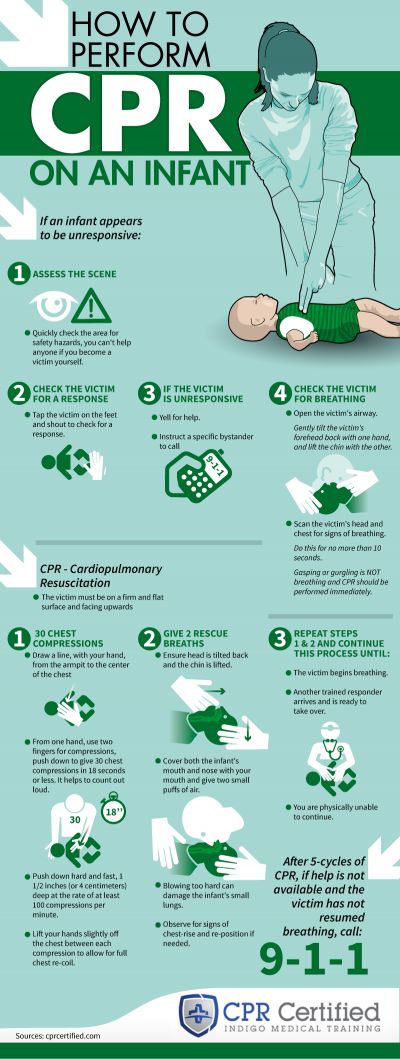
What can cause an ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentsMedically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Marissa Selner on January 8, 2018
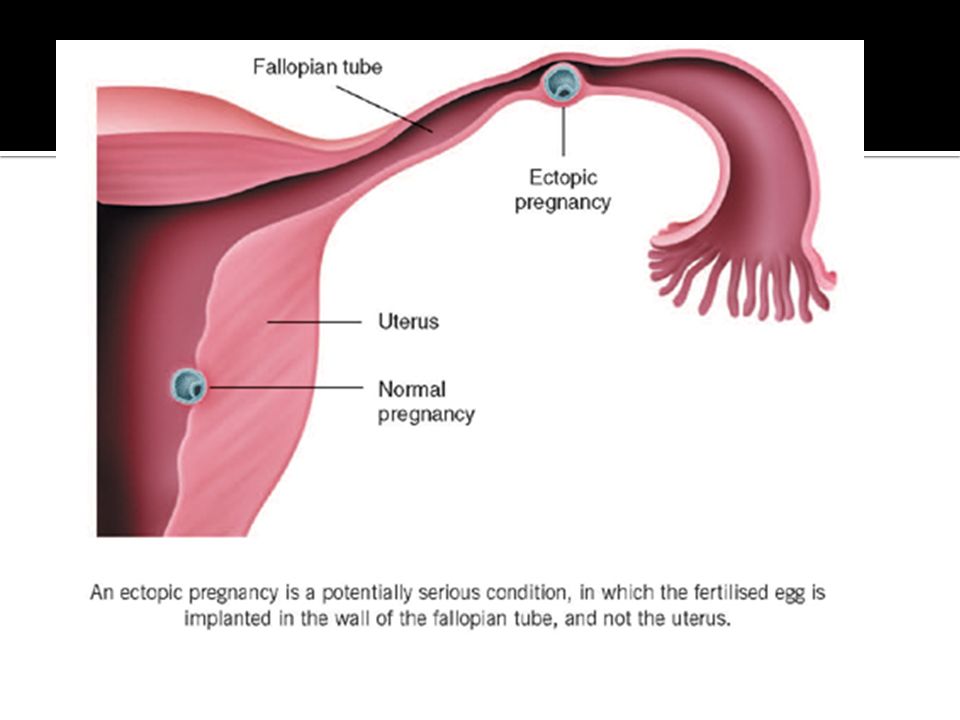
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
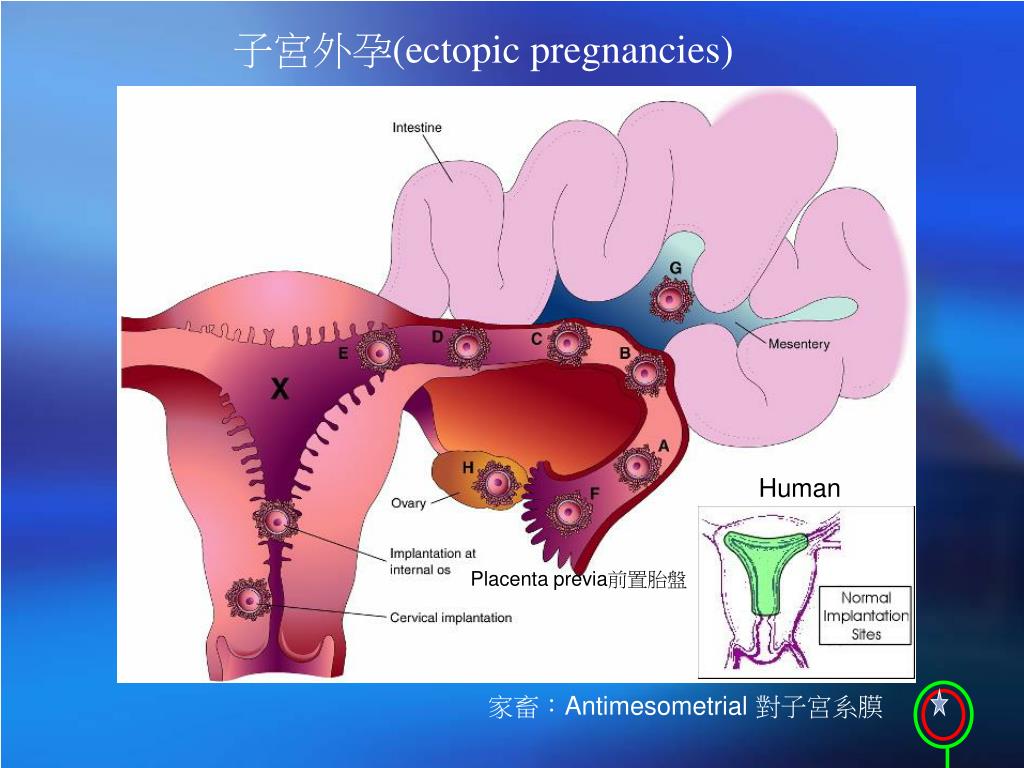
From fertilization to delivery, pregnancy requires a number of steps in a woman’s body. One of these steps is when a fertilized egg travels to the uterus to attach itself. In the case of an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg doesn’t attach to the uterus. Instead, it may attach to the fallopian tube, abdominal cavity, or cervix.
While a pregnancy test may reveal a woman is pregnant, a fertilized egg can’t properly grow anywhere other than the uterus. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), ectopic pregnancies occur in about 1 out of every 50 pregnancies (20 out of 1,000).
An untreated ectopic pregnancy can be a medical emergency. Prompt treatment reduces your risk of complications from the ectopic pregnancy, increases your chances for future, healthy pregnancies, and reduces future health complications.
