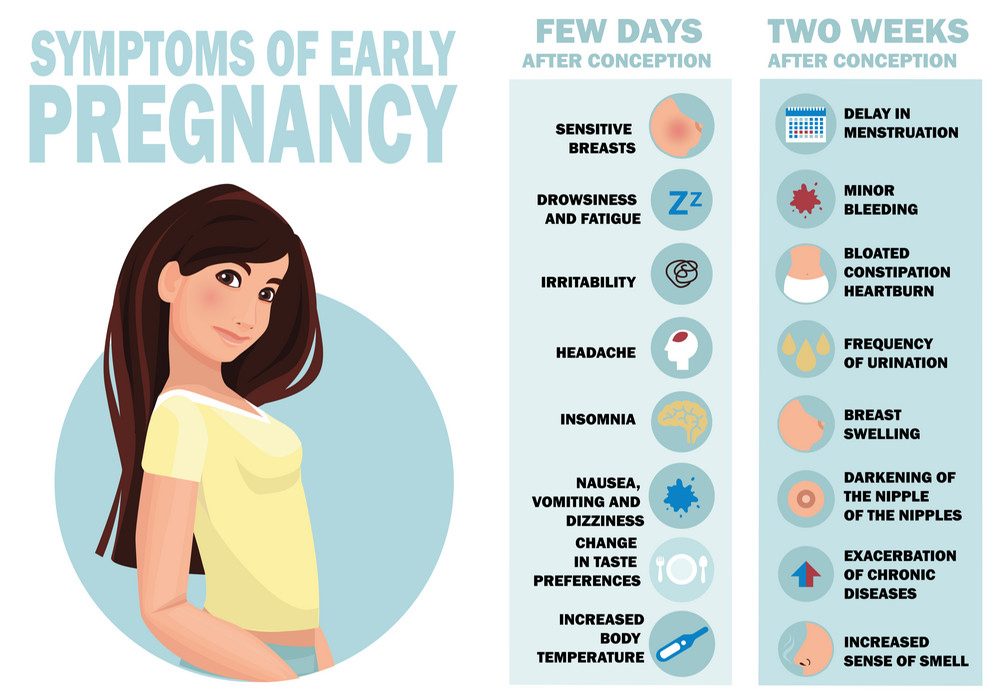
Symptoms of early
16 early signs of pregnancy
You’ve got one question on your mind: Could I be pregnant?
A pregnancy test is the only way to know for sure. But if it’s too early to take a test, you may be on the lookout for early signs – or maybe you think you’re already experiencing some early pregnancy symptoms.
Is it too early to tell if you’re pregnant? What symptoms may be the earliest signs of pregnancy? Below, we answer those questions and more.
How early can you tell if you’re pregnant?
Again, you’ll need to take a pregnancy test at the right time to confirm your hopes or suspicions. But when it comes to the first symptoms of pregnancy, everyone is different. Some people start to notice changes within a week after conception. Others might not notice anything until they miss their period.
When should you take a pregnancy test?
It’s usually recommended that you take a pregnancy test after you’ve missed your period. This is because pregnancy tests measure the level of human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) in your body, which is a hormone that starts to build up when you conceive. It can take around three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for there to be enough hCG in your body to show up on a test.
What are the first symptoms of pregnancy?
The most common sign of early pregnancy? A missed period.
Your menstrual cycle is your body’s way of preparing for a possible pregnancy each month. Part of that is the thickening of your uterine lining, which is where a fertilized egg would implant to begin a pregnancy.
If you’re not pregnant, your period is how your uterus sheds that extra lining. If you are pregnant, that lining stays put and you don’t get your normal flow. This is why a missed period is often the earliest sign of pregnancy.
Of course, a delayed or missed period doesn’t always mean you’re pregnant. If your body is under a lot of stress or you have a hormonal imbalance, you could be experiencing an irregular menstrual cycle.
What other symptoms can be early signs of pregnancy?
Every person – and every pregnancy – is different. So, if you are pregnant, you’ll likely experience a unique combination of common, not-so-common and sometimes overlapping symptoms. And, they may show up earlier or later than expected. Here are more than a dozen possible symptoms of early pregnancy.
So, if you are pregnant, you’ll likely experience a unique combination of common, not-so-common and sometimes overlapping symptoms. And, they may show up earlier or later than expected. Here are more than a dozen possible symptoms of early pregnancy.
1. Spotting or light bleeding
Many women are surprised to learn that spotting or light bleeding can be an early sign of pregnancy, but about one-third of women experience it. This is often called implantation bleeding because doctors believe it occurs as the fertilized egg attaches (or implants) itself into the uterine lining. This is different from bleeding that could occur from something like a miscarriage – which is usually heavier.
When does implantation bleeding occur?
Implantation bleeding typically occurs 10 to 14 days after conception, which is just before or right around the time your period is due. So, you may think you’ve gotten your period.
But implantation bleeding is a light flow, which may start and stop over a couple days. And while it can take on a range of colors, it’s more likely to be pink, brown or light red.
And while it can take on a range of colors, it’s more likely to be pink, brown or light red.
Your period, on the other hand, may start off light in flow and in color but after a couple days becomes heavier, changes to a crimson red color and lasts up to a week or so.
2. Lower abdominal pain or cramping
While cramps and lower-abdominal pain can signal a coming period, they can also be a sign of egg implantation.
What do implantation cramps feel like?
Implantation cramps can occur with or without spotting or bleeding, and may feel different from period cramps. For example, you might feel mild to moderate prickling, pulling or tingling that comes and goes over a few days.
But menstrual cramps can often feel like a throbbing or dull ache, and typically start a day or two before your period.
3. Higher basal body temperature
If you’ve been tracking your basal body temperature (BBT) to increase your chances of getting pregnant, you probably know that your BBT goes up slightly right after ovulation. If you’re pregnant, your temperature may remain elevated rather than dipping back down.
