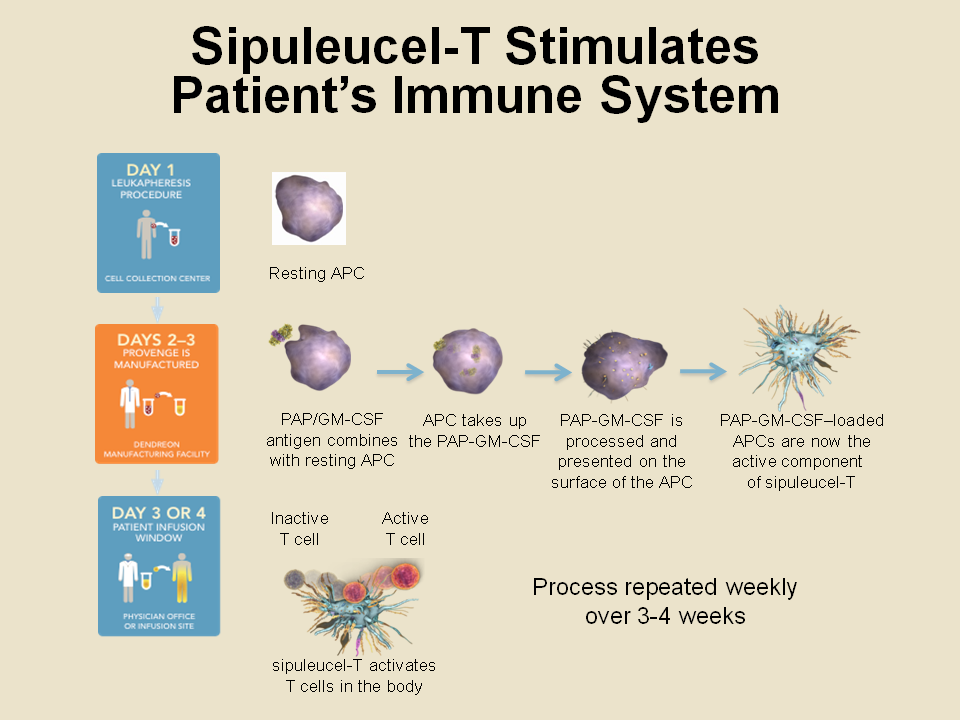
U s scan
Ultrasound scan - NHS
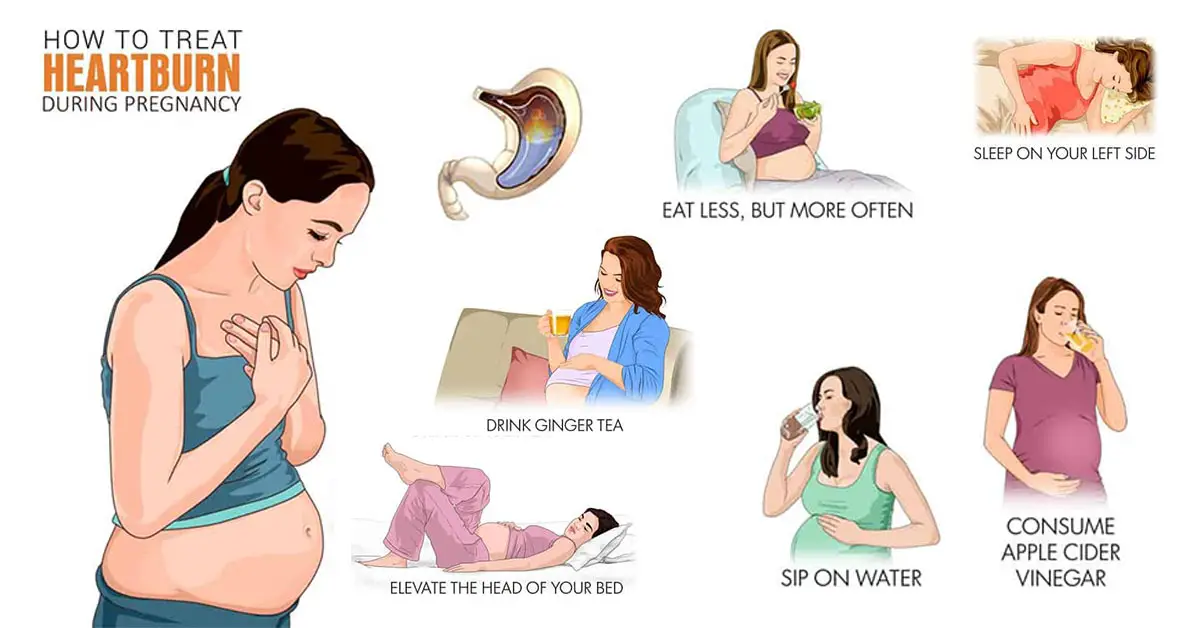
An ultrasound scan, sometimes called a sonogram, is a procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to create an image of part of the inside of the body.
