Chance of spina bifida
Spina bifida - Causes - NHS
It's not known what causes spina bifida but a number of things can increase the risk of a baby developing the condition.
Lack of folic acid
Not having enough folic acid during pregnancy is one of the most important factors that can increase your chances of having a child with spina bifida.
Folic acid (also known as vitamin B9) occurs naturally in some foods, such as broccoli, peas and brown rice. It's also added to foods, such as some breakfast cereals. Folic acid tablets are available from pharmacies and supermarkets, or a GP may be able to prescribe them for you.
It's estimated that taking folic acid supplements before you conceive and while you're pregnant may prevent up to 7 out of 10 cases of neural tube defects, such as spina bifida.
It's not clear how folic acid helps prevent spina bifida. It's likely that folic acid is needed for important biochemical reactions in the body.
Read more about why you need folic acid in pregnancy.
Family history
Having a family member with a neural tube defect, such as spina bifida, increases your chances of having a baby with spina bifida.
If you've previously had a child with spina bifida, your chance of having other children with the condition is increased.
If you have a family history of spina bifida, it's very important that you take high-dose folic acid, prescribed by a GP before you become pregnant, and for at least the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Medicine
Taking certain medicines during pregnancy has been linked to an increased risk of having a baby with spina bifida or other birth defects.
Valproate and carbamazepine are medicines linked to spina bifida. They're often used to treat epilepsy, and some mental health conditions, such as bipolar disorder.
Doctors will try to avoid prescribing these medicines if there's a chance you could get pregnant while taking them, but they may be needed if the alternatives are not effective.
It's advisable to use a reliable form of contraception if you need to take one of these medicines and are not trying to get pregnant.
Tell your doctor if you're thinking about trying for a baby and you need to take one of these medicines. They may be able to lower the dose and prescribe folic acid supplements at a higher than normal dose, to reduce the risk of problems.
If you're not sure whether a medicine could affect your pregnancy, check with your doctor, midwife or pharmacist before taking it. Never stop taking a prescribed medicine unless a GP or another healthcare professional responsible for your care advises you to.
Genetic conditions
Very rarely a baby can have spina bifida alongside a genetic condition such as Patau's syndrome, Edwards' syndrome or Down's syndrome.
If your baby is found to have spina bifida and it's thought they may also have one of these syndromes, you'll be offered a diagnostic test, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling. These tests can confirm if your baby has one of these genetic conditions.
Other risk factors
Other risk factors for spina bifida include:
- obesity – women who are obese (have a body mass index of 30 or more) are more likely to have a child with spina bifida than those of average weight
- diabetes – women with diabetes may have an increased risk of having a child with spina bifida
Page last reviewed: 20 April 2020
Next review due: 20 April 2023
Spina bifida | March of Dimes
Spina bifida is the most common kind of neural tube defect.
 These are conditions of the brain, spine and spinal cord.
These are conditions of the brain, spine and spinal cord.Taking folic acid every day before and in the first few weeks of pregnancy can help reduce your risk for spina bifida and other neural tube defects.
If you’ve had a baby who had a neural tube defect, your risk for having another baby who has a neural tube defect is higher.
Spina bifida can be diagnosed during pregnancy or after birth.
Spina bifida can cause health problems for your baby, such as fluid on the brain, paralysis (not being able to move parts of the body) and learning and developmental disabilities.
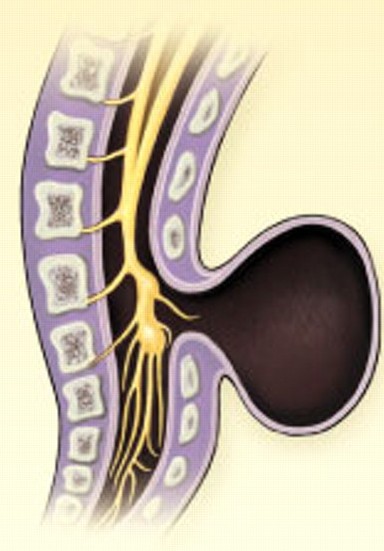
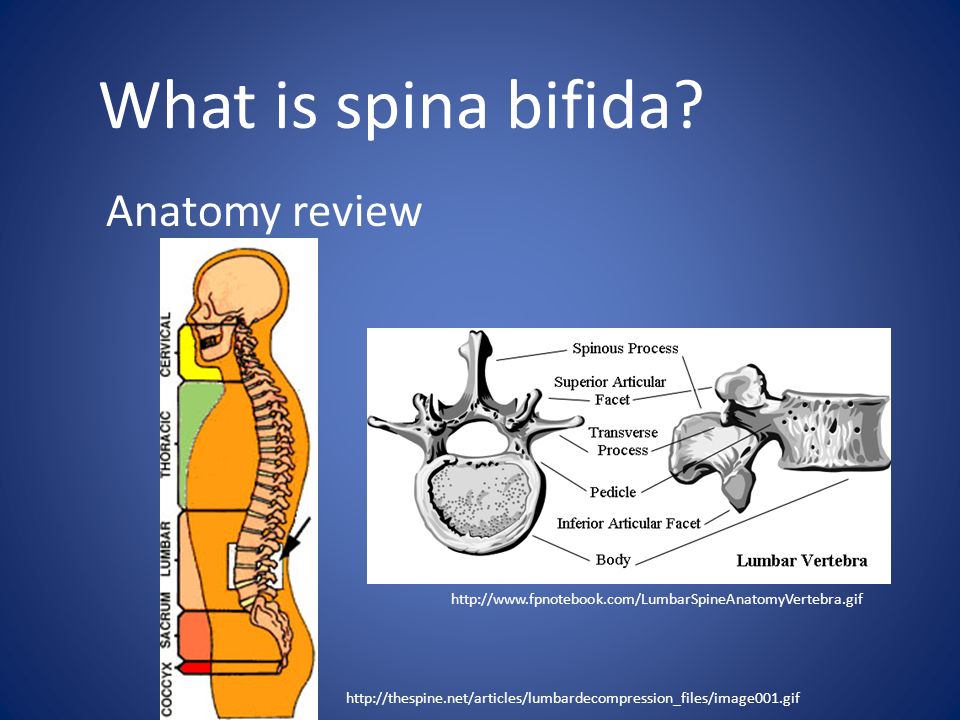
What is spina bifida?Spina bifida means “split spine” or “open spine.” The spine (backbone) protects the spinal cord, the bundle of nerves that runs down the middle of your back. The spinal cord carries signals back and forth between your body and your brain. Spina bifida happens when the spinal cord or bones in the spine don’t form correctly, leaving a gap or opening. Spina bifida can happen anywhere along the spine.
Spina bifida can happen anywhere along the spine.
Spina bifida is the most common kind of neural tube defect. These are conditions of the brain, spine and spinal cord. Birth defects are structural changes present at birth that can affect almost any part of the body. Spina bifida can affect how your baby’s brain, spine, spinal cord and meninges develop. Meninges are the tissues that cover and protect the brain and the spinal cord.
The neural tube starts out as a tiny, flat ribbon that grows into a tube. The neural tube usually closes in the first few weeks of pregnancy. In a baby who has a neural tube defect, the tube hasn’t closed completely.
About 1,400 babies are born with spina bifida in the United States each year. In this country, people who are Hispanic are more likely to have a baby who is affected by spina bifida than White or Black people.
Are you at risk for having a baby with spina bifida?We don’t always know for sure what causes spina bifida, but certain things may play a role.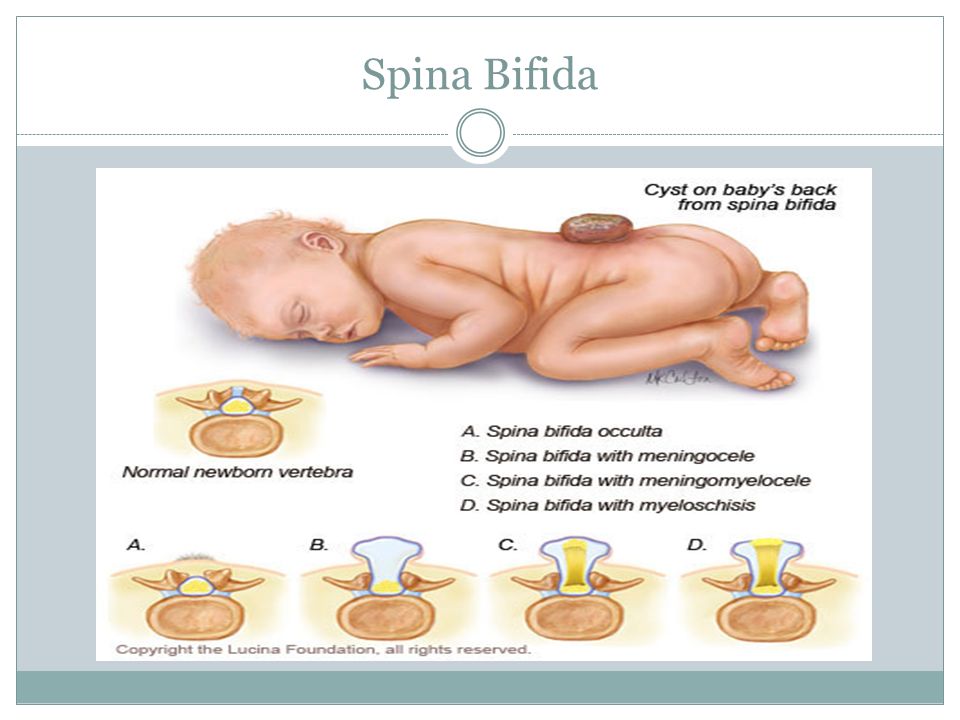 We do know that some things may make you more likely than others to have a baby who is affected by spina bifida. These are called risk factors. Having a risk factor doesn’t mean for sure that your baby will be affected, but it may increase your chances.
We do know that some things may make you more likely than others to have a baby who is affected by spina bifida. These are called risk factors. Having a risk factor doesn’t mean for sure that your baby will be affected, but it may increase your chances.
Talk to your provider about things you can do to help reduce your risk for spina bifida:
Take folic acid. Folic acid is a B vitamin that every cell in your body needs for normal growth and development. Taking folic acid before and during early pregnancy can help prevent neural tube defects in your baby.
Learn about your genes. Genes are the part of your body’s cells that store instructions for the way your body grows and works. Genes are passed from parents to children. Sometimes changes in genes can cause spina bifida and other conditions.
- If you already have a child who is affected by a neural tube defect, you have a slightly higher risk of having another baby with the same condition.
- If you are affected by a neural tube defect yourself, you’re more likely to have a baby who has spina bifida than a person who doesn’t have a neural tube defect.
If you, your partner, your children or someone in your families has a neural tube defect, you may want to see a genetic counselor. This is a person who is trained to help you understand about genes, birth defects and other medical conditions that run in families and how they can affect your health and your baby’s health. Most often, spina bifida occurs in people who don’t have any family history of the condition.
Manage your health. Certain health conditions, such as diabetes and obesity, may play a role in spina bifida. If you have these or other health conditions:
- Talk to your provider about how your condition affects your risk for spina bifida and other neural tube defects.
- Get your health under control before you get pregnant. And get regular treatment to manage your condition during pregnancy.

- Get to a healthy weight before pregnancy. Eat healthy foods and do something active every day.
Talk with your provider about medicines you take. This includes any prescription and over-the-counter medicines, supplements and herbal products. You may need to stop taking a medicine or switch to one that’s safer during pregnancy. For example, some anti-seizure medicines may increase your risk of having a baby who is affected by a neural tube defect. Here’s how to reduce your risk:
- Tell your provider about any medicine or supplement you take before you get pregnant.
- Don’t start or stop taking any medicine before or in the first few weeks of pregnancy without talking to your health care provider first.
- Make sure any provider who prescribes you medicine knows you’re pregnant or trying to get pregnant.
