Can you eat while pregnant
11 Foods and Beverages to Avoid During Pregnancy
One of the first things people learn when they’re pregnant is what they can’t eat. It can be a real bummer if you’re a big sushi, coffee, or rare steak fan.
Thankfully, there’s more you can eat than what you can’t. You just have to learn how to navigate the waters (the low mercury waters, that is). You’ll want to pay close attention to what you eat and drink to stay healthy .
Certain foods should only be consumed rarely, while others should be avoided completely. Here are 11 foods and beverages to avoid or minimize while pregnant.
Mercury is a highly toxic element. It has no known safe level of exposure and is most commonly found in polluted water.
In higher amounts, it can be toxic to your nervous system, immune system, and kidneys. It may also cause serious developmental problems in children, with adverse effects even in lower amounts.
Since it’s found in polluted seas, large marine fish can accumulate high amounts of mercury. Therefore, it’s best to avoid high mercury fish while pregnant and breastfeeding.
High-mercury fish you want to avoid include:
- shark
- swordfish
- king mackerel
- tuna (especially bigeye tuna)
- marlin
- tilefish from the Gulf of Mexico
- orange roughy
However, it’s important to note that not all fish are high in mercury — just certain types.
Consuming low mercury fish during pregnancy is very healthy, and these fish can be eaten up to three times per week, according to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Low mercury fish are plentiful and include:
- anchovies
- cod
- flounder
- haddock
- salmon
- tilapia
- trout (freshwater)
Fatty fish like salmon and anchovies are especially good options, as they are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for your baby.
This one will be tough for you sushi fans, but it’s an important one. Raw fish, especially shellfish, can cause several infections. These can be viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections, such as norovirus, Vibrio, Salmonella, and Listeria.
These can be viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections, such as norovirus, Vibrio, Salmonella, and Listeria.
Some of these infections may only affect you, causing dehydration and weakness. Other infections may be passed on to your baby with serious, or even fatal, consequences.
Pregnant women are especially susceptible to listeria infections. In fact, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), pregnant women are up to 10 times more likely to get infected by Listeria than the general population. Pregnant Hispanic women are 24 times more at risk.
This bacteria can be found in soil and contaminated water or plants. Raw fish can become infected during processing, including smoking or drying.
Listeria bacteria can be passed to your baby through the placenta, even if you’re not showing any signs of illness. This can lead to premature delivery, miscarriage, stillbirth, and other serious health problems, according to the CDC.
It’s definitely advised to avoid raw fish and shellfish, including many sushi dishes. But don’t worry, you’ll enjoy it that much more after baby is born and it’s safer to eat again.
Some of the same issues with raw fish affect undercooked meat, too. Eating undercooked or raw meat increases your risk of infection from several bacteria or parasites, including Toxoplasma, E. coli, Listeria, and Salmonella.
Bacteria may threaten the health of your little one, possibly leading to stillbirth or severe neurological illnesses, including intellectual disability, blindness, and epilepsy.
While most bacteria are found on the surface of whole pieces of meat, other bacteria may linger inside the muscle fibers.
Some whole cuts of meat — such as tenderloins, sirloins, or ribeye from beef, lamb and veal — may be safe to consume when not cooked all the way through. However, this only applies when the piece of meat is whole or uncut, and completely cooked on the outside.
Cut meat, including meat patties, burgers, minced meat, pork, and poultry, should never be consumed raw or undercooked. So keep those burgers on the grill well done for now.
Hot dogs, lunch meat, and deli meat are also of concern, which is sometimes surprising to pregnant people. These types of meat may become infected with various bacteria during processing or storage.
Pregnant women should not consume processed meat products unless they’ve been reheated until steaming hot.
Raw eggs can be contaminated with the Salmonella bacteria.
Symptoms of salmonella infections include fever, nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, and diarrhea.
However, in rare cases, the infection may cause cramps in the uterus, leading to premature birth or stillbirth.
Foods that commonly contain raw eggs include:
- lightly scrambled eggs
- poached eggs
- hollandaise sauce
- homemade mayonnaise
- some homemade salad dressings
- homemade ice cream
- homemade cake icings
Most commercial products that contain raw eggs are made with pasteurized eggs and are safe to consume. However, you should always read the label to make sure.
However, you should always read the label to make sure.
