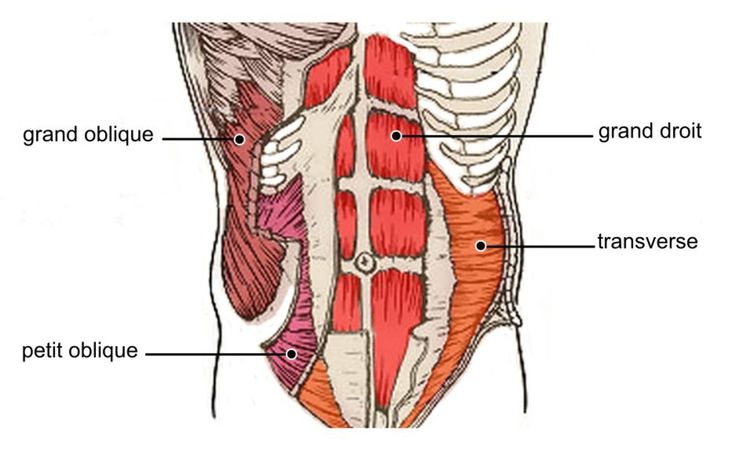
Ways to improve breast milk supply
Low Milk Supply | WIC Breastfeeding Support
Many moms worry about low milk supply, but most of the time your body makes exactly what your baby needs, even if you don't realize it. There are also ways to tell if your baby is getting enough milk. If you aren't making enough, there are ways you can build your supply. And your WIC breastfeeding staff is always there to help!
Am I Making Enough Milk?
First, look for these signs that your baby is getting enough milk. For example, pay attention to the number of wet and dirty diapers and your baby's weight gain.
Things you should NOT worry about:
- How your breasts feel. Your breasts will feel softer and less full as your milk supply adjusts to your baby's needs. This does not mean you have low supply.
- If your baby nurses for shorter periods of time, such as only 5 minutes on each breast.
- If your baby's feeds are bunched together. This is called cluster feeding and happens when your baby starts nursing more often and for longer.
This can happen in the evenings or because of growth spurts.
- Not getting much milk when you express. Your baby is much more effective than a pump or hand expression at getting out milk. Find tips to help you pump.
If you are still concerned, talk to your baby's doctor about their growth.
Causes of Low Milk Supply
While most moms make plenty of milk, some do have low milk supply. This might happen if you:
- Limit your baby's breastfeeding sessions. Remember, the more you feed on demand, the more milk you make.
- Give your baby infant formula instead of breastfeeding.
- Introduce solid foods before baby is 4-6 months old.
- Take certain birth control pills or other medicine.
- Don't get enough sleep.
- Drink alcohol or smoke.
- Have had breast surgery.
Talk to your doctor if you have hepatitis B or C, herpes, or diabetes. These conditions may also affect milk supply.
Increasing Your Milk Supply
Breastfeeding frequently—especially in the first hours, days, and weeks—is the main way to increase your milk supply. Your body will make milk to meet your baby's demand.
Try these tips to help you make more milk:
- Breastfeed every time your baby is hungry. In the early weeks, your baby will eat 8-12 times every 24 hours. It's best not to put your baby on a strict feeding schedule. Follow your baby's cues, and let your baby tell you when it's time to eat.
- Make sure your baby is latching well.
- Offer both breasts at each feeding. Let your baby finish the first side, then offer the other side.
- Empty your breasts at each feeding.
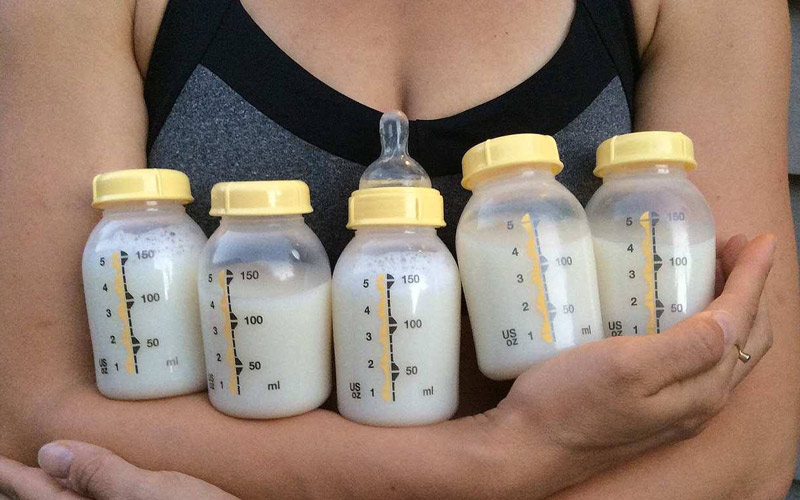 Hand express or pump after a feeding to draw out all the milk and signal your body to make more.
