What does a bulging fontanelle look like
Causes, treatments, and when to see a doctor
A bulging fontanel (or fontanelle) is a medical emergency. Parents or caregivers should call a pediatrician or take the baby to the emergency room immediately.
Sometimes, the fontanel bulges for harmless or temporary reasons, but it is important for a doctor to examine the baby immediately to rule out potentially life threatening issues, such as meningitis.
Babies are born with six fontanels, which people commonly refer to as soft spots. The most noticeable are the anterior and posterior fontanels, which are, respectively, on top of the head toward the front and at the back of the skull.
In this article, we look at the causes of a bulging fontanel, when to seek help, and what to expect at the hospital. We also explain how to prevent a bulging fontanel and what can happen if a baby with this issue does not receive care.
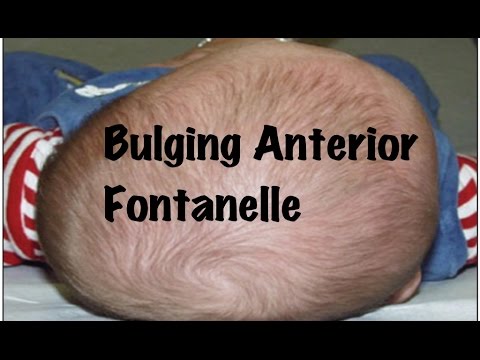
A bulging fontanel means that the soft spot looks bigger than usual.
The normally soft area may swell up taller than the rest of the skull.
The baby’s head may appear to change shape, or the soft spot might look misshapen. Sometimes, the baby’s whole head looks bigger.
Parents and caregivers can better detect a bulging fontanel if they know how the baby’s head usually looks. Therefore, it is advisable to pay close attention to the baby’s skull so that it is possible to detect any changes.
A bulging fontanel has many possible causes, which vary in severity. We explore some of these in more detail below.
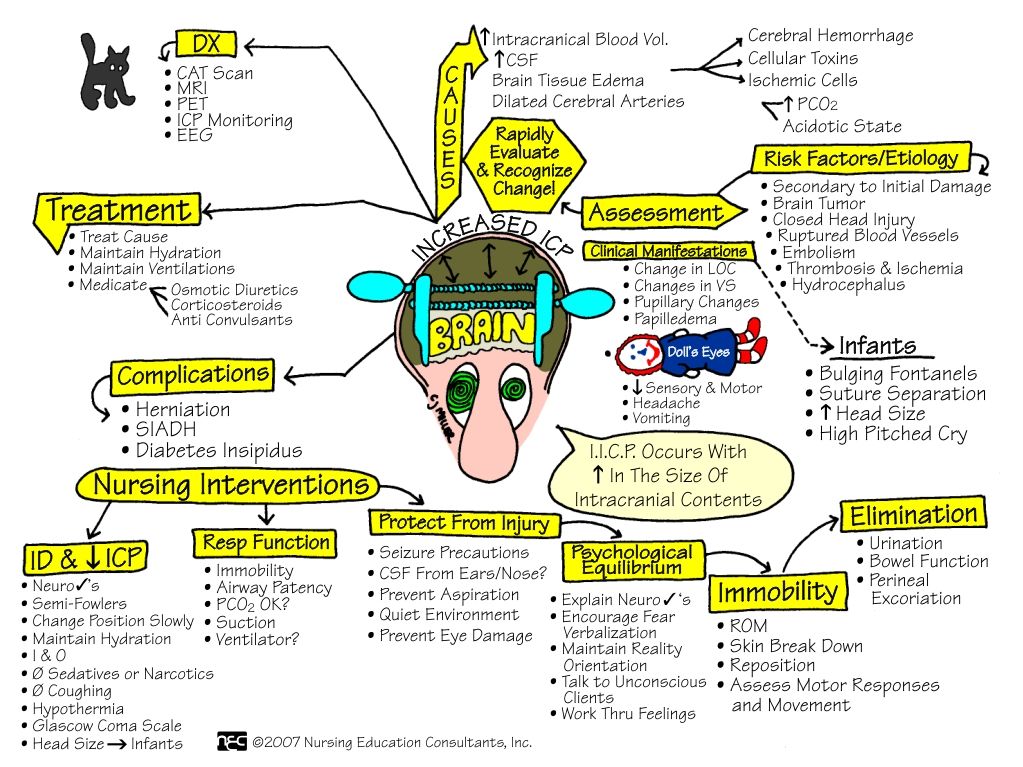
Hydrocephalus
A bulging fontanel often indicates that the baby has hydrocephalus.