To be on the safe side, make sure to always cook eggs thoroughly or use pasteurized eggs. Save those super runny yolks and homemade mayo until after baby makes their debut.
Organ meat is a great source of a variety of nutrients.
These include iron, vitamin B12, vitamin A, zinc, selenium, and copper — all of which are good for you and baby. However, eating too much animal-based vitamin A (preformed vitamin A) is not recommended during pregnancy.
Consuming too much preformed vitamin A, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy, can lead to congenital malformations and miscarriage.
Although this is mostly associated with vitamin A supplements, it’s best to keep your consumption of organ meats like liver to just a few ounces once per week.
You may be one of the millions of folks who love their daily cups of coffee, tea, soft drinks, or cocoa. You’re definitely not alone when it comes to our love of caffeine.
Pregnant people are generally advised to limit their caffeine intake to less than 200 milligrams (mg) per day, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG).
Caffeine is absorbed very quickly and passes easily into the placenta. Because babies and their placentas don’t have the main enzyme needed to metabolize caffeine, high levels can build up.
High caffeine intake during pregnancy has been shown to restrict fetal growth and increase the risk of low birth weight at delivery.
Low birth weight — defined as less than 5 lbs., 8 oz. (or 2.5 kg) — is associated with an increased risk of infant death and a higher risk of chronic diseases in adulthood.
So keep an eye on your daily cup of joe or soda to make sure baby doesn’t have exposure to too much caffeine.
Your healthy salad choice may not be free from rogue ingredients, either. Raw sprouts, including alfalfa, clover, radish, and mung bean sprouts, may be contaminated with Salmonella.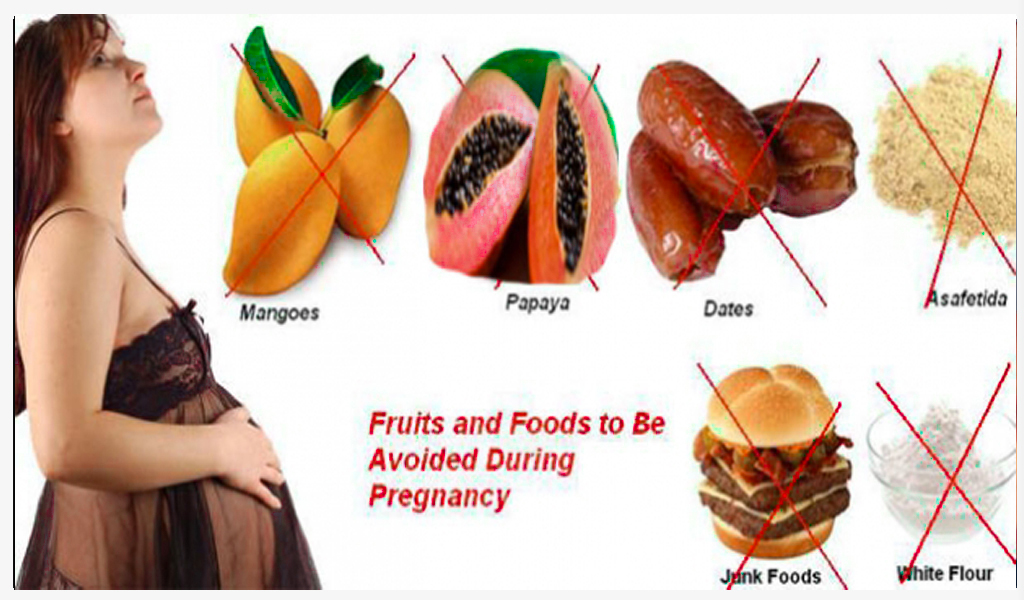
The humid environment required by seeds to start sprouting is ideal for these kinds of bacteria, and they’re almost impossible to wash off.
For this reason, you’re advised to avoid raw sprouts altogether. However, sprouts are safe to consume after they have been cooked, according to the FDA.
The surface of unwashed or unpeeled fruits and vegetables may be contaminated with several bacteria and parasites.
These include Toxoplasma, E. coli, Salmonella, and Listeria, which can be acquired from the soil or through handling.
Contamination can occur at any time during production, harvest, processing, storage, transportation, or retail. One dangerous parasite that may linger on fruits and vegetables is called Toxoplasma.
