What can pregnant women take for flu
Which Cold & Flu Medication Is Safe to Take During Pregnancy? | UNM Health Blog
By Maria Montoya, MD | February 04, 2022
You are pregnant and start feeling sick. Before you reach for that bottle of cold or flu medicine, are you certain it is safe for your baby?
When you are pregnant, your baby will be exposed to everything you are exposed to. This means that when you are sick with a cold or flu your baby will not only be exposed to the cold or flu virus, but also any medication you may take.
Typically, with most viruses, you must wait for your immune system to fight the infection. Over-the-counter medications can help soothe your symptoms while you wait.
However, not all over-the-counter medicines are safe to take during pregnancy. Certain medications may hurt the baby or cause problems for you, such as increasing your blood pressure.
Use this quick list of pregnancy-safe natural cold and flu remedies and over-the-counter medications as a starting point. Remember, read the directions on the package for any medication you might take. It’s also a good idea to talk with your doctor or midwife before taking a cold or flu medication.
Natural, Pregnancy-Safe Remedies
Before you try any medications, there are natural remedies you may find adequate relief from first. Here are a couple of safe, natural remedies to try:
- Gargle warm salt water
- Get as much restful sleep as possible
- Sip honey in hot water
- Stay well hydrated
- Use nasal saline sprays
- Try a humidifier
While not all herbs and supplements are safe in pregnancy. You may be able to safely take:
- Vitamin C
- Zinc
- Manuka Honey
- Elderberry
Talk with your doctor or midwife before taking any supplements or trying at-home remedies or essential oils during pregnancy.
If natural remedies don’t provide enough relief, consider these pregnancy-safe medications.
Pregnancy-Safe Cold & Flu Medication
It is best to avoid taking medications when possible. If you do need to take something, follow the package directions carefully. Talk with your doctor or midwife before taking medication during pregnancy.
These over-the-counter medications are considered safe for most pregnant patients:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Safe during the entire pregnancy.
- Take only as needed.
- Try to limit regular exposure.
- Not safe if you are allergic to it or have liver problems.
- Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed)
- Safe in the second and third trimester
- Not safe in the first trimester due to a small risk of abdominal wall birth defects
- Not safe if you have high blood pressure (hypertension) or a history of heart disease
- Chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton)
- Safe during pregnancy.
- Not safe while breastfeeding.

- Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- Safe throughout pregnancy.
Watch out for extra ingredients. Many cold and flu medications treat more symptoms than you may be experiencing. For example, Tylenol Cold Multi-Symptom treats headaches, fever, body aches, cough, chest congestion, stuffy nose, and more. If you just have a stuffy nose, this is more medication than you need.
A word about antibiotics. Some sinus infections are treated with antibiotics. In general, pregnant patients should not take antibiotics unless it is necessary. Make sure your health care provider knows you are pregnant if they prescribe antibiotics.
The dangers of high blood pressure in pregnancy
How to spot symptoms and get help
Read More
Medications to Avoid in Pregnancy
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) medications can hurt your developing baby. Do not take NSAIDs such as these when you are pregnant:
Do not take NSAIDs such as these when you are pregnant:
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
- Naproxen (Aleve, Midol)
- Celecoxib (Celebrex)
- Aspirin (Bayer), unless your doctor or midwife prescribes daily low-dose aspirin.
Do not take these medications during pregnancy. These drugs can hurt the developing baby:
- Benzocaine (throat lozenges/throat sprays)
- Codeine (a pain and cough medication)
- Phenylephrine (i.e., Sudafed PE): it not considered safe while pregnant because studies with animals showed adverse effects to the fetus.
When you don’t feel well, the last thing you might want to do is read a medication label. However, it is worth taking a few extra moments to read the label and avoid additional risks. If you’re not sure what medicine is safe to take, call us. We are always here to help you.
To find out whether you or a loved one might benefit from Ob/Gyn care
Call 505-272-2245.
Categories: Women's Health
Influenza (flu) and pregnancy | March of Dimes
It’s safe to get the flu shot. It protects you and your baby from serious health problems during and after pregnancy.
Pregnant women who get the flu are more likely than women who don’t get it to have problems, like preterm labor and premature birth.
If you think you have the flu, call your health care provider right away. Quick treatment can help prevent serious flu complications.
What is the flu?
Influenza (also called flu) is a virus that can cause serious illness. It’s more than just a runny nose and sore throat. The flu can make you very sick, and it can be especially harmful if you get it during or right after pregnancy.
How does the flu spread?
