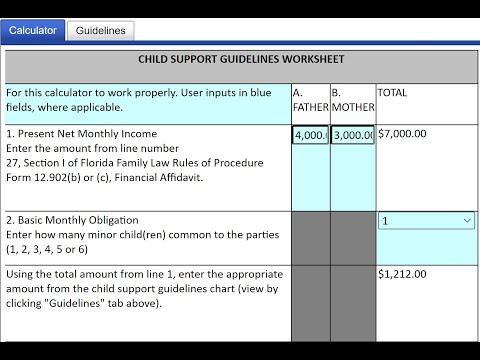
Foods to eat and avoid when pregnant
11 Foods and Beverages to Avoid During Pregnancy
One of the first things people learn when they’re pregnant is what they can’t eat. It can be a real bummer if you’re a big sushi, coffee, or rare steak fan.
Thankfully, there’s more you can eat than what you can’t. You just have to learn how to navigate the waters (the low mercury waters, that is). You’ll want to pay close attention to what you eat and drink to stay healthy .
Certain foods should only be consumed rarely, while others should be avoided completely. Here are 11 foods and beverages to avoid or minimize while pregnant.
Mercury is a highly toxic element. It has no known safe level of exposure and is most commonly found in polluted water.
In higher amounts, it can be toxic to your nervous system, immune system, and kidneys. It may also cause serious developmental problems in children, with adverse effects even in lower amounts.
Since it’s found in polluted seas, large marine fish can accumulate high amounts of mercury. Therefore, it’s best to avoid high mercury fish while pregnant and breastfeeding.
High-mercury fish you want to avoid include:
- shark
- swordfish
- king mackerel
- tuna (especially bigeye tuna)
- marlin
- tilefish from the Gulf of Mexico
- orange roughy
However, it’s important to note that not all fish are high in mercury — just certain types.
Consuming low mercury fish during pregnancy is very healthy, and these fish can be eaten up to three times per week, according to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Low mercury fish are plentiful and include:
- anchovies
- cod
- flounder
- haddock
- salmon
- tilapia
- trout (freshwater)
Fatty fish like salmon and anchovies are especially good options, as they are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for your baby.
This one will be tough for you sushi fans, but it’s an important one. Raw fish, especially shellfish, can cause several infections. These can be viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections, such as norovirus, Vibrio, Salmonella, and Listeria.
These can be viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections, such as norovirus, Vibrio, Salmonella, and Listeria.
Some of these infections may only affect you, causing dehydration and weakness. Other infections may be passed on to your baby with serious, or even fatal, consequences.
Pregnant women are especially susceptible to listeria infections. In fact, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), pregnant women are up to 10 times more likely to get infected by Listeria than the general population. Pregnant Hispanic women are 24 times more at risk.
This bacteria can be found in soil and contaminated water or plants. Raw fish can become infected during processing, including smoking or drying.
Listeria bacteria can be passed to your baby through the placenta, even if you’re not showing any signs of illness. This can lead to premature delivery, miscarriage, stillbirth, and other serious health problems, according to the CDC.
It’s definitely advised to avoid raw fish and shellfish, including many sushi dishes. But don’t worry, you’ll enjoy it that much more after baby is born and it’s safer to eat again.
Some of the same issues with raw fish affect undercooked meat, too. Eating undercooked or raw meat increases your risk of infection from several bacteria or parasites, including Toxoplasma, E. coli, Listeria, and Salmonella.
Bacteria may threaten the health of your little one, possibly leading to stillbirth or severe neurological illnesses, including intellectual disability, blindness, and epilepsy.
While most bacteria are found on the surface of whole pieces of meat, other bacteria may linger inside the muscle fibers.
Some whole cuts of meat — such as tenderloins, sirloins, or ribeye from beef, lamb and veal — may be safe to consume when not cooked all the way through. However, this only applies when the piece of meat is whole or uncut, and completely cooked on the outside.
Cut meat, including meat patties, burgers, minced meat, pork, and poultry, should never be consumed raw or undercooked. So keep those burgers on the grill well done for now.
Hot dogs, lunch meat, and deli meat are also of concern, which is sometimes surprising to pregnant people. These types of meat may become infected with various bacteria during processing or storage.
Pregnant women should not consume processed meat products unless they’ve been reheated until steaming hot.
