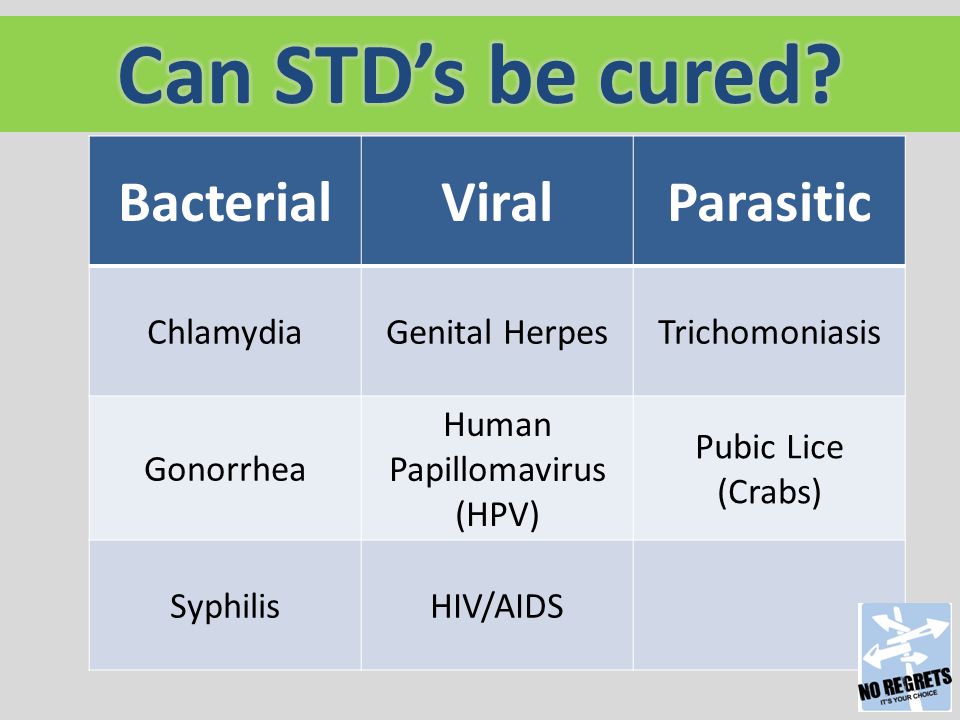
How often should i get my period
Periods and fertility in the menstrual cycle
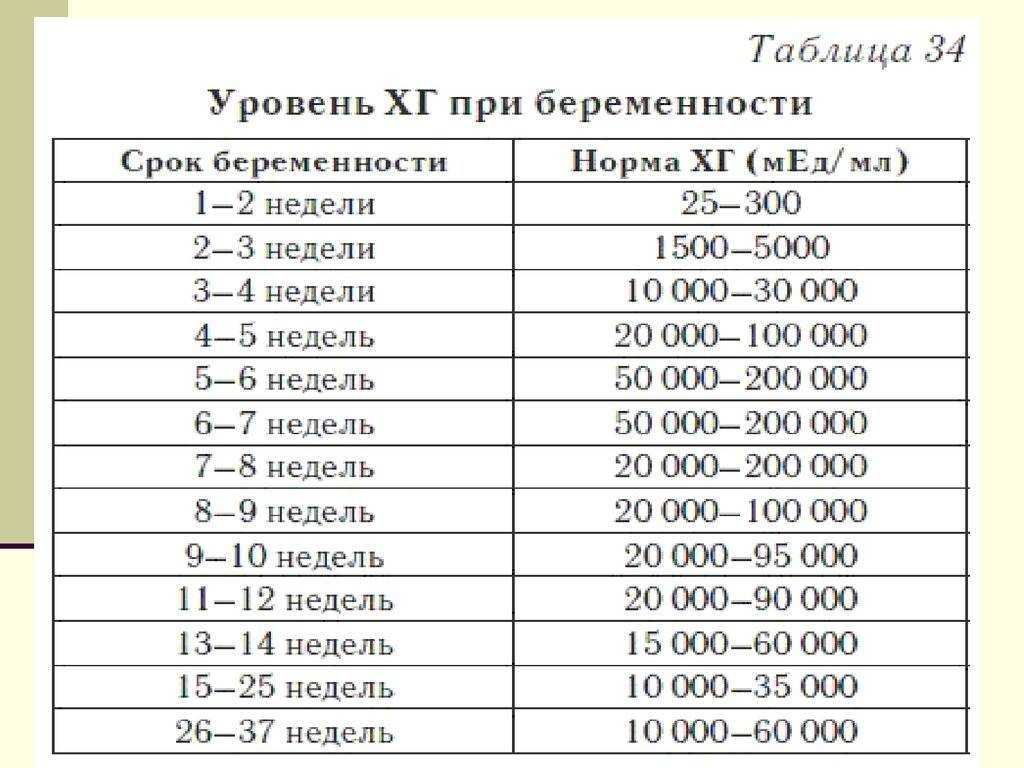
The length of the menstrual cycle varies from woman to woman, but the average is to have periods every 28 days. Regular cycles that are longer or shorter than this, from 21 to 40 days, are normal.
