Vitamin c bad for pregnancy
Vitamin C Abortions Don't Work, Here's What to Do Instead
Taking large amounts of vitamin C will not end a pregnancy. No matter where you live, there are safer ways to end a pregnancy at home.
Legal restrictions on abortion are constantly changing. With the overturn of Roe v. Wade, many people are understandably confused about where and when they can access abortion services. This uncertainty has left some people searching for alternative ways to end a pregnancy.
If you’ve been researching abortion methods, you may have come across rumors of something called the vitamin C technique. These rumors claim that taking large doses of vitamin C supplements, several days in a row, will end a pregnancy. But this is not true.
Whether it’s vitamin C, natural botanicals, or other substances, there is no such thing as a safe abortion home remedy.
However, there are safe, FDA-approved medications that you can use to induce an abortion at home. There are organizations that can help you get the abortion pill, no matter where you live. And there are organizations throughout the country that may be able to provide financial assistance.
Keep reading to learn more about why the vitamin C technique will not work and how you can get medication that allows you to safely end a pregnancy at home.
Stay informed
On June 24, 2022, the Supreme Court of the United States overturned Roe v. Wade, the landmark 1973 ruling that secured a person’s constitutional right to an abortion.
This means that individual states are now able to decide their own abortion laws. Many states will ban or severely restrict abortion access, and more states may follow suit.
The information in this article was accurate and up to date at the time of publication, but it’s possible the information has changed since. To learn more about your legal rights, you can message the Repro Legal Helpline via a secure online form or call 844-868-2812.
There is no credible scientific information suggesting that vitamin C has any effect on pregnancy, implantation, or menstruation.
The claims that vitamin C can cause an abortion may have originated from a Russian journal article from the 1960s. This study, which is no longer in print, did not use modern scientific research methods.
Since then, research has shown that this method is ineffective. A 2016 review of studies found that taking vitamin C had no effect on pregnancy and did not increase the risk of miscarriage.
Vitamin C is typically relatively harmless, even in large doses. But other abortion “home remedies” can be extremely dangerous.
At most, taking too much vitamin C will leave you with diarrhea and a stomachache. It could also increase your risk of kidney stones.
Generally speaking, when taking vitamin C supplements, it’s probably best not to exceed 2,000 milligrams each day.
Because vitamin C abortion does not work, wasting time on this method will only work against you.
Abortions are easier to get earlier on in a pregnancy. Medical abortions, in particular, are only available up to around 11 weeks after the first day of your last period.
Getting an abortion sooner rather than later has several benefits, such as:
- lower costs
- increased access, due to state laws regulating abortion
- shortened procedure time
- reduced risk of complications
Abortion access in your state
Trying to make sense of the limitations in your state? Our state-by-state guide to abortion restrictions can help.
There are many reasons why people prefer to have abortions in the privacy of their own homes. Whatever your reasons are, there is a better way to have an abortion at home: medical abortion.
The abortion pill, as it’s often called, is actually a combination of two different medications: mifepristone and misoprostol. Together, these medications work to stop the pregnancy and push the pregnancy tissue out of your body.
The process can take between 1 and 3 days to complete.
Mifepristone is an oral medication that blocks progesterone. Without progesterone, the pregnancy cannot continue. Depending on where you get your medication, you may take this first pill in a clinic or at home.
Depending on where you get your medication, you may take this first pill in a clinic or at home.
Misoprostol is a medication that dissolves when placed in your inner cheek or vagina. You take this medication at home 24 to 48 hours after the first medication. It causes the uterus to contract and bleed, which helps your body push out the embryo.
Medical abortion is very effective for people who are up to 9 weeks pregnant. If you are 9 to 12 weeks pregnant, your doctor may recommend a second dose of misoprostol.
If you are farther along, you’ll need to get a surgical abortion.
Are there any other abortion medications?
Other approaches to medical abortion include:
- Methotrexate, an arthritis medication. Methotrexate is taken on day 1, instead of mifepristone. Within 24 to 48 hours, you would then take misoprostol.
- Misoprostol alone. You can take several doses of misoprostol alone, without using mifepristone, to induce an abortion.
This is considered an off-label use of methotrexate, meaning it is not FDA approved for use in abortion.
With all the recent developments in abortion laws, it can be tough figuring out what is and is not available in your state.
