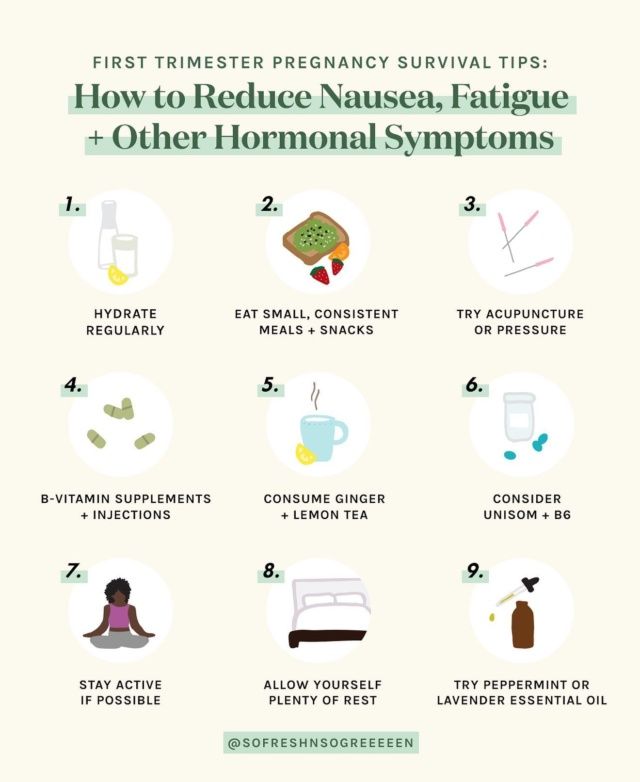
What is colostrum in pregnancy
Antenatal expression of colostrum - reasons for, when and how
Antenatal expression of colostrum - reasons for, when and how | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
During pregnancy, the breasts produce their first milk, known as colostrum. Colostrum is high in antibodies and protective substances that help to support a newborn baby's immunity. Although not much colostrum is produced, it is very high in energy, protein and fat. Colostrum is also easy for newborns to digest.
There can be benefits to expressing and storing colostrum during pregnancy in case it is needed after birth. If there is a risk of premature birth or of your baby having feeding problems, the person providing your maternity care may recommend you express and store some colostrum.
What is colostrum?
Colostrum is a type of early breast milk, produced by the breasts from around 20 weeks of pregnancy until the first few days after birth. Colostrum is a thick, sticky, yellowish liquid. It can leak from the breasts onto the nipples and cause yellow crusts to form. Sometimes colostrum leaks and absorbent nursing pads need to be worn.
When does colostrum appear?
Many pregnant women notice they are producing colostrum earlier than 20 weeks, especially if they’ve been pregnant before. It’s not always obvious that colostrum is being produced until the woman checks.
What are the benefits of expressing colostrum in pregnancy?
There are several benefits from expressing during pregnancy, including:
- helping to support successful breastfeeding after birth — women who express are generally motivated to do all they can to increase their likelihood of exclusively breastfeeding their baby
- building a supply of colostrum is useful in case the baby needs extra feeds and avoids offering formula
- managing potential feeding problems relating to prematurity or a congenital condition
- managing feeds for babies of diabetic mothers where there is a risk of having problems maintaining a normal blood sugar level
- having a store of colostrum if the baby is likely to need special care and is likely to be separated from their mother
Why might there be a low supply of breast milk?
Sometimes there are reasons why a mother’s breasts do not produce as much milk as their baby needs. Storing a small supply of colostrum means the baby can have access to extra kilojoules. These reasons include:
Storing a small supply of colostrum means the baby can have access to extra kilojoules. These reasons include:
- breast surgery or problems with breast growth during pregnancy
- some medical conditions, such as multiple sclerosis or polycystic ovarian syndrome
- a history of having low milk supply
Are there any reasons not to express colostrum during pregnancy?