If you’re pregnant, your temperature may remain elevated rather than dipping back down.
Of course, you could be running hot for other reasons, but if it lasts more than a few weeks, pregnancy may be the explanation.
4. Changes in cervical mucus
If you’ve already been checking your cervical mucus to figure out when you’re most fertile, here’s a reason to continue: In the first few weeks of pregnancy, the amount of cervical discharge may increase and become stickier and whiter.
5. Breast tenderness, swelling or tingling
When you’re pregnant, your body experiences big changes in hormones – specifically, increases in estrogen and progesterone – to support your growing baby. This change in hormones can contribute to many symptoms, including breast tenderness.
Oftentimes, increased breast tenderness, swelling or tingling start to become noticeable a few days before a missed period.
If you usually experience breast tenderness leading up to your period or shortly after it begins, pregnancy-related breast tenderness and swelling will likely be more intense than you’re used to and stick around. You may also experience nipple soreness.
You may also experience nipple soreness.
6. Fatigue
Fatigue in early pregnancy is common, and some women might notice it before they know they’re pregnant. In fact, fatigue may set in as soon as one week after conception. This is thanks to those sudden changes in hormone levels, particularly increasing progesterone.
7. Frequent urination
If you’re making more trips to the bathroom than usual around the time your next period is due, it may be a sign of pregnancy.
Certainly, your drinking habits play a big role in how many times you pee in a day. However, pregnancy increases the amount of blood in your body, which gives your kidneys more fluid to filter and more waste to get rid of.
So if you’re pregnant, you may notice you’re peeing a lot more – a symptom that can start early on and (unfortunately) last throughout your pregnancy.
8. Nausea or vomiting
Morning sickness might be the most well-known of all pregnancy symptoms, taking the form of food aversion or nausea, and even vomiting for some. This symptom can set in as early as two weeks after conception, which is around the fourth week of pregnancy and right around the time you’d miss your period if you were pregnant.
This symptom can set in as early as two weeks after conception, which is around the fourth week of pregnancy and right around the time you’d miss your period if you were pregnant.
But some may not experience nausea or vomiting at all. And despite its name, morning sickness can actually happen at any time of the day or night.
9. Darkening areolas
When you’re pregnant, your areolas (the areas round your nipples) will likely grow and darken. Usually, these changes are gradual and continue throughout pregnancy. However, some women notice these changes really early on in combination with other symptoms.
10. Bloating or constipation
We all experience bloating or constipation from time to time, but both are quite common during pregnancy. Once again, those changing hormones are the culprit. They slow down digestion, which can cause a buildup of air in the gut and lead to constipation.
Early on, bloating or constipation may be mild and accompanied with other pregnancy symptoms.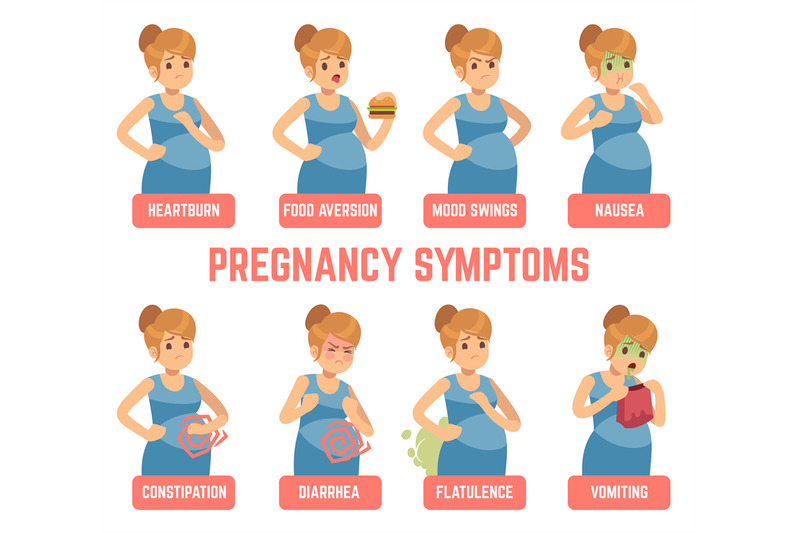 But – as a heads up – if you really are pregnant, these symptoms may stick around throughout your whole pregnancy.
But – as a heads up – if you really are pregnant, these symptoms may stick around throughout your whole pregnancy.
11. Metallic taste in your mouth
Many women report a metallic taste in their mouth during pregnancy. Once again, hormones are to blame – specifically, estrogen.
Typically, this symptom (as well as changes in taste overall) is common in the first trimester but may occur at other times too – including before a missed period.
12. Sensitivity to smell
Many women report that sensitivity to smell was one of their first signs of pregnancy. In fact, as many as two-thirds of women become more sensitive or reactive to the smells around them during pregnancy.
And oftentimes, this heightened sense of smell can stick around through the first trimester or beyond, and contribute to other symptoms such as nausea, and food cravings or aversions.
13. Mood changes
From a stressful day at work to the natural wonders of your menstrual cycle, there are a lot of things that can affect your mood. But changes in mood are very common during pregnancy – and they may be especially noticeable early on as your body gets a sudden burst of estrogen and progesterone.
But changes in mood are very common during pregnancy – and they may be especially noticeable early on as your body gets a sudden burst of estrogen and progesterone.
If you are pregnant, any mood changes you’re experiencing are likely coupled with other symptoms such as fatigue or nausea. You may feel more sensitive or weepy. Or perhaps your fuse is a little shorter and you’re more easily annoyed.
14. Headaches
Headaches are a part of life. They come with colds and allergies. They come with stress or fatigue, or when you cut down on caffeine to help prepare your body for pregnancy. But they can also come with pregnancy.
