Tums heartburn pregnancy
Can you take Tums while pregnant?
Many pregnant women get heartburn, sometimes referred to as acid indigestion or acid reflux. This condition is generally harmless, but it can be very uncomfortable. Fortunately, most cases can be safely treated with over-the-counter remedies, along with simple diet and lifestyle changes.
Many women get relief by eating small, frequent meals and avoiding spicy or acidic foods. For those who need additional help, some prescription and over-the-counter heartburn medications are considered safe to take during pregnancy.
Here are some guidelines to help you understand which heartburn medicines are appropriate to use during pregnancy. (As with any medication, get the okay from your healthcare provider before taking these.)
Can you take Tums while pregnant?
Yes, Tums are safe to take during pregnancy. In fact, your first line of defense should probably be these chewable antacids made from calcium carbonate (sometimes just called "calcium" on the label). Fast, portable, and effective, they may be all you need to handle heartburn. They even taste pretty good and double as a calcium supplement.
Antacids containing magnesium hydroxide or magnesium oxide – like Maalox, Mylanta, and Rolaids – are probably safe when used occasionally at the recommended dosage. But they're not your best option while pregnant because they also contain aluminum hydroxide. Aluminum can be constipating and, in large doses, toxic.
Bear in mind that swallowing any liquid, even the liquid you need to wash down a tablet, will cause your stomach to do what it does naturally: produce digestive juices – including acid, the very thing you're trying to reduce. So it's best to swallow or chew tablets with as little liquid as possible when you're having trouble with heartburn.
All of these antacid medicines work by neutralizing the acid that's already in your stomach and causing you pain. Chewable and liquid antacids act much more quickly than tablets because they're already dissolved. You can experiment to see which you prefer and what works most effectively for you.
You can experiment to see which you prefer and what works most effectively for you.
If you're regularly taking the recommended dosage and aren't getting relief from heartburn, talk to your doctor or midwife about whether you can take additional or different medications.
What about taking Alka-Seltzer while pregnant?
Remedies containing aspirin (such as Alka-Seltzer) should be avoided during pregnancy. Aspirin may be listed on a label as salicylate or acetylsalicylic acid. (Note: Sometimes aspirin is recommended for pregnant women, so it's not always unsafe, but in this instance it's not a good idea.)
Also steer clear of sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), which is sold as an antacid in tablet form, and sodium citrate. Both are high in sodium, which causes water retention. And if you're far enough along in your pregnancy to have gone into a panic trying to remove rings from your swollen fingers or looked down in horror at a pair of puffy ankles, you'll understand why that's the last thing you want right now.
Other heartburn medicine for pregnancy
If over-the-counter medicines aren't helping enough with your heartburn, you may want to ask your provider about using something more effective and longer lasting, usually called an acid reducer. Instead of neutralizing your stomach acid like antacids do, acid reducers actually stop your stomach from producing most of the acid it normally would.
Acid reducers won't help with the acid already in your stomach, so they work best when taken before a meal. Some acid-reducing medications, such as Pepcid Complete, are a combination of an acid reducer (such as famotidine) and an antacid (such as calcium carbonate or magnesium hydroxide), so they can provide immediate relief from the acid that's already distressing you and reduce further acid production for up to 12 hours.
Pepcid is safe to take daily during pregnancy to prevent heartburn, and you can take calcium carbonate chewables like Tums with it if you still need relief. If this doesn't help, many doctors will recommend proton pump inhibitors or PPIs. These include lansoprazole (Prevacid), omeprazole (Prilosec), pantoprazole (Protonix), and esomeprazole (Nexium)
These include lansoprazole (Prevacid), omeprazole (Prilosec), pantoprazole (Protonix), and esomeprazole (Nexium)
Some of these medicines are available over-the-counter and others require a prescription. All are currently considered safe to take during pregnancy, even during the first trimester. However, talk to your ob-gyn or midwife before taking medications for your heartburn. They can give you helpful tips, tricks, and safety guidance.