Raw eggs can be contaminated with the Salmonella bacteria.
Symptoms of salmonella infections include fever, nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, and diarrhea.
However, in rare cases, the infection may cause cramps in the uterus, leading to premature birth or stillbirth.
Foods that commonly contain raw eggs include:
- lightly scrambled eggs
- poached eggs
- hollandaise sauce
- homemade mayonnaise
- some homemade salad dressings
- homemade ice cream
- homemade cake icings
Most commercial products that contain raw eggs are made with pasteurized eggs and are safe to consume. However, you should always read the label to make sure.
However, you should always read the label to make sure.
To be on the safe side, make sure to always cook eggs thoroughly or use pasteurized eggs. Save those super runny yolks and homemade mayo until after baby makes their debut.
Organ meat is a great source of a variety of nutrients.
These include iron, vitamin B12, vitamin A, zinc, selenium, and copper — all of which are good for you and baby. However, eating too much animal-based vitamin A (preformed vitamin A) is not recommended during pregnancy.
Consuming too much preformed vitamin A, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy, can lead to congenital malformations and miscarriage.
Although this is mostly associated with vitamin A supplements, it’s best to keep your consumption of organ meats like liver to just a few ounces once per week.
You may be one of the millions of folks who love their daily cups of coffee, tea, soft drinks, or cocoa. You’re definitely not alone when it comes to our love of caffeine.
Pregnant people are generally advised to limit their caffeine intake to less than 200 milligrams (mg) per day, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG).
Caffeine is absorbed very quickly and passes easily into the placenta. Because babies and their placentas don’t have the main enzyme needed to metabolize caffeine, high levels can build up.
High caffeine intake during pregnancy has been shown to restrict fetal growth and increase the risk of low birth weight at delivery.
Low birth weight — defined as less than 5 lbs., 8 oz. (or 2.5 kg) — is associated with an increased risk of infant death and a higher risk of chronic diseases in adulthood.
So keep an eye on your daily cup of joe or soda to make sure baby doesn’t have exposure to too much caffeine.
Your healthy salad choice may not be free from rogue ingredients, either. Raw sprouts, including alfalfa, clover, radish, and mung bean sprouts, may be contaminated with Salmonella.
The humid environment required by seeds to start sprouting is ideal for these kinds of bacteria, and they’re almost impossible to wash off.
For this reason, you’re advised to avoid raw sprouts altogether. However, sprouts are safe to consume after they have been cooked, according to the FDA.
The surface of unwashed or unpeeled fruits and vegetables may be contaminated with several bacteria and parasites.
These include Toxoplasma, E. coli, Salmonella, and Listeria, which can be acquired from the soil or through handling.
Contamination can occur at any time during production, harvest, processing, storage, transportation, or retail. One dangerous parasite that may linger on fruits and vegetables is called Toxoplasma.
The majority of people who get toxoplasmosis have no symptoms, while others may feel like they have the flu for a month or more.
Most infants who are infected with the Toxoplasma bacteria while still in the womb have no symptoms at birth. However, symptoms such as blindness or intellectual disabilities may develop later in life.
However, symptoms such as blindness or intellectual disabilities may develop later in life.
What’s more, a small percentage of infected newborns have serious eye or brain damage at birth.
While you’re pregnant, it’s very important to minimize the risk of infection by thoroughly washing with water, peeling, or cooking fruits and vegetables. Keep it up as a good habit after baby arrives, too.
Raw milk, unpasteurized cheese, and soft-ripened cheeses can contain an array of harmful bacteria, including Listeria, Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter. (These are probably sounding familiar by now.)
The same goes for unpasteurized juice, which is also prone to bacterial contamination. These infections can all have life-threatening consequences for an unborn baby.
The bacteria can be naturally occurring or caused by contamination during collection or storage. Pasteurization is the most effective way to kill any harmful bacteria, without changing the nutritional value of the products.
To minimize the risk of infections, eat only pasteurized milk, cheese, and fruit juice.
It’s advised to completely avoid drinking alcohol when pregnant, as it increases the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. Even a small amount can negatively impact your baby’s brain development.
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy can also cause fetal alcohol syndrome, which involves facial deformities, heart defects and intellectual disability.
Since no level of alcohol has been proven to be safe during pregnancy, it’s recommended to avoid it altogether.
