Tightening of uterus in early pregnancy
Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
If you feel tightening or cramping in your abdomen during your pregnancy, you may be having Braxton Hicks contractions. This is normal and not a sign that you’re ready to give birth.
Braxton Hicks contractions are sometimes called ‘false’ or ‘practice’ contractions.
What are Braxton Hicks contractions?
Braxton Hicks contractions are a tightening in your abdomen that comes and goes. They are contractions of your uterus in preparation for giving birth. They tone the muscles in your uterus and may also help prepare the cervix for birth.
Braxton Hicks contractions don’t cause labour and aren’t a sign that labour is beginning.
If you’re not sure whether what you’re experiencing is Braxton Hicks contractions or actual labour, contact your doctor or midwife. They will be able to tell by doing a vaginal examination — if there are no signs that your cervix is changing, it is not labour.
What do they feel like?
Braxton Hicks contractions feel like muscles tightening across your belly, and if you put your hands on your belly when the contractions happen, you can probably feel your uterus becoming hard.
The contractions come irregularly and usually last for about 30 seconds. While they can be uncomfortable, they usually aren’t painful.
If the pain or discomfort of your contractions eases off, they’re probably Braxton Hicks contractions.
When do you get them?
Braxton Hicks contractions occur from early in your pregnancy but you may not feel them until the second trimester. If this is your first pregnancy, you might start to feel them from about 16 weeks. In later pregnancies, you may feel Braxton Hicks contractions more often, or earlier. Some women won’t feel them at all.
Some women won’t feel them at all.
In late pregnancy, you may experience Braxton Hicks contractions more often — perhaps as much as every 10 to 20 minutes. This is a sign that you are preparing for labour — known as prelabour.
How are Braxton Hicks contractions different from labour pain?
There are some differences between Braxton Hicks contractions and true labour contractions that will help your doctor or midwife decide whether you are in labour:
Braxton Hicks contractions:
- don’t result in your cervix thinning and opening
- usually last for about 30 seconds
- can be uncomfortable, but usually aren’t painful
- come and go at irregular times
- usually occur no more than once or twice an hour (until late in the pregnancy), a few times a day
- usually stop if you change position or activity or go for a walk
- usually go if you have a warm bath or shower
Real labour contractions:
- result in your cervix thinning and opening
- last 30 to 70 seconds
- become very regular
- get closer together
- last longer as time goes by
- get stronger or come more often when you walk
- get stronger over time
Should I call my doctor or midwife?
If you are less than 37 weeks pregnant, contractions can be a sign of premature labour. Contact your doctor or midwife immediately if:
Contact your doctor or midwife immediately if:
- you feel pain, pressure or discomfort in your pelvis, abdomen or lower back
- the contractions become stronger, closer together and more regular
- there is fluid leaking or gushing from your vagina
If you are full-term, you may choose to wait until a bit later in your labour, depending on what you have arranged with your doctor or midwife. If your waters break, or your contractions are strong and 5 minutes apart, it’s time to go to the hospital.
As any stage of pregnancy, you should contact your doctor or midwife immediately if you:
- you have persistent pain in your abdomen
- you have vaginal bleeding
- you notice your baby’s movements have slowed or stopped
- you feel very unwell
If you are in doubt, don’t hesitate to call your doctor or midwife for advice.
How can I ease the discomfort?
Braxton Hicks contractions are normal and don’t need treatment. But if you feel uncomfortable, you can try:
But if you feel uncomfortable, you can try:
- lying down
- taking a walk
- relaxing in a warm bath
- having a massage
It may help to practise your breathing exercises during your Braxton Hicks contractions.
Sources:
Raising Children Network (23 weeks pregnant), RANZCOG (Labour and birth), Elsevier Patient Education (Braxton Hicks Contractions)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: October 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Health professionals involved in your pregnancy
- Giving birth - stages of labour
- Premature baby
Need more information?