Read more about medications during pregnancy.
advertisement | page continues below
Heartburn and Pregnancy: What OB/GYNs Want You to Know
If you’re expecting, you may also experience heartburn. Discover what doctors have to say about heartburn and how to get relief, fast.
Along with swollen feet, frequent urination, and unusual cravings, heartburn is an issue that affects women during pregnancy. Heartburn is defined as a burning sensation in the upper part of the digestive tract and throat.1
If you are suffering from heartburn while expecting, read on to learn what obstetricians and gynecologists recommend for relief. However, you should still discuss your heartburn condition with your own doctor for a solution that’s right for you.
However, you should still discuss your heartburn condition with your own doctor for a solution that’s right for you.
Identifying the Cause of Heartburn During Pregnancy
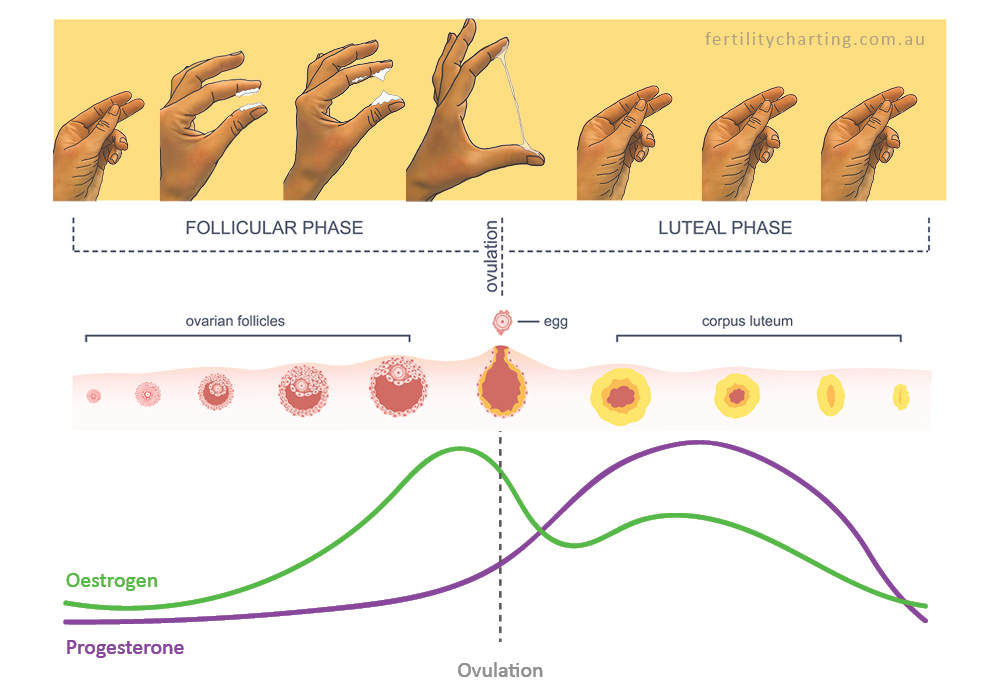
During pregnancy, a valve in the esophagus that typically acts as a seal relaxes due to an increase in a hormone known as progesterone. This allows for stomach acid to pass back into the esophagus and irritate the lining, which leads to heartburn.2, 3
Who Is the Most Likely to Get Heartburn?