Hand express or pump after a feeding to draw out all the milk and signal your body to make more. - Avoid bottles and pacifiers in the early weeks. Feed your baby from your breast whenever you can.
- Get plenty of sleep, and eat a healthy diet.
- Pump or express your milk. Pumping or expressing milk frequently between nursing sessions, and consistently when you're away from your baby, can help build your milk supply.
- Relax and massage. Relax, hold your baby skin-to-skin, and massage your breasts before feeding to encourage your milk to let down.
- Take care of yourself. Get plenty of rest, eat well, drink enough fluids, and let others help you.
Consider Charting Your Progress
Record how often your baby is breastfeeding, for how long, and on which sides. If you are supplementing with infant formula, record how much your baby is getting and decrease the infant formula as your milk supply increases. WIC breastfeeding staff can help you determine how much infant formula your baby needs.
WIC breastfeeding staff can help you determine how much infant formula your baby needs.
Still Have Questions?
Contact your WIC breastfeeding expert. They can talk to you about supply concerns and give you tips to increase your supply to meet your baby's needs.
Breastfeeding: Tips to Increase Your Milk Supply l University Hospitals l Northeast Ohio
Signs That a Breastfed Baby Is Being Well Nourished
- Your baby nurses at least 8 to 16 times in 24 hours, or every 2 to 3 hours. Your baby may be fussy once or twice a day. At these times, he or she wants to nurse often for several hours before seeming full. This is called cluster feeding.
- Your baby wets at least 6 cloth or 5 disposable diapers and has at least 1 bowel movement in 24 hours. This occurs by 1 week of age.
- You can hear your baby swallow milk while nursing or you can feel your baby swallow when lightly touching his or her throat.
- Your breasts seem softer after nursing.

- Your baby gains 4 to 8 ounces a week after the first week. There is no need to weigh your baby at home. Your baby’s doctor will do this for you. You may notice that your baby has outgrown his or her clothing.
- Your baby has regained his/her birthweight by 10 to 14 days after birth.
Factors Which Can Cause Your Milk Supply to Decrease
- Your baby feeds fewer than 8 to 16 times in 24 hours. Milk production is affected by how well the breast is drained.
- Your baby has a very weak suck, or has an improper latch.
- Giving bottles of formula or water after nursing. Most babies will suck on a bottle after nursing. This just means they need to suck. It does not mean they are still hungry. Babies cry or fuss for many reasons, such as being tired, bored, wet, hot or cold.
- Giving solid foods too early and/or before you breastfeed. Most babies do not need solid foods for the first 6 months if they are breastfeeding 8 to 16 times a day.

- Smoking can cause a decreased milk supply and interfere with the letdown reflex. Here are some things you should do:
- Try to quit or cut down.
- Smoke after nursing, not before.
- Don’t smoke in the same room with your baby.
- Beginning birth control pills too soon can decrease your milk supply. Wait at least 6 weeks before taking birth control pills and then use only the mini-pill (Progestin). If you still notice a decrease in your milk supply, talk to your doctor about other birth control options. Other medications may also affect milk supply. Check with your doctor. (Refer to PI-682, Breastfeeding and Birth Control: You Have Options.)
- Mothers who are exhausted may notice a decrease in milk supply. To keep yourself from getting too tired:
- Sleep or relax when your baby sleeps.
- Eat balanced diet that includes high-protein food.
- Drink when you are thirsty so that your urine is pale yellow in color.
 Both under and excessive over hydration can decrease milk supply.
Both under and excessive over hydration can decrease milk supply. - Take an iron supplement if your healthcare provider says you are anemic.
- Talk with your doctor or nurse midwife about the need for vitamin supplement.