What causes an ectopic pregnancy?
The cause of an ectopic pregnancy isn’t always clear. In some cases, the following conditions have been linked with an ectopic pregnancy:
- inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes from a previous medical condition, infection, or surgery
- hormonal factors
- genetic abnormalities
- birth defects
- medical conditions that affect the shape and condition of the fallopian tubes and reproductive organs
Your doctor may be able to give you more specific information about your condition.
Who is at risk for an ectopic pregnancy?
All sexually active women are at some risk for an ectopic pregnancy. Risk factors increase with any of the following:
- maternal age of 35 years or older
- history of pelvic surgery, abdominal surgery, or multiple abortions
- history of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- history of endometriosis
- conception occurred despite tubal ligation or intrauterine device (IUD)
- conception aided by fertility drugs or procedures
- smoking
- history of ectopic pregnancy
- history of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as gonorrhea or chlamydia
- having structural abnormalities in the fallopian tubes that make it hard for the egg to travel
If you have any of the above risk factors, talk to your doctor.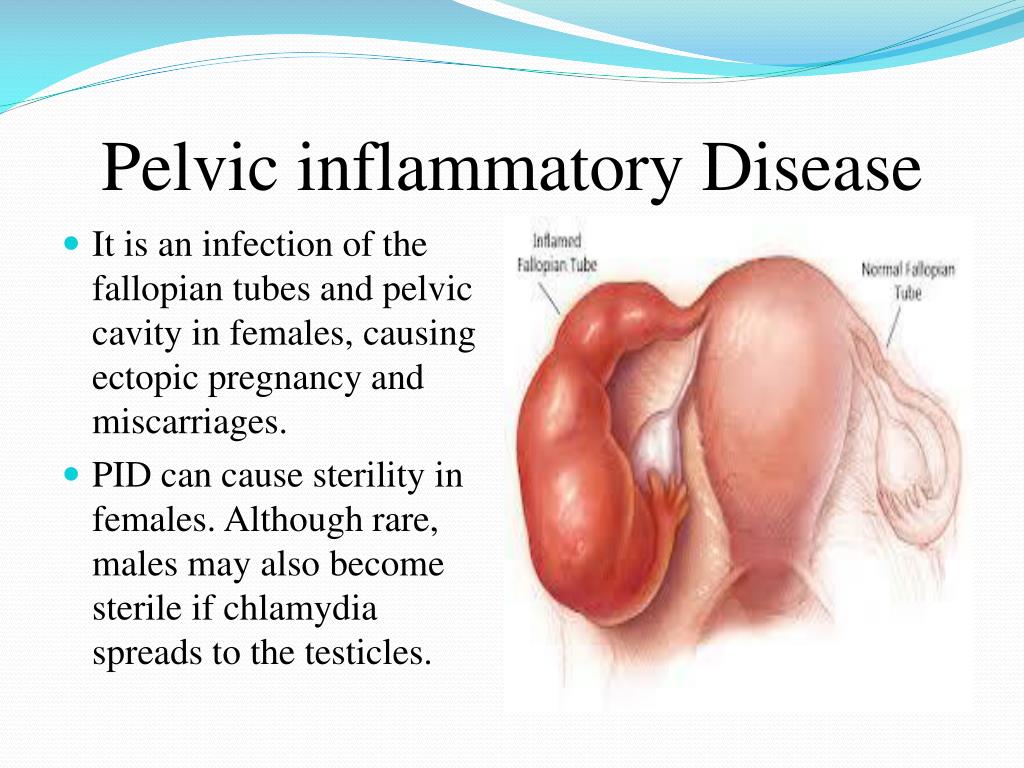 You can work with your doctor or a fertility specialist to minimize the risks for future ectopic pregnancies.
You can work with your doctor or a fertility specialist to minimize the risks for future ectopic pregnancies.
What are the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy?
Nausea and breast soreness are common symptoms in both ectopic and uterine pregnancies. The following symptoms are more common in an ectopic pregnancy and can indicate a medical emergency:
- sharp waves of pain in the abdomen, pelvis, shoulder, or neck
- severe pain that occurs on one side of the abdomen
- light to heavy vaginal spotting or bleeding
- dizziness or fainting
- rectal pressure
You should contact your doctor or seek immediate treatment if you know that you’re pregnant and have any of these symptoms.
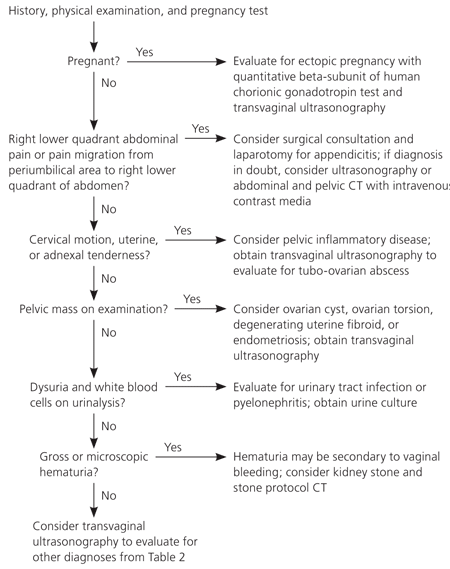
Diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy
If you suspect you may have an ectopic pregnancy, see your doctor immediately. Ectopic pregnancies can’t be diagnosed from a physical exam. However, your doctor may still perform one to rule out other factors.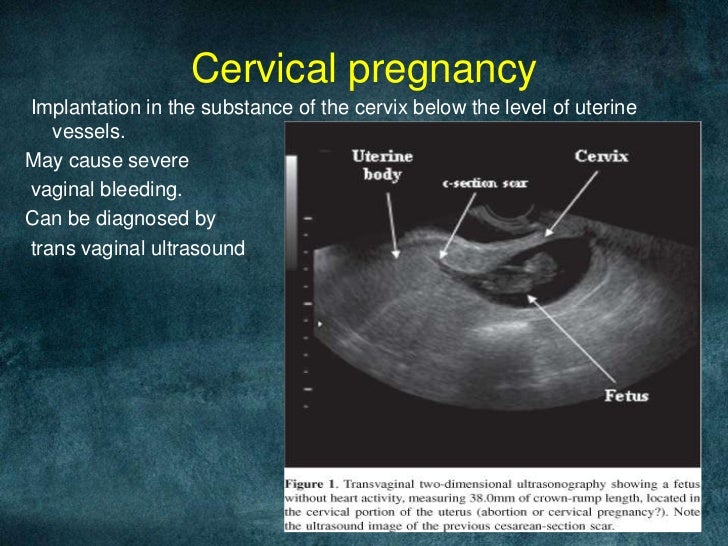
Another step to diagnosis is a transvaginal ultrasound. This involves inserting a special wand-like instrument into your vagina so that your doctor can see if a gestational sac is in the uterus.
Your doctor may also use a blood test to determine your levels of hCG and progesterone. These are hormones that are present during pregnancy. If these hormone levels start to decrease or stay the same over the course of a few days and a gestational sac isn’t present in an ultrasound, the pregnancy is likely ectopic.