Telehealth abortion
In some states, people who are up to 10 weeks pregnant can legally get the abortion pill mailed to them after a telehealth visit with a doctor. In most of these states, Planned Parenthood offers telehealth appointments for medical abortion and other services.
During a telehealth appointment, you meet with a doctor through electronic means, like video chats, phone calls, or text conversations. Your doctor will go over your options. If they prescribe the abortion pill, you can usually have it mailed to your home (in discreet packaging).
You take the medication and have the abortion at home. But if you have any questions or problems, you can reach out to your doctor.
Around 19 states currently have laws restricting telehealth abortions. But there may be some workaround.
But there may be some workaround.
Legal gray areas
The laws around abortion are constantly changing, as they are often challenged in the courts.
Some organizations, like Aid Access and Plan C, take advantage of legal gray areas and provide people with access to telehealth abortion, no matter where they live.
You can probably get abortion pills online, no matter where you live. But it’s important that you get them from a safe, reputable place. Here are a few options:
- AidAccess (everywhere)
- Plan C (options for all states)
- Planned Parenthood: Telehealth (many states)
- Abortion On Demand (20+ U.S. states)
- Hey Jane (CA, CO, IL, NM, NY, and WA)
- Just The Pill (WY, MN, MT)
Buying online: Is it safe?
Having an abortion supervised by a qualified healthcare professional is the safest option. But a medical abortion done with medication from a reputable source is much safer than attempting a self-abortion with home remedies.
Learn more about buying abortion pills online.
If you live in the United States, there are several organizations that can offer guidance on what your options are, help you find a healthcare professional who offers abortion services, and assist with covering the costs of an abortion.
Information and services
If you’re not sure where to start, consider reaching out to the Planned Parenthood nearest you.
Clinic staff can counsel you on what your options are and help you weigh the pros and cons of each.
You can also call the National Abortion Federation hotline at 800-773-9100. They can help get you a referral to a local provider.
Financial assistance
The National Network of Abortion Funds can help you find local organizations that may be able to provide financial assistance. Organizations within the national network have different guidelines and eligibility requirements, but if you are in need, they can often help you cover the cost of the abortion.
They may also be able to help with related costs, like transportation, childcare, and lodging. Some organizations provide logistical support, like giving you a ride to a clinic or a place to stay.
Legal information
For up-to-date information about abortion laws in your area, the Guttmacher Institute offers a handy guide to both federal and state regulations.
Watch out for crisis pregnancy centers (CPCs)
While some CPCs offer limited healthcare services like pregnancy tests or ultrasounds, they do not provide abortions or support accessing abortions.
CPC workers are known to shame and mislead people into believing that abortion is unsafe or harmful.
The Crisis Pregnancy Center Map can help you steer clear of these predatory groups. You can also check ReproAction’s Fake Clinic Database and the #ExposeFakeClinics resource hub.
Learn more about identifying, avoiding, and leaving CPCs.
Abortion laws vary from country to country. If you’re not sure about what’s available in your country, MSI Reproductive Services is a good starting point.
If you’re not sure about what’s available in your country, MSI Reproductive Services is a good starting point.
They have offices all over the world and can offer guidance on local laws and available services in your area. Choose your general area out of their list of locations to find country-specific information.
If you can’t safely access a clinic, Women on Web mails abortion pills to people in countries with restrictive laws. You’ll need to have a quick consultation online to make sure you qualify. If you do, a doctor will provide a prescription and mail the pills to you so you can have a medical abortion at home. If you’re having trouble accessing the site, you can find a workaround here.
Women Help Women also offers information about resources and hotlines in many countries.
You may feel like vitamin C and other home remedies are your only option, but there are many other resources available to you.
You can have a medication abortion at home. You may even be able to avoid going to a clinic by using a telehealth service or buying your pills online.
Though the laws and regulations surrounding abortion are constantly changing, support is available to help preserve your right to make decisions about what happens to your body.
What You Need to Know
Viral illnesses are a big worry for pregnant women. Many symptom-combating over-the-counter meds are off-limits — and thanks to a weakened immune system during pregnancy, a nasty virus can sometimes turn into an even nastier infection.
That’s why vitamin C supplements like Emergen-C — which promise to help you fight off every germ that cold, flu, and, er, pandemic season throws your way — are so tempting.
Talk to your doctor
If you have symptoms of COVID-19 or a fever while pregnant, don’t attempt to self-treat with vitamin C. Call your doctor.