"The menstrual cycle is the time from the first day of a woman's period to the day before her next period," says Toni Belfield, a specialist in sexual health information, and a trained fertility awareness teacher.
"Girls can start their periods anywhere from age 10 upwards, but the average is around 12 years," says Belfield. "The average age for the menopause (when periods stop) in this country is 50 to 55."
Between the ages of 12 and 52, a woman will have around 480 periods, or fewer if she has any pregnancies.
Read more about starting periods.
What happens during the menstrual cycle?
To understand the menstrual cycle, it helps to know about the reproductive organs inside a woman's body. These are:
- 2 ovaries – where eggs are stored, developed and released
- the womb (uterus) – where a fertilised egg implants and a baby develops
- the fallopian tubes – two thin tubes that connect the ovaries to the womb
- the cervix – the entrance to the womb from the vagina
- the vagina
The menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones. In each cycle, rising levels of the hormone oestrogen cause the ovary to develop and release an egg (ovulation). The womb lining also starts to thicken.
In the second half of the cycle, the hormone progesterone helps the womb to prepare for implantation of a developing embryo.
The egg travels down the fallopian tubes. If pregnancy doesn't occur, the egg is reabsorbed into the body. Levels of oestrogen and progesterone fall, and the womb lining comes away and leaves the body as a period (the menstrual flow).
The time from the release of an egg to the start of a period is around 10 to 16 days.
Watch an animation about how the menstrual cycle works.
Video: menstrual cycle
This animation explains in detail how the menstrual cycle works.
Media last reviewed: 21 October 2020
Media review due: 21 October 2023
What are periods?
A period is made up of blood and the womb lining. The first day of a woman's period is day 1 of the menstrual cycle.
"Periods last around 2 to 7 days, and women lose about 3 to 5 tablespoons of blood in a period," says Belfield.
Some women bleed more heavily than this, but help is available if heavy periods are a problem.
Find out about treatments for heavy periods.
What happens during ovulation?
Ovulation is the release of an egg from the ovaries. A woman is born with all her eggs.
A woman is born with all her eggs.
Once she starts her periods, 1 egg develops and is released during each menstrual cycle. After ovulation, the egg lives for 24 hours.
Pregnancy happens if a man's sperm meet and fertilise the egg. Sperm can survive in the fallopian tubes for up to 7 days after sex.
Occasionally, more than 1 egg is released during ovulation. If more than 1 egg is fertilised it can lead to a multiple pregnancy, such as twins.
A woman can't get pregnant if ovulation doesn't occur. Some methods of hormonal contraception – such as the combined pill, the contraceptive patch and the contraceptive injection – work by stopping ovulation.
When are you most fertile?
"Theoretically, there's only a short time when women can get pregnant, and that is the time around ovulation," says Belfield.
It's difficult to pinpoint exactly when ovulation happens but in most women, it happens around 10 to 16 days before the next period.
"It's not accurate to say that all women are fertile on day 14 of the menstrual cycle," says Belfield. This might be true for women who have a regular, 28-day cycle, but it won't apply to women whose cycles are shorter or longer.
Find out more about fertility awareness (natural family planning)
Normal vaginal secretions
Vaginal secretions (sometimes called vaginal discharge) change during the menstrual cycle. Around the time of ovulation, they become thinner and stretchy, a bit like raw egg white.
