What is hcg intact
What is Intact Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, its Roles, How to Detect It, and More
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- What is human chorionic gonadotropin?
- The Roles of Intact Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
- How to Detect Intact Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
- Uses of HCG Tests
Intact human chorionic gonadotropin is a variant of human chorionic gonadotropin hormone.
This helps tissue grow and form correctly during pregnancy.
What is human chorionic gonadotropin?
Human chorionic gonadotropin comes from trophoblastic tissue. Trophoblastic tissue is a tissue that develops in the baby during the early days of pregnancy. It later forms part of the placenta. The primary function of human chorionic gonadotropin is to help support your pregnancy. It does so by stimulating the corpus luteum (the follicle that houses a maturing egg) to make the hormone progesterone which keeps your pregnancy going.
It is a form of human chorionic gonadotropin that's active biologically.
Human chorionic gonadotropin is also made by your liver, pituitary gland, and colon.
The hormone is made of two subunits:
- Alpha subunit
- Beta subunit
Human chorionic gonadotropin also exists in other different variants in your urine and blood:
- Nicked human chorionic gonadotropin
- Nicked free beta subunit
- Free beta subunit
- Beta-core fragment (found in urine)
You may use traces of human chorionic gonadotropin in the urine to find out if you are pregnant. You can measure human chorionic gonadotropin levels to help you find out whether you are carrying a viable or an ectopic pregnancy.
An ectopic pregnancy is when there's a pregnancy outside of your uterus, where a baby normally grows.
Apart from pregnancy, other issues could be causing the production of human chorionic gonadotropin. Cancers are a known cause of high human chorionic gonadotropin levels in serum (the liquid part of your blood).
The Roles of Intact Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
Intact human chorionic gonadotropin performs several roles in your body:
- It prolongs the lifespan of the corpus luteum.
- It becomes thyrotropic (stimulates the thyroid gland) when at a high concentration.
- It helps keep the level of progesterone high during the early days of pregnancy.
Its role in screening Down's syndrome: Intact human chorionic gonadotropin increases chances of detecting Down's syndrome as early as the second trimester. It has higher accuracy than free beta-human chorionic gonadotropin subunits (which can also identify the condition in developing babies).
Also, using intact human chorionic gonadotropin reduces the risk of false-positive results.
How to Detect Intact Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
The following tests can detect intact human chorionic gonadotropin:
- Serum testing. Human chorionic gonadotropin can be found in serum (the liquid part of your blood).
 This test must be carried out in a lab. With the serum test, it is possible to do both quantitative and qualitative measurements.
This test must be carried out in a lab. With the serum test, it is possible to do both quantitative and qualitative measurements. - Urine testing. Urine tests are most common with pregnancy testing. The test is quite accurate in detecting pregnancies. However, you can only do qualitative testing. Quantitative testing of human chorionic gonadotropin is impossible with a urine sample. That means that the test can only show human chorionic gonadotropin is present, not the specific levels.
It is common to get false negative or positive human chorionic gonadotropin test results.
Potential factors that may interfere with these results include:
- Drugs or medication use
- Human error while interpreting results
- Blood or protein in the urine
- Diluted urine
- Taking measurement too early in the pregnancy
Uses of HCG Tests
Human chorionic gonadotropin tests are used to:
- Detect pregnancy.
 Testing human chorionic gonadotropin levels together with a good history and physical examination is an accurate way of finding out if you are pregnant. Human chorionic gonadotropin is detectable in urine one or two days after conception. In serum, the hormone may be seen after nine to 10 days. Human chorionic gonadotropin tests are FDA-approved to test for pregnancy.
Testing human chorionic gonadotropin levels together with a good history and physical examination is an accurate way of finding out if you are pregnant. Human chorionic gonadotropin is detectable in urine one or two days after conception. In serum, the hormone may be seen after nine to 10 days. Human chorionic gonadotropin tests are FDA-approved to test for pregnancy. - Detect some cancers. Human chorionic gonadotropin assays help find out the possibility of gestational trophoblastic disease. The presence of human chorionic gonadotropin without pregnancy is a common sign of cancer. Due to this, human chorionic gonadotropin is used as a tumor marker. Some common examples of cancers that produce human chorionic gonadotropin include lung cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, gastrointestinal (GI) cancers, melanomas, and more.
- Screening for Down syndrome. Measuring human chorionic gonadotropin levels during the first and second trimesters may help detect down syndrome.
- Diagnose ectopic pregnancy. An ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed after taking a series of human chorionic gonadotropin tests and careful observation of symptoms that are common with the condition.
Human chorionic gonadotropin levels in your serum increase two times every two days of the first trimester in a normal pregnancy. If it takes longer for the human chorionic gonadotropin concentration to double, this may show you have an ectopic pregnancy. A serum human chorionic gonadotropin test may be used to find out if you have an ectopic pregnancy.
