What is considered full term for twins
Twin Pregnancy: Answers from an Expert
Twin Pregnancy: Answers from an Expert | Johns Hopkins MedicineReviewed By:
When you’re expecting twins, you know you’ll need two of everything for your registry. But what about staying healthy during your pregnancy? Do you need to double your food intake, weight gain and visits to the doctor? With regard to the babies, are there two placentas and two amniotic sacs, or can they share these?
Johns Hopkins maternal-fetal medicine specialist Jeanne Sheffield answers eight commonly asked questions.
Do twins share a placenta and an amniotic sac?
While some twins may share a placenta and an amniotic sac, that is not the case for the vast majority of pregnancies. Here are three major possibilities that exist:
- Two placentas and two amniotic sacs.
A twin pregnancy with two placentas and two amniotic sacs is the optimal twin pregnancy, as each baby has its own nutritional source and protective membrane.
- One placenta and two amniotic sacs. In pregnancies with one placenta and two amniotic sacs, you will definitely have identical twins. Additionally, when your babies share a placenta, there is a greater risk for complications, such as twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome. Your physician will closely monitor your pregnancy to check for potential problems.
- One placenta and one amniotic sac. This is the riskiest and rarest type of twin pregnancy. Fetal complications can arise due to tangling of the umbilical cords or an imbalance in nutrients, blood or other vital life supporting systems.
- Two placentas and two amniotic sacs.
Do I need to double my caloric intake during a twin pregnancy?
A common misconception surrounding twin pregnancy is that you need to double your caloric intake to provide your babies with enough nutrients.
 However, pregnancy nutrition guidelines aren’t simply based on the number of babies you’re carrying. Instead, they’re based on your body mass index at the time you became pregnant.
However, pregnancy nutrition guidelines aren’t simply based on the number of babies you’re carrying. Instead, they’re based on your body mass index at the time you became pregnant. Your doctor will make individualized recommendations based on your starting weight. On average, it’s estimated that a woman’s caloric requirements will increase about 40 percent for a twin pregnancy. What’s most important, though, is that a woman eats as healthy as possible.
Do I need to take different prenatal vitamins for twins?
If you’re pregnant with twins, you should take the same prenatal vitamins you would take for any pregnancy, but your physician will recommend extra folic acid and iron. The additional folic acid and extra iron will help ward off iron-deficiency anemia, which is more common when you’re pregnant with multiples.
Will I need to visit my doctor more frequently?
While every pregnancy is different, most women carrying twins will have more frequent prenatal visits than women carrying only one baby.
 If your twins are sharing one placenta, you will automatically have a more frequent monitoring schedule.
If your twins are sharing one placenta, you will automatically have a more frequent monitoring schedule. If your pregnancy doesn’t have complications, your prenatal visits may not differ much from a singleton pregnancy until you get to the end of your second trimester. At that point, you’ll be seen more frequently because there is a higher risk of pre-eclampsia and preterm labor.
Do I have to see a maternal-fetal medicine specialist for a twin pregnancy?
Maternal-fetal medicine specialists see high-risk pregnancies, but not every twin pregnancy will fall into this category.
To find the best care provider for your twins, make sure that the physician is comfortable managing twins, including vaginal delivery of twins rather than only offering a cesarean section (C-section) for delivery.
Are all twin pregnancies delivered preterm?
A little more than half of twin pregnancies end in preterm delivery (before 37 weeks).
 While 40 weeks is the full gestation period of the average pregnancy, most twin pregnancies are delivered at approximately 36 weeks (range 32-38 weeks depending on the type of twin pregnancy).
While 40 weeks is the full gestation period of the average pregnancy, most twin pregnancies are delivered at approximately 36 weeks (range 32-38 weeks depending on the type of twin pregnancy). Unfortunately, preventing preterm labor with multiples is more challenging than with a singleton pregnancy because the interventions used with singleton pregnancies are not as effective with multiples.
Can bed rest reduce the risk of preterm delivery?
Scientific data show that bed rest does not prevent preterm delivery. In fact, bed rest can increase your risk of developing blood clots and have negative financial and social consequences.
Although bed rest is not prescribed as frequently as it once was, your doctor may suggest reducing your activity level if you’re showing signs of early labor at the end of your second trimester or early in your third trimester.
Is labor and delivery significantly different with twins?
Labor is generally the same whether you’re having one baby or two.
 During delivery is when things differ significantly.