Pregnancy at week 22
By week 22, some parts of your baby’s body are fully formed, while some women experience Braxton Hicks contractions about now.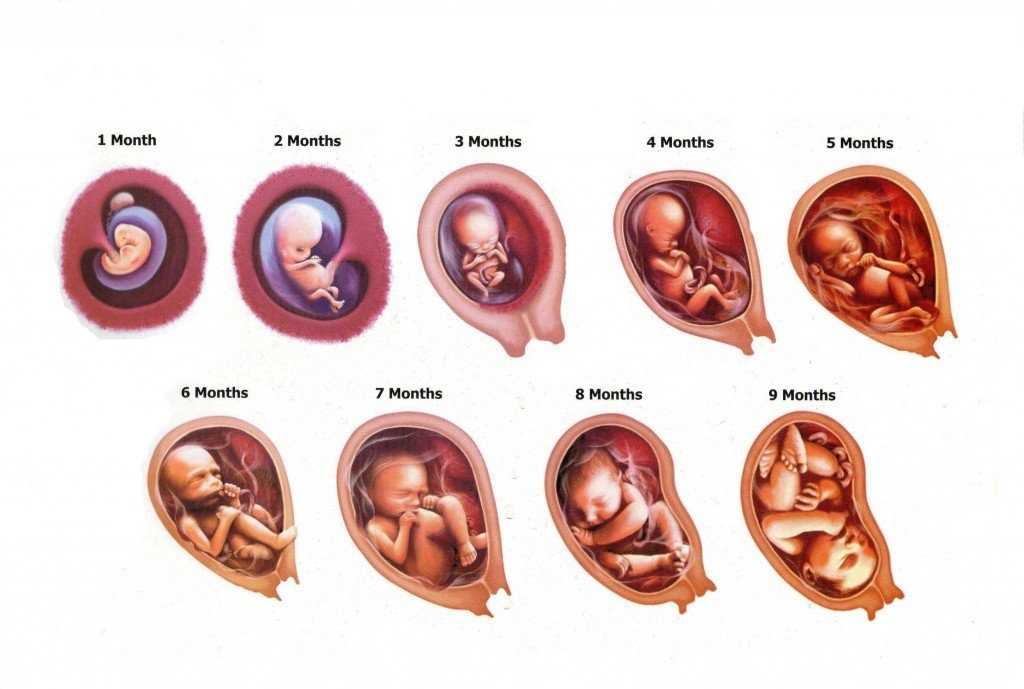
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 35
You'll probably be having lots of Braxton Hicks contractions by now. It's your body's way of preparing for the birth. They should stop if you move position.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Giving birth - contractions
Contractions are when the muscles in your uterus tighten and then relax. They occur throughout the later stages of your pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
What happens to your body in childbirth
During childbirth, your body's hormones, ligaments and muscles, as well as the shape of your pelvis, all work together to bring your baby safely into the world.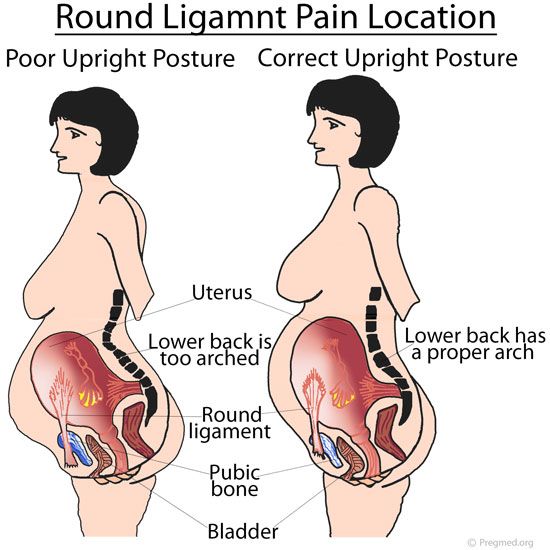
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth - uterus
The uterus is your growing baby’s home during pregnancy. Learn how the uterus works, nurtures your baby and how it changes while you are pregnant.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Preterm labour - MyDr.com.au
Going into labour before your 37th week of pregnancy is called preterm labour, or premature labour. Find out what it means for you and your baby.
Read more on myDr website
38 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
38 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
26 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
26 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Giving birth - early signs of labour
You can know the early signs of labour, even if you cannot predict when your labour will begin. Find out also what to do if something appears to be wrong.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth
From conception to giving birth, a woman's body goes through many physical changes. Learn what happens to your body during pregnancy and labour.
Learn what happens to your body during pregnancy and labour.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
When to see a doctor
Pregnancy is often an exciting time in a woman’s life, but it is also a time filled with strange new physical symptoms or experiences. Stomach-tightening is one such symptom that many women experience during pregnancy.
Stomach-tightening is one such symptom that many women experience during pregnancy.
There are many reasons for the stomach or abdomen to tighten during pregnancy, and these may vary, depending on the trimester.
In this article, we look at the causes, as well as when to speak to a doctor.
Share on PinterestAs the uterus grows in the first trimester, the stomach may feel tight.There are many reasons why a woman may feel her stomach is tightening during the first trimester of pregnancy, including:
Stretching
During the first trimester, the uterus is growing and stretching rapidly to accommodate the growing fetus.