Hydrocephalus causes fluid accumulation in the brain’s ventricles, which are spaces containing cerebrospinal fluid.
The pressure of the fluid widens the ventricles, potentially placing pressure on the brain tissue and causing the fontanel to swell.
There are many possible causes of hydrocephalus. Sometimes, it is present at birth, in which case, doctors call it congenital hydrocephalus. When people develop the condition after birth, it is called acquired hydrocephalus.
Congenital hydrocephalus
Some risk factors for hydrocephalus and a bulging fontanel at birth include:
- Infection: Certain infections, such as rubella, can transmit from a pregnant person to the baby, potentially causing brain swelling.
- Brain bleeding: This issue is more common in premature babies and those who sustain injuries or experience oxygen deprivation during the birth.
- Birth abnormalities: Abnormalities that affect the development of the brain, skull, spinal cord, or other parts of the nervous system can increase the risk of congenital hydrocephalus.
Acquired hydrocephalus
Some babies suddenly develop a bulging fontanel after birth. The possible causes of this medical emergency include:
- Infections: An infection in the brain or spinal cord, such as bacterial meningitis, may cause a bulging fontanel. This is more likely when the baby has a fever.
- Injuries: Brain and spinal cord injuries, including blows to the head, may cause swelling in the brain.
- Tumors: Tumors in the brain or spinal cord may cause hydrocephalus.
- Stroke: A stroke is very rare in babies but is still possible.
Other causes
Hydrocephalus does not cause all bulging fontanels. Some other potential causes include:
- Transient intracranial hypertension: This condition happens when a baby temporarily develops high blood pressure in the brain, causing it to swell. It sometimes follows an infection. While the condition usually goes away on its own, it is still a medical emergency and is not possible to diagnose from home.
- Crying: Sometimes, crying creates temporary pressure in the brain from cerebrospinal fluid. In these cases, the bulge usually goes away on its own. However, babies may cry a lot when they have a serious illness, so it is not safe to assume that crying is the direct cause of a bulging fontanel.
- Vomiting: Similar to crying, vomiting can create pressure in the skull. Vomiting may also occur with life threatening illnesses, so vomiting with a bulging fontanel is still an emergency.
- Vaccinations: Babies occasionally develop a benign and temporary bulging fontanel following vaccinations. The exact reason for this is unknown, but researchers believe that it is related to the fever that vaccinations can cause as a side effect.
- Drugs and nutrition: Certain nutritional issues, such as vitamin deficiencies, may cause the fontanel to bulge. Some drugs may also cause a bulging fontanel.
- Body position: If a baby is lying down, their fontanel may appear swollen. If the fontanel does not swell in an upright position, there is likely not a problem.
Parents and caregivers should always seek immediate medical help for a bulging fontanel, even if they suspect that the cause is something harmless.
It is important not to assume that crying or vomiting caused the swelling. It is just as likely that an infection or trauma caused the crying or vomiting, as well as the swelling.
Anyone who notices a bulging fontanel on their baby should take them to the hospital or call 911.
A bulging fontanel often signals a serious medical condition.
It may mean that there is fluid on or around the brain. This fluid can damage brain tissue, causing severe disabilities.
The cause may be a serious infection or other injury, which could be fatal.
It can be scary to see a bulging fontanel, and parents or caregivers may worry about painful or invasive treatments. However, the faster the baby gets treatment, the better their outlook.
Even in the case of a very serious infection, prompt treatment can help the baby feel better very quickly. Delaying care can cause permanent health issues.
Doctors will work as quickly as possible to determine the cause of the bulging fontanel.
They may ask questions about the baby’s development, daily routine, and medical history, including whether they have recently been ill.
In addition, doctors will take the baby’s temperature and do blood work. They may also take scans of the brain.
In many hospitals, doctors routinely perform a lumbar puncture, which some people call a spinal tap.
