Unable to eat food
Causes, other symptoms, and treatment
Anyone can experience a loss of appetite and for many different reasons. People may have less of a desire to eat, lose interest in food, or feel nausea at the idea of eating.
Alongside a loss of appetite, a person may also experience fatigue and weight loss if they are not eating enough food to sustain their body.
In this article, we look at what causes a loss of appetite, what it means, complications, and how to treat it.
Digestive issues may lead to a person losing their appetite.
A loss of appetite can be physical or psychological. It is often temporary due to factors such as infections or digestive issues, in which case appetite will come back when a person has recovered.
Some people may also lose their appetite as a symptom of a long-term medical condition, such as in the late stages of serious illness, including cancer. This is part of a condition that doctors call cachexia.
The medical term for a complete loss of appetite over a more extended period of time is anorexia. This is different to the eating disorder anorexia nervosa, which is a mental health issue.
Below, we look at the possible causes for a loss of appetite.
Common causes
Common viral or bacterial infections, such as flu or gastroenteritis, are often to blame for appetite loss. A person’s appetite usually returns when they start to recover.
Common short-term causes of feeling a loss of appetite include:
- colds
- flu
- respiratory infections
- bacteria or viral infections
- constipation
- an upset stomach
- digestive issues
- acid reflux
- food poisoning
- allergies
- food intolerances
- a stomach bug or gastroenteritis
- pregnancy
- hormonal imbalances
- stress
- medication side effects
- alcohol or drug use
People with pain in their mouths, such as sores, may also experience a loss of appetite if it becomes difficult to eat.
Medical conditions
Long-term medical conditions can cause a loss of appetite for a range of reasons that vary depending on the cause. Loss of appetite can be related to lowered immune system function, feeling unwell, and having an upset stomach.
Loss of appetite can be related to lowered immune system function, feeling unwell, and having an upset stomach.
Medical conditions that can cause a loss of appetite include:
- digestive conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome and Crohn’s disease
- a hormonal condition known as Addison’s disease
- asthma
- diabetes
- chronic liver or kidney disease
- high calcium levels in the blood
- HIV and AIDS
- underactive thyroid or hypothyroidism
- overactive thyroid or hyperthyroidism
- COPD
- heart failure
- stomach or colon cancer
Side effect of medications
A loss of appetite is a common side effect of many medications, along with other digestive issues, such as constipation or diarrhea. This is common when medications pass through a person’s stomach and digestive tract.
Medications and treatments that often cause a loss of appetite include:
- sedatives
- some antibiotics
- immunotherapy
- chemotherapy
- radiation therapy to the stomach area
If people have recently undergone major surgery, they may experience a loss of appetite after the operation. This feeling can be partly related to anesthesia drugs.
This feeling can be partly related to anesthesia drugs.
Using drugs recreationally, such as cocaine, cannabis, and amphetamines can also cause a loss of appetite.
Psychological causes
Psychological factors and mental health conditions can have a significant impact on a person’s appetite. These can include:
- depression
- anxiety
- panic attacks
- stress
- grief
- eating disorders, such as bulimia or anorexia nervosa
Age
A loss of appetite can also be more common in older adults. This can be due to increased use of medications and changes in the body as it ages. These changes can affect:
- the digestive system
- the hormones
- the sense of taste or smell
Some cancers
A loss of appetite or unexpected weight loss can sometimes be a symptom of certain cancers, such as pancreatic, ovarian, or stomach cancer.
Alongside a loss of appetite, people may experience the following symptoms:
- stomach pains
- heartburn
- feeling full quickly
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
- blood in their stools
If people experience any of these symptoms, they should see a doctor who will be able to find out the underlying cause.
A person should see a doctor if they are vomiting for more than a day and have a complete loss of appetite.
People with serious medical conditions may experience a loss of appetite that can be due to the illness itself or as a side effect of treatments, such as chemotherapy treatment for cancers.
Some people in the later stages of serious illnesses may experience cachexia.
Cachexia is the term for weight loss, muscle wastage, and general ill-health caused by chronic, life-limiting illnesses.
People with cachexia can get nutritional advice from their doctor who can help create a nutritional plan to make sure they get the necessary calories and nutrients.
