Throw up in mouth pregnancy
Acid Reflux During Pregnancy
What is acid reflux during pregnancy?
It’s when stomach acid doesn’t stay put in your stomach and creeps up into your esophagus. Acid reflux is more common in pregnancy because progesterone, the main hormone of pregnancy, slows your digestive system. That, combined with the pressure of a growing baby, increases the possibility that stomach acid will make its way upward.
What are the signs of acid reflux during pregnancy?
The most common symptoms of acid reflux are a burning sensation in your throat or upper chest. (Heartburn, anyone?) You might also feel nauseous. Burping and regurgitation can also be signs of acid reflux.
Are there any tests for acid reflux during pregnancy?
Most often, acid reflux in pregnancy is diagnosed based on symptoms alone. But if you keep getting it after pregnancy, your doc may order additional testing, including an upper endoscopy, a test that’s used to look at the inside of the upper digestive tract.
How common is acid reflux during pregnancy?
Acid reflux is “very, very common” during pregnancy, says Michelle Collins, CNM, an assistant professor of nurse-midwifery at Vanderbilt University. More than half of all pregnant women will experience acid reflux.
How did I get acid reflux during pregnancy?
“Because your digestion is slowed, you’re fuller; you’ve got less room in your stomach, so acid runs up your esophagus,” Collins says. “You’ve also got a baby pressing on your stomach.”
How will my acid reflux affect my baby?
Acid reflux shouldn’t affect your baby in any way, shape or form. (And the old wives’ tale that says your baby will be born hairy if you have heartburn? Not true.)
What’s the best way to treat acid reflux during pregnancy?
Over-the-counter (OTC) antacids can be very helpful. Pregnant moms can also take some of the OTC pills that decrease stomach acid. But talk to your OB or midwife before beginning an OTC med like Tagamet to treat acid reflux. “We want to make sure that it won’t interact with anything else you might be taking,” Collins says.
“We want to make sure that it won’t interact with anything else you might be taking,” Collins says.
Also, avoid peppermint tea, says Collins. While peppermint can be soothing to your stomach, it actually dilates the esophageal sphincter, the muscle that holds the esophagus shut, making it easier for stomach acid to back up into your throat.
Many moms-to-be have found relief by eating raw almonds, sucking on slippery elm lozenges or taking papaya enzyme tablets. You can also try propping up your upper body when you sleep; that position can decrease the amount of acid that backs up into your throat.
What can I do to prevent acid reflux during pregnancy?
Eat small, frequent meals. Avoid greasy, spicy foods, especially close to bedtime. And avoid milk. It might seem like milk’s a good idea, but it actually increases stomach acid, making things worse.
What do other pregnant moms do when they have acid reflux?
“My acid reflux gets horrible at night…so I usually take an antacid 75 right before bed, and it helps a lot. ”
”
“I was hoping I wouldn’t develop this fun pregnancy side effect, but no such luck. It’s especially bad if I eat late and then lie down too soon, and spicy and acidic foods make it worse.”
“If you want to go a home remedy path, apple cider vinegar works really well, or so does eating a red apple.”
Are there any other resources for acid reflux?
American Gastroenterological Association
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Plus, more from The Bump:
Heartburn During Pregnancy
Nausea During Pregnancy
Gas During Pregnancy
Indigestion and Acid Reflux in Pregnancy (Dyspepsia)
In this series Common Side Effects of Pregnancy (Morning Sickness, Acid Reflux, Constipation) Nausea and Vomiting in Pregnancy (Morning Sickness)
Indigestion (dyspepsia) occurs at some point in around half of all pregnant women. It is usually due to acid reflux from the stomach into the gullet (oesophagus).
It is usually due to acid reflux from the stomach into the gullet (oesophagus).
Indigestion in pregnancy is commonly due to acid reflux. Acid reflux occurs when acid from the stomach leaks up into the gullet (oesophagus). This may cause heartburn - usually felt as a burning pain which rises from the upper stomach behind the breastbone - and other symptoms. Attention to diet and lifestyle may help to ease symptoms. Antacids are commonly used. A medicine which prevents your stomach from making acid may be prescribed if symptoms remain troublesome.
What is indigestion?
Indiestion (dyspepsia) is a term which includes a group of symptoms (detailed below) that come from a problem in your upper gut. The gut (gastrointestinal tract) is the tube that starts at the mouth and ends at the anus. The upper gut includes the gullet (oesophagus), stomach and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). Various conditions cause dyspepsia.
