What kind of discharge is normal for pregnancy
Vaginal discharge - NHS
You will always have some vaginal discharge starting a year or 2 before puberty and ending after the menopause.
How much discharge you have changes from time to time. It usually gets heavier just before your period. When you're pregnant, it's normal to have more discharge than before.
Healthy vaginal discharge is usually thin, clear or milky white, and should not smell unpleasant.
Non-urgent advice: Call your midwife if you have vaginal discharge and:
- it smells unpleasant or strange
- it is green or yellow
- you feel itchy or sore around your vagina
- you have pain when you pee
Any of these could be symptoms of a vaginal infection.
Urgent advice: Urgent
Contact your midwife or doctor immediately if you have any vaginal bleeding while you're pregnant.
Is it normal to have vaginal discharge in pregnancy?
Yes. It is normal to have more vaginal discharge in pregnancy. This helps prevent any infections travelling up from the vagina to the womb.
Towards the end of pregnancy, the amount of discharge increases further. In the last week or so of pregnancy, it may contain streaks of sticky, jelly-like pink mucus.
This is called a "show", and happens when the mucus that's been present in your cervix during pregnancy comes away.
It's a sign that the body is starting to prepare for birth. You may have a few small "shows" in the days before you go into labour.
Read more about the signs that labour has begun.
Thrush in pregnancy
Thrush is an infection that can cause unusual vaginal discharge. if you get thrush when you're pregnant, it can easily be treated - talk to your midwife or doctor.
if you get thrush when you're pregnant, it can easily be treated - talk to your midwife or doctor.
Thrush can cause:
- increased vaginal discharge which is usually white (like cottage cheese), and does not usually smell
- itching and irritation around the vagina
Always talk to your doctor, pharmacist or midwife if you think you have thrush, as there are some thrush medicines you should not use while you're pregnant.
You can help prevent thrush by wearing loose cotton underwear. You may find it helps to avoid perfumed soap or perfumed bath products.
Find out more about vaginal discharge.
Page last reviewed: 31 March 2021
Next review due: 31 March 2024
Bleeding during pregnancy: When to worry about spotting in pregnancy
A little light bleeding or spotting during pregnancy is common, especially during the first trimester. Heavier or more consistent bleeding could signal a problem with the pregnancy. Early pregnancy bleeding can happen when the fertilized egg implants, or it could be from something more serious like a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. Common causes of bleeding later in pregnancy include placental problems or preterm labor. Any bleeding is worth letting your doctor know about as soon as possible, especially if it's heavy or it doesn't stop.
Heavier or more consistent bleeding could signal a problem with the pregnancy. Early pregnancy bleeding can happen when the fertilized egg implants, or it could be from something more serious like a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. Common causes of bleeding later in pregnancy include placental problems or preterm labor. Any bleeding is worth letting your doctor know about as soon as possible, especially if it's heavy or it doesn't stop.
Is it normal to have spotting during pregnancy?
A little light bleeding or spotting during pregnancy is common, especially in early pregnancy. Up to one in four pregnant women have some light bleeding in their first trimester. But even if the bleeding seems to have stopped, call your doctor, just to make sure everything is okay.
Spotting or light bleeding in pregnancy is probably from something minor. But it could also be a sign of a serious problem, such as an ectopic pregnancy, a miscarriage, or an infection.
Your doctor may want to do some tests, which can include a physical exam, an ultrasound, and blood tests, to check how well you and your baby are doing and to rule out any complications.
If you're actively bleeding or you have severe pain and can't reach your doctor, head to the emergency room right away.
What's the difference between spotting and bleeding during pregnancy?
Spotting is very light bleeding, similar to what you may have at the very beginning or end of your period. It will look like small drops of blood on your underwear, varying in color from pink to red to brown (the color of dried blood). Pregnancy spotting is common, especially during the first three months.
Bleeding means that you need to wear a panty liner or pad to avoid soaking your underwear. And heavy bleeding will soak through one or more pads. Continued or heavy bleeding could signal a problem with your pregnancy, which is why it's important to share with your doctor right away.
Early pregnancy bleeding: What causes it?
