What is it like to have a seizure
What Does a Seizure Feel Like, by Types of Seizure?
A seizure is a sudden change in the electrical activity of your brain. This can cause involuntary symptoms, like shaking or loss of consciousness.
There are many types of seizures. Some are related to epilepsy, while others are due to other health conditions, like alcohol withdrawal or high fever.
Depending on the type of seizure, the feeling of having one can vary greatly. It also depends on whether you lose consciousness.
Before a seizure, you might have warning signs like a headache or tingling. After the seizure, you may feel confused, tired, or sore.
Read on to learn about how having different types of seizures might feel.
The two main types of seizures are called focal and generalized seizures.
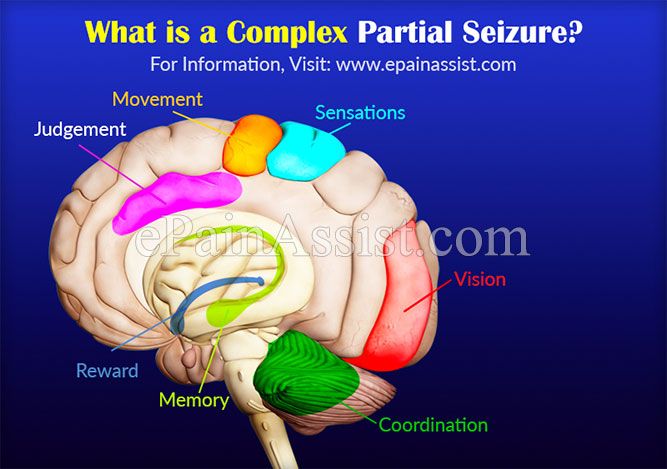
A focal seizure, or a partial seizure, occurs in one part of the brain. Since the seizure only affects one region, you might stay conscious or have a slight change in consciousness. You might be aware of sensations that occur during the seizure.
A generalized seizure involves both sides of the brain. In most cases, you lose consciousness. You likely won’t be aware of sensations during the seizure.
During a focal seizure, you might experience motor or sensory feelings. Your sensations depend on the part of the brain involved and whether you lose consciousness.
Here’s what different focal seizures may feel like:
Focal aware seizure
You’ll stay conscious during a focal aware seizure, also called a simple partial seizure, or aura. It may happen on its own or before the seizure progresses.
During a focal aware seizure, you might experience:
- a general strange feeling
- stiffness or twitching in a part of the body, such as an arm or hand
- feeling like events have happened before (déjà vu)
- tingling in your legs and arms
- “rising” sensation in your stomach
- extreme emotions (like joy, fear, or anxiety)
Focal impaired awareness seizure
If you lose consciousness during a focal seizure, it’s called a focal impaired awareness seizure or complex focal seizure.
Before this type of seizure, you may have an aura. During the seizure, you’ll be unaware of what is happening. You might feel confused or tired after the seizure.
Focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizures
If a focal seizure spreads to both parts of the brain, it’s called a focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizure.
Since this seizure starts as a focal seizure, you might feel an aura first. But as the seizure spreads, you may lose consciousness.
Gelastic and dacrystic seizures
A gelastic seizure causes uncontrollable laughing. A dacrystic seizure causes uncontrollable crying or grimacing. These seizures are typically associated with a rare tumor-like lesion called a hypothalamic hamartoma.
You’re usually conscious during these seizures. You may feel anxious and out of control.
Since generalized seizures affect both sides of the brain, you’re more likely to lose consciousness. However, you may feel symptoms before or after the seizure.
Here’s what different types of generalized seizures might feel like:
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures
A generalized tonic-clinic (GTC) seizure usually causes loss of consciousness. You won’t feel anything during the actual seizure.
You won’t feel anything during the actual seizure.
Before a GTC seizure occurs, you may feel an aura. When the seizure begins and you become unconscious, your body will contract during the tonic stage. Next, you will convulse during the clonic stage.
During the clonic stage muscles alternate between relaxation and rigidity. People can lose control of their bladder and bowels during or after the seizure.
After the seizure, you may feel confused, exhausted, and sore. If you fell during the seizure, you might have pain or discomfort. You’ll also likely have a severe headache.
Tonic seizures
A tonic seizure causes muscle stiffening for 10 to 20 seconds. It doesn’t progress to the clonic stage.
Typically, tonic seizures occur while you’re sleeping. But if they occur when you’re awake, you’ll lose consciousness and may fall over. You’ll feel fatigued and confused after the seizure.
Clonic seizures
A clonic seizure only involves muscle jerking.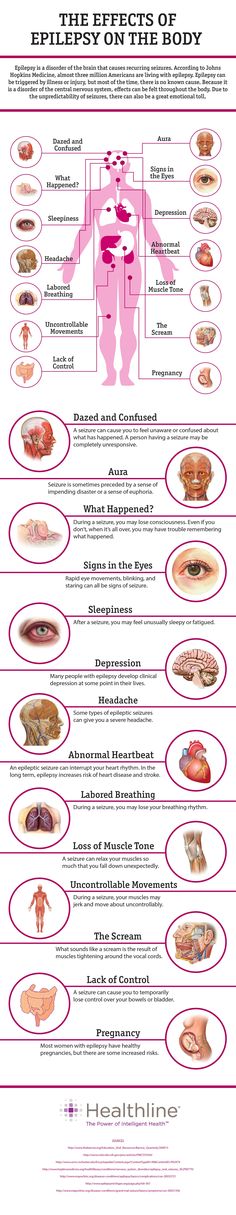 If you stay conscious, you may feel tingling or numbness. But if you lose consciousness, you won’t know what’s happening. Clonic seizures are rare.
If you stay conscious, you may feel tingling or numbness. But if you lose consciousness, you won’t know what’s happening. Clonic seizures are rare.
Absence seizures
An absence seizure, previously known as a petit mal seizure, causes loss of awareness for 3 to 30 seconds. You won’t feel confused after the seizure. However, these seizures occur often during a 24-hour period; around 50 to 100 times.
Myoclonic seizures
A myoclonic seizure feels like an electric shock. It causes twitching or jerking, which typically lasts less than 1 second. You stay conscious during this seizure, which may reoccur several times during a short amount of time.
Atonic seizures
During an atonic seizure, you suddenly lose muscle strength. It’s also known as an akinetic seizure or drop attack.
You may stay conscious or briefly lose consciousness during the seizure. You’ll feel your muscles suddenly relax, causing you to suddenly fall. But you should be able to get up right after.
Infantile or epileptic spasms
Infantile spasms, or epileptic spasms, affect babies. They typically happen during the first year of life.
Since these seizures occur in babies, it’s difficult to know what it feels like to experience them. However, a baby may briefly lose consciousness. The seizure might also cause head nodding and spasms.
Some seizures are not related to epilepsy. This includes:
Febrile seizures
Febrile seizures are caused by a high fever. They typically affect children between 6 months and 3 years old.
During a febrile seizure, a child will lose consciousness for a few minutes. They might feel sleepy after the seizure.
Non-epileptic event
A non-epileptic event (NEE) is a seizure that doesn’t involve abnormal electrical activity in the brain. They’re typically caused by physical or mental stress.
Examples of NEE include:
- fainting
- panic attacks
- dissociative seizure (related to mental or emotional causes)
Depending on the type of NEE, you may lose consciousness or feel:
- tingling
- fullness in your stomach
- rapid heart rate
- sweating
- dry mouth
- poor control of body movement
- confusion (after regaining consciousness)
A nocturnal seizure occurs when you’re sleeping. It can cause abnormal behaviors during sleep, like shouting or thrashing around.
It can cause abnormal behaviors during sleep, like shouting or thrashing around.
If you stay asleep during the seizure, you likely won’t feel anything. But it might feel like you’re having recurring nightmares.
If you wake up during the seizure, you’ll feel confused. You’ll also feel drowsy and tired during the day.
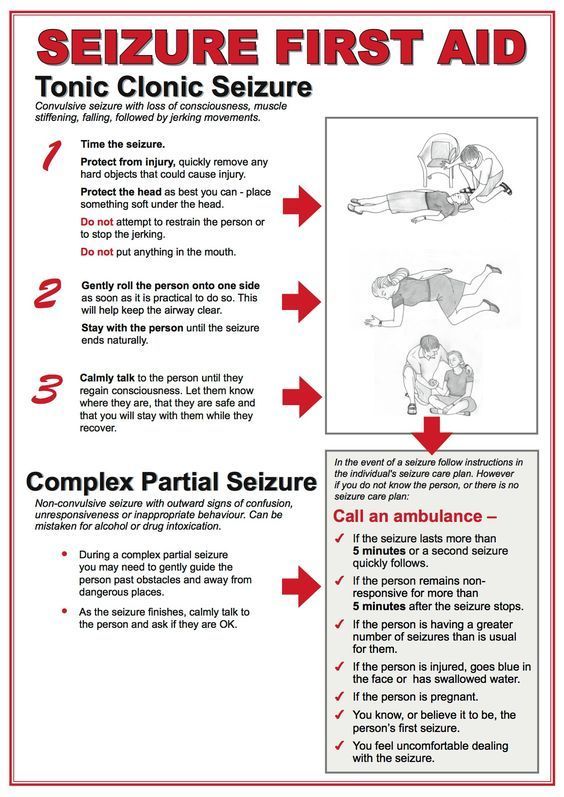
If you think you’re having a seizure, focus on staying calm. Try to move away from furniture or other large items. Slowly lie down on the floor and place your head on a soft surface, like a cushion. This will reduce your risk of injury.
