Stomach pains in second trimester
Stomach pain in pregnancy - NHS
Stomach (abdominal) pains or cramps are common in pregnancy. They're usually nothing to worry about, but they can sometimes be a sign of something more serious that needs to be checked.
It's probably nothing to worry about if the pain is mild and goes away when you change position, have a rest, do a poo or pass wind. But if you have stomach pains and are worried, call your midwife or maternity hospital.
Harmless stomach pains, which can be dull or sharp, may be caused by:
- ligament pain (often called "growing pains" as the ligaments stretch to support your growing bump) – this can feel like a sharp cramp on one side of your lower tummy
- constipation – which is common in pregnancy (find out how to avoid constipation)
- trapped wind
Urgent advice: Call your midwife immediately if you have stomach pain and:
- bleeding or spotting
- regular cramping or tightenings
- vaginal discharge that's unusual for you
- lower back pain
- pain or burning when you pee
- the pain is severe or does not go away after you've rested for 30 to 60 minutes
Any of these could be the symptoms of something that needs to be checked or treated urgently.
Possible causes of serious stomach pain
Some conditions that can cause stomach pain need to be checked urgently.
Ectopic pregnancy
This is when a fertilised egg implants outside the womb, for example in a fallopian tube. The pregnancy cannot survive and needs to be removed with medicine or surgery.
Symptoms typically appear between 4 and 12 weeks of pregnancy and can include:
- tummy pain and bleeding
- pain in the tip of your shoulder
- discomfort when pooing or peeing
Find out more about ectopic pregnancy
Miscarriage
Cramping pains and bleeding before 24 weeks of pregnancy can sometimes be a sign of miscarriage or threatened miscarriage (when you bleed but the pregnancy normally continues).
Pre-eclampsia
Pain just under the ribs is common in later pregnancy due to the growing baby and uterus pushing up under the ribs.
But if this pain is bad or persistent, particularly on the right side, it can be a sign of pre-eclampsia (high blood pressure in pregnancy) which affects some pregnant women. It usually starts after 20 weeks or just after the baby is born.
Other symptoms of pre-eclampsia include:
- severe headache
- vision problems
- swollen feet, hands and face
You'll need to be monitored in hospital.
Find out more about pre-eclampsia
Premature labour
If you're less than 37 weeks pregnant and are having regular abdominal cramps or tightenings, call your midwife.
This could be a sign of premature labour, and you'll need to be monitored in hospital.
Placental abruption
This is when the placenta starts to come away from the wall of the womb, usually causing bleeding and constant severe pain that does not come and go like a contraction pain.
It's sometimes an emergency because it means the placenta may not be able to support your baby properly.
You should go to the hospital so you and your baby can be checked.
Find out more about placental abruption
UTI (urinary tract infection)
UTIs are common in pregnancy and can usually be easily treated. They can cause tummy pain and sometimes, but not always, pain when you pee.
Find out more about UTIs
Page last reviewed: 20 June 2021
Next review due: 20 June 2024
Second trimester pains: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
Although all pregnancies are different, certain symptoms tend to occur in each trimester. For some women, the second trimester means the end of morning sickness and fatigue, but it also means the onset of specific types of pain.
For some women, the second trimester means the end of morning sickness and fatigue, but it also means the onset of specific types of pain.
Pregnancy consists of three trimesters. The second trimester lasts from weeks 13 to 28.
In this article, learn what causes pain in the second trimester and how to find relief.
Second trimester pains are not uncommon, as the uterus and abdomen are expanding.
Increased pressure from a growing uterus, along with hormonal changes, can lead to various types of pain.
Some common causes of second trimester pains include:
Round ligament pain
Share on PinterestCommon causes of second trimester pains include round ligament pain and back pain.The round ligaments support the uterus and hold it in place. During pregnancy, the expanding uterus causes these ligaments to stretch.
Round ligament pain often starts as the belly grows in the second trimester.