The flu spreads easily from person to person. When someone with the flu coughs, sneezes or speaks, the virus spreads through the air. You can get infected with the flu if you breathe it in or if you touch something (like a door handle or a phone) that has the flu virus on it and then touch your nose, eyes or mouth.
You can get infected with the flu if you breathe it in or if you touch something (like a door handle or a phone) that has the flu virus on it and then touch your nose, eyes or mouth.
People with the flu may be able to infect others from 1 day before they get sick up to 5 to 7 days after. People who are very sick with the flu or young children may be able to spread the flu longer, especially if they still have symptoms.
How can the flu harm your pregnancy?
Health complications from the flu, like a lung infection called pneumonia, can be serious and even deadly, especially if you’re pregnant. If you get the flu during pregnancy, you’re more likely than other adults to have serious complications. It’s best to get a flu shot before you get pregnant. Getting a flu shot can help reduce your risk of getting the flu, having serious flu complications and needing treatment in a hospital.
Pregnant women who get the flu are more likely than women who don’t get it to have preterm labor (labor that happens before 37 weeks of pregnancy) and preterm birth (birth that happens before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Fever from the flu may be linked to birth defects, like neural tube defects, and other problems in your baby. A birth defect is a health condition that is present at birth. Birth defects change the shape or function of one or more parts of the body. They can cause problems in overall health, how the body develops, or in how the body works. Neural tube defects are birth defects of the brain and spinal cord.
Fever from the flu may be linked to birth defects, like neural tube defects, and other problems in your baby. A birth defect is a health condition that is present at birth. Birth defects change the shape or function of one or more parts of the body. They can cause problems in overall health, how the body develops, or in how the body works. Neural tube defects are birth defects of the brain and spinal cord.
How does the flu shot help protect you from flu?
The flu shot contains a vaccine that helps prevent you from getting the flu. The flu shot can’t cause the flu. It’s safe to get a flu shot any time during pregnancy, but it’s best to get it before flu season (October through May). Even though you’re more likely to get the flu during flu season, you can get it any time of year.
There are many different flu viruses, and they’re always changing. Each year a new flu vaccine is made to protect against three or four flu viruses that are likely to make people sick during the upcoming flu season.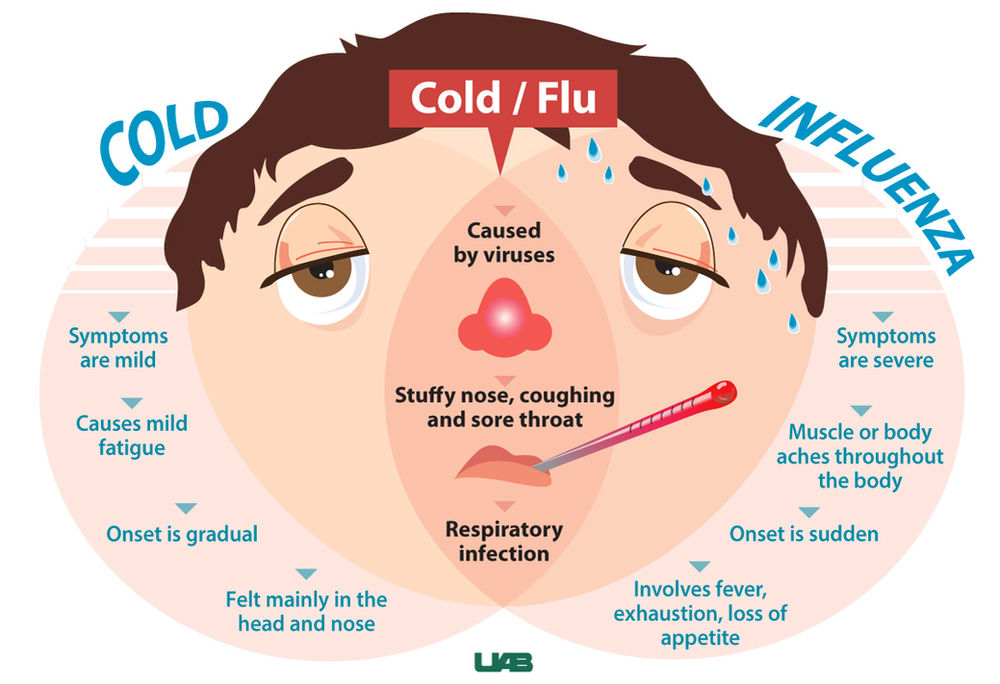 Protection from a flu shot only lasts about a year, so it’s important to get a flu shot every year. You can get the shot from your health care provider, and many pharmacies and work places offer it each fall. Use the HealthMap Vaccine Finder to find out where you can get the flu vaccine.