While no one is exempt from heartburn, OB/GYNs say there are certain factors that make it more likely for pregnant women. For instance, women who experience heartburn before pregnancy are also more likely to experience heartburn during pregnancy. Women who are overweight or obese prior to pregnancy also tend to be more likely to have heartburn during this time. And expecting moms who drink coffee during pregnancy are at increased risk for heartburn symptoms.4
Spotting Heartburn Symptoms During Pregnancy
If you are experiencing heartburn for the first time during pregnancy, you might not recognize the symptoms. True to its name, heartburn is a painful, burning feeling located just below or behind the breastbone.5 Although some women experience heartburn symptoms in their first trimester, the issue tends to occur more often in the third trimester.4 During these final weeks, the expanding uterus puts pressure on the intestines and stomach, which can push contents back up into the esophagus, according to OB/GYNs.3
True to its name, heartburn is a painful, burning feeling located just below or behind the breastbone.5 Although some women experience heartburn symptoms in their first trimester, the issue tends to occur more often in the third trimester.4 During these final weeks, the expanding uterus puts pressure on the intestines and stomach, which can push contents back up into the esophagus, according to OB/GYNs.3
How to Lower Your Risk of Heartburn During Pregnancy
For some women, diet and lifestyle changes during pregnancy can lessen the likelihood of heartburn. Suggestions from OB/GYNs include: monitoring overall food consumption, eating smaller meals throughout the day, and reducing caffeine intake.2 Avoid eating or drinking too close to bedtime and stay away from spicy and fatty foods to lower your risk of occasional heartburn after dinner and at night.2 As far as specific items are concerned, citrus fruits and chocolate have been linked to trigger heartburn during pregnancy. 6
6
How to Relieve Pregnancy Heartburn
Combined with all the other discomforts of pregnancy, that burning sensation can be really unpleasant. The good news is that there are ways to help stop heartburn quickly. Research shows that drinking milk and eating yogurt may help as well as over-the-counter antacids, like TUMS.3 The antacid relieves the stomach and esophagus, neutralizing stomach acid and providing reliable relief.6 Be sure to talk to your doctor about the heartburn treatment options that are right for you.
References
- Vazquez, Juan C. “Heartburn in Pregnancy.” BMJ Clinical Evidence, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2015, https://misuse.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/error/abuse.shtml.
- “Common Symptoms During Pregnancy.” MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000583.htm.
- “Heartburn During Pregnancy: Causes and Treatment.
 ” American Pregnancy Association, July 2015, americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-health/heartburn-during-pregnancy/.
” American Pregnancy Association, July 2015, americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-health/heartburn-during-pregnancy/. - “Heartburn in Pregnancy: A Prospective Look at Incidence, Risk Factors, Treatment.” Gastro Journal, AGA Abstracts, www.gastrojournal.org/article/S0016-5085(10)62191-9/pdf.
- “Heartburn.” MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 4 Dec. 2017, medlineplus.gov/heartburn.html.
- “Pregnancy and Heartburn.” University of Rochester Medical Center, University of Rochester, www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=134.
Heartburn during pregnancy - symptoms, causes and methods of treatment of the disease
Contents
- Causes of heartburn during pregnancy
- What to do for heartburn during pregnancy?
- Preparations for heartburn during pregnancy
Heartburn is an unpleasant feeling of burning or warmth behind the breastbone or in the epigastric region. The symptom occurs after eating or on an empty stomach and is associated with food reflux, that is, the reflux of food processed by gastric juice back into the esophagus. Since the mucous membrane of the esophagus is not adapted to the action of gastric juice, it becomes irritated, which is subjectively felt in the form of heartburn.
The symptom occurs after eating or on an empty stomach and is associated with food reflux, that is, the reflux of food processed by gastric juice back into the esophagus. Since the mucous membrane of the esophagus is not adapted to the action of gastric juice, it becomes irritated, which is subjectively felt in the form of heartburn.
Heartburn in pregnant women is an independent symptom that appears only during the period of bearing a child against the background of the absence of chronic diseases that cause reflux of gastric juice 1 . According to statistics, 30-50% of pregnant women suffer from heartburn, there is evidence that more than 80% of pregnant women complain of heartburn, especially in the third trimester 4 .
Causes of heartburn during pregnancy
Heartburn in pregnancy is a condition that is caused by the changes that occur to the female body during the period of gestation. All factors that can cause heartburn in women in an interesting position can be divided into physiological (natural) and pathological (disease-related).
