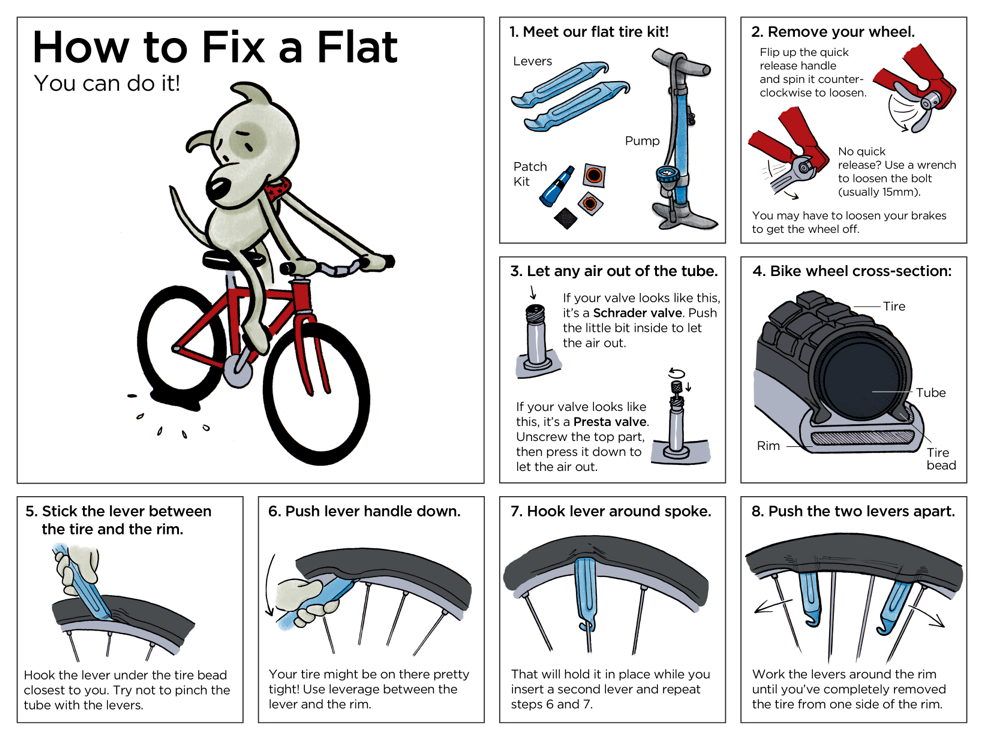
Baby pushing down
Recognizing Premature Labor | Patient Education
What is Premature Labor?
A term pregnancy takes about 40 weeks to complete. Babies born before 37 weeks may have problems breathing, eating and keeping warm. Premature labor occurs between the 20th and 37th week of pregnancy, when uterine contractions cause the cervix, the mouth of the uterus or womb, to open earlier than normal. This can result in premature birth.
Certain factors may increase a woman's chances of having premature labor, such as carrying twins. However, the specific cause or causes of premature labor are not known. Sometimes a woman may have premature labor for no apparent reason.
Warning Signs of Premature Labor
It may be possible to prevent a premature birth by knowing the warning signs of premature labor and by seeking care early if these signs occur. Warning signs and symptoms for premature labor include:
- Uterine contractions that happen six or more times in an hour, with or without any other warning signs.
- Menstrual-like cramps felt in the lower abdomen that may come and go or be constant.
- Low dull backache felt below the waistline that may come and go or be constant.
- Pelvic pressure that feels like your baby is pushing down. This pressure comes and goes.
- Abdominal cramping with or without diarrhea.
- Increase or change in vaginal discharge such as change into a mucousy, watery or bloody discharge.
Continue reading
Uterine Contractions: How to Tell What's Normal
It is normal to have some uterine contractions throughout the day. They often occur when you change positions, such as from sitting to lying down. It is not normal to have frequent uterine contractions, such as six or more in one hour. Frequent uterine contractions or tightenings may cause your cervix to begin to open.
Since the onset of premature labor is very subtle and often hard to recognize, it is important to know how to feel your abdomen for uterine contractions. You can feel for contractions in this way:
You can feel for contractions in this way:
- While lying down, place your fingertips on the top of your uterus
- A contraction is a periodic tightening or hardening of your uterus. If your uterus is contracting, you will actually feel your abdomen get tight or hard, and then feel it relax or soften when the contraction is over.
