part of the body. They feel like a small ball and can usually be moved around slightly.
- Keloids are smooth, raised growths that form around scars. They’re most commonly found on the chest, shoulders, and cheeks.
- Keratosis pilaris is a skin condition marked by an overgrowth of a protein called keratin. It causes small bumps around hair follicles on the body.
- Lipomas are collections of fatty tissue under the skin and are often painless. They usually form on the neck, back, or shoulders.
- Molluscum contagiosum are small, flesh-colored bumps with a dimple in the center that often form in all parts of the body. They can arise from skin-to-skin contact with someone affected with them.
- Nodules result from growth of abnormal tissue, and can appear on the skin in common areas like the armpits, groin, and head and neck region.
- Seborrheic keratoses are round, rough spots on the surface of the skin. They can affect many areas of the body, including the chest, shoulders, and back. They may be skin-colored, brown, or black.
- Skin tags are small, fleshy flaps of skin. They usually grow on the neck or in the armpits. They may be the same color as the skin or slightly darker.
- Strawberry nevus is a red birthmark also known as a hemangioma.
 They are most common in young children and usually disappear by age 10.
They are most common in young children and usually disappear by age 10. - Warts are raised, rough bumps caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They typically develop on the hands and feet. They may be skin-colored, pink, or slightly brown.
Less commonly, raised skin bumps are caused by more serious conditions that require treatment. Certain bacterial and viral infections cause bumps and will only get worse if they go undiagnosed and untreated. These serious conditions include:
- chickenpox, a common childhood virus characterized by red, itchy bumps that form all over the body
- impetigo, a bacterial skin infection common in young children that is highly contagious and results in reddish blisters that ooze and develop a honey-colored crust
- MRSA (staph) infection, an illness triggered by a staph bacteria that commonly lives on the skin, causing a swollen, painful bump with a white center
- scabies, a skin infestation caused by a tiny mite called Sarcoptes scabiei, producing an itchy, pimple-like rash
Other types of raised skin bumps can be caused by skin cancer. There are several types of skin cancer, all requiring medical management and treatment:
There are several types of skin cancer, all requiring medical management and treatment:
- Actinic keratosis is a precancerous skin condition characterized by scaly, crusty spots on areas of sun-exposed skin, such as hands, arms, or face. These spots are typically brown, gray, or pink. The affected area may itch or burn.
- Basal cell carcinoma is a form of cancer that affects the top layer of skin. It produces painful bumps that bleed in the early stages. The associated bumps appear on sun-exposed skin and may be discolored, shiny, or scar-like.
- Squamous cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that begins in the squamous cells. These cells make up the outermost layer of skin. The condition causes scaly, red patches and raised sores to develop on the skin. These abnormal growths often form in areas exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
- Melanoma is the least common but most serious form of skin cancer.
 It begins as an atypical mole. Cancerous moles are often asymmetrical, multi-colored, and large, with irregular borders. They can appear anywhere on the body.
It begins as an atypical mole. Cancerous moles are often asymmetrical, multi-colored, and large, with irregular borders. They can appear anywhere on the body.
Most skin bumps are harmless and aren’t cause for concern. However, you should see your doctor if:
- skin bumps change or worsen in appearance, or last for a long time
- you are in pain or they cause discomfort
- you don’t know the cause of the bumps
- you suspect you have an infection or skin cancer
Your doctor will perform a physical examination and inspect the skin bumps. Expect to answer questions about your bumps, medical history, and lifestyle habits.
Your doctor may also perform a skin biopsy to test if the skin bump is cancerous. This procedure involves taking a small sample of skin tissue from the affected area for analysis. Depending on the results, your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist or other specialist for further evaluation.
The Healthline FindCare tool can provide options in your area if you don’t already have a doctor.
Removal
Treatment for raised skin bumps depends on the underlying cause. Most of the common causes of skin bumps are harmless, so you probably won’t need treatment. However, if your skin bumps are bothering you, you might be able to have them removed for cosmetic reasons.
For example, a dermatologist can remove skin tags or warts by freezing them off. A dermatologist can also surgically remove certain skin bumps, including cysts and lipomas. Other bumps that are itchy or irritated may be treated with topical ointments and creams.
If your doctor finds that your skin bumps are cancerous or precancerous, they will most likely remove the bumps completely. You will also need to attend regular follow-up appointments so your doctor can check the area and make sure the cancer doesn’t come back.
Medication
In cases where additional medical treatment is required, your doctor will prescribe medications that can help eliminate your skin bumps and the underlying cause.