A person with a serious illness should see their doctor if they have a complete loss of appetite for a day or more or any of the following:
- vomiting for a day or longer
- inability to keep liquids down
- pain when trying to eat
- irregular urination
A doctor may prescribe certain medications to help increase appetite and reduce other symptoms, for example, nausea.
If depression or anxiety are causing people to experience a loss of appetite, talking therapies and sometimes antidepressants can help.
If a doctor thinks a specific medication is a reason for a loss of appetite, they may be able to change the dosage or the medication.
People may find it easier to eat several smaller meals a day instead of three bigger ones.
Aim to make these meals high in calories and protein to make sure the body is getting plenty of nutrients and energy. People may also find having liquid meals, such as smoothies and protein drinks, easier to take.
Adding herbs, spices, or other flavorings to meals may also encourage people to eat more easily. Eating meals in relaxing or social settings may make eating more enjoyable.
People can also keep drinking plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. Gentle exercise, such as a short walk, may sometimes increase appetite as well.
A doctor will look at all the symptoms a person is experiencing, and use these to work out the possible cause of their loss of appetite.
A doctor may examine a person’s abdomen by feeling with their hand for any unusual bloating, lumps, or tenderness. This can help them find out if a gastrointestinal disorder is causing a loss of appetite.
A doctor may also carry out tests to help them work out the cause. Tests can include:
- blood tests
- an abdominal X-ray
- an endoscopy, where a camera enables doctors to look inside the body
It is important to find out the reason for a loss of appetite, as it can lead to complications without treatment.
A continued loss of appetite can cause weight loss and malnutrition. It is vital for people to find out the reason for their loss of appetite, as leaving it untreated can be serious.
People can talk to a doctor if they have a loss of appetite for a prolonged period. If they notice any unexpected or rapid weight loss, they should also see their doctor.
An individual should seek medical help if they notice any other symptoms alongside a loss of appetite, such as:
- stomach pain
- fever
- shortness of breath
- coughing
- a rapid or irregular heartbeat
People can experience a loss of appetite for a wide range of reasons. Some of these are short-term, including colds, food poisoning, other infections, or the side effects of medication. Others are to do with long-term medical conditions, such as diabetes, cancer, or life-limiting illnesses.
Some of these are short-term, including colds, food poisoning, other infections, or the side effects of medication. Others are to do with long-term medical conditions, such as diabetes, cancer, or life-limiting illnesses.
Appetite loss often comes with feelings of fatigue or nausea. If a person is worried about a loss of appetite they should tell their doctor, also mentioning all other symptoms.
Treatments for appetite loss will depend on the cause. People may benefit from eating small, regular meals instead of three large meals, and liquid meals are often more palatable.
Read the article in Spanish.
Causes, other symptoms, and treatment
Anyone can experience a loss of appetite and for many different reasons. People may have less of a desire to eat, lose interest in food, or feel nausea at the idea of eating.
Alongside a loss of appetite, a person may also experience fatigue and weight loss if they are not eating enough food to sustain their body.
In this article, we look at what causes a loss of appetite, what it means, complications, and how to treat it.
Digestive issues may lead to a person losing their appetite.
A loss of appetite can be physical or psychological. It is often temporary due to factors such as infections or digestive issues, in which case appetite will come back when a person has recovered.
Some people may also lose their appetite as a symptom of a long-term medical condition, such as in the late stages of serious illness, including cancer. This is part of a condition that doctors call cachexia.
The medical term for a complete loss of appetite over a more extended period of time is anorexia. This is different to the eating disorder anorexia nervosa, which is a mental health issue.
Below, we look at the possible causes for a loss of appetite.
Common causes
Common viral or bacterial infections, such as flu or gastroenteritis, are often to blame for appetite loss. A person’s appetite usually returns when they start to recover.
Common short-term causes of feeling a loss of appetite include:
- colds
- flu
- respiratory infections
- bacteria or viral infections
- constipation
- an upset stomach
- digestive issues
- acid reflux
- food poisoning
- allergies
- food intolerances
- a stomach bug or gastroenteritis
- pregnancy
- hormonal imbalances
- stress
- medication side effects
- alcohol or drug use
People with pain in their mouths, such as sores, may also experience a loss of appetite if it becomes difficult to eat.