The most common causes of light spotting or bleeding during early pregnancy include:
Implantation. Some women have spotting even before they know they're pregnant, about a week or so after they ovulate. It's called "implantation bleeding" because it happens when the fertilized egg burrows (or implants) into the blood-rich lining of the uterus, a process that starts just six days after fertilization.
It's called "implantation bleeding" because it happens when the fertilized egg burrows (or implants) into the blood-rich lining of the uterus, a process that starts just six days after fertilization.
If you have a day or two of spotting in the week before your period is due, take a home pregnancy test. If the result is negative, wait a few days or a week. If your period doesn't start when you expect it, try testing again.
Subchorionic hematoma. Also called a subchorionic hemorrhage, this kind of bleeding can happen when the outer layer of the amniotic sac (chorion) separates from the wall of the uterus. It’s usually harmless and stops on its own. Small collections of blood like this early on are typically harmless. But if the collection of blood is larger, it will take longer to reabsorb, or go away. This can raise the risk of miscarriage or preterm labor, so your doctor may want to check on it regularly with ultrasound.
Miscarriage. Spotting or bleeding in the first trimester, especially if you also have abdominal pain or cramping, can be an early sign of miscarriage. But it isn't necessarily a sign, and actually, about half of women who miscarry don't have any bleeding prior to diagnosis. Other signs of a possible miscarriage are discharge of liquid or tissue from your vagina, and no longer feeling any pregnancy symptoms (like morning sickness). If feeling better is your only symptom, however, try not to worry! Many pregnant women don't experience nausea in the first trimester and have very healthy pregnancies.
Spotting or bleeding in the first trimester, especially if you also have abdominal pain or cramping, can be an early sign of miscarriage. But it isn't necessarily a sign, and actually, about half of women who miscarry don't have any bleeding prior to diagnosis. Other signs of a possible miscarriage are discharge of liquid or tissue from your vagina, and no longer feeling any pregnancy symptoms (like morning sickness). If feeling better is your only symptom, however, try not to worry! Many pregnant women don't experience nausea in the first trimester and have very healthy pregnancies.
Ectopic pregnancy. Early pregnancy bleeding also can warn of an ectopic pregnancy – when the embryo implants outside the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes. Sometimes bleeding is the only sign, but other common symptoms include pain in the belly, pelvis, or shoulder. An ectopic pregnancy can be life-threatening, so let your doctor know right away if you have bleeding or moderate to severe pain in your first trimester.
Molar pregnancy. This rare complication happens when the placenta doesn't develop properly, and it can't sustain the embryo. A molar pregnancy can be serious, and it needs prompt treatment.
Infection. An infection can irritate or inflame your cervix and make it more likely to bleed, especially after you have sex. These are some of the infections that can cause bleeding:
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Herpes
- Yeast infection
- Trichomoniasis
Because certain infections can cause pregnancy complications, your doctor might prescribe antibiotics or another treatment.
You might also notice some spotting or light bleeding after sexual intercourse or a pelvic exam. More blood flows to your cervix during pregnancy, so it's not unusual. A cervical polyp (a noncancerous growth on the cervix) can also cause spotting or bleeding after sex or an exam.
What causes second or third trimester bleeding?
Bleeding later in pregnancy might also be nothing to worry about. Light bleeding could be a sign of harmless inflammation, a cervical polyp, or other changes in your cervix. And a few days before your delivery date, bloody discharge called "show" is a sign that your cervix is getting ready for labor.
Light bleeding could be a sign of harmless inflammation, a cervical polyp, or other changes in your cervix. And a few days before your delivery date, bloody discharge called "show" is a sign that your cervix is getting ready for labor.
Heavy bleeding late in your pregnancy is a more worrisome sign. It's worth making a call to your doctor right away.
Here are some common causes of bleeding in your second and third trimesters:
Placental problems. Bleeding or spotting after the first trimester can be a sign of a problem with the placenta, such as:
- Placenta previa, when the placenta partially or fully covers the cervix; usually this is diagnosed at your mid-pregnancy ultrasound or anatomy scan. Your placental location will continue to be monitored as pregnancy progresses, and your obstetrician will recommend that you abstain from intercourse as long as the placenta is over or near the cervix.
- Placenta accreta, when the placenta becomes abnormally embedded in the uterine wall.
 Although this is a rare complication, the risk slowly increases with each cesarean delivery.