Not all women are keen or able to breastfeed. Some choose to express colostrum and offer this as well as formula after their baby is born. Although there are benefits in expressing colostrum during pregnancy, there are times when it’s not recommended. There is a risk of premature labour by stimulating the breasts.
Don’t express your breasts if you:
- are at risk of, or have had, threatened premature labour
- have had a cervical suture inserted, or been diagnosed with cervical incompetence
- have experienced bleeding during your pregnancy>
- have been diagnosed with placenta praevia
- have been advised by your maternity care provider not to
- cannot store colostrum safely and hygienically
When and how to express your colostrum
Pick a time when you’re relaxed and feeling calm.
- Wash your hands with soap and water and dry well.
- Using your thumb on top of your breast and your forefingers underneath, gently press your fingers towards your chest.
- Compress the breast tissue, hold briefly and then release. Try not to squeeze or pinch the nipple.
- Collect the colostrum in either a sterile syringe or a clean container.
- Express each breast twice during each expression. You can collect colostrum twice a day in each syringe or container. Between expressions, store the colostrum in the fridge. Label with the date, cap the syringe and put in a plastic bag and into the freezer.
Aim to express 2 to 3 times each day from around 36 weeks of pregnancy. Start gently and slowly, eventually building up to 3 to 5 minutes of expressing on each breast twice each day.
How to store colostrum
| Room temperature (26° C or lower) | Fridge (4° C or lower) | Freezer |
|
|
|
Top 5 tips for expressing colostrum
- Start expressing at around 36 weeks into your pregnancy.
 Stop if at any time you start to feel contractions or vaginal bleeding.
Stop if at any time you start to feel contractions or vaginal bleeding. - Remember that any amount of colostrum will be beneficial to your baby. The amount of colostrum women can express varies widely while they are pregnant.
- Be patient as you learn how to express and store the colostrum safely.
- Take the clearly labelled and frozen colostrum with you (in an esky or cooler bag) when you have your baby.
- Only use your hand, not a pump to express your colostrum.
The person who is providing your maternity care — such as your doctor or midwife — will be able to give you more advice about what’s right for you. Some pregnancy-related conditions increase the risk of premature labour and it’s important not to express colostrum if you’re at risk of having your baby early.
Sources:
Mater Mother's Hospital (Antenatal expression of colostrum), National Health and Medical Research Council (Infant Feeding Guidelines Information for Health Workers), Women and Newborn Health Service (Breastfeeding – antenatal expression of colostrum for women with Diabetes), Queensland Government (Expressing breastmilk)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2021
Back To Top
Related pages
- Storing expressed breast milk
- Expressing and storing breast milk
- Breastfeeding your baby
Need more information?
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
What Is It, Benefits & What To Expect
Overview
What is colostrum?
Colostrum (kuh-loss-trum) is the first milk your body produces during pregnancy. It forms in your mammary glands (breasts) and plays an important role in building your baby's immune system. If you plan on breastfeeding (nursing or chestfeeding), it's the first milk your baby will get from your breasts. If you don't want to breastfeed or if your baby is struggling to breastfeed, you can hand express colostrum. It's high in protein, vitamins, minerals and immunoglobulins (antibodies) that help build your baby's immune system. It's often called "liquid gold" because of its rich, golden color and valuable benefits.
If you don't want to breastfeed or if your baby is struggling to breastfeed, you can hand express colostrum. It's high in protein, vitamins, minerals and immunoglobulins (antibodies) that help build your baby's immune system. It's often called "liquid gold" because of its rich, golden color and valuable benefits.
What is colostrum made of?
Colostrum is high in protein and low in fat and sugar. It's filled with white blood cells that produce antibodies. These antibodies strengthen your baby's immune system, protecting him or her from infection. Colostrum is highly concentrated and nutrient-dense even in tiny doses, so your baby's tummy doesn't need a lot to reap its benefits.
What kind of nutrients are in colostrum?