Indigestion is really common in pregnancy - it occurs at some point in around half of all pregnant women. Indigestion in pregnancy is usually due to reflux of acid from the stomach into the oesophagus.
Indigestion in pregnancy is usually due to reflux of acid from the stomach into the oesophagus.
Understanding the oesophagus and stomach
Acid reflux inflammation
When we eat, food passes down the gullet (oesophagus) into the stomach. Cells in the lining of the stomach make acid and other chemicals which help to digest food.
Stomach cells also make mucus which protects them from damage caused by the acid. The cells lining the oesophagus are different and have little protection from acid.
There is a circular band of muscle (a sphincter) at the junction between the oesophagus and stomach. This relaxes to allow food down but normally tightens up and stops food and acid leaking back up (refluxing) into the oesophagus. In effect, the sphincter acts like a valve.
What causes acid reflux during pregnancy?
Acid reflux occurs when some acid leaks up (refluxes) into the gullet (oesophagus). The lining of the oesophagus can cope with a certain amount of acid. However, if more than the usual amount of acid refluxes, it may cause some inflammation on the lining of the oesophagus, which can cause symptoms.
However, if more than the usual amount of acid refluxes, it may cause some inflammation on the lining of the oesophagus, which can cause symptoms.
The sphincter at the bottom of the oesophagus normally prevents acid reflux. It is thought that when you are pregnant:
- The increased level of certain hormones that occurs has a relaxing effect on the sphincter muscle. That is, the tightness (tone) of the sphincter is reduced during pregnancy.
- The size of the baby in the tummy (abdomen) causes an increased pressure on the stomach.
One or both of the above increase the chance that acid will reflux into the oesophagus. The indigestion usually settles on its own after the birth of your baby when your hormones change back to their non-pregnant state and the baby is no longer increasing pressure on your stomach.
You are more likely to develop indigestion in pregnancy if you have previously had gastro-oesophageal reflux before you were pregnant.
What are the symptoms of acid reflux and indigestion in pregnancy?
Symptoms can vary from mild (in most cases) to severe. They can include one or more of the following:
They can include one or more of the following:
- Heartburn. This is a burning sensation which rises from the upper tummy (abdomen) or lower chest up towards the neck. (It is a confusing term as it has nothing to do with the heart!)
- Waterbrash. This is a sudden flow of sour-tasting saliva in your mouth.
- Upper abdominal pain or discomfort.
- Pain in the centre of the chest behind the breastbone (sternum).
- Feeling sick (nausea) and being sick (vomiting).
- Bloating.
- Quickly feeling full after eating.
Symptoms tend to occur in bouts which come and go, rather than being present all the time. They may begin at any time during pregnancy but happen more often, or are more severe, in the last three months of pregnancy. As soon as the baby is born, indigestion due to pregnancy usually disappears quickly.
Note: various other problems, associated with pregnancy and unrelated to pregnancy, are sometimes confused with indigestion. For example, pain in the right or left of the upper abdomen is not usually due to indigestion. Excessive vomiting is not usually due to indigestion. If symptoms change, or are not typical, or become severe, or are repeated (recurring), you should see your doctor.
For example, pain in the right or left of the upper abdomen is not usually due to indigestion. Excessive vomiting is not usually due to indigestion. If symptoms change, or are not typical, or become severe, or are repeated (recurring), you should see your doctor.
Do I need any investigations?
Indigestion in pregnancy is usually recognised by your typical symptoms. Investigations are generally not needed.
Lifestyle changes that may help with indigestion symptoms
The following are commonly advised. There has been little research to prove how well these lifestyle changes help to ease acid leaking back up (reflux) and indigestion in pregnancy. However, they are certainly worth a try.
Consider avoiding certain foods, drinks and large meals
Some foods and drinks may make reflux worse in some people. (It is thought that some foods may relax the sphincter and allow more acid to reflux.) It is difficult to be certain to what extent specific foods contribute to the problem.
Let common sense be your guide. If it seems that a food is causing symptoms, try avoiding it for a while to see if symptoms improve. Foods and drinks that have been suspected of making symptoms worse in some people include:
- Peppermint.
- Tomatoes.
- Chocolate.
- Spicy and fatty foods.
- Fruit juices.
- Hot drinks.
- Coffee.
- Alcoholic drinks. (Current advice is that you avoid all alcohol in pregnancy anyway.)
Also, avoid large meals if they bring on symptoms. Some women find that eating smaller meals more frequently is helpful.