HCG blood test - quantitative
Medical Tests
Definition
A quantitative human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) test measures the specific level of HCG in the blood. HCG is a hormone produced in the body during pregnancy.
Other HCG tests include:
- HCG urine test
- HCG blood test -- qualitative
Alternative Names
Serial beta HCG; Repeat quantitative beta HCG; Human chorionic gonadotropin blood test - quantitative; Beta-HCG blood test - quantitative; Pregnancy test - blood - quantitative
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed. This is most often taken from a vein. The procedure is called a venipuncture.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the Test is Performed
HCG appears in the blood and urine of pregnant women as early as 10 days after conception. Quantitative HCG measurement helps determine the exact age of the fetus. It can also assist in the diagnosis of abnormal pregnancies, such as ectopic pregnancies, molar pregnancies, and possible miscarriages. It is also used as part of a screening test for Down syndrome.
It is also used as part of a screening test for Down syndrome.
This test is also done to diagnose abnormal conditions not related to pregnancy that can raise HCG level.
Normal Results
Results are given in milli-international units per milliliter (mUI/mL).
Normal levels are found in:
- Non-pregnant women: less than 5 mIU/mL
- Healthy men: less than 2 mIU/mL
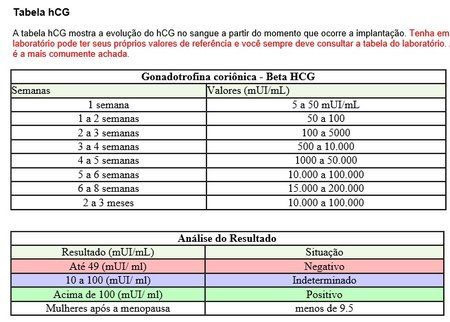
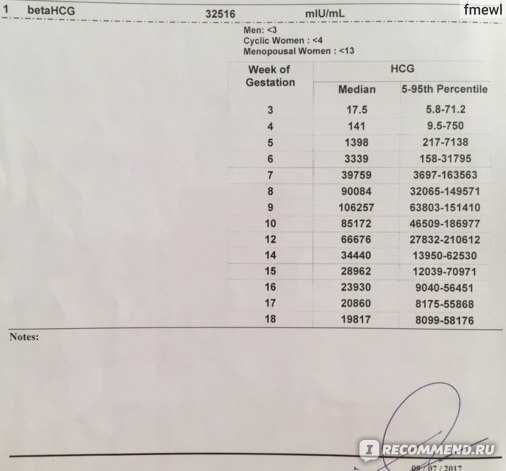
In pregnancy, HCG level rises rapidly during the first trimester and then declines slightly. The expected HCG ranges in pregnant women are based on the length of the pregnancy.
- 3 weeks: 5 - 72 mIU/mL
- 4 weeks: 10 -708 mIU/mL
- 5 weeks: 217 - 8,245 mIU/mL
- 6 weeks: 152 - 32,177 mIU/mL
- 7 weeks: 4,059 - 153,767 mIU/mL
- 8 weeks: 31,366 - 149,094 mIU/mL
- 9 weeks: 59,109 - 135,901 mIU/mL
- 10 weeks: 44,186 - 170,409 mIU/mL
- 12 weeks: 27,107 - 201,165 mIU/mL
- 14 weeks: 24,302 - 93,646 mIU/mL
- 15 weeks: 12,540 - 69,747 mIU/mL
- 16 weeks: 8,904 - 55,332 mIU/mL
- 17 weeks: 8,240 - 51,793 mIU/mL
- 18 weeks: 9,649 - 55,271 mIU/mL
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test result.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Higher than normal level may indicate:
- More than one fetus, for example, twins or triplets
- Choriocarcinoma of the uterus
- Hydatidiform mole of the uterus
- Ovarian cancer
- Testicular cancer (in men)
During pregnancy, lower than normal levels based on the gestational age may indicate:
- Fetal death
- Incomplete miscarriage
- Threatened spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
- Ectopic pregnancy
Risks
Risks of having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Blood accumulating under the skin (hematoma)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Jain S, Pincus MR, Bluth MH, McPherson RA, Bowne WB, Lee P. Diagnosis and management of cancer using serological and other body fluid markers. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 74.
Jeelani R, Bluth MH. Reproductive function and pregnancy. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 25.
University of Iowa Diagnostic Laboratories. Test directory: HCG - pregnancy, serum, quantitative. www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/path_handbook/rhandbook/test1549.html. Updated December 14, 2017. Accessed February 18, 2019.
Yarbrough ML, Stout M, Gronowski AM. Pregnancy and its disorders. In: Rifai N, ed. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. 6th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2018:chap 69.
St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2018:chap 69.