Although this is a rare complication, the risk slowly increases with each cesarean delivery. - Placental abruption, when the placenta entirely or partially separates from the wall of the uterus. This is more likely to occur as a result of trauma (car accident, domestic violence), uncontrolled hypertension, or labor.
Late miscarriage. Most miscarriages happen in the first trimester, but bleeding between 13 weeks and the middle of your pregnancy can be a sign of late miscarriage.
Preterm labor. Bleeding is one sign of preterm labor (labor that starts before 37 weeks). Other symptoms are:
- Abdominal pain, cramps, or contractions
- Low backache
- Changes in vaginal discharge
- Pressure in your pelvis or lower abdomen
How much bleeding during pregnancy is normal?
Some light bleeding is normal, especially early in your pregnancy when the fertilized egg implants. But really, bleeding can happen at any point in your pregnancy, and for many different reasons. And because some causes are more serious than others, it's always a good idea to let your doctor know about it.
And because some causes are more serious than others, it's always a good idea to let your doctor know about it.
Heavier bleeding that soaks through a pad, or bleeding that doesn't go away is more concerning. It could signal a serious problem with your pregnancy that needs immediate medical attention. Calling your doctor right away or going to an emergency room could help you head off a problem and protect both your health and your baby's.
When should I call my doctor about spotting or bleeding during pregnancy?
Any type or amount of bleeding in pregnancy is worth calling your doctor about, to make sure that nothing is wrong. This is important, even if your last ultrasound showed that your baby is healthy and growing according to schedule.
Heavy or consistent bleeding is a reason to call immediately. Your doctor can check for any problems, and either reassure you that you're ok, or treat the problem.
When you call your doctor, let them know how long you've been bleeding and how much you've bled. Also tell them about other symptoms, like cramps, that you've had along with the bleeding. Also, be sure to be honest with them about recent sexual activity and medical history when you call.
Also tell them about other symptoms, like cramps, that you've had along with the bleeding. Also, be sure to be honest with them about recent sexual activity and medical history when you call.
Lastly, whenever the bleeding occurs, if your blood type is RH-negative, your doctor will want to make sure you get a Rhogam shot to protect future pregnancies. Call your doctor if you are RH-negative and have bleeding anytime in pregnancy. If you are RH-positive, this isn't something you have to worry about.
Learn more:
- Pregnancy symptoms you should never ignore
- Vaginal discharge during pregnancy
- Rectal bleeding during pregnancy
advertisement | page continues below
What is it? Normal and abnormal discharge during pregnancy
Today we will talk with Elena Yurievna Romanova, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the Expert Center for Pregnancy Management at the Mother and Child Clinic, about what discharges during pregnancy should be feared and what discharges from the genital tract are regarded as normal.
Increased vaginal discharge during pregnancy is natural
Normal pregnancy discharge is milky white or clear mucus without a strong odor (although the smell may change from before pregnancy), this discharge does not irritate the skin and does not cause discomfort to the pregnant woman. The discharge can have a different color - from completely colorless (most often) to whitish and yellowish. The consistency of discharge at the beginning of pregnancy resembles raw chicken yolk - they are thick, jelly-like, often released in the form of clots.
With normal discharge, it is enough to use panty liners or change underwear twice a day.
Due to the activity of progesterone in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, the discharge will be scarce and viscous.
Due to the increase in estrogen activity from 13 weeks, the discharge becomes less viscous and more abundant.
By the end of the pregnancy, vaginal discharge becomes more and more abundant. Each time you need to evaluate the nature of the discharge, change the gasket. If the fluid continues to ooze, this may mean leakage of amniotic fluid and the need to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist in the emergency department of a hospital with a maternity ward. There are auxiliary tests, thanks to which, as well as obstetric ultrasound, leakage of water can be excluded.
Each time you need to evaluate the nature of the discharge, change the gasket. If the fluid continues to ooze, this may mean leakage of amniotic fluid and the need to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist in the emergency department of a hospital with a maternity ward. There are auxiliary tests, thanks to which, as well as obstetric ultrasound, leakage of water can be excluded.
Not all discharge in pregnant women is the norm.