A lumbar puncture involves inserting a needle into the area around the spine to get a sample of cerebrospinal fluid. While the procedure is generally safe and the most accurate way to determine whether an infection is causing the bulging fontanel, it can be stressful.
However, a 2008 study suggests that this might not be necessary if the baby seems healthy.
If a doctor suggests delaying a lumbar puncture, the hospital may admit the baby for monitoring.
If a lumbar puncture shows that there is no infection, and a doctor cannot identify the cause, the hospital may also recommend admitting the baby for monitoring.
The treatment will depend on the cause. If the baby has bacterial meningitis, they will need antibiotics.
Some forms of congenital hydrocephalus require ongoing support and care, such as physical and occupational therapy.
Babies with a head or spinal cord injury may also require ongoing care.
It is not always possible to prevent a bulging fontanel.
Some strategies that parents and caregivers can use to reduce the risk include:
- washing the hands regularly and keeping a distance from people who are sick
- getting regular checkups when pregnant to reduce the risk of infections, premature birth, and some birth abnormalities
- protecting the baby from head injuries by buckling them securely into the right size and type of car seat, never leaving them unattended on a bed, counter, or couch they could roll off, and never taking them on a bike without a helmet
- talking with a pediatrician about a healthful diet for the infant and adhering to the recommended well-baby visit and vaccination schedules
- seeking immediate care for any unusual symptoms in a baby or young child
A bulging fontanel on a baby may be a sign of a serious problem that requires urgent treatment.
Although some relatively harmless conditions may also cause the swelling, it is impossible to determine the cause just from the symptoms, so it is crucial to seek medical care immediately.
Fontanelles - bulging Information | Mount Sinai
Soft spot - bulging; Bulging fontanelles
A bulging fontanelle is an outward curving of an infant's soft spot (fontanelle).
The sutures or anatomical lines where the bony plates of the skull join together can be easily felt in the newborn infant. The diamond shaped space on the top of the skull and the smaller space further to the back are often referred to as the soft spot in young infants.
The diamond shaped space on the top of the skull and the smaller space further to the back are often referred to as the soft spot in young infants.
A tense or bulging fontanelle occurs when fluid accumulates in the skull cavity or when pressure increases in the brain. Common causes are hydrocephalus or increased intracranial pressure due to illness.
Considerations
The skull is made up of many bones, 8 in the skull itself and 14 in the face area. They join together to form a solid, bony cavity that protects and supports the brain. The areas where the bones join together are called the sutures.
The bones are not joined together firmly at birth. This allows the head to change shape to help it pass through the birth canal. The sutures get minerals added to them over time and harden, firmly joining the skull bones together.
In an infant, the space where 2 sutures join forms a membrane-covered "soft spot" called a fontanelle (fontanel). The fontanelles allow for growth of the brain and skull during an infant's first year.
The fontanelles allow for growth of the brain and skull during an infant's first year.
There are normally several fontanelles on a newborn's skull. They are located mainly at the top, back, and sides of the head. Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas.
- The fontanelle in the back of the head (posterior fontanelle) most often closes by the time an infant is 1 to 2 months old.
- The fontanelle at the top of the head (anterior fontanelle) most often closes between 7 to 19 months.
The fontanelles should feel firm and very slightly curved inward to the touch. A tense or bulging fontanelle occurs when fluid builds up in the brain or the brain swells, causing increased pressure inside the skull.
When the infant is crying, lying down, or vomiting, the fontanelles may look like they are bulging. However, they should return to normal when the infant is in a calm, head-up position.
Causes
Reasons a child may have bulging fontanelles include:
- Encephalitis.
 Swelling (inflammation) of the brain, most often due to infections.
Swelling (inflammation) of the brain, most often due to infections. - Hydrocephalus. A buildup of fluid inside the skull.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Meningitis. Infection of the membranes covering the brain.
Home Care
If the fontanelle returns to normal appearance when the child is calm and head-up, it is not a truly bulging fontanelle.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Immediate, emergency care is needed for any infant who has a truly bulging fontanelle, especially if it occurs along with fever or excess drowsiness.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions about the child's medical history, such as:
- Does the "soft spot" return to normal appearance when the infant is calm or head-up?