Colostrum is rich in nutrients that protect and nourish your baby unlike anything else. It's made up of things like:
- Immunoglobulin A (an antibody).
- Lactoferrin (a protein that helps prevent infection).
- Leukocytes (white blood cells).

- Epidermal growth factor (a protein that stimulates cell growth).
It gets its color from carotenoids (an antioxidant) and vitamin A. Vitamin A plays a vital role in your baby's vision, skin and immune system. Colostrum is rich in magnesium, which supports your baby’s heart and bones, and copper and zinc, which also support immunity.
What's the difference between colostrum and breast milk?
Colostrum is a nutrient-rich first milk produced by your breasts during pregnancy. It changes to transitional breast milk a few days after your baby is born. However, small amounts of colostrum remain in your breast milk for several weeks.
There are distinct differences between colostrum and breast milk:
- Colostrum is filled with immunoglobins to boost your baby's immune system and protect it from illness.
- Colostrum has two times as much protein.
- Colostrum has four times as much zinc.
- Colostrum is lower in fat and sugar so it's easier to digest.

- Colostrum is thicker and more yellow.
What are the stages of breast milk?
There are three different stages of breast milk: colostrum, transitional milk and mature milk.
- Colostrum: Your first milk that lasts between two and four days after birth.
- Transitional milk: Begins approximately four days after birth and lasts about two weeks.
- Mature milk: Milk that lasts from approximately 14 days after birth until you are done producing milk.
When does colostrum turn to milk?
After approximately three or four days, colostrum will turn to transitional milk. This is often referred to as someone's milk "coming in." Your breasts will feel firm, tender and full. It means your milk supply has ramped up. By this time your baby's stomach has expanded and they can drink more milk each feeding. Once your milk supply is established and your body has stabilized, transitional milk changes to mature milk.
What makes colostrum turn to breast milk?
The pregnancy hormones created by the placenta help you create colostrum. The hormone progesterone drops significantly when the placenta separates from your uterus (after your baby is born). This drop in progesterone triggers your breasts to create milk.
Function
What is the purpose of colostrum?
The function of your breasts, or mammary glands, is to produce milk to feed your baby. Colostrum is more than the first milk your baby consumes after birth. It's highly concentrated with nutrients and antibodies to fight infection and protect your baby. It provides a powerful, unique immunity that only it can provide. Because your baby only needs a little bit of colostrum, it also helps them learn to suck, swallow and breathe during feeding.
What are the benefits of colostrum?
Colostrum builds your baby's immune system and provides concentrated nutrition. Some of the benefits of colostrum are:
- Helps strengthen your baby's immune system.

- Helps to establish a healthy gut by coating the intestines. This helps keep harmful bacteria from being absorbed.
- Offers ideal nutrition for a newborn.
- Has a laxative effect that helps your baby clear meconium (your baby's first poop) and lessens the chance of jaundice.
- Easy to digest.
- Helps prevent low blood sugar in full-term babies.
Why is colostrum good for newborns?
Colostrum has all the nutrients your baby needs in the first few days of life. It's also packed with nutrients and vitamins to strengthen your baby's immune system.
The flow of colostrum from your nipples is slow so your baby can learn to breastfeed (nurse). Learning how to breastfeed takes practice and requires your newborn to not only learn to suck and swallow but breathe at the same time.
Does leaking colostrum mean labor is close?
Colostrum leaking from your breasts doesn't mean labor is coming. Leaking colostrum is normal and some people notice it as early as the second trimester. Some don't notice any signs of leaking colostrum while others will see dried colostrum on their nipples. If you are leaking colostrum, you can wear disposable or washable breast pads.
Some don't notice any signs of leaking colostrum while others will see dried colostrum on their nipples. If you are leaking colostrum, you can wear disposable or washable breast pads.
Can you express colostrum if you're pregnant?