These supplements are like vitamin boosts, providing as much immune-supporting vitamin C as a truckload of oranges — and that sounds like a pretty good idea when you’re pregnant or nursing and everyone around you is coughing.
But is it actually a good idea? Most supplements are considered unsafe during pregnancy because they aren’t regulated by the FDA in the same way as drugs. Plus, some supplements and medications taken while breastfeeding can affect your baby.
Emergen-C rests solidly in the check-with-your-doctor-first category, and we’ll tell you why.
There are several different kinds of Emergen-C supplements, all of which contain what the brand calls “high potency vitamin C.”
This is mostly a fancy term for “enough vitamin C to turn you into an orange,” but some vitamin manufacturers claim it means their formulas are less likely to cause digestive upset and more likely to be absorbed into the bloodstream than other kinds of vitamin C.
Some Emergen-C products, such as Everyday Immune Support and Enhanced Immune Support Formula, contain a whopping 1,000 milligrams per serving, along with:
- zinc
- B vitamins
- other electrolytes, like calcium and sodium
Other Emergen-C products include:
- energizing vitamins
- plant-based vitamins
- probiotics
- electrolyte drinks
- a sleep aid
These products may contain lower levels of vitamin C but also probiotic strains, vitamins D and E, elderberries, melatonin, ginseng, and caffeine.
We get it: No one wants to sit around peeling and eating oranges all day in an effort to ward off the plague. There’s a lot of appeal in dissolving some powder into water and chugging down all that sweet, immune-boosting vitamin C in just minutes (or popping a couple of gummies or chewable vitamins).
But if you’re pregnant, you should talk to your doctor first. Most doctors advise pregnant women to steer clear of supplements — other than prenatal vitamins and a handful of much-needed nutrients — for a healthy pregnancy.
That goes for vitamin C, too, as the research is unfortunately lacking. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that some studies have investigated vitamin C’s effects on pregnancy and birth outcomes, but the results have been mixed. Vitamin C improved outcomes in some cases, but not in others.
As such, the WHO doesn’t recommend the widespread supplementation of vitamin C during pregnancy. That doesn’t mean vitamin C use during pregnancy could harm you, but it does mean there’s not enough evidence that the benefits outweigh the risks.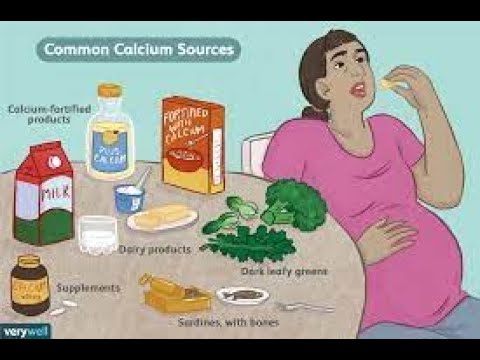 Plus, its effects on immune health specifically during pregnancy haven’t been closely studied.
Plus, its effects on immune health specifically during pregnancy haven’t been closely studied.
The restrictions are slightly more lax for nursing mothers, though there are things to know there, too.
According to the Drugs and Lactation Database, you can take a high daily dose of 1,000 milligrams — like what you would find in Emergen-C — without any adverse effects for you or your baby. However, high amounts of vitamin C could increase your milk supply, so if you’re already struggling with overproduction, keep that in mind.
The amount of vitamin C in Emergen-C products varies but tops off at 1,000 milligrams per serving for their immune-boosting formulas. Meanwhile, their energy vitamins and probiotics include between 250 and 500 milligrams.
According to the Office of Dietary Supplements (ODS), pregnant women over 19 years old should get 85 milligrams of vitamin C daily, while breastfeeding women over 19 should get 120 milligrams daily. These numbers are slightly lower — 80 and 155, respectively — if you’re under 19.
As for how much vitamin C you can take without having side effects, the makers of Emergen-C advise that no one consumes more than 2,000 milligrams of vitamin C per day. The ODS confirms that this is also the upper daily limit (UL) for pregnant and breastfeeding women over 19.
Short-term use of more than 2,000 milligrams per day may not cause any problems other than mild digestive distress, but some research has shown that long-term “megadoses” of vitamin C could cause kidney stones or excess iron absorption.
Unfortunately, pregnant women have more vulnerable immune systems. In fact, they’re usually lumped into that infamous “immunocompromised” category along with infants and the elderly. You know how you can’t eat soft cheese during pregnancy because you might get develop listeriosis? That’s because your immune system is weaker than usual.