- Does it bulge all the time or does it come and go?
- When did you first notice this?
- Which fontanelles bulge (top of the head, back of the head, or other)?
- Are all the fontanelles bulging?
- What other symptoms are present (such as fever, irritability, or lethargy)?
Diagnostic tests that may be done are:
- CT scan of the head
- MRI scan of the head
- Spinal tap (lumbar puncture)
Goyal NK. The newborn infant. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 113.
The newborn infant. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 113.
Rosenberg GA. Brain edema and disorders of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 88.
Somand DM, Meurer WJ. Central nervous system infections. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 99.
Last reviewed on: 2/2/2021
Reviewed by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
A bulging fontanel in a baby: causes and photos This is the name of the areas between the bones of the skull covered with membranes.
 The greatest interest among mothers and fathers, as well as specialists, is the largest of them, which has a diamond shape.
The greatest interest among mothers and fathers, as well as specialists, is the largest of them, which has a diamond shape. Its appearance may indicate a possible violation in the development of the baby. This is indicated by certain conditions: too large and small size, early and late closure, sunken or bulging fontanel in the baby. nine0004
From this article you will learn
- The structure and functions of the fontances
- Reasons for swelling of the fontanel
- What should you pay attention to
- Diagnostics and treatment
- Care for the fontanel
- Posterior, located at the junction of the parietal and occipital bones.
- Two wedge-shaped sections - membranes between the parietal, sphenoid, temporal and frontal bones on the sides of the skull.
- Two mastoid - between the temporal, occipital and parietal bones.
- Anterior fontanelle located in the upper part of the head, almost on top of the head.
 It is also called the soft crown. It performs an important function: it takes part in the thermoregulation of the brain when the temperature rises. nine0018
It is also called the soft crown. It performs an important function: it takes part in the thermoregulation of the brain when the temperature rises. nine0018 - ear or nose discharge;
- drowsiness, inappropriate behaviour;
- pupillary constriction or dilation;
- spots on the lower eyelids or behind the ears;
- convulsions, nausea, vomiting.
- fever;
- nausea, vomiting, stool disorder;
- physiological changes: drowsiness, lethargy or, conversely, excessive excitability, irritability, crying for no apparent reason; nine0018
- strabismus.
- Constantly
- Sometimes when crying
- Rarely
- First time
- How long ago did the fontanel start to bulge? nine0018
- Does the bulge occur constantly or under any circumstances?
- How was the birth?
- Does the soft crown return to normal if the child is calm?
- What symptoms are observed, besides the fact that the bump on the head is hard?
- Urinalysis for calcium levels.
- Computed tomography or MRI of the head.
- Neurosonoscopy. Through a large membrane between the bones of the skull, an ultrasound examination of tissues and parts of the brain is performed. This is possible because ultrasound can easily penetrate its structures.
- If the protrusion of the soft top of the head is associated with a neuroinfection, a lumbar puncture is indicated.
- Reasons for swelling of the fontanel
- Symptoms of pathological states
- Diagnostics
- Methods of therapy
- meningitis - inflammation of the meninges of the brain and spinal cord; nine0018
- enteroviral encephalitis - an inflammatory process occurs after an insect bite, vaccination, as a complication of infectious pathologies;
- hydrocephalus - a consequence of a violation of intrauterine development, birth or traumatic brain injury, infectious diseases, poisoning;
- roseola infantum, dysentery, mononucleosis;
- tick-borne borreliosis, cysticercosis, cerebral malaria;
- mastoiditis, poliomyelitis;
- endocrine pathologies - disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid or parathyroid glands, Addison's disease; nine0018
- heart failure;
- anemia, leukemia, erythrocythemia;
- metabolic disorders - diabetic ketoacidosis, uremia, osteoporosis, hepatic encephalopathy;
- Tumors, cerebral hemorrhage, brain abscess.

- discharge of clear or bloody fluid from the ears and nose;
- neck muscle tension;
- opisthotonus - convulsive posture with strong arching of the back, stretching of the legs, one of the main signs of meningitis; nine0018
- the baby cannot lie still, starts crying immediately, calms down a little in an upright position;
- child becomes lethargic, drowsy, or hyperexcitable;
- change in the size and shape of one or both pupils, strabismus;
- swelling and bruising under the eyes or behind the ears - noted after a fall, hitting the head;
- convulsions, tics, nausea, repeated vomiting, diarrhoea;
- sleep disturbance, frequent awakenings at night; nine0018
- epileptic seizures, loss of consciousness;
- high temperature.