An ultrasound scan can be used to monitor an unborn baby, diagnose a condition, or guide a surgeon during certain procedures.
How ultrasound scans work
A small device called an ultrasound probe is used, which gives off high-frequency sound waves.
You can't hear these sound waves, but when they bounce off different parts of the body, they create "echoes" that are picked up by the probe and turned into a moving image.
This image is displayed on a monitor while the scan is carried out.
Preparing for an ultrasound scan
Before having some types of ultrasound scan, you may be asked to follow certain instructions to help improve the quality of the images produced.
For example, you may be advised to:
- drink water and not go to the toilet until after the scan – this may be needed before a scan of your unborn baby or your pelvic area
- avoid eating or drinking for several hours before the scan – this may be needed before a scan of your digestive system, including the liver and gallbladder
Depending on the area of your body being examined, the hospital may ask you to remove some clothing and wear a hospital gown.
If you need a sedative to help you relax, this will be given through a small tube into the back of your hand or into your arm.
In some cases, you may also be given an injection of a harmless substance called a contrast agent before the scan, as this can make the images clearer.
What happens during an ultrasound scan
Most ultrasound scans last between 15 and 45 minutes. They usually take place in a hospital radiology department and are performed either by a doctor, radiographer or a sonographer.
They usually take place in a hospital radiology department and are performed either by a doctor, radiographer or a sonographer.
They can also be carried out in community locations such as GP practices, and may be performed by other healthcare professionals, such as midwives or physiotherapists who have been specially trained in ultrasound.
There are different kinds of ultrasound scans, depending on which part of the body is being scanned and why.
The 3 main types are:
- external ultrasound scan – the probe is moved over the skin
- internal ultrasound scan – the probe is inserted into the body
- endoscopic ultrasound scan – the probe is attached to a long, thin, flexible tube (an endoscope) and passed further into the body
These techniques are described below.
External ultrasound scan
Credit:
Peter Widmann / Alamy Stock Photo https://www. alamy.com/stock-photo-pregnant-woman-getting-an-ultrasound-checkup-13287915.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=858EDDE9-62F3-4E6F-9888-BE3E856C8DF9&p=28858&n=0&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3dbar%26st%3d0%26pn%3d1%26ps%3d100%26sortby%3d2%26resultview%3dsortbyPopular%26npgs%3d0%26qt%3dAD321G%26qt_raw%3dAD321G%26lic%3d3%26mr%3d0%26pr%3d0%26ot%3d0%26creative%3d%26ag%3d0%26hc%3d0%26pc%3d%26blackwhite%3d%26cutout%3d%26tbar%3d1%26et%3d0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3d0%26loc%3d0%26imgt%3d0%26dtfr%3d%26dtto%3d%26size%3d0xFF%26archive%3d1%26groupid%3d%26pseudoid%3d731695%26a%3d%26cdid%3d%26cdsrt%3d%26name%3d%26qn%3d%26apalib%3d%26apalic%3d%26lightbox%3d%26gname%3d%26gtype%3d%26xstx%3d0%26simid%3d%26saveQry%3d%26editorial%3d1%26nu%3d%26t%3d%26edoptin%3d%26customgeoip%3d%26cap%3d1%26cbstore%3d1%26vd%3d0%26lb%3d%26fi%3d2%26edrf%3d0%26ispremium%3d1%26flip%3d0%26pl%3d
alamy.com/stock-photo-pregnant-woman-getting-an-ultrasound-checkup-13287915.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=858EDDE9-62F3-4E6F-9888-BE3E856C8DF9&p=28858&n=0&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3dbar%26st%3d0%26pn%3d1%26ps%3d100%26sortby%3d2%26resultview%3dsortbyPopular%26npgs%3d0%26qt%3dAD321G%26qt_raw%3dAD321G%26lic%3d3%26mr%3d0%26pr%3d0%26ot%3d0%26creative%3d%26ag%3d0%26hc%3d0%26pc%3d%26blackwhite%3d%26cutout%3d%26tbar%3d1%26et%3d0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3d0%26loc%3d0%26imgt%3d0%26dtfr%3d%26dtto%3d%26size%3d0xFF%26archive%3d1%26groupid%3d%26pseudoid%3d731695%26a%3d%26cdid%3d%26cdsrt%3d%26name%3d%26qn%3d%26apalib%3d%26apalic%3d%26lightbox%3d%26gname%3d%26gtype%3d%26xstx%3d0%26simid%3d%26saveQry%3d%26editorial%3d1%26nu%3d%26t%3d%26edoptin%3d%26customgeoip%3d%26cap%3d1%26cbstore%3d1%26vd%3d0%26lb%3d%26fi%3d2%26edrf%3d0%26ispremium%3d1%26flip%3d0%26pl%3d
An external ultrasound scan is most often used to examine the heart or an unborn baby in the womb.