This can cause abdominal cramping or sharp, stabbing, or shooting pains along the side of the abdomen, as the ligaments and other tissues stretch.
Gas or constipation
Gas pain is a very common problem throughout pregnancy. It can cause cramping or shooting pain in the abdomen, and it can be very painful.
Constipation is also a common complaint in early pregnancy. The changing pregnancy hormones can slow down the gastrointestinal tract.
Also, the iron in some prenatal vitamins can harden stool and make it difficult to go to the bathroom. Both gas and constipation can sometimes make it feel as if the stomach is tightening.
Miscarriage
Rarely, tightening of the abdomen can signal a miscarriage, which is the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks.
However, a miscarriage is most common before the 12th week of pregnancy. Other signs of a miscarriage include:
- mild to severe back pain
- bright red or brown vaginal bleeding
- cramping
- vaginal discharge of tissue or clots
- decrease in the symptoms or signs of pregnancy, such as morning sickness or breast tenderness
The signs of a miscarriage vary between individuals and, in some situations, a woman may not have any signs at all. It is important for a woman to get regular prenatal care during early pregnancy so that her doctor can monitor the baby’s development.
In early pregnancy, a woman should call the doctor’s office with any vaginal bleeding, especially if it is red and resembles a period.
Stretching, cramping, and stabbing pain along the sides of the uterus often continues into the second trimester, and is known as round ligament pain. The round ligaments are located on either side of the uterus and connect the uterus to the groin.
During pregnancy, the ligaments stretch as the uterus grows, which can cause the sharp pain. This pain commonly occurs with changes in position, such as sitting to standing or bending down.
Most women start to feel their uterus contract and periodically tighten some time during the second trimester, the point in their pregnancy between 14 to 28 weeks. These are known as Braxton-Hicks contractions, false labor, or practice contractions.
The purpose of Braxton-Hicks contractions is for the uterus to prepare for the hard work of labor and delivery. It is thought that they help to tone the muscle in the uterus and promote blood flow to the placenta.
Braxton-Hicks contractions are normal and very common. They typically last for around 30 to 60 seconds but can be as long as 2 minutes. They are not as painful as regular contractions, but can still cause considerable pain and discomfort.
Some things may trigger or worsen Braxton-Hicks contractions:
- sex or orgasm
- dehydration
- a full bladder
- sharp kicking by the baby
Even though Braxton-Hicks contractions are common during pregnancy, it is important to mention them to the doctor at prenatal visits. The doctor can help determine whether they are Braxton-Hicks, or if they could be a sign of preterm labor.
It is important to call the doctor if:
- contractions get stronger or closer together
- contractions are not relieved by rest or drinking water
- there is fluid leaking from the vagina
- there is vaginal bleeding
A doctor should evaluate these symptoms to make sure that a woman is not experiencing complications or preterm labor.
Share on PinterestDuring the third trimester, Braxton-Hicks contractions may increase in strength.
Stomach-tightening associated with Braxton-Hicks contractions increases in strength and frequency during the third trimester. These contractions are especially common during the last few weeks of pregnancy as the uterus prepares for birth.
However, it is still important to notice and keep track of them. If a woman has more than a few in an hour, she should speak to her doctor.
Things a person can do to relieve the pain and stretching feeling include:
- Drinking a glass of water: Dehydration is a common trigger for Braxton-Hicks contractions. Try having a big glass of water and lying down for a few minutes.
- Using the bathroom: Having a full bladder is associated with increased Braxton-Hicks contractions. Sometimes, just using the bathroom and emptying the bladder can stop the contractions.
- Changing positions: Sometimes body position can put pressure on the uterus, triggering Braxton-Hicks contractions.
 Try shifting positions or lying down.
Try shifting positions or lying down. - Taking a warm bath or shower: Sitting in a warm tub can relax tired or achy muscles, including the uterus.
- Drinking a cup of tea or warm milk: Warm milk or herbal tea can be both relaxing and hydrating.
It is important to call a doctor if home remedies do not relieve stomach tightening or if there are more than four contractions in an hour.
Many women have called their doctor or gone to the hospital if they experience Braxton-Hicks contractions, especially near the end of their pregnancy. As Braxton-Hicks contractions get stronger and more frequent, it often feels as if labor is beginning for real.