Physiological heartburn of pregnant women can occur for two reasons:
- Hormonal - associated with a weakening of the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter. This is the name of the circular muscle between the stomach and the esophagus, which regulates the flow of food into the stomach and prevents its movement in the opposite direction. During pregnancy, the level of progesterone in the blood rises, which relaxes the uterine muscle, simultaneously acting on all other muscles of the body, including the esophageal sphincter. As a result, the sphincter does not close after eating, but remains open. Any change in body position or contraction of the stomach causes food reflux 4 . Heartburn also occurs if it is disturbed by the movement of food through the esophagus, for example, if the frequency of "reverse" contractions of the esophagus increases in the direction from the stomach to the esophagus 1 .
- Physical - due to the increase in the size of the uterus, the location of the internal organs changes and intra-abdominal pressure increases, which is transmitted to the wall of the stomach and contributes to reflux 4 .

In connection with such changes in the gastrointestinal tract during pregnancy, all pathologies that cause heartburn can worsen.
Pathological causes of heartburn during pregnancy include the following:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (reflux esophagitis) is a pathology of the esophageal sphincter, which occurs more often with diaphragmatic hernia, when the natural curve between the esophagus and stomach disappears, preventing reverse reflux 4 .
- Other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - gastritis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, pancreatitis, diseases of the liver and biliary tract, inflammatory bowel disease 2 . With gastritis and ulcers, the acidity of the stomach increases, and pathologies of other digestive organs cause bloating, constipation, enlargement of the liver, which increases intra-abdominal pressure.
- Taking drugs that relax the lower esophageal sphincter - heart drugs, theophylline, anti-inflammatory drugs, progesterone, antidepressants 4 .

What to do about heartburn during pregnancy?
In the first two hours after eating, hydrochloric acid is produced in the stomach, which is needed for food processing. It is at this time that heartburn is more likely to torment, especially if a woman consumes fatty, fried and spicy foods 7 . Burning behind the sternum can last for several minutes or several hours. Heartburn may recur several times during the day. It is characterized by its strengthening in a horizontal position, with torso tilts, as well as when turning to the other side.
To reduce the severity of heartburn, you first need to adjust the diet and some habits. This helps to reduce the increased acidity of the stomach and prevent the reflux of food back into the esophagus.
Pregnant women should follow the following dietary recommendations 4 :
- Do not eat excessively high-calorie foods.
- Avoid nighttime snacks and especially overeating.

- Eat often and in small portions.
- Do not lie down immediately after eating, do not sleep in a strictly horizontal position, it is necessary to raise the head end of the bed.
- Walk for 30 minutes after eating.
- Eat dinner no later than 3-4 hours before going to bed.
- Do not lift weights, do not make strong and frequent torso bends, do not overstrain the abdominal muscles.
- Do not wear corsets, bandages, tight belts that increase intra-abdominal pressure.
From the diet for heartburn should be excluded 4 :
- Carbonated drinks (they increase pressure in the stomach and stimulate the formation of hydrochloric acid).
- Cream, whole milk, fatty meats, fatty fish, goose, pork (fatty foods take a long time to digest).
- Chocolate, cakes, pastries, spices (relaxes the lower esophageal sphincter).
- Citrus fruits, tomatoes, onions, garlic (irritate the mucous membrane of the esophagus).

For heartburn, pregnant women can eat the following foods 6 :
- wheat bread, dry biscuits, dry biscuits;
- baked pies with apples, boiled meat or fish;
- soups of meat, fish, vegetables;
- lean beef, poultry, fish;
- soft-boiled eggs and scrambled eggs;
- sugar, copper, butter cream;
- tea, cocoa, sweet fruit juices, jams, compotes.
Pregnancy heartburn preparations
In 80% of pregnant women, heartburn disappears after childbirth, but severe heartburn during pregnancy, especially if it lasts for several weeks, can persist after the baby is born 4 .