Review Date: 09/25/2018
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright ©2019 A.D.A.M., Inc., as modified by University of California San Francisco. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
Information developed by A.D.A.M., Inc. regarding tests and test results may not directly correspond with information provided by UCSF Health. Please discuss with your doctor any questions or concerns you may have.
hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin, indications for the appointment, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
I confirm More
- INVITRO
- Library
- Laboratory...
- HCG, Chorionic...
Miscarriage
Pregnancy
1440 July 29
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0025 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0025 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable, the information below is for reference only.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, β-hCG, beta-hCG, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin): indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators. nine0031
Chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone produced by the outer shell of the embryo, and is normally determined in the blood and urine of a woman only when pregnancy occurs.
Chorionic gonadotropin consists of two subunits - alpha and beta. The beta subunit (β-hCG) used for the immunometric determination of the hormone is unique. To monitor the course of pregnancy, the determination of the beta subunit of hCG is used. The level of beta-hCG in the blood as early as 6-8 days after conception makes it possible to diagnose pregnancy (the concentration of β-hCG in the urine reaches the diagnostic level 1-2 days later than in the blood serum). nine0003
The beta subunit (β-hCG) used for the immunometric determination of the hormone is unique. To monitor the course of pregnancy, the determination of the beta subunit of hCG is used. The level of beta-hCG in the blood as early as 6-8 days after conception makes it possible to diagnose pregnancy (the concentration of β-hCG in the urine reaches the diagnostic level 1-2 days later than in the blood serum). nine0003
HCG has a multifaceted effect on the body of a pregnant woman: it affects the development of the embryo and fetus, stimulates the synthesis of estrogens and androgens by ovarian cells, promotes the functional activity of the chorion and placenta, and ensures the successful course of pregnancy.
The introduction of hCG into the body of non-pregnant women stimulates ovulation and the synthesis of sex hormones necessary for conception. In men, this hormone enhances the formation of seminal fluid, activates the production of gonadosteroids. nine0003
nine0003
In early pregnancy and up to the 2nd trimester, β-hCG supports the production of hormones necessary to maintain pregnancy, and in male fetuses it stimulates cells responsible for the formation and development of the male reproductive system.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, beta-hCG, b-hCG, Human Chorionic)
Synonyms: Beta-hCG general. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin; hCG; Pregnancy Quantitative hCG; Beta hCG; Total beta hCG. Brief description of the analyte Human chorionic gonadotropin ...
Up to 1 business day
Available with home visit
RUB 685
In garbage
Indications for determining the level of hCG in women
- Absence of menstruation (amenorrhea).

- Exclusion/confirmation of pregnancy, including ectopic (ectopic). nine0006
- Diagnosis of the state of the fetus at different stages of pregnancy.
- Assessment of the state of the placenta at different stages of pregnancy.
- Dynamic monitoring of fetal development during pregnancy, including in the diagnosis of malformations.
- Suspicion of the presence of neoplastic diseases of the reproductive system, such as hydatidiform mole (a rare pathology of the fetal egg, in which instead of developing the embryo, chorionic villi grow), chorionepithelioma (a malignant tumor that develops from the epithelium of the villi of the fetal egg). nine0006
- Performing artificial termination of pregnancy.
Indications for determining the level of hCG in men:
The presence of suspicion of tumors of the testicles.
Deadline for this test is 1 working day, excluding the day of taking the biomaterial.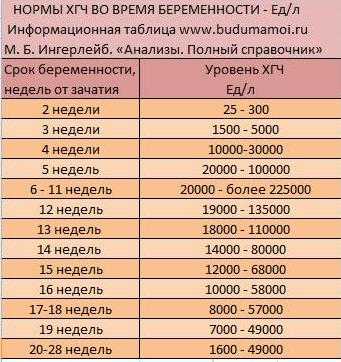
Rules for preparing for a blood test to determine the level of hCG
non-specific: it is enough to refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol on the eve of the procedure, limit stress and intense physical activity for a week; blood donation is carried out on an empty stomach. nine0003
The determination of hCG in the blood is possible already on the 6-8th day after conception. The use of urinary test systems (rapid pregnancy tests) will be informative starting from the 7th day after the fertilization of the egg. To confirm the result, it is recommended to re-determine the level of the hormone a few days after the first analysis.
You can take a blood test for hCG (thyroid stimulating hormone, thyrotropin, Thyroid StimulatingHormone, TSH) at the nearest INVITRO medical office. The list of offices where biomaterial is accepted for laboratory testing is presented in the "Addresses" section. nine0003
Reasons leading to high levels of β-hCG
- Multiple pregnancy.