Medical conditions
Long-term medical conditions can cause a loss of appetite for a range of reasons that vary depending on the cause. Loss of appetite can be related to lowered immune system function, feeling unwell, and having an upset stomach.
Medical conditions that can cause a loss of appetite include:
- digestive conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome and Crohn’s disease
- a hormonal condition known as Addison’s disease
- asthma
- diabetes
- chronic liver or kidney disease
- high calcium levels in the blood
- HIV and AIDS
- underactive thyroid or hypothyroidism
- overactive thyroid or hyperthyroidism
- COPD
- heart failure
- stomach or colon cancer
Side effect of medications
A loss of appetite is a common side effect of many medications, along with other digestive issues, such as constipation or diarrhea. This is common when medications pass through a person’s stomach and digestive tract.
Medications and treatments that often cause a loss of appetite include:
- sedatives
- some antibiotics
- immunotherapy
- chemotherapy
- radiation therapy to the stomach area
If people have recently undergone major surgery, they may experience a loss of appetite after the operation. This feeling can be partly related to anesthesia drugs.
Using drugs recreationally, such as cocaine, cannabis, and amphetamines can also cause a loss of appetite.
Psychological causes
Psychological factors and mental health conditions can have a significant impact on a person’s appetite. These can include:
- depression
- anxiety
- panic attacks
- stress
- grief
- eating disorders, such as bulimia or anorexia nervosa
Age
A loss of appetite can also be more common in older adults. This can be due to increased use of medications and changes in the body as it ages. These changes can affect:
- the digestive system
- the hormones
- the sense of taste or smell
Some cancers
A loss of appetite or unexpected weight loss can sometimes be a symptom of certain cancers, such as pancreatic, ovarian, or stomach cancer.
Alongside a loss of appetite, people may experience the following symptoms:
- stomach pains
- heartburn
- feeling full quickly
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
- blood in their stools
If people experience any of these symptoms, they should see a doctor who will be able to find out the underlying cause.
A person should see a doctor if they are vomiting for more than a day and have a complete loss of appetite.
People with serious medical conditions may experience a loss of appetite that can be due to the illness itself or as a side effect of treatments, such as chemotherapy treatment for cancers.
Some people in the later stages of serious illnesses may experience cachexia.
Cachexia is the term for weight loss, muscle wastage, and general ill-health caused by chronic, life-limiting illnesses.
People with cachexia can get nutritional advice from their doctor who can help create a nutritional plan to make sure they get the necessary calories and nutrients.
A person with a serious illness should see their doctor if they have a complete loss of appetite for a day or more or any of the following:
- vomiting for a day or longer
- inability to keep liquids down
- pain when trying to eat
- irregular urination
A doctor may prescribe certain medications to help increase appetite and reduce other symptoms, for example, nausea.
If depression or anxiety are causing people to experience a loss of appetite, talking therapies and sometimes antidepressants can help.
If a doctor thinks a specific medication is a reason for a loss of appetite, they may be able to change the dosage or the medication.
People may find it easier to eat several smaller meals a day instead of three bigger ones.
Aim to make these meals high in calories and protein to make sure the body is getting plenty of nutrients and energy. People may also find having liquid meals, such as smoothies and protein drinks, easier to take.
Adding herbs, spices, or other flavorings to meals may also encourage people to eat more easily. Eating meals in relaxing or social settings may make eating more enjoyable.
People can also keep drinking plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. Gentle exercise, such as a short walk, may sometimes increase appetite as well.
A doctor will look at all the symptoms a person is experiencing, and use these to work out the possible cause of their loss of appetite.
A doctor may examine a person’s abdomen by feeling with their hand for any unusual bloating, lumps, or tenderness. This can help them find out if a gastrointestinal disorder is causing a loss of appetite.
A doctor may also carry out tests to help them work out the cause. Tests can include:
- blood tests
- an abdominal X-ray
- an endoscopy, where a camera enables doctors to look inside the body
It is important to find out the reason for a loss of appetite, as it can lead to complications without treatment.