There’s no better time than pregnancy to start eating nutrient-dense foods to help both you and your growing little one. You’ll need increased amounts of many essential nutrients, including protein, folate, choline, and iron.
It’s also a myth that you’re “eating for two.” You can eat as you normally do during the first semester, then increase by about 350 calories per day in your second trimester, and about 450 calories per day in your third trimester.
An optimal pregnancy eating plan should mainly consist of whole foods, with plenty of nutrients to fulfill yours and baby’s needs. Processed junk food is generally low in nutrients and high in calories, sugar, and added fats.
While some weight gain is necessary during pregnancy, excess weight gain has been linked to many complications and diseases. These include an increased risk of gestational diabetes, as well as pregnancy or birth complications.
Stick to meals and snacks that focus on protein, vegetables and fruits, healthy fats, and fiber-rich carbohydrates like whole grains, beans, and starchy vegetables. Don’t worry, there are lots of ways to sneak veggies into your meals without sacrificing taste.
When you’re pregnant, it’s essential to avoid foods and beverages that may put you and your baby at risk.
Although most foods and beverages are perfectly safe to enjoy, some, like raw fish, unpasteurized dairy, alcohol, and high mercury fish, should be avoided.
Plus, some foods and beverages like coffee and foods high in added sugar, should be limited in order to promote a healthy pregnancy.
If you want to learn more about what foods you should eat during pregnancy, check out this article: Healthy Eating During Pregnancy.
Quick tips for foods to avoid when pregnant
- Avoid high-mercury fish including shark, swordfish, tuna, and marlin.
- Raw fish and shellfish can be contaminated with bacteria and parasites. Some of these can cause adverse health effects and harm both you and baby.
- Raw or undercooked meat may contain harmful bacteria. As a general rule, meat should be cooked all the way through.
- Raw eggs may be contaminated with Salmonella, and may put you and your baby at risk. Be sure to thoroughly cook eggs before eating.
- Organ meat is a great source of iron, vitamin B12, vitamin A, and copper. To prevent consuming too much vitamin A limit your intake of organ meat to a few ounces once a week.

- Limit caffeine intake to under 200 mg per day, which is about 2 to 3 cups of coffee. High caffeine intake during pregnancy may limit baby’s growth and cause low birth weight.
- Raw sprouts may be contaminated with bacteria. Only eat them thoroughly cooked.
- Fruits and vegetables may be contaminated with harmful bacteria, including Toxoplasma. It’s important to thoroughly wash all fruits and vegetables with plenty of clean water.
- Don’t consume unpasteurized milk, cheese, or fruit juice, as these foods increase the risk of bacterial infections.
- Avoid all alcohol. Drinking alcohol can increase the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, and fetal alcohol syndrome.
- Eating processed foods during pregnancy can increase your risk of excess weight gain, gestational diabetes, and complications. This can have long-term health implications for you and your child.
Foods to avoid in pregnancy
Most foods and drinks are safe to have during pregnancy. But there are some things you should be careful with or avoid.
But there are some things you should be careful with or avoid.
What you can eat
- pasteurised or unpasteurised hard cheeses, such as cheddar, Gruyere and parmesan
- pasteurised semi-hard cheeses, such as Edam and Stilton
- pasteurised soft cheeses, such as cottage cheese, mozzarella, feta, cream cheese, paneer, ricotta, halloumi, goats' cheese without a white coating on the outside (rind) and processed cheese spreads
- soft or blue cheese (pasteurised or unpasteurised) that has been cooked until steaming hot
- pasteurised milk, yoghurt, cream and ice cream
What to avoid
- any other foods made from unpasteurised milk, such as soft ripened goats' cheese
- pasteurised or unpasteurised mould-ripened soft cheeses with a white coating on the outside, such as Brie, Camembert and chèvre (unless cooked until steaming hot)
- pasteurised or unpasteurised soft blue cheeses, such as Danish blue, Gorgonzola and Roquefort (unless cooked until steaming hot)
- unpasteurised cows' milk, goats' milk, sheep's milk or cream
Why
There's a small chance that unpasteurised or soft ripened dairy products may contain Listeria bacteria. This can cause an infection called listeriosis.
This can cause an infection called listeriosis.
Listeriosis can lead to miscarriage or stillbirth, or make your newborn baby very unwell.