Having a high body temperature (also called hyperthermia) in the first 6 weeks of pregnancy. This may be caused by fever or by spending time in a hot tub or sauna.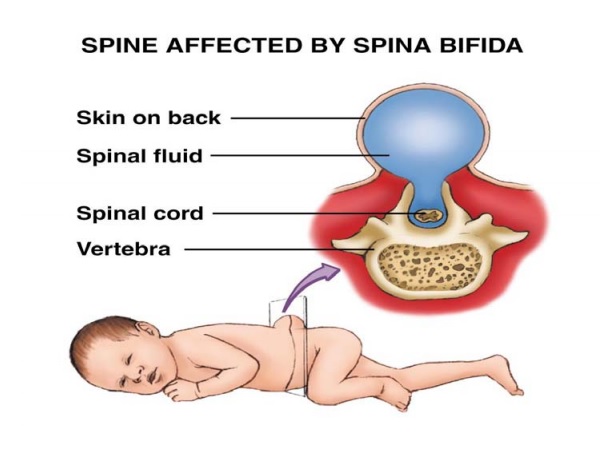 Having a high body temperature may increase your chances of having a baby who has spina bifida. Here’s what you can do to help reduce your risk:
Having a high body temperature may increase your chances of having a baby who has spina bifida. Here’s what you can do to help reduce your risk:
- If you have a fever in the first 6 weeks of pregnancy, call your provider right away.
- Don’t use hot tubs or saunas when you’re pregnant or if you’re trying to get pregnant.
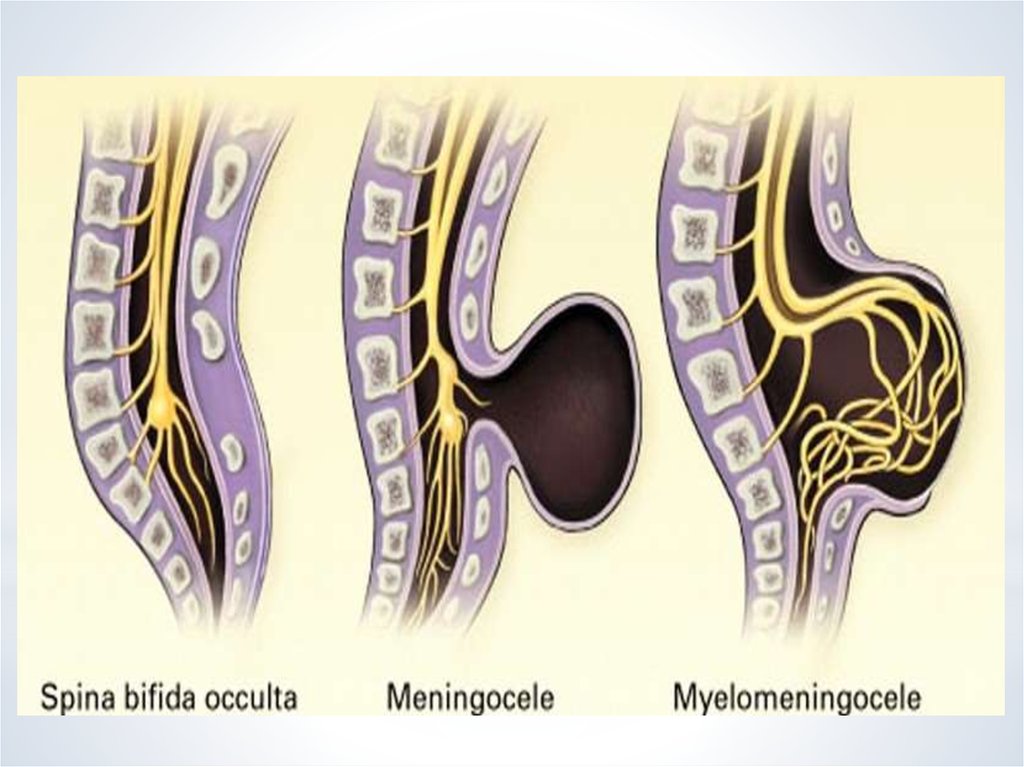
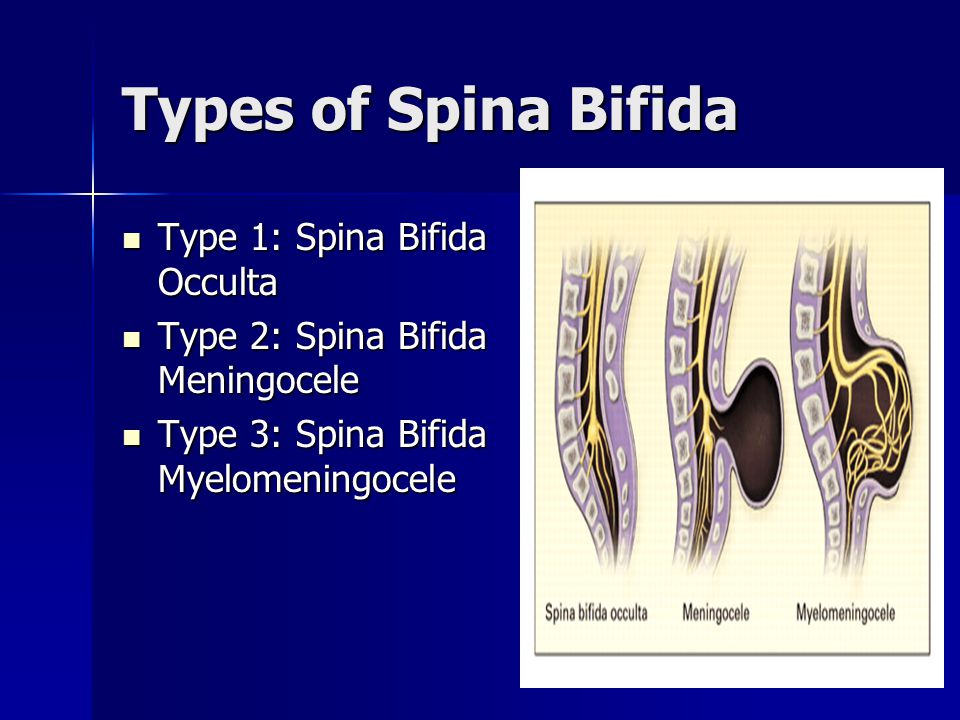
The four types of spina bifida are:
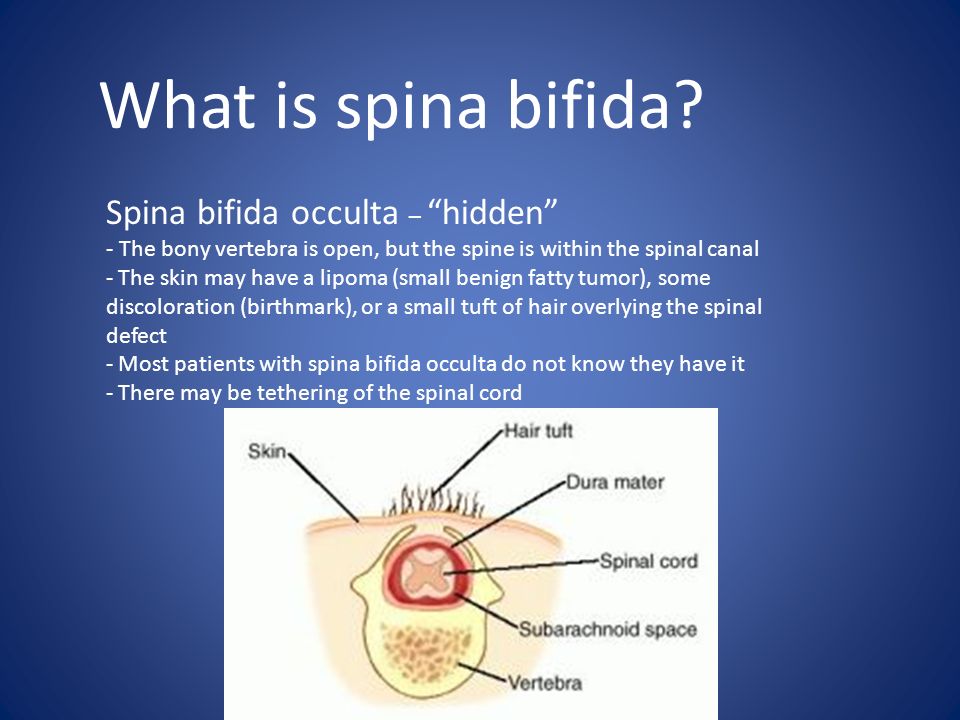
- Spina bifida occulta (also called hidden spina bifida). This is the mildest and most common form. It usually doesn’t cause health problems and you may never know your baby has it. In people who have this condition, the gap in the spine is small. The spinal cord and nerves stay in place and most often aren’t damaged. A dimple, hairy patch, dark spot or swelling may appear on the skin over the gap. If you see something like this at the bottom of your baby’s back, tell your baby’s health care provider.
- Closed neural tube defect.
 In people who have this condition, the fat, bone or meninges around the spinal cord don’t form correctly. This sometimes damages the nerves in the spinal cord. This condition often causes no symptoms, but some babies may have problems controlling their bladder and bowels.
In people who have this condition, the fat, bone or meninges around the spinal cord don’t form correctly. This sometimes damages the nerves in the spinal cord. This condition often causes no symptoms, but some babies may have problems controlling their bladder and bowels. - Meningocele. This is the rarest form of spina bifida. In this condition, the meninges push out through a gap in the spine. This creates a sac filled with fluid (called a meningocele) on the baby’s back. There’s usually little or no nerve damage, but some babies may have problems controlling their bladder and bowels. Surgery can remove the meningocele.
- Myelomeningocele (also called open spina bifida). This is the most severe form of spina bifida. In this condition, part of the spinal cord pushes out with the meninges through the opening in the spine to form a sac on the baby’s back. The spinal cord and nearby nerves are damaged. This can cause paralysis (when you can’t feel or move one or more parts of your body) and life-threatening infections.
 Babies who have this condition need surgery before birth or within the first few days of life. During surgery, a surgeon tucks the spinal cord and nerves back into the spine and covers them with muscle and skin. This can help prevent new nerve damage and infection. The surgery can’t fix any damage that’s already happened. Even with surgery, babies with this condition have lasting disabilities, such as problems walking and going to the bathroom.
Babies who have this condition need surgery before birth or within the first few days of life. During surgery, a surgeon tucks the spinal cord and nerves back into the spine and covers them with muscle and skin. This can help prevent new nerve damage and infection. The surgery can’t fix any damage that’s already happened. Even with surgery, babies with this condition have lasting disabilities, such as problems walking and going to the bathroom.
Doctors can diagnose most types of spina bifida when you’re pregnant or after your baby is born. If you baby has spina bifida occulta, it may not be diagnosed until later in your baby’s life.
Diagnosing spina bifida during pregnancyYou may have prenatal tests to check your baby for spina bifida and other birth defects. Prenatal tests used to diagnose spina bifida include:
- Maternal blood screening (also called quad screen).
 This blood test checks to see if your baby is at risk for certain birth defects, such as neural tube defects, heart defects and Down syndrome. The test is done at 15 to 22 weeks of pregnancy. If you have high levels of a substance called alpha-fetoprotein, your baby may have a neural tube defect such as spina bifida.
This blood test checks to see if your baby is at risk for certain birth defects, such as neural tube defects, heart defects and Down syndrome. The test is done at 15 to 22 weeks of pregnancy. If you have high levels of a substance called alpha-fetoprotein, your baby may have a neural tube defect such as spina bifida. - Amniocentesis. This test checks amniotic fluid taken from around your baby for birth defects such as neural tube defects. You can get this test at 15 to 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- Ultrasound. This test uses sound waves and a computer screen to show a picture of your baby. Providers may see spina bifida with this test.
Sometimes providers diagnose spina bifida after a baby is born. If your baby’s provider thinks your baby has spina bifida, they may use one of these tests to get a clearer view of your baby’s spine:
- Computed tomography (also called CT or CAT scan).
 CT scans use special X-ray equipment and powerful computers to make pictures of the inside of your baby’s body.
CT scans use special X-ray equipment and powerful computers to make pictures of the inside of your baby’s body. - Magnetic resonance imaging (also called MRI). This test uses a large magnet and radio waves to make a detailed picture of the inside of your baby’s body.
- X-ray. This test uses radiation to make a picture of your baby’s body.
Spina bifida can cause several health problems, including:
Bowel problems. Bowel control can be a problem for people who have spina bifida. Feeding your baby certain foods to keep stools soft or giving your child foods with extra fiber may help make bowel movements more regular.