Stop smoking if you are a smoker
The chemicals from cigarettes relax the sphincter muscle and make acid reflux more likely. Symptoms may ease if you are a smoker and stop smoking. In any case, it is strongly advised that pregnant women should not smoke for other reasons as well. See the separate leaflet called Pregnancy and Smoking.
Have good posture
Lying down or bending forwards a lot during the day encourages reflux. Sitting hunched-over may put extra pressure on the stomach, which may make any reflux worse.
Sitting hunched-over may put extra pressure on the stomach, which may make any reflux worse.
Bedtime
If symptoms return on most nights, it may help to go to bed with an empty, dry stomach. To do this, don't eat in the last three hours before bedtime and don't drink in the last two hours before bedtime. If you raise the head of the bed by 10-15 cm (with sturdy blocks or bricks under the bed's legs), this will help gravity to keep acid from refluxing into the gullet (oesophagus).
Consider any medicines that you are taking
Some medicines may make symptoms worse. Women are rarely prescribed these medicines during pregnancy. However, it's worth checking with your pharmacist or your doctor if you think medication you are on could be making your symptoms worse.
Is there any medication for indigestion in pregnancy?
For many women (especially if they have mild symptoms), making some lifestyle changes as above is enough to ease indigestion. However, if lifestyle changes do not help, medication may be needed to treat indigestion in pregnancy.
Antacids and alginates
Antacids are alkaline liquids or tablets that neutralise the acid. A dose usually gives rapid relief. You can use antacids when you need them for mild or infrequent bouts of indigestion. Antacids containing aluminium or magnesium can be taken on an 'as required' basis. Those containing calcium should only be used occasionally or for a short period. Antacids that contain sodium bicarbonate or magnesium trisilicate should be avoided: this is because they may be harmful to your developing baby.
You can buy many different brands of antacids, and some are available on prescription. A doctor or pharmacist can advise. Some points about antacids are:
- They can interfere with the absorption of iron tablets. Therefore, they should be taken at a different time of day from any iron supplements you are taking. If possible, you should take your antacid at least two hours before or after you take your iron supplement.
- It is probably best to use an antacid with a low sodium content if you have high blood pressure or pre-eclampsia (a complication of pregnancy).
Alginates are often combined with antacids. Alginates help to protect the gullet (oesophagus) from stomach acid. They form a protective raft when they come into contact with stomach acid, blocking the acid from entering the oesophagus. Some alginates are specifically licensed for use in pregnancy. Again, your pharmacist can advise.
Acid-suppressing medicines
Omeprazole is an acid-suppressing medicine that is licensed for use in pregnancy to treat indigestion that is still troublesome despite any lifestyle changes and antacids. Omeprazole needs to be taken regularly to be effective.
Note: Other medicines that are commonly used for heartburn, indigestion, acid reflux, etc, should not be used. For example, cimetidine, esomeprazole, lansoprazole and pantoprazole. It is not known whether these other medicines are safe to take during pregnancy.
Early toxemia of pregnancy - causes and treatment
- When does early toxemia begin during pregnancy
- Manifestation of early toxicosis
- Causes of early toxicosis
- Severity of toxicosis during pregnancy
- How to manage morning sickness and relieve symptoms
- Principles of treatment of early toxicosis
Most women, having barely learned about the onset of pregnancy, expect to feel unwell, bouts of nausea and even vomiting. Indeed, early toxicosis often becomes a constant companion of many expectant mothers in the early stages of pregnancy. Is there any way to alleviate these unpleasant symptoms?
Indeed, early toxicosis often becomes a constant companion of many expectant mothers in the early stages of pregnancy. Is there any way to alleviate these unpleasant symptoms?
Toxicosis (and doctors call this condition gestosis) is a syndrome that is defined as a violation of a woman's adaptation to pregnancy. According to the time of occurrence, early preeclampsia is distinguished, which will be discussed in this article, and late preeclampsia, which appears in the last 2-3 months of pregnancy and is manifested by edema, increased blood pressure and the appearance of protein in the urine.
When early morning sickness begins in pregnancy
Early morning sickness usually occurs in the first half of pregnancy. As a rule, after the end of the formation of the placenta, that is, at 12-13 weeks of pregnancy, the phenomena of toxicosis stop. During a normal pregnancy, adaptive changes in the function of almost all organs and systems occur in a woman's body, which are regulated by the nervous system with the participation of endocrine glands. Toxicosis also occurs due to the impossibility of the adaptive mechanisms of the body of the expectant mother to adequately meet the needs of the developing fetus.