Soft cheeses with a white coating on the outside have more moisture. This can make it easier for bacteria to grow.
Cooking cheese until it's steaming hot kills bacteria, reducing the risk of listeriosis.
Meat and poultryWhat you can eat
- meats such as chicken, pork and beef, as long as they're well-cooked with no trace of pink or blood; be especially careful with poultry, pork, sausages and burgers
- cold, pre-packed meats such as ham and corned beef
What to be careful with
- cold cured meats, such as salami, pepperoni, chorizo and prosciutto (unless cooked thoroughly)
What to avoid
- raw or undercooked meat
- liver and liver products
- all types of pâté, including vegetarian pâté
- game meats such as goose, partridge or pheasant
Why
There's a small risk of getting toxoplasmosis if you eat raw and undercooked meat, which can cause miscarriage.
Cured meats are not cooked, so they may have parasites in them that cause toxoplasmosis.
Liver and liver products have lots of vitamin A in them. This can be harmful to an unborn baby.
Game meats may contain lead shot.
EggsWhat you can eat
- raw, partially cooked and fully cooked British Lion hen eggs (they have a lion stamp on them) and hen eggs produced under the Laid in Britain scheme
- foods made with raw hen egg, such as mousse and mayonnaise, if made with British Lion eggs or hen eggs produced under the Laid in Britain scheme
- well cooked eggs (white and yolk) from any hen eggs that are not British Lion eggs or produced under the Laid in Britain scheme
- well cooked eggs (white and yolk) of all other eggs, including duck, goose or quail
What to avoid
- raw or partially cooked hen eggs that are not British Lion or produced under the Laid in Britain scheme
- raw or partially cooked duck, goose or quail eggs
Why
British Lion hen eggs and hen eggs produced under the Laid in Britain scheme are less likely to have salmonella in them.
Salmonella is unlikely to harm your unborn baby, but you could get food poisoning.
You should cook all eggs thoroughly, unless they are British Lion hen eggs or hen eggs produced under the Laid in Britain scheme.
FishWhat you can eat
- cooked fish and seafood
- sushi, as long as the fish has been cooked thoroughly
- cooked shellfish, such as mussels, lobster, crab, prawns, scallops and clams
- cold pre-cooked prawns
What to be careful with
- smoked fish, such as smoked salmon and trout
Important: Smoked fish and listeria
Due to a listeria outbreak linked to smoked fish, people at higher risk of serious infection (including people who are pregnant) should only eat smoked fish products that have been thoroughly cooked.
When cooking smoked fish products at home, make sure they are steaming hot all the way through.
Find out more about the listeria outbreak in smoked fish from the Food Standards Agency
What to limit
- you should eat no more than 2 portions of oily fish a week, such as salmon, trout, mackerel or herring
- you should eat no more than 2 tuna steaks (about 140g cooked or 170g raw) or 4 medium-size cans of tuna (about 140g when drained) per week
Information:
Tuna does not count as an oily fish
You can have 2 tuna steaks, or 4 medium-size cans of fish, as well as 2 portions of oily fish.
What to avoid
- swordfish
- marlin
- shark
- raw shellfish
Why
You should limit tuna because it has more mercury in it than other fish. If you eat too much mercury, it can be harmful to your unborn baby.
If you eat too much mercury, it can be harmful to your unborn baby.
You should limit oily fish because they can have pollutants such as dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls in them. If you eat too much of these, they can be harmful to your unborn baby.
You should avoid raw shellfish because they can have harmful bacteria, viruses or toxins in them. These can make you unwell and give you food poisoning.
Other foods and drinksCaffeine
You can have caffeine, but no more than 200mg per day.