- head measurement, checking reactions and muscle tone;
- neurosonoscopy - ultrasound of the brain is not performed on children older than 6 months of age;
- Head CT or MRI, encephalogram;
- urinalysis to determine the level of calcium;
- clinical and biochemical blood tests; nine0018
- if a neuroinfection is suspected, a lumbar puncture is performed, an analysis to detect the sensitivity of pathogens to antibiotics.
- broad-spectrum antibiotics, antivirals - prescribed when infections are detected;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, reduce fever, reduce pain;
- antiemetics;
- diuretics - prevent cerebral edema with increased intracranial pressure;
- enterosorbents - cleanse the body of toxic substances; nine0018
- vitamins, nootropics to improve blood supply to the brain;
- sedatives;
- drugs to eliminate endocrine pathologies.
Building and the functions of the relatives
during the intra -system period of development the baby is a membranous formation that protects the brain. As the fetus grows, bone plates begin to appear in the connective tissue. By the time of birth, five large bones are formed: two frontal, two parietal and one occipital. They are interconnected by elastic fibrous sutures. nine0004
nine0004
The soft remnants of the membranous skeleton provide a change in the shape of the baby's skull at the time of passage through the birth canal. The brain of a newborn develops continuously, during the year the increase in head circumference is approximately 9-10 centimeters. Such changes are possible due to fontanelles and soft sutures located at the junction of the bones of the skull.
Another function of the fontanelles is the role of a natural shock absorber. A small child in the process of learning to walk and crawl often falls, and flexible membranes on the head soften the blows. nine0004
An infant's fontanelles vary in size and location. These include:
Over time, these small areas gradually ossify and disappear, closing, in contrast to the sutures, which are open until the age of 20. In the first two or three months, the posterior fontanel disappears, the last is the anterior, largest. It is his condition that causes concern among parents and specialists in case of deviation from the norm.
Causes of swelling of the fontanel
Soft crown - a kind of barometer of developmental disorders in an infant. This is what the fontanel looks like when viewed from a healthy baby: it is slightly curved inward or located slightly higher than the bones surrounding it, barely noticeably pulsating. A bulge is formed when the baby is stressed: when he cries, pushes, when he vomits or burps. In a calm state, the fontanel returns to normal. nine0004
If the characteristic swollen fontanelle in the baby is constantly observed, regardless of the behavior of the child, you should contact the local pediatrician for advice. A tubercle on the top of the head can be formed as a result of diseases that provoke high intracranial pressure:
A tubercle on the top of the head can be formed as a result of diseases that provoke high intracranial pressure:
Excessive bulging of the fontanelle in an infant may indicate an injury received by the baby, internal bleeding or a tumor. According to Dr. Komarovsky, the following signs indicate the severity of injuries:
The child should also be shown to a specialist after an injury if any unusual behavioral disturbances are noted.
Important! The pulsation in the area of the soft top of the head is noticeable due to the proximity of the middle cerebral artery. In good light, you can see how this area is slightly swollen. A deviation from the norm is considered a strong and frequent pulse at rest or its absence.
nine0004
We advise you to watch a short video from Dr. Komarovsky, in which he talks about the main myths and misconceptions about fontanelles.
What to pay attention to
In addition to the bulging fontanel, the following factors indicate that the baby is not feeling well:
Increased intracranial pressure associated with a malfunction of body systems may be accompanied by convulsions, epileptic seizures, loss of consciousness. If parents notice this condition at night, you do not need to wait until the morning. These signs indicate that the baby needs urgent medical attention.
How often does your child's fontanel swell?