Headaches can happen thanks to the increasing blood volume and hormonal changes that occur in early pregnancy. You can also get headaches if you’re dehydrated as a result of nausea.
15. Dizziness
As blood flow increases during pregnancy, blood pressure can also decrease and lead to dizzy spells. Usually, dizziness is more of a second trimester symptom, but some women may notice it very early on, too.
16. Nasal congestion
A lot of people are shocked to learn that nasal congestion can be a pregnancy symptom. You may wonder if you’re coming down with something or your allergies are acting up. But if you’re noticing a stuffy or runny nose along with other pregnancy signs, you might be taking a pregnancy test in the near future.
The mucous membranes in the nose are also affected by hormones and increased blood flow throughout your body. This can cause blood vessels to swell, resulting in congestion and even sneezing.
Could you have early pregnancy symptoms and not be pregnant?
Yes. As we’ve mentioned, many early pregnancy symptoms can overlap with symptoms of other conditions, especially premenstrual symptoms. So, the best way to know if the symptoms you’re experiencing are pregnancy related is to try to relax and patiently wait until it’s time to take a pregnancy test.
When should you see a doctor about a new pregnancy?
If you’ve taken a pregnancy test and it’s positive, go ahead and make your first prenatal visit right away. This is also a great time to start looking into educational resources like the myHealthyPregnancy app.
This is also a great time to start looking into educational resources like the myHealthyPregnancy app.
At the first prenatal visit, you’ll get a physical exam and other tests to make sure everything is looking healthy, and you’ll learn about the rest of your prenatal appointment schedule. You’ll also get to talk through any expectations and questions you have, such as which foods to eat and avoid while pregnant.
What you can expect in your second trimester of pregnancy
You’ve just cleared a major hurdle and it’s time to celebrate – you’re into your second trimester! The second trimester generally lasts from week 14 to week 27 of pregnancy. (If you haven’t already shared your baby news with everyone, now might be the time to execute that baby announcement you’ve been eyeing on Pinterest.)
It’s during your second trimester that your growing baby bump will begin to pop out for the world to see. Your body will experience this and many more changes in your second trimester. Here’s a rundown of some symptoms and other milestones you can expect.
Here’s a rundown of some symptoms and other milestones you can expect.
Second trimester symptoms
As you enter the next 13 weeks, you may notice these changes:
Decreased morning sickness
If you experienced morning sickness in your first trimester, then you’re in luck – you’re probably going to experience less nausea in the second trimester. It’s not likely that morning sickness will come back in the second trimester, which means your appetite – and your energy – may return. But keep in mind that nausea could last for a few weeks into the second trimester, so you may need to keep drinking that ginger tea for just a bit longer.
Difficulty eating large meals
Your growing uterus might make it harder to eat larger meals. Instead, try to nibble on smaller amounts of food throughout the day. If you experienced morning sickness, you may already be used to this. Remember, you should be eating around 200 to 300 extra calories each day. You’ll feel better when you make healthy food choices, like lean proteins and complex carbohydrates. Fat takes more time to digest so it sits in your stomach longer, which can lead to constipation.
Fat takes more time to digest so it sits in your stomach longer, which can lead to constipation.
Increased energy
You’ll most likely feel less fatigued from pregnancy throughout the day, giving you more energy to do things you enjoy, like starting a baby registry. Make sure you get out and move, too. We recommend 30 minutes of activity a day such as walking, joining an exercise class, biking or swimming. Just stay away from activities that have a higher risk of injury (skiing – water or downhill, roller coasters, horseback riding, etc.). Be careful not to bump, injure or fall on your belly.
Some women still experience fatigue in their second trimester, so don’t get discouraged if it happens to you.
Dull headaches
Occasional headaches in the second trimester of pregnancy are normal but typically less frequent. They happen because your blood vessels have opened to get as much blood flow to the uterus as possible. They’re more common in the first trimester due to this increase in blood volume and the surge of hormones. By 12 to 15 weeks, your body will get used to the increased blood flow, and headaches usually decrease.
By 12 to 15 weeks, your body will get used to the increased blood flow, and headaches usually decrease.
Shortness of breath
With the heart working harder and your uterus starting to expand, shortness of breath may become a little more noticeable.
Round ligament pain
As your uterus grows, the ligaments in your midsection are getting stretched and pulled to support your uterus. This can cause discomfort on either side of your lower abdomen and can feel like light cramping, a stabbing pain or dull ache. Quick movements like turning from side-to-side in bed, standing, or laughing could cause the ligaments to stretch, triggering feelings of discomfort or pain. While minor pain is to be expected, if you experience extreme pain or bleeding, call your care team immediately.