Protection from a flu shot only lasts about a year, so it’s important to get a flu shot every year. You can get the shot from your health care provider, and many pharmacies and work places offer it each fall. Use the HealthMap Vaccine Finder to find out where you can get the flu vaccine.
Is it safe to get a flu shot during pregnancy?
It’s safe for most pregnant women to get the flu shot. Tell your health care provider if you have any severe allergies or if you’ve ever had a severe allergic reaction to a flu shot. Severe allergic reactions to flu shots are rare. If you’re worried about being allergic to the flu shot, talk to your provider to make sure it’s safe for you.
Some flu vaccines are made with eggs. Most women with egg allergies can get the flu shot. But if you have severe egg allergies, get the shot in a medical setting (like a doctor’s office, hospital or clinic) from a provider who knows how to treat severe allergies and allergic reactions.
Pregnant women should not get the flu nasal spray. This is a spray that’s put in your nose.
This is a spray that’s put in your nose.
What are signs and symptoms of the flu?
Signs of a condition are things someone else can see or know about you, like you have a rash or you’re coughing. Symptoms are things you feel yourself that others can’t see, like having a sore throat or feeling dizzy. Common signs and symptoms of the flu include:
- Being very tired or sleepy (also called fatigue)
- Cough
- Fever (100 F or above), chills or body shakes. Not everyone who has the flu has a fever.
- Headache, or muscle or body aches
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sore throat
- Vomiting (throwing up) or diarrhea (more common in children)
The flu often comes on quickly. Fever and most other symptoms can last a week or longer. But some people can be sick from the flu for a long time, including children, people older than 65, pregnant women and women who have recently had a baby.
Call 911 and get medical care right away if you have any of these signs or symptoms:
- Feeling your baby move less or not at all
- High fever that doesn’t go down after taking acetaminophen (Tylenol®).
 Don’t take any medicine without checking with your provider first.
Don’t take any medicine without checking with your provider first. - Pain or pressure in the chest or belly
- Sudden dizziness or confusion
- Trouble breathing or shortness of breath
- Vomiting that’s severe or doesn’t stop
- Flu signs or symptoms that get better but then come back with fever and a worse cough
How is the flu treated during pregnancy?
If you think you have the flu even if you’ve been vaccinated, call your health care provider right away. Your provider may prescribe an antiviral medicine to help prevent or treat the flu. Antivirals kill infections caused by viruses. They can make your flu milder and help you feel better faster. Antivirals also can help prevent serious flu complications, like pneumonia. For flu, antivirals work best if you take them within 2 days of having symptoms. Quick treatment with antiviral medicine can help prevent serious flu complications.
If you’ve had close contact with someone who has the flu during your pregnancy or in the 2 weeks after giving birth, tell your health care provider. Even if you don’t have signs or symptoms of flu, your provider may want to treat you with an antiviral medicine to help prevent you from getting the flu and having serious complications.
Even if you don’t have signs or symptoms of flu, your provider may want to treat you with an antiviral medicine to help prevent you from getting the flu and having serious complications.
Three medicines are approved in the United States to prevent or treat the flu in pregnant women and women who recently had a baby. Talk to your provider about which one is right for you:
- Oseltamivir (brand name Tamiflu®).This medicine comes as a capsule or liquid.
- Zanamivir (brand name Relenza®). This medicine is a powder that you breathe in by mouth. It isn’t recommended for people with breathing problems, like asthma.
- Peramivir (Rapivab®). This medicine is given through a needle into a vein (also called IV) by a health care provider.
If you have a fever, call your provider as soon as possible. Before taking any over-the-counter medication, be sure to check with your provider first. Not all medication is safe to take during pregnancy. If you have the flu, get lots of rest and drink plenty of fluids. You may not want to eat much. Try eating small meals to help your body get better.
You may not want to eat much. Try eating small meals to help your body get better.
How can you stop the flu from spreading?
When you have the flu, you can spread it to others. Here’s what you can do to help prevent it from spreading:
- Stay home when you’re sick and limit contact with others.
- Cough or sneeze into a tissue or into your arm. Throw used tissues in the trash.
- Try not to touch your eyes, nose or mouth.
- Wash your hands with soap and water before touching anyone. You also can use alcohol-based hand sanitizers. Use enough hand sanitizer so that it takes at least 15 seconds for your hands to dry.
- Wash your dishes and utensils well with hot soapy water, or in a dishwasher if you have one.
- Don’t share your dishes, glasses, utensils or toothbrush.
Why is the flu so harmful during pregnancy?