Chiari II malformation. This condition happens when the lower part of the brain sits in the upper part of the neck. Babies who have this condition usually have myelomeningocele.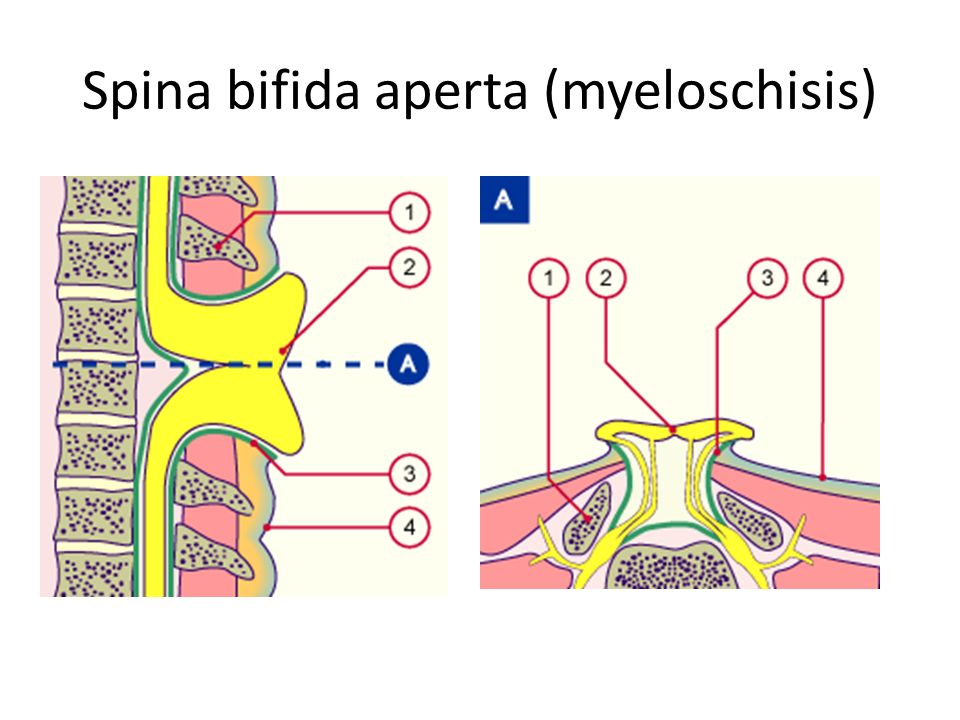 Some babies have:
Some babies have:
- Hydrocephalus. This is fluid buildup in the brain.
- Weakness or stiffness in the arms and hands
- Trouble feeding, breathing or swallowing
Hydrocephalus. Extra fluid in the head can cause it to swell and put pressure on the brain. In some cases, a surgeon needs to drain the extra fluid from a baby’s brain. The surgeon uses a shunt (a small hollow tube) that helps drain fluid and protects the brain from too much pressure. Hydrocephalus can cause intellectual and developmental disabilities.
Intellectual and developmental disabilities. These are problems with how the brain works that can cause people to have trouble or delays in physical development, learning, communicating, taking care of themselves or getting along with others. Children with spina bifida sometimes have problems with language, reading and math. They also may have trouble paying attention.
Latex allergy. Many babies who have spina bifida are allergic to latex (natural rubber). If your baby is allergic to latex, keep them away from items made of latex, such as latex bottle nipples, teething toys, changing pads, mattress covers and pacifiers. Your baby can wear a bracelet to let people know they have an allergy.
If your baby is allergic to latex, keep them away from items made of latex, such as latex bottle nipples, teething toys, changing pads, mattress covers and pacifiers. Your baby can wear a bracelet to let people know they have an allergy.
Meningitis. This is an infection that causes swelling in the brain and spinal cord. Meningitis can damage the brain and can be life-threatening. If your baby has meningitis, they may be treated with antibiotics.
Muscle weakness and joint pain. People who have spina bifida may have weak muscles and stiff joints because the nerves leading to the lower body are damaged. Surgery may help correct these conditions. Your baby may need physical therapy to help improve muscle weakness.
Paralysis. People who have spina bifida on the upper part of the spine may have paralyzed legs or feet. They may need to use wheelchairs. Those who have spina bifida lower on the spine (near the hips) may have more use of their legs.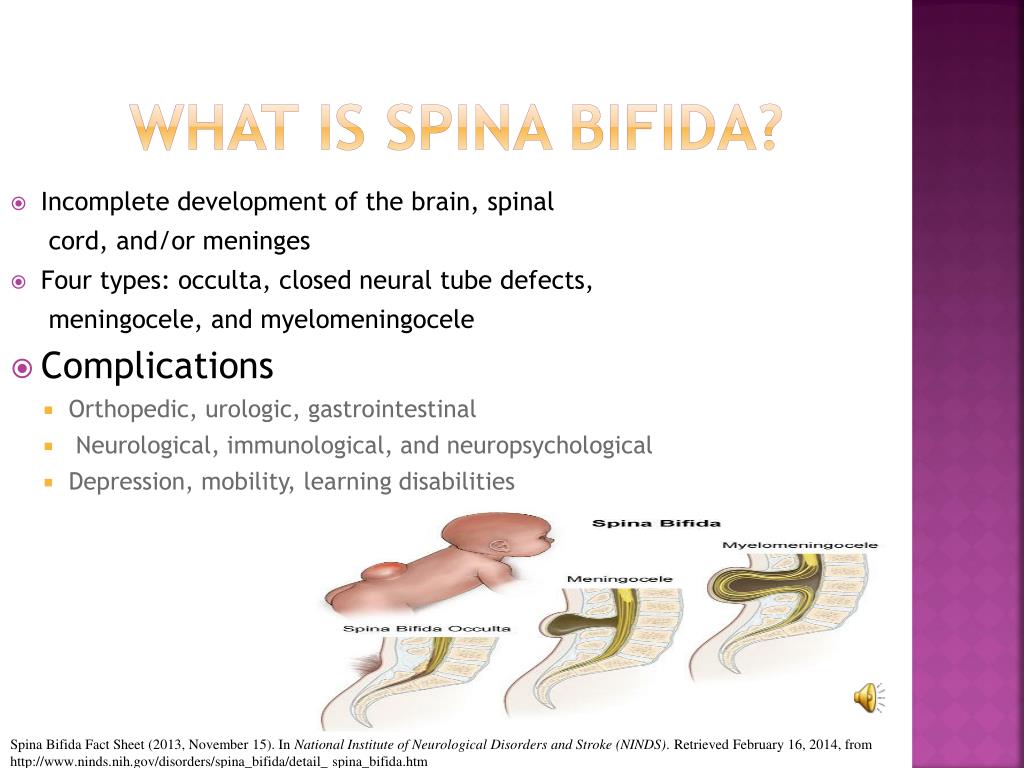 They may be able to walk on their own or use crutches, braces or walkers. Some babies can start exercises for the legs and feet to help them walk with braces or crutches when they get older.
They may be able to walk on their own or use crutches, braces or walkers. Some babies can start exercises for the legs and feet to help them walk with braces or crutches when they get older.
Skin problems. People who have spina bifida can develop sores, calluses, blisters and burns on their feet, ankles and hips. But they may not know they have these problems because they may not be able to feel certain parts of their body. Check your baby’s skin often for redness. Your baby’s health care provider can recommend ways to help prevent skin problems, such as giving cool baths and changing your baby’s position often.
Tethered spinal cord. Normally, the bottom of the spinal cord floats freely in the spinal canal (the hollow space around the spinal cord). If the cord becomes attached (also called tethered) to the spinal canal, the cord stretches as your baby grows. The stretching can cause nerve damage in the spine. The tethered spinal cord can be treated with surgery.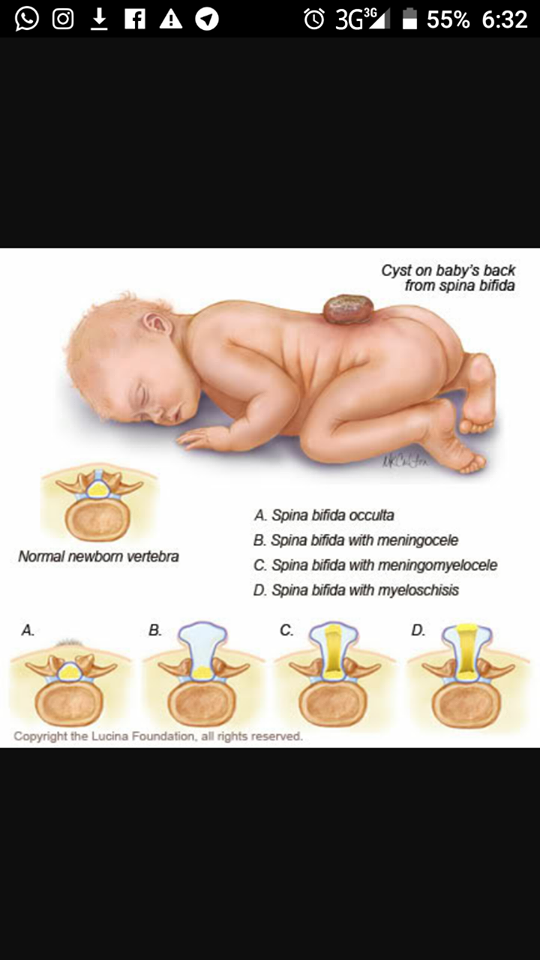 This condition affects babies who have myelomeningocele, meningocele and spina bifida occulta. Babies with a tethered spinal cord may have problems, including:
This condition affects babies who have myelomeningocele, meningocele and spina bifida occulta. Babies with a tethered spinal cord may have problems, including:
- Back pain
- Leg and foot weakness
- Bladder or bowel control problems
- A curved spine (also called scoliosis)
Urinary tract infections (also called UTIs). The urinary tract is the system of organs (including the kidneys and bladder) that helps your body get rid of waste and extra fluids in urine. Babies who have spina bifida often can’t control when they go to the bathroom because the nerves that help the bladder and bowels work are damaged. If your baby has problems emptying their bladder completely, it can cause UTIs and kidney problems. Your baby’s health care provider can teach you how to use a plastic tube called a catheter to empty your baby’s bladder.
Other conditions. Some people who have spina bifida have problems with:
- Obesity (being very overweight)
- Digestion (the process of how your body breaks down food after you eat)
- Social and mental health conditions, including depression.
- Vision
Your baby may have a team of providers who work together to treat health conditions caused by spina bifida. The team can include:
Doctors who treat your baby’s condition and related complications, including:
- A pediatrician who treats babies and children
- A neurologist who treats problems of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord and nerves
- An orthopedist who treats injuries and diseases of the bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles and nerves
- A psychiatrist who treats people with emotional or mental health problems, like depression
- A urologist who treats problems of the urinary tract (kidneys, bladder, ureters and urethra)
Other providers, including:
- A developmental therapist who helps people develop behavior and social skills
- An occupational therapist who helps people do everyday activities, such as holding and letting go of things, getting dressed and feeding themselves
- A physical therapist who creates exercise programs to help improve strength and movement
- A psychologist who takes care of people’s emotional and mental health
More Information
- CDC videos about spina bifida
- CDC spina bifida resources
See also: Neural tube defects
Last reviewed: July, 2021
symptoms, causes, treatment and surgery, complications, fund for helping children with spina bifida
Inna Inyushkina
founder of the Spina Bifida Charitable Foundation
Author Profile
Anastasia Zhvik
spoke with Inna
Author Profile According to unofficial statistics, about 1,500 children are born every year in Russia with spina bifida.
 And many doctors still do not know that one can live with such a disease.
And many doctors still do not know that one can live with such a disease. In 2012, at one of the planned ultrasounds during pregnancy, I learned that my child would have a severe form of disability. At that time, practically nothing was known about the diagnosis of spina bifida in our country, so I had to figure it out on my own.
In this article I will tell you what spina bifida is, what problems parents of children with this disease face, what kind of support they receive in Russia now, and how the Spina bifida foundation, which I founded in 2016, helps with this.