If you’re having severe symptoms, such as significant pain or bleeding, there may not be enough time to complete all these steps. The fallopian tube could rupture in extreme cases, causing severe internal bleeding. Your doctor will then perform an emergency surgery to provide immediate treatment.
Treating ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies aren’t safe for the mother. Also, the embryo won’t be able to develop to term. It’s necessary to remove the embryo as soon as possible for the mother’s immediate health and long-term fertility.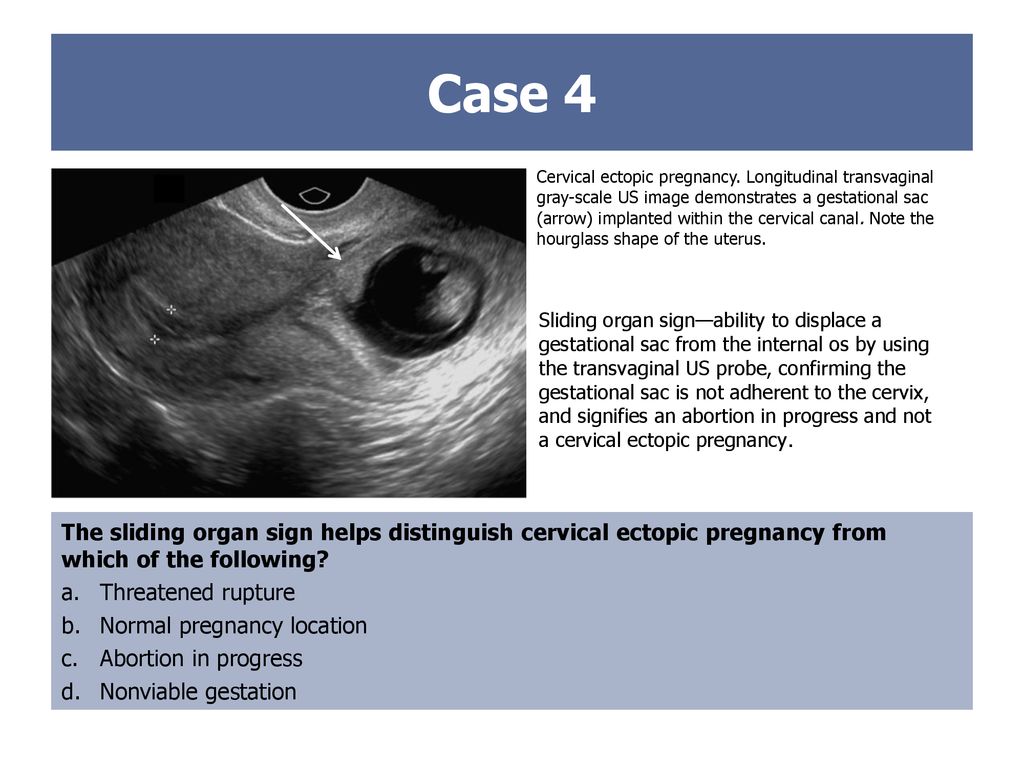 Treatment options vary depending on the location of the ectopic pregnancy and its development.
Treatment options vary depending on the location of the ectopic pregnancy and its development.
Medication
Your doctor may decide that immediate complications are unlikely. In this case, your doctor can prescribe several medications that could keep the ectopic mass from bursting. According to the AAFP, one common medication for this is methotrexate (Rheumatrex).
Methotrexate is a drug that stops the growth of rapidly dividing cells, such as the cells of the ectopic mass. If you take this medication, your doctor will give it to you as an injection. You should also get regular blood tests to ensure that the drug is effective. When effective, the medication will cause symptoms that are similar to that of a miscarriage. These include:
- cramping
- bleeding
- the passing of tissue
Further surgery is rarely required after this occurs. Methotrexate doesn’t carry the same risks of fallopian tube damage that come with surgery. You won’t be able to get pregnant for several months after taking this medication, however.
Surgery
Many surgeons suggest removing the embryo and repairing any internal damage. This procedure is called a laparotomy. Your doctor will insert a small camera through a small incision to make sure they can see their work. The surgeon then removes the embryo and repairs any damage to the fallopian tube.
If the surgery is unsuccessful, the surgeon may repeat a laparotomy, this time through a larger incision. Your doctor may also need to remove the fallopian tube during surgery if it’s damaged.
Home care
Your doctor will give you specific instructions regarding the care of your incisions after surgery. The chief goals are to keep your incisions clean and dry while they heal. Check them daily for infection signs, which could include:
- bleeding that won’t stop
- excessive bleeding
- foul-smelling drainage from the site
- hot to the touch
- redness
- swelling
You can expect some light vaginal bleeding and small blood clots after surgery. This can occur up to six weeks after your procedure. Other self-care measures you can take include:
This can occur up to six weeks after your procedure. Other self-care measures you can take include:
- don’t lift anything heavier than 10 pounds
- drink plenty of fluids to prevent constipation
- pelvic rest, which means refraining from sexual intercourse, tampon use, and douching
- rest as much as possible the first week postsurgery, and then increase activity in the next weeks as tolerated
Always notify your doctor if your pain increases or you feel something is out of the ordinary.
Prevention
Prediction and prevention aren’t possible in every case. You may be able to reduce your risk through good reproductive health maintenance. Have your partner wear a condom during sex and limit your number of sexual partners. This reduces your risk for STDs, which can cause PID, a condition that can cause inflammation in the fallopian tubes.
Maintain regular visits with your doctor, including regular gynecological exams and regular STD screenings. Taking steps to improve your personal health, such as quitting smoking, is also a good preventive strategy.
Taking steps to improve your personal health, such as quitting smoking, is also a good preventive strategy.
What’s the long-term outlook?
The long-term outlook after an ectopic pregnancy depends on whether it caused any physical damage. Most people who have ectopic pregnancies go on to have healthy pregnancies. If both fallopian tubes are still intact, or even just one, the egg can be fertilized as normal. However, if you have a preexisting reproductive problem, that can affect your future fertility and increase your risk of future ectopic pregnancy. This is especially the case if the preexisting reproductive problem has previously led to an ectopic pregnancy.
Surgery may scar the fallopian tubes, and it can make future ectopic pregnancies more likely. If the removal of one or both fallopian tubes is necessary, speak to your doctor about possible fertility treatments. An example is in vitro fertilization that involves implanting a fertilized egg into the uterus.
Pregnancy loss, no matter how early, can be devastating. You can ask your doctor if there are available support groups in the area to provide further support after loss. Take care of yourself after this loss through rest, eating healthy foods, and exercising when possible. Give yourself time to grieve.
Remember that many women go on to have healthy pregnancies and babies. When you’re ready, talk to your doctor about ways you can ensure that your future pregnancy is a healthy one.
Last medically reviewed on January 8, 2018
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Complications
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Cleveland Clinic Staff. (2014). Ectopic pregnancy.