The majority of people who get toxoplasmosis have no symptoms, while others may feel like they have the flu for a month or more.
Most infants who are infected with the Toxoplasma bacteria while still in the womb have no symptoms at birth. However, symptoms such as blindness or intellectual disabilities may develop later in life.
However, symptoms such as blindness or intellectual disabilities may develop later in life.
What’s more, a small percentage of infected newborns have serious eye or brain damage at birth.
While you’re pregnant, it’s very important to minimize the risk of infection by thoroughly washing with water, peeling, or cooking fruits and vegetables. Keep it up as a good habit after baby arrives, too.
Raw milk, unpasteurized cheese, and soft-ripened cheeses can contain an array of harmful bacteria, including Listeria, Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter. (These are probably sounding familiar by now.)
The same goes for unpasteurized juice, which is also prone to bacterial contamination. These infections can all have life-threatening consequences for an unborn baby.
The bacteria can be naturally occurring or caused by contamination during collection or storage. Pasteurization is the most effective way to kill any harmful bacteria, without changing the nutritional value of the products.
To minimize the risk of infections, eat only pasteurized milk, cheese, and fruit juice.
It’s advised to completely avoid drinking alcohol when pregnant, as it increases the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. Even a small amount can negatively impact your baby’s brain development.
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy can also cause fetal alcohol syndrome, which involves facial deformities, heart defects and intellectual disability.
Since no level of alcohol has been proven to be safe during pregnancy, it’s recommended to avoid it altogether.
There’s no better time than pregnancy to start eating nutrient-dense foods to help both you and your growing little one. You’ll need increased amounts of many essential nutrients, including protein, folate, choline, and iron.
It’s also a myth that you’re “eating for two.” You can eat as you normally do during the first semester, then increase by about 350 calories per day in your second trimester, and about 450 calories per day in your third trimester.
An optimal pregnancy eating plan should mainly consist of whole foods, with plenty of nutrients to fulfill yours and baby’s needs. Processed junk food is generally low in nutrients and high in calories, sugar, and added fats.
While some weight gain is necessary during pregnancy, excess weight gain has been linked to many complications and diseases. These include an increased risk of gestational diabetes, as well as pregnancy or birth complications.
Stick to meals and snacks that focus on protein, vegetables and fruits, healthy fats, and fiber-rich carbohydrates like whole grains, beans, and starchy vegetables. Don’t worry, there are lots of ways to sneak veggies into your meals without sacrificing taste.
When you’re pregnant, it’s essential to avoid foods and beverages that may put you and your baby at risk.
Although most foods and beverages are perfectly safe to enjoy, some, like raw fish, unpasteurized dairy, alcohol, and high mercury fish, should be avoided.
Plus, some foods and beverages like coffee and foods high in added sugar, should be limited in order to promote a healthy pregnancy.
If you want to learn more about what foods you should eat during pregnancy, check out this article: Healthy Eating During Pregnancy.
Quick tips for foods to avoid when pregnant
- Avoid high-mercury fish including shark, swordfish, tuna, and marlin.
- Raw fish and shellfish can be contaminated with bacteria and parasites. Some of these can cause adverse health effects and harm both you and baby.
- Raw or undercooked meat may contain harmful bacteria. As a general rule, meat should be cooked all the way through.
- Raw eggs may be contaminated with Salmonella, and may put you and your baby at risk. Be sure to thoroughly cook eggs before eating.
- Organ meat is a great source of iron, vitamin B12, vitamin A, and copper. To prevent consuming too much vitamin A limit your intake of organ meat to a few ounces once a week.

- Limit caffeine intake to under 200 mg per day, which is about 2 to 3 cups of coffee. High caffeine intake during pregnancy may limit baby’s growth and cause low birth weight.
- Raw sprouts may be contaminated with bacteria. Only eat them thoroughly cooked.
- Fruits and vegetables may be contaminated with harmful bacteria, including Toxoplasma. It’s important to thoroughly wash all fruits and vegetables with plenty of clean water.
- Don’t consume unpasteurized milk, cheese, or fruit juice, as these foods increase the risk of bacterial infections.
- Avoid all alcohol. Drinking alcohol can increase the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, and fetal alcohol syndrome.