Toxicosis also occurs due to the impossibility of the adaptive mechanisms of the body of the expectant mother to adequately meet the needs of the developing fetus.
Manifestation of early toxicosis
The most common manifestation of toxicosis is vomiting. Other forms of early toxicosis are very rare:
- pregnancy dermatosis is a group of skin diseases that occur during pregnancy and disappear after it. When it occurs in early pregnancy, dermatosis is caused by immune disorders in the body of a pregnant woman, and is also most often found in patients with diseases of the digestive and endocrine systems. The most common form of dermatoses of pregnancy is pruritus gravidarum, which can be on a small area of the skin or spread throughout the body, including the feet and palms.
- tetany (chorea) of pregnant women. This condition occurs when the function of the parathyroid glands decreases, as a result of which calcium metabolism in the body is disturbed.
 Clinically, the disease is manifested by muscle cramps, more often cramps occur in the fingers, sometimes in the muscles of the face.
Clinically, the disease is manifested by muscle cramps, more often cramps occur in the fingers, sometimes in the muscles of the face. - salivation - increased secretion of saliva, in connection with which there is a large loss of fluid (up to 1 liter per day). Salivation can be an independent manifestation of toxicosis or accompany vomiting of pregnant women. In the development of salivation, not only changes in the central nervous system are important, but also local disturbances in the salivary glands and their ducts under the influence of hormonal changes.
- Pregnancy bronchial asthma is an extremely rare form of preeclampsia.
- osteomalacia of pregnancy - softening of the bones due to a violation of the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus, while the bones of the pelvis and spine are more often affected
- neuropathy and psychopathy of pregnant women.
Learn more about the services:
- Tests for pregnant women
- Ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy
Causes of toxicosis in the early stages
There are many theories trying to explain the causes and mechanisms of development of early toxicosis: the most recognized are the so-called neuro-reflex and immunological.
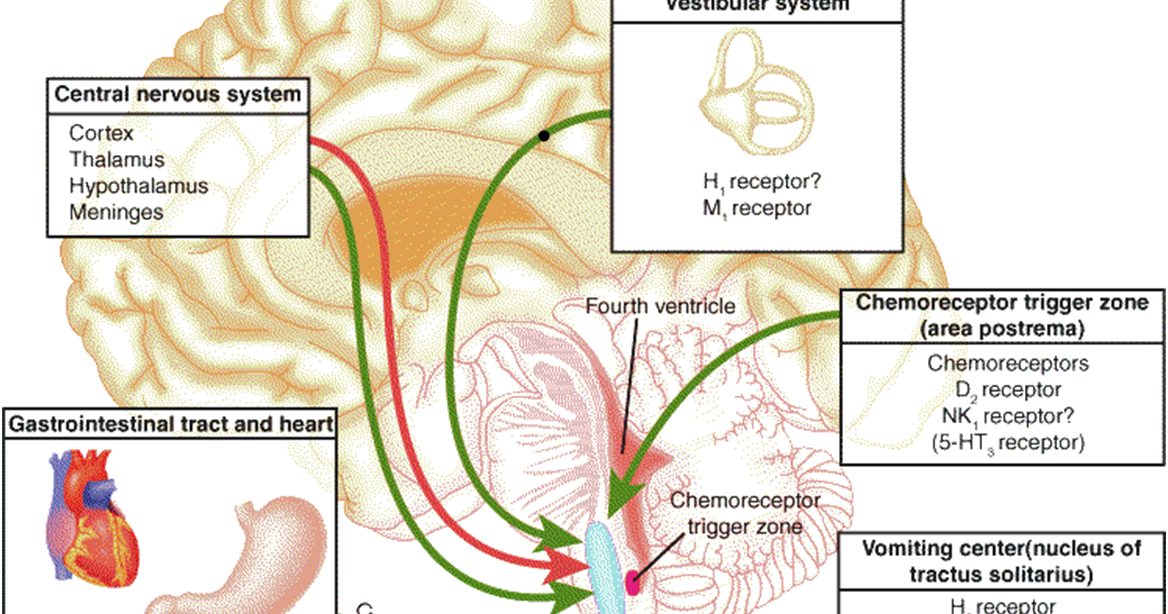
According to the neuro-reflex concept , vomiting occurs as a result of a violation of the relationship between the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures. During pregnancy, the subcortical centers of the brain begin to work more intensively than usual, which are responsible for most protective reflexes, including breathing and cardiac activity. In the same areas of the subcortical structures are the vomiting and salivary centers, the nuclei of the olfactory system of the brain. Excitation processes also capture them. Therefore, nausea and vomiting may be preceded by such phenomena as deepening of breathing, increased heart rate, an increase in the amount of saliva, pallor due to vasospasm, and a change in smell.