There are a couple of differences, however:
| Braxton-Hicks contractions | True labor |
| Irregular in intensity and frequency | Get closer together and progressively stronger |
| Uncomfortable | Painful |
| May be relieved with home measures, including drinking water or lying down | Home measures do not relieve them |
| No other signs of labor | May have other signs of labor |
Other signs of labor can include:
- back pain or cramping
- leaking of fluid from the vagina
- bloody vaginal discharge
As always, it is essential to contact the doctor or make a trip to the hospital with any questions or concerns.
Increased tone of the uterus during pregnancy
Nicotine constricts the blood vessels of the expectant mother, as well as the vessels of the placenta and umbilical cord, through which the fetus is nourished. Of course, smoking by itself is unlikely to lead to hypertonicity, but in combination with other factors, it may well
If the work is associated with constant stress, it has harmful effects or it is physically difficult, give it up as soon as possible. If this is not possible, use your rights, which are enshrined in the labor legislation of the Russian Federation
Hypertonicity must be distinguished from Braxton-Hicks contractions: it lasts much longer than these training contractions and usually does not go away on its own (or goes away only after a long time)
what is hypertonicity
, - muscle, and according to the laws of physiology, muscle tissue is reduced under the influence of any factor. Slightly the uterus contracts in women every month during menstruation, much stronger during labor pains. The uterus can also contract during pregnancy, doctors call this condition hypertonicity. What it looks like: suddenly, at some point, a woman feels that her stomach is tense, becomes hard, as if “hardening”. This state lasts for a long time - half an hour, an hour, half a day or even all day. Additionally, discomfort (or pain) in the lower back or sacrum may also appear. It is clear that such tension in the abdomen worries the mother, because since the uterus is contracting, then perhaps there is a threat of termination of pregnancy. But here it all depends on how much and how often the stomach tenses.
The uterus can also contract during pregnancy, doctors call this condition hypertonicity. What it looks like: suddenly, at some point, a woman feels that her stomach is tense, becomes hard, as if “hardening”. This state lasts for a long time - half an hour, an hour, half a day or even all day. Additionally, discomfort (or pain) in the lower back or sacrum may also appear. It is clear that such tension in the abdomen worries the mother, because since the uterus is contracting, then perhaps there is a threat of termination of pregnancy. But here it all depends on how much and how often the stomach tenses.
Braxton-Hicks contractions
It turns out that the stomach can tense up not only when there is a threat of miscarriage. Starting from the end of the second trimester, the expectant mother can feel the so-called training contractions (Brexton-Hicks contractions) - the stomach also tenses with them for a while, as if “hardening”, - in general, the sensations are the same as with hypertonicity. But the main difference between such contractions and hypertonicity is that they last for a very short time (a few seconds - a couple of minutes) and pass by themselves, as well as if you change the position of the body or take a shower. Braxton-Hicks contractions occur up to about ten times a day, and by the end of pregnancy they appear even more often. These contractions are completely normal during pregnancy, and they do not indicate any threat of interruption. It’s just that with their help, the uterus, as it were, prepares (trains) for childbirth.
But the main difference between such contractions and hypertonicity is that they last for a very short time (a few seconds - a couple of minutes) and pass by themselves, as well as if you change the position of the body or take a shower. Braxton-Hicks contractions occur up to about ten times a day, and by the end of pregnancy they appear even more often. These contractions are completely normal during pregnancy, and they do not indicate any threat of interruption. It’s just that with their help, the uterus, as it were, prepares (trains) for childbirth.
where does hypertonicity come from
Hypertonicity can appear in any trimester of pregnancy. In the early stages, it occurs more often due to the fact that there is not enough progesterone, a hormone that is needed for the normal course of pregnancy. Another cause of hypertonicity is some changes in the uterine wall, for example, fibroids (a knot of uterine muscle tissue), endometriosis (growth of the uterine mucosa into the thickness of the wall), and inflammatory diseases. In these situations, the wall of the uterus is not able to stretch as it should. At later dates, hypertonicity can develop, on the contrary, with overstretching of the uterus (with polyhydramnios, large fetuses, multiple pregnancies). Very often, hypertonicity is provoked by some kind of physical activity too strong for a woman, for example, if, in a fit of “nesting”, the mother suddenly began to move and rearrange something in the apartment herself, or she simply moved for a very long time without resting. Someone hypertonicity occurs after psychological overstrain.