See your GP if you are concerned about a change in your vaginal discharge.
Read more about getting pregnant, fertility and period problems.
Page last reviewed: 05 August 2019
Next review due: 05 August 2022
Periods - NHS
A period is the part of the menstrual cycle when a woman bleeds from her vagina for a few days.
For most women this happens every 28 days or so, but it's common for periods to be more or less frequent than this, ranging from day 21 to day 40 of their menstrual cycle.
Your period can last between 3 and 8 days, but it will usually last for about 5 days. The bleeding tends to be heaviest in the first 2 days.
When your period is at its heaviest, the blood will be red. On lighter days, it may be pink, brown or black.
You'll lose about 30 to 72ml (5 to 12 teaspoons) of blood during your period, although some women bleed more heavily than this.
Read more about heavy periods, period pain, irregular periods and stopped or missed periods.
When do periods start?
Periods usually begin at around the age of 12, although some girls will start them earlier or later.
A delay in starting periods isn't usually a cause for concern. Most girls will be having regular periods by age 16 to 18.
Read more about girls and puberty.
Sanitary products
Sanitary products soak up or collect the blood released during your period. The main types of sanitary products are:
- sanitary pads
- tampons
- menstrual cups
Sanitary pads
Sanitary pads are strips of padding that have a sticky side you attach to your underwear to hold them in place. One side of the pad is made of an absorbent material that soaks up the blood.
Pads come in many sizes, so you can choose one to suit how heavy or light your period is.
Pantyliners are a smaller and thinner type of sanitary pad that can be used on days when your period is very light.
Tampons
Tampons are small tubes of cotton wool that you insert into your vagina to soak up the blood before it comes out of your body.
There are 2 types of tampon - ones that come with an applicator and others without an applicator that you insert with your fingers. In both cases, there's a string at one end of the tampon, which you pull to remove it.
Tampons come with instructions that explain how to use them. If the tampon is inserted correctly, you should not be able to feel it inside you. If you can feel it or it hurts, it might not be in properly.
It is not possible for a tampon to get stuck or lost inside you. Your vagina holds it firmly in place and it expands inside you as it soaks up the blood.
Your vagina holds it firmly in place and it expands inside you as it soaks up the blood.
For more information, read:
- Can a tampon get lost inside me?
- What if I forget to remove my tampon?
Menstrual cups
Menstrual cups are an alternative to sanitary pads and tampons. The cup is made from silicone and you put it inside your vagina.
Menstrual cups collect the blood rather than absorb it. Unlike sanitary pads and tampons, which are thrown away after they've been used, you can wash menstrual cups and and use them again.
PMS (premenstrual syndrome)
Changes in your body's hormone levels before your period can cause physical and emotional changes.