The flu can be dangerous during pregnancy because pregnancy affects your immune system, heart and lungs. Your immune system is your body’s way of protecting itself from illnesses and diseases. When your body senses something like a virus that can harm your health, your immune system works hard to fight the virus.
Your immune system is your body’s way of protecting itself from illnesses and diseases. When your body senses something like a virus that can harm your health, your immune system works hard to fight the virus.
When you’re pregnant, your immune system isn’t as quick to respond to illnesses as it was before pregnancy. A lowered immune system means you’re more likely get sick with viruses like the flu.
During pregnancy, your lungs need more oxygen, especially in the second and third trimesters. Your growing belly puts pressure on your lungs, making them work harder in a smaller space. You may even find yourself feeling shortness of breath at times. Your heart is working hard, too. It’s busy supplying blood to you and your baby. All of this means your body is stressed during pregnancy. This stress on your body can make you more likely to get the flu. If you’re pregnant or had a baby within the last 2 weeks, you’re more likely than other women to have serious health problems from the flu.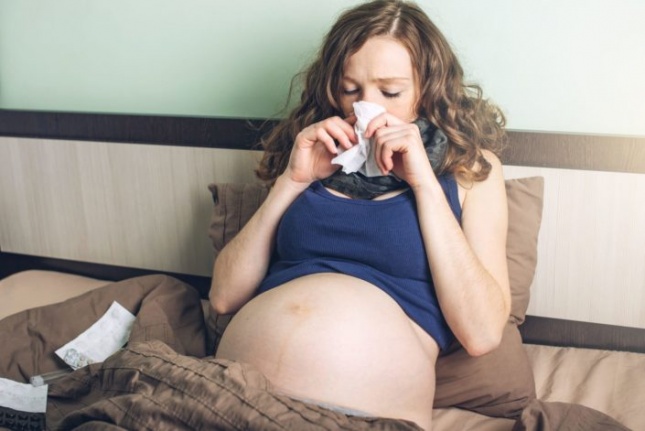
More information
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Flu & Pregnancy
Flu.gov
What is the Flu? Common Influenza Questions (familiesfightingflu.org)
Last reviewed: November, 2022
Colds during pregnancy: how to treat?
Any cold or respiratory disease in early pregnancy, during the primary formation of the fetus, can lead to unpredictable consequences and complications. The matter is complicated by the fact that most medications are absolutely contraindicated for use during gestation.
In this regard, the treatment and prevention of colds in pregnant women is an important issue, which should be approached especially responsibly! The main thesis is: be careful with medicines and apply mild preventive measures based on alternative medicine methods to avoid respiratory diseases and flu. nine0003
"One for two - immunity"
This is a very fragile system, it is not necessary to interfere in its work, but it is necessary to support and strengthen it. Pregnancy belongs to the category of special, albeit temporary, conditions during which a woman needs additional protection.
Pregnancy belongs to the category of special, albeit temporary, conditions during which a woman needs additional protection.
This issue will help simple recommendations that are available to everyone:
• During the period of frequent weather changes, it is necessary to dress warmer, paying special attention to shoes. nine0017 • During an epidemic, it is better for a pregnant woman to refrain from being in crowded places - transport, metro, shops and hospitals. If there is an urgent need, to prevent possible infection, a protective respiratory mask should be worn before leaving the house.
• Be especially careful about hygiene after visiting the street and public places. Upon returning home, the first thing to do is wash your hands thoroughly.
Interesting: More than 90% of all acute respiratory infections are caused by viruses, about 10% are bacteria and other pathogens. Accordingly, any soap can be used, not necessarily antibacterial.
• Before going outside, you can lubricate the nasal mucosa with oxolinic ointment. Upon returning home, flush the upper respiratory tract with soda solution.
• Rationalization of nutrition and intake of vitamins will strengthen the immune defense. It is especially useful to eat fruits and vegetables that are enriched with vitamins and have not undergone heat treatment. nine0003
Interesting: our grandmothers used to say: in order not to get sick, you need to drink chicken broth! Strange, but until recently, scientists did not attach much importance to this prophylactic. Pulmonologist Stefan Rennard decided to find out if this was true or not. The professor conducted a study and proved that the use of chicken broth affects the mobility of neutrophils, white blood cells that protect the body from infections and activate the immune system.
- Vitamins can be taken using ready-made pharmaceutical multivitamin complexes.
 Before choosing a drug, you should consult your doctor. nine0035
Before choosing a drug, you should consult your doctor. nine0035 - Compliance with the regimen and duration of sleep - at least 9 hours a day. The possibility of psychotraumatic situations should be minimized.
- Maintaining cleanliness in the living quarters (ventilation, wet cleaning).