Pelvic pain
Your ligaments stretch and loosen as your baby gets heavier, so the muscles supporting that weight have to work harder. You may start feeling more back, hip and pelvic discomfort or pain during the second trimester of pregnancy.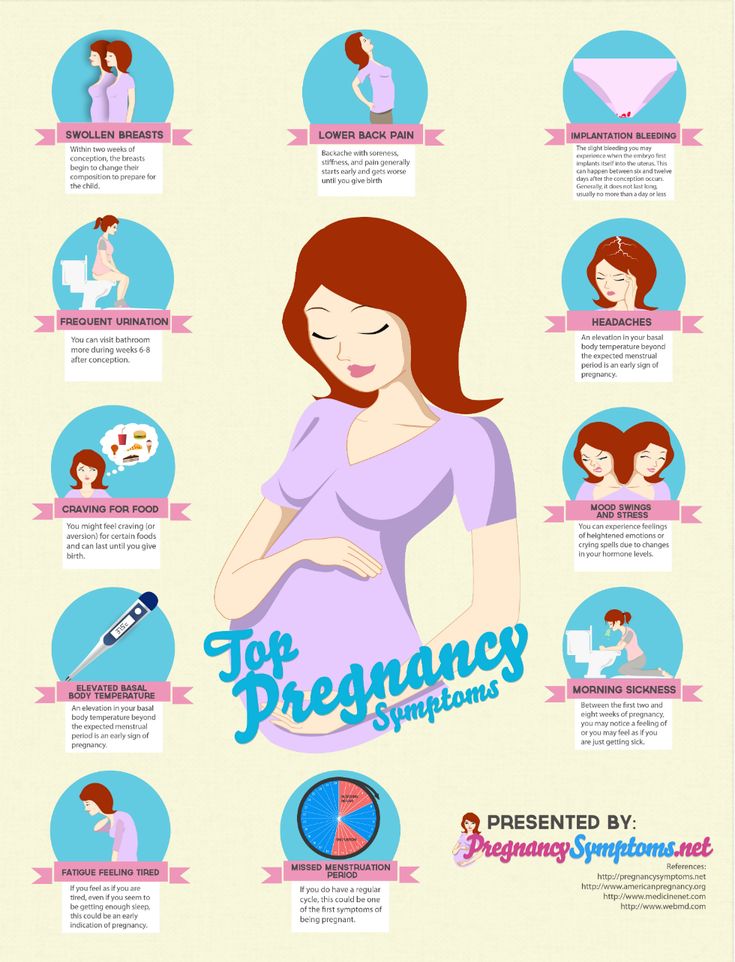
Emerging baby bump
By the 20-week mark, your uterus should be near your belly button. Depending on your body shape, you may start to see a prominent baby bump. If you haven’t started wearing pregnancy clothes already, now might be the time to start looking for new pieces of clothing. Or, you can try a trick for extending the waistband of your favorite pants: place a hair tie or rubber band around the button, loop it through the button hole on your pants and connect it back to the button.
Bleeding
Spotting or light bleeding in your second trimester is normal. But call your care provider if you’re bleeding enough to soak through more than one pad, or if your bleeding is paired with strong abdominal pain or passing pieces of tissue.
When will I feel my baby move for the first time?
Another joy that comes in the second trimester is finally feeling your baby move. It feels like flutters in your tummy, but these flutters can also be confused with gas bubbles. That’s why it may be tough for you to distinguish between your baby’s first kicks or the chicken salad sandwich you ate for lunch. You may be able to tell the difference by 20 to 22 weeks.
That’s why it may be tough for you to distinguish between your baby’s first kicks or the chicken salad sandwich you ate for lunch. You may be able to tell the difference by 20 to 22 weeks.
If you don’t feel your baby kick, don’t panic. Your placenta may be located at the front of your uterus. This creates a pillow between you and your baby. In a few more weeks, your baby will grow big enough so you can feel his or her movements through your placenta pillow.
What fetal development occurs in the second trimester?
In addition to starting to move, your baby undergoes a lot of changes during these weeks. Their fingers, toes and facial features develop and become more defined. Baby’s nervous system starts working, they start to store fat and in the latter half of the trimester, their eyes will open. By the time you reach the third trimester of your pregnancy, your baby will even respond to stimuli.
Other frequently asked questions
How should I sleep during the second trimester of pregnancy?
Until it becomes uncomfortable due to your baby bump, you can sleep on your stomach.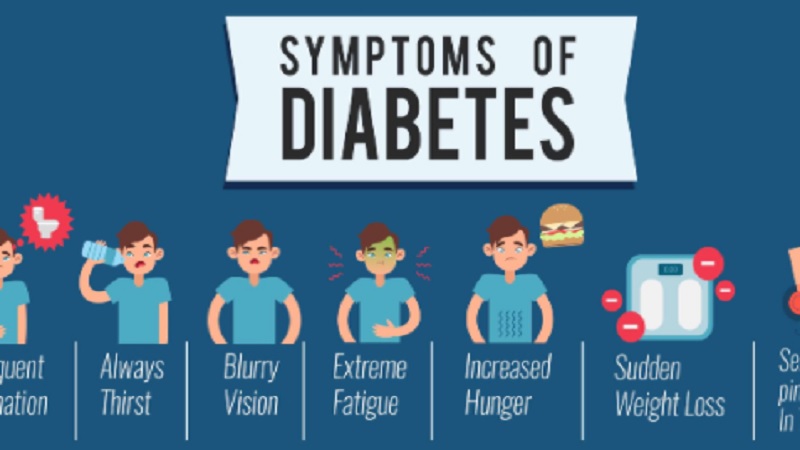 Otherwise, you can start getting used to sleeping on either your left or right side.
Otherwise, you can start getting used to sleeping on either your left or right side.
Is it safe to have intercourse during the second trimester of pregnancy?
Totally, unless your care team has told you otherwise (and you can still ask if you want to be sure). Just listen to your body, do what’s comfortable, and stop if you feel pain.
How much weight will I gain during the second trimester?
If you were at a healthy weight pre-pregnancy, you might start to gain weight a little faster now than you did in your first trimester. Overall recommended weight gain depends on your starting weight and how much you gained in the first trimester.
Is it normal to pee a lot in the second trimester?
While you may have experienced frequent trips to the bathroom during first trimester, it’s common to get a break in the second trimester. Your body is now more adapted to the change in hormones, plus your growing uterus will rise in your abdomen and take off some pressure, so you won’t feel the need to pee as often.
In the third trimester, you’re more likely to feel pressure on your bladder and take more trips to the bathroom. However, it’s still normal to feel like you have to pee a lot during any time in your pregnancy. Talk with your doctor if you notice pain when you urinate, cloudy, foul-smelling or blood-tinged urine, or are experiencing severe incontinence.