In these situations, the wall of the uterus is not able to stretch as it should. At later dates, hypertonicity can develop, on the contrary, with overstretching of the uterus (with polyhydramnios, large fetuses, multiple pregnancies). Very often, hypertonicity is provoked by some kind of physical activity too strong for a woman, for example, if, in a fit of “nesting”, the mother suddenly began to move and rearrange something in the apartment herself, or she simply moved for a very long time without resting. Someone hypertonicity occurs after psychological overstrain.
how to recognize hypertonicity
Hypertonicity must be distinguished from Braxton-Hicks contractions - as mentioned earlier, it lasts much longer than these training contractions and usually does not go away on its own (or goes away only after some long time). But if the mother cannot understand whether she has hypertension or not, you should consult a doctor. If there is still an increased tone of the uterus, the doctor, simply by placing his hand on his stomach, will feel a seal, tension, up to the feeling of a stone at hand. In addition, you can always do an ultrasound, on which, with hypertonicity, areas of local thickening of the muscular layer of the uterus are visible, and also look at the cervix, by the state of which you can also judge whether there is a threat of abortion or not.
In addition, you can always do an ultrasound, on which, with hypertonicity, areas of local thickening of the muscular layer of the uterus are visible, and also look at the cervix, by the state of which you can also judge whether there is a threat of abortion or not.
what to do in case of hypertonicity
If it appears, the first thing you need to do is:
1. Calm down and lie down if possible. Do not panic, extra stress will not bring any benefits, especially since without consulting a doctor it is still not clear whether there is hypertonicity and how pronounced it is. Or maybe it's a false alarm? In addition, you can use relaxation techniques (breathing, auto-training, etc.).
2. Call your doctor. Of course, the doctor will not make a diagnosis in absentia, but since he knows the history of the expectant mother, her real or possible problems, he will be able to give the right direction for further action.
3. If it is not possible to contact your doctor, you can contact any clinic or antenatal clinic where pregnant women are treated. If medical institutions are already closed (late evening, at night), you can call an ambulance - she will take you to the nearest hospital or maternity hospital (you can also get there by taxi).
If medical institutions are already closed (late evening, at night), you can call an ambulance - she will take you to the nearest hospital or maternity hospital (you can also get there by taxi).
4. Hypertonicity is well eliminated by special medicines that relax the uterus (tocolytics), and if the doctor has prescribed them, then you should not be afraid to take them: they help quickly enough and do not harm the child.
how to prevent hypertonicity
There are simple rules that can prevent hypertonicity or reduce the risk of its occurrence:
1. Quit smoking, watch your weight, do not eat surrogate foods. No matter how trite it may sound, but it is a healthy lifestyle that is the basis of our well-being.
2. Distribute your forces correctly. Laundry, cooking can wait if the expectant mother suddenly feels that she needs a rest. If any activities require physical or psychological stress, cancel them for a while. Do not attend events or places where you may feel uncomfortable, reduce communication with people that are unpleasant for you.
3. Follow your doctor's recommendations: if he recommends any examination or treatment, do not neglect them.
Listen to your body, follow the doctor's advice, tune in to the positive - this is the key to a successful pregnancy. And then no hypertonicity is terrible for you!
symptoms in the early stages, in the second and third trimesters, what to do, how to determine
So what is this “increased uterine tone”, why does it occur, does it harm the child a lot and how can it be prevented? Let's find out.
What is uterine tone
Let's start with the anatomy: the uterus is made of muscle tissue, and any muscle can be in a relaxed and tense state - tone. (1) In a non-pregnant woman, the uterus contracts during menstruation. During childbirth, these contractions help the baby to be born.
— Uterine contractions are usually irregular, relatively painless, and resolve spontaneously without medical intervention. Sometimes the tone of the uterus increases, this is normal - for example, in the last weeks of the term, when the pregnant woman begins training contractions, - says obstetrician-gynecologist Laysan Ibatullina .
If the period is still short, and the tone of the uterus persists for a long time, this may cause a threat of termination of pregnancy or premature birth. Uterine hypertonicity can provoke rejection of the ovum or deterioration of uteroplacental blood flow, which is fraught with intrauterine hypoxia (lack of oxygen) of the fetus.
Symptoms of uterine tone during pregnancy
— The following symptoms indicate that you have an increased tone: mild pain, tension, feeling of a “stone” in the lower abdomen. To relieve discomfort, it is often enough for a woman to relax, take a comfortable position. In the West, doctors consider hypertonicity to be a physiological condition (unless, of course, there is severe pain and discomfort passes quickly). The uterus contracts when we laugh or sneeze when we are stressed. Even during an examination on a gynecological chair, a woman is a little nervous, and her uterus comes into tone. It is possible to judge an increased tone as a norm or pathology, depending on its duration. If the tension lasts for a long time, the pulling pain in the abdomen and lower back does not go away, the pregnant woman needs urgent medical care, explains obstetrician-gynecologist Laysan Ibatullina .