During delivery is when things differ significantly. When it’s time to deliver your twins, you will go to an operating room even if you are delivering vaginally. This is a safety precaution known as a double setup. Following the vaginal delivery of the first baby, there is a small risk of an emergency cesarean section for the second baby. There is also the possibility of the second twin being delivered breech, which is a safe form of vaginal delivery if the obstetrician is experienced in this type of delivery.
Of women giving birth to twins over 32 weeks, only about 4 percent who try for a vaginal delivery will have a combined vaginal and cesarean section delivery. While it doesn’t happen very often, by delivering both babies in the operating room, physicians are better prepared to protect the health of the mother and the babies.
Although being pregnant with twins can seem very different, your doctor will treat your pregnancy like any other unless a complication occurs.

Sign Up for Our Free Newsletter
One of the best things you can do to protect and improve your health is to stay informed. Your Health is a FREE e-newsletter that serves as your smart, simple connection to the world-class expertise of Johns Hopkins.
Sign Up
Related
-
Fertility, Pregnancy and Childbirth
Complications of Pregnancy
-
Planning a Pregnancy
How to Prepare for Pregnancy
-
Sexual and Reproductive Health
Anatomy of Female Pelvic Area
Related Topics
What is Full Term for Twins? » TwinStuff
For mothers who are about to give birth to twins, the last trimester is imminently the time to be extra cautious. Because this last stretch can be a bit more stressful, knowing precisely when the full term for twins is will significantly bring a sense of comfort especially when mothers are especially particular about preterm labor and essential preparations.
Because this last stretch can be a bit more stressful, knowing precisely when the full term for twins is will significantly bring a sense of comfort especially when mothers are especially particular about preterm labor and essential preparations.
This article will give helpful insight as to knowing just when your twins are ready to pop out of the oven as well as the essentials to pre and post-natal care.
How Many Weeks is a Full Term Pregnancy for Twins?
Pregnancy Day By Day editor-in-chief Maggie Blott, M.B.,B.S., reports that there are about 1 in 31 twin births in the United since the 80’s. Among those births, more than half of the twins delivered were born at about 37 weeks, which is considered normal and healthy when giving birth to multiples.
Baby Center UK says, the average timeline for twin pregnancies is about 36.4 weeks and doctors consider 37 weeks as the full term pregnancy for twins. Babies born within this time (32 to 37 weeks) have no complications and actually do well.
Preparing for the Arrival of Your Twins
Since multiples are born earlier compared to singletons, it is important to already have a hospital bag packed as early as the 26th week of pregnancy. During the wait time, the Twins and Multiple Births Association (TAMBA) advises thinking about how you would want to feed your babies.
It is important to inquire and attend antenatal classes specifically for twin pregnancies. These classes include sessions on how to breastfeed more than one child. Being able to know the merits of bottle feeding, breastfeeding, or the mixed approach is also very helpful.
How to Take Care of Yourself and Your Twins
When pregnant with twins or multiples, there are a lot of changes that go through until you reach full term. One of which is that weight gain is rapid as early as the first trimester.
The vomiting and nausea can be pretty intense, as well as the pain of breast tenderness. Such physical changes call for extra TLC, so it is important to always have someone with you at home during these times.
Another important thing to note according to The Office on Women’s Health is to visit your doctor. With twins, visits to the doctor will happen more often than those moms who are pregnant with singletons.
Mothers who carry twins have a higher risk of low birth weight, preterm birth, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia and cesarean birth. To avoid complications, frequent prenatal visits are a must. Doing so, allows your doctor to monitor the health of your twins, including your own.
Close monitoring will give you the best chance of having your babies being born full term and at a healthy weight. Plus, you will be able to know the vitamins you need and what activities are unsafe during the pregnancy. In short, your doctor is your best friend at this critical time.
Taking care of yourself as a mom is important to have happy and healthy twins
What if I Give Birth Early? What Should I Know About Pre-Term Labor?
It is important to know the signs of preterm labor in order to avoid complications and be able to get help on time. Since preterm labor is “silent,” being aware of your body is key. The first thing to be keen with is contractions. If you experience these symptoms, be sure to contact your doctor as soon as possible:
Since preterm labor is “silent,” being aware of your body is key. The first thing to be keen with is contractions. If you experience these symptoms, be sure to contact your doctor as soon as possible:
- Having four or five contractions in an hour
- Pressure in the pelvic area that is persistently rhythmic
- An aching back
- Experiencing cramps
There are also other signs of preterm labor like diarrhea and vaginal discharge or bleeding. Any discharge that looks streaked or bloody may mean that the cervix is about to dilate.