If it’s your first seizure, see a doctor as soon as possible. They can provide a diagnosis and monitor your symptoms.
If you’ve been diagnosed with epilepsy, follow your seizure response plan when you feel a seizure coming on. Make sure your friends and family are familiar with your seizure response plan.
Since seizures can cause many possible sensations, they can mimic other conditions.
Conditions that may feel similar to a seizure include:
- fainting
- low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- low oxygen levels (hypoxia)
- panic attacks
- hyperventilating
- temper tantrums (in children)
- night terrors
- sleep apnea
- narcolepsy
- poor sleep quality
- transient ischemic attacks
- cardiac arrhythmias
- vertigo
- migraines
- tremors
- nervous tics
Most seizures are not a medical emergency. You likely won’t need to call 911.
You likely won’t need to call 911.
Usually, a seizure only lasts for a few seconds. After the seizure, wait until the person is fully awake, then calmly let them know what happened.
Medical emergencyYou should call 911 if someone:
- is having a seizure for the first time
- has trouble breathing or waking up after the seizure
- has a seizure for longer than 5 minutes
- has another seizure right after
- gets hurt during the seizure
- has a seizure in water
- has a seizure while pregnant
- also has diabetes, heart disease, or another chronic medical condition
The sensation of having a seizure depends on the type of seizure. For example, if you have a mild seizure, you may stay conscious. You might also feel strange and experience tingling, anxiety, or déjà vu.
If you lose consciousness during a seizure, you won’t feel anything as it happens. But you might wake up feeling confused, tired, sore, or scared.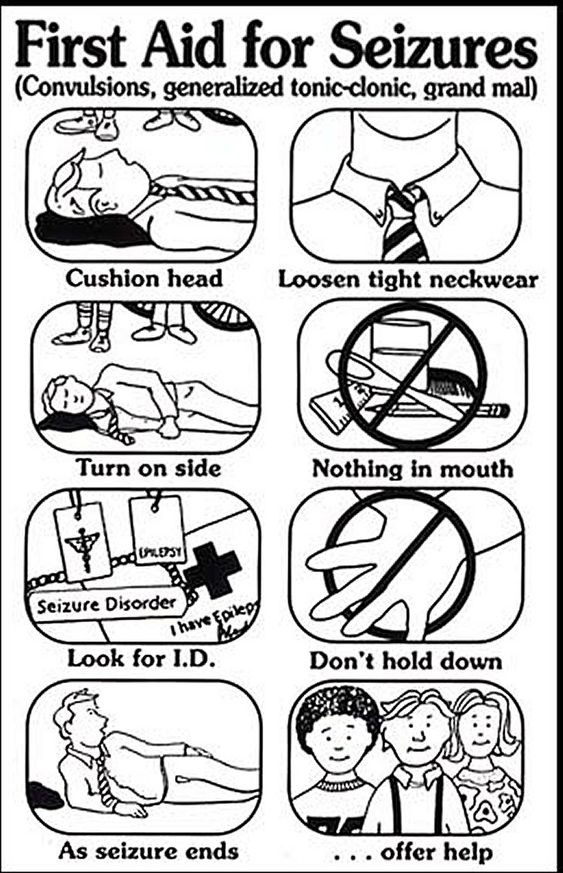
Most seizures are not a medical emergency. But if someone has a seizure for the first time, or if they have trouble waking up or breathing, call 911 immediately.
What Does a Seizure Feel Like, by Types of Seizure?
A seizure is a sudden change in the electrical activity of your brain. This can cause involuntary symptoms, like shaking or loss of consciousness.
There are many types of seizures. Some are related to epilepsy, while others are due to other health conditions, like alcohol withdrawal or high fever.
Depending on the type of seizure, the feeling of having one can vary greatly. It also depends on whether you lose consciousness.
Before a seizure, you might have warning signs like a headache or tingling. After the seizure, you may feel confused, tired, or sore.
Read on to learn about how having different types of seizures might feel.
The two main types of seizures are called focal and generalized seizures.
A focal seizure, or a partial seizure, occurs in one part of the brain. Since the seizure only affects one region, you might stay conscious or have a slight change in consciousness. You might be aware of sensations that occur during the seizure.
Since the seizure only affects one region, you might stay conscious or have a slight change in consciousness. You might be aware of sensations that occur during the seizure.
A generalized seizure involves both sides of the brain. In most cases, you lose consciousness. You likely won’t be aware of sensations during the seizure.
During a focal seizure, you might experience motor or sensory feelings. Your sensations depend on the part of the brain involved and whether you lose consciousness.
Here’s what different focal seizures may feel like:
Focal aware seizure
You’ll stay conscious during a focal aware seizure, also called a simple partial seizure, or aura. It may happen on its own or before the seizure progresses.
During a focal aware seizure, you might experience:
- a general strange feeling
- stiffness or twitching in a part of the body, such as an arm or hand
- feeling like events have happened before (déjà vu)
- tingling in your legs and arms
- “rising” sensation in your stomach
- extreme emotions (like joy, fear, or anxiety)
Focal impaired awareness seizure
If you lose consciousness during a focal seizure, it’s called a focal impaired awareness seizure or complex focal seizure.
Before this type of seizure, you may have an aura. During the seizure, you’ll be unaware of what is happening. You might feel confused or tired after the seizure.
Focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizures
If a focal seizure spreads to both parts of the brain, it’s called a focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizure.
Since this seizure starts as a focal seizure, you might feel an aura first. But as the seizure spreads, you may lose consciousness.
Gelastic and dacrystic seizures
A gelastic seizure causes uncontrollable laughing. A dacrystic seizure causes uncontrollable crying or grimacing. These seizures are typically associated with a rare tumor-like lesion called a hypothalamic hamartoma.
You’re usually conscious during these seizures. You may feel anxious and out of control.
Since generalized seizures affect both sides of the brain, you’re more likely to lose consciousness. However, you may feel symptoms before or after the seizure.
Here’s what different types of generalized seizures might feel like:
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures
A generalized tonic-clinic (GTC) seizure usually causes loss of consciousness. You won’t feel anything during the actual seizure.
You won’t feel anything during the actual seizure.
Before a GTC seizure occurs, you may feel an aura. When the seizure begins and you become unconscious, your body will contract during the tonic stage. Next, you will convulse during the clonic stage.
During the clonic stage muscles alternate between relaxation and rigidity. People can lose control of their bladder and bowels during or after the seizure.
After the seizure, you may feel confused, exhausted, and sore. If you fell during the seizure, you might have pain or discomfort. You’ll also likely have a severe headache.
Tonic seizures
A tonic seizure causes muscle stiffening for 10 to 20 seconds. It doesn’t progress to the clonic stage.
Typically, tonic seizures occur while you’re sleeping. But if they occur when you’re awake, you’ll lose consciousness and may fall over. You’ll feel fatigued and confused after the seizure.
Clonic seizures
A clonic seizure only involves muscle jerking. If you stay conscious, you may feel tingling or numbness. But if you lose consciousness, you won’t know what’s happening. Clonic seizures are rare.
If you stay conscious, you may feel tingling or numbness. But if you lose consciousness, you won’t know what’s happening. Clonic seizures are rare.
Absence seizures
An absence seizure, previously known as a petit mal seizure, causes loss of awareness for 3 to 30 seconds. You won’t feel confused after the seizure. However, these seizures occur often during a 24-hour period; around 50 to 100 times.
Myoclonic seizures
A myoclonic seizure feels like an electric shock. It causes twitching or jerking, which typically lasts less than 1 second. You stay conscious during this seizure, which may reoccur several times during a short amount of time.
Atonic seizures
During an atonic seizure, you suddenly lose muscle strength. It’s also known as an akinetic seizure or drop attack.
You may stay conscious or briefly lose consciousness during the seizure. You’ll feel your muscles suddenly relax, causing you to suddenly fall. But you should be able to get up right after.
Infantile or epileptic spasms
Infantile spasms, or epileptic spasms, affect babies. They typically happen during the first year of life.
Since these seizures occur in babies, it’s difficult to know what it feels like to experience them. However, a baby may briefly lose consciousness. The seizure might also cause head nodding and spasms.
Some seizures are not related to epilepsy. This includes:
Febrile seizures
Febrile seizures are caused by a high fever. They typically affect children between 6 months and 3 years old.
During a febrile seizure, a child will lose consciousness for a few minutes. They might feel sleepy after the seizure.
Non-epileptic event
A non-epileptic event (NEE) is a seizure that doesn’t involve abnormal electrical activity in the brain. They’re typically caused by physical or mental stress.
Examples of NEE include:
- fainting
- panic attacks
- dissociative seizure (related to mental or emotional causes)
Depending on the type of NEE, you may lose consciousness or feel:
- tingling
- fullness in your stomach
- rapid heart rate
- sweating
- dry mouth
- poor control of body movement
- confusion (after regaining consciousness)
A nocturnal seizure occurs when you’re sleeping. It can cause abnormal behaviors during sleep, like shouting or thrashing around.