This is known as PMS (premenstrual syndrome) or PMT (premenstrual tension).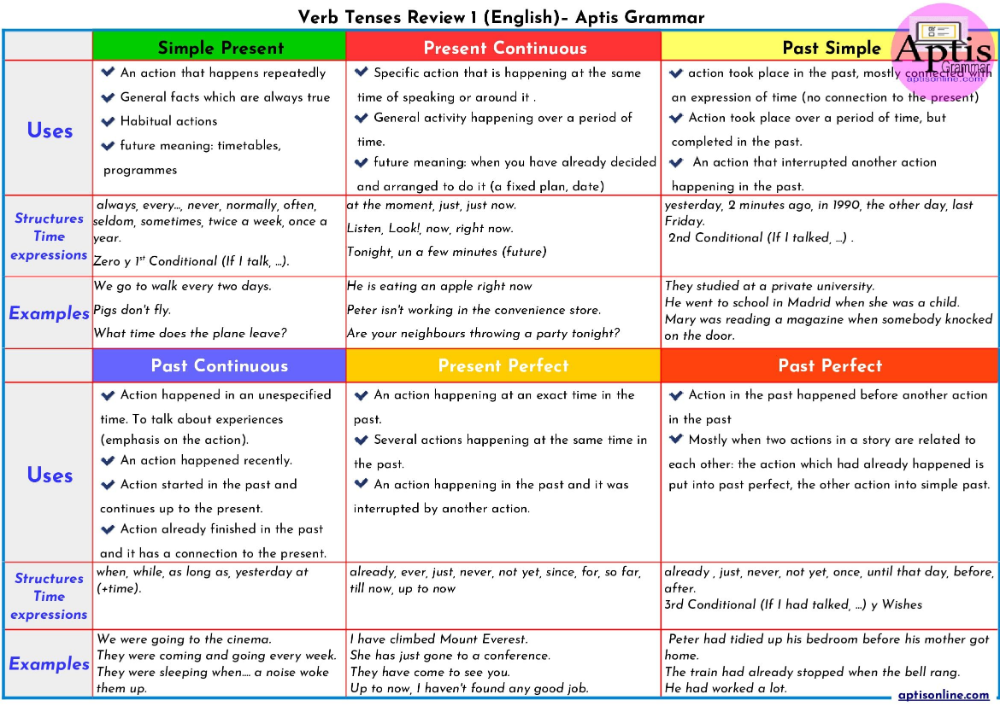
There are many possible symptoms of PMS, but typical symptoms include:
- feeling bloated
- breast tenderness
- mood swings
- feeling irritable
- spotty skin or greasy hair
- loss of interest in sex
These symptoms usually improve when your period starts and disappear a few days afterwards. Not all women who have periods get PMS.
Getting pregnant
Working out when you can get pregnant – your fertile time – can be difficult. It's around the time you ovulate, which is about 12 to 14 days before the start of your next period.
But sperm can survive inside a woman's body for up to 7 days before ovulation occurs. This means your fertile time extends back earlier in your cycle.
You can calculate when your period will start and your peak ovulation times using an online period calendar.
You cannot get pregnant if you do not ovulate. Some hormonal methods of contraception, such as the contraceptive pill, contraceptive patch and contraceptive injection, work by preventing ovulation.
Read more about the menstrual cycle, fertility, contraception and getting pregnant.
Changes in your periods
Your periods can change – for example, they may last longer or get lighter. This does not necessarily mean there's a problem, but it does need to be investigated.
You can see your GP, or visit your nearest women's clinic or contraceptive clinic.
Bleeding between periods, bleeding after having sex, or bleeding after the menopause needs to be checked by a doctor.
It might be caused by an infection, abnormalities in the neck of the womb (the cervix) or, in rare cases, it could be cancer.
You could be pregnant if you miss a period and you've had sex. See your GP if you've taken a pregnancy test and the result is negative (you're not pregnant) and you've missed 3 consecutive periods.
They will investigate the cause and recommend any necessary treatment.
Read more about stopped or missed periods.
When do periods stop?
Your periods will continue until you reach the menopause, which usually happens when you are in your late 40s to mid-50s. In the UK the average age of menopause is 51.
Your periods may start to become less frequent over a few months or years before stopping altogether. In some cases they can stop suddenly.
Video: Menstrual cycle
This animation explains in detail how the menstrual cycle works.
Media last reviewed: 21 October 2020
Media review due: 21 October 2023
Page last reviewed: 05 August 2019
Next review due: 05 August 2022
Menstruation and the menstrual cycle: what's the difference?
The menstrual cycle is a series of regularly repeated biological processes, which is one of the main differences between a woman and a man. The biological meaning of the menstrual cycle is to prepare the female orgasm for potential conception and pregnancy.
What is menstruation?
Menstruation is bleeding that usually occurs every month in sexually mature women if they have not been pregnant.
During menstruation, the mucous membrane of the uterus, the endometrium, is shed, which is accompanied by bleeding.