If you feel a gush of fluid or a leak from the vagina, this too can mean that the membranes have prematurely ruptured. This fluid is from the amniotic sac and when it breaks, the fluid gushes through the vagina. Finally, another symptom is that certain gut-feel that something is just not right. When things like these happen, go straight to your doctor.
After Giving Birth, What Now?
Although the pregnancy and delivery can be a cause of worry, it is essential to look forward to what happens next- your twins’ arrival! This is a joy for any mom but then, take note that care is still very much needed.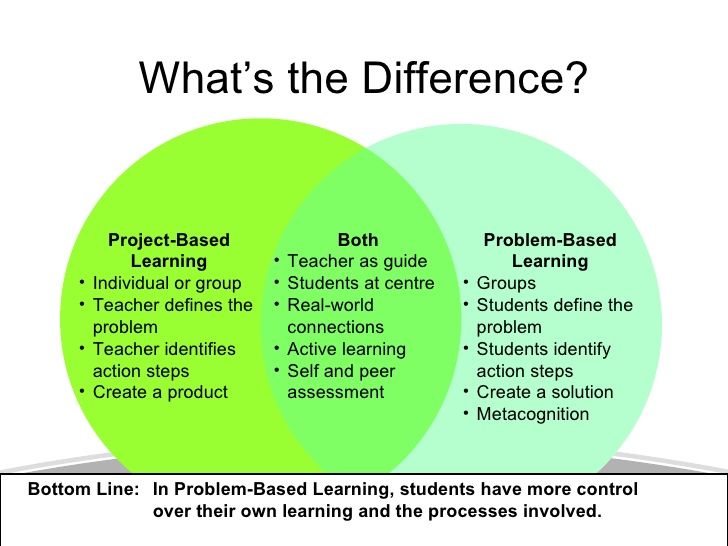 Because your body is still recovering, you’d definitely need to do a number of changes at home.
Because your body is still recovering, you’d definitely need to do a number of changes at home.
To allow ample rest, limit the number of visitors at home. Be sure to have some extra hands to help with preparing meals and cleaning up the house. Eat healthily. Drink a lot of water and take in a lot of fiber to avoid constipation. Prevent swelling in your legs by putting your feet up and to avoid vaginal discomfort, sit in a warm bath. Whenever the need arises, apply nipple cream to sore breasts to soothe the pain.
Always be in check with your emotional health. If you feel sad, be sure to open up to your partner and family. If the sadness doesn’t seem to go away, be sure to call your doctor. Take all the rest you can whenever possible. Your babies always need you at your best.
There is nothing like the joy of giving birth and being a mom.
Even if this brings a number of physical and emotional changes, being ready with the essentials throughout the journey of pregnancy to giving birth is a must and will be a source of comfort early on. From knowing when the full term for twins is, doing necessary preparations, being emotionally ready, and of course realizing complications and risks, achieving a safe and healthy pregnancy is more than possible.
From knowing when the full term for twins is, doing necessary preparations, being emotionally ready, and of course realizing complications and risks, achieving a safe and healthy pregnancy is more than possible.
Management of multiple pregnancy - clinic Family Doctor
Doctors
Clinic doctors
Multiple pregnancy is not only a great happiness, but also an increased burden on the body of the expectant mother. Therefore, special standards apply for its management: more frequent visits to the gynecologist and an extended examination, other recommendations regarding lifestyle.
It is good if the management of multiple pregnancy begins with its early diagnosis. The sooner this fact is revealed, the higher the chances of drawing up the most successful management plan and timely implementation of measures to prevent possible complications. For patients who plan to conceive and are at risk for multiple pregnancies, it is extremely important to start monitoring immediately after a successful conception.
Why multiple pregnancy occurs
The probability of multiple pregnancy is significantly higher in some categories of patients:
- heredity;
- women planning to conceive after giving up hormonal contraceptives;
- women over 35;
- those who have congenital non-standard structural features of the uterus;
- expectant mothers who have taken advantage of the possibilities of modern reproductive technologies (IVF procedure, etc.).
The number of fetuses can be any, as a rule, we are talking about twins or triplets. There are identical (fertilization of one egg, the birth of identical twins) and twin pregnancies. In the second case, two (or more) eggs are fertilized, as a result, different children are born. It is this case that is more often caused by the woman's age, interference in the reproductive processes (IVF, ovulation stimulation, the abolition of COCs). These factors lead to more active work of the ovaries, as a result of which several eggs mature in one menstrual cycle at once.