- Accept help when it is offered.
- Use nipple shields and pacifiers with caution.
- A breast flange that is too small or too large in size can hurt your milk supply.
- Pregnancy
- Breast reduction surgery may reduce milk supply.
If You Notice Your Milk Supply Is Low
You can increase your milk supply by:
- Nursing your baby often. Nurse every 2 hours during the day and every 3 to 4 hours at night (at least 8 to 16 times in 24 hours). If your baby will not nurse, use a good quality double electric breast pump to increase milk production. Pumping after breastfeeding signals your body to produce more milk.
- Nurse your baby at least 15 minutes at each breast.
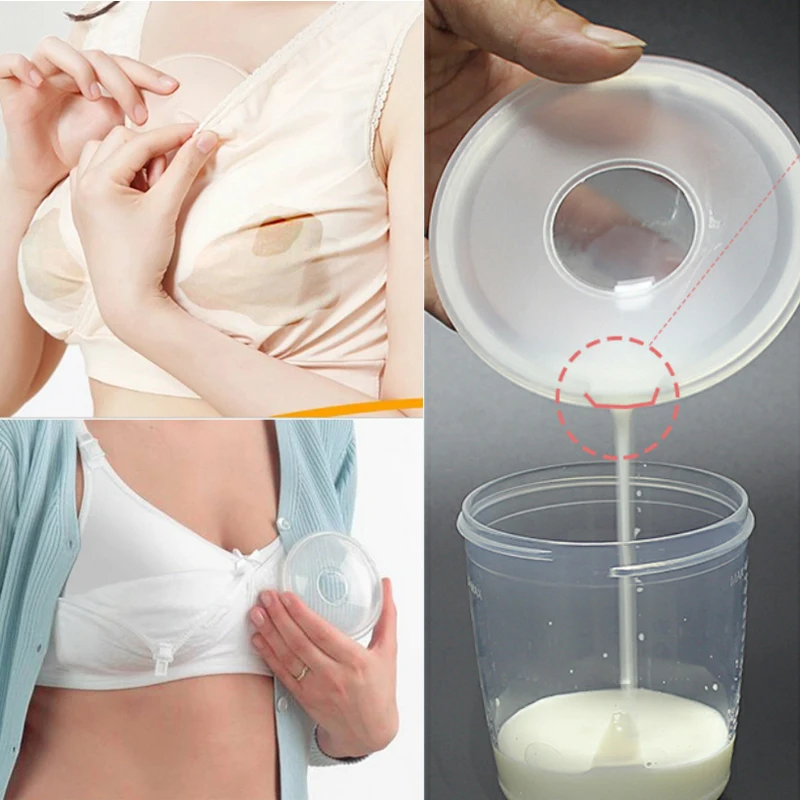 Do not limit nursing time. If your baby falls asleep after one breast, wake him or her and offer the second breast. A few babies may benefit from nursing at one breast per feeding to increase the fat content of the feeding. Switch nursing- switching breasts several times during a feeding has been shown to increase milk supply.
Do not limit nursing time. If your baby falls asleep after one breast, wake him or her and offer the second breast. A few babies may benefit from nursing at one breast per feeding to increase the fat content of the feeding. Switch nursing- switching breasts several times during a feeding has been shown to increase milk supply. - Gently massage breast before and during feedings.
- Use relaxation techniques to reduce stress and promote the flow of breast milk.
- Provide skin to skin time with your baby for about 20 minutes after feeds. This “kangaroo care” has been shown to increase milk supply.
- Be sure baby is positioned and latched correctly.
- Offer both breasts at each feeding.
- Try breast compression during the feeding to help drain the breast.
- Pump immediately after breastfeeding during the day. Rest at night. Some mothers find that they get more milk if they pump for 5 minutes, rest for 5 minutes, and pump for another 10 minutes.

Talk to your doctor about using medication or the herb fenugreek.
Works Cited
Wambach, Karen and Riordan, Jan “Breastfeeding and Human Lactation”, Fifth edition, Jones & Bartlett, 2016.