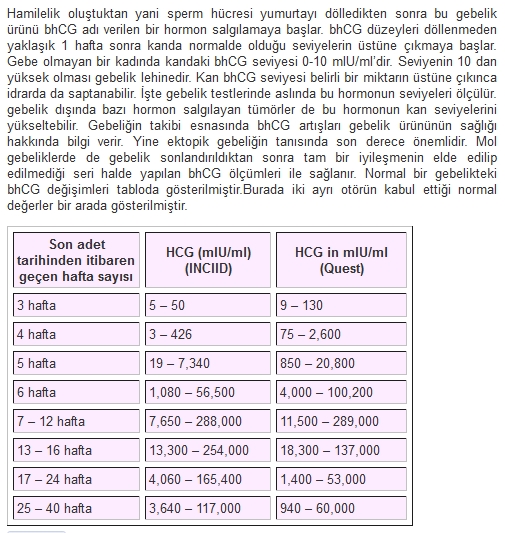
- Incorrect timing of pregnancy.
- Pathological pregnancy: the appearance of edema, increased blood pressure, loss of protein in the urine (preeclampsia), convulsions (eclampsia), toxicosis.
- The presence of a pregnant woman with chronic diseases (for example, diabetes mellitus). nine0006
- Multiple fetal malformations (in such a situation, the determination of the level of β-hCG is used together with other indicators, the so-called "triple test". This study is used as a screening, and not for diagnosis.).
Reasons for fixing a decrease in the level of β-hCG
- Incorrectly established terms of pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Frozen pregnancy. nine0006
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Fetal or placental disorders (including placental insufficiency).
- Intrauterine fetal death (in this case, it is informative to determine the level of the hormone in the first and second trimesters).
During abortions, the level of β-hCG is also monitored, the dynamics of growth / fall of which can be used to judge the completeness of the manipulation.
Determining the level of hCG, in addition to establishing the fact of pregnancy in the early stages, is part of the screening examination of pregnant women in the first trimester, along with ultrasound. nine0003
1st trimester prenatal screening for trisomies, PRISCA-1 (1st trimester biochemical screening - 1st trimester “double test”, risk calculation using PRISCA software)
Synonyms: Prenatal Screening Markers for Down Syndrome; PRISCA-1. Brief description of the study "Prenatal screening for trisomies of the 1st trimester of pregnancy, PRISCA-1)" Test run...
Up to 1 business day
Available with home visit
2 040 RUB
In garbage
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
Examination necessary to monitor the growth and development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy.
RUB 2,790 Sign up nine0003
In gynecological practice, human chorionic gonadotropin is used to treat infertility, stimulate ovulation, and synthesize sex steroids. In urology, it is used in the treatment of cryptorchidism (undescended testicles) and infertility associated with impaired spermatogenesis.