Colostrum can be expressed by about week 37 in pregnancy and is beneficial for some people. Using your hands to compress your breasts in a rhythmic pattern so that milk comes out is called hand expressing. Expressing colostrum before your baby is born carries some risks like contractions or premature labor. It can be beneficial to those at risk for premature birth, low milk supply or when certain health conditions present.
Speak with your healthcare provider before you remove colostrum from your breasts. If you are leaking colostrum, it may be safe to collect and store it for when your baby is born.
Can you pump colostrum?
It's difficult to pump colostrum with a breast pump because of its thick consistency. Most people recommend and prefer using their hands to express colostrum. Hand expressing colostrum usually produces more colostrum than a pump.
Hand expressing colostrum usually produces more colostrum than a pump.
Anatomy
What does colostrum look like?
Colostrum is often a deep, rich yellow or orange color, almost like the yolk of an egg. This is because it contains high levels of beta carotene. It can sometimes appear white, clear or creamy. It's a thicker consistency than breast milk (or cow's milk), but the thickness varies from person to person. Colostrum is often sticky and can contain faint traces of blood (this is normal).
How do I know I am making colostrum?
Your body begins producing colostrum between 12 and 18 weeks in pregnancy. Most people will produce anywhere from a tablespoon to an ounce of colostrum within the first 24 hours of delivery. This slowly increases until transitional milk comes in around the third or fourth day. In most cases, you will not know if you are making colostrum, however, it's very rare to be unable to produce colostrum. You will know if your baby is getting colostrum if he or she is maintaining their weight and wetting diapers.
How long do you have colostrum?
Your body produces colostrum for up to about five days after your baby is born. It changes to transitional milk around this time, then changes again to mature milk after about 14 days. Traces of colostrum are present in your breast milk for up to six weeks.
Conditions and Disorders
What happens if you don't produce colostrum?
Most people will produce some colostrum — not producing it is rare. It's normal to feel like nothing is coming out of your breasts and worry that your baby isn't getting enough. Your baby only needs a few teaspoons of colostrum to fill their tiny stomach.
Care
How do you store pumped colostrum?
If you and your healthcare provider decide it's safe to express and store colostrum, there are a few rules to follow. First, you should ensure the colostrum is stored in a sterile container or syringe. It can be kept in your refrigerator for about two or three days. It must be moved to a freezer after three days. Colostrum can be kept in a freezer for at least three months.
Colostrum can be kept in a freezer for at least three months.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much colostrum does a newborn need?
Your newborn's tummy is about the size of a marble. They only need about an ounce of colostrum per day. This equals about a teaspoon each feeding (you can expect to feed your newborn eight to 10 times the first few days). The amount of colostrum (and then transitional milk) your baby needs increases slowly each day as their stomach expands. As your body transitions to producing regular breast milk, your milk production will increase to meet their needs.
Do I need to supplement?
No, you shouldn't need to supplement. A tiny bit of colostrum goes a long way in filling up your baby. Check with your healthcare provider to make sure your baby is gaining weight. If your baby is wetting diapers and seems pretty happy, supplementing is usually not necessary.
Is it okay to squeeze out colostrum?
Yes, it's usually OK to squeeze out colostrum once you reach full-term pregnancy (37 weeks). Check with your healthcare provider if you wish to do this prior to your baby being born. If you want to hand express colostrum for your newborn, follow these steps:
Check with your healthcare provider if you wish to do this prior to your baby being born. If you want to hand express colostrum for your newborn, follow these steps:
- Cup your breasts with your hand in a "C" shape. Four fingers should be under your breast and your thumb should be above your nipple.
- Use your thumb and index finger to gently squeeze your areola and nipple.
- Repeat several times and in a pattern. Apply firm pressure but do not slide your fingers. If colostrum doesn't come out, try moving your fingers to another spot.
- Colostrum should slowly flow out within minutes. It's thick and comes out in drops.