- Eating processed foods during pregnancy can increase your risk of excess weight gain, gestational diabetes, and complications. This can have long-term health implications for you and your child.
Eat Healthy During Pregnancy: Quick tips - MyHealthfinder
Pregnancy
When you are pregnant, you need more of certain nutrients like protein, iron, folic acid, and iodine. It’s also important to get enough calcium.
It’s also important to get enough calcium.
Making smart food choices can help you have a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby. Here are some ideas to help you eat healthy during pregnancy.
Follow a healthy eating pattern.
Eating healthy means following a healthy eating pattern that includes a variety of nutritious foods and drinks.
- Eat a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fat-free or low-fat dairy products, and protein foods.
- Choose foods and drinks with less added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium (salt).
- Limit refined grains and starches, which are in foods like cookies, white bread, and some snack foods.
- If you are feeling sick, try eating a piece of whole-grain toast or whole-grain crackers.
Learn more about eating healthy.
Get the right amount of calories for you.
Being pregnant doesn't mean you need to eat twice as much food.
- First trimester (first 12 weeks) – Most women don’t need any extra calories.
- Second trimester (13 to 26 weeks) – Most women need about 340 extra calories a day.
- Last trimester (after 26 weeks) – Most women need about 450 extra calories a day.
Ask your doctor or midwife how many calories you need during pregnancy.
Create a personalized Daily Food Plan.
Make healthy snack choices.
Examples of healthy snacks include:
- Low-fat or fat-free yogurt with fruit (look for options with no added sugar)
- Whole-grain crackers with fat-free or low-fat cheese
- Carrots with hummus
Take a prenatal vitamin with folic acid, iron, and iodine every day.
- Folic acid helps prevent some birth defects of the brain and spine.
- Iron and iodine help keep you and your baby healthy.
Talk with your doctor or nurse about a prenatal vitamin that’s right for you.
Eat 8 to 12 ounces of seafood each week.
Fish and shellfish have healthy fats that are good for you and your baby. But some fish is high in mercury, a metal that can hurt your baby’s development. It’s a good idea to eat seafood that is high in healthy fats but lower in mercury.
But some fish is high in mercury, a metal that can hurt your baby’s development. It’s a good idea to eat seafood that is high in healthy fats but lower in mercury.
Best choices
These choices are lower in mercury, so you can eat 8 to 12 ounces a week.
- Canned light tuna
- Catfish
- Cod
- Herring
- Oysters
- Salmon
- Shad
- Shrimp
- Tilapia
- Trout
Good choices
You can eat 4 ounces of these fish a week if you don’t eat any other seafood that week.
- Canned or fresh white (albacore) tuna
- Chilean sea bass or striped bass
- Grouper
- Halibut
- Mahi-mahi
- Snapper
- Yellowfin tuna
Fish to avoid
Don’t eat bigeye tuna, king mackerel, marlin, orange roughy, shark, swordfish, or tilefish. They are high in mercury.
Learn more about choosing fish that is healthy and safe to eat [PDF - 308 KB].
Don’t eat certain foods.

These foods may have bacteria in them that can hurt your baby. Stay away from:
- Raw (uncooked) or rare (undercooked) fish or shellfish, like sushi or raw oysters
- Soft cheeses (like feta, Brie, and goat cheese), unless they are pasteurized
- Raw or rare meats, poultry, or eggs
- Unpasteurized juices or milk
- Lunch or deli meats, smoked seafood, and hot dogs – unless they are heated until steaming hot
- Prepared salads like ham salad, chicken salad, or seafood salad
- Raw sprouts, including alfalfa, clover, radish, and mung bean sprouts
Learn more about foods to avoid during pregnancy.
Limit drinks with caffeine and added sugars.
- If you drink coffee or tea, choose decaf. Pick unsweetened options and don’t add sugar.
- Drink water or seltzer instead of drinks with added sugars like soda, fruit drinks, and energy or sports drinks.
Don’t drink alcohol.
No amount of alcohol is safe during pregnancy.
Content last updated June 1, 2022
Reviewer Information
This information on healthy eating during pregnancy was adapted from materials from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the Office on Women’s Health, and the National Institutes of Health Weight-control Information Network (WIN).