Symptoms of round ligament pain include:
- a sharp or aching sensation, usually on one side of the belly
- pain that is more noticeable after exercise or when changing positions
- pain that may radiate to the groin or hip
Round ligament pain may last from a few seconds to several minutes.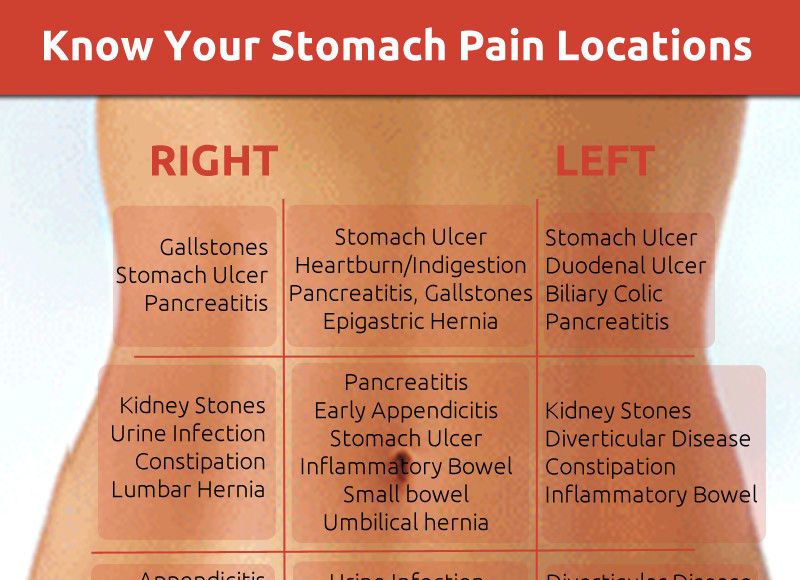
Braxton-Hicks contractions
Braxton-Hicks contractions may start anytime in the second trimester of pregnancy. They involve the tightening of the uterus’ muscles.
These contractions differ from true labor in a few critical ways — they are brief and do not come at regular intervals.
Symptoms of Braxton-Hicks contractions include:
- squeezing or tightening of the uterus
- pain that occurs more frequently at night
- pain lasting anywhere from 30 seconds to 2 minutes
Braxton-Hicks contractions may be mild at first, but they can become more painful as pregnancy progresses.
Leg cramps
Leg cramps are a common cause of pain during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
They can develop when blood vessels or nerves in the legs are compressed. A lack of magnesium in the diet can also cause leg cramps.
Restless legs syndrome, which causes discomfort in the legs, can also occur during pregnancy.
Some research indicates that restless legs syndrome develops 2 to 3 times more often in pregnant women than the rest of the population.
Symptoms of leg cramps include:
- sudden pain in the calf or foot
- involuntary contractions of the muscles in the calf
- pain that may be worse at night
Symphysis pubis dysfunction
Symphysis pubis dysfunction, or pelvic girdle pain, may occur in about 31 percent of pregnant women.
The weight of the uterus can place extra stress on the pelvic joints, causing them to move unevenly.
Symphysis pubis dysfunction can also result from hormonal changes. During pregnancy, the body releases hormones that loosen and stretch certain ligaments in preparation for childbirth. These changes can contribute to pelvic pain.
Symptoms of symphysis pubis dysfunction include:
- pain in the center of the pubic bone
- pain radiating to the thighs or perineum (the area between the vagina and anus)
- difficulty walking
Back pain
Low back pain is one of the most common types to arise during pregnancy, and it often starts during the second trimester.
According to some research, about two-thirds of pregnant women develop low back pain.
Usually, it occurs because the growing abdomen is placing strain on the back muscles and causing changes in posture.
Symptoms of low back pain include:
- achy or dull pain in the lower back
- pain that worsens when bending forward
- stiffness in the back
Share on PinterestWomen who experience vaginal bleeding, vomiting, or fever during the second trimester should see a doctor.
Most common causes of second trimester pain do not require medical attention. However, pain at this stage of pregnancy can signify a problem, such as preterm labor, an infection, or another complication.
See a doctor if any of the following symptoms develop:
- contractions that occur at regular intervals
- vaginal pressure
- vaginal bleeding
- a severe headache
- sharp pain in the belly that persists, even after resting or changing positions
- vomiting, chills, or fever
- menstrual-like cramps that grow more severe over time
- fluid leaking from the vagina
Before using pain relievers during the second trimester, it is vital to speak to a doctor. Some pain medications are not safe to take during pregnancy.
Some pain medications are not safe to take during pregnancy.
Certain complementary therapies may help reduce low back or pelvic pain.
A study involving 191 pregnant women found that complementary therapies, including acupuncture, aromatherapy, and reflexology, reduced symptoms in 85 percent of the participants.
Before trying any of these approaches during pregnancy, it is essential to talk with a doctor.
Home remedies can usually relieve second trimester pain, and the best approach will depend on the type of pain.
The following strategies may help:
- taking a warm (not hot) bath
- doing some light stretching to ease stiffness
- using a heating pad on the lower back
- wearing a maternity support belt
- using chairs with good back support
- avoiding standing in one spot for too long
- sleeping on the right or left side with a pillow between the legs
- avoiding changing positions too fast
- resting
Many types of pain can arise in the second trimester, including round ligament pain, back pain, and pain that results from symphysis pubis dysfunction.
In most cases, the underlying cause is a common issue, and a person can treat it at home.
In some instances, pain during the second trimester is a sign of something more serious. It is always best to see a doctor if the pain does not improve or otherwise causes concern.