Immunological disorders play a certain role in the development of preeclampsia . The timing of the onset of vomiting usually coincides with the formation of blood circulation in the placenta, increased reproduction of white blood cells - lymphocytes, which are involved in immune reactions. The fetus is foreign to the mother's body, and her immune system reacts to it in this way. After the full maturation of the placenta, which accumulates all these immune cells, toxicosis usually disappears.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) plays a certain role in the development of vomiting during pregnancy. This hormone is produced by the placenta during pregnancy. Its high concentration can provoke vomiting.
The severity of toxicosis during pregnancy
The main symptom of early toxicosis of pregnant women is vomiting. Depending on the frequency of its occurrence, as well as the degree of metabolic disorders in the body of the expectant mother, doctors distinguish three degrees of severity of vomiting during pregnancy.
How to manage morning sickness and relieve symptoms
Treatment for mild morning sickness is usually done at home. But, nevertheless, a pregnant woman should be under the supervision of doctors, take all the tests recommended by the doctor, and follow the appointments. This will allow the doctor to monitor the condition of the future mother's body and prevent possible complications in time. A woman needs to organize a normal sleep and rest regimen, walks in the fresh air, a calm atmosphere in the family are shown.
Proper nutrition
You need to eat in small portions, fractionally, every 2-3 hours. Food should be easily digestible, high-calorie and fortified whenever possible. In connection with a decrease in appetite, they recommend varied and pleasant food for the expectant mother, that is, products are selected taking into account the desires of the pregnant woman, with the exception of spicy dishes and smoked meats. It is important to remember that very hot or very cold food often induces vomiting, so the dishes should be warm. Reception of alkaline mineral waters in small volumes 5-6 times a day is shown.
If nausea and vomiting occur in the morning, immediately after waking up, it is recommended to have breakfast while lying in bed without getting up. For breakfast, you can eat dry crackers, crackers, drink tea or water with lemon, light yogurt is allowed. It is better to put all this next to the bed in advance or ask someone to bring breakfast.
Every woman chooses for herself a remedy that helps to fight nausea. Someone helps a slice of orange, lemon or apple, some expectant mothers carry crackers or mint sweets with them to alleviate the symptoms of toxicosis. Pumpkin juice has a good antiemetic effect. Many pregnant women benefit from ginger tea. It is prepared very simply:
ginger root finely chopped or grated on a coarse grater is poured with boiling water and infused for 15-20 minutes. Tea can be drunk warm or chilled, adding lemon, mint or honey to it.
Fats and proteins of animal origin are recommended to be consumed in the morning, when pancreatic enzymes are more active. Dairy products are best eaten after dinner or before bed.
Do not use food with preservatives, broiler meat, fast food, fast food.
To maintain metabolic processes in the body, it is advisable to drink 2-2.5 liters of fluid per day. With increased vomiting, it is not recommended to consume solid and liquid food at the same time. Liquids should not be drunk 30 minutes before and within 1.5 hours after eating, as this provokes vomiting by stretching the walls of the stomach and affecting the receptors.
Decoctions and infusions
Oat broth
As an enveloping agent, that is, a substance that forms a mucous film and prevents irritation of receptors on the walls of the stomach and intestines, oat broth is recommended. It is prepared as follows: 2-3 tbsp. spoons of oat grains are washed, pour 500-700 ml of water, boil over low heat under a lid for 30 minutes. The broth is drained, the grains are crushed and poured with new water and boiled until fully cooked. The resulting mass is crushed with a blender. You need to use the decoction on an empty stomach and in the evening before going to bed, but not earlier than 2 hours after dinner, and also throughout the day in small portions.
It has a particularly good effect in combination with rosehip infusion.
Rosehip infusion
This infusion is a good source of vitamins and microelements - it contains vitamins C, K, P and PP, potassium, manganese, iron, and contributes to the normalization of the gallbladder function. To prepare it, you need 1 tbsp. pour a spoonful of crushed rose hips with 250 ml of boiling water and insist in a thermos for about 2 hours.
The following infusions and decoctions contribute to reducing nausea and improving the condition of the expectant mother.