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases_conditions/hic_Ectopic_Pregnancy - Ectopic pregnancy. (2017).
acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Ectopic-Pregnancy - Gyn onc home care after your laparotomy. (2017).
uwhealth.org/healthfacts/gyn-onc/6081.pdf - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2015). Ectopic pregnancy.
mayoclinic.com/health/ectopic-pregnancy/DS00622 - Perkins KM, et al. (2015). Risk of ectopic pregnancy associated with assisted reproductive technology in the United States, 2001-2011.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4315158/
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Jan 8, 2018
Written By
Marissa Selner
Edited By
Frank Crooks
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.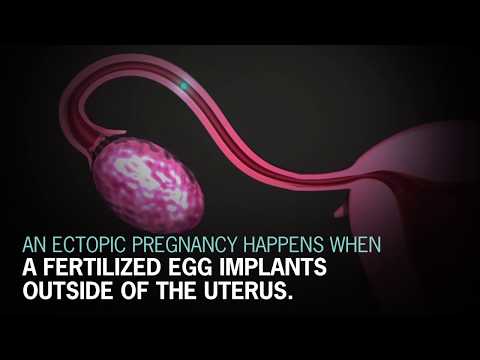 D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Marissa Selner on January 8, 2018
D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Marissa Selner on January 8, 2018
related stories
7 Causes for a False-Positive Pregnancy Test
Causes of a Negative Pregnancy Test with No Period
Pregnancy After Tubal Ligation: Know the Symptoms
What You Should Know About Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Depression After a Miscarriage
Read this next
7 Causes for a False-Positive Pregnancy Test
Reputable home pregnancy tests can be accurate, but they aren’t foolproof and can cause confusion. Here are 7 reasons you may receive a false-positive…
READ MORE
Causes of a Negative Pregnancy Test with No Period
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
If you miss your period but get a negative pregnancy test, there are a number of possible explanations. Here's what might be going on.
READ MORE
Pregnancy After Tubal Ligation: Know the Symptoms
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
If you've undergone a tubal ligation procedure, it's unlikely but still possible that you'll become pregnant. Here's what to watch for.
READ MORE
What You Should Know About Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.D., MSN
Blocked fallopian tubes can affect fertility, but with treatment, some women can go on to have healthy pregnancies.
READ MORE
Depression After a Miscarriage
Medically reviewed by Janine Kelbach, RNC-OB
It’s not uncommon to experience depression after the sudden loss of a pregnancy. Learn how to cope with the depression associated with miscarriage.
READ MORE
Pregnancy Complications
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
Sometimes a pregnant woman’s existing health conditions can contribute to problems, and other times new conditions arise because of body and hormonal…
READ MORE
Can Ectopic Pregnancy Be Diagnosed With Ultrasound?
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious condition that requires accurate and swift diagnosis. Ultrasound for ectopic pregnancy diagnosis is just one tool your…
READ MORE
Is It Safe to Consume Flaxseeds During Pregnancy?
Given the inconclusive and conflicting stances about eating flaxseeds during pregnancy, it might be better to err on the side of caution.
READ MORE
Pregnancy After Miscarriage: Answers to Your Questions
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
Getting pregnant after a miscarriage can be an emotional experience, filled with joy but also anxiety and guilt.
 Learn more about pregnancy after…
Learn more about pregnancy after…READ MORE
What Is a Nurse Midwife and How to Tell If They Are Right for You
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
A nurse midwife is a nurse with education, training, and certification to provide prenatal, delivery, and women's care.
READ MORE
Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentsMedically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Marissa Selner on January 8, 2018
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
From fertilization to delivery, pregnancy requires a number of steps in a woman’s body. One of these steps is when a fertilized egg travels to the uterus to attach itself. In the case of an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg doesn’t attach to the uterus. Instead, it may attach to the fallopian tube, abdominal cavity, or cervix.
While a pregnancy test may reveal a woman is pregnant, a fertilized egg can’t properly grow anywhere other than the uterus. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), ectopic pregnancies occur in about 1 out of every 50 pregnancies (20 out of 1,000).
An untreated ectopic pregnancy can be a medical emergency. Prompt treatment reduces your risk of complications from the ectopic pregnancy, increases your chances for future, healthy pregnancies, and reduces future health complications.
What causes an ectopic pregnancy?
The cause of an ectopic pregnancy isn’t always clear. In some cases, the following conditions have been linked with an ectopic pregnancy:
- inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes from a previous medical condition, infection, or surgery
- hormonal factors
- genetic abnormalities
- birth defects
- medical conditions that affect the shape and condition of the fallopian tubes and reproductive organs
Your doctor may be able to give you more specific information about your condition.
Who is at risk for an ectopic pregnancy?
All sexually active women are at some risk for an ectopic pregnancy. Risk factors increase with any of the following:
- maternal age of 35 years or older
- history of pelvic surgery, abdominal surgery, or multiple abortions
- history of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- history of endometriosis
- conception occurred despite tubal ligation or intrauterine device (IUD)
- conception aided by fertility drugs or procedures
- smoking
- history of ectopic pregnancy
- history of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as gonorrhea or chlamydia
- having structural abnormalities in the fallopian tubes that make it hard for the egg to travel
If you have any of the above risk factors, talk to your doctor. You can work with your doctor or a fertility specialist to minimize the risks for future ectopic pregnancies.
What are the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy?
Nausea and breast soreness are common symptoms in both ectopic and uterine pregnancies.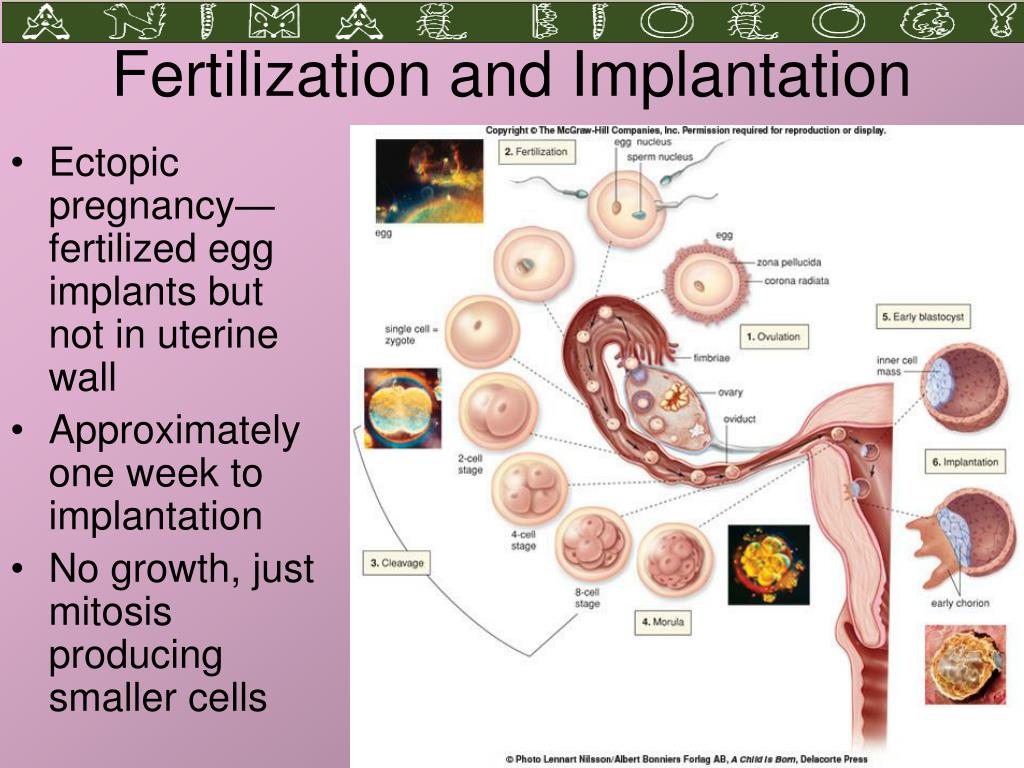 The following symptoms are more common in an ectopic pregnancy and can indicate a medical emergency:
The following symptoms are more common in an ectopic pregnancy and can indicate a medical emergency:
- sharp waves of pain in the abdomen, pelvis, shoulder, or neck
- severe pain that occurs on one side of the abdomen
- light to heavy vaginal spotting or bleeding
- dizziness or fainting
- rectal pressure
You should contact your doctor or seek immediate treatment if you know that you’re pregnant and have any of these symptoms.
Diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy
If you suspect you may have an ectopic pregnancy, see your doctor immediately. Ectopic pregnancies can’t be diagnosed from a physical exam. However, your doctor may still perform one to rule out other factors.
Another step to diagnosis is a transvaginal ultrasound. This involves inserting a special wand-like instrument into your vagina so that your doctor can see if a gestational sac is in the uterus.
Your doctor may also use a blood test to determine your levels of hCG and progesterone. These are hormones that are present during pregnancy. If these hormone levels start to decrease or stay the same over the course of a few days and a gestational sac isn’t present in an ultrasound, the pregnancy is likely ectopic.
These are hormones that are present during pregnancy. If these hormone levels start to decrease or stay the same over the course of a few days and a gestational sac isn’t present in an ultrasound, the pregnancy is likely ectopic.
If you’re having severe symptoms, such as significant pain or bleeding, there may not be enough time to complete all these steps. The fallopian tube could rupture in extreme cases, causing severe internal bleeding. Your doctor will then perform an emergency surgery to provide immediate treatment.
Treating ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies aren’t safe for the mother. Also, the embryo won’t be able to develop to term. It’s necessary to remove the embryo as soon as possible for the mother’s immediate health and long-term fertility. Treatment options vary depending on the location of the ectopic pregnancy and its development.
Medication
Your doctor may decide that immediate complications are unlikely. In this case, your doctor can prescribe several medications that could keep the ectopic mass from bursting.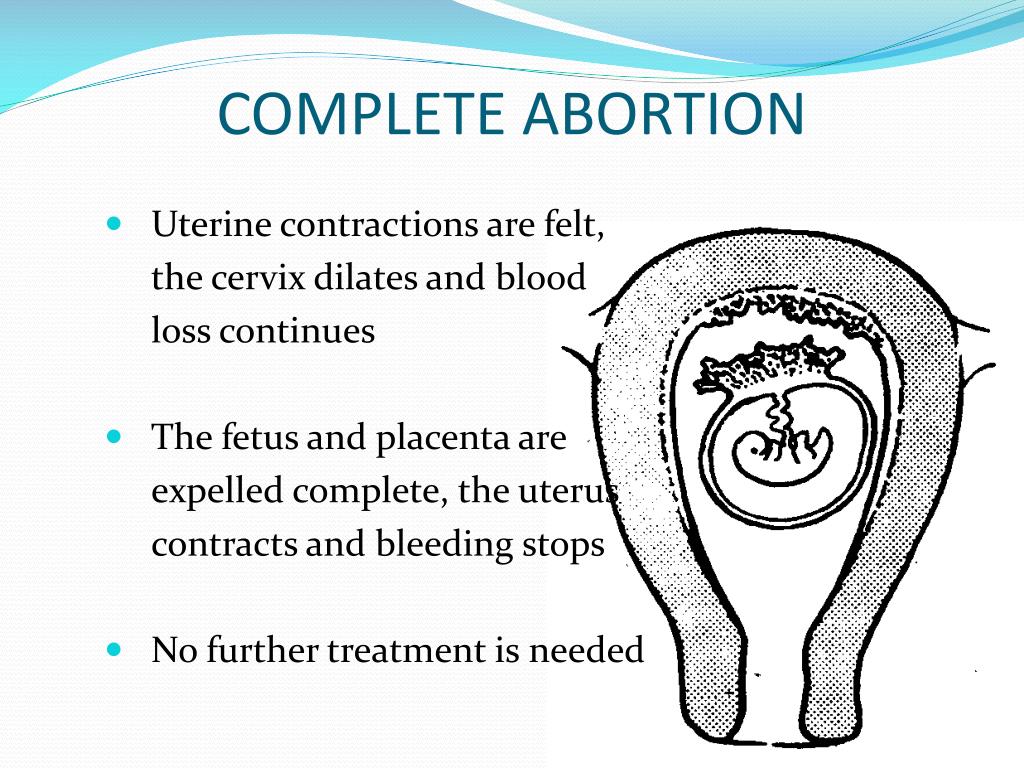 According to the AAFP, one common medication for this is methotrexate (Rheumatrex).
According to the AAFP, one common medication for this is methotrexate (Rheumatrex).
Methotrexate is a drug that stops the growth of rapidly dividing cells, such as the cells of the ectopic mass. If you take this medication, your doctor will give it to you as an injection. You should also get regular blood tests to ensure that the drug is effective. When effective, the medication will cause symptoms that are similar to that of a miscarriage. These include:
- cramping
- bleeding
- the passing of tissue
Further surgery is rarely required after this occurs. Methotrexate doesn’t carry the same risks of fallopian tube damage that come with surgery. You won’t be able to get pregnant for several months after taking this medication, however.
Surgery
Many surgeons suggest removing the embryo and repairing any internal damage. This procedure is called a laparotomy. Your doctor will insert a small camera through a small incision to make sure they can see their work. The surgeon then removes the embryo and repairs any damage to the fallopian tube.
The surgeon then removes the embryo and repairs any damage to the fallopian tube.
If the surgery is unsuccessful, the surgeon may repeat a laparotomy, this time through a larger incision. Your doctor may also need to remove the fallopian tube during surgery if it’s damaged.
Home care
Your doctor will give you specific instructions regarding the care of your incisions after surgery. The chief goals are to keep your incisions clean and dry while they heal. Check them daily for infection signs, which could include:
- bleeding that won’t stop
- excessive bleeding
- foul-smelling drainage from the site
- hot to the touch
- redness
- swelling
You can expect some light vaginal bleeding and small blood clots after surgery. This can occur up to six weeks after your procedure. Other self-care measures you can take include:
- don’t lift anything heavier than 10 pounds
- drink plenty of fluids to prevent constipation
- pelvic rest, which means refraining from sexual intercourse, tampon use, and douching
- rest as much as possible the first week postsurgery, and then increase activity in the next weeks as tolerated
Always notify your doctor if your pain increases or you feel something is out of the ordinary.