Poll Options are limited because JavaScript is disabled in your browser.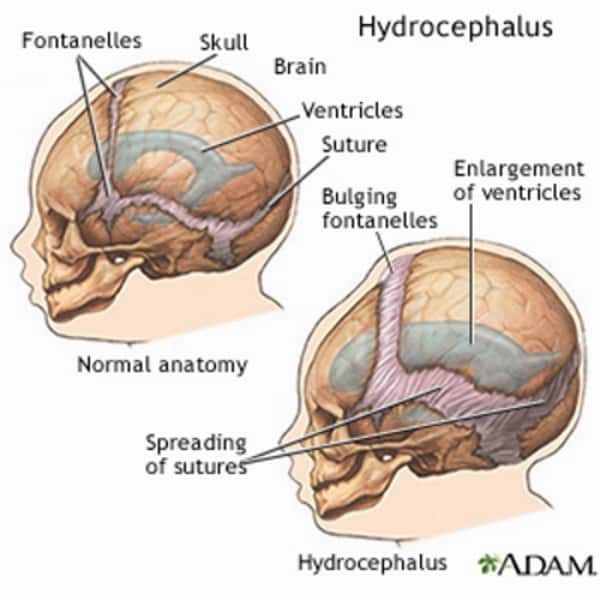
Diagnosis and treatment
To determine why the fontanel bulges in a baby, establish a diagnosis, decide what to do next, and prescribe treatment, if necessary, is the task of specialists. To do this, during the initial examination, the pediatrician can test and ask the following questions:
Most likely, if the swelling of the soft top of the head poses a threat to health, the pediatrician will prescribe an additional examination by narrow specialists: an endocrinologist, a neurologist, a geneticist. For a complete examination, the following procedures are required:
Important! Experts advise to conduct an ultrasound of the brain before the child is six months old. The explanation is simple: after the soft crown gradually overgrows, which makes it difficult to examine and diagnose. nine0004
Fontanelle care
Light touches on the soft top of the head during caring procedures: bathing, cutting hair, dressing - will not harm the baby. The head of the baby must be protected from drafts and hypothermia, so the baby must wear a hat. If the fontanel began to swell, a bump formed on the crown of the head, adults should understand that it is strictly forbidden to touch it and independently treat this deviation.
IMPORTANT ! *when copying article materials, be sure to indicate an active link to the source: https://razvitie-vospitanie.ru/zdorovie/vipuklij_rodnichok_u_grudnichka.html
If you liked the article - like and leave your comment below. We value your opinion !
Did you like our content? Subscribe to the channel in Yandex Zen.
Share with friends:
Recommended
the convex fontanel has become larger and sticks out like a bump or tubercle
A newborn has 6 fontanelles - these are areas between the bones of the skull, which are covered with membranes. To assess the state of health of the baby, the appearance and size of a large fontanel, which has the shape of a rhombus, is important. Bulging of the fontanel can be short-term, occur under the influence of physiological factors. If the problem does not disappear for a long time, is accompanied by other alarming symptoms, you should consult a doctor.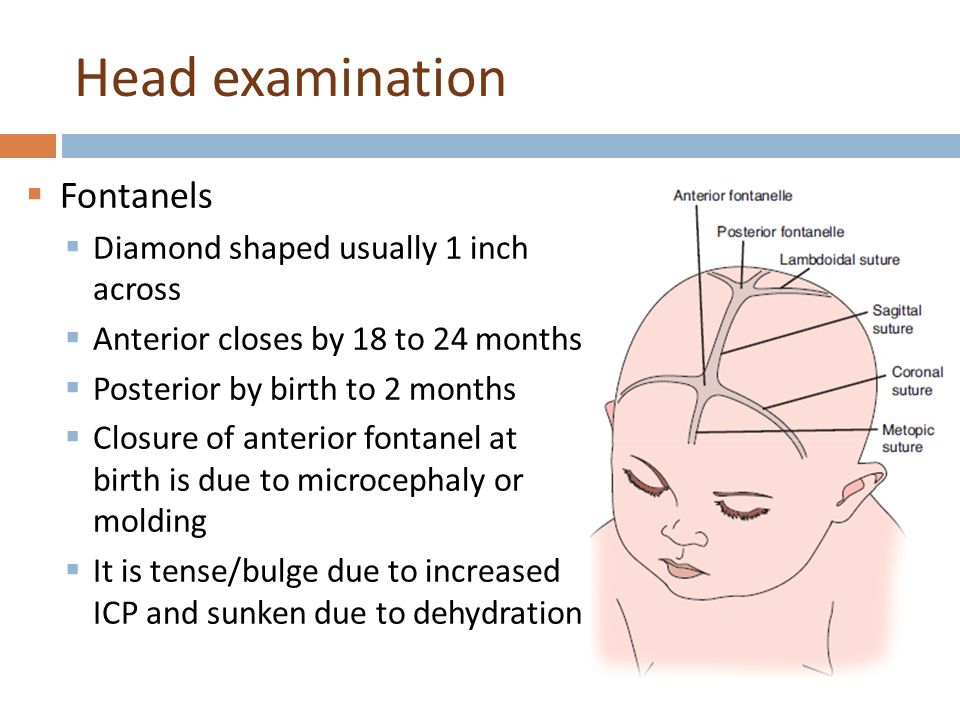 nine0004
nine0004
Content
Reasons for swelling of the nourishment in the baby may indicate an advanced leaf of
relatives - soft remains of the natives - soft remains during the passage of the child through the birth canal. After birth, these mobile areas allow the skull to grow, the brain to increase in size, and act as shock absorbers. nine0004
The anterior or large fontanel is located in the upper part of the head, near the crown, at the junction of the frontal and parietal bones. Another name is soft crown. Functions - thermoregulation of the brain with an increase in temperature. In a healthy baby, it bends slightly inward or slightly rises above the surrounding tissues, slightly pulsating. Closing terms - 3 months-1.5 years. Late overgrowth of the soft top of the head is not a sign of rickets, such a diagnosis can only be made on the basis of a combination of other characteristic manifestations and examination results. nine0004