- Air humidification is an important aspect in the prevention of influenza and respiratory diseases. If air conditioners or heaters are used in the house of a pregnant woman, it would be best to purchase a mechanical humidifier. nine0035
Medications for prevention
- Grippferon - a drug in the form of drops for the nose, which provides prevention and treatment of influenza, is not contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women. The medicine stimulates an increase in immunity, has a pronounced antiviral effect that can protect against colds, infections and influenza varieties.
- Ascorbic acid - can be used as a separate source of vitamin C in a synthetic version, with a reduced daily intake from food.
 Ascorbic acid not only prevents infection, but also fights viruses that have already entered the body of a woman. nine0035
Ascorbic acid not only prevents infection, but also fights viruses that have already entered the body of a woman. nine0035 - Viferon - nasal ointment, which is prescribed for the prevention of influenza and respiratory infections during an epidemic. The ointment has protective and immunomodulatory effects, and also allows you to deal with disorders that are already occurring in the body at the time of use. Viferon in the form of a nasal ointment has no contraindications for use in pregnant women at any time, including the first trimester.
- Aquamaris is a natural drug in the form of a nasal spray that allows you to moisturize the nasal mucosa, thereby reducing the risk of influenza viruses entering the nasal cavity. nine0035
I would like to say a few words about such a method of prevention as vaccination. Most often, the expectant mother may be at risk of infection due to the annual influenza epidemic. This disease is dangerous for a pregnant woman precisely because of its complications: pneumonia, bronchitis, otitis media. Influenza in a pregnant woman can also affect the health of the fetus. Most of all, it is dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy, when the tissues and organs of the human embryo are laid and formed. Viral intoxication or drug exposure can lead to pathology of the child's organs. In later pregnancy, there is a risk of infection of the fetus. nine0003
Influenza in a pregnant woman can also affect the health of the fetus. Most of all, it is dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy, when the tissues and organs of the human embryo are laid and formed. Viral intoxication or drug exposure can lead to pathology of the child's organs. In later pregnancy, there is a risk of infection of the fetus. nine0003
The most dangerous consequence of influenza in a pregnant woman is threatened miscarriage or premature birth!
It is quite natural that expectant mothers often wonder whether or not to vaccinate.
Studies have concluded that the use of inactivated ("killed") influenza vaccines does not have a teratogenic effect on the fetus and does not harm the health of a pregnant woman. After consulting with your doctor about such an inoculation, you can come to an optimal solution. nine0073 If an influenza epidemic is inevitable, and the pregnant woman has no contraindications, then the vaccine should be given. If a pregnant woman has a negligible risk of infection, she does not come into contact with a large number of people, or is opposed to vaccination, then you can not do it. According to research, it is known that vaccination of mothers reduces the risk of influenza infection of a born child by 63%. Seasonal influenza prevention is carried out in September, October. Vaccinations for pregnant women are recommended from the second trimester of pregnancy. nine0003
If a pregnant woman has a negligible risk of infection, she does not come into contact with a large number of people, or is opposed to vaccination, then you can not do it. According to research, it is known that vaccination of mothers reduces the risk of influenza infection of a born child by 63%. Seasonal influenza prevention is carried out in September, October. Vaccinations for pregnant women are recommended from the second trimester of pregnancy. nine0003
In the period of a planned pregnancy, a flu shot is given 1 month before it: the formation of immunity occurs 2-4 weeks. Protection after vaccination lasts about a year.
If infection does occur, action should be taken immediately if at least one symptom of the disease is detected. The health of a pregnant woman and her unborn child depends entirely on her responsibility and respect for her own body.
Proven folk remedies will be used first. Since pregnant women cannot steam their legs, steam their hands, and this will facilitate nasal breathing. Bundle up, put on woolen socks and crawl under the covers: warmth, peace and sleep are good for colds. Do not forget to drink plenty of water - hot green tea with lemon and honey, lime blossom tea, cranberry juice, rosehip broth, dried fruit compote. Ginger in the form of tea also helps, not only with catarrhal symptoms, but with nausea in the morning. nine0003
Bundle up, put on woolen socks and crawl under the covers: warmth, peace and sleep are good for colds. Do not forget to drink plenty of water - hot green tea with lemon and honey, lime blossom tea, cranberry juice, rosehip broth, dried fruit compote. Ginger in the form of tea also helps, not only with catarrhal symptoms, but with nausea in the morning. nine0003
Various hot milk drinks are also suitable. Honey can be added to milk, and it is best to boil it on onions. It must be emphasized right away that not all herbs for colds during pregnancy can be used. Here is a list of medicinal plants that are contraindicated: aloe, anise, barberry, elecampane (grass and root), sweet clover, oregano, St. John's wort, strawberries (leaves), viburnum (berries), raspberries (leaves), lemon balm, lovage, wormwood, licorice ( root), celandine, sage. Accordingly, preparations containing these plants should not be taken. nine0003
The use of medicines for colds during pregnancy must be treated with great care!