Quantitatively, β-hCG is determined in the blood, for a qualitative determination, special test systems (pregnancy tests) are used, and in this case, urine serves as a biomaterial.
Quantitative determination of the level of hCG allows you to monitor the course of pregnancy in dynamics. To do this, obstetrician-gynecologists have developed tables for increasing the level of hCG, depending on the duration of pregnancy in weeks. The sensitivity of the determination is in the range of 1.2-1125000 mU/ml. nine0025
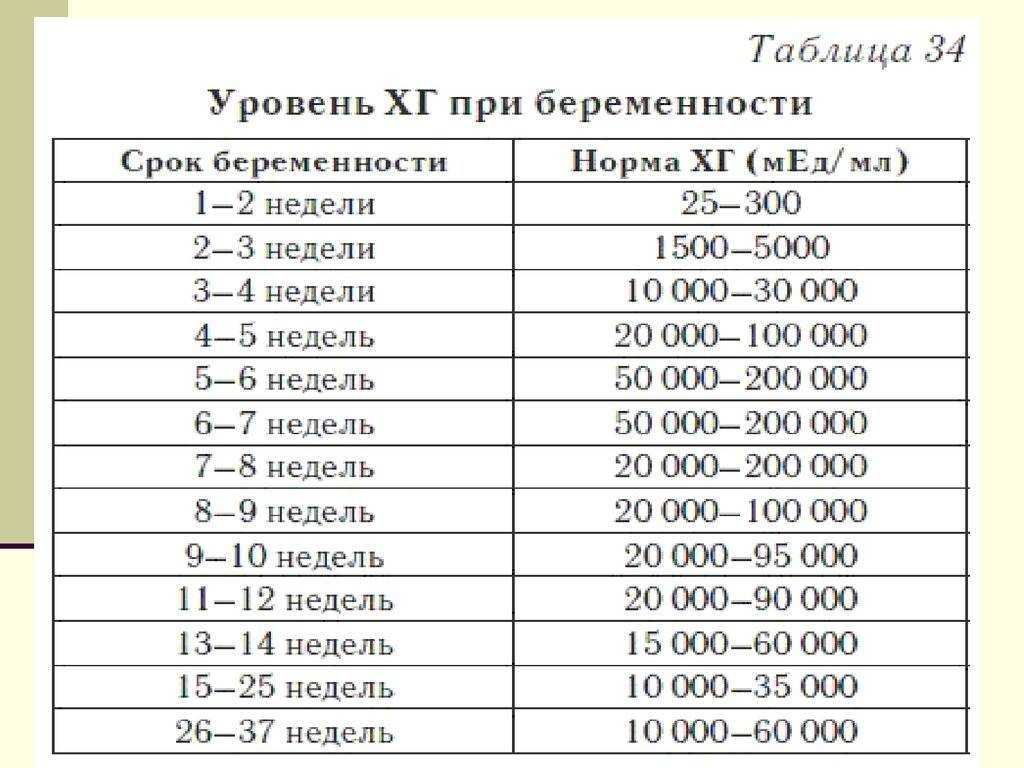
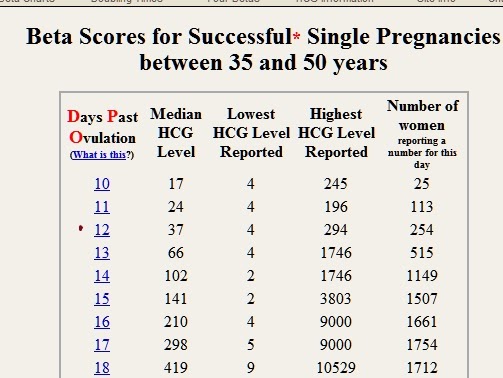
Reference values of hCG levels in dynamics by gestational age
| Pregnancy (weeks from conception) | HCG level (mU / ml) |
| 2 | 25–300 |
| 3 | 1500–5000 | nine0195
| 4 | 10000–30000 |
| five | 20000–100000 |
| 6–11 | 20000–>225000 |
| 12 | 19000–135000 |
| 13 | 18000–110000 | nine0195
| fourteen | 14000–80000 |
| fifteen | 12000–68000 |
| 16 | 10000–58000 |
| 17–18 | 8000–57000 |
| nineteen | 7000–49000 | nine0195
| 20–28 | 1600–49000 |
| Men and non-pregnant women | 0–<5 mU/ml |
Values ranging from 5 to 25 mU / ml do not allow unambiguous confirmation or denial of pregnancy, therefore, a second study is required after two days.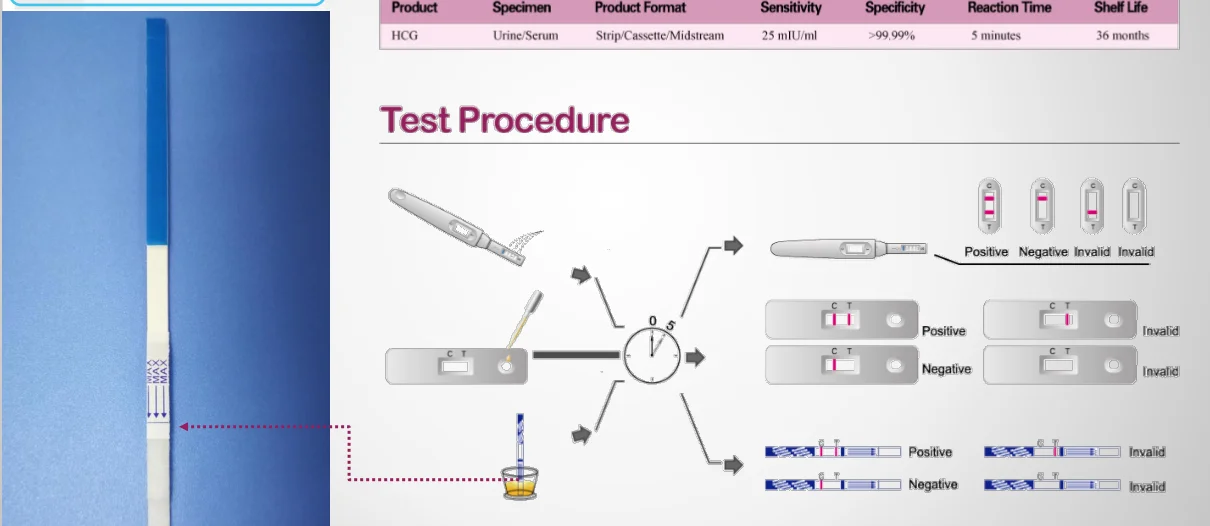
Since the hormone is produced by the placenta, during normal pregnancy, with placental pathology (for example, with fetoplacental insufficiency - a violation of the development of the fetus and placenta), with multiple pregnancies, the values of β-hCG will differ. With a normal pregnancy until the fifth week, the level of the hormone rises exponentially: every two days its concentration doubles, reaching a peak by the 11th week of gestation. Accordingly, in a multiple pregnancy, the level of β-hCG will be even higher than in a single pregnancy. nine0003
If the indicator deviates from the norm, additional ultrasound of the pelvic organs (uterus, appendages) is required.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (uterus, appendages)
Ultrasound scanning of the organs of the female reproductive system to assess the shape and size, as well as exclude pathology.