- You can repeat this a few times per day.
Please note that expressing colostrum before your baby is born carries risks. Some people can go into premature labor or begin having contractions. Talk to your healthcare provider before you express colostrum.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Colostrum is the first milk produced by your breasts. It's rich in nutrients and high in antibodies and antioxidants. Getting started with breastfeeding can be difficult and usually requires assistance, so don't be ashamed to ask your healthcare provider for help. Breastfeeding early and often is the best way to make sure your baby gets the many benefits from colostrum. Hand expressing colostrum and feeding your baby with a syringe is also an option. Ask your healthcare team for help if feeding your baby colostrum is something you wish to do.
It's rich in nutrients and high in antibodies and antioxidants. Getting started with breastfeeding can be difficult and usually requires assistance, so don't be ashamed to ask your healthcare provider for help. Breastfeeding early and often is the best way to make sure your baby gets the many benefits from colostrum. Hand expressing colostrum and feeding your baby with a syringe is also an option. Ask your healthcare team for help if feeding your baby colostrum is something you wish to do.
Colostrum during pregnancy | Medela
Colostrum is sometimes called liquid gold, and not only because of its color. We will tell you why this first food is so important for a newborn baby.
Share this information
Colostrum, the first milk produced at the start of breastfeeding, is the ideal nutrition for a newborn. It is very concentrated and rich in proteins and nutrients, so even in small quantities it saturates the tiny tummy of a newborn for a long time. Colostrum is low in fat and easy to digest, yet provides the baby with all the essential ingredients for an optimal developmental start. And perhaps most importantly, it plays a decisive role in the formation of the baby's immune system.
Colostrum is low in fat and easy to digest, yet provides the baby with all the essential ingredients for an optimal developmental start. And perhaps most importantly, it plays a decisive role in the formation of the baby's immune system.
Colostrum looks thicker and yellower than mature milk. Its composition also differs in accordance with the special needs of the newborn.
Colostrum fights infections
Almost two-thirds of the cells in colostrum are white blood cells, which not only protect the baby's body from infections, but also teach them to fight them themselves. 1 “White blood cells are very important for the development of immunity. They provide protection and counteract pathogenic microbes,” says Professor Peter Hartmann of the University of Western Australia, a leading lactation expert.
After giving birth, your body no longer protects the baby, and he must confront the new dangers of the world on his own. The white blood cells found in colostrum produce antibodies that can neutralize bacteria and viruses. These antibodies are especially good at dealing with indigestion and diarrhea, which is very important for very young children, whose intestines are not yet fully developed.
These antibodies are especially good at dealing with indigestion and diarrhea, which is very important for very young children, whose intestines are not yet fully developed.
Colostrum supports the child's immune system and intestinal function
Colostrum is especially rich in secretory immunoglobulin A -
is the most important antibody that protects the child from diseases, but not through the circulatory system, but as a protective coating of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. 2 “The molecules that provide the mother's immune defenses enter the mother's bloodstream into the breast, where they combine to form secretory immunoglobulin A, which is then transferred to the baby along with colostrum,” explains Professor Hartmann. “Secretory immunoglobulin A accumulates on the mucous membranes of the intestines and respiratory system of the child and protects him from diseases that the mother has already had.”
Colostrum also contains many other immunological components and growth factors that stimulate the development of protective mucous membranes in the intestines of the child, and the prebiotics contained in it contribute to the formation of beneficial microflora. 3
3
Colostrum prevents jaundice
Colostrum not only protects against indigestion, but also has a laxative effect. This helps newborns to empty the intestines frequently, removing from it everything that was digested there in the prenatal state, in the form of meconium - dark and viscous feces.
Frequent stools in newborns also reduce the risk of jaundice. A baby is born with a high level of red blood cells that absorb oxygen from the air. As these cells break down, the liver helps to process them, producing a by-product called bilirubin. If the child's liver is not yet sufficiently formed to process it, bilirubin begins to be deposited in the body, causing jaundice. 4 The laxative properties of colostrum help the baby to remove bilirubin from the body along with the stool.