Reviewed by:
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the U.S. Department of Agriculture Dietary Guidance Review Committee
For more information on healthy eating during pregnancy, visit:
- http://www.choosemyplate.gov/moms-pregnancy-breastfeeding
- https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/staying-healthy-and-safe
Nutrition of a pregnant woman
So, your plans and decisions to give birth to a child have come true - you are pregnant! But this news causes you a double feeling: - on the one hand, a feeling of joy, and on the other hand, a feeling of certain fear and even fear of unknown trials for your life and the fate of the unborn baby. What will he be like? - healthy, beautiful, happy?...
And this largely depends on the woman herself, on what lifestyle she will lead during pregnancy and, most importantly, how she will eat. nine0003
Nutrition of a woman in different periods of pregnancy
The main thing in the menu of a future mother is variety. She should consume foods from all food groups: meat, fish, vegetables and fruits, dairy products, bread and cereals.
A woman's nutrition during pregnancy can be roughly divided into three periods (trimesters).
If before pregnancy a woman ate normally, felt comfortable, did not experience allergies to any products, then it is not worth changing her diet at an early stage of the first trimester of pregnancy. nine0003
During this period, all organs and systems in the child's body are formed, tissues are formed. The body needs complete proteins and vitamins: lean meat (rabbit, chicken, turkey), fish and seafood, dairy products. Be sure to eat rice, fresh or frozen vegetables, seasonal fruits. In the first trimester, many expectant mothers are still working. No matter how difficult it is to control your diet in the workplace, you need to do it - find time for a full breakfast and lunch. nine0003
In the first trimester of pregnancy, there is an active restructuring of the body and adaptation to a new state. During this period, it is recommended to switch to a low-calorie diet, which includes more fruits, juices, decoctions of dried fruits, including rose hips. At the very beginning of pregnancy, especially if toxicosis torments, more frequent, but less plentiful meals are recommended.
Always keep a hematogen, a bag of nuts or dried fruit in your pocket to have a snack on the street. If your condition does not allow you to eat regular food, you should pay attention to baby food. Baby products literally save expectant mothers suffering from severe toxicosis. These are boxed cereals, children's curds, cookies and fruit purees. nine0003
In the first trimester, special attention must be paid to the quality of products. Gradually abandon sauces, semi-finished products and canned food containing harmful chemical additives. Do not forget that the placenta freely accumulates and passes chemistry. The importance of products containing folic acid is great, without it intensive metabolism is impossible, its deficiency can cause developmental abnormalities. Folic acid is found in greens, nuts, white cabbage and broccoli, beets, legumes, and eggs. nine0003
According to nutritionists, the diet of pregnant women should be 300 kcal / day higher than that of non-pregnant women, but in the first trimester there is no need to increase the energy value of the diet at all; in the second trimester, an additional 340 kcal / day is required; in the third trimester - 452 kcal / day. Pregnant women generally get enough calories, and more than 80% of women achieve and even exceed the required weight gain. These extra calories benefit the fetus. An underweight woman should gain 16–20 kg during her entire pregnancy, an overweight woman about 7 kg, and a normal body weight of 11–12 kg. nine0003
nine0003
In the second trimester there are active jumps in the height and weight of the baby and uterus, so the caloric content of the diet needs to be increased. It is desirable to eat more and better. At this time, the need for trace elements increases: iron, magnesium, zinc, selenium, calcium, potassium. The child creates his own "reserve" of trace elements using the mother's resource, which means that the mother should have enough of them for two.
Very often in pregnant women in the second trimester hemoglobin drops, this is a normal physiological phenomenon, if it is not threatening to health. You can increase hemoglobin by eating red meat, chicken, fish, dried fruits, pomegranates, green vegetables and fresh herbs, buckwheat, citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits, pomelo, lemons), rosehip and berry infusions. nine0003
In the second trimester, a pregnant woman should limit the intake of smoked and fried foods, as well as salt in her diet. In no case should you limit the liquid. Pure water is the best drink for a pregnant woman, and water should be consumed up to 2-2.5 liters per day. Water is a natural drink for the body, it does not cause complications and has no contraindications. Edema is caused not by water, but by salt, which we not only add in its pure form, but also consume with canned food, mayonnaise, cheese, and sausage. The absence of salt is not harmful, it is naturally found in many products: vegetables, bread, so the diet will not remain completely without it. Excess salt disrupts metabolism. nine0003
Pure water is the best drink for a pregnant woman, and water should be consumed up to 2-2.5 liters per day. Water is a natural drink for the body, it does not cause complications and has no contraindications. Edema is caused not by water, but by salt, which we not only add in its pure form, but also consume with canned food, mayonnaise, cheese, and sausage. The absence of salt is not harmful, it is naturally found in many products: vegetables, bread, so the diet will not remain completely without it. Excess salt disrupts metabolism. nine0003
During this period, you can increase the calorie content of food. Childbirth must be approached physically strong. It is better to eat meat and fish in the morning, for breakfast and lunch, and for dinner, prepare dairy and vegetable dishes: cheesecakes, stewed vegetables, cottage cheese and vegetable casseroles. It is necessary to minimize the intake of canned food, smoked meats, pickles and marinades, hot spices and fatty foods. Frequent walks in the air, physical activity are recommended.