If the tension lasts for a long time, the pulling pain in the abdomen and lower back does not go away, the pregnant woman needs urgent medical care, explains obstetrician-gynecologist Laysan Ibatullina .
In the early stages - the first trimester
In the early stages, hypertonicity may occur due to a lack of progesterone, a hormone that plays an important role in conception and the development of pregnancy. Progesterone prevents the uterus from actively contracting, because this can cause a miscarriage. Also, increased tone can cause inflammation, fibroids or endometriosis in a pregnant woman.
In the first trimester, increased tone is indicated by pain or a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen (pain may radiate to the groin, sacrum or lower back).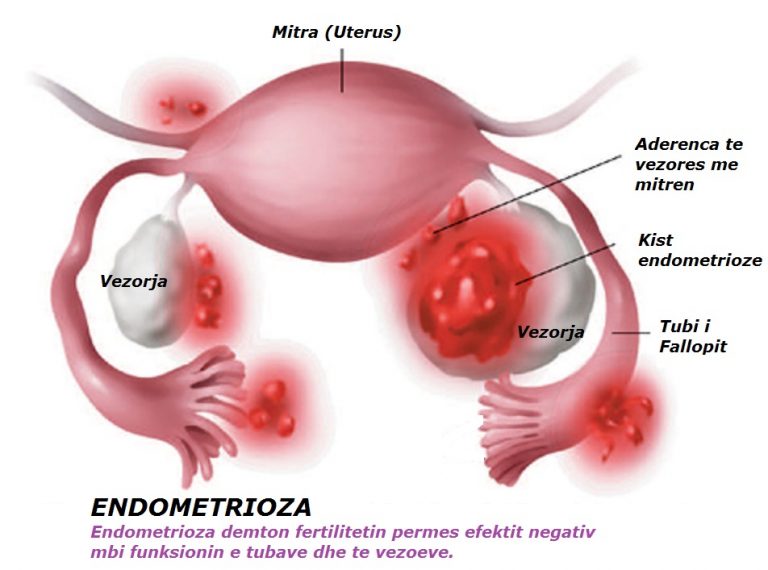 Especially the expectant mother should be alerted by spotting or if the pain and discomfort do not subside.
Especially the expectant mother should be alerted by spotting or if the pain and discomfort do not subside.
- In the early stages, the main symptoms of uterine tone are pulling pain and heaviness that occurs in the lower abdomen. In the second, as well as the third trimester, the tone of the uterus can already be observed: the stomach becomes hard and shrinks, while the uterus seems to “harden,” explains doctor Laysan Ibatullina . - In the early stages, hypertonicity can lead to fetal death if you do not seek help from specialists in time. Due to the tense muscles of the uterus, the vessels of the umbilical cord are in a compressed position, oxygen is supplied to the fetus in insufficient quantities, and hypoxia develops. For the same reason, the child does not fully receive the nutrients necessary for its development, which can provoke the appearance of malnutrition. In other words, the child stops growing.
Second trimester
In the second trimester of pregnancy, the child actively grows and develops, so it can put pressure on the uterus and internal organs, hence the increased tone. Hypertonicity can also be caused by polyhydramnios, and Rhesus conflict, and an irregular shape of the uterus, if the child is too large or the expectant mother is expecting twins.
Hypertonicity can also be caused by polyhydramnios, and Rhesus conflict, and an irregular shape of the uterus, if the child is too large or the expectant mother is expecting twins.
— A pregnant woman should not perceive a high uterine tone as a tragedy. But this is a great reason to be more attentive to your health, reconsider your daily routine, and get more rest, - the specialist is sure.
Third trimester
— In the third trimester of pregnancy, uterine tone can cause miscarriage or premature birth. Bleeding may also open, which is very dangerous for both the fetus and the woman herself. In such cases, you should immediately seek medical help, explains obstetrician-gynecologist Laysan Ibatullina .
How to distinguish hypertonicity from training contractions
In late pregnancy, when the body begins to prepare for childbirth, a pregnant woman begins training contractions (Braxton-Hicks contractions) (2). This is a natural physiological state that should not frighten the expectant mother, but tell her that the baby is ready to be born soon.
- The state is considered normal when the uterus begins to contract slightly and with a certain frequency. These are training contractions that occur 1-2 weeks before delivery. Their main difference from hypertonicity is that they are painless, short-term and irregular. Training contractions are not considered a pathology and do not require treatment. Their duration can be up to one minute or several seconds, and they can be repeated after 4-5 hours. Rarely, some women experience quite severe pain during such contractions. And most expectant mothers simply do not notice them, - the specialist notes.