That said, you’ll get some supplemental vitamin C in your prenatal vitamin, though the amount will vary by brand. Most contain about 85 milligrams per serving, which puts you squarely in the “recommended daily value for pregnant women” camp and should be enough to keep you healthy under normal circumstances.
Whether you choose to add an additional vitamin C supplement is up to you — you may feel you need it during sick season (or if you have other small children at home constantly sharing all their preschool germs with you). But you should ask your doctor first if that’s OK, and how much extra you should take.
Don’t forget that you can also get an extra boost of vitamin C from foods, which is a safer but just-as-effective way to increase your levels. Try eating lots of citrus fruits, red and green pepper, broccoli, cherries, spinach, and strawberries.
We understand the impulse to load up on as much vitamin C is safe during pregnancy, especially when there’s a viral pandemic raging in your neighborhood. But more is not always best when it comes to supplements, so you need to check with your doctor before you consume extra amounts of vitamin C.
Furthermore, the good people at Emergen-C agree. In their FAQ section, consumers are instructed to consult their healthcare provider if they’re pregnant or nursing.
Vitamin C supplements like Emergen-C are probably fine for occasional use, but there’s not much evidence proving their safety or usefulness when it comes to fighting illnesses during pregnancy.
Stay healthy these 9 months by eating a diet rich in vitamins and minerals and practicing good hand hygiene. If you still feel like you need an additional boost of vitamin C, talk to your doctor.
Vitamins and pregnancy - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Kurbatskaya Olga Nikolaevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Lapino-1 Clinical Hospital "Mother and Child"
One of the most common questions that pregnant women ask their doctor is what vitamins should I take during pregnancy? Let's say right away whether expectant mothers need to drink pharmaceutical vitamins or not - there is no unequivocal answer to this question. Some doctors believe that the necessary nutrients should be obtained from natural products. Others are in favor of taking pharmaceutical multivitamins. It can only be said unequivocally that vitamins and microelements must necessarily enter the body of a pregnant woman. We will tell you which of them are most important for the expectant mother. nine0010
Others are in favor of taking pharmaceutical multivitamins. It can only be said unequivocally that vitamins and microelements must necessarily enter the body of a pregnant woman. We will tell you which of them are most important for the expectant mother. nine0010
Folic acid
Other names for this vitamin are vitamin B 9 or B with . This vitamin is necessary for cell division and reproduction, so it is especially important in the first trimester of pregnancy, when all organs and systems of the child are being laid. Folic acid plays an important role in the synthesis of hemoglobin, and with its deficiency, anemia can develop. And folic acid also helps to reduce the likelihood of spinal defects in a child, takes care of the correct formation of his psyche and intellect. It is better to start taking folic acid three months before the planned conception, since a small supply of this vitamin will only be useful for both the expectant mother and the baby. If the pregnancy has come unplanned, then folic acid must be taken as soon as the woman finds out about her situation. On average, the dosage of this vitamin is from 0.4 to 0.8 mg per day. nine0003
If the pregnancy has come unplanned, then folic acid must be taken as soon as the woman finds out about her situation. On average, the dosage of this vitamin is from 0.4 to 0.8 mg per day. nine0003
Calcium
An expectant mother needs about 1200–1400 mg of calcium daily, while an ordinary woman needs 800–1000 mg of this trace element. Why? During pregnancy, the amount of calcium in the body of the expectant mother is significantly reduced, since it is also spent on the growth and development of the child. Especially a lot of calcium is needed in the third trimester, when the baby's skeleton is calcified. But calcium is needed not only for the growth of bones and teeth of a child - with its help, his nervous system, his heart, muscles, skin tissues, eyes, ears, hair and nails are formed. A pregnant woman needs calcium for the full functioning of the kidneys, the prevention of muscle pain, constipation, osteoporosis, caries and toxicosis. In addition, this trace element protects the expectant mother from stress and nervous overload. nine0003
nine0003
Vitamin E
This vitamin is involved in the process of tissue respiration, it helps oxygen to penetrate into every cell of the body. At the same time, vitamin E is an excellent antioxidant: it protects cells from the formation of free radicals that can provoke various diseases. This protective function is especially important at the stage of embryo formation. In addition, vitamin E helps to normalize the hormonal balance of the body. In the early stages, it participates in the formation of the placenta, and also protects against abortion. The dose of vitamin E during pregnancy is 15 mg. nine0003
Vitamin E is found in vegetable oils, not less than this vitamin in lettuce, tomatoes, rose hips, parsley, spinach and peas. Some vitamin E is found in meat, eggs and milk.