Prevention
Prediction and prevention aren’t possible in every case. You may be able to reduce your risk through good reproductive health maintenance. Have your partner wear a condom during sex and limit your number of sexual partners. This reduces your risk for STDs, which can cause PID, a condition that can cause inflammation in the fallopian tubes.
Maintain regular visits with your doctor, including regular gynecological exams and regular STD screenings. Taking steps to improve your personal health, such as quitting smoking, is also a good preventive strategy.
What’s the long-term outlook?
The long-term outlook after an ectopic pregnancy depends on whether it caused any physical damage. Most people who have ectopic pregnancies go on to have healthy pregnancies. If both fallopian tubes are still intact, or even just one, the egg can be fertilized as normal. However, if you have a preexisting reproductive problem, that can affect your future fertility and increase your risk of future ectopic pregnancy. This is especially the case if the preexisting reproductive problem has previously led to an ectopic pregnancy.
This is especially the case if the preexisting reproductive problem has previously led to an ectopic pregnancy.
Surgery may scar the fallopian tubes, and it can make future ectopic pregnancies more likely. If the removal of one or both fallopian tubes is necessary, speak to your doctor about possible fertility treatments. An example is in vitro fertilization that involves implanting a fertilized egg into the uterus.
Pregnancy loss, no matter how early, can be devastating. You can ask your doctor if there are available support groups in the area to provide further support after loss. Take care of yourself after this loss through rest, eating healthy foods, and exercising when possible. Give yourself time to grieve.
Remember that many women go on to have healthy pregnancies and babies. When you’re ready, talk to your doctor about ways you can ensure that your future pregnancy is a healthy one.
Last medically reviewed on January 8, 2018
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Complications
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Cleveland Clinic Staff. (2014). Ectopic pregnancy.
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases_conditions/hic_Ectopic_Pregnancy - Ectopic pregnancy. (2017).
acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Ectopic-Pregnancy - Gyn onc home care after your laparotomy. (2017).
uwhealth.org/healthfacts/gyn-onc/6081.pdf - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2015). Ectopic pregnancy.
mayoclinic.com/health/ectopic-pregnancy/DS00622 - Perkins KM, et al. (2015). Risk of ectopic pregnancy associated with assisted reproductive technology in the United States, 2001-2011.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4315158/
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Jan 8, 2018
Written By
Marissa Selner
Edited By
Frank Crooks
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Marissa Selner on January 8, 2018
related stories
7 Causes for a False-Positive Pregnancy Test
Causes of a Negative Pregnancy Test with No Period
Pregnancy After Tubal Ligation: Know the Symptoms
What You Should Know About Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Depression After a Miscarriage
Read this next
7 Causes for a False-Positive Pregnancy Test
Reputable home pregnancy tests can be accurate, but they aren’t foolproof and can cause confusion. Here are 7 reasons you may receive a false-positive…
READ MORE
Causes of a Negative Pregnancy Test with No Period
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
If you miss your period but get a negative pregnancy test, there are a number of possible explanations. Here's what might be going on.
READ MORE
Pregnancy After Tubal Ligation: Know the Symptoms
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
If you've undergone a tubal ligation procedure, it's unlikely but still possible that you'll become pregnant. Here's what to watch for.
READ MORE
What You Should Know About Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.D., MSN
Blocked fallopian tubes can affect fertility, but with treatment, some women can go on to have healthy pregnancies.
READ MORE
Depression After a Miscarriage
Medically reviewed by Janine Kelbach, RNC-OB
It’s not uncommon to experience depression after the sudden loss of a pregnancy. Learn how to cope with the depression associated with miscarriage.

READ MORE
Pregnancy Complications
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
Sometimes a pregnant woman’s existing health conditions can contribute to problems, and other times new conditions arise because of body and hormonal…
READ MORE
Can Ectopic Pregnancy Be Diagnosed With Ultrasound?
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious condition that requires accurate and swift diagnosis. Ultrasound for ectopic pregnancy diagnosis is just one tool your…
READ MORE
Is It Safe to Consume Flaxseeds During Pregnancy?
Given the inconclusive and conflicting stances about eating flaxseeds during pregnancy, it might be better to err on the side of caution.
READ MORE
Pregnancy After Miscarriage: Answers to Your Questions
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
Getting pregnant after a miscarriage can be an emotional experience, filled with joy but also anxiety and guilt.
 Learn more about pregnancy after…
Learn more about pregnancy after…READ MORE
What Is a Nurse Midwife and How to Tell If They Are Right for You
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
A nurse midwife is a nurse with education, training, and certification to provide prenatal, delivery, and women's care.
READ MORE
Ectopic pregnancy - terms, causes, symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment (surgery, removal)
Causes
Signs
Diagnosis
Treatment
What to do
Ectopic pregnancy is one of the most dangerous pathological conditions in which the fetus develops outside the uterine cavity. The place of its implantation can be the fallopian (uterine) tubes, as well as other organs of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis.
Termination of an ectopic pregnancy is accompanied by intra-abdominal bleeding and severe complications requiring surgical intervention.
In the female body, normal gestation is possible only in the uterus, but in practice, the location of the embryo, in addition to the uterus, may vary.
There are several types of ectopic pregnancy: tubal, ovarian, abdominal, cervical and with a location in the rudimentary horn of the uterus.
The sites listed are unfavorable for gestation, so an ectopic pregnancy is terminated at 4 to 8 weeks to prevent serious complications.
Attached in an atypical place, the vessels of the fetal egg grow into the surrounding tissues. Other organs, besides the uterus, are not able to stretch and form blood vessels for the placenta. As a result, damage to surrounding tissues occurs, exfoliation of the fetal egg, as a result, severe bleeding occurs that threatens the life of the patient.
The appearance of a tubal form of pathology is associated with the presence of obstacles in the movement of a fertilized egg. If the fertilized egg does not reach the uterine cavity, then it is implanted in the fallopian tube. Ectopic fetal development occurs in approximately 2% of cases among all types of pregnancy, of which 9 fall on the tubal form.eight%. Fetal implantation in other parts of the uterus and appendages, as well as in the abdominal cavity, is much less common.
Ectopic fetal development occurs in approximately 2% of cases among all types of pregnancy, of which 9 fall on the tubal form.eight%. Fetal implantation in other parts of the uterus and appendages, as well as in the abdominal cavity, is much less common.
The release of a fertilized egg into the abdominal cavity with further implantation to the omentum, peritoneum or intestine leads to the development of abdominal pregnancy. One of the causes of this pathology may be in vitro fertilization.
In cervical pregnancy, the egg is implanted in the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal. As a result of deep penetration of the embryonic villi into the muscular layer of the cervix, the pregnancy ends in very heavy bleeding.