How to increase lactation - products for lactation, how to increase milk lactation: read on Nutrilak website
09/23/2019 48519
Content of article
- What is breastfeeding for
- What determines lactation
- What affects lactation
- Signs of insufficient lactation
- Initiation of breastfeeding
- Next stages of lactation
- Lactation crises
- Nutrition for nursing mothers
- Products to increase lactation
- Folk remedies for increasing lactation
The processes of establishing lactation begin to occur in the body of the mother immediately after the birth of the baby. To accelerate them in maternity hospitals, the method of attaching the child to the mother's breast is practiced, which triggers the natural development of lactation.
To accelerate them in maternity hospitals, the method of attaching the child to the mother's breast is practiced, which triggers the natural development of lactation.
What is breastfeeding for
Breastfeeding has not only nutritive, but also great psychological significance, it has an impact on the development of mother-child relationships in later age periods**. According to studies conducted in Australia, among such factors of the psychological development of a child as age, education, the presence of bad habits in the mother, the absence of breastfeeding at least up to 6 months has a 1.45 times greater impact on the mental ill health of the baby than others** *.
What determines lactation
The most important rule for establishing lactation and maintaining it throughout the entire period of breastfeeding is the correct psychological attitude of the mother and desire, the so-called dominant for breastfeeding. You must always remember and be firmly convinced that your milk is the best food for your child. The prevalence and duration of breastfeeding is a controlled process, determined, on the one hand, by the psychological readiness of the pregnant woman for motherhood and breastfeeding during the first year of a child’s life, and, on the other hand, by support from the family and medical institutions for obstetrics and childhood**. Medical institutions in this situation should create the right conditions for the start of lactation and its support in the first year of a baby's life.
The prevalence and duration of breastfeeding is a controlled process, determined, on the one hand, by the psychological readiness of the pregnant woman for motherhood and breastfeeding during the first year of a child’s life, and, on the other hand, by support from the family and medical institutions for obstetrics and childhood**. Medical institutions in this situation should create the right conditions for the start of lactation and its support in the first year of a baby's life.
What affects lactation
Various factors influence lactation in women, which can be conditionally divided into 4 groups: psychological, organizational, social and medical. Organizational and medical factors are mainly important in the early stages of breastfeeding, while psychological and social ones are of long-term effect.
Organizational and medical factors
These include factors that depend on the correctness of the actions of employees of medical institutions in the postpartum period. Joint stay of mother and child in the maternity hospital, early breastfeeding, lack of labor induction and pre-lactation feeding, feeding from the first days of the baby's life, timely and reasonable assistance from medical personnel**. An important aspect is the early attachment of the baby to the breast. Immediately after birth, the baby is placed on the mother's stomach so that she can attach the baby to her breast. Early contact between newborn and mother stimulates the production of breast milk in greater volume. In addition to medical professionals, lactation consultants who specialize in helping mothers can help build the right breastfeeding technique.
Joint stay of mother and child in the maternity hospital, early breastfeeding, lack of labor induction and pre-lactation feeding, feeding from the first days of the baby's life, timely and reasonable assistance from medical personnel**. An important aspect is the early attachment of the baby to the breast. Immediately after birth, the baby is placed on the mother's stomach so that she can attach the baby to her breast. Early contact between newborn and mother stimulates the production of breast milk in greater volume. In addition to medical professionals, lactation consultants who specialize in helping mothers can help build the right breastfeeding technique.
Psychological and social factors
An equally important role is played by the psychological state of the mother during the period of feeding the child. The formed dominant of motherhood and lactation, comfortable conditions in the family, the mother's ability to relax during feeding, the absence of stressful situations have a positive effect on the nature of lactation and its duration**. Since milk arrives differently for different women, if there is not enough milk, you should not despair at the first stage and keep a positive attitude and self-confidence. Worry only reduces the amount of milk. It is important not to start artificial feeding while there is hope of establishing breastfeeding*****.
Since milk arrives differently for different women, if there is not enough milk, you should not despair at the first stage and keep a positive attitude and self-confidence. Worry only reduces the amount of milk. It is important not to start artificial feeding while there is hope of establishing breastfeeding*****.
To assess the adequacy of lactation, a thorough analysis of the child's behavior, the frequency of urination, and the nature of the stool is necessary. Possible signs of insufficient lactation are:
- crying and restlessness of the child during or immediately after feeding;
- the need for frequent breastfeeding;
- prolonged feeding, in which the child makes a lot of sucking movements in the absence of swallowing;
- feeling by the mother of the rapid complete emptying of the mammary glands during the active sucking of the child, when decanting after feeding, there is no milk;
- restless sleep, frequent crying, "hungry" cry;
- low baby weight gain;
- infrequent stools and urination*.

Initiation of breastfeeding
In the first days after childbirth, it is important to follow the following principles.
- Feed the baby on demand (up to 10-12 times a day). The growing need of the child for breast milk stimulates the formation of more and more of it in the mother; the child himself "dictates" to the mammary gland how much milk to produce not only in the first, but also in all subsequent days and months.
- Stop using teats, bottles. If a baby is started artificially feeding in the first 3-4 days after birth, then the chances of breastfeeding success are reduced.
- Prevention of cracks and engorgement of the mammary glands (lactostasis).
Next stages of lactation
At the next stages of lactation, it is important:
- pay special attention to night feedings, the maximum amount of the hormone prolactin (responsible for the secretion of breast milk) is produced from 4 to 7 in the morning;
- eat right;
- if necessary, include in your diet products for lactation, with a lactogenic effect;
- establish a rational daily routine for good sleep and rest;
- keep calm and have a positive, positive attitude towards feeding in all situations.

Lactation crises
This is important!
According to statistics, most mothers experience "lactation crises", which refers to a temporary decrease in the amount of milk (for no apparent reason). Therefore, the issue of increasing lactation is relevant for 80% of breastfeeding mothers.
Lactation crises are based on the peculiarities of hormonal regulation of lactation. Crises occur at 3-6 weeks, 3, 4, 7, 8 months of lactation. Their duration is on average 3-4 days. To go through crises, it is enough to put the baby to the breast more often and feed from both mammary glands. It is also necessary to ensure the rest and peace of the mother, a varied and nutritious diet, the consumption of lactogenic products, drinking drinks containing lactogenic preparations or herbs 15–20 minutes before feeding*.
Diet for nursing mothers
During breastfeeding, the mother's need for nutrients increases. Therefore, it is necessary to provide a complete diet: the amount of protein should increase to 120 g per day, fat - 100-120 g, carbohydrates - 450-500 g. The calorie content of the diet increases to 3200-3500 kcal. A breastfeeding mother should eat 5-6 times a day, preferably shortly before feeding her baby, to increase her milk supply****.
The calorie content of the diet increases to 3200-3500 kcal. A breastfeeding mother should eat 5-6 times a day, preferably shortly before feeding her baby, to increase her milk supply****.
Products to increase lactation
To stimulate the production of breast milk, a nursing mother can include special foods in her diet, such as Lactamil. It contains a complex of special herbs that give a lactogenic effect: cumin, nettle, anise, fennel. "Lactamil" contains not only herbs, but also milk protein, fatty acids, dietary fiber, a complex of vitamins, microelements. Their combination can contribute to a rapid recovery after childbirth, an increase in the quantity and quality of breast milk. Unlike folk recipes and homemade "herbal preparations", lactation products are clinically tested and have the exact dosage of medicinal plants.
Folk remedies for increasing lactation
There are many folk recipes to increase lactation. But it is always worth remembering: what helped one mother may not help or even harm another. Below we give a few recipes that can cause an increase in lactation. Before use, be sure to consult a doctor, because all herbs contain essential oils with a stimulating function and biologically active components with a hormone-like effect.
But it is always worth remembering: what helped one mother may not help or even harm another. Below we give a few recipes that can cause an increase in lactation. Before use, be sure to consult a doctor, because all herbs contain essential oils with a stimulating function and biologically active components with a hormone-like effect.
Infusion of fennel fruit, dill seeds and anise
Mix 1 to 1 anise seeds, fennel seeds and dill seeds. Pour 1 teaspoon of the resulting mixture with a glass of boiling water and let it brew for 10-15 minutes. Take 3 cups per day.
Infusion of cumin, hops, nettle leaves, dill seeds
Mix 20 g of hops, 25 g of dill and cumin seeds and dried nettle leaves. Take 30–40 g from the mixture, dilute with 1 liter of hot water and leave for 10 minutes. Take 50 ml before or during meals.
Aniseed infusion
2 teaspoons of anise seeds pour a glass of hot water and leave for an hour. Take 2 tablespoons 2-3 times a day.