What To Do If You Think You May Have Symptoms of Premature Labor
If you think you are having uterine contractions or any other signs and symptoms of premature labor:
- Lie down tilted towards your side. Place a pillow at your back for support.
- Sometimes lying down for an hour may slow down or stop the signs and symptoms.
- Do not lie flat on your back, because lying flat may cause the contractions to occur more often.
- Do not turn completely on your side, because you may not be able to feel the contractions.
- Hydrate yourself by drinking several large glasses of water. Sometimes being dehydrated can cause contractions.

- To tell how often contractions are occurring, check the minutes that elapse from the beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the next.
- You have six or more uterine contractions in one hour
- You have any of the other signs and symptoms for one hour
- You have any spotting or leaking of fluid from your vagina
With acknowledgement to Dr. Robert K. Creasy for his assistance and to the March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation for their support.
What week does baby dropping happen?
Baby dropping is when a baby’s head moves lower down into the pelvis ready for labor. It usually happens towards the end of the third trimester of pregnancy.
Also called lightening, baby dropping is a sign that a baby is nearly ready to be born. Before dropping, the baby may rotate, so the back of its head is toward the front of the tummy, head facing down. Then, the baby may drop down into the pelvis.
Before dropping, the baby may rotate, so the back of its head is toward the front of the tummy, head facing down. Then, the baby may drop down into the pelvis.
When the baby has settled in the pelvis, doctors describe it as engaged. This means it is ready for birth.
Share on PinterestBaby dropping is when the baby’s head moves to the bottom of the pelvis.Precisely when it happens is different for every woman. There is no set day or week that women should expect their baby to drop.
For some women, baby dropping happens just as labor starts or a few hours before. For other women, it may happen a few weeks before labor begins.
Baby dropping might happen closer to labor for women who have had babies before. This is because their body has been through labor before, so their pelvis may need less time to adjust to the process.
Women who are pregnant for the first time may find that baby dropping occurs some days or weeks before labor. This may be because their pelvic muscles need to adjust to the birthing position before labor can begin.
If a woman thinks her baby has dropped, she should speak to a doctor. The doctor can check the position of the baby, which helps them estimate when labor may begin.
Some women may feel baby dropping as a sudden, noticeable movement. Others may not notice it happening at all.
Some women may notice that their abdomen feels lighter after the baby has dropped. This might be because the baby is positioned lower in the pelvis, leaving more room in her middle.
This feeling of increased space in the abdomen is why baby dropping is also called lightening.
Lightening may seem an inappropriate term for some. Baby dropping sometimes makes women feel like they are carrying a bowling ball between their legs.
Every woman’s experience of baby dropping is different.
Share on PinterestPelvic pain may be a sign of the baby dropping.
The following signs suggest a baby may have dropped:
1. Lower belly
A woman’s pregnancy bump may look like it is sitting lower when the baby drops.
2. Pelvic pressure pain
As the baby drops into the pelvis, the pressure in this area may increase.
This may cause a woman to feel like she is waddling when she walks.
3. Pelvic pain
When the baby drops, some women may experience flashes of pelvic pain. This may be due to the baby’s head pushing against ligaments in the pelvis.
4. Easier breathing
There is less pressure on the diaphragm once the baby has dropped. This may make breathing easier.
5. Hemorrhoids
After the baby drops, its head may put pressure on the nerves in the pelvis and rectum. This pressure may cause hemorrhoids.
6. More discharge
Baby dropping increases pressure on the cervix. This causes it to lose the mucus plug that sits at the top of the cervix until the end of pregnancy. It is there to stop bacteria from entering the uterus.
After baby dropping, the mucus plug may exit the vagina as jelly or yolk-like discharge.
7. Frequent need to urinate
When the baby sits lower in the pelvis, its head may put pressure on the bladder. This may make a woman need to urinate often.
8. Back pain
Baby dropping may put additional pressure on the muscles in the lower back. This may cause back pain.
9. Feeling hungrier
When the baby drops, it may reduce pressure on the stomach. This may ease heartburn and increase hunger.
If a woman thinks her baby has dropped, she should see the doctor. The doctor can work out what position the baby is in using a fetal stations scale. Some doctors use a three-point scale; others use a five-point scale.
The five-point scale is more traditional and more widely used. A 2015 article describes it as a system which divides the pelvis above and below the ischial spines into fifths.
The ischial spines are on the pelvis. When the baby drops ready for labor, its head is level with the ischial spines.
The five-point scale measures from -5 to +5. Each step forward on the scale means the baby is a centimeter closer to being born.