Colostrum contains vitamins and minerals
Carotenoids and vitamin A give colostrum its characteristic yellow color. . 7 Babies are usually born with a low supply of vitamin A, 8 and colostrum helps to replenish it.
"The first three days are especially important for establishing breastfeeding"
In addition, colostrum is rich in minerals, such as magnesium, which is good for the baby's heart and bones, and copper and zinc, which are involved in the development of the immune system. 9.10 Zinc also contributes to the development of the brain, and there is almost four times more zinc in colostrum than in mature milk, 10 because the brain of a newborn must develop rapidly.
Colostrum helps your baby grow and develop
Colostrum contains many other ingredients that help your baby grow and develop. The role of some of them is still unknown to scientists.
“Colostrum retains its composition for about 30 hours after the baby is born,” says Prof. Hartmann. - It contains quite a lot of proteins, because all the antibodies in its composition are essentially proteins. It is relatively low in lactose [milk sugar] and has a different fat composition than mature milk. ”
”
In addition, colostrum is close in composition to the amniotic fluid that your baby swallowed and excreted while in the womb, making it ideal for adapting to the outside world. 11
Transition from colostrum to mature milk
Breast milk usually begins to arrive two to four days after delivery. The breasts become firmer and fuller, and instead of colostrum, transitional milk is excreted, which is whiter in color and creamier in consistency.
“The first three days are especially important for establishing breastfeeding,” says Prof. Hartmann. “If everything is done correctly during this period, lactation is likely to be good, and the baby will be able to grow normally.”
It seems unbelievable now, but in just one year your baby will be able to walk and maybe even talk. Colostrum is produced for only a few days, but makes an invaluable contribution to the development of the baby during the first 12 months, and the resulting benefits remain with him for life.
Want to know more? Read our free e-book Surprising Breast Milk Facts and article What is Transitional Milk?.
Literature
1 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4): e 3. - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3. 2 Pribylova J et al. Colostrum of healthy mothers contains broad spectrum of secretory IgA autoantibodies. J Clin Immunol. 2012;32(6):1372-1380. - Pribylova J. et al., "Healthy mother's colostrum contains a broad spectrum of secretory autoimmune antibodies to immunoglobulin A". W Clean Immunol. 2012;32(6):1372-1380. 3 Bode L. Human milk oligosaccharides: every baby needs a sugar mama. 4 Mitra S, Rennie J. Neonatal jaundice: aetiology, diagnosis and treatment. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 20172;78(12):699-704. - Mitra S, Rennie J, Neonatal Jaundice: Etiology, Diagnosis, Treatment. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 20172;78(12):699-704. 5 Patton S et al. Carotenoids of human colostrum. Lipids. 1990;25(3):159-165. - Patton S. et al., Carotenoids in Maternal Colostrum Lipidz. 1990;25(3):159-165. 6 Gilbert C , Foster Childhood blindness in the context of VISION 2020--the right to sight. Bull World Health Organ. 2001;79(3):227-232. 7 Bates CJ. Vitamin A. Lancet. 1995;345(8941):31-35. — Bates S.J., "Vitamin A". Lancet (Lancet) 1995;345(8941):31-35. 8 World Health Organization. e-Library of Evidence for Nutrition Actions (eLENA) [Internet]. Geneva , Switzerland : WHO ; 2018 [ Accessed : 05/14/2018]. Available from Evidence-based electronic library on WHO nutrition activities ( eLENA ) [Internet]. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2018 [visited 14 May 2018] Article at: [ www.who.int/elena/titles/vitamina_infants/en/ ] 9 Kulski JK, Hartmann PE. Changes in human milk composition during the initiation of lactation. Glycobiology. 2012;22(9):1147-1162. - Bode L., "Oligosaccharides in breast milk: a sweet mother for every baby." Glycobiology (Glycobiology). 2012;22(9):1147-1162.