Magnesium
Magnesium is involved in all metabolic processes, helps to cope with stress, normalizes the functioning of the cardiovascular system and blood pressure, and keeps blood vessels in good shape. Due to a lack of magnesium in the body, cramps in the muscles (usually in the calves) may appear. And since the uterus is also a muscular organ, with a lack of magnesium during pregnancy during gestation, the excitability of the myometrium increases, which leads to active uterine contractions. Therefore, with hypertension and the threat of abortion, magnesium is often prescribed. nine0003
Due to a lack of magnesium in the body, cramps in the muscles (usually in the calves) may appear. And since the uterus is also a muscular organ, with a lack of magnesium during pregnancy during gestation, the excitability of the myometrium increases, which leads to active uterine contractions. Therefore, with hypertension and the threat of abortion, magnesium is often prescribed. nine0003
Magnesium is rich in whole grains and whole grain breads, figs, almonds, seeds, dark green vegetables, and bananas.
iodine
Iodine is usually prescribed for pregnant women in the first trimester. Up to 16 weeks of pregnancy, the development of the child and the laying of all its organs and systems are "under the protection" of the mother's thyroid gland. And if a woman has little iodine, then this means that some system or organ of the baby may suffer. And even when the child’s own thyroid gland is formed and starts working, she can still take iodine only from the mother’s body. Its daily dose is 250 mg per day. nine0003
Its daily dose is 250 mg per day. nine0003
Iodine is easiest to get from seafood and sea or iodized salt. A lot of iodine is found in sea fish, seaweed, squid, persimmon, feijoa, dates, dried figs, dairy products and meat. However, iodine is destroyed by temperature effects, which means that after heat treatment, the amount of iodine in the products decreases sharply.
Iron
Iron is necessary primarily for the prevention of anemia. After all, it is part of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen throughout the body of the mother and child. In addition, iron is involved in protein synthesis, which is involved in the formation of muscle tissue. And iron deficiency can lead to increased uterine tone. The average daily dosage of iron is 30–60 mg. In some cases, if the woman's iron supply was initially reduced, the dosage may be higher. nine0003
Iron is found in meat, especially a lot of it in veal, turkey, hare, pork and beef. There is iron in plant foods, but from there it is absorbed much worse. Iron is best absorbed when taken together with vitamin C.
Iron is best absorbed when taken together with vitamin C.
If a pregnant woman eats properly and varied, eats a lot of fruits and vegetables, then she may not need an additional complex of vitamins for pregnant women. It may be necessary to drink some vitamins separately, but this should be determined by the doctor. If, before pregnancy, a woman had signs of vitamin deficiency, she eats incorrectly or poorly, then multivitamins cannot be dispensed with. nine0010
Inset
Vitamin B 9 (folic acid) is found in animal liver, spinach, asparagus, lentils, Brussels sprouts, beans and wholemeal flour. However, it is absorbed very poorly from food, no more than 50%. That is why it is prescribed to almost all pregnant women.
At one time, our body will not be able to absorb more than 500 mg of calcium. Therefore, you should not try to get the entire daily norm of this trace element in one meal. Try to eat foods containing calcium in small portions several times a day. nine0003
nine0003
To increase the concentration of magnesium in tissues, vitamin B 6 (pyridoxine) is needed, which facilitates its absorption and acts as a conductor of magnesium into the cell. Therefore, magnesium and vitamin B 6 are often prescribed together.
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Kurbatskaya Olga Nikolaevna
Lapino-1 Clinical Hospital "Mother and Child"
PregnancyHome birthBirth
By clicking on the send button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
Clinical Hospital MD GROUPClinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child"Clinic KG "Lapino" in Odintsovo (branch)Clinic "Mother and Child" Khodynskoye PoleClinic "Mother and Child" KuntsevoClinic "Mother and Child" SavelovskayaClinic "Mother and Child" Yugo-ZapadMother and Child Clinic NovogireyevoMother and Child Clinic Lefortovo
All directionsSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children)Laboratory of molecular geneticsGeneral clinical examinationsProcedural roomTelemedicine for adultsTherapeutic examinationsUltrasound examinations for adults
01.
Specialist consultations (adults)
02.
Specialist consultations (children)
03.