For a bacterial infection, such as MRSA, you may need antibiotics. For a viral infection, such as chickenpox, your doctor may recommend over-the-counter medications and home treatments. Some viral infections, such as herpes, can’t be cured. However, your doctor can give you medications to ease symptoms.
For most skin bumps, the long-term outlook is excellent. The majority of bumps are caused by harmless, temporary conditions that don’t require treatment. If skin bumps are caused by an infection or long-term condition, timely medical treatment should either clear it up or effectively ease the symptoms. The outlook is also good when skin cancer is caught early. However, frequent follow-ups will be necessary to ensure the cancer doesn’t return or grow. The outlook for more advanced forms of skin cancer varies with each situation.
Acne and pimples - what is it, causes, symptoms, acne treatment in the Clinic under the supervision of doctors
There are many reasons why people have various rashes on their faces: acne, pimples. Acne, or acne, is a phenomenon that is characteristic, first of all, for adolescence. But sometimes it worries both adult men and women. If the problem is not taken seriously, the situation can worsen over time. It's not just that the skin on which the rash appears looks ugly. If inflammation begins, acne on the face can cause more serious diseases.
Acne, or acne, is a phenomenon that is characteristic, first of all, for adolescence. But sometimes it worries both adult men and women. If the problem is not taken seriously, the situation can worsen over time. It's not just that the skin on which the rash appears looks ugly. If inflammation begins, acne on the face can cause more serious diseases.
People want to look beautiful. But not everyone is naturally lucky to have healthy skin. Many face various rashes on the face: acne, pimples.
Do not try to solve the problem on your own. Acne treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. He will determine how serious the disease is and determine the optimal treatment tactics.
Acne: what is it?
Acne on the face is a pathological manifestation of an inflammatory nature. It appears as a result of damage to the sebaceous glands and excretory ducts. When this disease occurs, the composition of sebum changes in a person: the proportion of fatty acids in it decreases, it loses its disinfectant properties and cannot effectively prevent the growth of bacteria.
As a result, the pores are clogged with a viscous and hard fatty secret. It mixes with particles of dead skin cells. At the same time, bacteria actively multiply in the glands, and because of this, pus is formed. Fat can also accumulate under the skin.
The main area where acne appears is the face. But rashes can often be seen on other parts of the body, for example, on the shoulders or on the back between the shoulder blades. In this case, acne must be distinguished from acne. Usually a reddened tubercle is called a pimple, and an acne is an inflamed duct of the sebaceous gland, which manifests itself in the form of a black dot on the skin.
Causes of acne
There are many reasons leading to the appearance of acne and blackheads. Usually, their occurrence is influenced by several factors at once, which can be divided into two large groups - internal and external.
Internal factors are, in particular:
- Hormonal imbalance, which can be caused by puberty, pregnancy, childbirth and other causes
- Metabolic disorders
- Malnutrition
- Avitaminosis
- Decreased immunity
- Allergy
- Stress
External factors include:
- Wrong skin care
- Use of cosmetics that clog pores
- Increased perspiration
- Subcooling or overheating
- Miscellaneous skin injuries
Squeezing rashes will not help solve the problem, on the contrary, over time, the number of blackheads and pimples will increase. Treatment of the cause of acne is required, eliminating the factors that cause them to appear.
Treatment of the cause of acne is required, eliminating the factors that cause them to appear.
Main symptoms
How do you know if you need acne treatment on your face or other areas of your body? The rashes are clearly visible, and if, when looking in the mirror, you see that not everything is in order with the skin, you should consult a specialist.