It can also be used to examine the liver, kidneys and other organs in the tummy and pelvis, as well as other organs or tissues that can be assessed through the skin, such as muscles and joints.
A small handheld probe is placed on your skin and moved over the part of your body being examined.
A lubricating gel is put on your skin to allow the probe to move smoothly. This also ensures there's continuous contact between the probe and the skin.
You shouldn't feel anything other than the sensor and gel on your skin (which is often cold).
If you're having a scan of your womb or pelvic area, you may have a full bladder that causes you a little discomfort.
There will be a toilet nearby to empty your bladder once the scan is complete.
Internal or transvaginal ultrasound scan
Credit:
A. NOOR / BSIP/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/865228/view
NOOR / BSIP/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/865228/view
An internal examination allows a doctor to look more closely inside the body at organs such as the prostate gland, ovaries or womb.
A "transvaginal" ultrasound means "through the vagina". During the procedure, you'll be asked to either lie on your back, or on your side with your knees drawn up towards your chest.
A small ultrasound probe with a sterile cover, not much wider than a finger, is then gently passed into the vagina or rectum and images are transmitted to a monitor.
Internal examinations may cause some discomfort, but don't usually cause any pain and shouldn't take very long.
Endoscopic ultrasound scan
Credit:
LA LOUVIERE / ASTIER/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://www. sciencephoto.com/media/104779/view
sciencephoto.com/media/104779/view
During an endoscopic ultrasound scan, an endoscope is inserted into your body, usually through your mouth, to examine areas such as your stomach or food pipe (oesophagus).
You'll usually be asked to lie on your side as the endoscope is carefully pushed down towards your stomach.
The endoscope has a light and an ultrasound device on the end. Once it's been inserted into the body, sound waves are used to create images in the same way as an external ultrasound.
You'll usually be given a sedative to keep you calm and local anaesthetic spray to numb your throat, as an endoscopic ultrasound scan can be uncomfortable and may make you feel sick.
You may also be given a mouth guard to keep your mouth open and protect your teeth, in case you bite the endoscope.
After an ultrasound scan
In most cases, there are no after-effects and you can go home soon after the scan is finished.
If a sedative wasn't used, you can drive, eat, drink and return to your other normal activities straightaway.
If you had an endoscopic ultrasound and were given a sedative to help you relax, you'll usually be advised to stay in hospital for a few hours until the medication starts to wear off.
You'll need to arrange for someone to pick you up from the hospital and stay with you for the next 24 hours.
You shouldn't drive, drink alcohol or operate machinery during this time.
You may be told the results of your scan soon after it's been carried out, but in most cases the images will need to be analysed and a report will be sent to the doctor who referred you for the scan.
They'll discuss the results with you a few days later or at your next appointment, if one's been arranged.
Are there any risks or side effects?
There are no known risks from the sound waves used in an ultrasound scan. Unlike some other scans, such as CT scans, ultrasound scans don't involve exposure to radiation.
Unlike some other scans, such as CT scans, ultrasound scans don't involve exposure to radiation.
External and internal ultrasound scans don't have any side effects and are generally painless, although you may experience some discomfort as the probe is pressed over your skin or inserted into your body.
If you're having an internal scan and are allergic to latex, it's important to let the sonographer or doctor carrying out the scan know this so they can use a latex-free probe cover.
Endoscopic ultrasounds can be a bit more uncomfortable and can cause temporary side effects, such as a sore throat or bloating.