Laboratory of molecular genetics
04.
General studies
05.
Procedure room
06.
Television and adults
07.
Therapeutic studies
08.
Ulzvous Valzvous Studies. adults
Nothing found
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to timely update the price list posted on the website, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services and the timing of the tests by calling
Vitamins during pregnancy - good or bad? Encyclopedia of the IVF Clinic
How to take vitamins during pregnancy: how many days, when to take a break and for how long is there a need for vitamin preparations? Chief Physician of the Medical Clinic of Reproduction "MAMA", Victoria Viktorovna ZALETOVA.
How to take vitamins correctly during pregnancy: how many days, when to take a break and for how long is there a need for vitamin preparations? Viktoria Viktorovna ZALETOVA, Chief Physician of the Medical Clinic of Reproduction "MA-MA", tells:
What are girls made of?. .. Well, from cakes, for example... The question is old, but it was asked not to the eyebrow, but to the eye. This problem becomes especially relevant when the girl grows up and prepares to become a mother herself. It's no secret that we are all made up of water and substances that come from food. From vitamins too. How many of them are needed - a lot or a little, and is there a lot of them in general? As scientists have found, the impact of unbalanced or malnutrition is comparable to the negative impact of genetic factors, chemical or infectious agents. The vast majority of diseases that are immediately detected in a newborn "baby" come from intrauterine life when he was an embryo. The problem became full-blown when it was proved that there is a connection between malformations with a deficiency in the nutrition of pregnant women at the stage of formation of the child's organs - protein, folic acid, zinc, copper. Now all pregnant women are prescribed folic acid at a dose of 300-400 mcg per day to prevent the most severe malformation of the nerve trunk.
.. Well, from cakes, for example... The question is old, but it was asked not to the eyebrow, but to the eye. This problem becomes especially relevant when the girl grows up and prepares to become a mother herself. It's no secret that we are all made up of water and substances that come from food. From vitamins too. How many of them are needed - a lot or a little, and is there a lot of them in general? As scientists have found, the impact of unbalanced or malnutrition is comparable to the negative impact of genetic factors, chemical or infectious agents. The vast majority of diseases that are immediately detected in a newborn "baby" come from intrauterine life when he was an embryo. The problem became full-blown when it was proved that there is a connection between malformations with a deficiency in the nutrition of pregnant women at the stage of formation of the child's organs - protein, folic acid, zinc, copper. Now all pregnant women are prescribed folic acid at a dose of 300-400 mcg per day to prevent the most severe malformation of the nerve trunk. The consequence of folate deficiency may be the occurrence of anemia, an increase in the frequency of toxicosis, placental abruption, and preterm birth. A relationship has been found between a lack of vitamin B2 and intrauterine death of the fetus, uncontrollable vomiting, and a decrease in lactation. Vitamin C deficiency is a risk of early rupture of membranes. As you understand, most of the visits to a pregnancy consultation are postponed for several weeks. And after the words "it seems to me that I am pregnant" a lot of time will pass. And just at this time, the child's organ formation takes place! Therefore, precautionary measures should be taken by everyone who is planning a pregnancy. All over the world, the problem is solved simply. Food products, soft drinks are enriched with necessary substances, food additives, multivitamin preparations are produced. For example, in the United States, about 60% of the total population and 90-100% of pregnant women take vitamins regularly for preventive purposes.