There is:
- 100mg in a mug of instant coffee
- 140mg in a mug of filter coffee
- 75mg in a mug of tea (green tea can have the same amount of caffeine as regular tea)
- 40mg in a can of cola
- 80mg in a 250ml can of energy drink
- less than 25mg in a 50g bar of plain dark chocolate
- less than 10mg in a 50g bar of plain milk chocolate
Alcohol
Drinking alcohol in pregnancy can lead to long-term harm to your baby.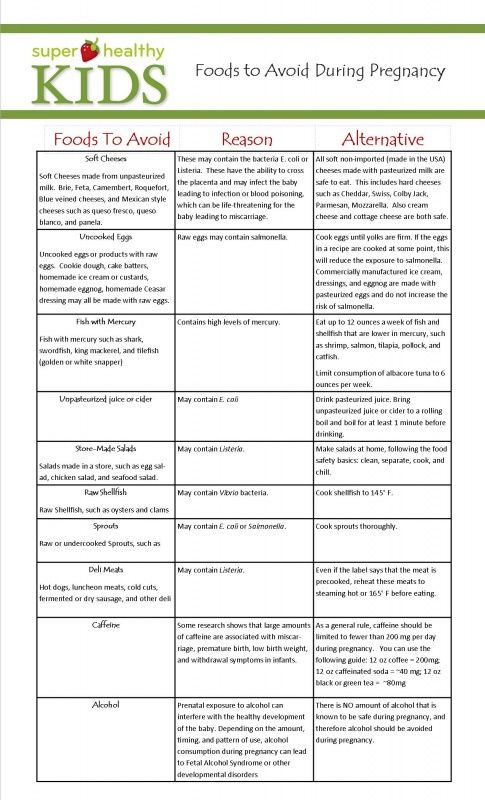
If you're pregnant or planning to get pregnant, the safest approach is to not drink alcohol at all.
This keeps risks to your baby to a minimum.
Herbal teas
You should drink no more than 4 cups of herbal tea a day.
Liquorice
Liquorice is safe to eat. But you should avoid liquorice root.
Fruits, vegetables and salads
Be careful with fruits, vegetables and salads as they can have soil on them, which can make you unwell.
Make sure to thoroughly wash all fruits, vegetables and salad ingredients.
Peanuts
You do not need to avoid eating peanuts when you're pregnant.
Only avoid eating peanuts if you're advised to by a healthcare professional or if you have a nut allergy.
Vitamins
Do not take high-dose multivitamin supplements, or any supplements with vitamin A in them.
Urgent advice: Call 111 if:
- you feel unwell after eating one of the foods to avoid
- you have signs of listeriosis or toxoplasmosis infection
Try not to worry if you've eaten one of the foods to avoid.
Get Start4Life pregnancy and baby emails
Sign up for Start4Life's weekly emails for expert advice, videos and tips on pregnancy, birth and beyond.
Page last reviewed: 16 April 2020
Next review due: 16 April 2023
Proper nutrition during pregnancy - what you can and can't eat
search support iconSearch Keywords
Shopping Cart
There are currently no items in your shopping cart.
- {{#each curatedBundle.items}}
- {{#if miniCartProductpath}} {{/if}} {{#if miniCartProductpath}} {{/if}}
{{#if miniCartProductpath}} {{/if }}
{{#iff curatedBundleQuantity 'gt' '1'}} {{curatedBundleQuantity}} x {{/iff}} {{#if familyName}} {{familyName}} {{/if}} {{#if descriptor}} {{descriptor}} {{/if}}
{{#if miniCartProductpath}} {{/if}}
{{/each}} {{#if isPersonalizedBundle}}
{{#if curatedBundle.price}}
{{curatedBundle.price }}
{{curatedBundle.discountPrice}}
{{/if}}
{{/if}} {{#if isSubscriptionBundle}}
{{#if curatedBundle.displayPrice}}
{{curatedBundle.displayPrice}}
+{{curatedBundle.displayRecurringCharge.totalFormattedValue}} / {{curatedBundle. ratePlanDuration}}
ratePlanDuration}}
{{/if}}
{{/if}} {{/if}} {{#if isBundle}} {{#each bundle}}
{{#if bundle.label}}{{bundle.label}}{{else}}Bundled Item{{/if}}
{{#if totalPrice}} {{#if formerPrice}}
{{formerPrice}}
{{/if}}
{{totalPrice}}
{{/if}}
{{/each}} {{/if}} {{#if isSingleItem}}
-{{discountValue}}
{{/if}}{{#if miniCartProductpath}}
{{/if}}{{#iff quantity 'gt' '1'}} {{quantity}} x { {/ff}} {{#if familyName}} {{familyName}} {{/if}} {{#if descriptor}} {{descriptor}} {{/if}}
{{#if miniCartProductpath}}{{/if}} {{#if sellerName}} {{soldBySiteText}} {{sellerName}} {{/if}}
{{#if totalPrice. formattedValue}} {{#if formerPrice.formattedValue}}
formattedValue}} {{#if formerPrice.formattedValue}}
{{formerPrice.formattedValue}}
{{/if}}
{{totalPrice.formattedValue}}
{{/if}}
An error occurred while deleting an item from the cart. Try again
{{/if}} {{/each}}
{{#iff cart.attributes.pricing.orderDiscountNoDelivery.value 'gt' 0}}
Discount: - {{cart.attributes.pricing.orderDiscountNoDelivery.formattedValue}}
{{/ iff}}
Shipping cost: {{#iff cart.attributes.pricing.totalDelivery.value 'gt' 0}} {{cart.attributes.pricing.totalDelivery.formattedValue}} {{else}} FREE {{/iff }} nine0003
Subtotal: {{cart.attributes.pricing.total.formattedValue}}