Second trimester tests
Both your body and your baby are growing rapidly and changing fast. This means your provider will want to monitor the health of you and your baby even more. During your second trimester, there are some routine, as well as optional, tests including:
Ultrasound
You’ve probably heard your baby’s heartbeat during your regular appointments. But during your ultrasound, you’ll get the first actual look at your baby. This ultrasound is scheduled around 19 to 22 weeks. This anatomy scan takes a closer look at your baby’s brain, heart, facial features and bone structure to make sure your baby is developing normally.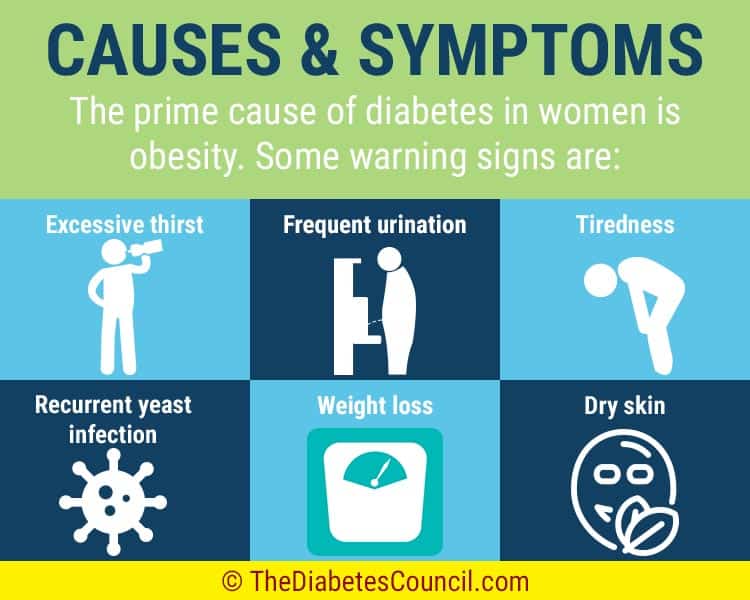 You can also use this ultrasound as an opportunity to find out if you are having a boy or a girl.
You can also use this ultrasound as an opportunity to find out if you are having a boy or a girl.
Gestational diabetes test
You’ll be scheduled for your gestational diabetes test around 24 to 28 weeks. There aren’t any symptoms associated with gestational diabetes, which is why taking this test is so important. During the test, you’ll drink a sugary juice and then we’ll monitor the glucose levels in your bloodstream. If your glucose levels are high, you’ll be asked to retake the test on another day. This second test will be longer and require you to fast beforehand.
Anemia screening
Your blood vessels are opening during your second trimester and, as a result, the amount of blood pumping through your veins is increasing. When this happens, your red blood cell count could decrease and you could become anemic. This is quite common during pregnancy and it means you’ll probably need to add more iron and vitamins to your diet.
Genetic testing
These are optional screening tests that can be started as early as 11 weeks into your pregnancy. These tests include a blood draw to evaluate pregnancy hormones levels and may include an ultrasound. They can help determine if your baby has genetic abnormalities like Down syndrome or spina bifida.
These tests include a blood draw to evaluate pregnancy hormones levels and may include an ultrasound. They can help determine if your baby has genetic abnormalities like Down syndrome or spina bifida.
Genetic tests may be recommended during your pregnancy if you are over age 35 or have other risk factors. It’s best to talk with your provider to find out more information and discuss the specific types of tests available. Then you can decide if there are any that are right for you.
Routine tests will likely be covered under your insurance benefits. In some instances, genetic screenings may not be covered. When in doubt, call your insurance provider to learn more about your specific benefits.
One down, two to go
The second trimester is an exciting part of your pregnancy. You often feel better and have more energy, (which is super helpful as you begin to prepare the nursery or make a birth plan!). And of course, as your pregnancy progresses, don’t hesitate to ask your provider questions about your symptoms or what to expect as you approach your due date.
Early signs of autism in children
Children's Medical Center of Neurology and Pediatrics offers you a service - diagnosis of early autism in children. Our experts have many years of experience and excellent reviews!
Signs of early autism in children can manifest themselves quite differently, but the disease and symptoms are individual. In some cases, the early signs of autism can even be confused with the good behavior of the baby: he is undemanding, calm and independent. Therefore, you should pay attention to whether your child corresponds to the main stages of development of peers. There are a number of markers that need to be highlighted. nine0003
Signs of early autism in children under 1 year old:
- By 6 months the child does not show obvious emotions, even meeting with his mother does not cause him to change his emotional background.
- By 9 months, the baby does not try to babble, does not look for visual contact, it may seem that he is not looking into your eyes, but through you.
 Does not respond to his name, while in other situations does not show hearing problems. The child does not attempt to initiate or respond to the mother's hugs. He doesn't even like tactile contact. nine0010
Does not respond to his name, while in other situations does not show hearing problems. The child does not attempt to initiate or respond to the mother's hugs. He doesn't even like tactile contact. nine0010 - By the age of 1 year, a delay or lack of development of spoken language is clearly noticeable, not accompanied by attempts to compensate for it with other forms of communication, for example, gestures.
The disease itself, as a rule, manifests itself before the age of two, it is at this age that a diagnosis can be clearly made. However, the sooner we start treatment, the more chances for a fruitful result!
Signs of early autism in children 2 years old:
- The child does not point to objects that could interest him in the world around him. At the age of 14-16 months, ordinary children actively use sign language. nine0010
- Does not understand simple one-step instructions, such as asking to show where a block or toy is.
- The kid does not use speaking skills, there are often cases when the child goes into some kind of regression, i.
 e. before that, he tried to show verbal activity and suddenly begins to lose verbal skills. Similar cases of regression occur in the social field, as if the child withdraws into himself.
e. before that, he tried to show verbal activity and suddenly begins to lose verbal skills. Similar cases of regression occur in the social field, as if the child withdraws into himself. - Quite often the child limits his motor activity. nine0010
- Shows emotions in a way that others do not understand, for example, may laugh or cry inappropriately.