How and for how long is diagnosed
Early diagnosis is the key to a healthy, successful and full-term multiple pregnancy. The doctor can establish the fact of the presence of two or more fetuses for a short period of time, up to 5 weeks.
The basis for suspecting a larger number of fruits is an examination. The volume of the uterus will be larger than for the expected period. Without fail, a woman takes an analysis for hCG in dynamics - the level of human chorionic gonadotropin, growing at a fast pace, is a sign of multiple pregnancy. Subsequently, during palpation, the doctor will determine the parts of several fetuses, and when listening to heart sounds, they will be observed in different parts of the abdomen.
Driving features
Conducting multiple pregnancy is carried out with special attention. Features of observation when carrying two or more babies are as follows:
- relatively more frequent visits to the obstetrician-gynecologist: 1 time in 14 days up to 30 weeks and every week until childbirth;
- the appointment of increased doses of vitamins, minerals;
- a more rigorous assessment of the dynamics of weight gain: an increase of no more than 25 kg is considered normal;
- drawing up a special plan for physical activity, its significant reduction from 20-25 weeks;
- more frequent ultrasound, which is associated with the need to assess the dynamics of fetal development and take measures in case of delay, as well as to prevent the threat of preterm birth.
 It is important to assess the condition of the placenta in order to timely determine the compliance of its changes with the gestational age;
It is important to assess the condition of the placenta in order to timely determine the compliance of its changes with the gestational age; - the appointment of drugs that prevent common complications (fetoplacental insufficiency, anemia, preeclampsia, etc.).
Recommendations and standards
There are special standards for the management of two, three and more pregnancies. Immediately after the diagnosis, the doctor will develop a regimen of physical activity and nutrition. This will ensure the high needs of the expectant mother in proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals, as well as maintain normal health in conditions of high stress on the spine.
Particular attention is paid to the functions of the heart and blood vessels, kidneys. Therefore, the patient more often gives urine tests, additional consultation with a cardiologist, nephrologist, urologist may be required.
The high risk of preterm birth obliges to monitor the slightest changes. If the patient feels well and there are no complications, she is sent to the maternity hospital 2-3 weeks before the preliminary date of delivery. If we are talking about triplets, in 4 weeks.
If the patient feels well and there are no complications, she is sent to the maternity hospital 2-3 weeks before the preliminary date of delivery. If we are talking about triplets, in 4 weeks.
At 30-34 weeks, the likelihood of preterm birth is especially high, which is associated with maximum tension and stretching of the uterus. In addition, shortening and partial opening of the cervix is often observed. The doctor will definitely recommend bed rest if necessary, which will increase the chances of carrying it to the due date. Drugs that relieve muscle spasm, as well as tocolytics, drugs that affect the contractile activity of the uterus, can be prescribed.
FPI or fetoplacental insufficiency is more often observed precisely when carrying several fetuses. Abnormal location of the placenta is also common. This obliges to regularly monitor the condition of the fetus and placenta: perform Doppler ultrasound, CTG. So, starting from the 30th week, it is better to do this once every 7 days until delivery. An experienced specialist should evaluate the blood flow in each fetus individually. FPI can be prevented with the help of preventive drug therapy: drugs that improve uteroplacental, fetoplacental blood flow, antioxidants, metabolic drugs, etc.
An experienced specialist should evaluate the blood flow in each fetus individually. FPI can be prevented with the help of preventive drug therapy: drugs that improve uteroplacental, fetoplacental blood flow, antioxidants, metabolic drugs, etc.
Features of delivery
Delivery can be natural or by caesarean section. In the absence of pathologies and complications, the presence of two fetuses, favorable examination results, a natural option is allowed. Indications for operative delivery are as follows:
- clinically narrow pelvis;
- features of the presentation of one of the fetuses;
- transverse arrangement of one or both babies;
- signs of hypoxia in at least one fetus;
- pregnancy complications in the mother.
These indications are more often related to the planning of the operation. An emergency cesarean may be required after the onset of labor. The doctor makes a decision based on the situation. In some cases, the first child is born naturally, and the second through surgery.
In some cases, the first child is born naturally, and the second through surgery.
The presence of three or more babies is a direct indication for a planned operation. This will significantly reduce the likelihood of complications for both mother and children.
You can apply for a comprehensive pregnancy management service to experienced obstetrician-gynecologists at the Family Doctor clinic. Modern equipment with diagnostic equipment, highly qualified doctors, the ability to undergo all the necessary examinations in one place - all this is the standard for providing high-quality medical care to an expectant mother.