A continued loss of appetite can cause weight loss and malnutrition. It is vital for people to find out the reason for their loss of appetite, as leaving it untreated can be serious.
People can talk to a doctor if they have a loss of appetite for a prolonged period. If they notice any unexpected or rapid weight loss, they should also see their doctor.
An individual should seek medical help if they notice any other symptoms alongside a loss of appetite, such as:
- stomach pain
- fever
- shortness of breath
- coughing
- a rapid or irregular heartbeat
People can experience a loss of appetite for a wide range of reasons. Some of these are short-term, including colds, food poisoning, other infections, or the side effects of medication. Others are to do with long-term medical conditions, such as diabetes, cancer, or life-limiting illnesses.
Appetite loss often comes with feelings of fatigue or nausea. If a person is worried about a loss of appetite they should tell their doctor, also mentioning all other symptoms.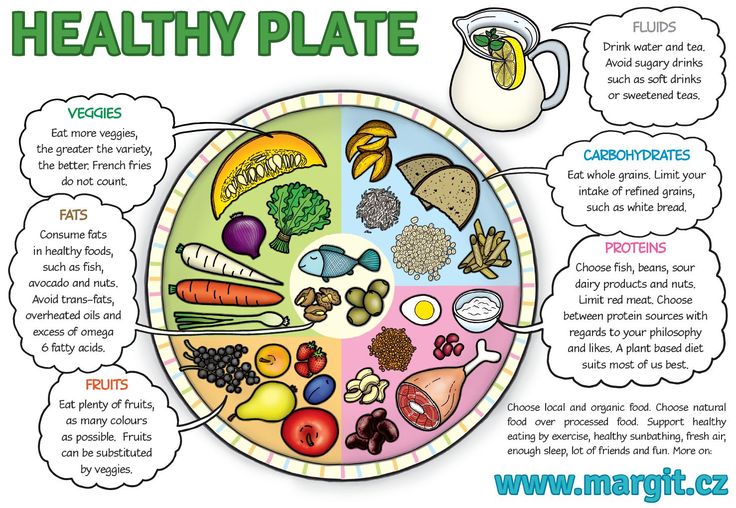
Treatments for appetite loss will depend on the cause. People may benefit from eating small, regular meals instead of three large meals, and liquid meals are often more palatable.
Read the article in Spanish.
An elderly person refuses to eat - what to do?
Caring for an elderly relative is a huge challenge for all family members. In addition to health and mood problems, situations often arise when a grandfather or grandmother does not eat anything and constantly sleeps. At first, loved ones may not pay attention to this, but poor appetite, increased sleepiness and refusal to eat in the elderly is a serious cause for concern. In order not to bring the malaise to a chronic state, you need to start taking measures as soon as possible and immediately contact a specialist. nine0003
Why an elderly person may refuse food
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor must determine against the background of which the desire to eat has disappeared. Among the most common causes of poor appetite are the following factors:
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- stomatitis;
- pneumonia;
- oncology;
- diseases of the thyroid gland;
- infections of various etymologies; nine0010
- acute respiratory infections;
- mental disorders, dementia;
- consequences of physical or psychological injury;
- side effects of drugs.

In addition, refusal to eat can be triggered by bad habits: drinking alcohol or smoking. The doctor conducts diagnostics, prescribes examinations that will help identify the cause and choose therapy.
It is important to remember: the longer this condition is left unattended, the less chance of recovery. The last stage begins when the grandfather or grandmother does not eat, only drinks, bile and vomiting go. In this case, urgent hospitalization is required: only emergency measures will help. nine0003
When an elderly person is simply a hostage of circumstances
Poor appetite in old age is quite common. The natural functions of the body weaken, a person leads a sedentary lifestyle, spends less energy. Accordingly, the desire to eat decreases. The work of taste buds is deteriorating: favorite dishes no longer deliver their former pleasure. It turns out a vicious circle: the pensioner needs less food, because of this, weakness and loss of strength appear. Gradually, interest in food disappears completely. nine0003
Gradually, interest in food disappears completely. nine0003
Refusal of food often occurs gradually. First, the pensioner stops eating meat, as it takes a long time to digest. Then he prefers some light food: cereals, mashed potatoes, soups. After some time, even such dishes begin to be digested with difficulty, the patient eats less and only drinks water, milk, sour-milk products.