Causes of pathology
The development of pregnancy outside the uterine cavity occurs as a result of failures of natural processes that prevent the penetration of a fertilized egg into it. The most common causes of ectopic pregnancy include:
- previously transferred infectious lesions of the appendages caused by pathogenic microflora;
- the presence of adhesions in the fallopian tubes;
- defects in the structure of the genital organs;
- installed IUD in the uterus;
- infantilism;
- the presence of a tumor in the appendages or uterus;
- use of assisted reproduction methods;
- use of hormonal contraceptives;
- the presence of an inflammatory focus in the pelvic cavity;
- previous surgical interventions on the appendages;
- stimulation of the ovulation process;
- history of abortion;
- endometriosis.

Features
It is not possible to determine the pathology at home. In this regard, timely registration can play a decisive role in the correct diagnosis.
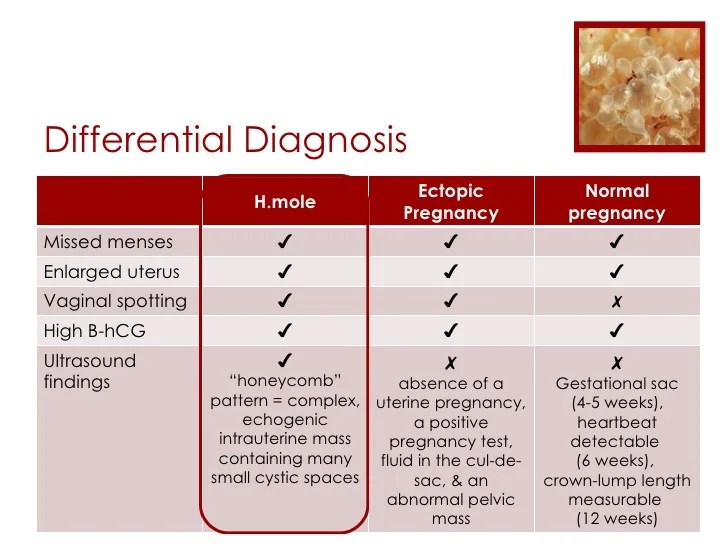
At an early stage of development, an ectopic pregnancy has no distinguishing features. As a rule, it is characterized by:
- absence of menstruation;
- breast engorgement;
- manifestations or absence of toxicosis;
- a positive pregnancy test, although in the presence of ectopic pathology it is not pronounced;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen with irradiation to the rectal area, as well as "spotting" discharge from the vagina.
Clinical manifestations of fetal development in the fallopian tube
An ectopic pregnancy can have a progressive form, in which case the growing fetal egg penetrates the muscular layer of the fallopian tube, leading to its gradual destruction. The patient has all the symptoms of pregnancy, but there are small bleeding from the genitals.
The patient has all the symptoms of pregnancy, but there are small bleeding from the genitals.
Also ectopic pregnancy can be terminated:
- as a tubal abortion. In this case, there is a partial or complete detachment of the membranes of the embryo from the wall of the tube and its entry into the abdominal cavity. Symptoms of manifestations depend on the severity of bleeding. Characterized by the presence of vaginal discharge in the form of blood clots. A pronounced soreness in the lower abdomen joins. Bimanual examination reveals an increase in the size of the uterus and appendages. Palpation of the posterior vaginal fornix is very painful;
- is like a ruptured fallopian tube. May occur after the 6th week of pregnancy. This condition is life threatening due to internal bleeding. Patients complain of very severe pain in the lower abdomen on both sides. There is a protrusion of the posterior fornix of the vagina and a "floating" uterus during a bimanual examination.

How to detect an ectopic pregnancy
In the initial period, it is difficult to diagnose pathology. Symptoms indicate, as a rule, the presence of pregnancy, but there are no signs typical for the pathology.
Diagnosis is carried out by examining a woman in a gynecological chair, as well as using additional research methods:
- blood test for B-hCG, which in case of ectopic pregnancy shows a shorter period than it actually is;
- Ultrasound, which will give more complete information about the development of the fetal egg and its location.
Interrupted tubal pregnancy is accompanied by intra-abdominal bleeding. Typical symptoms of a pipe rupture will be:
- acute pain in the lower abdomen radiating to the anus, lumbar region, legs;
- secretion of blood from the genital tract;
- rapid, weak pulse;
- sudden drop in blood pressure;
- loss of consciousness.

Clinical manifestations of an interrupted tubal pregnancy should be differentiated from appendicitis and ovarian apoplexy. When the embryo is located in the cervical region, pregnancy should be distinguished from incomplete abortion and tumors.
An ectopic pregnancy can be confirmed or denied after ultrasound diagnostics and a blood test for B-hCG.
Treatment
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy is carried out only by surgery. All the efforts of doctors are aimed at maintaining the integrity and function of the fallopian tube, into which the implantation of the fetal egg has occurred. With timely detection of pathology and a small blood loss, a laparoscopic operation is performed.
When localizing the embryo in the tube, the following types of surgical intervention are used:
- tubotomy (removal of the fetal egg while preserving the tube). In the case of choosing this method, the possibility of recurrence of the pathology is taken into account;
- tubectomy (excision of the tube) - performed in the presence of severe damage.
The choice of methodology is influenced by the following factors:
- whether the woman plans to have a child in the future;
- repeated ectopic pregnancy will require removal of the tube;
- whether there is an adhesive process in the small pelvis;
- change in the structure of the wall of the fallopian tube.
If the blood loss is large, then in order to save a life during an ectopic pregnancy, it is necessary to perform an abdominal operation, in which the fetal egg and tube are removed. Plasma transfusion may be required to restore blood loss. It is important that the remaining second pipe fully retains its function.
How to deal with an ectopic pregnancy
To avoid serious complications that can occur during a pathological pregnancy, a timely visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist will help. Attempts to save the fetus can lead to sad consequences: as a result of a ruptured tube, blood flows into the abdominal cavity, which leads to fatal hemorrhagic shock.
When a patient is diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy, urgent hospitalization is required to terminate the pregnancy.