A woman's body has everything it needs to bear a healthy baby. However, good nutrition and the rejection of certain foods will help Mother Nature better fulfill this mission. What are the features of nutrition during pregnancy? Is it not enough to just eat well? What foods should you eat during pregnancy? Which foods should be limited, and which should be avoided completely? In this article, you will find answers to all your questions, as well as get important tips on nutrition during pregnancy. nine0003
What are the features of nutrition during pregnancy? Is it not enough to just eat well? What foods should you eat during pregnancy? Which foods should be limited, and which should be avoided completely? In this article, you will find answers to all your questions, as well as get important tips on nutrition during pregnancy. nine0003
Our goal is to help you, but remember that every pregnancy is different and the best advice is no substitute for a visit to the doctor. Be sure to consult with your doctor about changes in your diet.
Products, which should be abandoned during pregnancy
The good news is that good nutrition during the pregnancy is not much distinguished from healthy foods. Try to eat regularly and eat more natural, organic foods such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. Minimize high-sugar and processed foods on your table. nine0003
Minimize high-sugar and processed foods on your table. nine0003
To be safe, avoid raw or undercooked meats, liver, sushi, raw eggs, soft cheeses, and unpasteurized milk and juices. Below we detail what foods to avoid during pregnancy 1,2,3 .
- High mercury fish, raw fish and seafood
Avoid high mercury fish such as macaira, swordfish, mackerel, whitefin tuna and tilefish. Canned diet tuna is allowed in moderation. nine0003
Disappointing sushi lovers: Raw fish and seafood are also among the foods prohibited during pregnancy, as they may contain bacteria or parasites. Smoked seafood should also be excluded from the menu.
- Unpasteurized soft cheeses
Soft cheeses such as feta, brie or camembert are also on the list of foods that pregnant women should not consume. They are made from raw milk and can therefore be contaminated with Listeria 4 .
Practical tip: Look for the label that says the product has been pasteurized!
- Unpasteurized milk and juices
The same rule applies to juices and milk. Freshly squeezed and any unpasteurized juices may contain pathogenic bacteria (E. coli, listeria, salmonella) 5 and should not be consumed during pregnancy.
- Raw eggs
The list of foods that should not be consumed during pregnancy includes raw eggs, as well as foods containing raw protein or yolk - pastry dough, soft-boiled eggs and scrambled eggs. Be wary of foods that contain undercooked eggs. These are salads, sauces, eggnog and ice cream. During pregnancy, you can only eat hard-boiled or pasteurized eggs.
- Undercooked, undercooked or raw meat and poultry
Raw meat and undercooked meat may be contaminated with listeria. It is better to play it safe and not to eat semi-finished meat products during pregnancy. Alternatively, steam them up. Chilled pâtés and meat spreads are also taboo. For whole cuts of meat, make sure they have been thoroughly cooked before eating.
- Raw or undercooked sprouts
Eating raw sprouts of alfalfa, radish, clover, legumes or any other plant may cause various foodborne illnesses. Sprouts should be cooked to reduce the risk of bacterial contamination. 6 Unwashed fruits and vegetables and store-bought salads pose the same danger.
Foods to be restricted during pregnancy
Some products are not on the prohibited list. But if you want to stay healthy and happy while expecting a baby, it is better to reduce their consumption to a minimum:
- Fresh meat with stuffing
Be careful with stuffed meat. If you decide to buy a whole stuffed bird, make sure the meat is frozen. Bacteria can grow in fresh stuffed meat 7 .