Phytonast
Take equally: valerian root, common anise fruits, fireweed leaves, linden flowers, marigold flowers, common blueberry shoots, blood red hawthorn fruits. 1 st. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over a spoonful of the mixture ground in a coffee grinder and insist in a thermos for 2 hours, then strain. Take the infusion as needed, up to 6 times a day in a heated form, 1/3 cup.
Benediktov's collection
To prepare this collection you will need: common yarrow (10 g), peppermint herb (20 g), shepherd's purse herb (20 g), valerian officinalis rhizomes (10 g), calendula officinalis inflorescences (20 g) and inflorescences of chamomile officinalis (20 g). Pour 10 g of the mixture with 400 ml of water, soak in a water bath for 30 minutes, strain. Take 50 ml 6 times a day for 25 days, three courses with 15-day breaks.
Viburnum with honey
Grind 2 tbsp. tablespoons of fresh viburnum berries, pour 250 ml of boiling water over them, heat for 10 minutes in a water bath, strain, add a little honey. Take 1/3 cup of warm infusion before meals 3-4 times a day.
Cranberries with mint, honey and lemon
Squeeze the juice from 250 g of cranberries, cool it, boil the pulp in 1 liter of water, add 1 tbsp. a spoonful of mint leaves and leave for 15 minutes under the lid. Strain, dissolve in a hot broth 2-3 tbsp. tablespoons of honey, let cool to room temperature, add chilled cranberry juice and a slice of lemon. Drink 0.5 cup after meals or when nausea occurs.
Rose hips with apples
Crushed rose hips (about 1 tbsp) pour 250 ml of boiling water, add 0.5 tbsp. tablespoons of dried apples, heat in a water bath for 15-20 minutes. This drink can be consumed throughout the day instead of tea.
Rosehip with garden berries
To make a drink you will need: 1 tbsp. a spoonful of rose hips, 1 tbsp. spoon of raspberries, 1 tbsp. spoon of blackcurrant leaves, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of lingonberry leaves. 2 tbsp. spoons of the mixture pour 500 ml of boiling water, boil for 5 minutes, leave for 1 hour, strain. Take 100 ml of decoction 3 times a day.
Therapeutic exercise
Among non-drug treatments, exercise therapy has a good effect. The complex of exercises includes walking, deep breathing with stretching of the muscles of the trunk and limbs. It is necessary to exclude inclinations, they can increase nausea. The complex includes dynamic exercises for training the muscles of the arms, legs, relaxation exercises. Remedial gymnastics also includes training in breathing techniques. As a result, the body is saturated with oxygen, the excitability of the vomiting center decreases - toxicosis is relieved.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapeutic procedures for the treatment of early toxicosis include electrosleep, acupuncture, laser therapy . Electrosleep is a method that uses low frequency currents to induce sleep. The duration of the procedure is from 60 to 90 minutes, the course of treatment is 6-8 sessions.
Laser therapy
In the complex therapy of early toxicosis, blood is irradiated with a helium-neon laser through a light guide passed through a needle placed in the cubital vein. The procedure lasts 15-20 minutes. The therapeutic effect is achieved due to the influence of the laser on blood cells, changes in its properties, accumulation of biologically active substances in the blood. As a result, the metabolism in cells changes, the resistance of tissues and the body to adverse conditions increases, and the vitality increases.
Acupuncture, acupuncture
Treatment methods based on stimulation of biologically active points and zones on the body and face. With early toxicosis, such an effect changes the tone of the nervous system of a pregnant woman. A session of acupuncture is carried out 1-2 times a week and lasts 15-30 minutes.
Acupressure method is effective for morning sickness and vomiting of pregnant women. To do this, you need to press your finger on a point that is located on the inside of the wrist, in the middle, 3 transverse fingers above the palm.
Aromatherapy
The use of plant aromas has a positive effect on the expectant mother and baby. By inhaling pleasant aromas, you can achieve a good psychological effect, create a good mood, and reduce the effects of toxicosis. During pregnancy, aroma lamps, aroma medallions, pads - sachets are mainly used. To relieve nausea and vomiting, oils of noble laurel, lemon, lavender, cardamom present, dill, lemon balm, peppermint, anise, eucalyptus, ginger are suitable. To flavor the air, you can use the following mixture 0 3 drops of lavender oil, 1 drop of peppermint oil, 1 drop of eucalyptus oil.