It can cause abnormal behaviors during sleep, like shouting or thrashing around.
If you stay asleep during the seizure, you likely won’t feel anything. But it might feel like you’re having recurring nightmares.
If you wake up during the seizure, you’ll feel confused. You’ll also feel drowsy and tired during the day.
If you think you’re having a seizure, focus on staying calm. Try to move away from furniture or other large items. Slowly lie down on the floor and place your head on a soft surface, like a cushion. This will reduce your risk of injury.
If it’s your first seizure, see a doctor as soon as possible. They can provide a diagnosis and monitor your symptoms.
If you’ve been diagnosed with epilepsy, follow your seizure response plan when you feel a seizure coming on. Make sure your friends and family are familiar with your seizure response plan.
Since seizures can cause many possible sensations, they can mimic other conditions.
Conditions that may feel similar to a seizure include:
- fainting
- low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- low oxygen levels (hypoxia)
- panic attacks
- hyperventilating
- temper tantrums (in children)
- night terrors
- sleep apnea
- narcolepsy
- poor sleep quality
- transient ischemic attacks
- cardiac arrhythmias
- vertigo
- migraines
- tremors
- nervous tics
Most seizures are not a medical emergency.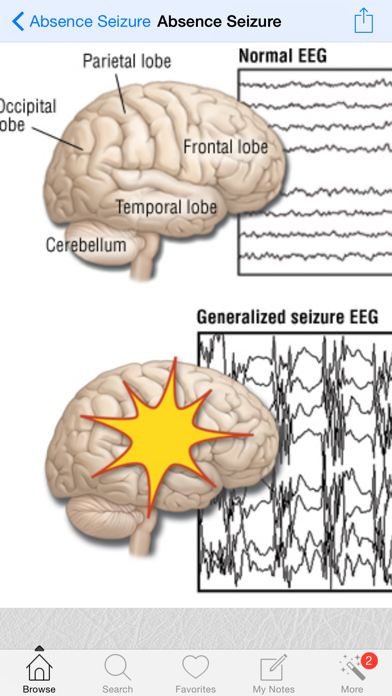 You likely won’t need to call 911.
You likely won’t need to call 911.
Usually, a seizure only lasts for a few seconds. After the seizure, wait until the person is fully awake, then calmly let them know what happened.
Medical emergencyYou should call 911 if someone:
- is having a seizure for the first time
- has trouble breathing or waking up after the seizure
- has a seizure for longer than 5 minutes
- has another seizure right after
- gets hurt during the seizure
- has a seizure in water
- has a seizure while pregnant
- also has diabetes, heart disease, or another chronic medical condition
The sensation of having a seizure depends on the type of seizure. For example, if you have a mild seizure, you may stay conscious. You might also feel strange and experience tingling, anxiety, or déjà vu.
If you lose consciousness during a seizure, you won’t feel anything as it happens. But you might wake up feeling confused, tired, sore, or scared.
Most seizures are not a medical emergency. But if someone has a seizure for the first time, or if they have trouble waking up or breathing, call 911 immediately.
Epilepsy: all about the disease
There are more than 50 million people with epilepsy in the world. Someone got the disease as a hereditary factor, someone became its owner due to a head injury, and someone developed the disease due to a tumor formed in the brain. Today there are communities of epileptics who communicate in reality and via the Internet. Among sick people there are many bright and extraordinary personalities. Anyone can find help and support. Tips, recommendations, stories of successful treatment - all this ceases to be a secret with seven seals! Look for useful information on our website and be sure that the fight against epilepsy gives an excellent result!
Description of epilepsy - signs of the manifestation of the disease
Children and adolescents most often suffer from epilepsy. It is believed that the disease under the age of 18 is inherent in 1% of the total population of this age group. Epilepsy occurs in adults and the elderly. However, in this case, it often acts as a complication after strokes, injuries and other vascular pathologies. In Russia, the development of epilepsy is progressing at a pace similar to the world level.
It is believed that the disease under the age of 18 is inherent in 1% of the total population of this age group. Epilepsy occurs in adults and the elderly. However, in this case, it often acts as a complication after strokes, injuries and other vascular pathologies. In Russia, the development of epilepsy is progressing at a pace similar to the world level.
When we hear about an illness, most of us imagine a fallen person with convulsions. Foam appears from his mouth, he makes inarticulate sounds, and, tired from an attack that has not stopped for a long time, he falls silent and slowly falls asleep, exhausted. This is a classic manifestation of epilepsy, in medicine called a generalized tonic-clinical seizure. Often, the disease is accompanied by other symptoms, including loss of consciousness, inadequate reactions to others, and withdrawal into oneself.
Seizure time can be as short as a few seconds. Doctors say that such a condition is often imperceptible from the outside, it can be mistaken for absent-mindedness or inattention. However, if such symptoms tend to recur with a certain frequency, loved ones notice alarming phenomena and consult a doctor. In medicine, these cases are called absences.
However, if such symptoms tend to recur with a certain frequency, loved ones notice alarming phenomena and consult a doctor. In medicine, these cases are called absences.
During an absence, you will not notice a patient trembling in convulsions, but you will only see a person falling out of reality for no more than 30 seconds. He will not react to the people around him, show attention to them, be distracted by questions and extraneous stimuli. At this time, he seems to be given to himself and is alone with his own thoughts. It is important to pay attention to the manifestation of such behavior in time, since in the future the frequency of these attacks increases. They can occur up to several dozen times a day, which scares others.
Children also have nocturnal seizures, which do not resemble a traditional epileptic seizure. During sleep, the child tends to take unusual postures, in which the increased tension of certain parts of the body clearly appears. You can notice how the mouth is twisted, how the awakened baby is trying to say something, but cannot do it due to tension spasms. It is important not to be mistaken that disturbances of consciousness are related to epileptic seizures. In the case of epilepsy, seizures always occur spontaneously, without the presence of a specific cause. It is difficult to predict their appearance, since in most cases they appear from scratch.
It is important not to be mistaken that disturbances of consciousness are related to epileptic seizures. In the case of epilepsy, seizures always occur spontaneously, without the presence of a specific cause. It is difficult to predict their appearance, since in most cases they appear from scratch.
Causes of epilepsy - where does the attack come from
WHO groups the causes of the disease into several main forms, including:
- the ability to immediately identify the root cause of the origin of the disease. In this form, there is no organic brain damage, but there is a specific reaction of neurons to external stimuli. The course of seizures is unstable, seizures occur for no reason.
- Symptomatic form - trauma, tumors, intoxication of the body, malformations have a significant impact on the development of the disease. The attack has a sudden manifestation and can be caused even by the slightest irritant from the outside (injection, resentment, severe frustration).

- Cryptogenic form - the cause of the manifestation of impulse foci is not precisely identified.
Why does disease occur? What are the causes of epilepsy that cause terrible convulsions? It is believed that there are a great many forms of the disease and its causes. The reason may be a difficult pregnancy, pathological childbirth, mechanical injuries of the pregnant woman and the baby. In these cases, epilepsy occurs early and manifests itself in the first or second years of a child's life.
Despite a long period of study of the disease, there is no certainty that epilepsy in most cases occurs due to the presence of a genetic predisposition. According to statistics, 40% of epileptics have a history of relatives with a similar illness, but this does not give the right to say that unfavorable heredity is always transmitted from generation to generation. Among the most common causes of the disease can also be noted:
- the presence of a traumatic brain injury in the past;
- diseases of parasitic or viral origin, resulting in complications in the form of emerging epileptic seizures;
- insufficient blood supply to the brain and resulting oxygen starvation;
- tumors, abscesses and formations of unknown etiology that have arisen in various parts of the brain.

Medicine is unable to determine the exact causes of epilepsy in 70% of cases. However, specially organized studies have shown that the sensitivity of the brain tissue in people with epilepsy is many times higher than in healthy people for the same stimuli. If a healthy person does not notice the impact of a certain signal from the outside, then the patient's response is an epileptic seizure.
By nature, an attack is the result of synchronous excitation of brain neurons. Nerve cells of a certain area of the cortex are excited - the so-called epileptogenic focus, which gives a reaction. The causes can be meningitis, stroke, alcoholism, drug addiction, multiple sclerosis. It has been proven that every 10th alcoholic is prone to epileptic seizures. Another interesting trend is that more than 60% of people with epilepsy experienced their first epilepsy before the age of 18.
It is easy for a person unfamiliar with the problem to confuse hysteria with epilepsy. Seizures are similar in many ways, but they have obvious differences. A hysterical fit is a consequence of a strong stressful effect on the psyche. It arises as a response to frustration, strong resentment, chagrin, may be the result of fear or other experiences. Usually a tantrum happens in the presence of other people, it can last from 15 minutes to a couple of hours, it can be accompanied by convulsive body movements.
Seizures are similar in many ways, but they have obvious differences. A hysterical fit is a consequence of a strong stressful effect on the psyche. It arises as a response to frustration, strong resentment, chagrin, may be the result of fear or other experiences. Usually a tantrum happens in the presence of other people, it can last from 15 minutes to a couple of hours, it can be accompanied by convulsive body movements.