If an elderly person does not eat well, what should relatives do, and should they be forced to eat? It is unlikely that it will be possible to feed through force: a pensioner can simply spit out food or tightly compress his lips, not succumbing to the persuasion of loved ones. Such demonstrative behavior requires radical measures, only a doctor and specially selected therapy will help here. nine0003
You can not scream and put pressure on the patient - this will only aggravate the condition. Sometimes the patient simply does not understand what is happening to him due to psychological reasons or various diagnoses. Relatives have to show maximum patience and attention. If there is no time and opportunity for full-fledged care, you can use the services of private boarding houses. Such institutions have the necessary feeding equipment, and the staff is trained to work with even the most capricious and demanding guests. nine0003
Relatives have to show maximum patience and attention. If there is no time and opportunity for full-fledged care, you can use the services of private boarding houses. Such institutions have the necessary feeding equipment, and the staff is trained to work with even the most capricious and demanding guests. nine0003
Refusal to eat in bedridden elderly after stroke
If you can still somehow cope with age-related whims and stubbornness, then how to make an elderly person eat if he is bedridden? In such cases, refusal to eat indicates irreversible destructive processes occurring in the body. The patient gradually fades away, and there is practically no hope for recovery.
Relatives, trying to feed the patient, believe that they are helping him, but in reality they are only making it worse. In such situations, it remains only to ensure that the person receives a sufficient amount of liquid. If he can no longer swallow water or tea, you need to periodically moisten his lips with a wet cotton pad or a clean cloth so that the patient does not have a dry mouth. nine0003
nine0003
If a grandfather or grandmother does not eat anything, only drinks water, this is not the worst thing. When the body stops taking even liquid, it's time to connect special devices for artificial feeding, but this should be done only under the supervision of specialists.
Eating habits for the elderly after a stroke
There are several alternative ways to help feed an elderly person without causing inconvenience:
Nasogastric Tube
Probe installation is indicated in the following situations:
- stroke resulting in partial and complete dysfunction of swallowing;
- edema of the larynx, esophagus, pharynx;
- surgical interventions, after which the usual food intake is temporarily impossible;
- psychological disorders accompanied by food refusal;
- unconscious and comatose patient. nine0010
Using a probe, you can not worry about how to make an elderly person eat. Food is served using a sterile syringe and funnel. Dishes should be warm, puree. The diet mainly consists of cereals, broths, kefir, special nutritional mixtures.
Food is served using a sterile syringe and funnel. Dishes should be warm, puree. The diet mainly consists of cereals, broths, kefir, special nutritional mixtures.
Gastrostomy
The device allows you to enter food directly into the digestive tract, bypassing the oral cavity and esophagus. It is used most often after surgical interventions or for oncological diseases of the throat, pharynx, larynx. With the help of a gastrostomy, soups, cereals, jelly, raw eggs, milk and sour-milk products are administered to the patient. nine0003
Parenteral nutrition
The method is a special form of intravenous therapeutic nutrition. It is used in cases where the patient cannot eat independently. Special preparations are administered intravenously and provide the body with the necessary nutrients to maintain life. Mixtures are selected individually, taking into account the age and condition of the patient.
What to do if an elderly person refuses to eat
In order not to take the situation to the extreme, older people need to be constantly monitored, pay attention to what they eat and how many times a day they eat. If, for example, an 84-year-old grandmother refuses to eat, this may mean that she lacks care from her loved ones, she wants to attract attention. In the initial stages of loss of appetite, interest in food can be restored in simple ways:
If, for example, an 84-year-old grandmother refuses to eat, this may mean that she lacks care from her loved ones, she wants to attract attention. In the initial stages of loss of appetite, interest in food can be restored in simple ways:
- Adjust mode. It is desirable that during the day there are 4-5 meals. At the same time, portions should be small - this improves metabolism. Not without reason, in private boarding houses, meals for guests are carried out in this way, in accordance with the recommendations of specialists. nine0010
- Review diet. Focus on light, low-fat meals. Add more fresh fruits and vegetables to your menu. If an older person has difficulty chewing solid foods, use a blender to grind. It is recommended to include foods that cause thirst in the menu, such as pickles or tomatoes (in limited quantities). Increasing the daily volume of water consumed can provoke a good appetite.