About important things
This article is part of the T—Zh “On important things” support program for philanthropists. As part of the program, we choose topics in the field of charity and publish stories about the work of foundations, the lives of their wards, and significant social projects. You can read all the materials about those who need help and those who help in the “About the Important” thread.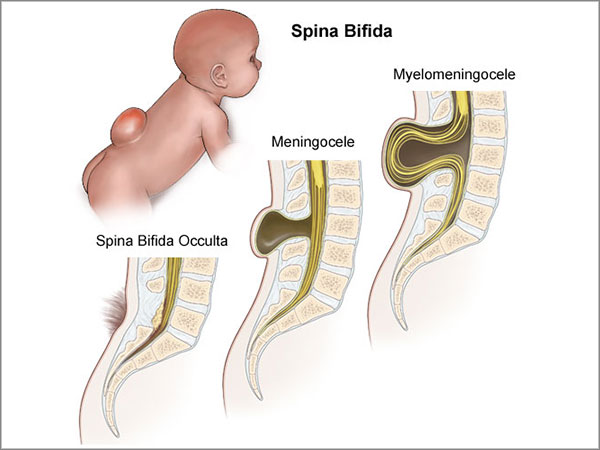
What is spina bifida
Spina bifida is Latin for "split spine". This is a developmental defect in which the vertebrae do not heal, and as a result, incomplete closure of the spinal canal occurs. Because of this, a hernial sac with cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid - can form on the back. Spina bifida leads to orthopedic, urological and neurosurgical problems.
Some patients with spina bifida move in a wheelchair, some have problems with fecal and urinary incontinence, others have hydrocephalus - accumulation of CSF inside the brain. At the same time, if all medical examinations are carried out on time, the intelligence of such patients remains intact. The disease does not affect a person's life expectancy in any way, especially if you do not skip examinations and prevent secondary disorders.
/tsr/
What are technical means of rehabilitation
There are three most common forms of spina bifida: occult, meningocele and myelomeningocele. Occult, or hidden spina bifida, is a mild form of the disease without a spinal hernia: the spinal cord and surrounding tissues remain inside, but the bones in the lower back cannot form normally. At the site of splitting, there may be a hairy area, a dimple, or a birthmark. You can live with this form of the disease and not even know about it.
Occult, or hidden spina bifida, is a mild form of the disease without a spinal hernia: the spinal cord and surrounding tissues remain inside, but the bones in the lower back cannot form normally. At the site of splitting, there may be a hairy area, a dimple, or a birthmark. You can live with this form of the disease and not even know about it.
In case of meningocele, a sac filled with CSF appears on the outer surface of the back, but there is no spinal cord and nerve tissue in it. In myelomeningocele, the spinal cord and nerves develop outside the body - in a sac on the back. My son has just such a form of the disease.
These are the three most common forms of spina bifida. It can be seen how, depending on the degree of spina bifida, the spinal cord and nerves develop inside or outside the body - on the outer part of the back. This is how the three most common forms of spina bifida look like. It can be seen how, depending on the degree of spina bifida, the spinal cord and nerves develop inside or outside the body - on the outer part of the back Spina bifida is a congenital pathology: a spinal defect is formed in a child in the womb, as a rule, when the fetus is not yet 40 days old.
According to Russian clinical guidelines, the disease occurs with a frequency of 1-3 people per 10,000 pregnancies, but mild cases are often not recognized. According to unofficial data, the disease occurs in one of 1500-2000 newborns. There are several reasons for the defect, but the main one is the lack of folic acid in the body of a woman.
Federal Clinical Guidelines. Diagnosis and treatment of children with myelodysplasiaPDF, 927 KB
See a doctor
Our articles are written with love for evidence-based medicine. We refer to authoritative sources and go to doctors with a good reputation for comments. But remember: the responsibility for your health lies with you and your doctor. We don't write prescriptions, we make recommendations. Relying on our point of view or not is up to you.
How I found out about my son's illness
When I became pregnant with Matvey, I was 27 years old. I already had a healthy daughter, I was married and lived in Moscow.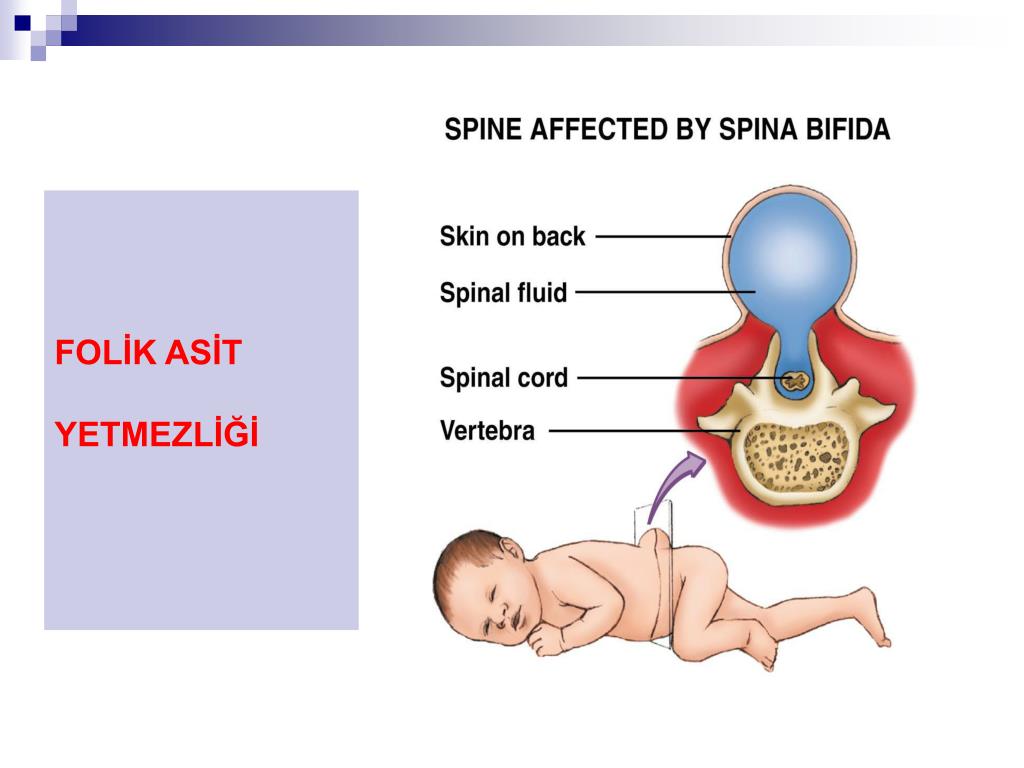 I was examined in a private clinic, and at the 32nd week of pregnancy I was told that my child had spina bifida.
I was examined in a private clinic, and at the 32nd week of pregnancy I was told that my child had spina bifida.
The doctor could not explain anything, except that it was a severe form of disability, and did not give any predictions. There was no information in Russian on the Internet, and in Russia there was not a single foundation where one could get support and answers to questions about spina bifida. I applied to various Russian NGOs, but everywhere I got the same answer: sorry, our organization helps children with Down syndrome, or children with heart disease, or children with autism. No one helped children with spina bifida.
I felt as if my life was collapsing and everything was falling into the abyss: it is impossible to prepare a pregnant woman who already has a healthy child to have a son with a severe disability. It always happens very unexpectedly, and you do not understand how to continue to live.
Then one of my friends recommended one of the most famous and best maternity hospitals in Moscow to me. The birth was scheduled for June 14, 2012, and on June 12, an anonymous call was received from the maternity hospital with a request not to come.
The birth was scheduled for June 14, 2012, and on June 12, an anonymous call was received from the maternity hospital with a request not to come.
I was told: “You have a difficult pregnancy, there is a possibility of a fatal outcome in a child during childbirth. We don't want to spoil the statistics."
So, literally a couple of days before the birth, I had to independently look for a maternity hospital through my acquaintances and friends, where, as a result, I had a caesarean section.
When Matvey was born, we moved to the neurosurgery center: our son had to be operated on on the first day after birth in order to close the spinal hernia and avoid infection of the spinal cord - this could lead to meningitis and ultimately to death.
But Matvey could not be operated on for three weeks. Everyone was waiting: either when the head physician returns from vacation, or until the child gains weight, or something else. At some point, I realized that the doctors were just playing for time so as not to do the operation anymore: they thought that there would be no sense in it. Then, through friends, I found a doctor in Israel, and my family and I went to Tel Aviv to operate on my son there. When his condition became stable, we returned to Russia.
At some point, I realized that the doctors were just playing for time so as not to do the operation anymore: they thought that there would be no sense in it. Then, through friends, I found a doctor in Israel, and my family and I went to Tel Aviv to operate on my son there. When his condition became stable, we returned to Russia.
Time passed, Matvey grew up, but it remained unclear how to live with such a diagnosis: in Russia, there was still no help for children with spina bifida. Then I decided that it was necessary to combine the efforts of doctors, public figures and the parent community and create a system from scratch. So, four years after the birth of my son, I founded the Spina Bifida Foundation.
/readers-and-charity/
6 reasons to start doing charity work right now
Matvey in the first months after birth. At that time, practically nothing was known about spina bifida in Russia. Therefore, I did not understand how to live with such a diagnosis and whether it was even possibleWhat are the options for parents of children with spina bifida
Parents who are expecting a child with spina bifida now have four options.
Terminate pregnancy. If a woman finds out about the child's illness before the 12th week of pregnancy, she can have an abortion if she wishes. But most often the defect can be seen on a simple ultrasound after this period. Then you can terminate the pregnancy for medical reasons by the decision of a council of doctors.
Some doctors still scare parents with back bifida, and under pressure they decide to have an abortion. The psychologists of our partner fund "Light in Hands" support such parents and help them recover from the loss.
Perform intrauterine surgery. At 24-26 weeks of pregnancy, intrauterine surgery can be performed to minimize the chance of orthopedic, urological and neurosurgical complications in the baby. In Russia, since 2016, such an operation has been carried out free of charge. Studies show that it has a better effect on the health of the child than the operation after birth, the one that we did to Matvey.
Thanks to intrauterine surgery, excess fluid is removed from the brain, the formed cavities in the spinal cord dissolve and the pressure between the cranial cavity and the spinal column normalizes. There are many children who have no disability at all after the operation, they live a normal life: they do not have a hernia, problems with the genitourinary system, they walk with their own feet.
/pregnancy/
How much does it cost to carry a baby? Another intrauterine operation for children with spina bifida is done at the Lapino private hospital in Krasnogorsk.
We are trying to disseminate information about intrauterine operations, because not all doctors in the regions still know about them. Our foundation helps families with travel, accommodation and related expenses. As of October 2021, more than 50 families in Russia decided to have such an operation.
Dasha became one of 50 children who were operated on in utero. So far, she is too small to say how the operation affected her life, but the girl's condition is now stable Perform the operation on the first day after the birth of the child.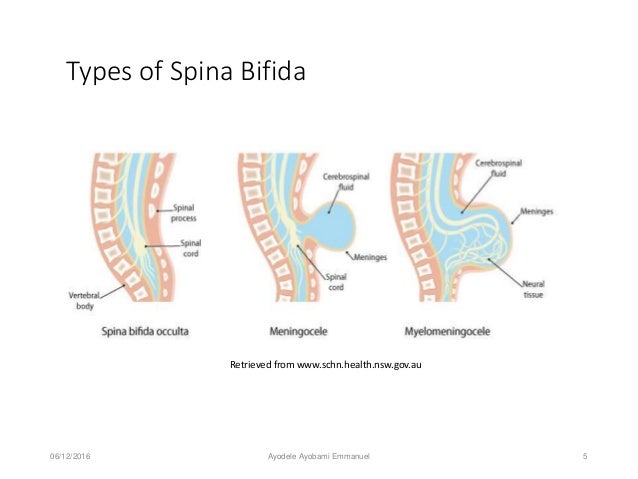 Some women have contraindications for intrauterine surgery: for example, twin pregnancy, intrauterine infection, diabetes mellitus or tachycardia. In addition, in Russia there is a problem with the diagnosis of spina bifida: a defect is noticed when an intrauterine operation can no longer be performed. So it was with me.
Some women have contraindications for intrauterine surgery: for example, twin pregnancy, intrauterine infection, diabetes mellitus or tachycardia. In addition, in Russia there is a problem with the diagnosis of spina bifida: a defect is noticed when an intrauterine operation can no longer be performed. So it was with me.