A person in this state screams, falls, performs picturesque actions in public. But if you look closely, he does not seek to harm himself with careless movements, does not try to cause serious damage and is in a state of consciousness. Waking up from hysteria, a person does not experience the stupor and drowsiness characteristic of epilepsy. He quickly comes to his senses and begins to control his own behavior.
In the case of mild epilepsy, an attack may look like a brief loss of contact with the outside world. The patient's eyelids twitch slightly, the face trembles convulsively, there is a slight pulsation of the muscles. From the outside, this state looks like immersion in one's own thoughts or deep thought. Others may not even notice the attack. Moreover, the seizure may go unnoticed by the patient.
From the outside, this state looks like immersion in one's own thoughts or deep thought. Others may not even notice the attack. Moreover, the seizure may go unnoticed by the patient.
A distinctive feature that indicates the approach of an attack is the presence of an aura - a special reaction of the body. As warning symptoms, fever, dizziness, unreasonable restlessness and fussiness can act. During an attack, the patient does not understand anything, does not feel pain and discomfort. The attack lasts for several minutes, so it often goes unnoticed by others.
Benign and malignant epilepsy
The epilepsy disease is divided into benign and catastrophic (pathological) form of the course. The first is characterized by rare seizures that do not have a detrimental effect on personality development. It is recognized that this form of the disease can go away on its own without the appointment of specialized treatment and the intervention of doctors. However, this type of disease is typical only for the children's audience.
Another name for catastrophic forms of epilepsy is epileptic encephalopathies. The disease is also observed only in childhood, however, unlike benign epilepsy, it proceeds very hard and is accompanied by impaired speech, neuropsychic functions. The disease has a significant impact on the development of the individual and can cause mental illness.
Living with epilepsy is a struggle for health
To neutralize the manifestations of epilepsy, doctors prescribe medications that vary in strength and intensity of effects, depending on the overall clinical picture of the disease. Their reception is long-term and requires great responsibility from the patient. It is strictly forbidden to skip taking the drugs recommended by the doctor. Even a benign form of epilepsy can be treated for several years before its manifestations pass.
In the case of a complex form of the disease, medication is taken for decades. It is not always possible to cure a pernicious condition, but it is possible to achieve control over it, which greatly facilitates life and improves its quality. For the patient, the absence of seizures is the opportunity to live fully. A person with epilepsy, in the absence of sudden seizures and seizures, can go in for sports, have various hobbies, travel the world, learn the traditions of different countries and cultures. Physical and intellectual stress, as well as emotional stress, rarely become factors provoking the manifestation of an attack. Therefore, it is not worth significantly limiting yourself with a favorable course of the disease.
For the patient, the absence of seizures is the opportunity to live fully. A person with epilepsy, in the absence of sudden seizures and seizures, can go in for sports, have various hobbies, travel the world, learn the traditions of different countries and cultures. Physical and intellectual stress, as well as emotional stress, rarely become factors provoking the manifestation of an attack. Therefore, it is not worth significantly limiting yourself with a favorable course of the disease.
Abroad, people with epilepsy who have not had seizures for a long time are given a driver's license and a permit to drive a vehicle on an equal basis with everyone else. However, getting rid of seizures for a long time, you should be careful about your health. It is required to observe a balanced regime of sleep and wakefulness, rest and exercise. Alcohol is strictly prohibited. With caution, you should choose the type of activity, trying to avoid extreme activities. Although the likelihood of an attack can be reduced with medication, the risk of recurrence in the future cannot be ruled out.
Pregnancy and epilepsy - a precautionary factor
The period of gestation is a particularly important time in the life of every woman. Therefore, great attention should be paid to all possible risk factors that can pose a threat to the mother and the child developing in the womb. If a pregnant woman had epilepsy as a child, which later went away, there is no reason to worry about the safety of the child. The situation is different when the conversation turns to a future woman in labor who suffers from an illness during pregnancy. It must be under the control of an epileptologist. Pregnant women suffering from epilepsy are observed in accordance with the standards of the International League against the disease.
It is believed that taking medicines prescribed by a doctor and strictly following the recommendations of a specialist give a 95% guarantee that a healthy baby will be born, and the birth process will not cause a negative reaction of the body. Moreover, the opinion of professional doctors is known, arguing that pregnancy in some situations can mitigate the course of epilepsy and make the manifestation of seizures more rare.
Moreover, the opinion of professional doctors is known, arguing that pregnancy in some situations can mitigate the course of epilepsy and make the manifestation of seizures more rare.
Perception of the patient with epilepsy in society
Russian society is not yet accustomed to the normal perception of sick people on the streets, in schools, state companies and commercial structures. Therefore, a sudden attack of epilepsy in front of passers-by can become a serious psychological trauma for a sick person. Most people suffering from an illness seek to hide their own illness, to keep silent about it, not to make it known to colleagues at work, housemates, business partners. Unfortunately, epilepsy is perceived as some kind of shameful stigma, inferiority, inferiority. What can we say about ordinary people, when even some doctors believe that the disease in any of its manifestations has a serious impact on the level of the patient's intellect, violating and deforming it. In reality, things are different.
In reality, things are different.
Most people with epilepsy do not have any mental or personality disorders. These are ordinary people, among whom there are enough professionals in a particular industry. The more insulting is the perceived cruelty of others who refuse epileptic admission to kindergarten, school, and work.
Since ancient times, little has changed in the everyday perception of epileptics, when they were spoken of as people endowed with demonic powers. It was believed that they were able to infect by simply touching or inhaling the same air in a room with healthy people. However, not everyone held this view. There is another opinion, according to which epilepsy is a disease of the elite. Napoleon, Gaius Julius Caesar, Alexander the Great suffered from it. These great personalities made history, conquered continents and cities, decided destinies.
Comparing the level of social support for sick patients abroad and in Russia, it should be noted that in our country there is no legislative framework that upholds the rights of epileptics. Abroad, the presence of public organizations lobbying the interests of patients is considered normal. Active information work is being carried out with them, within the framework of which experts explain the rights, interests and characteristics of the life of these people. In Europe, epileptics are not perceived by society as outcasts, they do not have the stigma of inferiority.
Abroad, the presence of public organizations lobbying the interests of patients is considered normal. Active information work is being carried out with them, within the framework of which experts explain the rights, interests and characteristics of the life of these people. In Europe, epileptics are not perceived by society as outcasts, they do not have the stigma of inferiority.
Symptoms of epilepsy - learning to distinguish an attack
The disease can look different in different forms of the course of the disease. It depends on the manifestation of a pathological discharge in a particular area of the brain. The consequence of its influence can be speech disorders, a failure in coordination of movements, a change in muscle tone (increase and decrease in muscle tension), mental deviations from the norm. Symptoms can appear both in separately expressed reactions, and in their complex. Let's consider several types of epilepsy in more detail in order to study the symptoms of the disease.
Jacksonian seizures - since a clearly localized area of the brain is irritated, the symptoms are specific and affect a specific muscle group. The sudden onset of a psychomotor disorder is short-lived and usually lasts a few minutes. The patient has confusion, loss of contact with other people. He does not realize that he has undergone an epileptic seizure, so he rejects the help offered from outside. Weak cramps or slight numbness begin to appear in the limbs - hands, shins, feet. If convulsions spread throughout the body or capture most of it, a generalized or large convulsive seizure occurs, which is characterized by:
- Harbingers in the form of a state of anxiety and restlessness that occurs a few hours before the onset of an attack. Nervous excitement of the patient has the increasing character.
- Tonic convulsions when the patient's head is thrown back, the muscles of the body tense up, the body is stretched into a kind of arc, resembling a bow in shape.
 Stopped breathing blocks the access of oxygen to the lungs, the patient's face acquires a bluish tint. The phase lasts no more than 30 seconds, in rare cases it reaches a minute.
Stopped breathing blocks the access of oxygen to the lungs, the patient's face acquires a bluish tint. The phase lasts no more than 30 seconds, in rare cases it reaches a minute. - Clonic convulsions in which there is a rhythmic contraction of the muscles of the body. There is an increase in salivation, foam comes out of the mouth. The phase lasts no more than 5 minutes, after which the convulsions go away. Breathing is restored, puffiness disappears from the face and manifested from a lack of oxygen, the cyanosis of the skin disappears.
- Stopper - a sharp relaxation of the muscular corset, possible involuntary excretion of urine and feces. The patient may lose consciousness and faint. The phase lasts half an hour. Reflexes are absent at this time.
- Sleep.
After a seizure, the patient may experience headaches and dizziness for several days. At this time, a manifestation of muscle weakness is characteristic.
Small seizures - have a milder manifestation. During their course, there is a twitching of the facial muscles, a sharp relaxation or, on the contrary, a toning of the muscular corset of the body. Consciousness is not lost, an absence is possible. The patient may roll his eyes, freeze for a short time. These attacks are most often manifested in preschool age. After their completion, patients cannot remember what happened recently.
During their course, there is a twitching of the facial muscles, a sharp relaxation or, on the contrary, a toning of the muscular corset of the body. Consciousness is not lost, an absence is possible. The patient may roll his eyes, freeze for a short time. These attacks are most often manifested in preschool age. After their completion, patients cannot remember what happened recently.