Menstruation usually lasts 3 to 5 days. On average, the first menstruation, menarche, begins at 11-14 years of age. Approximately half of girls aged 12 are already menstruating, however, doctors recognize the normal age of the onset of menstruation from 9 to 16 years.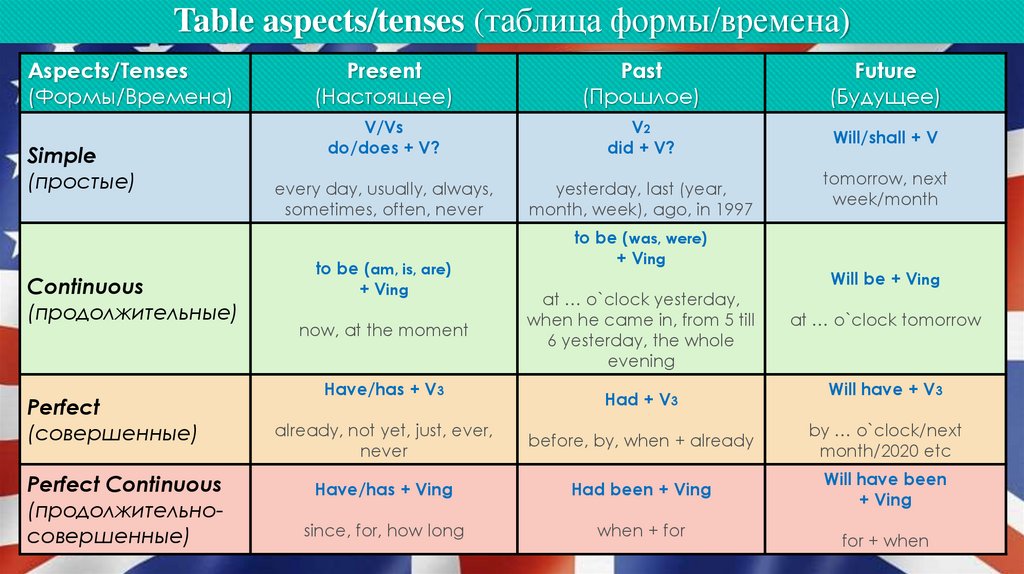 From this point on, the female body is capable of fertilization and pregnancy. Around the age of 40-55, menstruation stops and menopause occurs.
From this point on, the female body is capable of fertilization and pregnancy. Around the age of 40-55, menstruation stops and menopause occurs.
What is the menstrual cycle?
If menses or periods come regularly, then they are called the menstrual cycle. However, the length of the menstrual cycle may vary slightly from month to month, this is also normal. A longer menstrual cycle is typical for adolescents, with age there is a tendency for a decrease in the duration of the cycle and a clearer regularity. Typically, the menstrual cycle lasts from 21 to 35 days.
The female body controls the menstrual cycle through a complex hormonal balance. The human body's response to stress involves changes in hormone levels, which affect many bodily processes, and thus can affect the menstrual cycle.
Important: A regular menstrual cycle is a sign that the important organs of your body are functioning normally.
That is why it is extremely important to monitor your cycle, not only when you are afraid or trying to get pregnant: any deviations from the usual in the cycle can be signs of some unusual processes in the body or diseases that are always better to exclude immediately, because if the concern turns out to be justified, treatment is always better to start as soon as possible!
What should be the menstrual cycle and how to calculate its length?
Unfortunately, a huge number of women, even today, do not have the opportunity to receive reliable scientific information about reproductive health, including menstruation. This topic is still taboo and indecent. However, knowing about your body structure and its processes is very important to maintain your health, this also applies to menstruation. To monitor your own health, you need to track the duration of your own cycle, and for this, mark the days of the beginning and the duration of menstruation in a calendar or a special application on your phone, which will allow you to draw conclusions about the regularity of menstruation in a couple of months.
Let's see how to mark the menstrual cycle.
The first day of menstruation is considered the first day of the menstrual cycle.
The end of the menstrual cycle is celebrated on the first day of the next, that is, on the first day of the next menstrual bleeding.
The average menstrual cycle lasts 28 days, but the norms are variable: 21-35 days in adults and 21-45 days in adolescents 12-15 years old.
On average, menstruation in women lasts 3-5 days, but the norm applies to any number of days from 2 to 7. On average, the volume of menstrual bleeding is about 40-100 ml (this is about 8 used ordinary hygienic pads or tampons), and the composition of menstrual blood, in addition to blood itself, includes mucous secretions of the cervix, vaginal glands and endometrial tissue.
Why is menstrual flow different from normal blood?
Menstrual flow is different from the blood that flows through our vessels: it does not clot, and it is darker: this is due to the fact that it contains enzymes that prevent its clotting - anticoagulants.