The reddish pimples and blackheads mentioned above are symptoms that can be called classic. But other options are possible, for example:
- White pustules - cavities filled with pus and appearing as spots or small bumps of white color
- Rosacea - pinkish nodules that form in places of dilation of the subcutaneous vessels and usually occur on the nose and in the nasolabial folds
- Acne erythematosus - characteristic of women over 30 years of age and occurs as a reaction of the body to problems with the vascular and neurovegetative systems
Of course, if you find a single pimple, you are unlikely to need medical treatment.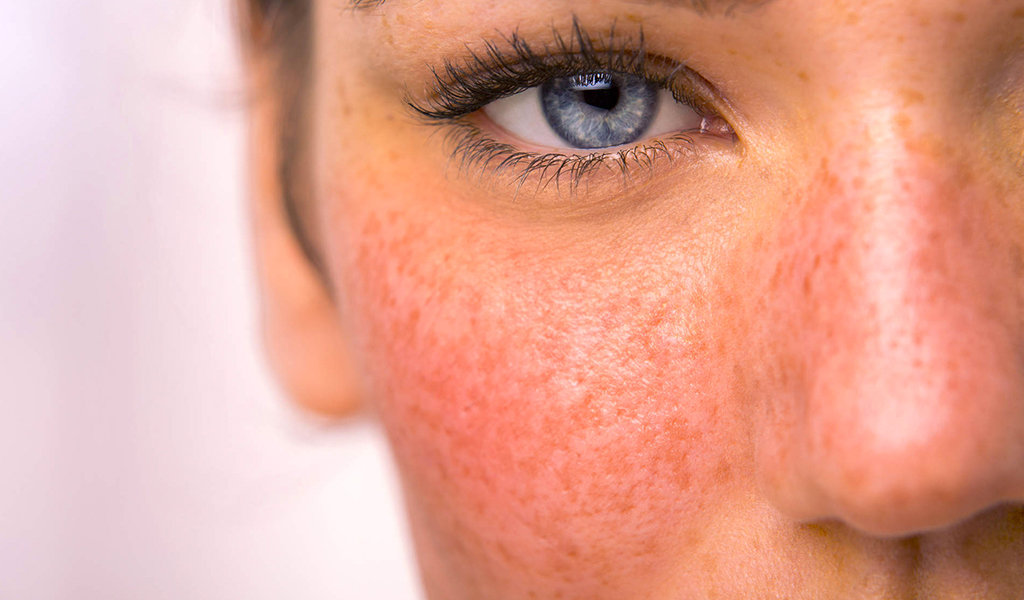 Just do not squeeze it out and do not use other methods of self-treatment. When the disease is at an early or intermediate stage, special attention should be paid to skin care. But if within one and a half to two months you were not able to eliminate acne on your face, the treatment should be taken to a new level - contact a doctor who will conduct an examination and tell you what to do next.
Just do not squeeze it out and do not use other methods of self-treatment. When the disease is at an early or intermediate stage, special attention should be paid to skin care. But if within one and a half to two months you were not able to eliminate acne on your face, the treatment should be taken to a new level - contact a doctor who will conduct an examination and tell you what to do next.
Also, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible if the rash is extremely plentiful and painful.
Acne treatment
Acne treatment largely depends on the cause of the disease. Therefore, diagnosis is important. The specialist interviews the patient to get more information about his lifestyle, and if necessary, sends him to take tests: these can be, for example, a biochemical blood test or hormonal studies.
Treatment of acne on the face and other rashes, as a rule, is carried out in a complex manner. The drug effect is combined with the regulation of nutrition, correction of hormonal levels and the use of various skin care products.
In no case should you squeeze blackheads and pimples, as this can lead to scarring or the development of inflammation. It is also important to choose the most suitable cosmetics - for example, creams and lotions that do not clog pores.
The treatment of acne, which is particularly complex, requires the use of antibiotics, and in some cases vitamins. In parallel with antibiotics, probiotics are usually prescribed to preserve the normal digestive activity of the body. This is another reason why you need to see a doctor. Only a specialist can choose a complex of medicines that will suit a particular patient and ensure maximum effectiveness of treatment.
If stress is recognized as the main cause of skin rashes, you need to focus on eliminating the causes that cause it.
Separately, it is worth mentioning salon procedures. It can be:
- Skin cleaning - mechanical, vacuum or ultrasonic
- Peeling
- Phototherapy
- Ozone therapy
The technique is selected taking into account both the needs of the patient and his financial capabilities.
Acne nutrition
Acne and acne treatment will not be effective enough without adjusting the patient's eating behavior. Necessary:
- Reduce high glycemic index foods such as white bread, muffins and sweet pastries
- Increase your intake of foods containing vitamins A, C and E
You also need to adjust the diet in such a way as to ensure the removal of toxins from the body.
To get more vitamin A in the body, you need to eat carrots, cabbage, spinach and a variety of orange vegetables, such as pumpkin. Vitamin C is found in cabbage, potatoes, strawberries and various citrus fruits - oranges, tangerines, lemons. Other sources of vitamin A include almonds, peanuts, and leafy vegetables.
White rice, white flour products, and sugar lead to an excess of insulin in the blood. Therefore, they should not be abused. It is also desirable to exclude from the diet all smoked, spicy, salty and fried foods, stop eating fast food, give up sweet pastries, sweets, sauces and mayonnaise.