- Provide adequate physical activity. Elementary morning exercises, walks in the fresh air, Nordic walking - these exercises do not require much strength, but they awaken the appetite well.
 When it comes to a lying patient, you can arrange special devices for training the arms or upper shoulder girdle. nine0010
When it comes to a lying patient, you can arrange special devices for training the arms or upper shoulder girdle. nine0010 - Create a favorable emotional environment. Sometimes, in order to understand why an elderly person refuses to eat, you need to look at the conditions in which he lives. Difficult relationships with loved ones, a tense atmosphere, discontent from relatives - all this does not contribute to a good appetite. A pensioner who finds himself in such a difficult situation will prefer to move to a private nursing home: in such institutions they carefully monitor that the guests do not receive any negative. nine0010
- Establish a trusting relationship with the patient. If a person cannot eat on his own and uses the help of outsiders, it is important that the one who feeds the patient inspires confidence and disposition. It could be a relative, a friend, or a good neighbor. Perhaps, in the process of feeding, you will have to use persuasion and affection, the main thing is that there should be a result.

It is recommended to pay special attention to the quality of the dishes offered to the patient. Tasteless food is not able to stimulate appetite. You can ask an elderly person what he would like to eat the most - it is quite possible that he dreams of some particular treat. nine0003
Medical and professional assistance
In some cases, medications can help improve appetite. First of all, we are talking about special vitamin complexes that are sold in pharmacies. Vitamin B12 and ascorbic acid have a good effect on the state. The doctor should choose the drug, he will also prescribe the dosage.
The same applies to tablets: today the market has an abundance of drugs that can restore and improve appetite. But in no case should you self-medicate: each remedy has contraindications and features of use. nine0003
Competent specialists, including experienced gastroenterologists, work in the network of boarding houses “Warm Talks”, who will help you choose an effective treatment regimen for loss of appetite. The daily menu is compiled taking into account the peculiarities of the age of the guests, the emphasis is on healthy dishes rich in fiber and vitamins. If an elderly relative refuses to eat and complains of a lack of appetite, you can try to settle him in one of the modern, comfortable boarding houses on a temporary or permanent basis. Attentive staff will definitely find an approach to the patient, help restore interest in food and life. nine0003
The daily menu is compiled taking into account the peculiarities of the age of the guests, the emphasis is on healthy dishes rich in fiber and vitamins. If an elderly relative refuses to eat and complains of a lack of appetite, you can try to settle him in one of the modern, comfortable boarding houses on a temporary or permanent basis. Attentive staff will definitely find an approach to the patient, help restore interest in food and life. nine0003
An elderly person does not want to eat, what is the reason for refusing food
Contents
It is recommended to show increased attention and care to the elderly: at this age, people are characterized by frequent mood swings, increased sensitivity, and a tendency to experience. If an older person refuses to eat, this can be a wake-up call. Most often, loss of appetite indicates the presence of health problems - physical or psychological. It is important to seek help from a specialist as soon as possible to find out the cause of the ailment. nine0003
nine0003
Causes of loss of appetite in old age
As people age, their physiological needs change. The older a person is, the more time he needs to rest and sleep, he becomes less active, and a slight decrease in appetite is a natural phenomenon, since the body requires fewer resources. But a systematic unwillingness to eat is not normal, one of the following diseases can be the cause of weakness and loss of strength:
- Poisoning; nine0010
- Virus or infection;
- Oncology;
- Stroke;
- Diseases of the endocrine system;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Mental disorders, senile dementia.
Decreased appetite may be the result of taking antibiotics or other medications. Many medications provoke allergies, eating disorders, and damage the intestinal microflora. If there is a suspicion that the depression is caused by drugs, it is recommended to immediately inform the attending physician about this and discuss their replacement with analogues. nine0003
nine0003
Depression and loss of appetite often accompany Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia. With developing dementia, the patient often experiences discomfort while eating, has problems with swallowing, because of which the desire to eat and drink disappears.