You can make an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist at the Family Doctor clinic, a specialist in multiple pregnancy, by calling the contact center in Moscow +7 (495) 775 75 66 or through the online registration form.
Information verified and confirmed by an obstetrician-gynecologist at the Family Doctor clinic
Obstetrician-gynecologists
On medical records
Gravchikova Tatyana Petrovna
Akusher-gynecologist, doctor of ultrasound diagnostics, leading specialist of the clinic
Clinic on Novoslobodskaya
On Doerading
Zakharova0003
Clinic for Novoslobodskaya
On medical records
Zekhareva Marina Mikhailovna
Akusher-gynecologist, an ultrasonic diagnostic doctor, leading specialist of the clinic
Clinic on Ozerkovskaya
On Medimina Valeriyevna Kokareva
ultrasound diagnostics, leading specialist of the clinic
Clinic on Usacheva
About doctor Record
Kuzina Anastasia Vadimovna
Acusher-gynecologist, Ultrasound diagnostic doctor
Clinic at Baumanskaya
On medical recording
Rodyukova Anna Vadimovna
Akusher-Gynecologist, Ulzosvuki Diagnostics Doctor 9000 obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound specialist
Novoslobodskaya Clinic
leave feedback
Features of adaptation and development of premature babies.
 Medical Center Doctor Plus
Medical Center Doctor Plus The first year of a child's life is characterized by the most intensive growth and rapid development. But during this period, the body is extremely vulnerable, the defenses are weak and imperfect. This is especially true for children who were born prematurely and are considered premature.
Premature are children born at gestational age from 28 to 37 completed weeks, weighing from 1000 - 2500 grams, height 35 - 45 cm.
The reasons for their premature birth are varied: too young age and, accordingly, the mother's body; hemolytic disease of the fetus, which develops as a result of Rhesus conflict; pathological (not normal) course of pregnancy; previous abortions, illness, physical and mental trauma; harmful working conditions, the use of nicotine and alcohol.
What a premature baby looks like. Anatomical and physiological signs.
There are 4 degrees of prematurity, depending on the weight of the child:
Grade 1: 2500 -2001 grams Grade 3: 1500 - 1001 grams
Grade 2: 2000 – 1500 grams Grade 4: 1000 grams or less.
Since body weight may or may not correspond to the gestational age at the time of birth, premature babies are divided into 2 groups also according to these signs
• children whose physical development corresponds to the gestational age at the time of birth;
In premature babies, the subcutaneous fat layer is not sufficiently developed, i.e. they suffer more from overheating and hypothermia. The skin is thin, dry, wrinkled, abundantly covered with fluff. Insufficient maturity of blood vessels is manifested by the Harlequin symptom. If you put the baby on its side, the skin acquires a contrasting pink color.
The bones of the skull are malleable, not only a large, but also a small fontanel is open.
The auricles are soft - the cartilage in them has not yet formed, they are pressed to the head, and not separated from it, as in full-term ones.
The nails do not reach the edge of the phalanges of the fingers, the umbilical cord is located below the middle of the body, and not in the center.
The underdevelopment of the genital organs is indicative: in girls, the labia minora are not covered by the large ones. In boys, the testicles are not descended into the scrotum.
The child sucks badly, swallows with difficulty. The cry is weak, breathing is not rhythmic. Physiological jaundice often lasts up to 3-4 weeks.
The umbilical cord falls off much later, and the umbilical wound heals more slowly.
It has its own characteristics and physiological weight loss. It is restored only by 2-3 weeks of life, and the timing of weight recovery is directly dependent on the maturity of the child, i.e. not only the date of his birth, but also the degree of adaptation of the baby to environmental conditions.
In premature babies, the nerve centers that regulate the rhythm of breathing are not fully formed. The formation of lung tissue has not been completed, in particular, a substance that prevents the “falling off” of the lungs - Surfactant. Therefore, their respiratory rate is not constant. With anxiety, it reaches 60-80 in 1 minute, at rest and during sleep it becomes less frequent, respiratory arrests may even be observed. The expansion of the lungs due to an insufficient amount of Surfactant is slowed down, and respiratory failure may occur.
Therefore, their respiratory rate is not constant. With anxiety, it reaches 60-80 in 1 minute, at rest and during sleep it becomes less frequent, respiratory arrests may even be observed. The expansion of the lungs due to an insufficient amount of Surfactant is slowed down, and respiratory failure may occur.