For example, a white, thick, crumbly, odorless discharge that itchs and burns the skin and causes discomfort during intercourse is likely a sign of a yeast infection (candidiasis).
White or grayish discharge, the smell of which after sex begins to resemble the smell of fish, is the main symptom of bacterial vaginosis, vaginal dysbacteriosis.
A yellowish or greenish discharge that has a strong unpleasant odor usually occurs with nonspecific vaginitis, and a foamy discharge is a sign of trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted disease.
In all these cases, contact your doctor immediately. It should not be treated with over-the-counter drugs and folk remedies. According to some external signs, a diagnosis cannot even be made by a doctor, in addition, infections in pregnant women should be treated especially carefully and only by a professional. After proper treatment, the discharge returns to normal. There is no need to get rid of the usual discharge for pregnant women. After childbirth, they will stop naturally, and before that they are a sign of the normal course of pregnancy.
Allocations can change their nature and amount under the influence of irritants or intolerance to a particular substance, for example, when using panty liners. Such secretions are transparent and abundant, they stop when the irritant is removed.
"Thrush" is a disease caused by fungi of the genus Candida, present in small quantities in all women. During pregnancy, immunity decreases and fungi begin to actively multiply, causing inflammation, abundant white flocculent discharge with a sour smell, burning and itching in the vulva.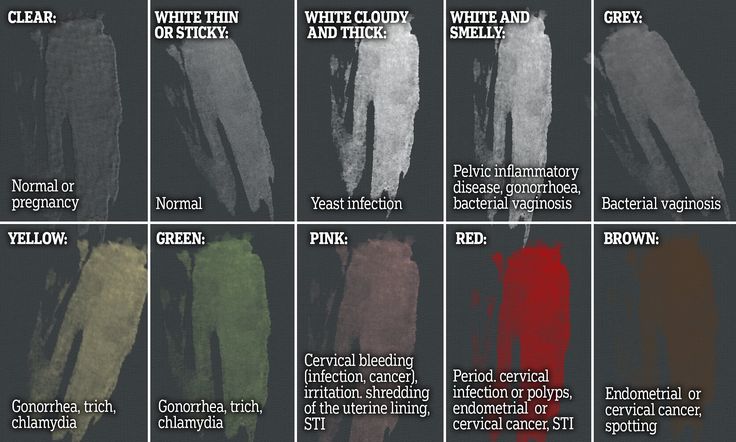 The disease can manifest itself throughout pregnancy.
The disease can manifest itself throughout pregnancy.
Bloody discharge in the first half of pregnancy usually indicates a lack of the hormone progesterone, which can lead to spontaneous miscarriage. Discharge may be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. In the treatment of the threat of abortion, the appointment of progesterone drugs, such phenomena disappear.
If bleeding from the vagina appeared during pregnancy during the second or third trimester, then this is a sign of a formidable complication, namely, placenta previa or its premature detachment. With improper attachment of the placenta in the uterine cavity and overlapping of the placental tissue with the area of the internal pharynx, they speak of placenta previa. In this case, spotting occurs in a third of pregnant women. This most often occurs between 28 and 30 weeks, when the lower segment of the uterus is most prone to stretching and thinning. The discharge is repeated, the woman does not experience any pain, so it may be too late to see a doctor for an examination. This threatens the child with a lack of nutrients and oxygen, because it is through the placenta that the fetus is nourished. For a pregnant woman, this is fraught with acute placental abruption and severe bleeding, which is always problematic to stop, especially at home.
This threatens the child with a lack of nutrients and oxygen, because it is through the placenta that the fetus is nourished. For a pregnant woman, this is fraught with acute placental abruption and severe bleeding, which is always problematic to stop, especially at home.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy should force a woman to immediately contact her obstetrician-gynecologist.