It is contraindicated to use the following drugs : Pertussin, Tussin plus, Joset, Glycodin, Ascoril, Travisil, Broncholitin, ACC, Grippeks, Codelac, Terpinkod. Do not use lozenges and lozenges for sore throat or cough are also undesirable due to the likelihood of allergic reactions.
Do not use lozenges and lozenges for sore throat or cough are also undesirable due to the likelihood of allergic reactions.
Spray Pinosol, judging by the components indicated in the instructions, is not dangerous during pregnancy. However, the essential oils contained in the preparation - pine, peppermint, eucalyptus, thymol, guaiazulene (wormwood oil) - can lead to an allergic reaction with swelling of the nasal mucosa. nine0003
Viferon suppositories are allowed to be used only after 14 weeks from the start of conception. This drug contains recombinant human interferon alpha-2, ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol acetate and has antiviral, immunomodulatory and antiproliferative effects. It is used in the treatment of various infectious and inflammatory diseases in adults and children (including newborns). In the form of an ointment, Viferon is used to treat herpetic lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. The ointment is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days. nine0003
nine0003
The homeopathic preparation Stodal, which includes predominantly herbal ingredients, acts on various types of cough and has an expectorant and bronchodilator effect.
Viburkol - homeopathic suppositories - have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, sedative, antispasmodic action. They are prescribed in the complex therapy of acute respiratory viral infections and other uncomplicated infections (including in newborns), as well as in inflammatory processes of the upper respiratory tract and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. nine0003
So, you can try to eliminate a slight ailment on your own, but there are conditions under which you need to call a doctor at home:
- Prolonged fever;
- Myalgia, fatigue, fatigue, general malaise;
- Difficulty breathing, nasopharyngeal lumps and dry or wet barking cough;
- A pregnant woman is troubled by severe pressing headache. nine0035
In conclusion, I would like to emphasize the importance of treating chronic diseases before pregnancy, a healthy lifestyle during childbearing and following all doctor's orders.
I wish expectant mothers and their loved ones to try to maintain a good mood: optimists live longer and happier, they are more productive. Remember your victories and pleasant moments more often and everything will be fine!
Cold during pregnancy, what can pregnant women with a cold, how to treat if the temperature, what you can drink. nine0001
Cold treatment during pregnancy
Acute respiratory diseases, also called colds, can also occur in pregnant women. Over the entire period of bearing a child, approximately 2/3 of expectant mothers suffer one or more episodes of a cold, which can have a course of varying severity. In most cases, colds are caused by viruses. 1
A cold while carrying a child can adversely affect its development. Oxygen deficiency due to a runny nose negatively affects the baby. At the same time, the treatment of a cold is fraught with difficulties - pregnant women should not take many medicines, as they can also affect the development of the fetus. nine0003
nine0003
Causes and risk factors
Most often, pregnant women get sick with a cold in the autumn-winter-spring periods. It is during these seasons that flu and SARS epidemics are observed. The main cause of the development of a cold are pathogens from the group of rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, enteroviruses, as well as influenza and parainfluenza viruses. Bacteria usually lead to the development of lower respiratory tract infections - tracheitis, bronchitis, etc.
Risk factors include various concomitant diseases in pregnant women. These can be diseases of the cardiovascular, digestive, immune, endocrine and other systems. Respiratory diseases are considered the most dangerous risk factor, especially if they occur in a chronic form. Pregnancy itself is also a risk factor, since in this natural state for a woman, immunity decreases and protective mechanisms weaken. nine0120 1
Cold risk for pregnant women
Cold pathogens initially enter the upper respiratory tract (usually the nasal cavity) and begin to actively multiply in the epithelium of the mucous membrane. As a result, an inflammatory reaction develops, which leads to the appearance of characteristic symptoms - a runny nose, nasal congestion and difficulty in nasal breathing.
As a result, an inflammatory reaction develops, which leads to the appearance of characteristic symptoms - a runny nose, nasal congestion and difficulty in nasal breathing.
In case of a severe course of a cold (flu), other parts of the respiratory system may also be affected with the development of more serious complications that affect the health of the mother. These complications can also affect the course of pregnancy, leading to conditions such as: nine0003
- Fetal malformations.
- Miscarriages.
- Intrauterine infections.
- Intrauterine growth retardation.