How to remove the tone of the uterus during pregnancy
If the increased tone of the uterus is not caused by serious pathologies and does not threaten the life and health of the unborn baby, it is easy to remove it.
Most often it is enough to lie down for half an hour, relax and listen to your inner state. Sometimes a doctor may prescribe bed rest or limit physical activity.
Phytotherapy also helps to relieve increased tone (be sure to consult your doctor before use!). Valerian infusion relieves spasms well - 25-30 drops half an hour before meals. Tea with lemon balm or mint helps, you can use a mix of mint with valerian or motherwort. A lamp with aromatic oils, such as vanilla, jasmine, rose or chamomile, helps to relax - the main thing is not to overdo it. In the second and third trimester, special therapeutic exercises can help. But if it is allowed for you, you should ask the doctor.
Diagnosis
An increased tone of the uterus during pregnancy is usually detected during a routine examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist. First, the doctor palpates the uterus. With increased tone, the doctor feels a seal, and sometimes even petrification. If necessary, the specialist prescribes an ultrasound scan, which will help assess the condition of the cervix - whether there is a premature opening, whether there is a threat of termination of pregnancy. Depending on the situation, the doctor will prescribe rest for the pregnant woman, special drugs, or write out a referral for hospitalization.
Depending on the situation, the doctor will prescribe rest for the pregnant woman, special drugs, or write out a referral for hospitalization.
Medications
— In order to bring the uterine muscles into a relaxed state, papaverine, no-shpu, is often prescribed. It is permissible in this condition to use Magne-B6, - explains the obstetrician Laysan Ibatullina. - In each case, it is important to identify the cause of the increased tone of the uterus. If it is observed due to insufficient production of the "hormone of pregnancy", the doctor may prescribe the use of drugs such as "Utrozhestan", "Dufaston". In the presence of bloody discharge from the genital tract, one cannot do without hemostatic drugs - Dicinon, Tranexam and others.
Photo: @mart-production, pexels.comPrevention of uterine tone during pregnancy
— Prevention of uterine hypertonicity during pregnancy is simple: you need to work less, avoid serious physical exertion, eat right, follow all the recommendations of your doctor. It is important to sleep 8-10 hours a day, because proper rest is very important during pregnancy. Of course, the expectant mother should get rid of bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol, which negatively affect the health and development of the child, can even provoke the development of pathologies in the fetus or miscarriage. Stay away from sick people, do not forget to undergo ultrasound and other examinations on time, take all the necessary tests. Remember that a pregnant woman should in no case be worried and nervous, explains obstetrician-gynecologist Laysan Ibatullina. - In order for the uterus not to be subjected to heavy stress, it needs support. There is a special bandage for pregnant women, comfortable clothes and underwear. A bandage is an excellent prevention of the appearance of uterine tone.
It is important to sleep 8-10 hours a day, because proper rest is very important during pregnancy. Of course, the expectant mother should get rid of bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol, which negatively affect the health and development of the child, can even provoke the development of pathologies in the fetus or miscarriage. Stay away from sick people, do not forget to undergo ultrasound and other examinations on time, take all the necessary tests. Remember that a pregnant woman should in no case be worried and nervous, explains obstetrician-gynecologist Laysan Ibatullina. - In order for the uterus not to be subjected to heavy stress, it needs support. There is a special bandage for pregnant women, comfortable clothes and underwear. A bandage is an excellent prevention of the appearance of uterine tone.
When you need to go to the hospital
Most often, increased uterine tone can be removed at home with the help of antispasmodics and bed rest. But if the attending physician suggested hospitalization, the pregnant woman has bloody discharge and severe pain, you need to go to the hospital (3). There, the expectant mother will be under the constant supervision of doctors, they will conduct all the necessary examinations, prescribe injections and droppers that effectively relieve hypertonicity.
There, the expectant mother will be under the constant supervision of doctors, they will conduct all the necessary examinations, prescribe injections and droppers that effectively relieve hypertonicity.
— In case of pulling pain in the lower abdomen, you should immediately drink a No-shpa tablet and lie down. If during the day the pain does not subside or becomes stronger, be sure to call an ambulance, ”the doctor explains.
Popular Questions and Answers
Uterine tone is not the most dangerous, but very unpleasant condition. With a gynecologist, we will answer the most popular questions that worry expectant mothers.
Does nutrition affect uterine tone?