Before the baby drops, a woman may be at station -5. When the baby drops (and is engaged) a woman may be at station zero. When the baby crowns (fills the vagina) a woman may be at station +5.
According to a 2014 study, 95 percent of women have a station of zero or lower when fully dilated.
To estimate which station a woman is at, the doctor examines a woman’s vagina and feels for the baby’s head.
Share on PinterestWalking may help to encourage baby dropping.
If a woman’s due date is imminent, but her baby is yet to drop, she can try specific activities to encourage the baby to descend.
These include:
- walking
- sitting on a birthing ball
- squatting
- pelvic tilts
These activities all help to open the hips and stretch the pelvic muscles. This may encourage the baby to drop down into the pelvis.
It is normal to experience some pelvic pain after the baby drops. That said, some types of pelvic pain may need investigating.
Speak to the doctor if pelvic pain is constant or regular. Or if it is accompanied by:
- bleeding
- loss of fluids
- fever
Baby dropping typically happens towards the end of pregnancy. It may occur as labor starts, hours before, or sometimes a few weeks before. It is more likely to happen weeks before labor for women who are pregnant for the first time.
Baby dropping may feel like a sudden, noticeable movement for some women, while others may not feel it happening. Baby dropping, or lightening, may make it easier to breathe and increase appetite. This is because there is more space in the abdomen and less pressure on organs.
When the baby drops, pressure on the pelvis may cause some pain. If the pain is continuous or regular, it is a good idea to speak to a doctor.
How the baby behaves before birth
Pregnancy
Article
0 reviews
The activity of a child in the mother's womb is a key sign of his life. The baby moves and pushes throughout the entire period of pregnancy. The frequency and nature of these movements is constantly changing - from very tangible shocks to barely perceptible stirring. The end of the third trimester - 38-40 weeks of pregnancy - the period when the baby slows down a little, calms down and begins to prepare for the moment of its birth.
The baby moves and pushes throughout the entire period of pregnancy. The frequency and nature of these movements is constantly changing - from very tangible shocks to barely perceptible stirring. The end of the third trimester - 38-40 weeks of pregnancy - the period when the baby slows down a little, calms down and begins to prepare for the moment of its birth.
4 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
How does a child behave before giving birth, why count the number of movements and when to start preparing for a trip to the hospital? More on this later.
Behavior of the baby in the womb at 38-40 weeks of pregnancy
At the beginning of the third trimester of pregnancy, the baby is very active - constantly somersaults and pushes, constantly reminding his mother of his presence. He has enough space for such acrobatic tricks. Toward the end of the gestation period, the amniotic fluid is increasingly restricting his movements, so the behavior of the crumbs changes noticeably. He becomes calmer, and only from time to time announces himself with strong, but confident pushes. This is due not only to the lack of space, but also to the fact that the baby begins to prepare for his first meeting with the outside world.
He becomes calmer, and only from time to time announces himself with strong, but confident pushes. This is due not only to the lack of space, but also to the fact that the baby begins to prepare for his first meeting with the outside world.
What happens to the baby before delivery:
- he changes his position
- all organs and systems are already fully formed
- the body begins to produce cortisol - a hormone that helps the lungs to fully mature
- the first feces are formed in the intestines
- the weight of the crumbs reaches an average of 3250 kg, and the height is 48 cm
Why count the number of baby's movements before birth
As we have already noted, at the final stage of pregnancy, the baby calms down. This condition is absolutely normal. However, the dynamics of its activity must be monitored. If the child behaves too quietly, or vice versa - moves too often - this is a cause for concern.
Approximately 10-12 movements within 6 hours are considered normal. That is - 1-2 times per hour. If you find this to be quite common, don't worry. This has its advantages - so you can better feel the baby, understand his claims and discontent.
That is - 1-2 times per hour. If you find this to be quite common, don't worry. This has its advantages - so you can better feel the baby, understand his claims and discontent.
If the child does not move more than 6 times a day, consult a doctor immediately. After all, this may indicate a danger to the life of the crumbs. This usually happens with intrauterine hypoxia, when the umbilical cord is wrapped around the neck. That is why it is so important to record everything that happens to the baby in the womb.
How the baby behaves before birth: the position of the fetus
In preparation for the birth, the whole small organism inside you gathers strength and takes a low start position. He turns his head down. This is considered the correct position of the fetus before childbirth. This position is the key to normal childbirth.
But quite often the baby takes other positions, which are less comfortable both for the mother and for him/herself.
-
Pelvic position.