Often, proper nutrition and adherence to lifestyle recommendations do not always help get rid of heartburn. If heartburn is caused by any disease, adequate treatment of the underlying pathology with medications helps to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
The use of folk and non-traditional ways to eliminate heartburn during pregnancy is also not effective enough and even potentially dangerous. Many of the herbs used during pregnancy can harm both the woman and her unborn baby 4 .
Many of the herbs used during pregnancy can harm both the woman and her unborn baby 4 .
Therefore, it is advisable to discuss the choice of a drug with a doctor who will help you choose the right remedy for heartburn during pregnancy, paying attention from the standpoint of safety for the fetus and potential impact on the course of pregnancy 4
The results of epidemiological studies of Omez ® 10 mg in the treatment of heartburn in pregnant women show no clinically significant adverse effects on pregnancy and the health of the fetus or newborn 5 .
Omez ® 10 mg is dispensed without a doctor's prescription, but you can take it yourself without specialist advice for no longer than 14 days 5 .
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, READ THE INSTRUCTIONS FOR MEDICAL USE OR CONSULT A DOCTOR.
References:
- Vyuchnova E.S., Yurenev G.L., Mironova E.
 M. "The use of proton pump inhibitors in pregnant women: indications and choice" article in the journal "Evidence-based gastroenterology" - 2016 .
M. "The use of proton pump inhibitors in pregnant women: indications and choice" article in the journal "Evidence-based gastroenterology" - 2016 . - ZIMMERMAN Y.S., MIKHALEVA E.N. "Possibilities of pharmacotherapy in the treatment of gastroenterological diseases during pregnancy" scientific review - 2015
- Kharkevich D. A. "Pharmacology" textbook - 2010.
- Trukhan D.I., Grishechkina I.A. Treatment of pregnancy heartburn: focus on alginates. Consilium Medicum. 2016;
- Instructions for use Omez ® 10 mg
- Dietary recommendations of the Scientific Society of Gastroenterologists of Russia for patients with GERD
- Obstetrics. National leadership” edited by G.M. Savelieva - 2018.
Heartburn during pregnancy - Juno
Heartburn during pregnancy - Junohome
Articles
Heartburn during pregnancy
Most often, heartburn begins to bother pregnant women in the later stages, in the second or third semester. What is the cause of heartburn during pregnancy and how to deal with it? Read our article!
What is the cause of heartburn during pregnancy and how to deal with it? Read our article!
Causes of heartburn during pregnancy
Heartburn (acid dyspepsia) is an unpleasant burning sensation in the chest and mouth. In pregnant women, heartburn may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, pain in the throat, abdomen and stomach, as well as a disorder in the swallowing mechanism. Also, heartburn during pregnancy is fraught with sleep and eating disorders.
Consider the main causes of heartburn during pregnancy.
Hormonal changes
During pregnancy, the production of progesterone, or the so-called pregnancy hormone, rises. He is responsible for relaxing the muscles of the uterus in order to avoid abortion. The difficulty lies in the fact that the action of this hormone also extends to the esophagus, stomach and intestines.
Between the esophagus and the stomach is a sphincter that must close after food enters the stomach. But under the influence of progesterone, the performance of the sphincter worsens, due to which the food returns to the esophagus, and with hydrochloric acid, which aggravates the situation. In addition, due to a violation of the hormonal background, the acidity of the gastric juice increases, which also provokes the appearance of heartburn.
In addition, due to a violation of the hormonal background, the acidity of the gastric juice increases, which also provokes the appearance of heartburn.
Mechanical action
From the second trimester, the size of the uterus increases significantly, so there is pressure on the digestive tract. In this case, the volume of the stomach decreases, which creates conditions for throwing the contents of the stomach into the esophagus.