- Placental abruption.
- Fetal hypoxia.
The effect of the common cold on pregnancy can occur in a variety of ways. First of all, any infection leads to a change in the functioning of the immune system, namely, to the development of immunodeficiency. Against the background of an already existing immunodeficiency during pregnancy, such changes can lead to the activation of diseases that have been in a “dormant” state for a long time (allergies, bronchial asthma, etc. ). In addition, ARI pathogens have a toxic effect on the body of the expectant mother, which manifests itself in a change in the circulatory system. As a result, the risk of developing thrombosis or bleeding increases. Toxic exposure can lead to oxygen starvation of the mother and fetus, which is also accompanied by an increased risk of complications. nine0003
). In addition, ARI pathogens have a toxic effect on the body of the expectant mother, which manifests itself in a change in the circulatory system. As a result, the risk of developing thrombosis or bleeding increases. Toxic exposure can lead to oxygen starvation of the mother and fetus, which is also accompanied by an increased risk of complications. nine0003
Fortunately, acute respiratory infections in pregnant women usually occur in a mild form, like a cold. 1 Therefore, when prescribing timely treatment for colds during pregnancy, health risks can be reduced to a minimum.
Pregnancy 1st trimester
The most dangerous period. At this time, the organs of the fetus are just being formed, so the risk of pathology is high. In addition, the onset of gestation is accompanied by a decrease in the mother's immunity. At this stage, prevention is very important. nine0003
Complications that may require antibiotics are no less dangerous. It is advisable to treat a cold during pregnancy using rinsing the nose and throat with solutions of sea water, bed rest and drinking plenty of water.
Pregnancy 2nd trimester
In this period, the placenta is formed, as well as the main organs of the child, so the risks of the disease are less. The therapy is predominantly symptomatic: washing the nose and throat with solutions of sea water, antipyretic at high temperatures. nine0003
Pregnancy 3rd trimester
It is characterized by more severe symptoms, because the woman's body at this stage has to work for two. The disease can provoke premature birth, so bed rest is recommended. For the treatment of colds, sea water solutions are also used to wash the nose and throat. Additionally, you can use other drugs that are allowed during pregnancy, which are prescribed by a doctor.
Features of the course of a cold during pregnancy
In pregnant women, acute respiratory infections can have a long course. The causative agents of infections from the upper respiratory tract, together with the blood, enter the placenta, where they begin to multiply actively. This is associated with a high risk of fetal complications. 2
This is associated with a high risk of fetal complications. 2
The symptoms of a cold during pregnancy are the same as those of other people. These include cough, runny nose, sore throat, nasal congestion. Also, a cold during pregnancy can be manifested by an increase in body temperature. Along with this symptom, there are complaints of weakness, fatigue, poor appetite. nine0003
Prevention
Difficulties in treatment make prevention especially relevant. A product such as Aqualor can be used as a prophylaxis for washing the nasal cavity and removing pathogens of respiratory infections from it in the autumn-winter-spring period. It helps not only to prevent, but also to help treat the disease at the first symptoms.
Danger
Some viruses pose a threat to the fetus, they can cause changes in its development. Also, the disease is dangerous for its complications, so the treatment of a cold at home should be carried out only after consulting a doctor.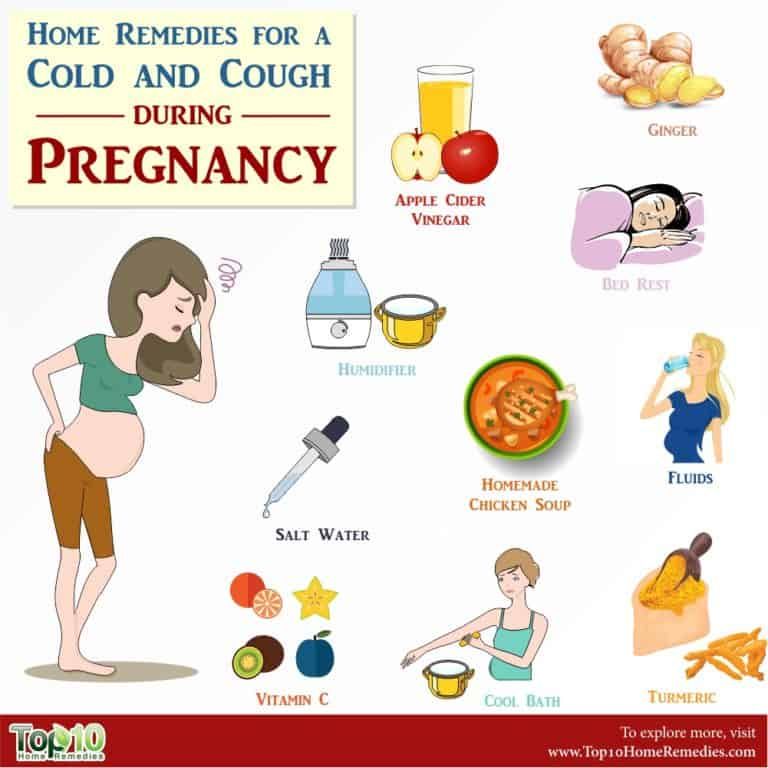 A timely diagnosed cold in the nose allows you to stop the spread of infection, prevents the development of bronchitis, otitis media and other complications. nine0003
A timely diagnosed cold in the nose allows you to stop the spread of infection, prevents the development of bronchitis, otitis media and other complications. nine0003
What to do at the first symptoms of a cold
Like the treatment of a cold in children, a disease in pregnant women requires medical supervision. You can help your body with a light plant-based diet, plenty of fluids, and regular nose and throat rinsing.