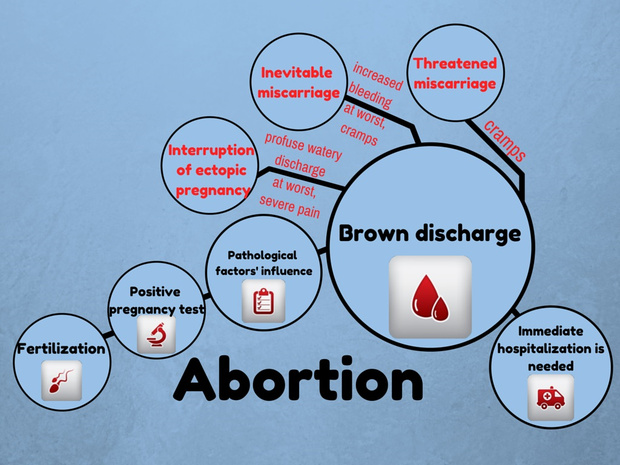
Brown discharge during pregnancy also indicates the threat of termination of pregnancy, or bleeding "erosion" (decidual polyp) of the cervix. Therefore, you should not understand these issues on your own; when brown discharge appears, it is better to consult your doctor.
Brown discharge during a delay in menstruation as a sign of an ectopic pregnancy is very dangerous. This condition requires immediate surgical care, as the growing embryo can rupture the wall of the fallopian tube at any time and cause internal bleeding. Therefore, with pain in the lower abdomen, which is accompanied by brown discharge from the genital tract and delayed menstruation, you should immediately call an ambulance.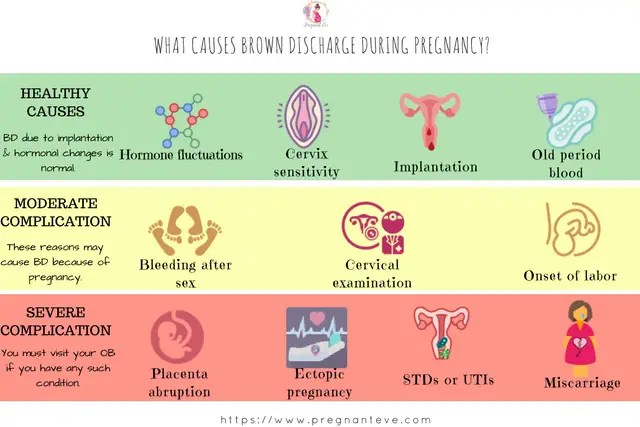
When the vagina becomes inflamed, the mucous discharge acquires a mucopurulent character, a greenish-yellow color, an unpleasant odor, burning and itching appear in the genital area. This is how chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis manifest themselves. Is it necessary to treat the infection during pregnancy, or is it better to do it after childbirth?
All sexually transmitted infections in pregnant women require treatment, as they can pass to the fetus and cause intrauterine infection (IUI). IUI is very dangerous for a child - it leads to his death or serious illness. Infection of a child during childbirth can lead to such serious complications as pneumonia, severe damage to the brain, kidneys, liver, and blood poisoning (sepsis).
Today, obstetricians and gynecologists have learned to treat any infection in pregnant women in accordance with special guidelines for the timing of pregnancy, so that it is effective and safe for mother and fetus. It is not the treatment that should be feared, but the infection itself and its consequences.
It is not the treatment that should be feared, but the infection itself and its consequences.
Medicines that are used to treat pregnant women have passed the necessary clinical trials, during which it was proved that they do not have a negative effect on the pregnant woman and the fetus, including that they do not have a teratogenic effect (do not cause deformities in the fetus).
Sometimes the discharge is mucous in nature, occurs upon contact with an irritant or allergen. It can be synthetic tight underwear, allergies to fabrics, toiletries, personal care products. If irritation and allergens are not eliminated in time, then an infection that lives on the mucous membranes of the genital organs will definitely join.
Hygiene measures are mandatory for pregnant women. Twice a day you need to take a warm shower, using special gels for pregnant women to wash the genitals. Be sure to monitor the cleanliness of the whole body and underwear - it must be changed daily. Pads (but not tampons!) can be used for discharge. The oral cavity can become the source of infection, so you need to monitor your teeth, brush them twice a day and get an examination by a dentist. Good nutrition strengthens the immunity of a pregnant woman. The diet should contain fresh vegetables and fruits, lean meats and fish, daily dairy products, vegetable oil, a variety of cereals.
Pads (but not tampons!) can be used for discharge. The oral cavity can become the source of infection, so you need to monitor your teeth, brush them twice a day and get an examination by a dentist. Good nutrition strengthens the immunity of a pregnant woman. The diet should contain fresh vegetables and fruits, lean meats and fish, daily dairy products, vegetable oil, a variety of cereals.