nine0004
Constantly bulging fontanel, regardless of the behavior of the child, is a sign of diseases in which intracranial pressure increases. Externally, the swollen soft crown looks like a noticeable hemisphere that rises above the hard tissues of the head. Inspection should be carried out when the baby is in an upright position.
With meningitis, a child develops a rash all over his body and the fontanel bulges outCauses of a swollen fontanel in a child:
The fontanel may swell with an excess of vitamin A in the child's body. Another reason is shaken baby syndrome or shaken baby syndrome. Accidental brain damage occurs when the baby is shaken excessively, tossed up. As a result, hemorrhage occurs in the subarachnoid space. The pathology is asymptomatic, the only external manifestation is the soft top of the head begins to swell. nine0004
Disorders of liquorodynamics, impaired cerebral circulation develops against the background of asphyxia in newborns on the first day. This leads to the appearance of a tubercle on the fontanel in the baby.
A short-term increase and strong pulsation of the large fontanel is observed with prolonged crying, constipation or colic, belching. The retraction of the soft crown most often indicates exicosis - severe dehydration of the body during fever, vomiting, diarrhea. In this case, there is pallor and dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, a decrease in the number of urination, crying without tears.
nine0004
Symptoms of pathological conditions
Irregular shape of the baby's head is a danger signalIf the baby's fontanel begins to swell against the background of pathological processes in the body, other dangerous manifestations are observed.
When you need to see a doctor urgently:
In case of pathologies, the appearance of a bump on the fontanel in a child is accompanied by an increased pulsation of the soft top of the head or a complete absence of a pulse in the top of the head.
Diagnosis
MRI for infants is performed under anesthesiaIf the fontanel is swollen, other dangerous symptoms are observed, it is necessary to show the child to the pediatrician or call an ambulance. To make it easier for the doctor to make an initial diagnosis, parents need to tell in detail when the problem arose, describe the behavior and well-being of the baby. It is important to describe in detail the state of the soft crown - how it pulsates, sticks out constantly or under certain circumstances. nine0004
After the examination, you may need to consult narrow specialists - a neurologist, endocrinologist, osteopath, infectious disease specialist.
Diagnostic methods for bulging of the large fontanel:
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor selects safe and effective methods of therapy. Treatment of pathological conditions is carried out in a hospital.
Methods of therapy
If the child has increased ICP, diuretics are prescribed to reduce the amount of fluid in the brainMedicines will help eliminate the protrusion of the fontanel. The choice of medicines depends on the reasons that provoked the swelling of the soft crown. nine0004
What drugs can the doctor prescribe if the fontanel has become larger: