Watery cervical mucus early pregnancy
What cervical mucus looks like after ovulation if you are pregnant
A few weeks after they ovulate, a person may notice more cervical mucus, or cervical fluid, than usual. The mucus may also have a different consistency. Sometimes, this is a sign of pregnancy.
In this article, we describe how cervical fluid might change if a person is pregnant, other possible causes of these changes, and other early signs of pregnancy.
Cervical mucus is a fluid that comes from the cervix. It is one of the main components of vaginal discharge, it is typically clear or white, and it may have a faint odor.
In early pregnancy, there may be noticeably more of this mucus than usual. It may also have a runny, watery consistency.
If a person experiences implantation bleeding, the cervical fluid may have a pink tinge. Implantation bleeding occurs 8–10 days after ovulation, when a fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the womb.
However, not everyone experiences implantation bleeding, and some people who are pregnant do not have noticeably different cervical fluid.
Also, it is normal for cervical fluid to change in quantity and consistency over the course of a menstrual cycle. The changes vary from person to person, but generally, they are as follows:
- after menstruation, cervical fluid is often thick, opaque, and less abundant
- approaching ovulation, the fluid may temporarily become clear and elastic, similar in consistency to uncooked egg whites
- after ovulation, the fluid again becomes opaque and thick
Finally, it is important to note that other factors can change the consistency of cervical mucus. We describe these later in this article.
Hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, and human chorionic gonadotropin, sometimes called HCG, are responsible for the early symptoms of pregnancy. It takes several weeks after implantation for these hormones to build up in the body.
As a result, a pregnant person may not see any changes in their cervical fluid or have any other signs of pregnancy until several weeks after conception.
If a person notices a change in their cervical fluid immediately after ovulation, the cause may be something other than pregnancy. And if there is no change, this does not necessarily mean that the person is not pregnant.
The simplest way to check for pregnancy is to use a home testing kit after the next missed period.
Anyone who wants to check their cervical mucus should:
- Wash their hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Insert a finger or two into the vagina, reaching up to the cervix.
- Sweep around the cervix to touch the fluid.
- Pull the finger or fingers out and observe the fluid.
A person may instead be able to check any cervical mucus on their underwear or wiped on a tissue.
Abundant, elastic cervical mucus can be an indication of when a person is most fertile. Anyone trying to conceive may find that checking the fluid regularly helps with identifying their fertile window.
Other factors besides pregnancy can influence what the cervical fluid looks like.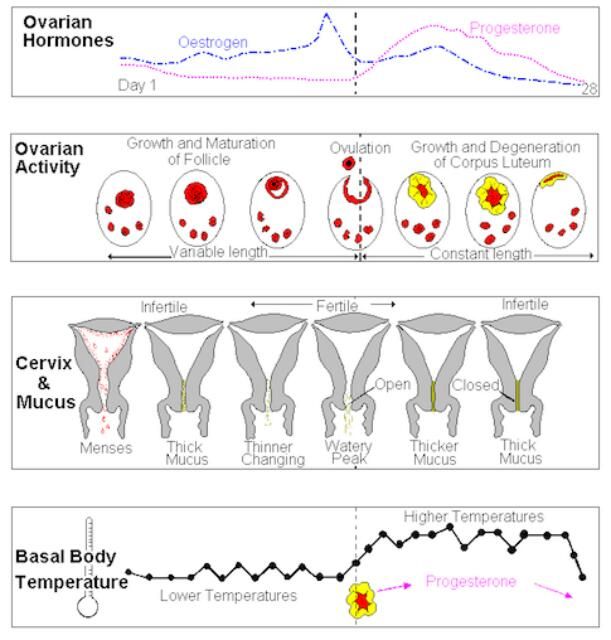 Some common reasons for changes in cervical mucus include:
Some common reasons for changes in cervical mucus include:
Semen
When semen mixes with vaginal fluids, it may temporarily change the texture of cervical mucus. The mucus may become cloudy or white or appear more abundant. Some may mistake this for a sign of pregnancy.
Lubricants and other products
Any products that a person uses in, on, or around the vagina may change the color or consistency of cervical fluid, or mimic it.
Some lubricants look similar to cervical fluid, for example, and a person may mistakenly believe that they are producing more than usual.
The menstrual cycle
Around ovulation, a person can produce up to 30 times more cervical fluid than earlier in their cycle. If a person ovulates later than usual, they may interpret this as a sign of pregnancy.
Keeping track of ovulation can help explain changes in cervical fluid.
Infection
Some infections can cause changes to vaginal discharge, including yeast infections and bacterial vaginosis.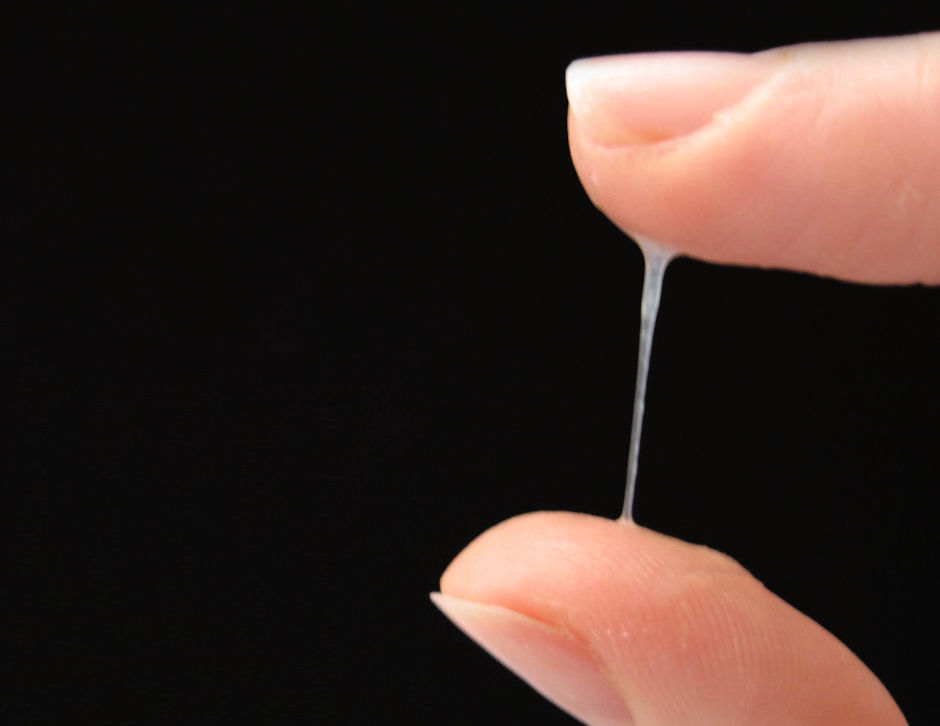 Contact a doctor if vaginal discharge becomes:
Contact a doctor if vaginal discharge becomes:
- thick and white, with a similar texture to cottage cheese
- gray
- bright yellow or green
- foul-smelling
It is especially important to receive treatment if pregnancy is a possibility, as some vaginal infections can pose a risk to pregnant people and fetuses.
The most reliable indicator of pregnancy is a positive test result after a missed period.
Some other potential signs include:
- aversions to certain foods or smells
- food cravings
- nausea or vomiting
- dizziness
- spotting
- breast pain or tenderness
- feeling tired
- mood changes
- headaches
- needing to urinate more often
It is important to keep in mind that many other health conditions can cause these symptoms.
A missed period alone is not enough to determine pregnancy, as many factors can cause a delay in menstruation. For the most reliable result, use a home pregnancy testing kit or contact a doctor for a blood test.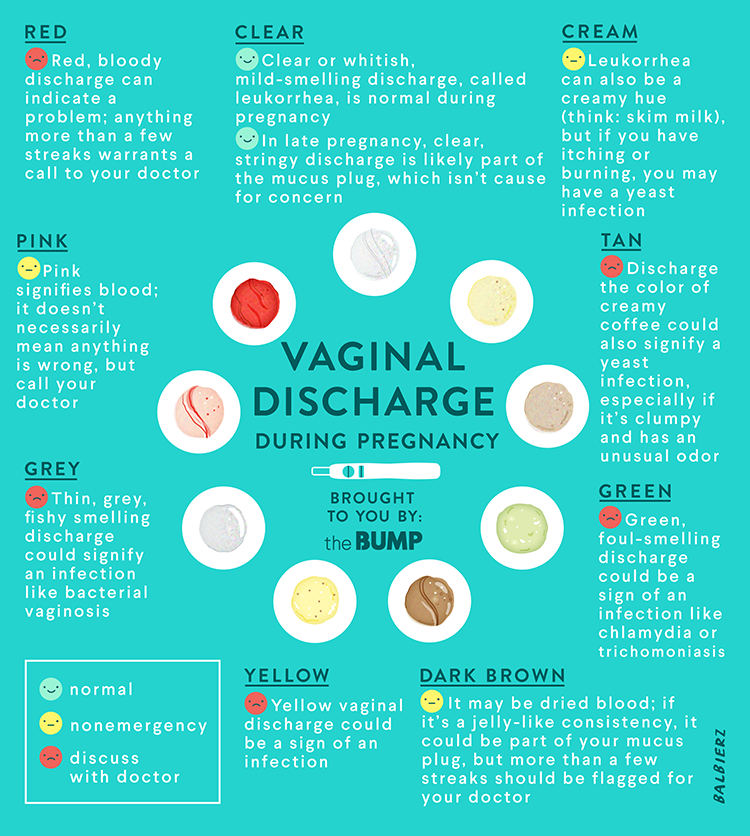
A person should speak with a doctor if they:
- have discharge that is thick and cloudy, like cottage cheese
- have discharge that is yellow, gray, or green
- have discharge with a foul odor
- experience itching, burning, or odor coming from the vagina
- experience pain during sexual intercourse or urination
Also, a person should speak with a doctor if they could be pregnant or have been trying to become pregnant for over a year but have not yet conceived.
During early pregnancy, cervical fluid may look thinner or more watery. If a person experiences implantation bleeding, the fluid may contain a little blood.
However, other factors can also cause these changes, along with the other early signs of pregnancy.
Tracking changes in cervical mucus is not a reliable way to detect pregnancy. Anyone who wants to check whether they are pregnant should use a home testing kit or schedule a blood test with a doctor.
Watery Discharge During Pregnancy- What To Expect
Women certainly go through a lot of changes during pregnancy. Right from morning sickness, fatigue, and achy feet to severe mood swings, pregnant women experience so many changes that can be both normal and unexpected. It’s natural for you to get worried about every little change that happens in your body. One such thing is the watery vaginal discharge during pregnancy that is faced by all women. This watery discharge is more during early pregnancy, and before labor, you might experience blood-tinged mucus discharge. Read on as we take you through watery discharge during pregnancy and what to expect.
Right from morning sickness, fatigue, and achy feet to severe mood swings, pregnant women experience so many changes that can be both normal and unexpected. It’s natural for you to get worried about every little change that happens in your body. One such thing is the watery vaginal discharge during pregnancy that is faced by all women. This watery discharge is more during early pregnancy, and before labor, you might experience blood-tinged mucus discharge. Read on as we take you through watery discharge during pregnancy and what to expect.
The kind of watery discharge could differ depending on the stage of pregnancy you’re at.
What Is The Creamy White Discharge During Pregnancy?
The white creamy discharge during pregnancy is nothing but the fluid that comes out of your vagina. Your watery discharge differs depending on the different stages of pregnancy. This discharge can start 1-2 weeks after conception, sometimes even before you’ve missed your periods.
Additionally, you will experience a heavy discharge towards the end of your pregnancy. This happens because of the pregnancy hormone also known as estrogen. The blood flow in your pelvic area increases and spurs your mucus membranes.
Here are some of the characteristics of watery discharge during pregnancy, and what stage to expect it in:
First Trimester
- Has a pungent smell
- Similar to the blood released when on your menstrual cycle and can stain your undergarments
- Estrogen levels increase the blood flow in the vaginal area
Second Trimester
- Has a milky, egg white color
- More frequent compared to the first trimester
- Signs of foul-smelling or bloody discharge are indicators to consult a doctor
Third Trimester
- Blood flow to the cervical area increases
- Mucus discharge is milky-white, mucusy and may have a mild odor
- Discharge can differ depending on color, odor, frequency and the amount of blood
Normal Pregnancy Discharge
Experiencing a watery discharge during pregnancy is one of the many surprising things about it, yet can be completely normal. When you experience sticky, clean or white fluid discharge with a slight odor from your vagina, you can be at ease as that is considered normal discharge during pregnancy. Don’t worry if you ever notice a tint of yellow fluid on your underwear as it’s completely normal. Of course, you should turn to your doctor the moment something concerns you, but it’s better to be informed so you reduce your panic.
When you experience sticky, clean or white fluid discharge with a slight odor from your vagina, you can be at ease as that is considered normal discharge during pregnancy. Don’t worry if you ever notice a tint of yellow fluid on your underwear as it’s completely normal. Of course, you should turn to your doctor the moment something concerns you, but it’s better to be informed so you reduce your panic.
As you move into the second and third trimester of pregnancy, your estrogen and progesterone hormone levels will increase. They are responsible for increasing the blood flow to your vagina. This is a natural way for your body to keep your vagina clean and protect your baby from any kind of infection.
Leukorrhea
The common term for any fluid-like discharge from your vagina is called leukorrhea. Every woman experiences a white mucus-like discharge during puberty. Again, this leukorrhea differs for all women as it depends on your menstrual cycle. For most women, leukorrhea appears during the first few weeks after conception and then increases gradually.
For most women, leukorrhea appears during the first few weeks after conception and then increases gradually.
Amniotic Fluid
At the end of your pregnancy, you’ll notice that your watery discharge is similar to your urine and can have flakes in it. That is known as amniotic fluid and could be a cause of concern if you’re leaking amniotic fluid prematurely. Excessive amniotic fluid that feels like a gush can mean your water is breaking, and you’re not too far off from labor!
An additional problem arises when your fluid discharge is somewhat greenish in color in copious amounts. That can be an indicator that your baby has passed meconium, or early stool, in the womb. So, if you experience a greenish discharge, make sure you consult your doctor immediately.
Abnormal Pregnancy Discharge
It shouldn’t come to you as a surprise that the risk of vaginal infections is high during pregnancy. In case you notice that your discharge is green in color, has a bad odor, and causes you a lot of pain, itching or irritation, it can be an indicator of infection or any other problem.
In case you notice that your discharge is green in color, has a bad odor, and causes you a lot of pain, itching or irritation, it can be an indicator of infection or any other problem.
Here are some things you need to be mindful of with respect to abnormal pregnancy discharge:
Premature Labor
- Excessive blood flow in the last weeks of pregnancy
- Continuous watery, mucus-like or bloody vaginal discharge
Yeast Infection
- Thick, white, gray, yellowish or chunky looking discharge
- Irritation or pain while urinating
- Redness in your vaginal area
- Bacterial discharge has a strong fishy odor
STIs (Sexually Transmitted Diseases)
- Yellow or green color frothy discharge
- Odd or foul smell from your discharge
Vaginosis
- Itchiness or irritation while urinating
- Discharge has foul odor
- Can lead to premature labor or miscarriage
When To Call The Doctor?
It’s natural to experience vaginal discharge during pregnancy. Having said that, any signs of changes in your fluid’s consistency, smell or color need to be reported to your doctor. Also, if you experience any burning sensation, itchiness or redness in your vaginal area, you should immediately consult your doctor. You can’t stop your vaginal discharge, however, there are certain measures you can take to keep your vaginal area clean and healthy.
Having said that, any signs of changes in your fluid’s consistency, smell or color need to be reported to your doctor. Also, if you experience any burning sensation, itchiness or redness in your vaginal area, you should immediately consult your doctor. You can’t stop your vaginal discharge, however, there are certain measures you can take to keep your vaginal area clean and healthy.
Here are some things that you should take care of during pregnancy:
- Avoid using tampons
- Gently wash your vaginal area while bathing
- Change your undergarments frequently
- Refrain from wearing synthetic and tight clothes if you experience itching or redness on your skin
- Avoid douching in case you have a sensitive vulva
Watery discharge during pregnancy is natural. But do reach out to your doctor if you notice any drastic changes or experience any discomfort.
Conclusion
It’s okay if you find your vaginal discharge to be unpleasant, but remember that it is a natural process of your body. You just have to make sure that you keep a track of your discharge and its frequency. We’ve covered everything you need to know about your vaginal discharge during pregnancy and what to expect. After giving birth, you’ll have to take care of many other things like your child’s immunization and vaccination schedules. To help you with that, the ImmunifyMe app helps you keep a digitized record of your little one’s vaccination records.
FAQs On Watery Discharge During Pregnancy
What Does It Mean When Liquid Comes Out During Pregnancy?
The liquid that comes out during pregnancy can be milky vaginal discharge. It can happen in the first few weeks after conception and it gradually increases thereafter. The common medical term for this liquid discharge is leukorrhea.
Does Pregnancy Discharge Look Watery?
Pregnancy discharge or vaginal discharge can leave stains on your underwear. It is thin, watery and milky during the early stages of pregnancy and later on gets thick towards the end of your pregnancy.
Why Is My Discharge Watery?
You don’t have to worry if you have a watery discharge as it’s normal during pregnancy and assures you that there’s no sign of infection in your vaginal area. It happens because of changes in your hormones like your estrogen levels. They are responsible for increasing the blood flow towards your vagina during pregnancy.
How Can You Tell The Difference Between Discharge And Amniotic Fluid?
When your discharge is watery, milky and doesn’t have a foul odor, it can be considered as a normal vaginal discharge. As opposed to that, discharge of yellow or green color in copious amounts are signs of amniotic fluid; in this case, you need to consult your doctor immediately.
Vaginal discharge - useful information for womenReproductive Health Training Center
Pregnancy is an extremely important period in the life of any woman. Discharge from the genitals almost always causes anxiety, so it is extremely important to know the mechanisms of their occurrence, types and possible consequences for the body.
Discharge from the genitals almost always causes anxiety, so it is extremely important to know the mechanisms of their occurrence, types and possible consequences for the body.
Outside of pregnancy, the cervix constantly produces mucus, with several types of mucus being produced during the menstrual cycle:
- the first half of the menstrual period. The work of the whole organism, primarily the organs of the reproductive system, is aimed at the release of the egg from the ovary and possible fusion with the sperm. For this, the woman's body produces a rich and liquid secret, the purpose of which is to facilitate the movement of spermatozoa;
- second half of the menstrual period. When the egg is fertilized, the woman's body prepares for its direct introduction into the uterus. In this case, an opaque and viscous mucus is produced, the purpose of which is to protect the entrance to the uterus from foreign microorganisms.
The first half of the cycle is regulated by the female sex hormone estrogen, the second half by the hormone progesterone. In the first trimester of pregnancy, the work of the uterus and its appendages is regulated by progesterone. She produces a small amount of thick discharge. However, starting from the thirteenth week, the female body begins to produce significant amounts of estrogen, so the vaginal discharge becomes plentiful and liquid.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, the work of the uterus and its appendages is regulated by progesterone. She produces a small amount of thick discharge. However, starting from the thirteenth week, the female body begins to produce significant amounts of estrogen, so the vaginal discharge becomes plentiful and liquid.
Normal pregnancy discharge
The course of the first trimester of pregnancy (the first twelve weeks) is determined by the influence of the female sex hormone progesterone. At first, it is secreted by the corpus luteum of the ovarian menstruation (it is formed after the rupture of the follicle, from which the egg is released during ovulation). After fertilization of the egg occurs, the corpus luteum of ovulation expands under the action of the pituitary luteinizing hormone and then turns into the corpus luteum of pregnancy, producing large amounts of progesterone. This hormone helps to retain the embryo (fertilized egg) in the uterine cavity by blocking the exit from the cavity of this organ (a thick mucous plug forms in the cervical canal), as well as suppressing the contractility of its muscles.
Under the influence of progesterone, very thick, glassy, transparent, in some cases whitish discharges appear directly in the first trimester of pregnancy, which can be found on linen in the form of mucus clots. This is the norm only in cases where the discharge does not have any odor and does not bother the pregnant woman, that is, it does not cause itching, burning and other unpleasant sensations.
If these symptoms appear, it is necessary to look for another reason, that is, immediately seek help from a gynecologist.
After the first trimester of pregnancy, when the fetus is firmly strengthened in the uterine cavity and the placenta almost matures (the organ that connects the mother and fetus and provides the latter with all the necessary nutrients, hormones, biologically active compounds), they again begin to be excreted in large quantities estrogen. The task of this period is the development of the uterus (it is the organ in which the fetus develops, therefore it must constantly increase in size) and the mammary glands (new glandular tissue begins to form in them and new milk ducts begin to form).
Under the influence of these hormones in the second half of pregnancy, women develop copious discharge, colorless or slightly whitish in color, from the genitals. They should not be classified as any pathological conditions, however, such discharge should not have an unpleasant odor, cause symptoms such as itching, burning and other manifestations of discomfort.
White discharge during pregnancy
White discharge occurs most often during pregnancy. They can be a cause for concern in women, but only in extremely rare cases are they associated with any pathological condition.
The composition of secretions includes the following components:
- mucus. Its source is the numerous glands of the woman's reproductive system: the uterus, her cervix, vestibule, and also the vagina itself;
- microorganisms. The microflora is always present in the vagina, which can have a diverse composition, which is different for each woman.
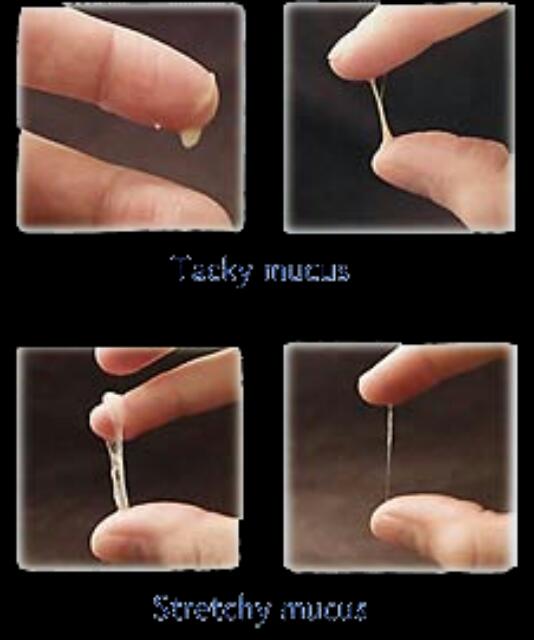 If it is healthy, then it is mainly the so-called lactic acid bacteria. The presence of other microorganisms does not yet allow us to judge the development of any disease;
If it is healthy, then it is mainly the so-called lactic acid bacteria. The presence of other microorganisms does not yet allow us to judge the development of any disease; - epithelial cells. They cover all the structures of the female reproductive system, are constantly exfoliated and replaced by new ones.
Vaginal discharge can be both pathological and normal. Usually, white discharge is directly related to the menstrual cycle. In its first half, there are not abundant discharges of a watery consistency, with the course of ovulation they become thick and viscous, and may acquire a beige tint. By the end of the menstrual period, the amount of discharge increases again. White discharge can also appear due to other factors: after intercourse, accompanied by the use of hormonal contraceptives. Pathological white discharge may be associated with infectious diseases, such as candidiasis.
White discharge can be called the first sign of pregnancy. At this stage, they are associated with the influence of the hormone progesterone. From the thirteenth week, its influence decreases, increases, respectively, the action of estrogen. During this period, the discharge becomes more abundant, they are transparent and do not have a certain smell. They do not cause unpleasant symptoms, such as burning, itching, which is extremely important for the diagnosis of pathological conditions.
From the thirteenth week, its influence decreases, increases, respectively, the action of estrogen. During this period, the discharge becomes more abundant, they are transparent and do not have a certain smell. They do not cause unpleasant symptoms, such as burning, itching, which is extremely important for the diagnosis of pathological conditions.
Despite the fact that such discharge during pregnancy is quite normal, it is necessary to pay attention to their consistency, color and amount. A change in these indicators may indicate the addition of an infection, hormonal status disorders, and diseases of the genital organs. The most common cause of such changes is candidiasis or thrush of the female genital organs. In this case, the discharge will look like cottage cheese, exude a beer smell and become plentiful. Other conditionally pathogenic microflora can also join, since during pregnancy there is a decrease in immunity.
To prevent thrush, doctors prescribe probiotics to women during pregnancy, including dairy products. If it is not possible to prevent the development of pathology, then special antifungal drugs are prescribed.
If it is not possible to prevent the development of pathology, then special antifungal drugs are prescribed.
Another source of discharge is bacterial vaginosis. At the same time, they have a watery consistency and a transparent shade, and a rather unpleasant smell.
If pain in the lower abdomen joins the discharge, then this condition requires immediate hospitalization, since there is a high risk of ectopic pregnancy and the threat of miscarriage.
Thus, white discharge in women during pregnancy is quite normal, but it is necessary to pay attention to indicators such as smell, appearance.
Yellow discharge during pregnancy
The presence of yellow discharge is not normal, but it may not cause any concern if it is not accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, such as an unpleasant smell, burning, itching and pain. Otherwise, you need to urgently visit a gynecologist, especially if the discharge is dark yellow.
There are several reasons for the appearance of such a pathological sign. The first of these is the presence of inflammatory processes of any nature, which are exacerbated by pregnancy or other factors. Immunity during this period is weakened, which allows pathological microorganisms to easily penetrate the vagina and accumulate there, causing a similar unpleasant symptom. In addition to all this, discharge can be triggered by spontaneous abortion. Therefore, you need to respond to them as quickly as possible.
The first of these is the presence of inflammatory processes of any nature, which are exacerbated by pregnancy or other factors. Immunity during this period is weakened, which allows pathological microorganisms to easily penetrate the vagina and accumulate there, causing a similar unpleasant symptom. In addition to all this, discharge can be triggered by spontaneous abortion. Therefore, you need to respond to them as quickly as possible.
The appearance of dark yellow discharge may be an allergic reaction to underwear or intimate hygiene products. Certain micro-organisms can also cause a specific yellowish discharge.
If the color of the discharge changes to green, then the problem that has arisen indicates the development of serious abnormalities. For example, this may indicate the presence of sexually transmitted diseases. They are also characterized by the appearance of itching, pain when urinating, burning in this area.
If the discharge is bright yellow, it is most likely caused by inflammation of the fallopian tubes or ovaries, as well as various bacterial infections in the vagina.
Many infections and inflammatory diseases that manifest themselves during pregnancy with specific yellow discharge, at this time only become aggravated, and do not appear in connection with the onset of pregnancy. Therefore, before the moment of conception, the expectant mother must undergo a complete examination. This will help determine the state of the body, identify unwanted pathological conditions and diseases and get rid of them even before the pregnancy period.
Brown discharge during pregnancy
Brown discharge can occur suddenly in almost all women during pregnancy. There are several reasons for the development of this condition.
The first of these is an ectopic pregnancy. When it occurs, the egg is inevitably rejected. One of the characteristic signs of its development is brown discharge. Bleeding may also occur. Unfortunately, many women at this time do not even know about the onset of pregnancy.
In many cases, the appearance of brown discharge indicates a threatened miscarriage. In this case, an experienced gynecologist should take all possible measures in order to save the fetus (surgery or conservative treatment). A miscarriage is a serious complication that occurs only in the early stages of pregnancy. At first, bleeding may be minor and not accompanied by pain. However, it is not able to stop within a certain period of time and gradually increases.
In this case, an experienced gynecologist should take all possible measures in order to save the fetus (surgery or conservative treatment). A miscarriage is a serious complication that occurs only in the early stages of pregnancy. At first, bleeding may be minor and not accompanied by pain. However, it is not able to stop within a certain period of time and gradually increases.
Incomplete miscarriage may cause significant bleeding, it is thick red with a brown tint, and clots may be present. All this is accompanied by infrequent, but intense pain in the lower abdomen. In this case, it is necessary to scrape the uterine cavity and remove the remnants of a dead fetal egg.
The appearance of discharge that is brown in late pregnancy may be evidence of placental dysfunction. This organ may disintegrate. As a result, minor bleeding may occur.
The next reason for the appearance of such symptoms may be diseases associated with inflammatory processes or erosion of the cervix.
If the due date is already approaching and brown discharge suddenly appears, then this indicates the onset of childbirth. Another extremely important reason for the appearance of such secretions is uterine rupture. Most often, it develops in those women who have previously had abortions or have scars on the uterus.
Thus, the most common causes of brown discharge are sexual diseases, as well as cervical erosion. To eliminate such pathological conditions, it is necessary to contact a specialist gynecologist.
In case of placental rupture, bed rest is prescribed, any emotional and psychological stress is excluded, as well as the use of hormonal drugs.
Bleeding during pregnancy
Bleeding is quite common, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy. According to statistics, eighty percent of women calmly and without any deviations continue to bear the fetus.
There are many reasons for bleeding. For example, active blood supply to the internal genital organs or their excessive sensitivity. This usually happens after an ultrasound examination, if it is carried out with a special vaginal probe or when used when examining a gynecological speculum.
This usually happens after an ultrasound examination, if it is carried out with a special vaginal probe or when used when examining a gynecological speculum.
Similar discharge may also occur after sexual intercourse, as there is irritation of the cervix, as well as the mucous membrane of the vagina. Discharge also begins due to a slight detachment of the placenta: a certain amount of blood accumulates under it. When released to the outside, it has a pinkish tint.
Women often have discharge on days when they had their period before pregnancy. They are also accompanied by pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen. This is due to hormonal disruptions in the body in early pregnancy and it is absolutely safe.
The appearance of blood clots is a signal that indicates dangerous complications. It is urgent to consult a doctor, because, most likely, this is a threat of miscarriage.
If the discharge has a brownish tint, then a hematoma may have formed in the body.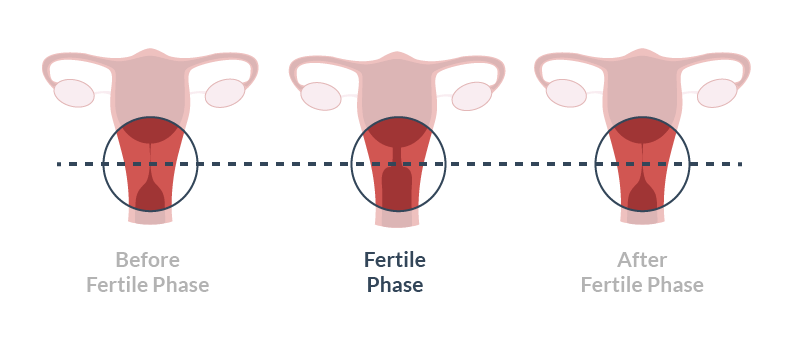
When an ectopic pregnancy develops, the woman may also experience spotting. Another reason is a “frozen” pregnancy. In this case, a week after intrauterine death of the fetus, a spontaneous miscarriage develops.
A rare cause of spotting is hydatidiform mole, in which there is an overgrowth of placental tissue. Allocations in this case are abundant, but they are absolutely painless. The outcome of this condition is the death of the baby.
The most dangerous spotting occurs in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. They can be evidence of pathology, threaten the life of not only the fetus, but also the mother.
Bleeding may also develop in the presence of fibroids, cervical erosion, cervical canal polyps, genital trauma.
Despite the fact that bleeding in most cases does not pose a danger to the fetus and mother, it is necessary to contact a specialist in time in order to exclude the development of dangerous complications and ensure the normal course of pregnancy.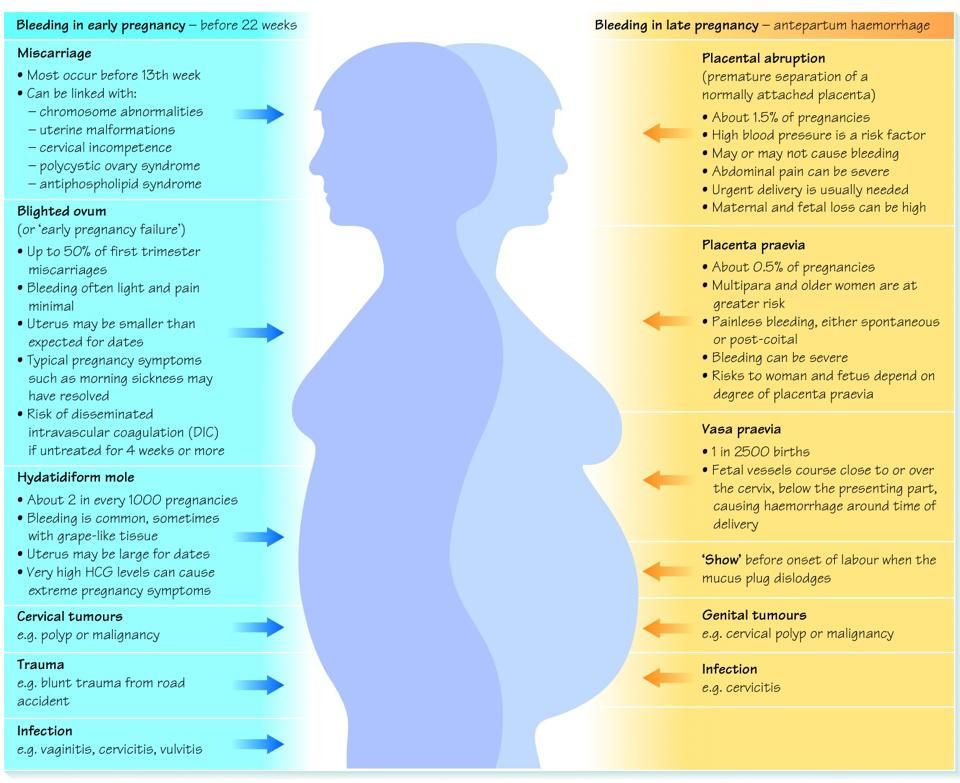
Discharge during early pregnancy
Discharge that occurs early in pregnancy can be either normal or abnormal. A change in discharge in the first weeks after conception is an inevitable process. This is due to the fact that in the female body the secretion of the hormone progesterone increases. It provides attachment to the uterine wall of the egg fertilized by the sperm, is involved in the preservation of the fetus and the formation of the placenta. At the same time, vaginal discharge becomes scarce, opaque and viscous. This nature of the secretions contributes to the formation of a protective plug in the cervical canal, which protects the uterus from the ingress of pathological microorganisms.