According to experts, you need to drink more water. Every day you need to drink at least 7 glasses, because with a lack of moisture, the processes of healing and skin renewal slow down. At the same time, it is worth reducing the consumption of coffee. It is better to refuse the use of alcoholic beverages altogether.
Prevention
There are effective methods of acne prevention, and if you pay more attention to them, you can not be afraid of the appearance of acne: treatment, accordingly, will not be needed at all. The basic principles are simple, all you need to do is:
- Pay more attention to hygiene
- Choose water-based cosmetics, do not use scrubs for skin care - they can injure the skin, which leads to infection, the development of inflammatory processes and the appearance of rashes
- Normalize weight, minimize junk food, sugary sodas, baked goods, and anything else that can cause skin problems
- Balance hormones
- More outdoor activities, more rest, less nervousness and avoiding stressful situations
If you need advice on proper nutrition, you should contact a specialist. It will help you adjust your diet based on your lifestyle, financial capabilities and other factors.
It will help you adjust your diet based on your lifestyle, financial capabilities and other factors.
Benefits of acne treatment at MEDSI
The MEDSI network of clinics offers help to everyone who is concerned about acne. Our specialists are well versed in such a problem as acne and its treatment. They own modern techniques that allow not only to get rid of the symptoms, but also to eliminate the causes that led to the appearance of acne, pimples and other rashes. Clinic staff can:
- Quickly relieve inflammation
- Reduce breakouts
- Cleanse the skin, give it a beautiful and healthy look
The clinic provides assistance to patients regardless of age: adolescents and mature people, men and women. An individual approach makes it possible to choose the optimal treatment for each person, taking into account his characteristics. Our employees successfully cope with diseases of any level of complexity.
To make an appointment with a specialist, call +7 (495) 7-800-500.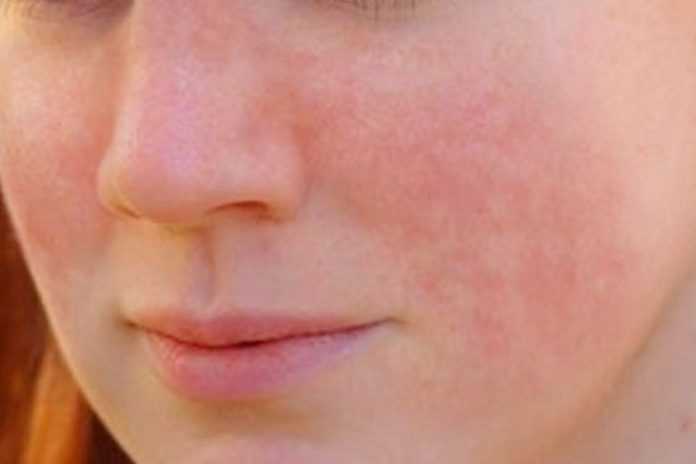
Do not delay treatment, see a doctor now:
- Cosmetologist's consultation
- Dermatologist's appointment
- Facial peeling - PRX-T33 therapy
Rash COVID-19 | Rash may be a symptom of coronavirus
Onset of COVID-19may be associated with the appearance of various types of skin lesions. They resemble papules, nodules, vesicles, excoriations (abrasions), scales, ulcers, some are in the form of spots, indurations or nets. The rash can occur in people who are asymptomatic with COVID-19. In 21% of patients, dermatosis was the only symptom of SARS-CoV-2 infection. At the same time, 17% of patients reported skin rash as the first manifestation of the disease.
The incidence of skin symptoms of COVID-19 is difficult to determine. There is also no known relationship between some skin symptoms and disease severity. In addition, it cannot be ruled out that in some patients, skin lesions may be a manifestation of a reaction to multiple COVID-19 treatments..
There is also no known relationship between some skin symptoms and disease severity. In addition, it cannot be ruled out that in some patients, skin lesions may be a manifestation of a reaction to multiple COVID-19 treatments..
Contents:
1. Covid-19 rash - where does it appear?
2. What does a COVID-19 rash look like?
Coronavirus - when does it occur and how long does it last? How is the rash different?
8. Rash treatment for COVID-19
Covid-19 rash - where does it appear?
Skin lesions are often the body's response to viral infections. However, in the case of COVID-19, doctors are surprised by the variety of skin rashes, the time of their appearance and location.
Skin lesions associated with COVID-19 occur on various parts of the body, such as around the mouth, trunk, limbs, legs and arms. They are not always accompanied by itching.
What a rash looks like with COVID-19?
The rashes associated with Covid-19 are varied and similar to skin lesions associated with other viral diseases, according to a study conducted by experts in Spain. They noted that skin changes did not correlate with the severity of the infection: some were accompanied by asymptomatic COVID-19, others were severe forms of infection.