The consequence of folate deficiency may be the occurrence of anemia, an increase in the frequency of toxicosis, placental abruption, and preterm birth. A relationship has been found between a lack of vitamin B2 and intrauterine death of the fetus, uncontrollable vomiting, and a decrease in lactation. Vitamin C deficiency is a risk of early rupture of membranes. As you understand, most of the visits to a pregnancy consultation are postponed for several weeks. And after the words "it seems to me that I am pregnant" a lot of time will pass. And just at this time, the child's organ formation takes place! Therefore, precautionary measures should be taken by everyone who is planning a pregnancy. All over the world, the problem is solved simply. Food products, soft drinks are enriched with necessary substances, food additives, multivitamin preparations are produced. For example, in the United States, about 60% of the total population and 90-100% of pregnant women take vitamins regularly for preventive purposes. In our conditions, it is easiest and most realistic to take the optimal amount of vitamin preparations, fortified milk, drinks based on vitamin mixtures. However, it turned out that a third of pregnant women take vitamins 1.5-2 times more than is normally required. Recommended norms for the consumption of various nutrients have been approved, but at the same time they exceed the average physiological need, which is explained by the possible variation in the physiological needs of most people. So, a discrepancy with individual characteristics can have the opposite adverse effect. nine0003
In our conditions, it is easiest and most realistic to take the optimal amount of vitamin preparations, fortified milk, drinks based on vitamin mixtures. However, it turned out that a third of pregnant women take vitamins 1.5-2 times more than is normally required. Recommended norms for the consumption of various nutrients have been approved, but at the same time they exceed the average physiological need, which is explained by the possible variation in the physiological needs of most people. So, a discrepancy with individual characteristics can have the opposite adverse effect. nine0003
Vitamin A can be supplied to the fetus in excess through the placenta. Its teratogenic effect has been proven at a dose of 24,000-30,000 IU per day. Described cases of defects with increased use of the liver. The daily dose should not exceed 750 micrograms for pregnant women - this is the opinion of the British and French. At the same time, it is not recommended to abuse such foods as liver, fish oil, food supplements with a large amount of vitamin A.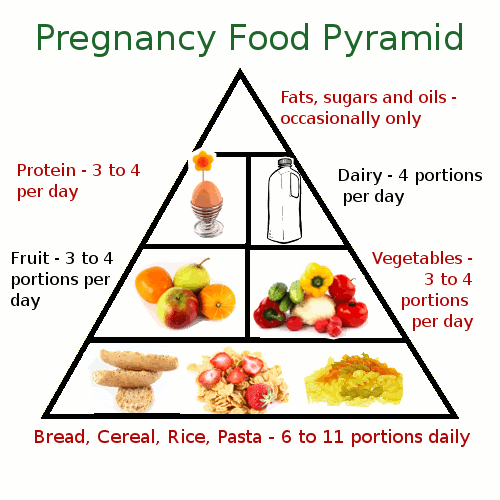 Pediatricians remember the wave of carotene jaundices when babies were fed carrot puree and juices from 2-3 months of age. Of course, it is difficult to link the developmental defects of a child, the underdevelopment of some organs with vitamin A in each case. But the fact is obvious - a third of pregnant women consume vitamin A at a dose of 230% of the daily requirement. In many cases, families have liver diseases, cholelithiasis, pancreatitis, which are a relative contraindication to the appointment of large doses of vitamin A. Therefore, excessive fortification is useless. nine0003
Pediatricians remember the wave of carotene jaundices when babies were fed carrot puree and juices from 2-3 months of age. Of course, it is difficult to link the developmental defects of a child, the underdevelopment of some organs with vitamin A in each case. But the fact is obvious - a third of pregnant women consume vitamin A at a dose of 230% of the daily requirement. In many cases, families have liver diseases, cholelithiasis, pancreatitis, which are a relative contraindication to the appointment of large doses of vitamin A. Therefore, excessive fortification is useless. nine0003
With an excess of vitamin C, doctors state an increase in kidney diseases and associated gestosis. While the mother is heavily nourished with vitamin C, the level of the same vitamin decreases in the blood of the newborn and causes the threat of "bleeding". In the UK, the recommended doses have been reduced to 60 mg per day, in the US - 75 mg.
The placenta is not very permeable to vitamin E. In domestic and foreign preparations, its level is different (Glutamevit - 20 IU, Gendevit - 5 IU), Pregnavit - 10 IU, Materna - 30 IU. The need is 10 IU. An overdose can cause hemorrhagic complications in organs due to impaired platelet function. nine0003
The need is 10 IU. An overdose can cause hemorrhagic complications in organs due to impaired platelet function. nine0003
By increasing the intake of vitamins A, C, E, B1, B2 to two or more times, we increase the intake of vitamin D. This is enough for the development of calcification of the mother's vessels in the kidneys, calcification of the placenta, womb bones and skull of the child. Therefore, hence the tendency to increase pressure and the occurrence of kidney disease in the mother, impaired placental circulation, traumatism in childbirth. The need for pregnant women in vitamin D is 600 IU per day. It is absolutely not necessary to take vitamin D orally, in our climate (who does not live in the Arctic), this is provided by a 30-minute walk to develop "one's own, internal" vitamin D. With individual correction, you can resort to nutritional supplements. For everyone else, maybe this will help to avoid diseases of both cardiovascular and kidney diseases. nine0003
Taking folic acid at a dose of 400 micrograms both before and during pregnancy is undeniable.