Status epilepticus is the most terrible condition that requires immediate medical attention due to increasing brain hypoxia. The successive manifestation of a whole series of seizures is accompanied by a lack of consciousness, reduced muscle tone, and the absence of reflex manifestations of the body.
It should be noted that any epileptic seizures begin spontaneously and also end abruptly.
Which examinations need to be done
Before diagnosing a disease, the doctor examines the patient, fills out his health card, identifies risk factors associated with a history of relatives who suffered from epilepsy. The systemic and chronic diseases of the patient are identified, the symptoms of the attacks that have manifested are checked and carefully studied. The frequency of occurrence of seizures, their strength, intensity and duration are studied. For this, the patient himself and people close to him are interviewed. This helps to restore the picture in detail, since in most cases the patient does not remember what happened to him. In addition to the specified set of measures, the epileptologist directs the patient to electroencephalography, as a result of which a pulsed recording of brain activity and neuron activity is carried out. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may also be used.
The systemic and chronic diseases of the patient are identified, the symptoms of the attacks that have manifested are checked and carefully studied. The frequency of occurrence of seizures, their strength, intensity and duration are studied. For this, the patient himself and people close to him are interviewed. This helps to restore the picture in detail, since in most cases the patient does not remember what happened to him. In addition to the specified set of measures, the epileptologist directs the patient to electroencephalography, as a result of which a pulsed recording of brain activity and neuron activity is carried out. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may also be used.
Prognostic map of the disease
Provided that epilepsy was detected in a timely manner and received competent treatment, life without seizures is observed in 80% of cases. These people are active, social, fully developed. Many of them adhere to the drug therapy of the disease throughout their lives according to the schedule recommended by the doctor. They take special medications, neutralizing the possibility of manifestation of seizures. The list of drugs, as well as the dosage of the drugs, are determined by the attending physician, depending on the form and nature of the course of the disease. Patients with generalized tonic-clonic seizures need constant care and control from close relatives, since in the event of a seizure, there is a high probability of death under unfavorable circumstances.
They take special medications, neutralizing the possibility of manifestation of seizures. The list of drugs, as well as the dosage of the drugs, are determined by the attending physician, depending on the form and nature of the course of the disease. Patients with generalized tonic-clonic seizures need constant care and control from close relatives, since in the event of a seizure, there is a high probability of death under unfavorable circumstances.
Treatment of epilepsy - stages of therapy
Stable remission is achieved in 80% of cases of epilepsy treatment. About 35% manage to get rid of the disease permanently with the support of doctors and close relatives. With the initial diagnosis, a timely course of drug therapy helps to drown out seizures for several years in advance or completely neutralize the disease in most cases.
The content of the therapeutic course depends on the form of the disease, the manifestation of symptoms, the age of the patient and his general state of health.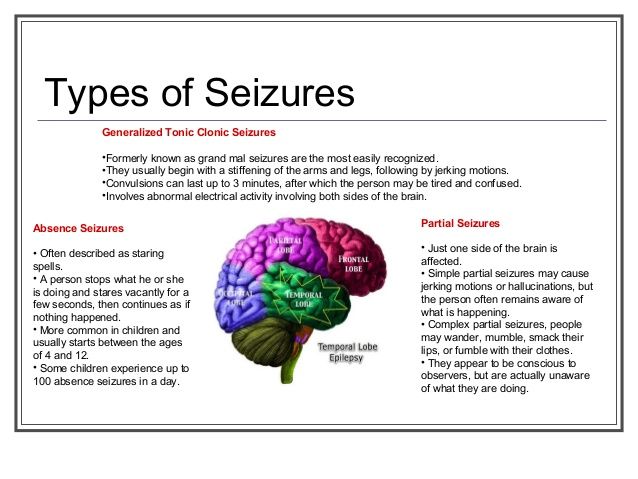 Epilepsy is treated conservatively or by surgery. Doctors most often try to avoid the second method, since with proper prescription of drugs and their timely intake, it is possible to achieve a successful result in 90% of cases. Drug treatment is based on the observance of the main stages of therapy:
Epilepsy is treated conservatively or by surgery. Doctors most often try to avoid the second method, since with proper prescription of drugs and their timely intake, it is possible to achieve a successful result in 90% of cases. Drug treatment is based on the observance of the main stages of therapy:
- Diagnosis of epilepsy with determination of the type and form of the disease for the competent selection of an effective drug.
- Identification of the root causes of the disease. In the case of a symptomatic form of the disease, a detailed examination of the brain is carried out, aneurysms, malignant tumors, and benign neoplasms are detected.
- Development of a schedule of activities to eliminate risk factors to prevent the development of seizures. It is necessary to exclude stressful factors, minimize situations of mental and physical overwork, drinking alcohol, hypothermia and overheating of the body.
- Relief of seizures by providing immediate assistance, taking anticonvulsants and other drugs prescribed by a doctor.

The main task of the attending physician is to inform relatives caring for the patient about the correct behavior during periods of convulsions, epileptic attacks. Timely assistance will help protect the patient from injury and prevent death where it can be avoided.
Omega-3 treats epilepsy and reduces seizures
This is evidenced by data from a study conducted by the University of California, USA. The sample consisted of 24 people with epilepsy and prone to seizures. The result of the experiment showed that omega-3 acids consumed daily in food help to reduce the manifestation of epileptic seizures by up to 36%. The intake of useful substances into the body was due to fish oil capsules. The duration of the study was 2.5 months. In addition to reducing the symptoms of epilepsy and reducing the excitability of brain cells in patients, normalization of blood pressure in the body was observed.
You can take Omega-3 not only in the form of capsules. Contributes to the intake of a useful element by eating sea fish of fatty varieties. These include Atlantic herring, mackerel, sardine, trout, tuna, salmon. All kinds of dietary supplements based on the use of Omega-3 in their composition have shown themselves well.
Contributes to the intake of a useful element by eating sea fish of fatty varieties. These include Atlantic herring, mackerel, sardine, trout, tuna, salmon. All kinds of dietary supplements based on the use of Omega-3 in their composition have shown themselves well.
The catogenic diet for epileptics works wonders
Doctors agree that the catogenic diet improves the quality of life for epileptics by reducing seizures and making them less frequent. The technique is prohibited for children under one year old. Since food intake follows strictly regulated norms, only a doctor can prescribe a diet after a complete study of the patient's clinical picture.
Prolonged dietary restriction reduces the frequency of seizures. There are cases when, after the application of a catogenic diet, the symptoms of eilepsy completely disappeared. However, the aggressive nature of the diet is not for everyone. The doctor must carefully monitor the condition of patients, sensitively respond to any changes in well-being.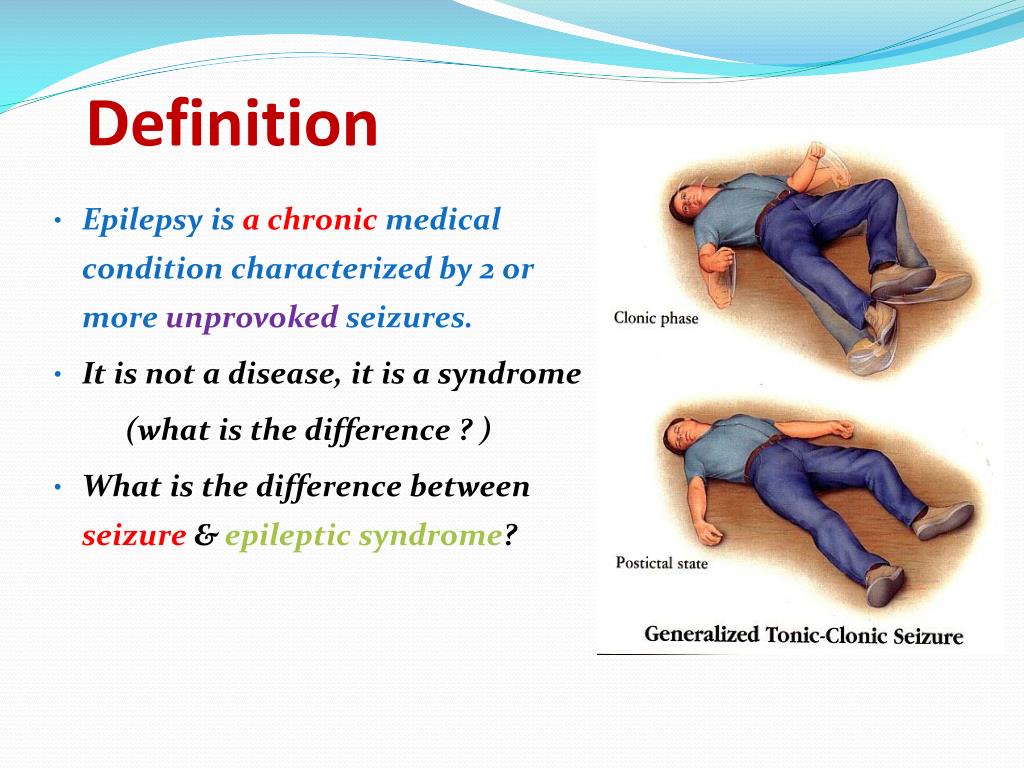 The essence of the diet is fasting. In the first three days, the patient is invited to take only plain water without gases. During this period, physical activity is reduced, bed rest can be maintained.