By the way, those clots that sometimes occur in women are caused precisely by the fact that the blood does not coagulate, but this is not at all a sign of some pathological processes in the body, it often happens on the days of the most profuse bleeding, and is often associated with stress, such as malnutrition.
Don't be afraid to ask!
Unfortunately, the topic of menstruation in society is still considered taboo and shameful by many, and menstruation is often presented as something that needs to be hidden from everyone. However, even if you are embarrassed to ask a doctor something, then remember: women have periods for most of their lives, this is a normal biological process and in fact there is nothing shameful or dirty about them, so if you have something worries or you want to know if this is the case for others, then ask.
If someone shames you because you have your period, remember that this person is deeply wrong and he should be ashamed, not you.
Why are some people embarrassed to talk about menstruation?
The taboo of the topic of menstruation is also connected with the fact that for a long time menstruation was used by society in order to justify social inequality in the status of men and women, because a woman during menstruation was considered “dirty” in many cultures. This is due to the fact that in ancient times people did not understand what caused menstruation and for them this phenomenon was mysterious and incomprehensible.
Even in the twenty-first century, when the biological essence of menstruation has long been clear, many religions consider women during menstruation "unclean": in Orthodoxy, for example, women are forbidden to participate in sacred sacraments, for example, take communion during menstruation, touch icons and prosphora, and even drink "holy" water, and in some parishes even go to church.
However, these rules vary, and there are more progressive priests who oppose the notion of so-called "ritual impurity. " If you are an Orthodox believer, it is better to clarify this issue with the priest of the church you are going to visit in advance.
" If you are an Orthodox believer, it is better to clarify this issue with the priest of the church you are going to visit in advance.
Menstrual cycle (menstrual cycle) - what is it | Norms of the days of menstruation, duration, intensity of bleeding in women
The structure of the female genital organs
The external genital organs of a woman include large (labia majora) and small (labia minora) labia and clitoris. 2.3 Small lips border the opening of the urethra (urethra) and vestibule of the vagina 3 . The point of their connection is the clitoris, covered with a thin mucous membrane, the so-called mucosa. The clitoris, due to its sensitivity, plays a significant role in sexual arousal. Inside, the vagina is connected to the cervix, which is its lower part 2.3 . Further, the uterus expands, and it is into it that the egg enters, and the embryo and fetus develop during pregnancy 2. 3 .
The menstrual cycle and its phases
The duration of the menstrual cycle is about 28 days 2.3 . However, it is recognized that a normal menstrual cycle can last from 21 to 35 days 3 . All processes occurring in a woman's body during menstruation and after are conditionally divided into several phases 1,2,3 .
Menstrual phase 1,2,3 . This is the time of bleeding from the uterine cavity. During this period, lasting from 3 to 6 days, the body rejects the mucous membrane layer - the endometrium, to which, in the event of pregnancy, a fertilized egg should have attached.
Follicular phase 1,2,3 . It begins simultaneously with menstruation and lasts an average of 14 days. In this phase, a new follicle is formed in the ovaries - a special component in which a new egg matures. In addition, the process of renewal of the endometrium in the uterus begins.
Ovulatory phase 1,2,3 . It lasts about 3 days, during which time, under the influence of hormones, the mature follicle ruptures and a mature and ready-to-fertilize egg comes out of it. This process is called ovulation. During ovulation, some women may experience pain in the lower abdomen, on the side where the egg was released.
Luteal phase 1,2,3 . It lasts 11-16 days. At this time, the hormones estrogen and progesterone are actively produced, which prepare the entire body for pregnancy 2.3 . In the luteal phase, a phenomenon such as premenstrual syndrome (PMS) often occurs. This is a complex of symptoms associated with a natural change in hormonal levels: normally, before the days of menstruation, a woman may experience pain in the lower abdomen, increased appetite, mood changes, swelling of the mammary glands, etc.
Days of menstruation
Let us consider in more detail what changes in the female body occur during menstruation 3 .
Day 1. At the beginning of the menstrual cycle begins with the rejection of the "old" endometrium - a special layer of the uterine mucosa - and the bleeding itself 3 . This process, necessary for the female body, often becomes one of the most uncomfortable periods of everyday life. Unpleasant sensations during menstruation are the norm and are caused by uterine contractions.