Previously, more than half of spina bifida cases were detected after the 30th week of pregnancy at the third screening. But from the beginning of 2021, by order of the Ministry of Health, it was canceled. Then the parents could at least somehow prepare: find a maternity hospital with intensive care, find out everything about the diagnosis, contact the foundation, come to Moscow for childbirth. Now they don't have that opportunity either.
/platnie-rodi/
How much does it cost to give birth in Moscow? In Moscow, the leading expert of our foundation, neurosurgeon Dmitry Zinenko, performs more than a hundred such operations a year.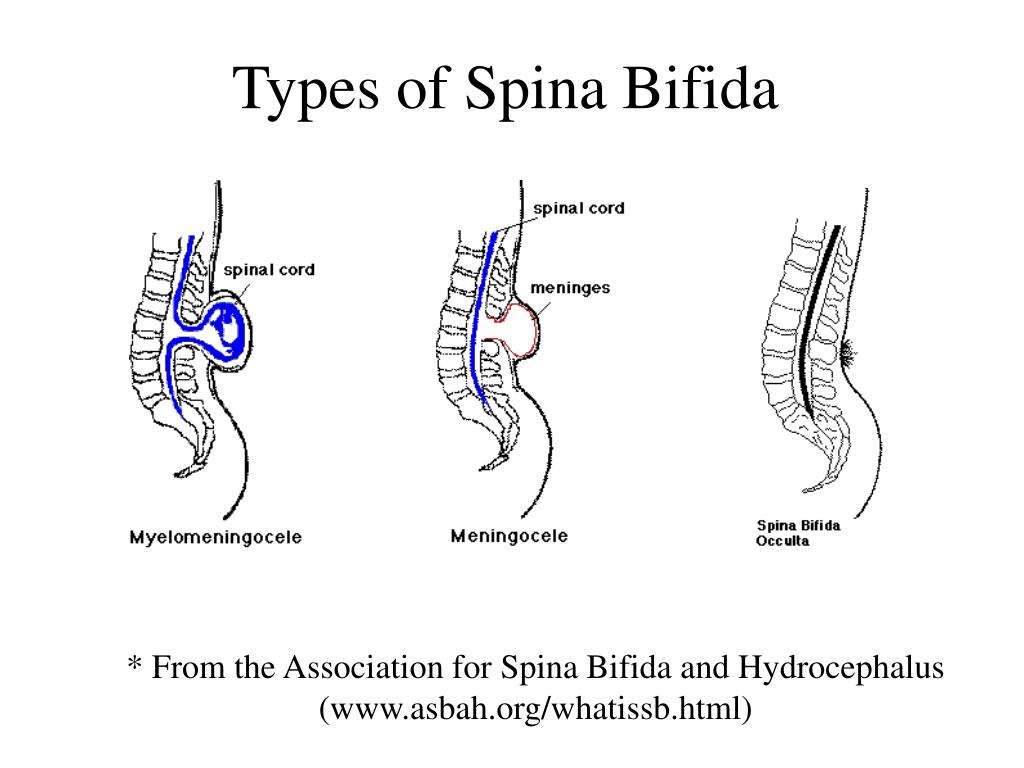
In general, surgery after birth can be done in any city, because it is conditionally called classical, but not all doctors have the necessary experience. Therefore, our foundation highly recommends mothers to contact us and come to Moscow for childbirth and postpartum surgery.
Anya was operated on after she was born. Now her condition is stableAbandon the child. Many parents are not ready for the birth of a child with spina bifida, including because of the frightening stories of doctors. Therefore, some are forced to abandon their children.
Since the foundation was established, the number of children with spina bifida in orphanages has decreased. It makes me very happy. Now there are more than 130 children in our orphanage program. Of these, only four children were born in 2017-2021. I attribute this to increased awareness of the diagnosis.
What problems do families face after the birth of a child with spina bifida
Life with a child with spina bifida is a quest.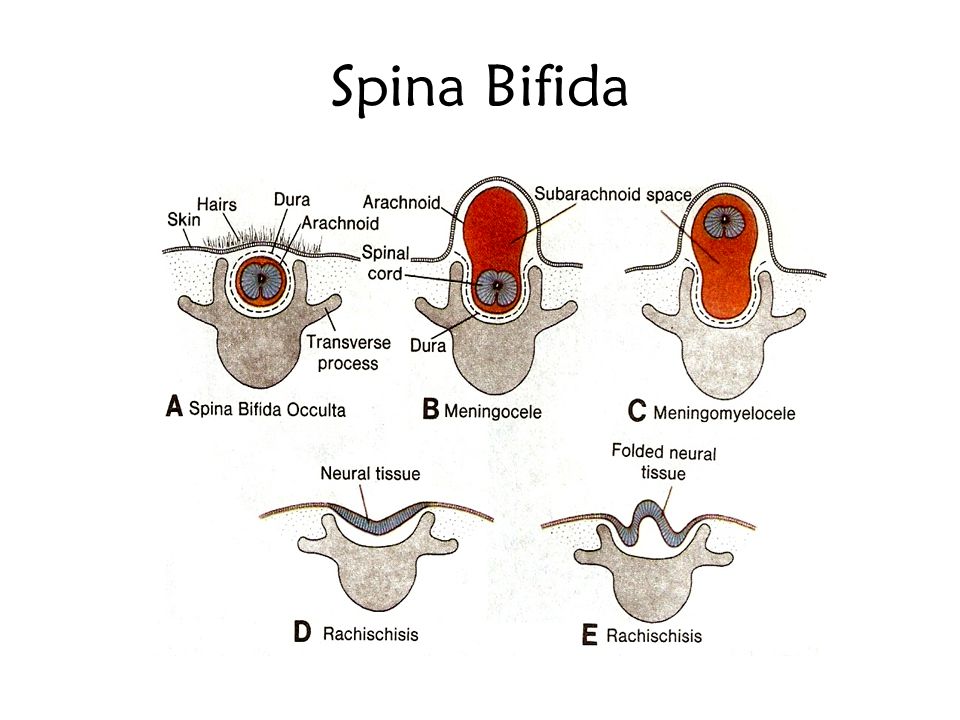 It's like a game where mice jump out of the circles and you need to hit them with a hammer so that they hide.
It's like a game where mice jump out of the circles and you need to hit them with a hammer so that they hide.
A child with spina bifida constantly has something unknown: problems with the kidneys, bedsores, osteoporosis or lack of calcium. This is a constant "game", in which you need to constantly monitor the child's condition, prevent complications and be in touch with all doctors.
Hydrocephalus. Spina bifida is often accompanied by hydrocephalus, since the paths through which the liquor can get from the skull into the spinal canal are pinched. Due to an excess of cerebrospinal fluid, squeezing of the brain occurs - this disrupts its work. Violation can be noticeable visually - a person will have a big head.
To eliminate the disease, surgeons install a special tube - a shunt - from the spina bifida to the patient. It drains excess fluid into the abdominal cavity, and thanks to this, hydrocephalus is compensated - the child does not have problems with the brain.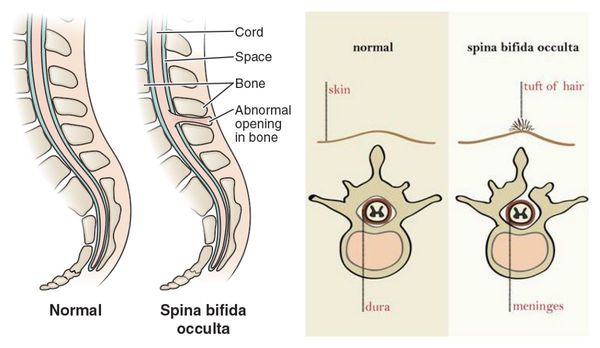 It can live for many years if you monitor the operation of the shunt: change and reinstall it in time.
It can live for many years if you monitor the operation of the shunt: change and reinstall it in time.
Unfortunately, shunts are often not of good quality, it happens that they are installed by inexperienced doctors. In 2021, two wards of the foundation died, whose bypass systems became unusable.
What to do? 17.02.20
How to insure against medical errors before surgery?
Diseases of the kidneys. In addition to hydrocephalus, children develop urinary and fecal incontinence in almost 99% of cases. Therefore, they are recommended regular catheterization. Children are given a urethral catheter - a special tube that removes stagnant urine from the bladder. The lack of timely examinations causes a high risk of kidney disease, so they must be constantly monitored. The kidneys are a life-supporting organ that must work.
Many parents often think about putting their child from dorsal bifida to his feet. They throw all their strength into it, but forget about the brain and spinal cord and about the genitourinary system. The legs are not a life-threatening or life-supporting system: a child in a wheelchair with broken legs can live to be 100 years old if their kidneys, brain, and spinal cord are functioning.
The legs are not a life-threatening or life-supporting system: a child in a wheelchair with broken legs can live to be 100 years old if their kidneys, brain, and spinal cord are functioning.
In 2021, we began to cooperate with clinics that conduct neuro-urological examinations in Yekaterinburg, Kazan and St. Petersburg. This includes a comprehensive urodynamic study, ultrasound of the bladder, cystoscopy, cystography, consultations of a neurourologist. Now we can examine 100 children a year in these cities and prevent the risk of kidney inflammation, dialysis, and death from kidney failure.
Regular inspections. All children with spina bifida should undergo regular magnetic resonance imaging, MRI, and electroneuromyography, ENMG to avoid recurrent complications. An MRI can reveal how correctly the shunt works, the state of the brain and spinal cord, and whether there is fixation - tension - of the spinal cord. If there is fixation, a second operation is necessary to free the spinal cord.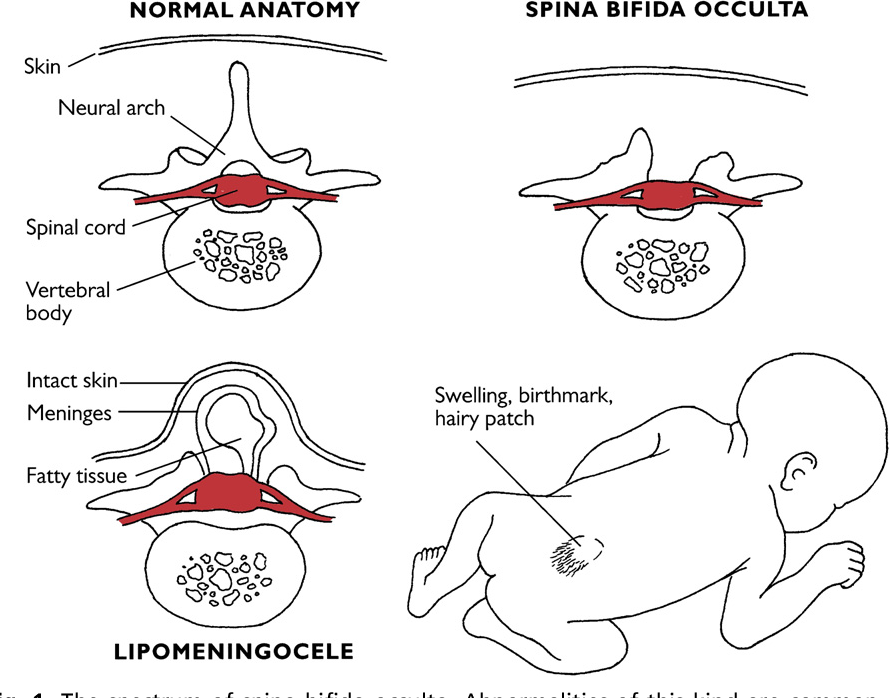 ENMG is needed to understand how the dynamics change when impulses are conducted through the nerves of the legs and pelvis. We send all wards for regular check-ups to Dr. Dmitry Zinenko.
ENMG is needed to understand how the dynamics change when impulses are conducted through the nerves of the legs and pelvis. We send all wards for regular check-ups to Dr. Dmitry Zinenko.
Also, patients with spina bifida should undergo annual examinations with a physical therapist, occupational therapist, neurourologist, neurosurgeon and orthopedist.
/list/pediatr-deti/
11 important questions to pediatrician Sergei Butriy
In Russia, there is still no single center for people with spina bifida. That is, a family cannot just go to one place and go through all the examinations at once. I have to fly to Kurgan to treat the spine, to St. Petersburg - legs, to Moscow - for hydrocephalus surgery, and so on.