The essence of the diet is fasting. In the first three days, the patient is invited to take only plain water without gases. During this period, physical activity is reduced, bed rest can be maintained.
Starting from the fourth day, the patient gradually introduces solid foods into his diet, which are chicken breast, eggs, sausages, cottage cheese. These days, fasting is prohibited. You need to eat in small portions, at least 5-6 times a day. Products are carefully calculated. As a result, on the “edible” days of the week, you should get a menu with the following proportions: 4 shares of fat / 1 share of proteins / 1 share of carbohydrates. You can not eat potatoes, beets, cereals, bread, pasta, carrots.
For children with epilepsy from one to 12 years of age, the catogenic diet is transformed. Nutritionists include in the diet milkshakes prepared according to a special recipe. The main task of the diet is to teach patients to eat foods rich in fats. Fats have antiepileptic properties, so they help the body fight disease more effectively.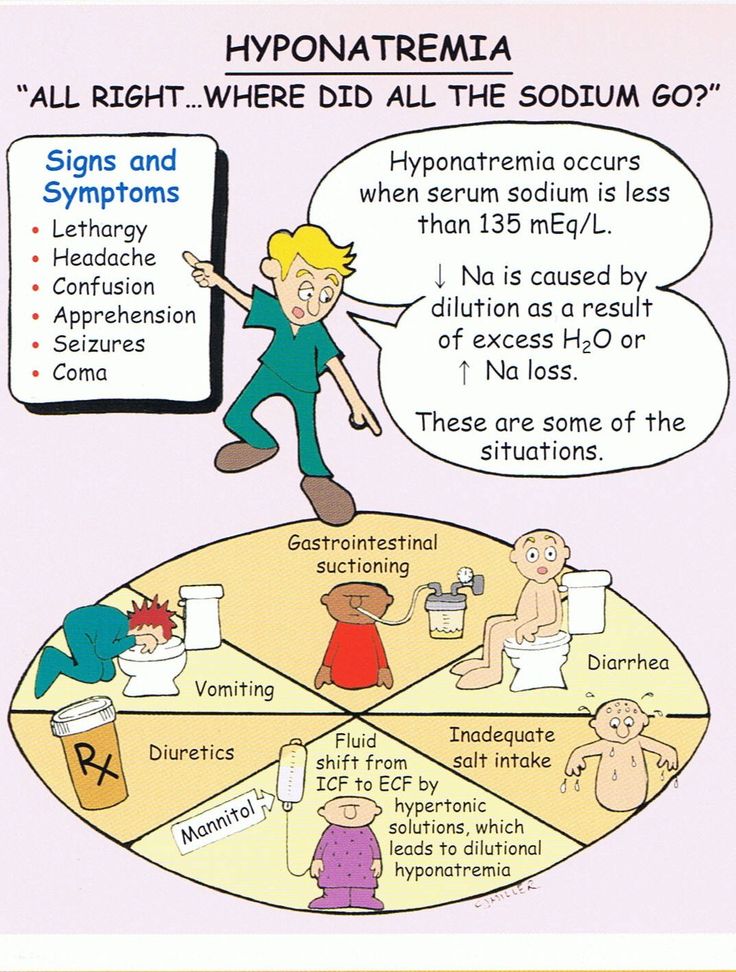
During the catogenic diet, it is allowed to eat sour-milk and dairy products, lean meat of turkey and chicken, sea fish, eggs, full-fat cottage cheese, vegetables, tea and coffee with cream. It is recommended to drink plenty of water to remove toxins and decay products. On the Internet, you can find many recipes for a catogenic diet, which will make it more interesting and original.
Folk medicine recipes in the fight against epilepsy and
Folk wisdom offers its own means of dealing with epileptic seizures. However, the fascination with prescriptions can be fatal if they are not coordinated with the attending physician or traditional medical medicine is neglected. Among the most popular folk remedies are:
Stone oil rich in vitamins, minerals and trace elements. It has pronounced antispasmodic and immunomodulatory properties. The most widespread was the "Siberian" recipe for combating the disease. According to him, 3 grams of oil is diluted in 2 liters of water. The solution is taken before meals for a month three times a day, not more than once a year in a full course.
The solution is taken before meals for a month three times a day, not more than once a year in a full course.
Herbal powder , for the preparation of which equal parts of dried peony, licorice and duckweed are taken. You can grind the raw materials using a blender, mortar or coffee grinder. The remedy is taken in half a teaspoon along with a difein tablet three times a day for up to 2 weeks, followed by a week break and a repetition of a two-week schedule. A total of three courses are recommended. Since the remedy includes a drug, it is worth getting a doctor's recommendation for taking it.
Maryin root is used as an alcoholic tincture of petals. The tincture has a beneficial effect on neurasthenia, paralysis, epilepsy. Infused 3 tablespoons of the solution in a bottle of vodka for a month. It is taken with meals three times a day for a teaspoon.
On the Internet you can find a lot of recipes, thanks to which epilepsy is treated and seizures are neutralized. According to naturopathic doctors, such herbs as Sinyuha Blue, Hogweed, Shiksha, Chernobyl, Oregano, Bone, St. John's wort and Meadowsweet help well. However, the selection of herbs is best done together with the doctor on an individual basis. Incorrectly prescribed therapy can delay the timing of epilepsy correction and adversely affect the general condition of the body.
According to naturopathic doctors, such herbs as Sinyuha Blue, Hogweed, Shiksha, Chernobyl, Oregano, Bone, St. John's wort and Meadowsweet help well. However, the selection of herbs is best done together with the doctor on an individual basis. Incorrectly prescribed therapy can delay the timing of epilepsy correction and adversely affect the general condition of the body.
Phytotherapeutists say that medicinal plants can give good results, but they need to be used for a long time. The cumulative effect of the positive action of plant components contributes to long-term use. Sometimes homeopathic treatment lasts for several years.
In addition to herbs, manual techniques for the treatment of epilepsy are also known, which came to us from the recipes of folk wisdom. During an attack, it is recommended to press the left hand of the epileptic to the floor, at the same time stepping on the left little toe of the patient's foot. This is easy to do when the patient is in the supine position during the attack. In addition to these recipes, there are techniques based on smell. It is recommended to constantly place in the room of the epileptic myrrh resin, which can be bought in the church. With the help of a miraculous substance, priests treated in ancient times. Resin calms the nervous system, has a positive effect on mood and harmonizes the emotional background.
In addition to these recipes, there are techniques based on smell. It is recommended to constantly place in the room of the epileptic myrrh resin, which can be bought in the church. With the help of a miraculous substance, priests treated in ancient times. Resin calms the nervous system, has a positive effect on mood and harmonizes the emotional background.
Medication therapy for epilepsy is a must
Taking medications exactly according to the dosage and schedule allows you to control epilepsy attacks. Missing pills and lack of consistency in treatment create significant risks for the onset of epileptic seizures. With conservative treatment, it is mandatory to comply with the following conditions:
- follow the schedule for taking medications and the exact dosage recommended by the doctor;
- avoid self-medication and the use of any drugs without the consent of your doctor. If acquaintances recommended a remedy or a pharmacist in a pharmacy praised a new drug, discuss the possibility of taking it with a specialist who carries out your treatment;
- therapy should not be stopped at times when stable results have been achieved.
 An independent decision to cancel the drug can provoke an attack. Only an epileptologist or a neuropathologist can cancel the appointment.
An independent decision to cancel the drug can provoke an attack. Only an epileptologist or a neuropathologist can cancel the appointment.
The patient is obliged to notify the doctor supervising the treatment of the manifestation of non-standard reactions of the body to external or internal stimuli. If you experience previously unusual symptoms, you should notify the doctor about them immediately.
The majority of people with epilepsy successfully cope with seizures by taking medications prescribed by a doctor. A properly selected drug and its competent dosage can stop the development of the disease for many years, forcing the patient to forget about the attacks that appeared earlier. According to standard practice, the doctor initially prescribes the minimum dose of the antiepileptic drug, after which the patient is monitored. If it is impossible to prevent seizures with small doses, the dosage is increased. As soon as a stable remission occurs, a successfully selected dosage is fixed in the patient's medication schedule.
Among the drugs prescribed are carboxamides, valproates, phenytoins, phenobarbital. Wherein
Epilepsy and pregnancy: how to give birth to a healthy child
A few years ago, doctors did not recommend pregnancy if one of the partners had epilepsy. She justified this by saying that the disease would be transmitted to the child, or that he would be born with developmental disabilities. What do doctors think now?
What are the chances of a couple having a healthy baby if one of the partners has epilepsy? And what can be done to increase these chances? Read about it in our article.
All information and statistics are provided by neurologists of the world's leading clinics with which Bookimed cooperates, and such reputable organizations as the International League Against Epilepsy, the American Epilepsy Foundation, etc. All data is verified and confirmed by our medical editors.