Signs of early autism in a child of 3 years old:
The older the child becomes, the stronger the symptoms, here we can already talk about the current picture of the disease.
- During everyday play, a child with early autism tends to focus on one object or detail, i.e. he may be interested only in the wheel of the machine. Therefore, he does not carry the machine on the carpet, but simply turns its wheel with his fingers. Thus, all games look one-sided, they are devoid of creativity and fantasy. nine0010
- Interested in unusual objects or activities.
- Such a child likes the same type of movements, for example, flipping through a book, playing with a switch, turning the lights on and off in the room repeatedly.
 He spends a lot of time arranging objects in a certain order.
He spends a lot of time arranging objects in a certain order. - He does not understand games related to imitation, he will not participate in pretend play, artistic creativity is not for them.
- They are not interested in games with their peers, they prefer to spend time alone. nine0010
- Such a child often uses stereotyped behavior, any deviation from the usual state of affairs can cause a violent reaction, up to hysteria. For example, a simple trip to the store or a walk along a new route can lead to the above described explosion of emotions. The same applies to eating habits, the baby can react sharply to a new dish, refuses to eat many foods.
- Is overly sensitive to various types of external stimulation, for example, external noise, unfamiliar smell, even new clothes or some kind of accessory on it can affect the child's mood. Unexpectedly reacts to the manifestation of painful or irritating factors, from a sharp sound, he may panic, while some real pain syndrome may go unnoticed.
 nine0010
nine0010 - Also, the baby is selective about fears, he can be afraid of an ordinary, everyday household item and at the same time not be afraid of objects that can bring a real threat to health or life.
- Another very obvious manifestation is trouble sleeping. Such a child falls asleep heavily, his sleep is interrupted and disturbing.
- A child with early autism is prone to repetitive behavior.
- Prone to changes in emotional background and behavior. nine0010
All medical and nursing staff of our clinic are highly qualified and professional. All our doctors are constantly practicing specialists, doctors of the highest category, doctors of sciences, associate professors. Thanks to our working methods, you can be sure that you are in a professional clinic, which means that we guarantee the result.
Also read about the disease: autism in children.
Early menopause. What is Early Menopause? nine0001
IMPORTANT
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Early menopause is a complex of changes that occur with estrogen deficiency and are accompanied by early (up to 45 years) or premature (up to 40 years) cessation of menstruation. The level of female sex hormones at a young age decreases with aggravated heredity, trauma, inflammation and neoplasms of the ovaries, their removal, drug or toxic inhibition of function. Early menopause can also be manifested by vasomotor, emotional and metabolic-trophic disorders. The diagnosis is established on the basis of typical complaints and a laboratory-confirmed decrease in estrogen levels. The main method of treatment is hormone replacement therapy. nine0003
- Causes of early menopause
- Pathogenesis
- Classification
- Symptoms of early menopause
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of early menopause
- Prognosis and prevention
- Prices for treatment
General
Early onset of menopause (early menopause or menopause) is a fairly rare condition, the prevalence of which has not yet been precisely established.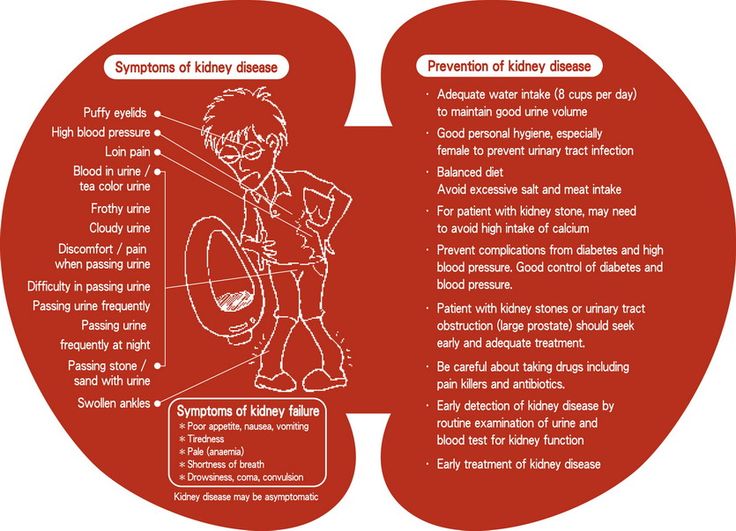 It is observed in women under the age of 35-45 years with previously normal menstrual and reproductive functions. Some experts in the field of gynecology refer to cases of premature ovarian failure, not associated with their damage or removal, wasted ovary syndrome. Although menopause is one of the physiological periods of a woman's life, its early development in 60-80% of cases is accompanied by uncomfortable subjective sensations of varying severity and pathological changes in various organs and systems. nine0003
It is observed in women under the age of 35-45 years with previously normal menstrual and reproductive functions. Some experts in the field of gynecology refer to cases of premature ovarian failure, not associated with their damage or removal, wasted ovary syndrome. Although menopause is one of the physiological periods of a woman's life, its early development in 60-80% of cases is accompanied by uncomfortable subjective sensations of varying severity and pathological changes in various organs and systems. nine0003
early menopause
Causes of early menopause
Premature extinction of a woman's reproductive function is associated with a decrease or cessation of the production of sex hormones. As a rule, early menopause lead to:
- Genetic anomalies. Scientists have identified genes that prematurely stop ovarian function or reduce their sensitivity to the action of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
 Early onset of menopause due to ovarian exhaustion is also observed in a number of hereditary diseases (galactosemia, blepharophimosis, etc.). nine0010
Early onset of menopause due to ovarian exhaustion is also observed in a number of hereditary diseases (galactosemia, blepharophimosis, etc.). nine0010 - Tumors of the ovaries. Volumetric neoplasms with intensive growth can damage healthy follicular tissue.