Glycobiology. 2012;22(9):1147-1162. - Bode L., "Oligosaccharides in breast milk: a sweet mother for every baby." Glycobiology (Glycobiology). 2012;22(9):1147-1162.  - Gilbert S., Foster A., "Childhood Blindness in Context VISION 2020 - the right to see". Bull World Health Organ. 2001;79(3):227-232.
- Gilbert S., Foster A., "Childhood Blindness in Context VISION 2020 - the right to see". Bull World Health Organ. 2001;79(3):227-232.  AUST J EXP Biol
AUST J EXP Biol
10 Casey CE Studies in human lactation: zinc, copper, manganese and chromium in human milk in the first month of lactation. Am J Clin Nutr 1985;41(6):1193-1200. - Casey S.I. et al., Female Lactation Study: Zinc, Copper, Magnesium, and Chromium in Breast Milk in the Early Months of Lactation. Am J Clean Nutr. 1985;41(6):1193-1200.
11 Marlier L et al. Neonatal responsiveness to the odor of amniotic and lacteal fluids: a test of perinatal chemosensory continuity. Child Dev . 1998;69(3):611-623. - Marlier L. et al., "Newborn responses to amniotic and milk odors: testing perinatal chemosensory continuity. Child Dev. 1998;69(3):611-623.
1998;69(3):611-623. - Marlier L. et al., "Newborn responses to amniotic and milk odors: testing perinatal chemosensory continuity. Child Dev. 1998;69(3):611-623.
Important Information / Important Information / Breastfeeding / Information for Patients / Perinatal Center / Departments of the CDMC
- home
- Subdivisions of KDMC
- __/uslugi/__
- perinatal center
- __/uslugi/perinatalnyj-centr/__
- Information for patients
- __/uslugi/perinatalnyj-centr/informaciya-dlya-pacientov/__
- Breast-feeding
- __/uslugi/perinatalnyj-centr/informaciya-dlya-pacientov/grudnoe-vskarmlivanie/__
- Important information
Colostrum is the secret of the mammary glands, which is produced during pregnancy and the first 3-5 days after childbirth (before the arrival of milk). It is a saturated thick liquid from light yellow to orange color.
The color is due to the presence of the coloring matter of fat, and the saturation of the color of colostrum for each mother is individual and does not indicate the degree of nutritional value of colostrum for the child.
Colostrum differs in composition and quantity from mature milk.
- Very little colostrum is produced, but it is enough for a newborn. A large amount of fluid in the early days creates an increased burden on the baby's kidneys. The baby's body is simply not ready to process volumes of nutrition greater than the mother's colostrum is produced. That is why healthy, well-sucking newborns do not need, and may even be harmful, supplementation or supplementation with glucose water.
- Colostrum contains several times more protein than mature milk, especially immunoglobulin A. Immunoglobulins are responsible for protecting the baby from infections and allergens, thanks to special mechanisms they are quickly absorbed in the baby's stomach and intestines.
- Colostrum contains less fat and sugar (milk sugar lactose) than mature milk.
- Colostrum contains several times more carotene, ascorbic acid, vitamins A, B12 and E.
- Colostrum contains many enzymes, hormones, antioxidants, as well as protective cells - leukocytes.
- The calorie content of colostrum is very high, many times higher than that of mature milk.
Getting colostrum is extremely important for a baby in the first days of life! Thus, the child's immunity is being laid, the normal settlement of the child's gastrointestinal tract sterile from birth with microflora is maintained. Colostrum feedings are important for the mother as well. with frequent application in the first days in the breast, the number of prolactin receptors (areas sensitive to this hormone) increases, which further contributes to sufficient milk production. Frequent applications in the early days contribute to a more relaxed flow of milk, without pronounced symptoms of engorgement.