- Planning pregnancy
- Taking antiepileptic drugs
- Pregnancy management
- Childbirth
- Seizures that appeared during pregnancy
- Doctors' recommendations
Pregnancy with epilepsy: is it dangerous
Most women planning pregnancy are more likely to worry about the health of their child than about their own.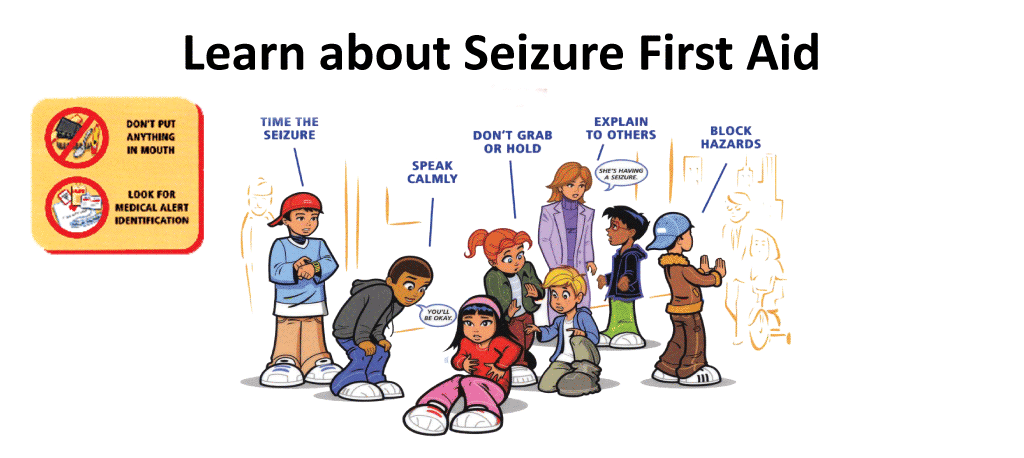 But it is important for a future mother diagnosed with epilepsy to understand that the risk for the baby is not as high as for her.
But it is important for a future mother diagnosed with epilepsy to understand that the risk for the baby is not as high as for her.
| According to the American Epilepsy Foundation, the preparation and management of pregnancy by an epileptologist is of great importance, following all his recommendations. This allows 90 out of 100 women with this disease will give birth to healthy children . |
How pregnancy affects maternal epilepsy
Experts estimate that in almost 85% of women, pregnancy does not affect epilepsy in any way . In other cases, seizures may increase slightly, especially in the first and third trimesters. Doctors found that this does not depend on the form of the disease and its duration. Even if the seizures are associated with the menstrual cycle (catamenial epilepsy), the absence of periods during pregnancy does not guarantee the complete absence of episodes of the disease.
Such unpredictability is connected not only with hormonal changes in the body. It can be caused by fluid retention, stress and excitement, changes in blood composition and the level of antiepileptic drugs in it.
Most women who have not had a seizure in the last 9 months will not experience one during pregnancy.
Talk to your epilepsy doctor about how pregnancy can affect your epilepsy. It is worth finding a specialist who has experience in the treatment and management of just such patients.
Is epilepsy inherited
The probability of having a sick child depends on the form of epilepsy in his father or mother. So, according to the AboutKidsHealth portal, an idiopathic form of the disease, which is genetically determined, can be transmitted to the baby. But even parents with such a diagnosis in more than 90% of cases have healthy children. At the same time, the probability of transmission of the disease from the father to the child is lower than from the mother.
| The American Epilepsy Foundation emphasizes that epilepsy, including idiopathic epilepsy, is not a reason to refuse to have children. They recommend undergoing genetic testing, which will help future parents objectively assess all possible risks. |
Pregnancy planning for epilepsy
Pregnancy planning for epilepsy is necessary because the disease can greatly affect a woman's body, especially when the disease cannot be completely controlled. Doctors have determined that if an attack occurs in the preovulatory period, it can disrupt this process. In addition, uncontrolled episodes of epilepsy provoke a failure of the menstrual cycle as a whole or cause cycles during which ovulation does not occur at all (anovulatory).
Basic steps for a woman with epilepsy when planning a pregnancy:
Consultation with a treating neurologist who has experience in managing such pregnancies.
Comprehensive neurological examination. It is mandatory even if there have been no seizures for a long time.
Review of drug therapy. The doctor analyzes the drugs that the patient takes and, if necessary, adjusts the therapy taking into account the new features of the female body.
Comprehensive gynecological examination. It must be taken when planning any pregnancy to make sure that the woman is healthy, able to endure and give birth to a healthy child. Read about what should include a standard diagnosis of the body before pregnancy.
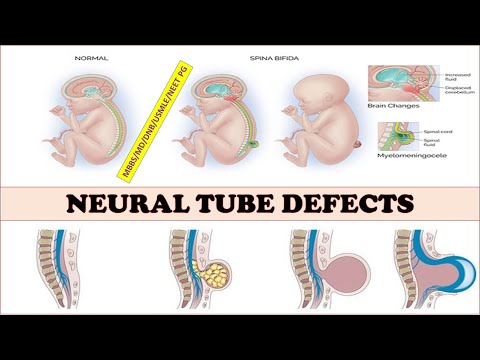
Folic acid intake. This substance reduces the risk of developing neural tube pathologies of the fetus, which is higher in women with epilepsy. Gynecologists recommend taking it to women at the stage of pregnancy planning (3 months before the expected date of conception) and during the 1st trimester.
Important! Talk to your doctor before taking any vitamins. Perhaps he will consider it necessary to prescribe you a multivitamin complex, which includes not only folic acid, but also selenium, zinc, vitamins K, D and others.
Man's epilepsy and pregnancy planning
Men with epilepsy need to approach pregnancy planning as seriously as women. Taking antiepileptic drugs can affect the possibility of conception and the health of the unborn baby. Some drugs reduce the mobility and concentration of spermatozoa or change their structure, significantly reducing the likelihood of conception. Therefore, an important stage of planning for the future father is a visit to a neurologist-epileptologist, who, if necessary, will adjust the treatment regimen or temporarily select other drugs.
Some antiepileptic drugs affect the fetus and may cause birth defects. This risk is especially increased if the mother-to-be is taking several high-dose medications at the same time. Here is what one of the top epileptologists in Europe, Professor Antonio Russi (Teknon Medical Center, Barcelona, Spain) says about this:
Neurologists do not yet have enough data on new antiepileptic drugs developed in the last 5 years.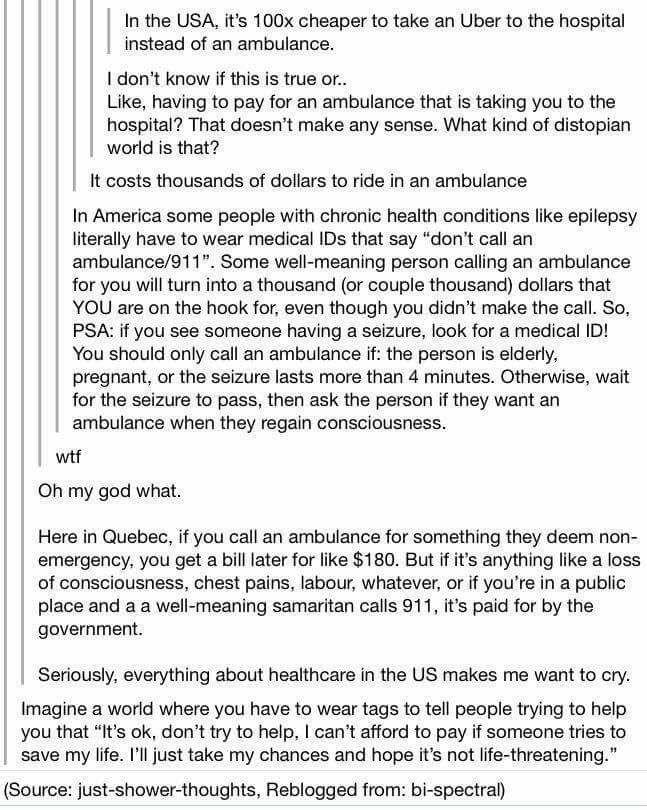 But classic medicines have already been studied enough, and most of them are completely harmless to the health of the unborn child.
But classic medicines have already been studied enough, and most of them are completely harmless to the health of the unborn child.
According to studies, valproic acid is the most dangerous:
- If used to treat epilepsy in the first days of pregnancy, there is a risk of fetal neural tube defects (1-2%) and other congenital anomalies (10%).
- The child of a woman who took the drug during pregnancy has a lower level of mental development and a higher risk of autism than other children.
- The higher the dose a woman takes, the higher all possible risks.
According to studies conducted in 2018, the active substance Topiramate (Topomax) may also cause some disorders in the fetus (for example, cleft lip or cleft palate). The drug is dangerous in high doses, which are prescribed for the treatment of epilepsy, and almost harmless in other cases.
If you are prescribed one of these drugs, talk to your doctor. Ask him about other medicines you can take during pregnancy.
Never discontinue antiepileptic drugs on your own. This can lead to uncontrolled seizures and harm you and your baby.
| According to studies, with the right medication, almost 96% of women with epilepsy give birth to healthy children. In healthy women, this figure is 98%. The difference is only 2%. |
Management of pregnancy with epilepsy
To manage pregnancy with epilepsy, it is worth choosing specialists of different profiles (neurologist, obstetrician, gynecologist, nutritionist). They should have experience working with such patients and the ability to exchange medical information with each other in order to most comprehensively approach possible issues.
Epilepsy Foundation of America Guidelines for Women During Pregnancy:
- Get regular check-ups and check your blood levels of antiepileptic drugs with tests. To do this, you need to donate blood for analysis.