Take 2 tablespoons 2-3 times a day.
Compliance with the basic principles of breastfeeding and a positive attitude can help a mother both increase lactation and cope with crises, support breastfeeding for a long period. We recommend that all mothers seek the advice of a breastfeeding specialist.
Video "How to support lactation and increase breastfeeding"
Kushalieva Ksenia, pediatrician, breastfeeding specialist
Links to sources
* National program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation, https://xn--b1aaisgq1jga.xn--p1ai/Files/RussiaGuid/Programma2019.pdf.
** Factors affecting lactation. M. V. Gmoshinskaya, Research Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/faktory-vliyayuschie-na-laktatsiyu.
*** Article. JPeds. Long-term mental health effects of breastfeeding in children and adolescents, Wendy H. Oddy, PhD, Garth E. Kendall, PhD, Jianghong Li, PhD, Peter Jacoby, MSc, Monique Robinson, BA (Hons) Psych, Nicholas H. de Klerk, PhD, Sven R. Silburn, MSc, Stephen R. Zubrick, PhD, Louis I. Landau, MD, and Fiona J. Stanley, MD http://gvinfo.ru/node/156.
Oddy, PhD, Garth E. Kendall, PhD, Jianghong Li, PhD, Peter Jacoby, MSc, Monique Robinson, BA (Hons) Psych, Nicholas H. de Klerk, PhD, Sven R. Silburn, MSc, Stephen R. Zubrick, PhD, Louis I. Landau, MD, and Fiona J. Stanley, MD http://gvinfo.ru/node/156.
**** A book about tasty and healthy food / Ed. edited by Doctor of Technical Sciences, prof. I. M. Skurikhina, Moscow: Agropromizdat, 1992.
***** Child and care for him. B. Spock - M .: RUSSLIT. 1991.
(38 ratings; article rating 4.7)
How to increase the lactation of a breastfeeding mother
PreviousNext
- Plentiful drink
- herbal teas
- Products that increase lactation
- Vitamins and drugs that increase lactation
- Other ways to stimulate the production of prolactin.
 lactation crisis
lactation crisis
Contents:
Today we're going to talk about how to give your baby optimal nutrition. And, of course, we are talking about breastfeeding and ways to increase lactation.
First, a few praises for breast milk.
Only breast milk is the ideal food for newborns and infants. In terms of nutritional value, the balance of the chemical composition and the degree of digestibility of nutrients, none of the most perfect and adapted milk formula can be compared with breast milk. The nutritional value of breast milk - a product created by nature itself - ensures the rapid growth and development of a child in the first year of life. But it brings the greatest benefit for the baby precisely in the first months, when there is no other complementary food yet. Therefore, it is important to establish breastfeeding immediately after the birth of a child. How to do it right, read here.
And, of course, mothers, especially beginners, are interested in ways to increase lactation. Let's consider the most effective of them in more detail:
Let's consider the most effective of them in more detail:
Plentiful drink
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of this factor. For reference: the amount of food for a child in the first year of life starts from 700 ml (1/5 of body weight), gradually increasing to 1 liter per day. Accordingly, the volume of liquid consumed by a nursing mother should also increase by at least 1 liter. At home, there should always be herbal teas in a thermos and boiled water (mineral water, compotes or fruit drinks) at the same time. Especially effective is the combination of drinking hot herbal decoctions with feeding: you put a mug on the table and, periodically drinking, put the baby to your chest. A wonderful feeling of rush in the chest is guaranteed!
Herbal teas
Most herbal preparations contain oregano, anise, fennel, lemon balm, dill, nettle, wild strawberry leaves. All of these herbs have a calming, antispasmodic effect, which has a beneficial effect on the production of oxytocin, one of the two main hormones responsible for lactation. Therefore, during stress, overwork, nervous exhaustion, when the production of oxytocin decreases, herbal preparations are absolutely indicated for use. But sage and thyme (thyme) should be treated with caution - they have a depressing effect on the production of breast milk. From a lack of food, babies can often be capricious and lose a lot of weight, so it is important not to deviate from the daily diet. How much a newborn should eat per feeding - read here.