The heart rate also depends on the condition of the child and environmental conditions. With an increase in the ambient temperature and the child's anxiety, the heart rate increases to 200 beats per minute.
In premature newborns, asphyxia and cerebral hemorrhage occur more often. They are more likely to suffer from acute respiratory diseases, intestinal infections, which is due to weak immunity and insufficient development of many adaptive reactions.
These babies are more likely than full-term babies to develop anemia (anemia).
Especially during the period when intensive growth and weight gain begins (2-3 months). With proper nutrition of the child and the mother, if she breastfeeds, these phenomena quickly pass.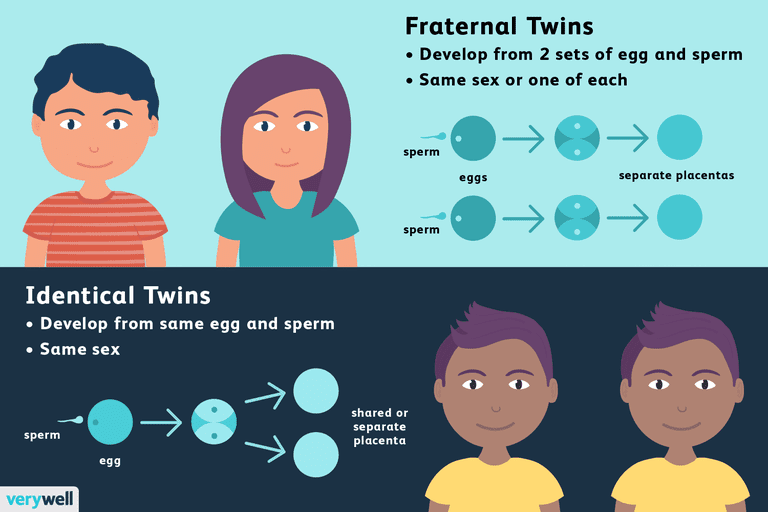 In the case when anemia is of a protracted nature, it is necessary to prescribe iron preparations.
In the case when anemia is of a protracted nature, it is necessary to prescribe iron preparations.
The further development of the child is determined not only by the degree of prematurity, but also in many respects, by the state of his health for a given period of time.
If the child is practically healthy, from the 2nd month of life, he gains weight and height in the same way as full-term ones. By the end of the 1st year, the weight increases by 5-10 times compared to the weight at birth.
The average height is 70-77 cm.
The nervous system of premature babies is also more immature. The development of various skills, their intellectual development lags behind by 1-2 months.
These children sit down later, start walking later, they may have anomalies in the structure of the foot, curvature of the legs, and spine. If children are born very premature and often get sick, their development slows down by about a year. In the future, it levels off, approximately to preschool age.
If you have suffered intrauterine malnutrition, i.e. the nutrition of the fetus was disturbed for some reason - diseases of the mother, anomalies in the development of the child itself, anomalies in the development of the umbilical cord and placenta, then its central nervous system can recover for a long time (therefore, the observation of a neurologist is very important).
There may be lability of the nervous system (mood changes easily, often gives in to emotions, conflicts with other people are not uncommon), night terrors, enuresis (urinary incontinence), lack of appetite, a tendency to nausea.
However, in general, premature babies grow up as quite normal people.
Caring for a premature baby after discharge from the maternity hospital.
For a child born prematurely, dispensary observation is established at the place of residence up to 7 years.
Periodic consultations of specialists are obligatory, first of all - a neurologist, as well as a surgeon, an otolaryngologist, an ophthalmologist
From the age of 2-4 weeks, rickets is prevented (ultraviolet
irradiation - quartzization, the addition of vitamin D to food, massage, hardening).
The most adequate type of nutrition for a premature baby is breastfeeding. But given that the baby can suck out an insufficient amount of breast milk, you can supplement it with expressed milk or adapted mixtures.
From 4 months - vegetable purees, 5 months. - porridge, 6 months. - give meat soufflé.
Correction of protein and fat deficiency is carried out by adding the required amount of kefir and cottage cheese, starting with 5 ml, gradually increasing the dosage.
The room in which a premature baby lives should be bright, dry and thoroughly ventilated. The optimum room temperature is 20-22 *. S. Walks are very important. Sufficient exposure to fresh air prevents the development of pathological conditions.
In winter, walks start from the age of 2 months at an air temperature not lower than -8, -10*C. The duration of the walk is from 15 minutes to 2 hours. In summer, a child can spend all the intervals between feedings during the day in the fresh air.