RUB 2,390 Sign up
However, with a normal hCG value, additional examinations may also be needed:
- Ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy (required to confirm pregnancy, specify the term).

Ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy
Examination to confirm pregnancy and determine the place of attachment of the ovum (to exclude ectopic pregnancy).
RUB 2,290 Sign up
- Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days) - to assess the characteristics and confirm the normal development of the fetus.
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
Examination necessary to monitor the growth and development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy.
RUB 2,790 Sign up nine0003
- Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of multiple pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days) - to confirm the presence of several fetuses, determine their characteristics; It is necessary for planning the subsequent actions of the doctor and the management of pregnancy.

Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of multiple pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
A study that allows you to assess the growth and development of fetuses, their position in the uterus, and make a plan for further pregnancy management. nine0003
RUB 3,840 Sign up
- Fetal ultrasound according to indications (before the 20th week) - performed in case of suspected ectopic pregnancy.
Fetal ultrasound according to indications (before the 20th week)
Additional ultrasound, which is prescribed in the presence of concomitant pathologies to monitor the condition of the fetus.
RUB 2,540 Sign up nine0003
- Lab tests to be performed in the first trimester are collected in the Pregnancy: 1st trimester (1-13 weeks) profile.
For professional assistance in interpreting the results, contact
obstetrician-gynecologist
.
Sources:
- www.invitro.ru
- Clinical guidelines "Ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians-Gynecologists, Association of Obstetric Anesthesiologists-Resuscitators. – 2021.
- Clinical guidelines "Premature birth". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians-Gynecologists, Association of Obstetric Anesthesiologists-Resuscitators. – 2020.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0025 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
Recommendations
-
PSA (prostate specific antigen) test
7218 may 13 nine0003
-
Human papillomavirus
11413 04 May
-
Alkaline phosphatase
3243 16 April
Similar articles
ECO
Hypogonadism
Menopause
Climax
nine0020 Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH, AMH, anti-Mullerian hormone) Anti-Mullerian hormone: indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
More
ECO
Thrombophilia
nine0002 StrokeObesity
COVID-19
Nephrotic syndrome
Pregnancy
Thrombosis propensity in pregnancy - minimum panel
Tendency to thrombosis during pregnancy: indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and normal indicators.
More
ECO
Thrombophilia
Pregnancy
nine0020 Thrombosis: extended panel 114GPThrombosis, extended panel: indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for an analysis, interpretation of results and norm indicators.
More
Hypogonadism
ECO
nine0002 MenopauseClimax
Estradiol
Estradiol: indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
More
Malabsorption syndrome
nine0002 PregnancyVegetarianism
Celiac disease
Crohn's disease
Osteoporosis
nine0002 Tuberculosis25-OH vitamin D
25-OH vitamin D: indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
More
Nothing found
Try changing your query or select a doctor or service from the list.
Doctor not found
Try changing your query or select doctor from list
Medical office not found
Try changing your query or select medical office from the list
Therapist Traumatologist-orthopedist Endocrinologist Urologist Gynecologist Ultrasound doctor Cardiologist Pediatrician
Nothing found
Please try editing your query
Thank you!
You have successfully made an appointment
Detailed information has been sent to your e-mail
Subscribe to our newsletters
Enter e-mail
I consent to processing of personal data nine0003
Subscribe
what shows the norm during pregnancy, how and when to take, decoding
June 2, 2020
608232
0
share
Contents
What is HCG?
The role of the hormone in the diagnosis of pregnancy
When should I donate blood for hCG?
How to prepare for the analysis?
HCG test interpretation
How accurate is the hCG test?