Eating disorders: the consequences are clear
Regular refusal of food in the elderly invariably leads to the fact that vitamins and microelements necessary for normal life cease to enter the body. It is not surprising that in the absence of a full-fledged source of energy and strength, weakness appears, a general deterioration in well-being. Nutrient deficiency leads to rapid weight loss, rapid physical and moral exhaustion. The body simply does not have the resources to recover. nine0003
In addition to external changes, there are interruptions in the work of internal organs. First of all, the pancreas suffers: without water and food, insulin is not produced. Relatives and loved ones can resort to artificial feeding: this may improve the situation, but will not replace full meals.
The patient spends almost all the time in bed, even minimal loads lead to severe fatigue. The body is sorely lacking heat and energy. nine0003
An elderly person does not want to eat, what to do and how to help him?
If the causes of loss of appetite are psychological in nature, only relatives or people who surround him can help the patient. Delicate persuasion, unobtrusive conditions, perhaps some kind of encouragement in case of eating - older people are like children, the main thing is to interest them. Sometimes this reluctance to eat is provoked by a change in habitual conditions. For example, when a patient enters a hospital or moves to live in a boarding house. In these cases, only the patience and attention of the staff will help. It is very important to establish contact and explain to the person what consequences await him if he does not establish a full-fledged diet. nine0003
Perhaps the patient has some desires associated with food. You can ask about his taste preferences and please the patient with his favorite dish. In some cases, a person refuses food, but at the same time drinks a lot of water. This is observed after poisoning. No need to restrict it in liquid: the body restores water balance.
You can ask about his taste preferences and please the patient with his favorite dish. In some cases, a person refuses food, but at the same time drinks a lot of water. This is observed after poisoning. No need to restrict it in liquid: the body restores water balance.
Stimulate appetite walks in the fresh air. The body gives signals that it is necessary to replenish the energy expended during walking. Moderate physical activity is also one of the ways to regain interest in food. nine0003
Sometimes it is impossible to do without the help of a specialist.
Only a doctor can prescribe a particular drug to a patient. Consultation with a specialist is required.
No appetite in a bedridden patient: causes, help
With bedridden patients, the situation is more complicated: refusal to eat most often indicates destructive processes in the body. If the appetite is not returned, it can lead to irreversible consequences, including death. nine0003
nine0003
First of all, when you refuse to eat, dysphagia gradually develops - a violation of the function of swallowing. Weak muscles lose the ability to push food on their own. There is weight loss, which can lead to serious consequences: headaches, muscle atrophy, disorders in the musculoskeletal system, the formation of bedsores.
Regular refusal to eat a lying elderly person is often the result of psychological problems. This is a kind of protest when the patient expresses dissatisfaction with his condition. He does not want to be a burden to others, he suffers from changes in the usual course of life. It is important to show maximum patience, try to provide moral support to the patient, set him up in a positive way. nine0003
If a recumbent elderly person is rapidly losing weight, special medical devices are used. Depending on the indication, this may be a gastrostomy or a probe. Meals are usually divided into 5-6 meals; the number of calories is calculated individually. Basic rules to follow when compiling a diet:
Basic rules to follow when compiling a diet:
- Optimal balance of proteins, fats, carbohydrates;
- Feeding at fixed hours;
- Comfortable food temperature;
- Small serving sizes.
It is strictly forbidden to force-feed the patient from a spoon in the supine position. It is necessary to raise and hold the head. If you can’t feed the patient, it’s better not to insist and still contact a specialist.
Whatever the reasons why an elderly person does not eat, this alarm signal cannot be ignored. The first steps with which it is recommended to start helping are attention, patience and care. Only timely quality support can return the patient to a normal state. nine0003
Read also
09/08/2022
Myocardial infarction in the elderly - signs, causes, first aid
03/17/2020
Vitamins for the elderly: whim or necessity?
nine0002 12/10/2019Body temperature in an elderly person
24.