Principles of treatment of early toxicosis
Even with a mild course of early toxicosis of pregnant women, the attending physician will definitely prescribe a number of tests - a general blood test, a general urinalysis, a biochemical blood test, a hemostasiogram. This is necessary to control the condition of a pregnant woman and to timely prescribe medications to correct the changes that occur in the body.
If non-drug remedies are ineffective, the doctor prescribes medications that help fight toxicosis. First of all, these are herbal sedatives, homeopathic medicines for nausea, vitamin B6 preparations, antiemetics.
If, despite all the therapy, vomiting increases, the doctor detects changes in blood and urine tests, and body weight continues to progressively decrease, hospitalization is indicated.
An intravenous infusion of medicines is carried out in the hospital, which restores the fluid, microelements and proteins lost by the body. A pregnant woman receives at least 2-2. 5 liters of fluid intravenously per day.
To improve blood flow through the placenta and improve oxygen supply to the fetus, oxygen therapy can be prescribed - inhalation of an oxygen-air mixture for 20-30 minutes twice a day.
Most often, the effects of toxicosis gradually decrease by 12-13 weeks of pregnancy.
Mild
Mild vomiting on an empty stomach or after meals occurs 3 to 5 times a day. Despite vomiting, part of the food is still retained and significant weight loss is not observed in such pregnant women. The general condition does not suffer significantly, there are no changes in blood and urine tests. Such vomiting is easily treatable with various non-drug means, and often resolves on its own after the normalization of the diet and rest.
Moderate vomiting
Moderate vomiting (or moderate vomiting) is expressed in the increase in vomiting up to 10 times a day, regardless of food intake. Characterized by persistent nausea. There comes dehydration of the body, a decrease in body weight by 3-5 kg (6% of the initial weight). The general condition of pregnant women worsens. Expectant mothers complain of weakness, apathy, tearfulness, sometimes depression. The skin is pale, dry, the tongue is covered with a white coating, yellowness of the skin may be noted.
Excessive vomiting
The severe form (excessive pregnancy vomiting) is rare. The frequency of vomiting up to 20 times a day or more. Excessive vomiting is characterized by severe dehydration and intoxication. This condition can occur as a continuation of moderate vomiting of pregnant women or initially acquire a severe character. With excessive vomiting, body weight decreases rapidly, on average by 2-3 kg per week, the skin becomes dry and flabby, subcutaneous fat quickly disappears, the tongue and lips are dry, there is a smell of acetone from the mouth, body temperature can rise up to 38 degrees. Vomiting of moderate and severe degrees is treated in a hospital.
Nausea and vomiting in pregnant women - what to do with toxicosis so as not to feel sick? | Blog
Nausea is a common symptom in pregnant women during the first trimester of pregnancy. Its manifestations range from mild to quite pronounced and can cause significant obstacles to normal nutrition.
Acute nausea and vomiting during pregnancy occurs in 50% of women. Realizing that every second pregnant woman is faced with this condition, a dietitian, gastroenterologist Oleg Vitalievich Shvets helped us figure out the causes, possible consequences and shared tips on how to alleviate her condition during toxicosis and what to do so as not to feel sick.
In the article you will learn:
- What is toxicosis?
- Effects of toxicosis on the fetus?
- Causes of toxicosis
- Is it possible to take vitamin complexes
- How to eat during toxicosis
- What to do in case of complications
- How to curb nausea?
What is toxicosis?
As we wrote above, every second pregnant woman faces acute nausea and vomiting in the first trimester of pregnancy. In the English-language literature, the term "morning sickness" is used for this condition, although in fact nausea and vomiting can occur at any time of the day, and not just in the morning.
Significant hormonal changes during the first months of pregnancy are believed to be the cause of the malaise. In most pregnant women, the symptoms of nausea and vomiting are significantly weakened or disappear before 12-14 weeks.
However, in 1-3% of pregnancies, nausea and vomiting are severe and become debilitating - this condition is called toxicosis or preeclampsia of pregnancy . In English-speaking countries, the term hyperemesis (Hyperemesis Gravidarum) is used.
Toxicosis can be potentially life threatening and often requires specialized treatment: IV fluids for dehydration or antiemetics.
The main symptoms of toxicosis include:
- severe persistent nausea and vomiting,
- suboptimal nutrition,
- dehydration and rapid weight loss.
This condition can significantly impair routine and quality of life, especially if women work or have other children in need of care.
Effects of toxemia on the fetus
Women with toxemia worry that the condition will harm their unborn baby. In fact, with moderate toxicosis, the fetus receives all the nutrients necessary for healthy growth and development.