An hCG blood test is one of the most important tools for monitoring a developing pregnancy.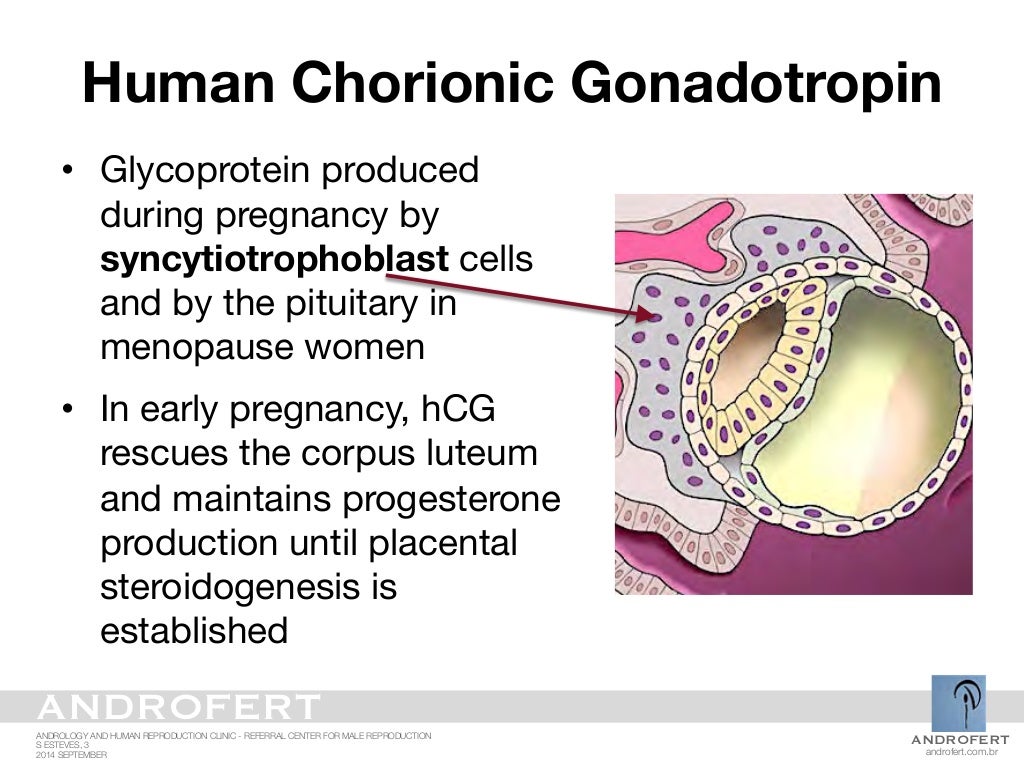
What is HCG?
An hCG blood test is a reliable way to determine pregnancy in the early stages. HCG is a protein consisting of two units. Alpha particles of the hormone are similar to biologically active substances secreted by the pituitary gland. Beta particles are unique. The mass of the CG molecule is approximately 46 kDa. During pregnancy, glycoprotein is synthesized in the placenta. The biological properties of CG are in many ways similar to the properties of other hormones: luteinizing and follicle-stimulating. In some malignant diseases, hCG begins to produce tumor cells. In a non-pregnant woman and a healthy man, the hormone is practically absent in blood tests. nine0003
In obstetrics and gynecology, the test for b hCG, along with ultrasound, is used to monitor pregnancy throughout the entire period. Deviations in the readings of the analysis are the basis for further examination and require the consultation of a geneticist. An artificial increase in the level of hCG is used in the IVF process. As a result of injections of hCG in women, the maturation and release of the egg is stimulated, the production of estrogen and progesterone increases. In men, the introduction of exogenous hCG activates the growth of the number of spermatozoa. nine0003
As a result of injections of hCG in women, the maturation and release of the egg is stimulated, the production of estrogen and progesterone increases. In men, the introduction of exogenous hCG activates the growth of the number of spermatozoa. nine0003
It is proved that the substance also has the properties of corticotropic hormone. HCG has an effect on the adrenal glands, stimulating the synthesis of steroids in their cortex. Thus, he is involved in preparing the body of a pregnant woman for the upcoming physiological stress. Since the fetus is perceived as foreign by the mother's body, some immunosuppressive influence of hormones, including hCG, is required for its normal development.
HCG promotes the maturation of placental tissues. Thanks to him and other hormones, its functional activity increases and the number of chorionic villi increases. nine0003
Without the hormone, the normal development of the embryo is not possible. HCG ensures the production of estrogens and progesterone, and also maintains their balance in the body of the expectant mother. Therefore, any pregnancy support program always contains regular tests for hCG levels.
Therefore, any pregnancy support program always contains regular tests for hCG levels.