 During pregnancy, the concentration of the active substance may decrease, so drug therapy may require adjustment.
During pregnancy, the concentration of the active substance may decrease, so drug therapy may require adjustment. - Get an AFP test and a high resolution ultrasound. This is necessary in order to detect and eliminate possible violations in the development of the internal organs of the baby in time.
- Follow your antiepileptic medication regimen to avoid triggering an attack.
- Follow nutritional guidelines and watch your weight gain. Since a woman's metabolism can be disturbed due to epilepsy or medication, it is necessary to be sure that the child receives everything that is needed for normal development. If necessary, take vitamins.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle and recommended sleep schedule.
Childbirth with epilepsy
Doctors recommend choosing a medical center for childbirth and not having it at home. This is due to the fact that contractions and stress can trigger an epileptic seizure, and a woman will need medical attention.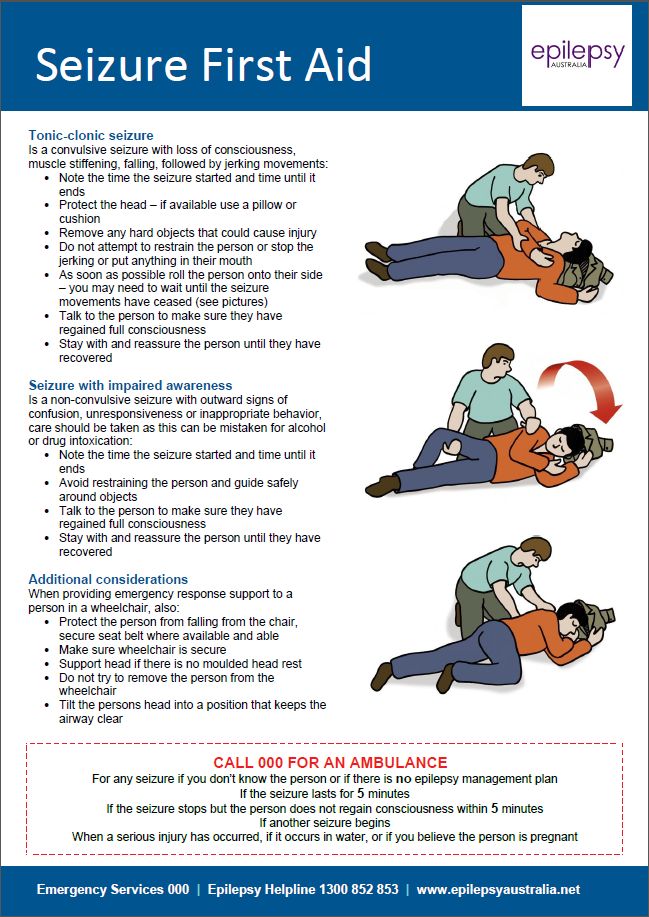
Otherwise, epilepsy does not affect childbirth and preparation for it.
| According to the British Epilepsy Society, most women with epilepsy have a natural birth without any complications. |
Breastfeeding and epilepsy
Studies show that breastfeeding with epilepsy does not harm the baby. Even before birth, he gets used to a certain dose of medicine that his mother takes. In breast milk, the concentration of the drug is usually much lower than in the blood that enters through the umbilical cord. To further reduce it, doctors recommend taking the drug immediately after feeding or at the beginning of the child's longest sleep.
What to do if epilepsy occurs only during pregnancy
If a woman has her first epilepsy during pregnancy, you should immediately consult a doctor. He must prescribe a comprehensive examination, select an effective treatment that will be safe for the child.
| One attack can be caused by changes in the work of the female body during the bearing of the baby, therefore it cannot be the basis for making a diagnosis. |
In the future, the expectant mother will need more careful medical supervision than a normal pregnancy.
Pregnancy and epilepsy: doctor's advice
For women with epilepsy who are planning to have children, doctors have made the following recommendations:
- Preparation for pregnancy should begin approximately 6 months before the expected date of conception. During this time, women must undergo a comprehensive examination to be sure that her body will be able to endure and give birth to a child.
- It is necessary to plan pregnancy together with the attending neurologist. If necessary, he will reduce the dose of the drugs taken or replace them with others.
- Do not stop medication on your own. This can lead to an increase in seizures.

- Take your doctor's prescribed vitamins regularly and follow his diet and sleep recommendations.
- Undergo all regular examinations in order to detect and correct possible violations in the development of the fetus in time.
- Give birth at a health center as a priority. So you can be sure that you will receive qualified assistance at the right time.
- Inform the doctors at the maternity hospital about your illness and take medical records from your neurologist with you.
- Follow your medication schedule even during labor and delivery.
- Give preference to breastfeeding after the baby is born.
- To prevent your baby from being injured if you suddenly have an attack, do not carry him in your arms for a long time, choose the floor for swaddling, not the table, do not bathe the baby yourself.
There seem to be a lot of rules. But in fact, they are quite simple, and if strictly adhered to, parents with epilepsy can raise a healthy child.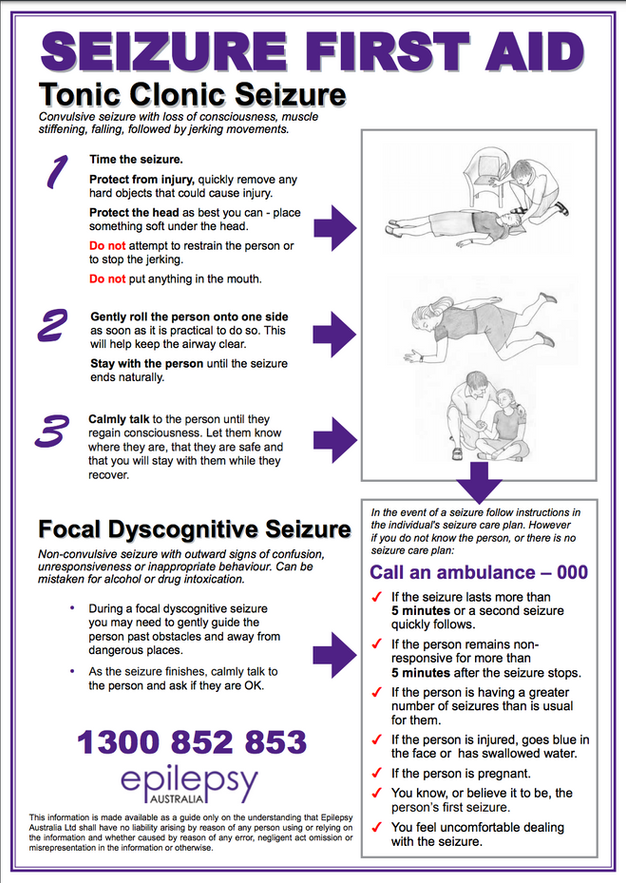
Top 3 clinics our patients choose for the treatment of epilepsy
Spain, Barcelona
264 reviews
TrustScore
All reviews have been verified
- Bookimed patients in Teknon are received by Prof. Antonio Russi. This is an epileptologist with 35 years of experience. He specializes in the diagnosis of rare and most complex cases, therapy and surgery of epilepsy at any age. 95 of the doctor's patients out of 100 successfully control epileptic seizures after treatment. In 30 patients out of 100, it does not confirm the form of epilepsy that was determined at home. After additional tests, only 1 correctly prescribed medicine helps them to completely get rid of seizures.
- Only with Antonio Russi you will undergo an extended examination - electroencephalography of the brain during sleep and wakefulness for several days. During this period, the professor prescribes various antiepileptic drugs and evaluates how they affect the seizures.
 Such diagnostics allows you to accurately determine the location of the epileptic focus and select an effective treatment.
Such diagnostics allows you to accurately determine the location of the epileptic focus and select an effective treatment. - In addition, Professor Russi prescribes pharmacogenetic testing. This is a study of the genetic characteristics of a person, which allows you to determine the reaction of his body to prescribed medications.
- The duration of a comprehensive examination for epilepsy is 7 days.
Read more
| Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) | $67663 - $78072 |
| Stereotactic operations | $26024 - $67663 |
| Vagus nerve stimulation | $46843 - $48925 |
Turkey, Istanbul
174 reviews
TrustScore
All reviews have been verified
- High success rate of neurosurgical operations.
 Surgical treatment of epilepsy at Liv Hospital takes place in the Department of Neurosurgery. According to the clinic, here the highest success rate of brain surgery is 91%, while the national average is 81%.
Surgical treatment of epilepsy at Liv Hospital takes place in the Department of Neurosurgery. According to the clinic, here the highest success rate of brain surgery is 91%, while the national average is 81%. - More than 250 successful neurosurgical interventions are performed annually at the clinic.
- You will be diagnosed with epilepsy using the latest generation MRI machine, which creates the most accurate image of brain structures.
- The duration of a complete diagnosis is 3-5 days.
Read more
Israel, Tel Aviv
126 reviews
TrustScore
All reviews have been verified
- Children with epilepsy at the Ichilov clinic are treated by the creator of the unique medical bracelet , which warns of an attack - professor Uri Kramer .
- Adult patients are treated by an epileptologist with 20 years of experience , chief physician of the department of electroencephalography and epileptology - professor Miri Neufeld .