Baby takes upright position with butt down. This position does not necessarily involve a caesarean section. Natural childbirth is also possible. It all depends on the individual indicators of pregnancy. Modern medicine recommends only girls, as it is believed that boys during childbirth experience too much stress on the genitals.
-
Oblique position.
Successful natural childbirth requires the fetus to be in an upright position. But sometimes he takes a position slightly oblique in relation to the pelvic floor. Most often, in the process of labor activity, the baby aligns the position and is safely born. When this does not happen, doctors recommend surgery.
Cases of this position of the child are rare, only about 4% of women in labor. Moreover, a large fetus does not take such a position, because it is inconvenient for him. But small ones can. They have enough space in the womb, so they spin as they want. Perhaps this is the only case when doctors and obstetricians are unanimous in favor of a caesarean section.
Perhaps this is the only case when doctors and obstetricians are unanimous in favor of a caesarean section.
What does a woman feel at 38-40 weeks. Harbingers of childbirth
Expectant mother in this period is not easy. Against the background of a general tense emotional state, she also experiences quite a strong physical discomfort. Now every movement of her crumbs is painful and palpable.
When the baby changes his position, turning his head down, it becomes easier for the woman to breathe. After all, the fetus no longer presses on the diaphragm. But at the same time, it becomes harder for her to walk.
38-39 weeks of pregnancy is a period when the probability of childbirth is very high. Therefore, it is worth preparing everything you need for the maternity hospital and not leaving home without an exchange card. A very small percentage of women give birth on a predetermined date. But you can find out when this moment is likely to come with the help of the birth date calendar.
Periodic short-term pains in the lower abdomen will be the first harbingers of approaching labor. They indicate that the body has started the process of preparing for this event. It is often difficult for pregnant women to distinguish training contractions from real ones. However, there are clear differences.
Childbirth can begin either with the outflow of amniotic fluid, or with contractions. If it all started with contractions, note their frequency and duration. Record them every 10 minutes? Then slowly get ready for the hospital. If the waters have broken, this is a reason to hurry.
In conclusion, we would like to note that the body of every woman is special. Therefore, it makes no sense to worry if your baby behaves somehow differently, not like a pregnant girlfriend. Just relax more, recharge with positive emotions and carefully record all the movements and movements of the crumbs. If you're worried, just talk to your doctor.
Latest Reviews
Average Customer Rating
0 customer ratings
Snapshot of community ratings
- 5 0
- four 0
- 3 0
- 2 0
- one 0
How and how often should the baby push? Terms of shocks during pregnancy by weeks and months
The baby begins to move inside you at 8-9 weeks of pregnancy, but it is impossible to feel it, because it is still too small, and there is enough space for movement. Every day you eagerly listen to your body - when will this long-awaited moment come and can you recognize it? At what time does the baby start to push? How often should you feel movement? Look for answers to these and other questions in our material.
Every day you eagerly listen to your body - when will this long-awaited moment come and can you recognize it? At what time does the baby start to push? How often should you feel movement? Look for answers to these and other questions in our material.
When does the baby start pushing?
Each woman's pregnancy is individual, so the first tangible push can occur at different times. The first shocks should be expected around the 16-24th week of pregnancy. Moreover, during the second and subsequent pregnancies, most women feel the first movements earlier, at the 16-18th week, and during the first pregnancy a little later, as a rule, after the 20th.
How to understand that the baby began to push?
Recognizing the first shock is not always easy. Some mothers mistake this movement for intestinal discomfort. Others describe it as the flutter of a butterfly or the splashing of a fish in water, while others immediately feel a confident push.
When and how much should the child push?
Despite the fact that no pregnancy proceeds strictly according to the schedule, experts have made an approximate "schedule" of the movements of the child.
Weeks 20-24
You are already beginning to get to know your baby's temperament. The baby, in turn, feels changes in your mood and reacts to them: it can start to actively push, or it can calm down for a while. During this period, the expectant mother should avoid stressful situations and grief.
24-28 weeks
At this time, the baby can already hear you and respond to your voice. The baby may kick sharply if he hears a loud sound, but this will not harm him. Don't be surprised if your baby starts to hiccup.
28-30 weeks
The baby is growing and there is less room to move. Now he can push less often, but harder than before.
31st-35th weeks
Before turning upside down, the baby may become more active and push the mother in the ribs, which can cause discomfort; but this only means that the child grows and it becomes crowded.
36-40 weeks
At this point, the baby will already be in the correct position - head down.