On the tenth day immediately after conception, bloody discharge from the vagina may appear, which is also not considered a pathological condition. This is due to the attachment of a fertilized egg to the uterus. This organ has an extensive network of blood vessels and capillaries, which can be slightly damaged when the embryo attaches. This phenomenon is called implantation bleeding and lasts no more than two days. Strong and longer bleeding indicate the development of a pathological condition.
This phenomenon is called implantation bleeding and lasts no more than two days. Strong and longer bleeding indicate the development of a pathological condition.
Discharges that are yellowish, brown, greenish in color, curdled in texture and have an unpleasant odor are considered pathological.
Yellowish discharge from the vagina, which has a sharp and unpleasant odor, indicates the presence of inflammation in the uterus and its appendages. Inflammatory processes in the internal organs during pregnancy are very dangerous, as they often lead to its interruption.
If bleeding is observed that does not stop within three days, then this indicates the development of serious complications and requires immediate medical attention, as this is one of the signs of a developing miscarriage. Often, such a sign is accompanied by pulling, severe pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, loss of appetite, and intestinal dysfunction.
Bloody discharge in early pregnancy may be a sign of cervical erosion. They are almost always painless and stop within a few hours.
They are almost always painless and stop within a few hours.
The appearance of dark red, brown or bloody discharge a few days after conception may indicate the development of an ectopic pregnancy. In this case, the blood is released after the rejection of the fertilized egg. An ectopic pregnancy poses a significant threat to a woman and reduces the chance of a future pregnancy.
Thus, white, smooth, stringy, and odorless discharge during early pregnancy is normal and should not cause any concern, while curdled, yellow, malodorous discharge may be a sign of candidiasis or inflammation of the uterus. Abundant brownish, bloody discharge is also an alarming symptom and requires immediate medical attention.
Late discharge
Usually, late pregnancy refers to the period from the thirty-fifth week until the onset of labor. At this time, the body is actively preparing for the birth of a child. The discharge has a mucous consistency, milky color, they have no smell. Normally, they do not cause unpleasant discomfort, burning, itching and any other irritations.
Normally, they do not cause unpleasant discomfort, burning, itching and any other irritations.
Often before the expected delivery, at about the thirty-seventh week, there may be a discharge of brown color and a mucous consistency. This is due to the fact that the cervical mucosa begins to prepare for childbirth. It softens, then opens slightly and is released from the mucous plug. A similar phenomenon indicates an imminent birth.
However, if foamy discharge with a greenish, bright red or brown tint is observed in the last days of the week, this indicates the development of dangerous complications.
Bright red discharge may indicate placental abruption. In this case, urgent emergency medical care is needed.
Greenish frothy discharge, which is accompanied by itching, most likely indicates the addition of an infection. In this case, it is extremely important to eliminate their cause before childbirth, since otherwise their course may be complicated and there is a threat of infection of the fetus.
Discharge after pregnancy
After the birth of a child, regardless of the type of delivery, a woman has bloody discharge from the genital tract. Such postpartum discharge is called lochia.
They are caused by the healing process on the inside of the uterus, usually where the placenta was attached to the wall of the uterus. If timely release from all non-viable tissues occurs, then the postpartum period proceeds without any complications.
It is extremely important to pay attention to the length and color of the lochia. Their nature changes - the discharge becomes scarcer over time and changes its color:
- red lochia. They begin in the first two or three days after birth. This is a bright red, bloody, copious discharge with a small amount of blood clots;
- serous lochia. They begin on the fourth day after birth. The discharge turns pale and acquires a serous-sanious (pinkish-brown) color with a high content of leukocytes.
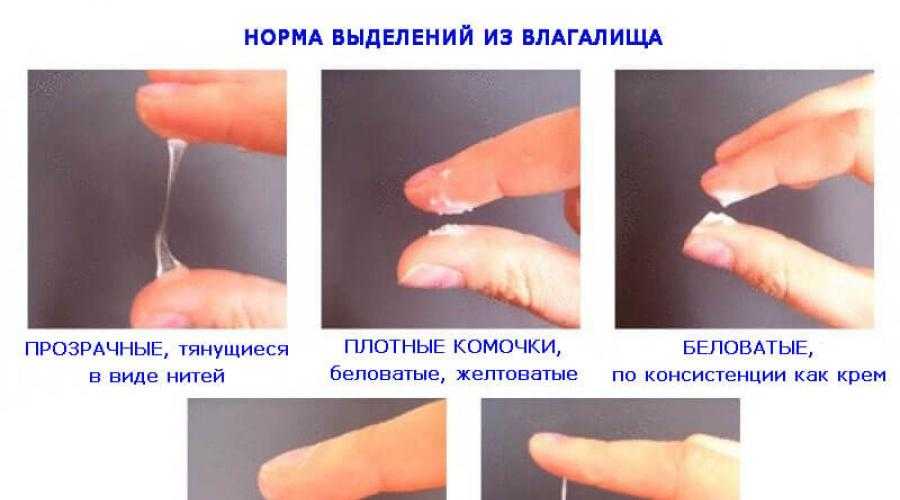 During this period, there should be no bright red lochia and hemorrhagic clots.
During this period, there should be no bright red lochia and hemorrhagic clots. - white lochia. They begin approximately from the tenth day and continue until the twentieth day. Allocations acquire a yellowish-white or yellow color, become spotting, odorless liquid and blood impurities.