For example, I had to spend a year with Matvey in Kurgan to install a metal structure in his spine: his son has a severely curved spine, and the metal structure corrects and aligns his back. Unfortunately, Matvey's design did not take root: osteomyelitis began, and it had to be removed. The curvature of the spine returned again.
The curvature of the spine returned again.
Our foundation has a dream to initiate the creation of a center where all doctors will be gathered in one place. This will make life much easier for both parents and children with spina bifida.
How our foundation helps families
The Spina Bifida Charitable Foundation has been operating for the sixth year, and now we have two main programs. In the first one, we help 1000 wards from spina bifida. Among them are pregnant women, children left without parental care, and children in families. We help 100 children with spina bifida who were taken from orphanages. We provide legal and targeted assistance to pregnant women, help with medical examinations.
In addition, we are doing a lot of outreach work, in which we share our experience. On September 1, we launched the Spina Bifida Institute online project. The first nine courses are devoted to the basics of working with children with spina bifida for early intervention specialists, occupational therapists, physical therapists, rehabilitation therapists, sports coaches, psychologists, as well as for parents of children with such a diagnosis.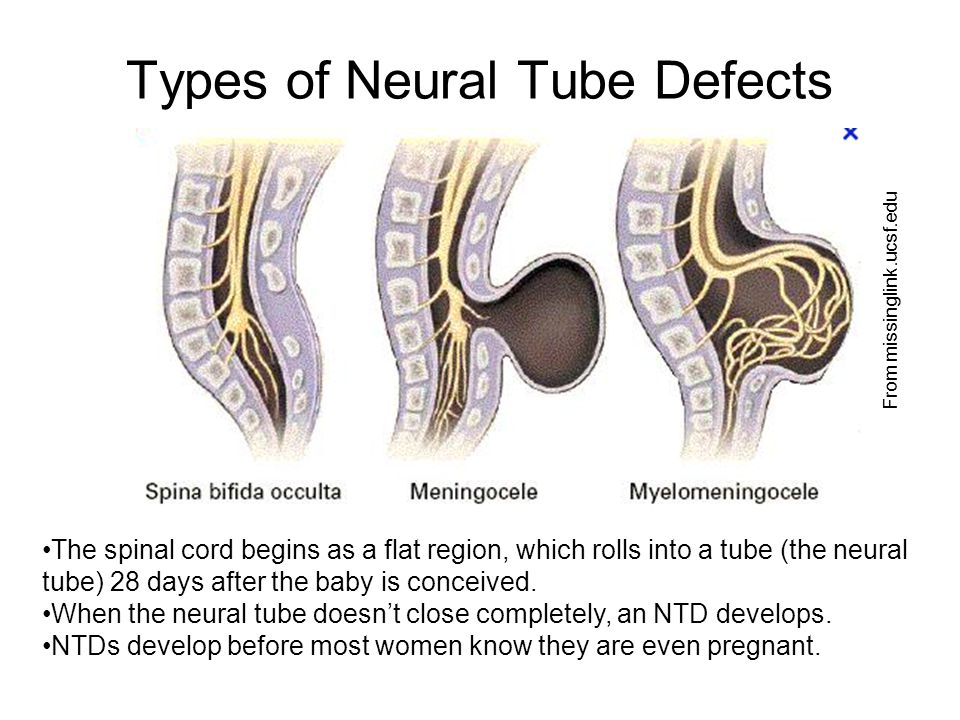 Training will start in 2022.
Training will start in 2022.
Our specialists work all over the country. If we find a child with spina bifida in some city or village, then the specialist comes to this family right at home, looks at the child and the conditions in which he lives. After that, the specialist draws up an individual plan to help the child and family for the next year.
For example, we provide legal or psychological assistance to a mother or child, help organize an accessible environment for the patient. We agree to take the child to school and install a ramp in it. Then there will be no need for external rehabilitation: the child will be able to live a quality life in his home, in his family, go to school, go to the pool and ride in a wheelchair.
/rehabcenter/
How to choose a rehab center
How to reduce the risk of spina bifida in a child
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention - CDC - conducted a study that showed that folic acid intake before pregnancy reduces the risk of neural tube defects .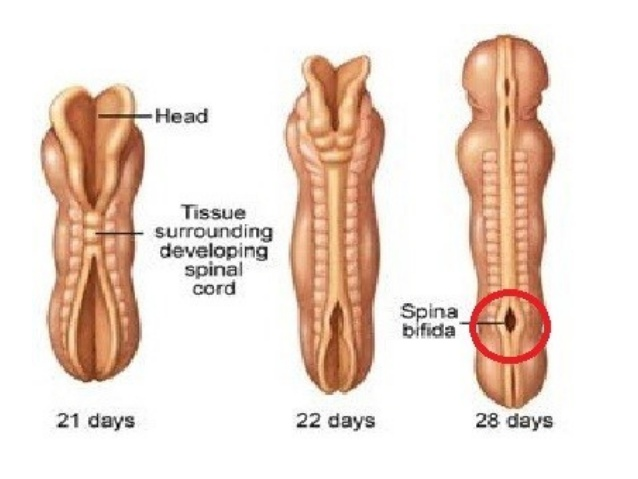 It is they that lead to spina bifida and other diseases. Folic acid is prescribed not only for the prevention of spina bifida, but also for heart disease and even autism.
It is they that lead to spina bifida and other diseases. Folic acid is prescribed not only for the prevention of spina bifida, but also for heart disease and even autism.
It often happens in Russia like this: a mother finds out about spina bifida in a child during pregnancy, comes to the doctor, and he prescribes folic acid to her. But a neural tube defect or spina bifida is formed in the first weeks of a child's life. Therefore, it is important to take folic acid at a dosage of 400 mg per day just before pregnancy, preferably from the age of 18.
Recommendations for the use of folic acid to reduce the incidence of spina bifida and other neural tube defects - CDC
If a family member is known to have spina bifida, the woman should take 10 times more folic acid. For example, my daughter needs it, because I gave birth to a son with such a disease.
To date, there are no other proven ways to prevent spina bifida.
In some countries, the program for the prevention of this disease has been brought to the state level.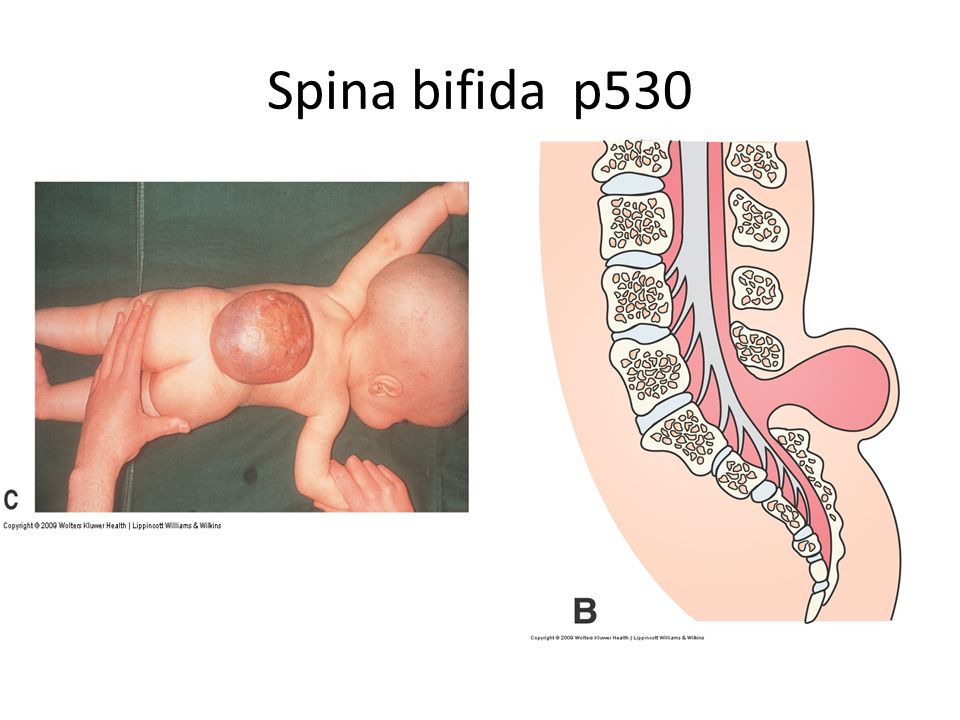 For example, in the UK and many other countries, all bread is fortified with folic acid. In Africa, corn is enriched with it as a popular food product. We hope that at some point we will be able to lobby for this program in Russia as well. We would like bread to be fortified with folic acid at the very least.
For example, in the UK and many other countries, all bread is fortified with folic acid. In Africa, corn is enriched with it as a popular food product. We hope that at some point we will be able to lobby for this program in Russia as well. We would like bread to be fortified with folic acid at the very least.
/pay-for-childbirth/
“I duplicated any tests if there were doubts”: how much does it cost to bear a child
In other countries, there have long been no such severe forms of spina bifida as in Russia. When foreign rehabilitation specialists came to our conference and saw my child, they said that they had not met children with this form for decades. I think this is due to the fact that early diagnosis of the disease is more developed there, intrauterine operations were started earlier, and there is also prevention of spina bifida.
How my son lives now
Now Matvey is nine years old, he is in the third grade. He does not feel his legs and cannot stand on them, so he moves in a wheelchair. Matvey and I often travel, he loves to swim and dreams of becoming a swimming coach for children with spina bifida.
Matvey and I often travel, he loves to swim and dreams of becoming a swimming coach for children with spina bifida.
Like me, Matvey has a motto: delegate or die.
He learned to ask others for help, so he can live completely on his own. That is, he knows how to organize the environment around him so that someone helps him if necessary. That is why I am calm for him and I am sure that at the conditional 18 years old, Matvey will be able to leave home and live on his own. The world around always responds.
My son loves the sea and wants to connect his future profession with itDuring the pandemic, our foundation went online and started a small community of people from spina bifida. This is how we met Paralympic champions, athletes, world champions in dance, tennis, and people who skydive in wheelchairs.
Among them was Nursina Galiyeva in a wheelchair from Kazan, who at the age of 17 just got on a train alone, went to Moscow, entered an institute and began to live in a hostel.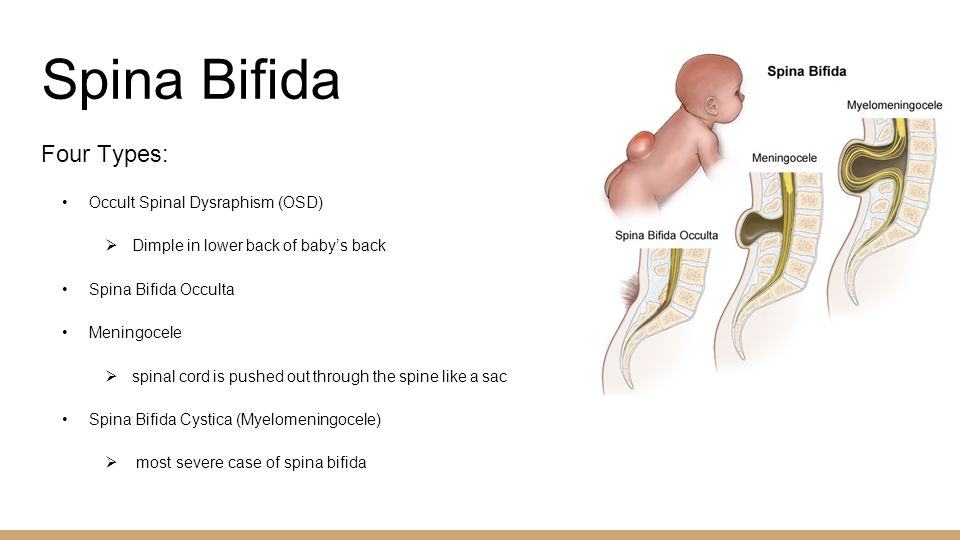 Now she is a world champion in wheelchair dancing and works for the Downside Up Charitable Foundation.
Now she is a world champion in wheelchair dancing and works for the Downside Up Charitable Foundation.
/list/make-life-brighter/
Find a friend and go on stage: 5 projects for people with disabilities
We also met Riyana, who at the age of 12 became the champion of Tatarstan in tennisI realized that absolutely everything is possible . The task of the parents of children with spina bifida is to teach the child independence so that he can cook his own food and clean up after himself. This will probably be the main contribution to his life. After all, when the parent is gone, the child should be able to live on his own. Therefore, my son spends a lot of time without me: at school, in society, with friends, traveling.