Therefore, during stress, overwork, nervous exhaustion, when the production of oxytocin decreases, herbal preparations are absolutely indicated for use. But sage and thyme (thyme) should be treated with caution - they have a depressing effect on the production of breast milk. From a lack of food, babies can often be capricious and lose a lot of weight, so it is important not to deviate from the daily diet. How much a newborn should eat per feeding - read here.
Herbs can be prepared in advance by yourself, bought at a pharmacy to make a collection at home, or you can buy ready-made herbal teas, including in filter bags.
Products that increase lactation
Lactation is a very energy intensive process. Before the introduction of complementary foods, you feel like a sort of small dairy. And nutrition during feeding should be balanced - taking into account not only losses with breast milk, but also the energy spent on its creation in the mammary gland. Therefore, when breastfeeding, not only the volume of food increases (mainly due to liquid), but also its calorie content. But not at the expense of cakes and pastries! A sufficient amount of protein-containing foods will ensure adequate lactation with good milk quality. Low-fat meats, fish (no more than 2 times a week), cottage cheese, cheese, dairy products, eggs must be in the diet of a nursing woman. Hot soups and broths made from lean veal, chicken, turkey, and rabbit are especially good at stimulating lactation. They should be on the menu every day.
But not at the expense of cakes and pastries! A sufficient amount of protein-containing foods will ensure adequate lactation with good milk quality. Low-fat meats, fish (no more than 2 times a week), cottage cheese, cheese, dairy products, eggs must be in the diet of a nursing woman. Hot soups and broths made from lean veal, chicken, turkey, and rabbit are especially good at stimulating lactation. They should be on the menu every day.
But alcohol, including the legendary beer, as a means of increasing milk production, is under an absolute ban. In the case of using beer, including with sour cream, the main effect is calming and relaxing, which positively affects the production of oxytocin. Herbal teas have the same effect, and the effects of alcohol on a child's body can be catastrophic. But you can use brewer's yeast as a source of B vitamins.
Any new product should be introduced with caution, observing the child's reaction to it within 2-3 days. And one of the main indicators is the nature of the chair. For a healthy child of the first month of life, the norm is the passage of stool after each feeding. And here, Huggies ® Elite Soft diapers for newborns can become your assistant, which have a unique Soft Absorb absorbent layer that absorbs loose stools and moisture in seconds. And for even more tenderness as part of the new Huggies ® Elite Soft contains 100% organic cotton. The elastic waistband of the diaper fits perfectly to the baby's body, and a special pocket for loose stools will provide additional protection against leakage. Use with pleasure!
For a healthy child of the first month of life, the norm is the passage of stool after each feeding. And here, Huggies ® Elite Soft diapers for newborns can become your assistant, which have a unique Soft Absorb absorbent layer that absorbs loose stools and moisture in seconds. And for even more tenderness as part of the new Huggies ® Elite Soft contains 100% organic cotton. The elastic waistband of the diaper fits perfectly to the baby's body, and a special pocket for loose stools will provide additional protection against leakage. Use with pleasure!
Vitamins and drugs that increase lactation
During lactation, the woman's body's need for vitamins and trace elements increases. The resulting relative hypovitaminosis can contribute to a decrease in the function of the mammary gland. Preference is given to multivitamin complexes containing retinol (vitamin A), tocopherol (vitamin E), thiamine (vitamin B 1 ), ascorbic acid, microdoses of iodine, glutamic and lipoic acid. Of the biogenic stimulants, Apilak, Laktogon are used.
Of the biogenic stimulants, Apilak, Laktogon are used.
Considering that almost all drugs pass into breast milk and, accordingly, to the child, medications to increase lactation should be used only as directed by a doctor.
Other ways to stimulate the production of prolactin. lactation crisis
It should be noted that the production of breast milk is a cyclical process. There is the concept of lactation crises that occur every 1.5–2 months, when the amount of milk a woman may slightly decrease. In this situation, the most important thing is not to reduce the number of feedings, but, on the contrary, to put the baby to the breast more often. This stimulates milk production. And the child, as a rule, feels the approach of a lactation crisis and “stocks up” food in advance, increasing his appetite a day or two before the start of the decline in lactation. You can not refuse night feedings. The maximum production of prolactin occurs at night, and with proper stimulation by applying to the chest, lactation is easily restored.