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle begins with the rejection of the "old" endometrium - a special layer of the uterine mucosa - and the bleeding itself 3 . This process, necessary for the female body, often becomes one of the most uncomfortable periods of everyday life. Unpleasant sensations during menstruation are the norm and are caused by uterine contractions.
Day 2. On the second day of the monthly cycle, pain and heaviness in the abdomen may persist. Meanwhile, the formation of a new egg cell 3 begins in the body. During menstruation, due to hormonal changes, the work of the sebaceous glands can change, so it is important to pay special attention to personal hygiene.
Day 3. After rejection of the "old" endometrium, a wound surface is formed on the walls of the uterus 3 . At this stage of the menstrual cycle, the risk of infection is especially high, so gynecologists recommend abstaining from sexual activity while menstruation lasts.
Day 4. By the 4th day of the menstrual cycle, the woman feels better, but during menstruation it is still worth limiting physical activity and trying not to overwork. If these recommendations are followed, the volume of blood loss during menstruation decreases.
Day 5. As a rule, menstruation lasts 5 days, but there may be individual discrepancies 3 . During this time, the healing process in the uterus is completed 3 . In the renewed body, the metabolism is accelerated, and the woman feels much better and more cheerful compared to the beginning of the menstrual period.
Intensity of bleeding
Bleeding, which we call "discharge" or "period", is not always the same in intensity. Various life circumstances - the birth of a child, diet, stress, various methods of contraception - can affect how long menstruation lasts and the intensity of discharge during this period. It is different for different women, and also sometimes different for the same woman in different menstrual cycles - all this is not a deviation from the norm 3 . Therefore, tampons are available in many formats and with varying degrees of absorbency. By choosing the right product, you will be protected and able to feel comfortable every day of the month - so that nothing gets in the way of enjoying life without compromise, even during your period. Use our tampon selector to find out which tampon is right for you. Talk to your GP or gynecologist if you have questions about your period or problems with your menstrual cycle.
Therefore, tampons are available in many formats and with varying degrees of absorbency. By choosing the right product, you will be protected and able to feel comfortable every day of the month - so that nothing gets in the way of enjoying life without compromise, even during your period. Use our tampon selector to find out which tampon is right for you. Talk to your GP or gynecologist if you have questions about your period or problems with your menstrual cycle.
Rules of conduct and hygiene during menstruation
Relaxation can help relieve the pain of menstruation. Activities that promote blood circulation will help reduce spasms. Go for a walk, ride a bike, put a heating pad on your stomach, or take a warm bath.
It is important before menstruation to do things that bring you pleasure: chat with friends, buy your favorite treat, sleep more, in a word, do what will help neutralize the negative symptoms of PMS (premenstrual syndrome). 4.5
Drinking water will help with bloating and reduce fluid retention in the body before menstruation. It's hard to believe, but eating it can actually reduce PMS symptoms. Eat vegetables and fruits with high water content, drink warm herbal tea, juices. Add foods high in magnesium and vitamin E (dried apricots, bananas, avocados, etc.) to your diet. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of black and green tea, coffee, salt and sugar.
It's hard to believe, but eating it can actually reduce PMS symptoms. Eat vegetables and fruits with high water content, drink warm herbal tea, juices. Add foods high in magnesium and vitamin E (dried apricots, bananas, avocados, etc.) to your diet. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of black and green tea, coffee, salt and sugar.
Personal hygiene during menstruation 6.7 : use pads or tampons to absorb secretions, shower daily, wash 2-3 times a day. Experts recommend stopping sexual activity during menstruation.
Literature
- L.V. Dikareva. Diagnostic value of menstrual flow in gynecological pathology // L.V. Dikareva, E.G. Shvarev / Astrakhan Medical Journal, 2013, pp. 12-17.
- G.R. Burganov. Female reproductive system // G.R. Burganova, A.A. Gumerova / Teaching aid Kazan University, 2018, p. 6-14, 20-32.
- V.I. Duda. Obstetrics / studies. - Minsk: RIPO, 2013, p. 44-78.
- E.