Urinalysis for hCG (beta particles)
Compared to blood, expectant mother's urine contains less of the hormone. Therefore, determining the concentration of a substance in the urine can diagnose pregnancy only from a period of 8-10 days. Like a laboratory study, pharmacy tests are also based on the determination of hCG in the urine. Home tests have a lower threshold of sensitivity than laboratory tests, and, accordingly, a lower degree of reliability. Their positive result requires a visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist to confirm a normal pregnancy. nine0003
Free hCG assay (beta-hCG subunit)
The range of application of this test is quite wide. In oncology, it is in demand as a marker of malignant tumors. Measurement of the number of independent particles of hCG in the blood is informative in relation to testicular cancer in men. In addition, this indicator is important in the diagnosis of trophoblastic tumors in women.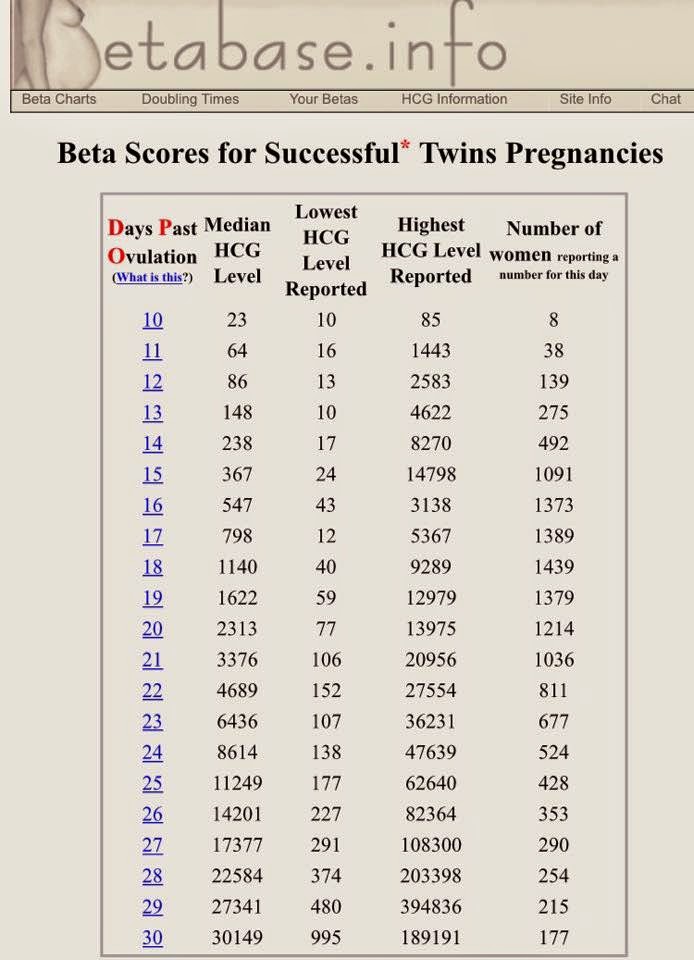 It is included in 1 and 2 pregnancy screenings. The study helps to assess the risk of such congenital fetal pathologies as Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome. nine0003
It is included in 1 and 2 pregnancy screenings. The study helps to assess the risk of such congenital fetal pathologies as Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome. nine0003
The role of the hormone in the diagnosis of pregnancy
An analysis of the amount of total hCG occupies a special place in confirming pregnancy in the early stages. This is due to the fact that the hormone begins to be actively released already a few days after the attachment of the fetal egg to the wall of the uterus. With the normal development of the embryo, the level of the substance doubles every 1.5-2 days. By the tenth week, the amount of hCG in a woman's tests can reach maximum values - up to 225,000 mU / ml. nine0003
Simultaneously with the blood for total hCG, other examinations are prescribed for the pregnant woman. So the patient should visit the ultrasound scanning room at least three times. Within nine months, several studies may be required. Comprehensive screenings of the 1st and 2nd trimesters also include an hCG test.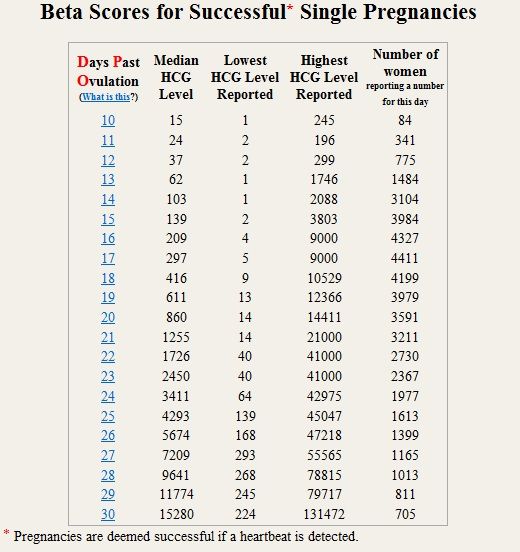
When to donate blood for hCG
A blood test for the hormone is given as needed. The hCG test is prescribed for the first time directly during the diagnosis of pregnancy itself. The second is as part of screening with ultrasound and other tests. Screening is designed to identify a risk group for congenital fetal pathologies among pregnant women. nine0003
Approximate dates of studies on hCG:
- confirmation of pregnancy - from the 6th day after conception;
- first - from 11 to 13 weeks;
- second from 19 to 23 weeks;
- 3rd trimester screening is done after 28 weeks of gestation.
How to prepare for a blood test
Preparing for an hCG test involves a number of standard requirements for hormone testing. The analysis is given on an empty stomach, after an overnight fast in the morning or afternoon. You should come to the treatment room in good health. In order for the results of the hCG test to be as reliable as possible, it is recommended in 2-3 days: nine0003
- stop drinking alcohol;
- exclude spicy and fatty foods from the diet;
- cancel strength training;
- Avoid smoking a couple of hours before donating blood.