- Operations on the ovaries. Resection or removal of the ovaries is performed in case of their traumatic injury, surgical treatment of benign and malignant tumors, ectopic pregnancy.
- Intense radiation exposure. Receiving a total radiation dose of 6 Grays during radiation therapy of the pelvic organs or radiation during an accident at a nuclear facility causes irreversible damage to ovarian tissue. nine0010
- Chemotherapy. The production of estrogens can be disturbed in the treatment of tumors using drugs that suppress cell division. The treatment regimen for hormone-sensitive malignant neoplasms involves the appointment of drugs that depress ovarian function.
- Autoimmune diseases. With autoimmune processes occurring in the gonads, there is a replacement of follicles with scar tissue.
 Ovarian damage also occurs with Addison's disease, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and some other diseases. nine0010
Ovarian damage also occurs with Addison's disease, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and some other diseases. nine0010
Pathogenesis
With early menopause in the ovaries, the number of follicles gradually decreases and, accordingly, the secretion of estrogens decreases. By the end of the third year of postmenopause, only single follicles can be identified, which subsequently completely disappear. Against the background of a reduced level of estrogen, the pituitary gland secretes more FSH, which leads to the occurrence of hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Since receptors for female sex hormones are found in most organs and tissues, the development of estrogen deficiency is accompanied not only by reproductive dysfunction (amenorrhea, uterine involution, etc.), but also by changes in the limbic and other systems. nine0003
Classification
The classification of early menopause is based on the phased nature of its development. There are the following phases:
There are the following phases:
- Premenopause. The stage between the first symptoms and the last menstruation, lasting an average of 6-8 years.
- Menopause. A period of 12 months without menstruation after the last period, which passed on its own as a result of the functioning of the ovaries.
- Postmenopausal. Time span after menopause up to 65-69years: early postmenopause - the first 5 years after menopause; late postmenopause - more than 5 years after menopause.
Symptoms of early menopause
The first sign of premature ovarian failure is a change in the menstrual cycle. The interval between individual periods is usually extended to 35 days or more, less often it is shortened. Allocations become plentiful or, conversely, scarce. At the end of early premenopause, there are periods of secondary amenorrhea - the absence of menstruation for six months or more. A woman, as a rule, cannot become pregnant. Due to a lack of hormones, hot flashes are observed: a fever is felt, the face reddens, and in some cases the upper body, sweat is plentiful, and shortness of breath occurs suddenly. The patient becomes irritable, tearful, her sleep is disturbed, her working capacity decreases, her performance of tasks related to memorizing and analyzing information worsens. nine0003
Due to a lack of hormones, hot flashes are observed: a fever is felt, the face reddens, and in some cases the upper body, sweat is plentiful, and shortness of breath occurs suddenly. The patient becomes irritable, tearful, her sleep is disturbed, her working capacity decreases, her performance of tasks related to memorizing and analyzing information worsens. nine0003
Dishormonal changes in the myocardium lead to shortness of breath when walking and physical activity, interruptions in the work of the heart. Discomfort and stabbing pains appear in the left half of the chest, not associated with stress, but sometimes quite intense and prolonged. Violation of vascular tone is accompanied by headaches, dizziness, a sudden increase or decrease in blood pressure. Due to the slowdown in lipid metabolism, body weight increases. In the area of the chin and above the upper lip, excess hair occurs. nine0003
In menopause and early postmenopause, the skin looks drier and wrinkled, nails and hair become brittle, dull, and their growth slows down.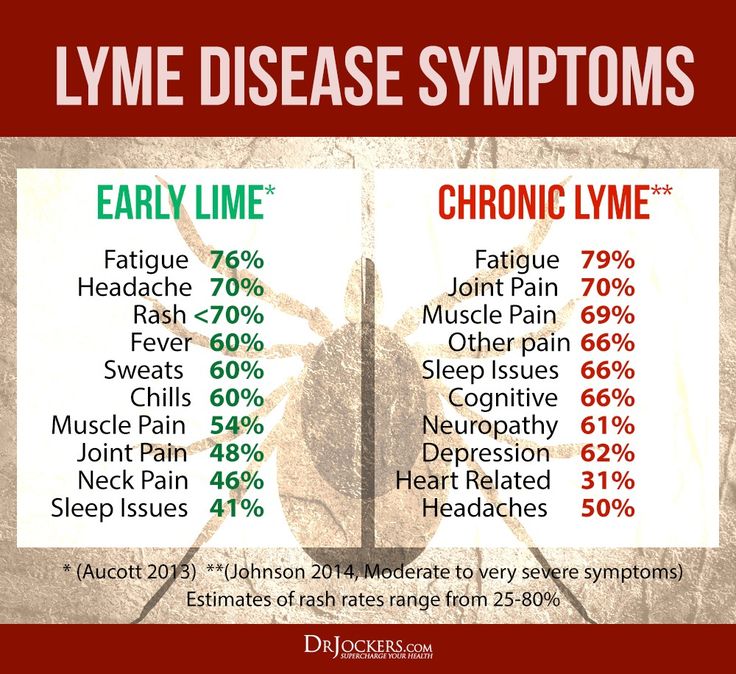 Typical urogenital disorders develop: imperative urge to urinate, urinary incontinence during sudden movements, during coughing and laughter. Due to the dryness of the mucous membranes of the external genital organs and the vagina, itching and burning appear. Decreased sex drive. In the period of late postmenopause, memory, hearing and vision may be impaired, blood pressure may increase, there may be curvature and increased fragility of bones, bone and joint pain, posture disorders, and arthritis. nine0003
Typical urogenital disorders develop: imperative urge to urinate, urinary incontinence during sudden movements, during coughing and laughter. Due to the dryness of the mucous membranes of the external genital organs and the vagina, itching and burning appear. Decreased sex drive. In the period of late postmenopause, memory, hearing and vision may be impaired, blood pressure may increase, there may be curvature and increased fragility of bones, bone and joint pain, posture disorders, and arthritis. nine0003