Certain foods may help increase uterine tone.
Legumes, cabbage, sour milk products, dried fruits and the like affect gas formation. Since the uterus and intestines are in close proximity to each other, discomfort can be felt both there and there.
Nuts and mushrooms. The vegetable protein contained in them is heavily processed by the body. In addition, mushrooms tend to accumulate toxic substances in themselves and can be dangerous to the health of a woman and fetus.
The vegetable protein contained in them is heavily processed by the body. In addition, mushrooms tend to accumulate toxic substances in themselves and can be dangerous to the health of a woman and fetus.
Undercooked meat, raw eggs. Not recommended due to the risk of poisoning and the possibility of intestinal infection.
Coffee and strong tea. The caffeine contained in them can help increase tone.
Of course, when choosing a diet, it is important to be guided by common sense. For example, if the expectant mother is used to drinking coffee in the morning, it is not necessary to give up this pleasure. One cup will definitely not hurt, and if you are afraid, you can dilute it with milk or cream. There is also nothing wrong with the fact that a woman will eat some dried fruits or drink a glass of kefir. The main thing in everything is to know the measure.
Is it possible to have sex with hypertonicity?
Increased uterine tone is a direct contraindication for sexual intercourse.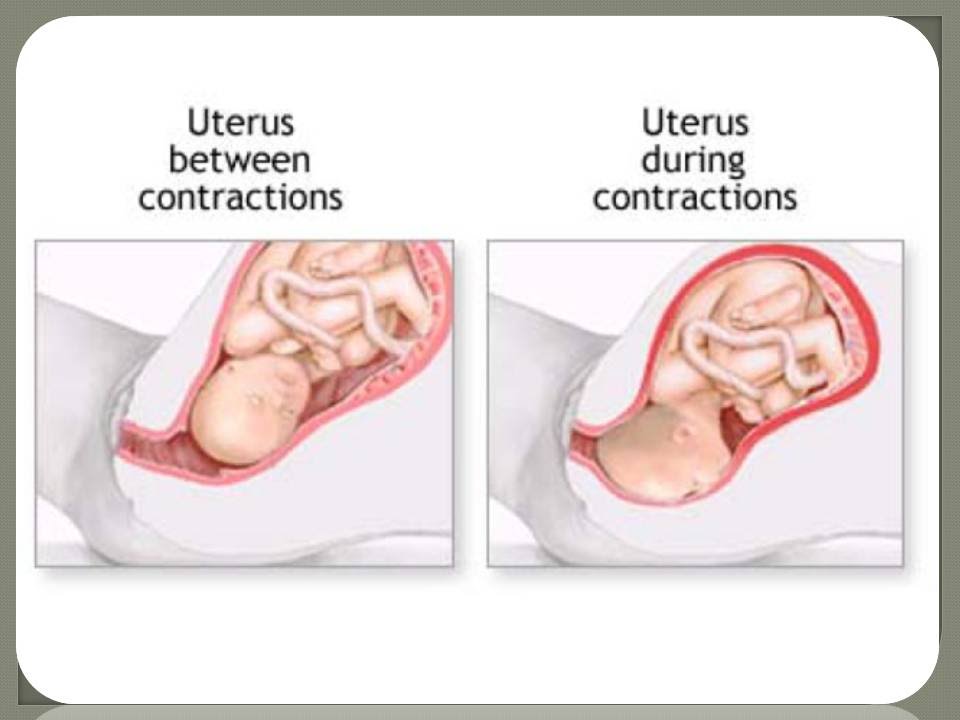 During orgasm, the uterus contracts more strongly, respectively, spasms intensify. Therefore, during this period, it is necessary to refrain from intimacy. Permission to resume sexual relations must be given by a doctor after an examination.
During orgasm, the uterus contracts more strongly, respectively, spasms intensify. Therefore, during this period, it is necessary to refrain from intimacy. Permission to resume sexual relations must be given by a doctor after an examination.
Is it possible to go in for sports with increased uterine tone?
Sport during pregnancy is useful, but do not overload yourself. Classes should be moderate: gymnastics, yoga, exercises, water aerobics and the like. With hypertonicity, it is better to postpone sports until the uterus “calms down”. But there is one exercise recommended for relieving spasm: cat pose.
Get on all fours with your back arched. Inhale deeply while raising your head. Try to relax your facial muscles while holding the backbend. Arch your back to the opposite side, lowering your head as you exhale. Do 3-4 sets.
Then you need to lie down and rest. Exercise helps to reduce tone and is useful at any stage of pregnancy.