There's also a small risk of more serious complications, such as internal bleeding.
Page last reviewed: 28 July 2021
Next review due: 28 July 2024
Ultrasound scans: How do they work?
An ultrasound scan uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. It is suitable for use during pregnancy.
It is suitable for use during pregnancy.
Ultrasound scans, or sonography, are safe because they use sound waves or echoes to make an image, instead of radiation.
Ultrasound scans are used to evaluate fetal development, and they can detect problems in the liver, heart, kidney, or abdomen. They may also assist in performing certain types of biopsy.
The image produced is called a sonogram.
Fast facts on ultrasound scans
- Ultrasound scans are safe and widely used.
- They are often used to check the progress of a pregnancy.
- They are used for diagnosis or treatment.
- No special preparation is normally necessary before an ultrasound scan.
The person who performs an ultrasound scan is called a sonographer, but the images are interpreted by radiologists, cardiologists, or other specialists.
The sonographer usually holds a transducer, a hand-held device, like a wand, which is placed on the patient’s skin.
Ultrasound is sound that travels through soft tissue and fluids, but it bounces back, or echoes, off denser surfaces. This is how it creates an image.
This is how it creates an image.
The term “ultrasound” refers to sound with a frequency that humans cannot hear.
For diagnostic uses, the ultrasound is usually between 2 and 18 megahertz (MHz).
Higher frequencies provide better quality images but are more readily absorbed by the skin and other tissue, so they cannot penetrate as deeply as lower frequencies.
Lower frequencies penetrate deeper, but the image quality is inferior.
How does it capture an image?
Ultrasound will travel through blood in the heart chamber, for example, but if it hits a heart valve, it will echo, or bounce back.
It will travel straight through the gallbladder if there are no gallstones, but if there are stones, it will bounce back from them.
The denser the object the ultrasound hits, the more of the ultrasound bounces back.
This bouncing back, or echo, gives the ultrasound image its features. Varying shades of gray reflect different densities.
Ultrasound transducers
The transducer, or wand, is normally placed on the surface of the patient’s body, but some kinds are placed internally.
These can provide clearer, more informative images.
Examples are:
- an endovaginal transducer, for use in the vagina
- an endorectal transducer, for use in the rectum
- a transesophageal transducer, passed down the patient’s throat for use in the esophagus
Some very small transducers can be placed onto the end of a catheter and inserted into blood vessels to examine the walls of blood vessels.
Share on PinterestUltrasound images are made from reflected sound, and a diagnosis can then be made.
Ultrasound is commonly used for diagnosis, for treatment, and for guidance during procedures such as biopsies.
It can be used to examine internal organs such as the liver and kidneys, the pancreas, the thyroid gland, the testes and the ovaries, and others.
An ultrasound scan can reveal whether a lump is a tumor. This could be cancerous, or a fluid-filled cyst.
It can help diagnose problems with soft tissues, muscles, blood vessels, tendons, and joints. It is used to investigate a frozen shoulder, tennis elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome, and others.
It is used to investigate a frozen shoulder, tennis elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome, and others.
Circulatory problems
Doppler ultrasound can assess the flow of blood in a vessel or blood pressure. It can determine the speed of the blood flow and any obstructions.
An echocardiogram (ECG) is an example of Doppler ultrasound. It can be used to create images of the cardiovascular system and to measure blood flow and cardiac tissue movement at specific points.
A Doppler ultrasound can assess the function and state of cardiac valve areas, any abnormalities in the heart, valvular regurgitation, or blood leaking from valves, and it can show how well the heart pumps out blood.
It can also be used to:
- examine the walls of blood vessels
- check for DVT or an aneurysm
- check fetal heart and heartbeat
- evaluate for plaque buildup and clots
- assess for blockages or narrowing of arteries
A carotid duplex is a form of carotid ultrasonography that may include a Doppler ultrasound. This would reveal how blood cells move through the carotid arteries.
This would reveal how blood cells move through the carotid arteries.
Ultrasound in anesthesiology
Ultrasound is often used by anesthetists to guide a needle with anesthetic solutions near nerves.
An ultrasound can be done at a doctor’s office, at an outpatient clinic, or in the hospital.
Most scans take between 20 and 60 minutes. It is not normally painful, and there is no noise.
In most cases, no special preparation is needed, but patients may wish to wear loose-fitting and comfortable clothing.
If the liver or gallbladder is affected, the patient may have to fast, or eat nothing, for several hours before the procedure.