The author of the article:
Shklyar Aleksey Alekseevich
obstetrician-gynecologist, surgeon, KMN, head of the direction "Obstetrics and Gynecology"
work experience 10 years
reviews leave feedback
Clinic
m. Sukharevskaya
Reviews
Inna
30.12.2021 21:55:20
Clinic
m. Sukharevskaya
Doctor
Shklyar Aleksey Alekseevich
I turned to Shklyar Aleksey Alekseevich I want to express my deepest gratitude to the entire staff of the operating unit Aleksey Alekseevich Shklyar. You are all doctors with a capital letter. I never tire of thanking God for bringing me to you. I came to you on the recommendation of Sorvacheva M.V. We got in touch with the doctor by phone and appointed the day of the operation.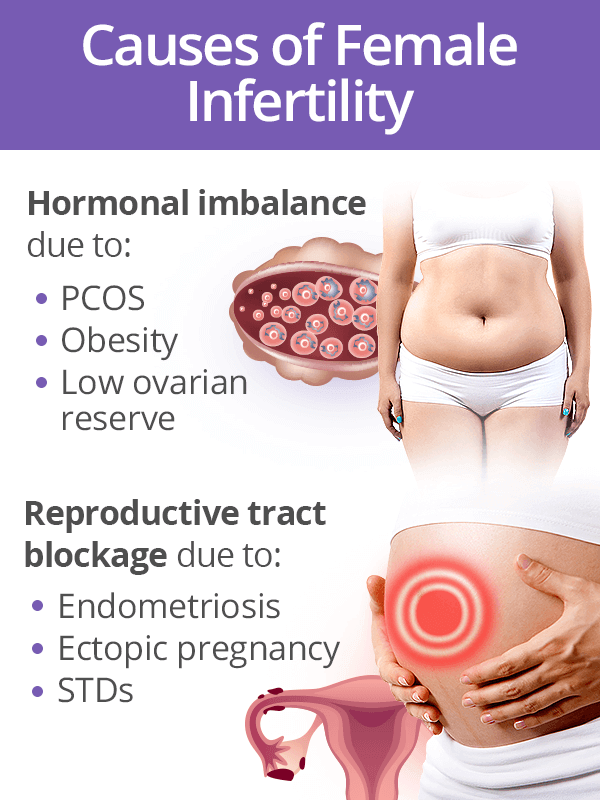 For the first time, I was pleasantly surprised how Alexey Alekseevich told me everything in detail and reassured me. A couple of weeks later, I arrived at the clinic at 10.00 with a complete list of tests, and already at 11 I was lying on the operating table, to be honest, I didn’t even have time to get scared) Then the anesthetist magician came and I fell asleep sweetly. I woke up already in bed, nothing hurt, there were no side effects, just a normal morning awakening. I would never have believed that this was even possible, I am very grateful for a wonderful dream. Before that, I had more than one general anesthesia in state hospitals, and now I understand for sure that they apparently wanted to kill me there, but it didn’t work out. For the next two hours, until it was impossible to get up, wonderful nurses came to me asking how I felt and if I needed something, they put droppers, and I lay and did not believe that everything terrible was over)) 2 hours after the operation, I was already getting up and drank delicious broth and tea.
For the first time, I was pleasantly surprised how Alexey Alekseevich told me everything in detail and reassured me. A couple of weeks later, I arrived at the clinic at 10.00 with a complete list of tests, and already at 11 I was lying on the operating table, to be honest, I didn’t even have time to get scared) Then the anesthetist magician came and I fell asleep sweetly. I woke up already in bed, nothing hurt, there were no side effects, just a normal morning awakening. I would never have believed that this was even possible, I am very grateful for a wonderful dream. Before that, I had more than one general anesthesia in state hospitals, and now I understand for sure that they apparently wanted to kill me there, but it didn’t work out. For the next two hours, until it was impossible to get up, wonderful nurses came to me asking how I felt and if I needed something, they put droppers, and I lay and did not believe that everything terrible was over)) 2 hours after the operation, I was already getting up and drank delicious broth and tea. The rest of the time before sleep, I walked around the ward, I didn’t feel any pain at all, a little weakness and nothing more. The next morning I was fed deliciously and discharged home. After being discharged, Aleksey Alekseevich is constantly in touch, he worries about my well-being more than even my relatives. I needed further treatment, he even helps me with this by calling the best doctors and clinics, supporting me. And now I know for sure that I am in the most reliable hands. Thank you very much again. Prosperity to your clinic and low bow to all your doctors. You are the best!!!
The rest of the time before sleep, I walked around the ward, I didn’t feel any pain at all, a little weakness and nothing more. The next morning I was fed deliciously and discharged home. After being discharged, Aleksey Alekseevich is constantly in touch, he worries about my well-being more than even my relatives. I needed further treatment, he even helps me with this by calling the best doctors and clinics, supporting me. And now I know for sure that I am in the most reliable hands. Thank you very much again. Prosperity to your clinic and low bow to all your doctors. You are the best!!!
Lilia
05/15/2021 15:57:57
Clinic
m. Sukharevskaya
Doctor
Shklya Alekseyevich
on May 7, 2021, underwent a male gynecological surgery, and would like to express gratitude to the attending physician, to the head of the gynecological department Shklyar Aleksey Alekseevich, - for high professionalism, and exceptionally friendly attitude, understandable recommendations. The doctor communicates very correctly, clearly and with explanations.
The doctor communicates very correctly, clearly and with explanations.
Special thanks to the anesthetist Alexey Valeryevich Fomin for the quality anesthesia (I was more afraid of anesthesia than the operation itself), but everything went well, I was “not present” at the operation, and the condition after anesthesia was normal, as after waking up in the morning, no “side effects” ' did not feel.
After the operation, nothing hurt after half an hour, and after an hour and a half, I went home.
The attitude in the hospital was the most friendly, including from the nurses and the administrator at the reception (unfortunately, I did not ask for names).
It's been a week since the operation, and only the discharge summary # 140035314 reminds me of it.
I'm very glad that I trusted the experience of the Polyclinic.
Services
- Title
- Primary appointment, consultation of an obstetrician-gynecologist3590
- Reception, consultation of an obstetrician-gynecologist repeated2200
- Reception, consultation of the doctor of the head of the department of gynecology / Ph.
 D. primary4300
D. primary4300 - Reception, consultation of the head of the department of gynecology / Ph.D. repeated2750
Health articles
All articlesAllergistGastroenterologistHematologistGynecologistDermatologistImmunologistInfectionistCardiologistCosmetologistENT doctor (otolaryngologist)MammologistMassageNeurologistNephrologistOzone therapyOncologistOphthalmologistProctologistPsychotherapistPulmonologistRheumatologistTherapistTraumatologistTrichologistUltrasound (ultrasound examination)UrologistPhysiotherapistPhlebologistSurgeonFunctional diagnostics and Energist 905 years. Red Gates. AvtozavodskayaPharmacy. Glades. Sukharevskaya. st. Academician Yangelam. Frunzenskaya ZelenogradOkocha Victoria Aleksandrovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductive specialist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound doctor
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Frunzenskaya
Frunzenskaya
Ellinskaya Anastasia Aleksandrovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound doctor
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Smolenskaya
m. Polyanka
Akabirova Shakhlooy Anvarovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, endocrinologist, ultrasound doctor, KMN
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Red Gate
m. Avtozavodskaya
Gazdieva Irina Khasanovna
obstetrician-gynecologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Street 1905 Goda
Zharova Natalya Anatolyevna
obstetrician-gynecologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Street 1905 Goda
Street 1905 Goda
Zotova Natalya Yurievna
obstetrician-gynecologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Street 1905 Goda
Meshcheryakova Elena Alexandrovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound doctor, online consultations
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Sukharevskaya
Rodina Tatyana Lvovna
obstetrician-gynecologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Avtozavodskaya
Ryabova Olga Borisovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound doctor
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m.