Heartburn can occur due to weight gain, because under the influence of extra pounds, blood pressure begins to affect the abdominal cavity. It is advisable to avoid tight clothing, because if the clothing squeezes and tights the stomach, this can provoke the release of acid from the stomach.
The use of certain foods.
During pregnancy, heartburn can cause the following types of food:
- Fatty food (fish, meat).
- Dairy products (ryazhenka, kefir, etc.).
- Baking.
- Fast food.

- Some types of fruits: citrus, kiwi, green apples, honeysuckle, currants.
- Tomatoes.
- Chocolate.
- Smoked products.
- Marinades.
- Carbonated drinks.
- Hard boiled eggs.
Treatment of heartburn during pregnancy
To treat heartburn during pregnancy in mild cases, it is enough to follow the following points:
- Dieting. For pregnant women, oatmeal, natural milk, boiled or baked meat and fish of low-fat varieties, steamed omelettes are recommended. A diet for heartburn implies certain restrictions, especially in plant foods, which can lead to a deficiency of minerals and vitamins necessary for the body. To avoid this situation, you can take vitamin and mineral complexes designed specifically for pregnant women. Such drugs, for example, include the Pregnoton Mama complex. It contains folic acid, Omega-3, liposomal iron, iodine, selenium, biotin, zinc, and vitamins. All these substances are necessary for the proper formation and development of the fetus.
 The drug is available in the form of soft capsules that are easy to swallow. Thus, mother and baby will receive all the necessary substances, even if the diet is followed.
The drug is available in the form of soft capsules that are easy to swallow. Thus, mother and baby will receive all the necessary substances, even if the diet is followed. - Lifestyle change. Not only for the prevention of heartburn, but in general, during pregnancy, it is necessary to give up alcohol and cigarettes, including electronic ones. After each meal, it is better to walk a little or sit quietly. It is strictly not recommended to take a horizontal position and bend over.
- Proper sleep. To prevent heartburn, pregnant women are shown to sleep with the head end of the bed raised. This is where an extra pillow can come in handy.
- Proper food intake. Food must be chewed thoroughly, not in a hurry. It is better to reduce the amount of servings, but increase the number of meals.
How to quickly get rid of heartburn during pregnancy?
What helps with heartburn: treatment with folk remedies
- The use of baking soda for heartburn during pregnancy is one of the most common "folk" ways to deal with heartburn.
 This method really gives a quick effect, but it passes quickly, and in addition, soda interacts with gastric juice, which leads to the release of additional portions of hydrochloric acid and, accordingly, to heartburn.
This method really gives a quick effect, but it passes quickly, and in addition, soda interacts with gastric juice, which leads to the release of additional portions of hydrochloric acid and, accordingly, to heartburn. - Milk. The drink contains a large amount of proteins and antacids, which reduce the level of acidity. Often it is enough to drink one glass of milk for heartburn to recede. To enhance the effect, you can add a few drops of fennel.
- Potato juice, squeezed from a grated raw potato, can be an effective remedy for heartburn during pregnancy, as it normalizes acidity. However, not everyone can force themselves to drink potato juice, as it has a peculiar taste.
- Ground eggshell. The shell contains calcium carbonate, which reduces the level of acidity in the body. Note that with long-term use, this method will give the opposite effect, that is, the acidity will increase.
- Carrot juice. Helps neutralize acidity.
- Oatmeal has an enveloping property, thanks to which it is able to block discomfort.
However, before resorting to "folk" ways to deal with heartburn, still discuss with your doctor how best to deal with the problem in your case.
In the final months, heartburn tends to subside as the body reduces progesterone production, and the pressure on the internal organs decreases as the belly sinks down.
Other articles
11/20/2022
Endometriosis: causes and treatment
Among gynecological diseases, endometriosis occupies one of the first places. In this article, we will analyze what endometriosis is, what are the causes of its occurrence and how to treat it.
11/10/2022
Endometriosis in women over 40: causes and treatment
Endometriosis is a fairly common disease among women over the age of 40 years.