Aqualor sprays can help treat colds and runny nose: they remove pathogens from the surface of the mucous membrane of the nose and throat, cleanse the nose of crusts and excess mucus, moisturize the mucous membrane and create all the conditions for recovery. nine0003
How to treat a pregnant woman for a cold
The first question that worries expectant mothers is how to treat a cold during pregnancy so as not to harm the baby? "Classic" drugs in this case are not always used due to the lack of information about their safety. In some cases, women themselves refuse any drugs for fear of affecting the course of pregnancy. Therefore, the treatment of a cold in such cases begins with general recommendations. The main requirements are plenty of fluids, rest, light meals and cleansing of the nasopharynx. Treatment during illness with fever includes the use of antipyretics prescribed by a doctor. It is important to provide assistance as soon as possible and prevent the development of complications. nine0003
Therefore, the treatment of a cold in such cases begins with general recommendations. The main requirements are plenty of fluids, rest, light meals and cleansing of the nasopharynx. Treatment during illness with fever includes the use of antipyretics prescribed by a doctor. It is important to provide assistance as soon as possible and prevent the development of complications. nine0003
Exact treatment regimens are selected based on the causes and characteristics of the course of a cold in a particular patient. The disease can be caused by both viruses and bacteria, and it can occur in acute and chronic forms. Also, do not forget about possible complications that may require more complex and lengthy treatment.
In almost all cases, the treatment of a cold at home can be started with a universal method - irrigation of the mucous membrane with a solution of sea water. The unique mineral composition activates natural defenses, the optimal water-salt balance creates conditions for the normal functioning of tissues. nine0003
nine0003
Aqualor refers to those drugs that are allowed and recommended for pregnant women for treatment. The product is based on sea water, improves nasal breathing, prevents maternal and fetal hypoxia.
The drug is available both in 150 ml bottles, suitable for long-term use at home, and in 50 ml mini-formats, which are convenient to take with you. All Aqualor products are suitable for pregnant women, with the exception of Aqualor Protect. The choice is made depending on the causes and characteristics of the course of a cold. Aqualor Soft spray is suitable for regular nasal rinsing, Aqualor Forte can be used to relieve congestion. With a severe runny nose, you can use the Aqualor Active Forte spray, with a prolonged runny nose - Aqualor Active Soft. The products of the Aqualor Active line are enriched with CO 9 bubbles0206 2 , which contribute to the destruction of bacterial biofilms, which can cause prolonged and severe rhinitis.
What not to do
It is important to understand that therapy in pregnant women is very different from usual. It is strictly forbidden to take medicines without the consent of the doctor. Many drugs are contraindicated during pregnancy, others are prescribed only if the potential benefit outweighs the harm.
It is strictly forbidden to take medicines without the consent of the doctor. Many drugs are contraindicated during pregnancy, others are prescribed only if the potential benefit outweighs the harm.
Symptomatic relief requires a cold without fever. Her treatment excludes drugs that include alcohol, antibiotics, sulfonamides. Their appointment should be supervised by a doctor. nine0003
Flushing and drinking plenty of water are good if the first signs of a cold are observed. Treatment of complications is always carried out by a specialist. Help is urgently needed if:
- high temperature (above 39 degrees) or it does not go astray;
- there is constant vomiting;
- uterine tone or contractions are observed;
- there is bloody discharge from the vagina;
- on the fifth day there is no improvement, the general condition worsens; nine0035
- has rashes.
Terminals
Therapy of acute respiratory infections in pregnant women, as well as the treatment of a cold during breastfeeding, requires caution in prescribing medications.