- Sweets, carbohydrates and fast foods
Despite the lack of convincing scientific evidence, sweets, fast food and products with a high content of the residues are usually led by a “wish list” expectant mothers. If you are one of the women who experience cravings for certain foods during pregnancy, try to find a healthy alternative. Do you always crave fried potatoes? Fry food in a small amount of oil or without oil in the multi-oven. This approach will allow you to enjoy delicious fried food, which contains 90% less fat*. However, remember that a balanced, healthy diet plays an important role in your safety and the safety of your unborn child.
- Too much caffeine
During pregnancy, it is important not only to avoid certain foods. You should also pay attention to what you drink. Drinks with a high content of caffeine are banned.
Drinks with a high content of caffeine are banned.
The World Health Organization recommends that pregnant women who drink caffeinated beverages (more than 300 mg per day) reduce their daily caffeine intake to reduce the risk of miscarriage and neonatal weight loss 8 .
Healthy nutrition tips for expectant mothers
Pregnancy is a time of intensive growth and development of the baby. The physiological changes that occur in your body and properly organized nutrition will help turn this process into an exciting journey. Discuss your diet with your doctor. This will ensure that you are taking in the right amounts of the right nutrients. Here are some basic rules for a healthy, balanced diet during pregnancy:
- Eat whole grains such as whole grain bread and pasta, opt for lean meats or poultry, and aim for 230-350 grams of boiled fish per week (remember to choose fish with a low mercury content).

- Make sure your diet includes five main food groups: grains, fruits, vegetables, protein and dairy products. ukti. The other half - whole grain products 9 . Half of the conventional plate should be vegetables and fruits. The other half is whole grains. nine0014
- Talk to your doctor about your diet and the need for prenatal vitamins and minerals, especially folic acid and iron. During pregnancy, women experience an increased need for vitamins and trace elements, and it is often difficult for them to get everything they need from food.
- Choose foods rich in mono- or polyunsaturated fats, such as olive oil and avocados, and limit foods high in saturated fats and empty calories, such as candy and sugary drinks. nine0014
Remember: Before making any changes in your diet, be sure to consult your doctor.
* Compared to fried potatoes cooked in a conventional deep fryer.
- https://www.foodsafety.
 gov/risk/pregnant/chklist_pregnancy.html
gov/risk/pregnant/chklist_pregnancy.html
- https://www.fda.gov/food/people-risk-foodborne-illness/safe- eats-food-safety-moms-be
- https://www.fda.gov/media/83740/download
- https://www.fsis.usda.gov/wps/portal/fsis/topics/food-safety-education/get-answers/food-safety-fact-sheets/foodborne-illness-and-disease/protect- your-baby-and-yourself-from-listeriosis/CT_Index
- https://www.foodsafety.gov/risk/pregnant/chklist_pregnancy.html
- https://www.foodsafety.gov/keep/types/fruits /sprouts.html
- https://www.fda.gov/food/people-risk-foodborne-illness/safe-eats-food-safety-moms-be
- https://www.who.int/ elena/titles/caffeine-pregnancy/en/ get 25% off your next purchase
You are leaving the Philips Healthcare (“Philips”) official website. Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you.
 Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain.
Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain. I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
Continue
You are about to visit the Philips USA website.
I understand
8 foods that pregnant women should not eat
June 15, 2019 Likbez Health
Even scrambled eggs and healthy fish oil can do harm.
If you are pregnant, you should reduce the amount of coffee and avoid alcohol altogether. Everyone knows this.
But there are far more insidious foods. At first glance, they seem innocent and even useful. But in fact, they can harm mom or an unborn baby more than a couple of cups of double espresso three times a day. nine0003
Here is a list of popular foods to avoid during pregnancy. Or at least think twice before you eat.
1.
 Raw eggs
Raw eggs As well as products containing them: eggnog, homemade mayonnaise, raw dough, poached eggs, fried eggs with raw yolk, tiramisu.