But there is a hypothetical risk that weight loss during pregnancy could result in a low birth weight baby.
Causes of morning sickness in pregnant women
Studies show a connection between nausea and vomiting of pregnant women and a number of factors:
➡️ High levels of the sex hormones estrogen and progesterone, as well as the hormone of pregnancy - chorionic gonadotropin.
➡️ Nausea and vomiting during previous pregnancies or family history (if your family has had this). Being aware of the risk helps prepare mentally for the next pregnancy.
➡️ Obesity - body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more at the beginning of pregnancy. If you are planning to have a baby, losing weight before pregnancy is beneficial and reduces the chance of morning sickness.
➡️ Vitamin B6 Deficiency
Research indicates a link between vitamin B6 levels and nausea during pregnancy. Vitamin B6 contributes to the optimal use and storage of energy by the body. If you eat a healthy, balanced diet before conception and during pregnancy, you will usually get the amount of B6 you need. At the same time, with insufficient intake of food or absorption of nutrients, its deficiency may occur.
Try to eat enough foods containing vitamin B6: brown rice, whole grain bread, fish and poultry, fortified breakfast cereals, nuts, green leafy vegetables.
Can I take vitamin complexes during pregnancy?
You can take vitamin complexes for yourself or not - this question is worth discussing with your doctor.
If you have no contraindications, the appointment and use of special vitamin-mineral complexes for pregnant women is possible. They, in particular, contain the optimal amount of vitamin B6, and also help to supply the body with the necessary vitamins, minerals and trace elements in case of nausea and vomiting of pregnant women.
How to eat with toxicosis?
It is important for a pregnant woman that the necessary amount of energy, micro, macro, nutrients and water enter the body along with food. During toxicosis, when a woman is constantly worried about nausea and vomiting, this is sometimes quite difficult to do.
Helpful Dietary Advice for Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy:
- If you are having trouble eating regularly during pregnancy due to nausea and vomiting, then there is no need to worry about the calorie content of your individual meals.
- Determine the time of day when you are easiest and can eat, and then increase your food intake at that time.
Try to eat foods that are high in energy and protein to get the maximum amount of nutrients from a smaller serving.
- Enrich foods to make them more nutritious. For example:
- add yogurt, cream or condensed milk to fruit;
- eat vegetables with melted butter;
- put cream and cheese in mashed potatoes, pasta dishes, soups and stews;
- Eat dairy and sour-milk products with normal fat content.
- cereal with milk,
- tuna or chicken sandwiches,
- cream cheese on toast,
- soups,
- crackers,
- bread sticks and other dry starchy foods.
Dealing with complications
Dehydration, malnutrition and prolonged vomiting can lead to associated symptoms such as constipation, sleep problems, acid reflux or heartburn, etc.
Some of these will help you minimize your meals.
➡️ Constipation
- Drink more fluids.
- Increase your fiber intake from fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
- Include three to four kiwi fruits in your meal plan.
- Try dried fruits or prunes for breakfast.
➡️ Chapped lips and mouth ulcers
- Drink plenty.
- Take a multivitamin recommended for pregnant women.
➡️ Acid reflux or heartburn
- Eat slowly while sitting upright.
- Eat small meals and often.
- Avoid fatty and spicy foods.
- Do not eat 2 hours before bedtime.
➡️ Trouble sleeping
- Drink a warm milky drink before going to bed.
- You should also eat some unsweetened crackers.
➡️ Vitamin and mineral deficiency
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Eat little and often, every 1-2 hours.
- Take a multivitamin recommended for pregnant women at the time of day when you are least likely to vomit.
How to curb nausea?
- Drink more frequently throughout the day. Suitable cold and carbonated drinks, smoothies and fruit juices.
- Try lollipops, ice cream and frozen fruit juice ice cubes. They are also a great way to stay hydrated.
- It is easier for the stomach to digest soft foods. Avoid overly spicy foods, sugary desserts, fatty or fried foods. If you can't digest meat and fish, eat more plant-based protein sources like beans, chickpeas, and lentils.
- Dry foods such as crackers, toast or regular biscuits are often better tolerated.
- A small study found that fresh ginger root or ginger oral capsules at 250 mg 4 times a day can help with severe nausea (four days). But, if you are taking anticoagulants, use ginger with caution. You can also try gingerbread cookies or other products with ginger.
- Peppermint and chamomile teas are effective for some women.
❇️ Important! If you have persistent nausea, let alone vomiting, this is a reason to seek emergency medical care.