They noted that skin changes did not correlate with the severity of the infection: some were accompanied by asymptomatic COVID-19, others were severe forms of infection.
Five types of rash were noted:
• Irregular frostbite-like patches on the arms and legs, sometimes accompanied by soreness and itching. Mostly encountered in young patients with a mild course of the disease, appeared in the later stages and lasted about 12 days. Registered at 19% of cases.
• Focal eruption in the form of small vesicles, which can cause itching, located on the body and upper and lower limbs. Occurred during the onset of any other symptoms and was noted in 9% of cases in middle-aged patients; kept for 10 days.
• Urticaria-like patchy eruption, white or pink, often itchy. They were noted in 19% of cases, mainly on the body, but also happened on the palms.
• Maculopapular eruptions in the form of small flat or bulging vesicles, which were observed in 47% of cases. These rashes persisted for about a week and appeared simultaneously with other symptoms, but most often accompanied by a severe course of the disease.
These rashes persisted for about a week and appeared simultaneously with other symptoms, but most often accompanied by a severe course of the disease.
• The appearance of a vascular red-blue network or signs of skin necrosis on the skin was observed in 6% of patients, mostly elderly with a severe course of the disease.
At the same time, experts note that the rash can have a different origin, and it is difficult to classify it without having the appropriate experience and knowledge.
In case of any skin symptoms, Medicover dermatologists with many years of experience and extensive experience in diagnosing various skin lesions are always ready to help you!
Skin lesions and diagnosis of COVID-19
Diagnosis of dermatological changes caused by COVID-19 consists primarily in the exclusion of other possible causes of rashes, such as, for example, allergies.
This may require a series of studies to determine if the rash is related to SARS-CoV-2 infection, or if it is a reaction of the body to certain medications, or if the infection is caused by other pathogens.
If finger pressure on purple-red skin lesions does not cause them to disappear, this is an alarm that indicates the need to seek medical attention in order to rule out infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
In Medicover clinics, you can get professional advice from a dermatologist and undergo all the necessary examinations to establish an accurate diagnosis, as well as get advice on effective treatment in accordance with modern international clinical guidelines.
Coronavirus rash - when does it occur and how long does it last?
The first symptoms of COVID-19 can occur approximately 5-6 days after infection, sometimes this period is extended up to 14 days. However, a rash can be both the first symptom and the only sign of COVID-19..
Depending on the type of skin lesions and their severity, they last from several days to several weeks.
Skin rash may be accompanied by other systemic symptoms associated with COVID-19. These include:
• fever
• Permanent cough
• shortness of breath, breathing problems,
• Fatigue
• Chill
• Dizziness
• Loss of smell and taste.
rash as a manifestation of children inflammatory multisystem syndrome (PIMS) after COVID-19in children
Viral diseases are a common cause of skin lesions in children. A rash caused by SARS-Cov-2 may appear on a child's skin up to 2-4 weeks after infection and indicate the development of childhood inflammatory multisystem syndrome associated with SARS-CoV-2.
PIMS with multiform inflammatory syndrome in children sometimes occurs after COVID-19 infection, sometimes even after asymptomatic infection. PIMS most commonly occurs in schoolchildren around the age of 9years.
In the case of children, skin lesions caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection may appear as reddish papules, resembling other viral exanthems. Papules may appear on the face and back, and within 3-5 days they disappear spontaneously.
Any rash in children should be consulted with a pediatrician. Until an accurate diagnosis is established and the connection with COVID-19 is excluded, children should not come into contact with other people, especially the elderly, who are prone to a severe course of coronavirus infection up to death.
"Coronavirus fingers"
Skin lesions in the form of so-called "coronavirus fingers" are more often diagnosed in young people, adolescents and children. They take the form of red spots, vesicles and even ulcers, accompanied by swelling of the skin of the fingers and interdigital spaces.
COVID-19 and chickenpox - how is the rash different?
The papulo-vesicular eruption of COVID-19 and chickenpox are very similar. They differ in the age of patients and localization of skin lesions.
In SARS-CoV-2 infection, skin lesions are more common in adults with a mean age of 60 years. However, one of the main clinical features is the localization of lesions in the trunk area, the elements are diffuse in nature, they are characterized by the absence of itching.
The rash appears 3 days after the onset of symptoms of COVID-19 and spontaneously disappears after 8 days without leaving marks, while with chickenpox the rash can be biphasic and last up to 2 weeks.