For a scan during pregnancy, and especially early pregnancy, the patient should drink plenty of water and try to avoid urinating for some time before the test.
When the bladder is full, the scan produces a better image of the uterus.
The scan usually takes place in the radiology department of a hospital. A doctor or a specially-trained sonographer will carry out the test.
External ultrasound
The sonographer puts a lubricating gel onto the patient’s skin and places a transducer over the lubricated skin.
The transducer is moved over the part of the body that needs to be examined. Examples include ultrasound examinations of a patient’s heart or a fetus in the uterus.
The patient should not feel discomfort or pain. They will just feel the transducer over the skin.
During pregnancy, there may be slight discomfort because of the full bladder.
Internal ultrasound
If the internal reproductive organs or urinary system need to be evaluated, the transducer may be placed in the rectum for a man or in the vagina for a woman.
To evaluate some part of the digestive system, for example, the esophagus, the chest lymph nodes, or the stomach, an endoscope may be used.
A light and an ultrasound device are attached to the end of the endoscope, which inserted into the patient’s body, usually through the mouth.
Before the procedure, patients are given medications to reduce any pain.
Internal ultrasound scans are less comfortable than external ones, and there is a slight risk of internal bleeding.
Most types of ultrasound are noninvasive, and they involve no ionizing radiation exposure. The procedure is believed to be very safe.
However, since the long-term risks are not established, unnecessary “keepsake” scans during pregnancy are not encouraged. Ultrasound during pregnancy is recommended only when medically needed.
Anyone who is allergic to latex should inform their doctor so that they will not use a latex-covered probe.
How to improve content crawlability and make it more readable — Design on vc.ru
The UX Collective talked about the main reading patterns and shared recommendations for improving content crawlability. Adapted translation of material from product editor Alexander Marfitsin.
6362 views
If we need information, we google it. Then we scan the title and description, and when we get to the right page, we look for clues in the content. Trying to figure out if it's worth reading in full. nine0003
Trying to figure out if it's worth reading in full. nine0003
Such information retrieval behavior can be compared to the behavior of predators. Wild animals are looking for food to survive. People are looking for information to satisfy the ever-increasing information hunger. Usability experts and cognitive psychologists call this the information scent effect.
Users evaluate how much useful information they will receive and after searching compare the actual result with the forecast. When the "information smell" weakens, people switch to another source of information. nine0003
That's why we scan information. We are not lazy, it's just that our brain is designed in such a way that, with the help of our instincts, it tries to solve the problem as quickly as possible with the least amount of energy. There is no fight between reader laziness and artsy content, it's a matter of empathy.
You need to shape your content
This will help users track down the "smell of information" and get the most out of your message. We will talk about the main reader patterns and share recommendations for enhancing the "information smell" in your content. nine0003
We will talk about the main reader patterns and share recommendations for enhancing the "information smell" in your content. nine0003
4 basic scanning patterns
Since 1997, the F-pattern has been considered the most popular reading pattern. But with the development of the Internet and gadgets, a lot has changed. Now NN/g highlights 4 main patterns by which people scan information.
1. F pattern
Users use this pattern for large amounts of unformatted text:
UX Collective
This looks like a real text wall. Do it - c The most common content creation mistake people find such content unattractive So they scan from left to right, top to bottom, then top to bottom at the beginning of sentences. Only if certain words seem relevant to them do they read on.
You can improve this pattern by highlighting key content and shortening the text.

2. Spotted pattern
The reader's eyes jump from one place to another, looking for key elements or guided by highlighted fragments:
UX Collective
This pattern supports the scannability of information well, adds a visual rhythm to the text. But it is still far from ideal. Readers will jump from one fat sentence to another in search of a particular keyword, rather than reading the material sequentially.
To improve this pattern, divide the material into chunks with subheadings. And add some "air" between these pieces. nine0050
3. Layer cake pattern
In this case, the reader does not scan words individually, but entire text fragments :
UX Collective
This template helps you read headings and then scan the appropriate part of the text. So users can read more. But this is not the best pattern.
But this is not the best pattern.
To improve this pattern, use lists and download key information right away. nine0050
4. "commitment" or "commitment" pattern
In this scenario, people sequentially view the content . They read word by word because the material seems to them to be knocked down and whole. This template can be considered the best for improving content crawlability:
UX Collective
This pattern is the goal of any writer. Need to strengthen the "information smell" of your content not only guides the eye towards the answers sought, but also delivers key messages.