The number of lochia gradually decreases, from the third week after birth they become scarce and contain an admixture of mucus from the cervical canal. From the uterus, the discharge stops at the fifth or sixth week after childbirth. Only vitreous mucus flows out of the cervical canal, in which single leukocytes are noted.
Therefore, the discharge that begins after childbirth and lasts up to a month and a half has nothing in common with menstrual bleeding. They pass on their own and do not depend on whether the woman is breastfeeding or the child is bottle-fed.
Source: http://kinderok.com/beremennost/oslozhneniya-pri-beremennosti/vydeleniya-pri-beremennosti. html
html
Mucus in the uterus: an early sign of pregnancy?
od Oscar
We include products that we find useful for our readers. If you buy from links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here is our process.
Changes in color, consistency and amount of cervical mucus (vaginal discharge) during the menstrual cycle are normal. It can also change in early pregnancy.
Although cervical mucus changes can be seen in early pregnancy, these changes are usually subtle. They can also vary greatly from person to person.
Read on to learn about cervical mucosal changes and whether this is a reliable method for early detection of pregnancy.
contents
What does the uterine mucus look like in early pregnancy?
In early pregnancy, changes in cervical mucus may not be noticeable. The amount of discharge from the cervix usually increases. However, the change may be so small that it can hardly be noticed.
However, the change may be so small that it can hardly be noticed.
Even at the beginning of pregnancy, you may feel wetter than usual in your underwear. At the bottom or at night, you may notice more dry, whitish-yellow discharge on your underwear.
What causes changes in cervical mucus during pregnancy?
Uterine mucus, also called leucorrhoea, is a normal part of the female cycle. It helps to keep the tissues of the vagina healthy, protecting them from irritation and infection, and also moisturizes the vagina.
During your menstrual cycle, you may notice changes in cervical mucus. One day it may be, for example, white and sticky, and the next day clear and watery.
When you become pregnant, your hormone levels will increase dramatically. These hormonal changes help prepare your body for growth and also help protect and nourish your baby.
Hormonal changes may cause increased vaginal discharge as pregnancy progresses. This happens naturally because your body is working to prevent vaginal infections, especially in the later stages of pregnancy.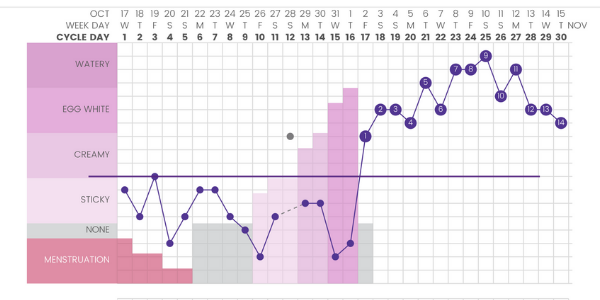
What type of cervical mucus is normal?
Healthy cervical mucus is thin, white or clear, with a slight odor. As long as cervical mucus changes throughout the cycle, even during pregnancy, it should still have these qualities.
What type of cervical mucus is not normal?
The following discharge characteristics are not typical:
- smell
- light yellow, green or gray
- causes itching, swelling, burning or irritation
Discharge from the uterus with any of these signs may be a sign of infection. It is important to see your doctor if you notice any of these changes or symptoms.
Other early signs of pregnancy
A slight increase in cervical mucus is just one of many early signs of pregnancy. Being so subtle, it is often overlooked. Other common, more noticeable early signs of pregnancy include:
- missing period; however, a number of other conditions, including stress, extreme exercise, eating disorders, hormonal imbalances, and other health problems, can cause a missed period
- cramps
- food cravings pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin, which causes frequent urination
- fatigue caused by increased levels of the hormone progesterone
- light spotting called “implantation bleeding, “which can occur 6–12 days after conception and last no more than 24–48 hours.
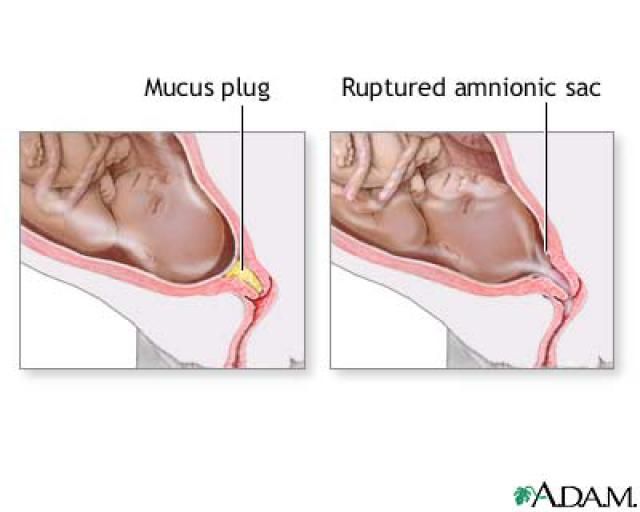 ”
” - nausea, often in the morning (morning sickness)
- breast changes that usually involve tender painful, swollen breasts
- metallic taste in the mouth
- headaches and dizziness
Can cervical mucus tell you when you are most fertile? by your urination, you can track the days when you are most fertile.0005
When your cervical mucus is clear and slippery, you are likely to ovulate. This is the time when you are most likely to get pregnant. You are less likely to get pregnant if you notice cloudy and sticky mucus or feel dry.
Recording your cervical mucus characteristics over the course of a month can reveal your ovulation patterns and help you determine when you are most fertile.
While it is possible to control your fertility by focusing on cervical mucus for a month, you may find it difficult to rely on this method to determine when you are in your most fertile state.
Therefore, experts generally recommend the use of more accurate fertility monitoring methods, such as fertility monitoring.