Complications
Early menopause is complicated by dysfunctional uterine bleeding, infertility and diseases associated with a lack of estrogen. Without correction of disorders, osteoporosis with a tendency to pathological fractures, atherosclerosis with an increased risk of developing hypertension, myocardial infarction and stroke are significantly more common. Autoimmune processes occur or worsen - Hashimoto's thyroiditis, autoimmune alopecia, adrenal insufficiency, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.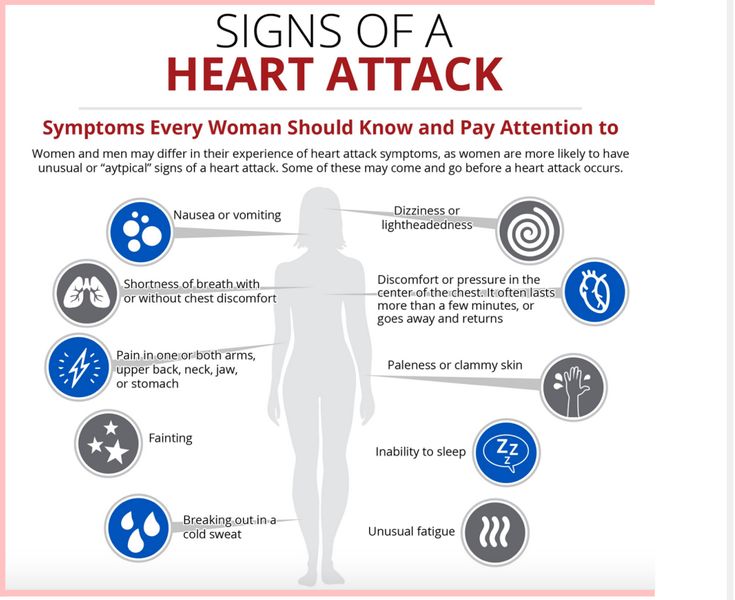 The risk of developing benign and malignant neoplasms of the mammary glands, ovaries, and uterus increases. nine0003
The risk of developing benign and malignant neoplasms of the mammary glands, ovaries, and uterus increases. nine0003
Diagnostics
Timely detection of signs of early onset of menopause allows not only to prevent the development of quite serious diseases, but also to improve the quality of life of a woman. The comprehensive survey plan includes:
- Gynecological consultation. When collecting an anamnesis, typical symptoms are revealed, which are assessed using the Kupperman index. When viewed in dynamics, the “pupil” symptom always remains negative, and the cervical mucus tension indicator is low. nine0010
- Hormonal studies. Already in the initial period of early menopause, the concentration of estradiol, inhibins (especially inhibin B), and sex hormone-binding globulins (SHBG) decreases. At the same time, the content of FSH increases. The ratio of levels of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones is disturbed. Both an increase and a deficiency of androgens can be observed.
- Colpocytological examination. There is a shift to the left of the maturation index (MI) with an increased content of parabasal and basal cells of the vaginal epithelium. nine0010
- Study of lipid metabolism. The total level of cholesterol and low density lipoproteins increases, the content of high density lipoproteins decreases.
- Transvaginal ultrasound. Thinning of the endometrium, hypoechoic areas characteristic of myometrial fibrosis, in postmenopausal women - synechia and a slight accumulation of fluid in the uterus are revealed.
- Doppler ultrasound. There is a decrease in blood flow in the muscular layer of the uterus.
In the postmenopausal period, studies play an important role in determining possible complications: osteodensitometry to detect osteoporosis, ECG to diagnose heart pathology, mammography and cervical scraping cytology (PAP test) to detect neoplasms that occur against the background of hormonal imbalance. The severe course of early menopause must be differentiated from diseases of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, hyperprolactinemia, tumors of the pituitary gland and ovaries. Consultations of an endocrinologist, oncologist, oncogynecologist, neuropathologist are shown. nine0003
The severe course of early menopause must be differentiated from diseases of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, hyperprolactinemia, tumors of the pituitary gland and ovaries. Consultations of an endocrinologist, oncologist, oncogynecologist, neuropathologist are shown. nine0003
Early menopause treatment
Since the clinical manifestations of the climacteric syndrome are associated with estrogen deficiency, with its pathological course, hormonal correction is indicated. For this purpose, the patient is assigned:
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT). The most effective female sex hormones. Depending on the underlying disease that provoked the early development of menopause, estrogens, gestagens, combinations of estrogens with progestins or androgens are used. Given the possible side effects from the use of hormonal drugs, the presence of absolute and relative contraindications to hormone therapy, a specific scheme should be selected by a gynecologist.
 nine0010
nine0010 - Phytoestrogenic medicines. If there are contraindications to HRT or if a woman refuses to take hormonal drugs, phytoestrogenic drugs are recommended. They are produced from plant materials containing non-steroidal molecules with an estrogen-like effect.
- Topical application of estrogen-containing agents. The appointment of suppositories, creams, gels, etc. is justified with involutive changes in the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, vagina and external genital organs. nine0010
In order to prevent and treat possible complications, sedatives, agents that improve cardiac and cerebral blood flow, vitamin and vitamin-mineral complexes, and calcium preparations can be used. Physiotherapy is effective, aimed at maintaining the tone of the muscles of the pelvic floor and the functional state of the musculoskeletal system.
Prognosis and prevention
With the preservation of ovarian tissues, the appointment of hormone replacement therapy can reduce typical menopausal symptoms by 92-95% of cases, reduce the severity of urogenital disorders in 85% of women, improve the condition of the skin and hair, and in some cases maintain and even restore menstruation (up to 10% of patients).