What is the danger
One word is enough: salmonellosis. This acute intestinal infection is fortunately not fatal, but is accompanied by severe diarrhea and vomiting that can cause dehydration. But this is already bad: the normal blood supply to the fetus and the level of amniotic fluid in the uterus depend on the amount of moisture. Water deficiency can result in violations in the development of the unborn baby, as well as an increased risk of miscarriage. nine0003
What to do
If you have no strength to give up eggs, make sure that they are thoroughly washed and heat-treated. Hard boiled eggs, scrambled eggs, baked goods are safe.
2. Raw meat
As well as rare fried steaks (“with blood”), raw smoked and cured sausages, poorly fried minced meat, for example, in fast food.
What is the danger
Raw meat can be infected with parasites.
 For example, Toxoplasma. They are able to penetrate the placental barrier and cause serious disturbances in the development of the unborn baby. nine0003
For example, Toxoplasma. They are able to penetrate the placental barrier and cause serious disturbances in the development of the unborn baby. nine0003 What to do
Removing parasites from meat is easy - heat it properly. If we are talking about dried or smoked products, freezing them for four days will help reduce the risk.
3. Raw fish
Be especially careful with river and wild ocean fish, shellfish (oysters, mussels), dried, smoked fish of all kinds and sushi.
What is the danger
The range of troubles that you can get by eating a roll or dried perch is wide:0003
- like meat, fish can be infested with parasites;
- Pathogenic bacteria are also found in the pulp - for example, Listeria or Botulinum bacteria, which cause deadly botulism (including for the mother);
- river fish can be caught in chemically polluted reservoirs - and all toxic substances will go to both mother and baby;
- oceanic fish accumulate mercury.
 Shark, swordfish, king mackerel and tilefish are especially dangerous in this regard. Mercury poisoning affects the health of both the mother and the unborn baby - this element can cause brain damage and developmental delays. nine0014
Shark, swordfish, king mackerel and tilefish are especially dangerous in this regard. Mercury poisoning affects the health of both the mother and the unborn baby - this element can cause brain damage and developmental delays. nine0014
What to do
Eat only properly cooked fish. You can take a chance with canned food: just keep an eye on the expiration date and in no case use the product from swollen cans.
4. Liver
As well as liver pate and sausage, cod liver oil.
What is the danger
Too much vitamin A. Its excess can lead to the development of birth defects in the fetus.
What to do
Do not abuse liver products. Especially if for some reason you are taking vitamin A supplements. Yes, and in no case should you prescribe vitamins and supplements for yourself - only your doctor can do this. nine0003
5. Soft cheeses
Special attention:
- soft cheeses with white mold - brie and camembert;
- blue cheeses - gorgonzola, roquefort, danish blue.

What is the danger
Due to the high humidity and mold, such cheeses are an ideal environment for the development of all kinds of bacteria, including those dangerous to the fetus. The same listeria, once in the body of a future baby, can provoke severe developmental disorders, miscarriage or stillbirth. nine0003
What to do
The ideal option is to switch to hard cheese (cheddar, parmesan, stilton and others): it is safe. Soft cheeses can also be consumed, but only if they are made from pasteurized milk. These are mozzarella, feta, ricotta, cream cheeses, halloumi, processed cheeses.
6. Unpasteurized milk
As well as yogurt and ice cream prepared from it.
What is the danger
All in the same high risk of bacteria content. Unpasteurized milk is a product that has not undergone heat treatment. Therefore, the same listeria, which is deadly for the unborn child, can be found in it. nine0003
What to do
Try to drink only pasteurized milk.
 If for some reason only raw is available, be sure to boil it before drinking.
If for some reason only raw is available, be sure to boil it before drinking. 7. Caffeinated products
In addition to coffee, this includes green tea, chocolate, cola, energy drinks, and some cold and flu medications.
What is the danger
An excess of this substance can cause the baby to have a low birth weight - and this increases the risk of health problems later. Sometimes the abuse of caffeine products provokes a miscarriage. nine0003
What to do
You don't have to cut out caffeine completely, you just need to go no more than 200 mg per day. In order not to cross the line, be guided by approximate values:
- 1 cup of instant coffee - 100 mg of caffeine;
- 1 cup espresso - 140 mg;
- 1 cup tea - 75 mg;
- 1 can cola (330 ml) - 40 mg;
- 1 Energy Drink (250 ml) - 80 mg;
- 50 g dark chocolate - up to 25 mg;
- 50 g milk chocolate - up to 10 mg.
Once again, we emphasize: these are approximate figures.