A mobile lifestyle, therapeutic exercises and maximum exposure to fresh air are very important. Hiking is useful even at the very end of pregnancy - they will help not only maintain immunity, but also strengthen the muscles that will be required during childbirth. Be healthy!
Pregnancy discharge | What are the discharge during pregnancy? | Blog
In the absence of menstruation, girls usually suspect that conception has occurred. However, during pregnancy, the female body may continue to secrete a secret of a different color and character. We recommend that you keep a close eye on everything that happens so as not to miss the development of adverse events. We will talk about how to recognize problem situations during pregnancy in the article.
We will talk about how to recognize problem situations during pregnancy in the article.
What secretions can occur during conception
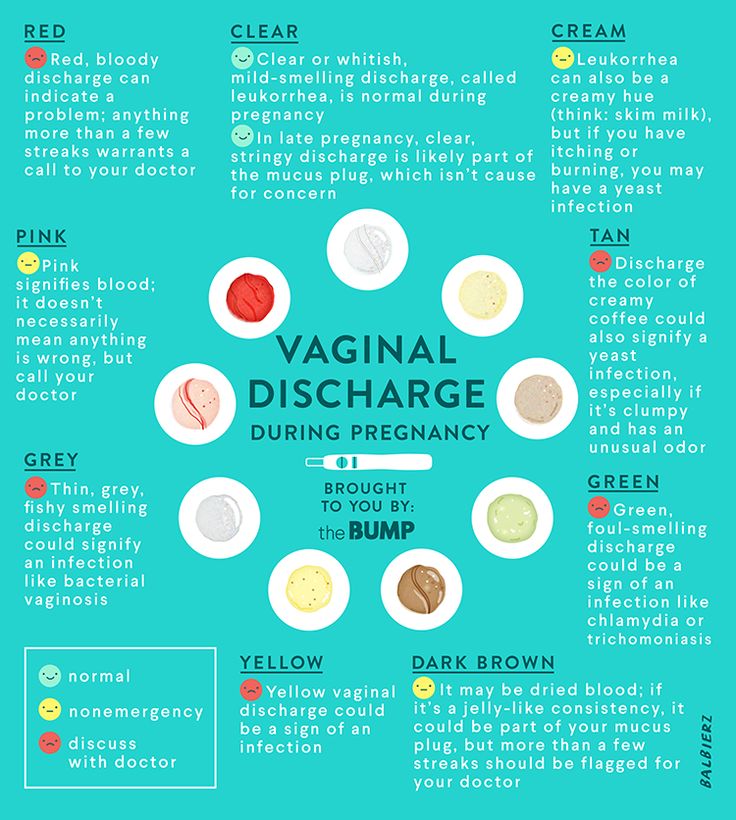
Many women note that immediately after the delay and in the later stages, the nature of the secretion changes. It can be:
- With or without scent.
- Depending on the color - transparent, white, cream, yellow, greenish, bloody.
- By consistency - thick, liquid, cheesy.
- As a symptom for assessing the state of health - threatening, safe.
During ovulation, the egg is released from the ovary, its membrane is blown away, a small amount of fluid is released - so it becomes ready for fertilization. At this time, the thick mucus that fills the cervical canal of the cervix becomes less viscous. This makes it easier for the spermatozoa to penetrate and move further into the tubes for fertilization. At this time, you may notice an abundance of clear mucous secretion.
After the fusion of the egg with the spermatozoon, movement into the uterus begins, which should end with implantation in the inner layer. During penetration, its slight detachment may occur - this causes damage to the blood vessels that abundantly penetrate the muscular layer of the uterus. You may see light brown discharge, which is common during pregnancy. The color is due to the fact that the blood has time to clot.
Sometimes the discharge is brightly colored and some women mistake it for early menses. But in this case, a short duration is characteristic, a different shade (dark or scarlet), a slight mark on the linen.
With some features of the structure of the female genital organs (for example, with a bicornuate uterus), after implantation of the embryo in one part, rejection of the endometrium may begin in the other, as is usually the case with menstruation. This rarely happens.