It's great that children with spina bifida are intellectually and emotionally intact and develop absolutely normally. This means that they have great potential and can do a lot for society.
They feel the world a little differently because they are in a slightly vulnerable position themselves. Therefore, they can bring a lot of good and make the world a better place, so that society becomes more tolerant, kind and open.
Therefore, they can bring a lot of good and make the world a better place, so that society becomes more tolerant, kind and open.
How to help children with spina bifida and their parents
Since 2016, the Spina Bifida Charitable Foundation has been helping people with this diagnosis so that they can live a full life. You can support the work of the foundation and make a regular donation in its favor:
- on the website of the Spina Bifida Foundation;
- in the Dobro Mail.ru service;
- on the Need Help platform;
- through the Tinkoff mobile app and the Tinkoff Cashback for Good service.
Everything you need to know about spina bifida
S pina bifida.
 What's this?
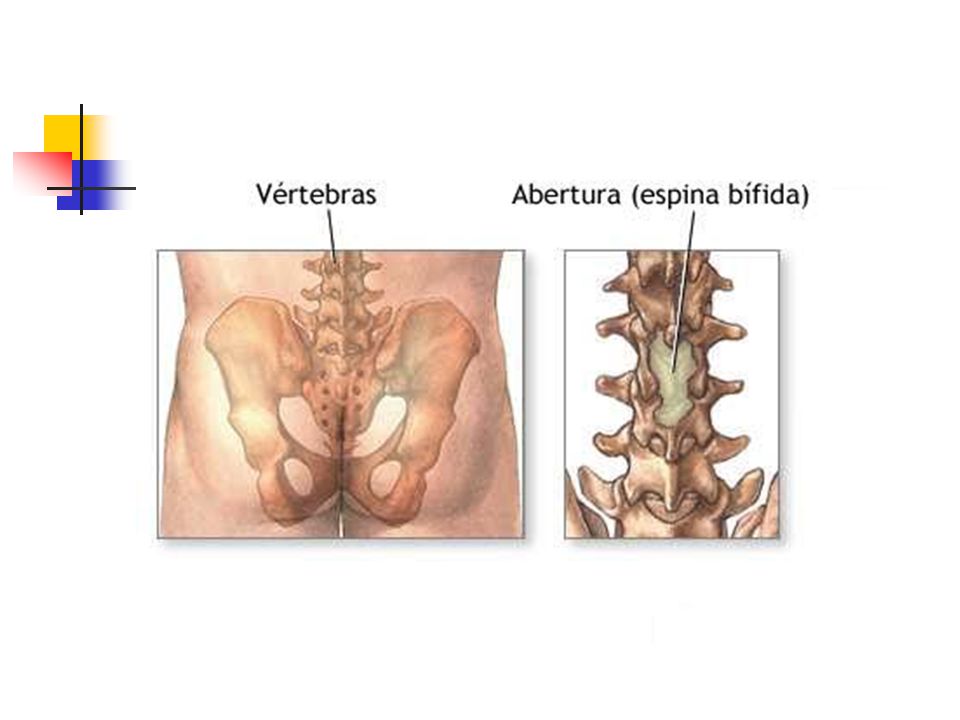
What's this? Spina bifida (spina bifida) is a malformation of the spine when the vertebrae are not fully developed. Behind they are not closed, and the spinal cord is visible through the hole formed.
The disease occurs in the prenatal period due to an anomaly in the development of the "neural tube" - the organ from which the brain and spinal cord of the unborn baby is formed.
Causes
Unknown. Risk factors - lack of folic acid in the mother's body during pregnancy, heredity, maternal diabetes, taking certain drugs (for example, valproate), as well as infections and intoxications during pregnancy.
What does it look like?
Varies, depending on the severity.
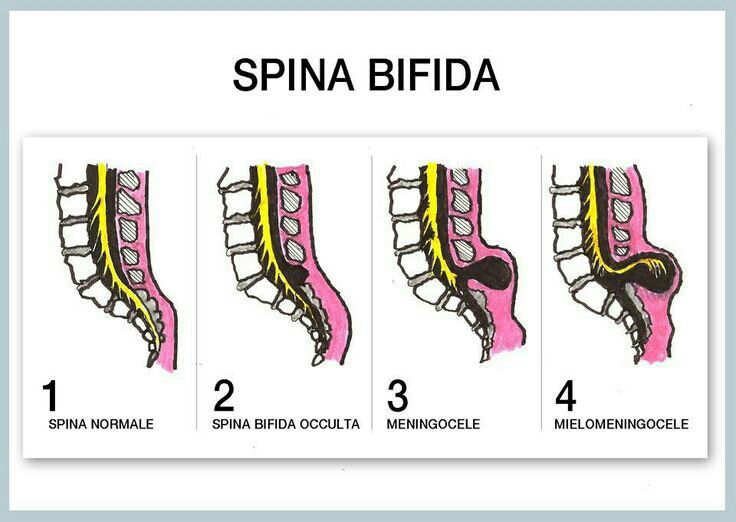
If the spinal cord does not protrude outward from the spine, this is a closed form, spina bifida occulta.
If the spinal cord protrudes into the openings of the vertebra, this is a spinal hernia and an open form, spina bifida aperta.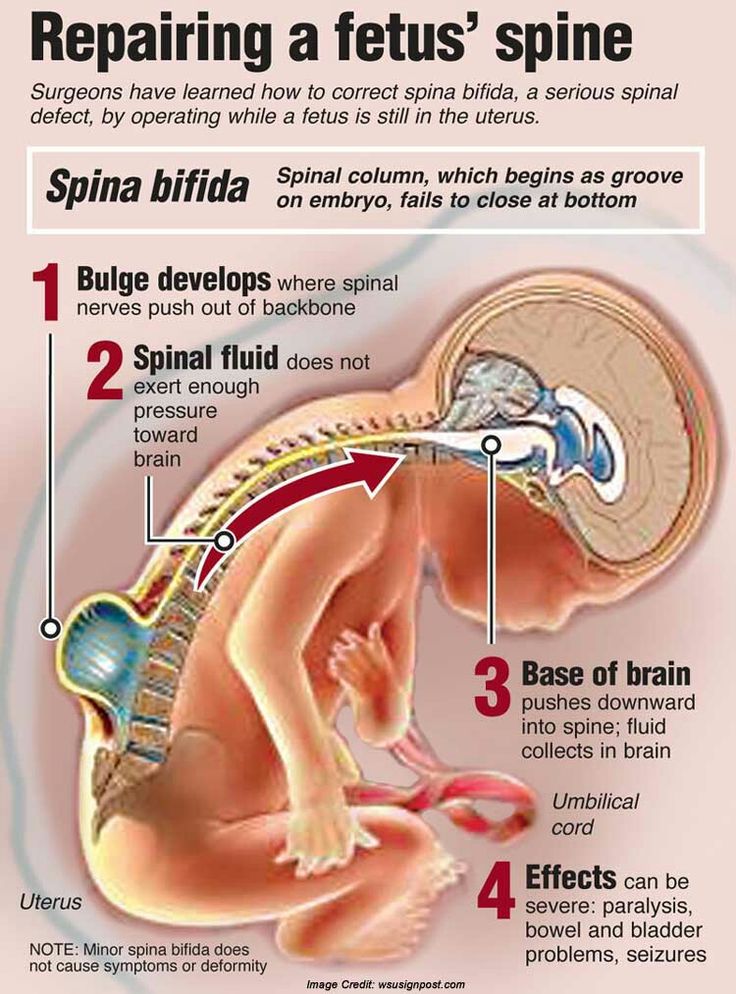
In mild cases of , the child does not have any obvious health problems, and a defect in the vertebrae is accidentally detected on an x-ray.
With a moderately severe closed form, the child develops fistulas in the spine.
In especially severe cases myelomeningocele occurs is a gap in the spinal column, into which a spinal hernia protrudes on the back - a skin sac filled with the spinal cord. In cases of extreme severity, the hernia has no sheath.
The open form may be complicated by meningocele - when the membranes of the spinal cord have come out into the external hernia, or meningoradicolocele - when the roots of the spinal cord protrude into the hernia.
In all parts of the spine below the level of the hernia, depending on the degree of damage to the spinal cord, sensitivity is either reduced or absent altogether. Often the entire body below the level of the hernia is paralyzed.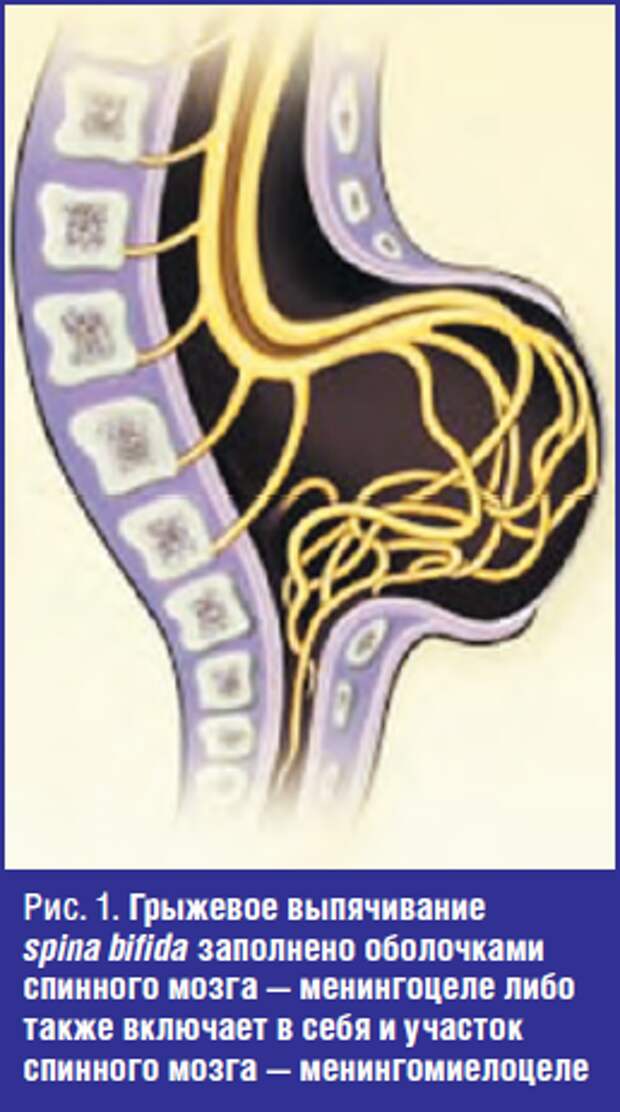
Sometimes the sacrum is underdeveloped in patients (one or more sacral vertebrae may be missing), the lower part of the body may be underdeveloped - then there are features in the structure of the legs (a special clubfoot characteristic of this diagnosis), underdevelopment of the genital organs, pathology of the structure of the urinary tract.
Since both the spinal cord and the brain are not properly formed in spina bifida, this diagnosis is often accompanied by hydrocephalus (accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain) (more than 80% of cases), other malformations of the brain and skull. Congenital anomalies and tumors around the spinal cord may also be present.
The intellect of patients is preserved, but there may be problems with impaired attention.
How common is this?
According to US statistics, one newborn in 1500. According to Russian statistics, 1-3 cases per 10,000, however, the compilers of Russian clinical guidelines admit that mild cases often go unrecognized in the first weeks of life.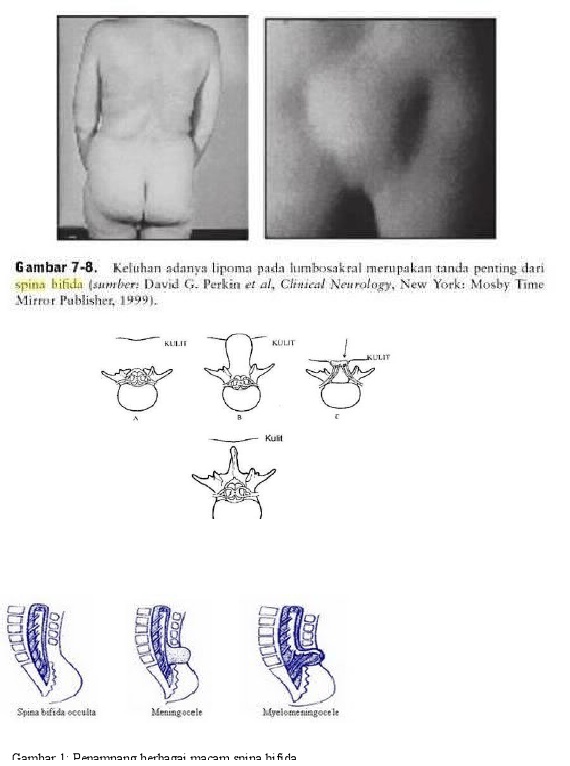
Diagnosis
Before birth
Ultrasound. Severe forms (with an open spinal fissure) can be diagnosed on ultrasound quite early, there are known cases of diagnosis at 9-10 weeks of gestation. Most diagnoses are first made at 14-16 weeks.