In the third trimester, it is necessary to reduce the calorie content of foods at the expense of confectionery and flour products, eat less fatty meat, as well as cheese and sour cream. nine0003
By the end of this period, many experts advise pregnant women to give up meat altogether in order to increase tissue elasticity and prevent ruptures.
During the entire period of pregnancy, special attention should be paid to the combination of products. If you combine foods wisely, you can ensure more efficient absorption of food. If the food is digested poorly, then this can lead to rotting and fermentation of products and the formation of substances harmful to the body of the mother and child. In addition, the fermentation process is accompanied by gas formation, which can lead to flatulence (bloating) and discomfort. This is especially harmful in the last stages of pregnancy. nine0003
Try not to take the first, second and third course at the same time; this overflows the stomach and presses on the fetus, the food is poorly digested and poorly absorbed. Eat little and often. It is not recommended to eat immediately before starting work, a long walk, before charging and immediately after it; it is advisable to rest for 10 minutes before eating.
Eat little and often. It is not recommended to eat immediately before starting work, a long walk, before charging and immediately after it; it is advisable to rest for 10 minutes before eating.
Eat only when you are hungry, try not to snack on the go. Follow the diet, eat at about the same time. nine0003
Proper preparation of food will help to maximize the useful substances contained in the products. Do not overcook food, try not to reheat the same dish several times, it is better to set aside only the portion that will be used. Cook in the most gentle way: baking, steaming, stewing. Avoid frying, boiling in large amounts of water, with this method of processing products, many useful substances are lost. If possible, do not cook for several days at once. Do not use aluminum cookware when cooking. Remember that for a pregnant woman, it is not calories that are important, but the quality of food, its naturalness, primarily a “living cell” (whole cereals, raw vegetables and fruits, fresh meat and dairy products). nine0003
nine0003
What can harm the pregnant woman and the fetus
Smoking and alcohol – quit smoking from the first days of pregnancy, if you have smoked before, avoid "passive" smoking, and do not consume alcoholic beverages in any doses.
Lack of vitamins and microelements in the body - their absence or deficiency can lead to irreparable consequences. So, for example, iodine deficiency can lead to mental retardation of a child, folic acid deficiency - to severe fetal deformities, calcium deficiency - to a violation of the formation of the child's skeleton, iron deficiency - to anemia and a delay in the physical and neuropsychic development of the child. It is necessary to consult a doctor, perhaps he will recommend switching to iodized salt, as well as supplementing your diet with a vitamin-mineral complex and folic acid. nine0003
Excess weight is the risk of having a large child, which means the risk of complications during childbirth and the child's tendency to become obese at an older age.
The use of food additives (sauces, seasonings such as vegeta, bouillon cubes), exotic fruits, semi-finished products, carbonated drinks - the risk of allergies and anomalies in a child, unfortunately, increases.
Recommended for pregnant women:
- Do not eat hot dogs and other snacks containing meat that has not been heated on fire or boiled in boiling water. nine0058
- Avoid soft cheeses. Hard cheeses are safe.
- Do not eat raw frozen pies and meat pastes, seafood. Canned analogues are safe.
- Do not consume raw vegetables, unpasteurized juices, liver, meat, poultry and eggs that have not been sufficiently cooked. These products may contain Salmonella taxins.
- Limit sweets.
- In no case do not resort to starvation and various diets. nine0058
- Regularly monitor blood pressure and do not miss visits to the gynecologist.