Characteristics of discharge in case of threatened miscarriage
Spontaneous abortion is the rejection of an embryo in the early stages after conception. If at the first signs of pregnancy, you notice spotting, there is a high probability that a miscarriage begins.
If at the first signs of pregnancy, you notice spotting, there is a high probability that a miscarriage begins.
Also, miscarriage symptoms include:
- pulling or pressing on the lower abdomen, sacrum, lower back;
- the muscles of the uterus are tense.
The woman may experience cramps. This continues all the time or intermittently. From the vagina there are scarlet or brown discharge during pregnancy, which was previously confirmed. Sometimes the period may be still small, and the first signs did not have time to appear.
After 22 weeks, this phenomenon is called preterm labor. The child in this case is still weak, the organs are not sufficiently developed, and there is little chance of survival.
The following factors increase the risk of miscarriage:
- various diseases;
- progesterone deficiency;
- nervous and physical strain;
- pathologies in the genitals;
- fetal developmental defects.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound scan. If it shows that the fetal heart rate is disturbed, the tone of the uterus is increased, its size differs from normal for this period, hospitalization will be recommended to maintain pregnancy.
What discharge during pregnancy is considered normal
This secretion does not pose a threat to health:
- transparent;
- whitish;
- yellowish;
- odor free;
- mucous;
- without itching, burning, redness of the genitals.
Clear fluid on underwear is a symptom of ovulation. During pregnancy, the activity of ongoing processes in the body increases, so the amount of secretion secreted may increase. However, a violation of the norm is the leakage of amniotic fluid. You can determine the problem with the help of special diagnostic tests that the doctor will prescribe if he has suspicions.
White color, small amount, homogeneous structure should also not cause concern. The increased volume of fluid in this case is associated with increased hormonal activity.
The increased volume of fluid in this case is associated with increased hormonal activity.
One of the variants of the norm is mucous discharge, which smells of slight sourness. If there is no pain, discomfort, there is nothing to worry about.
Yellow discharge, there are signs of pregnancy, there is no unpleasant odor - you are all right. Some women had this color before conception, only they did not pay attention. Now there are more of them, therefore more noticeable.
Sometimes a woman observes that the laundry gets wet and there is a smell of urine. This may indicate incontinence due to the constant pressure of the growing uterus. In this case, it is recommended to go to the toilet more often, change underpants twice a day.
What discharge during pregnancy is considered a sign of infection?
White discharge during pregnancy with a cheesy texture is a symptom of thrush (candidiasis). In pregnant women, it is diagnosed quite often - the reason is a change in hormonal levels. The disease is accompanied by itching, redness of the vulva, a strong sour smell. Sometimes external manifestations are not detected, then treatment is not carried out.
The disease is accompanied by itching, redness of the vulva, a strong sour smell. Sometimes external manifestations are not detected, then treatment is not carried out.
Infection is indicated by pain, pain, skin irritation, ulcers, smell of rot or fish, gray or green color, frothy discharge, increased nervousness, large inguinal lymph nodes. The reason may lie in sexually transmitted infections. This includes syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others. They are dangerous because they cause premature birth and fetal developmental defects.
What kind of discharge during pregnancy should I pay special attention to and should I consult a doctor?
The following indicates that pregnancy is at risk:
- Severe pain in the perineum, bleeding, difficulty defecation, convulsions - these may be injuries to the vaginal mucosa.
- Nausea, profuse vomiting, edema, headaches, cough, hypertension, bright red secretion are symptoms of hydatidiform mole (abnormal development of the embryo).
- A drop in blood pressure, pallor, weakness, sweating, pulling sensations, bleeding during pregnancy against the background of a lack of growth of hCG in the blood - this is how an ectopic attachment manifests itself.
- Discharge of clots, sharp pain, vomiting, diarrhea may indicate a frozen fetus.
If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
It is also necessary to contact the clinic if you have been physically abused, had rough sex, had an accident, fell, hit. The likelihood that the situation will be resolved successfully is much higher if you do not delay the visit, listen to the symptoms and take good care of your health.
Remember, despite the fact that pregnancy is a normal state of health of the female body, the diagnosis and treatment tactics are still different, due to the many restrictions on manipulations and medications during pregnancy. That is why diagnosis and treatment during pregnancy should take place only under the supervision of a doctor.