How to enhance the "information smell" of content
To achieve the "commitment" pattern for sequential scanning of content, you need to:
- Divide content into fragments
- Download key information immediately
- Create visual hierarchy
- Reduce distractions
Learn more about each of these items.
Divide content into chunks
As you noticed in the examples above, 3 paragraphs of 3 lines is much better than 1 paragraph of 9 lines. Therefore:
- Use subheadings as often as possible . Make them meaningful and include important information for the reader.
- Write short sentences . Divide ideas into several simple sentences instead of complicated ones with commas. nine0109
- Keep paragraphs short . Keep them within 2-5 lines.
- Break paragraphs into lists . Bulleted and numbered lists help create short sentences and increase reading time.
Hemingway Editor is suitable for assessing the readability of English texts. For Russian speakers, you can use "Glavred". If you know more suitable tools, share in the comments. nine0050
Download key information quickly
Answer the user's question first, then go to the details.
- Rule of two . Pay close attention to what is written in the first two paragraphs. Then in the first two lines, then in the first two words of the sentence. If they catch the reader's attention, he will continue to scan the material.
- Add pomace at the very beginning . So that users immediately understand the key idea and make sure that the article is worth reading.
- Add a table of contents with links to subsections . They describe your content and help the person jump straight to the right information.
- Set the content hierarchy . Answer in the first two paragraphs: what, when, who and where. Then delve into the "why" while retaining additional details.
nine0002 This requires experience. For English-language texts, Grammarly and ProWritingAid may be suitable. If you know an analogue for Russian-language texts, share in the comments.
Create a visual hierarchy
Text size, colors and padding are vital to understanding how one piece of content relates to another. This helps the reader understand what to look for first.
- Typography . It is well written about in the Canva material. The most important thing is to preserve and convey through typography the reading order. nine0109
- Key ideas in bold guide the reader throughout the text, providing the most important information. Use bold type in moderation, do not highlight more than one sentence in each paragraph.
- Meaningful images complement your ideas and encourage further exploration. Do not use them as decorative elements - they can steal the reader's attention. nine0142
- Center-aligned text . It breaks the reading flow and people only scan it. For example, when we read news, we often pay attention only to the headline and large quotes. nine0109
- Color spots . They grab attention easily, but like centered text, they detract from the main flow of reading.
Take a screenshot of your content, blur it, and check if the page passes the read stream correctly.
Learn Gestalt principles to improve visual hierarchy.
Reduce distractions
Use the following elements carefully:
People need answers. Do not complicate this process and feed the "information predator" in the user's head.
Scanned content will deliver your key messages safe and sound. From the previous recommendations, you realized that you do not need to create flashy content. You need to understand reading patterns and strengthen the “information smell”. It's a matter of understanding people's habits. nine0003
nine0003
More about the benefits of product content in my Editor Tools Telegram channel, Medium blog and monthly newsletter. Thanks to Mikhail Khananashvili for the tip on the article.
Scanning of large amounts of information
Document scanning has become a part of our daily life. We scan documents to email them, we scan passports to travel abroad. Modern students no longer rewrite lectures, but use scanning. But in this article we will not talk about such scanning, but about scanning large amounts of information. Such scanning is necessary as a stage of preparation for the creation of an electronic archive of an organization. nine0003
Document scanning and electronic filing
In any organization, over time, a large number of documents accumulate that need to be stored. To reduce the archive space in the office, some companies use the off-site document storage service. Others try to scan documents and create electronic archives on their own.
Problems when scanning large amounts of documents.

Let's consider what pitfalls await you when scanning large arrays of documents. nine0003
Scanning equipment
Choosing the right scanning equipment is essential. It should be borne in mind that one powerful scanner with an automatic document feeder is indispensable. There are always stapled and bound documents in the archive that cannot be unfastened, as well as dilapidated documents. A handheld scanner is required to scan an array of these documents.
Wrong organization of scanning
When scanning a large array of documents, it is very important to follow the reverse acquisition of the archive . If scanning is done incorrectly, many archived documents may be lost. Such a turn of events would be very undesirable, for example, when creating an electronic archive of personnel documentation, because the archive of some personnel documents must be stored in the organization for up to 75 years (The retention periods for documents are determined by Articles 16-20 of the Federal Law of October 22, 2004 N 125-FZ "On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation")
Personnel scanning training
Staff need to be trained to scan.