Remember!
Your child's development and health depend on your diet and lifestyle during pregnancy!
What not to eat during pregnancy TEA.
 RU
RU Pregnancy is a wonderful time when a woman's body needs energy and strength more than ever, as it goes through internal changes. For the easiest passage of this period, the diet of the expectant mother should be complete, varied and balanced - this is the key to a woman's health and the proper development of the fetus. nine0003
First trimester
At an early stage of pregnancy, the diet can not be changed much, but some foods and dishes should be excluded:
- fast food;
- smoked products;
- fatty and spicy foods;
- canned food;
- exotic products;
- carbonated drinks;
- products containing allergens;
- raw eggs; nine0088
- raw and half-cooked meat;
- liver;
- sushi;
- soft cheeses;
- unpasteurized milk and juices.

Fish (raw and high mercury), seafood
You can not eat makaira, swordfish, mackerel, tiled and white tuna. Raw fish may contain bacteria and parasites. Smoked fish should also be avoided.
Unpasteurized soft cheeses
Feta and camembert may contain listeria bacteria as they are made from raw milk. These bacteria, once in the body of the fetus, can cause severe developmental disorders and even miscarriage. If you want to consume these cheeses, then look for a product that says pasteurized on the label (mozzarella, ricotta, cream cheeses, halloumi, processed cheeses).
Unpasteurized milk and juices
Unpasteurized milk and freshly squeezed juices can be contaminated with E. coli, listeria, salmonella bacteria, which are pathogenic and undesirable for pregnant women. nine0003
Raw eggs
You should not eat dishes containing raw protein or yolk, or that have not undergone sufficient heat treatment. For example, soft-boiled eggs, sauces, eggnog. During pregnancy, it is better to eat hard-boiled or pasteurized eggs.
For example, soft-boiled eggs, sauces, eggnog. During pregnancy, it is better to eat hard-boiled or pasteurized eggs.
Raw and semi-raw meat and poultry
Such meat may also be contaminated with Listeria. Pates and meat spreads should also be temporarily forgotten. Before eating meat dishes, make sure that the meat has been properly cooked. nine0003
Fast food and fried foods
This kind of food was not included in the list of strictly prohibited, but it is worth remembering that it can harm the gastrointestinal tract and cause an imbalance in the body, which can negatively affect the general condition of the expectant mother. If during the period of bearing a child, you really want to eat something harmful, try to find a healthy alternative. For example, fry food in a small amount of oil, or better bake. The main thing to remember is that a balanced diet and a healthy diet are the foundation of your health, and therefore the health of your baby. nine0003
nine0003
Caffeine
Too much caffeine can lead to a number of problems:
Sleep disturbance, as this substance increases the reflex excitability of the nervous system.
Anemia - the phenol contained in caffeine does not allow the absorption of iron in the blood, which can adversely affect the body of the mother and child.
Heartburn – coffee is a hydrochloric acid stimulant, so even the weakest drink can increase heartburn.
High sugar foods
A large amount of sugar during pregnancy can lead to active and rapid weight gain, which will put stress on the spine and joints. Calcium will also begin to leach out - this can cause a loss of vitamin B1 and problems with teeth and liver. If there were prerequisites, then excessive consumption of sweets can cause diabetes, digestive disorders in pregnant women.
Late pregnancy
In the last months of pregnancy, the fetus grows rapidly. Therefore, the diet of a pregnant woman should be rich in vitamins, minerals and trace elements. To help the body cope with stress, pregnant women should adhere to the following recommendations:
Therefore, the diet of a pregnant woman should be rich in vitamins, minerals and trace elements. To help the body cope with stress, pregnant women should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Reduce the amount of spicy, smoked and salty foods.
- Reduce the amount of salt. It retains fluid that causes swelling and stresses the kidneys.
- Exclude convenience foods and canned food. They are low in nutrients and contain harmful additives. nine0088
To make pregnancy an exciting journey, a woman needs to eat healthy and wholesome food. It is necessary to increase the amount of whole grains, meat, poultry and fish. Be sure to include vegetables, fruits, protein and dairy products in your diet. It is useful to consume olive oil and avocado, they are rich in mono- and polyunsaturated fats. During pregnancy, the body needs more calcium, for this reason, you need to increase the intake of milk and dairy products.