Ultrasound and special blood test. An increased content of α-fetoprotein in the mother's blood serum up to 24 weeks indicates the presence of a defect in the fetus with a probability of 7-10%, and in the third trimester - with a probability of more than 50%. The specific defects of the feet, legs and asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain, as well as polyhydramnios, revealed on ultrasound, indicate the diagnosis in 65% of cases.
The combination of the defects listed above on ultrasound and increased α-fetoprotein in the third trimester - in 80%.
In general, spina bifida is considered a defect that is difficult to diagnose using ultrasound.
After the birth of a child
Clarification of the present symptoms by ultrasound and MRI.
Requirements for childbirth
If the ultrasound showed a vertebral hernia in the child, delivery by caesarean section is indicated. The exception is children with a particularly severe form - a non-sheathed (without a skin bag) hernia, in which case natural childbirth is possible, but such a child is often not viable.
Manifestations of the disease, in addition to signs visible during external examination. Urological problems persist in 90% of patients.
Possible neurological symptoms ranging from sensory loss to complete paralysis of the lower extremities.
In the future, complications in the functioning of the pelvic organs, such as pyelonephritis, as well as arthrogryposis, hip dislocation (up to half of children in the first 2-3 years of life), may occur.
Some children have a curvature of the spine, more frequent fractures than normal children (children with spina bifida move less and do not get enough sun, therefore vitamin D deficiency and osteoporosis develop).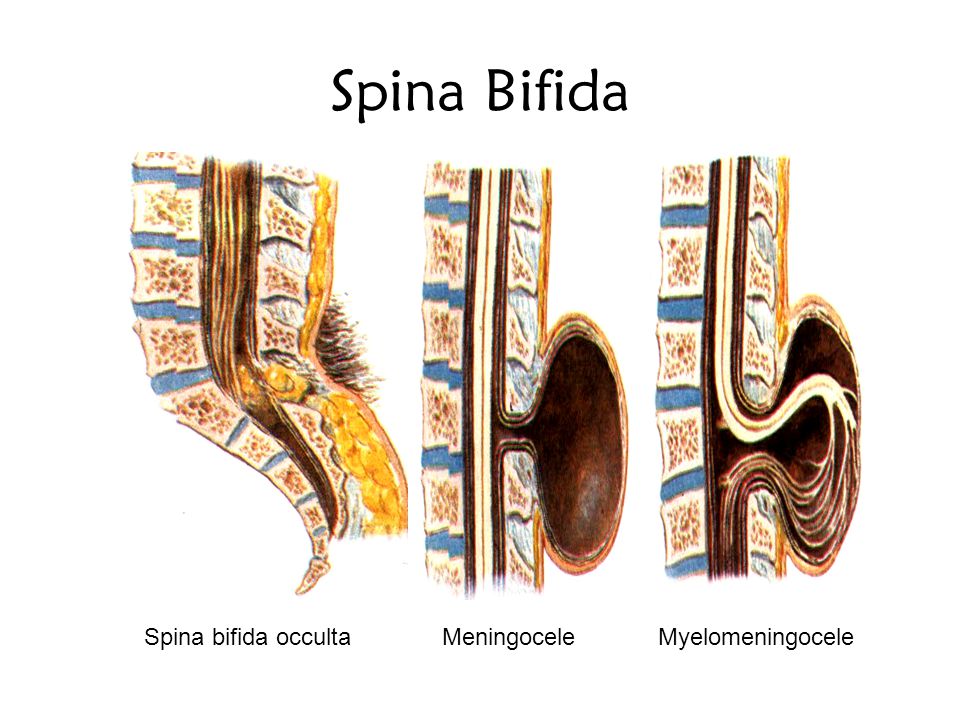
Children with spina bifida often have an increased reaction to latex - it is better not to use latex gloves when handling them.
Children with a closed form, however, often have reduced sensation in the legs. It is better not to let them walk barefoot. In the future, it is necessary to carefully monitor the quality of orthoses and shoes, since patients with this diagnosis are prone to poorly healing injuries and bedsores.
Prenatal surgery
In recent years, the world has developed a technology for intrauterine surgery of a fetus diagnosed with spina bifida. In such interventions, the doctor makes an incision in the uterus, rotates the fetus so that the defect of the spinal tube (future hernia) is accessible, and reconstructs the missing back of the vertebrae from the surrounding muscles and skin.
Thus, the protrusion of the hernia is removed, the spinal cord has the opportunity to develop closer to normal. If the operation is done before the 26th week of pregnancy, in 36% of cases the child is born healthy, in the rest - the severity of the defects decreases.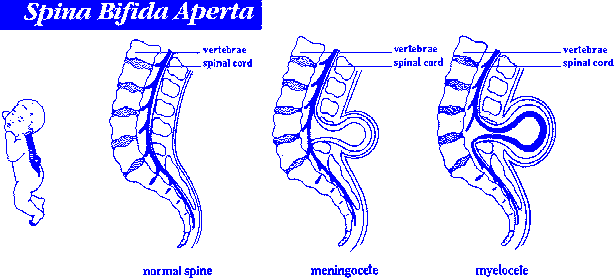
Postnatal surgery
According to national regulations, surgery for reduction of a hernia in spina bifida is indicated for up to one year in a pediatric neurosurgical department. It is good if in the operating team, in addition to the neonatologist, there is a neurosurgeon.
Complications of a hernia (rupture of the membranes, or the threat of rupture, bleeding or flow of cerebrospinal fluid from the hernia) require immediate surgery.
The child must lie on their stomach during transport.
Repeated surgical interventions in the spinal cord at an older age are indicated in the development of the "fixed spinal cord" syndrome - a situation when the spinal cord adheres to the dura mater. Normally, with age, the spine lengthens, with spina bifida, the location of the spinal cord in the spine can be hindered by structural features, wen and adhesions, which are removed during a second operation. If this defect is not corrected, pain, numbness of certain areas, muscle spasticity, enuresis and incontinence are possible.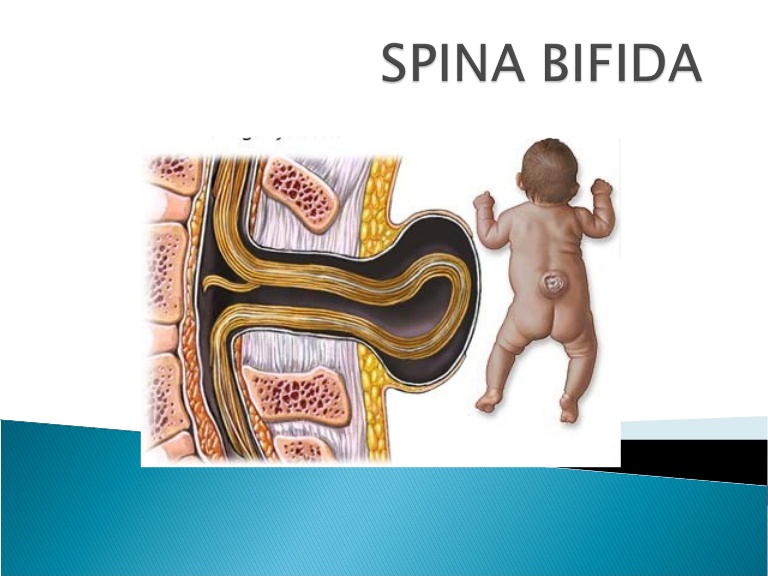
Treatment of concomitant anomalies and rehabilitation
In case of severe problems with the bladder antibiotic therapy and placement of a catheter are indicated. In the future, there is a constant monitoring and treatment of the urinary tract, the development of a catheterization strategy (selection of a catheter, reconstruction of organs for a more convenient installation of the catheter). The main tasks here are not to miss pyelonephritis and, if possible, to minimize surgical interventions.
Uncomplicated spinal hernia with paralytic clubfoot requires orthopedic treatment starting from the seventh day of life. In the future, all patients will need constant supervision of an orthopedist, and therapy from special exercises to orthotics for learning to stand and walk independently.
Since spina bifida is often accompanied by joint asymmetries and muscle weakness , walking problems may occur with age, even in those patients who walked alone during childhood.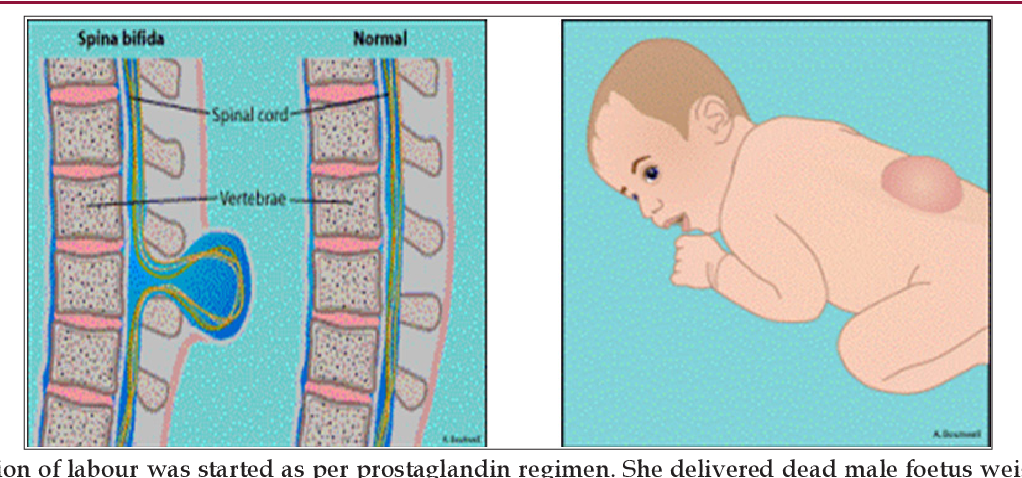
Each patient is given an individual program of treatment, rehabilitation with terms of observation, hospitalizations, drugs. With a favorable course, the program can be implemented in a day hospital without hospitalizations.
Which doctors to contact
A newborn with spina bifida from the first days of life, in addition to the observation of a neonatologist and a pediatrician, needs consultations of a neurosurgeon, neurologist, urologist, orthopedist, and also an ophthalmologist, since the concomitant hydrocephalus (if it is not obvious) increased intracranial pressure is diagnosed by examination of the fundus.
The Take a Step Foundation, under the Spina Bifida program, provides an early intervention specialist, occupational therapist and physical therapist.
Prognosis
The prognosis for spina bifida depends on the degree of spinal cord injury, the number and severity of concomitant anomalies. The prognosis worsens with lesions in the higher parts of the spine, as well as with poor child care.
Prevention
Timely (according to the recommendations of doctors) intake of folic acid in sufficient doses (prescribed by a specialist) reduces the risk of developing the disease in the fetus by 70%.
Where to go for help
Since spina bifida often requires complex intervention of several specialists, the equipment is of good quality, not everything can be done according to CHI. The program of the Take a Step Foundation is dedicated to helping children with spina bifida.
We would like to thank the Take a Step Foundation for the information provided.You can make a donation to the Spina Bifida program on the foundation's website. You can also donate
via SMS to 3443 with the message text: SPINA 100 or SPINA 100, where "100" is the amount in rubles (can be any from 10 to 15000).
For regular support, send SMS to 3443: SPINA month 100 or SPINA month 100.
Be sure to confirm your transfer in the response SMS , otherwise the donation will not reach.