Second trimester — Motherhood in Khabarovsk
How the body changes, 16 week
How your body changes in the 15th week of pregnancy
The fundus of the uterus is already a few centimeters below the navel, but your pregnancy is not yet visible to outsiders.
In this trimester, your skin changes - spider veins may appear, and moles and freckles become darker. In addition, you may develop tiny skin growths called polyps and cryptic bumps. nine0003
The hormonal boom of early pregnancy has subsided and you feel much better.
How the body changes, 17 week
How your body changes in the 16th week of pregnancy
The uterus and placenta are growing, and the amount of amniotic fluid is gradually increasing. At this time, they are about 250 milliliters. There is more blood, which is why you probably noticed that the skin is "radiant" and the hair is thicker. Perhaps your vaginal discharge has changed.
At this time, they are about 250 milliliters. There is more blood, which is why you probably noticed that the skin is "radiant" and the hair is thicker. Perhaps your vaginal discharge has changed.
Beginning of month 4: how you feel
From this month, the uterus extends beyond the small pelvis and grows quite rapidly in the abdominal cavity. At the beginning of the month, the bottom of the uterus barely shows above the pubic joint, and by the end it is almost at the level of the navel. Such a rapid increase in the uterus causes stretching of its ligamentous apparatus, which many pregnant women perceive as a sharp pain in the lower abdomen and in the inguinal regions. Such pains come on suddenly and pass quickly. nine0003
At the beginning of the month, the bottom of the uterus barely shows above the pubic joint, and by the end it is almost at the level of the navel. Such a rapid increase in the uterus causes stretching of its ligamentous apparatus, which many pregnant women perceive as a sharp pain in the lower abdomen and in the inguinal regions. Such pains come on suddenly and pass quickly. nine0003
Usually, by this time, the toxicosis is weakening, the hormonal background is evened out. You don't have mood swings that often anymore. Constipation, if tormented you - recede. All the baby's organs are formed and their "polishing" begins. He already knows how to move his arms and legs, swallow amniotic fluid. You can already actively engage in physical activity, visit the pool, yoga for pregnant women, if you have no contraindications. The body of the fetus is already less susceptible to harmful environmental influences. nine0003
How the body changes, 18 week
How your body changes in the 17th week of pregnancy
The breast changes even more noticeably.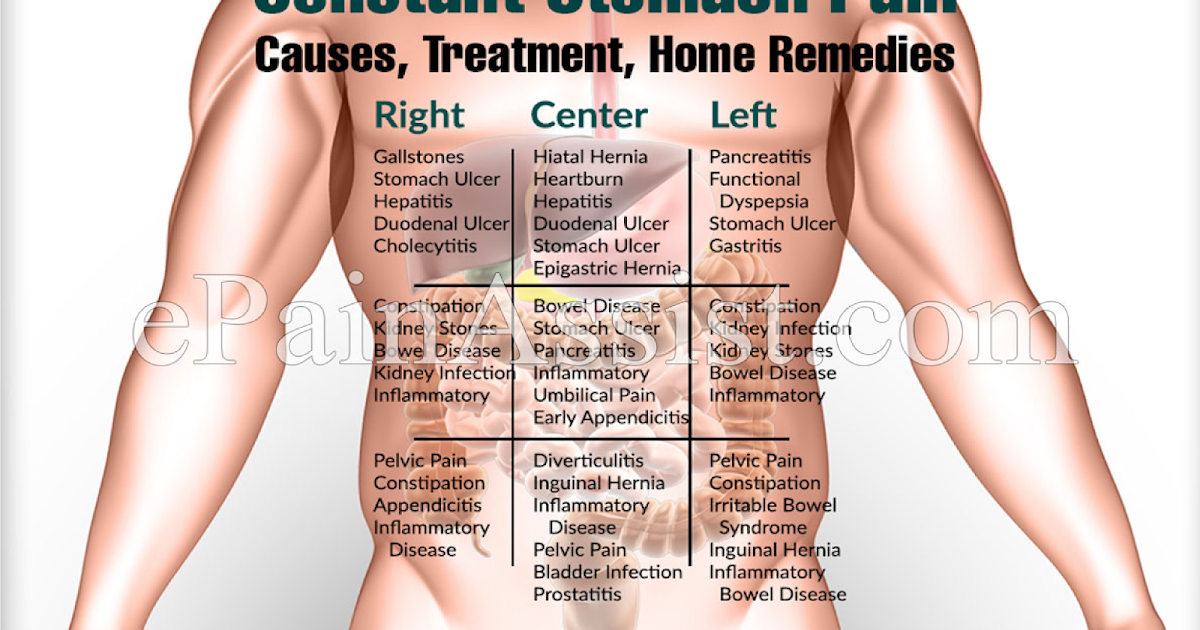 Probably, your nipples have grown, and the skin around them - the areola - has darkened. The uterus is growing, and your tummy is already noticeable. The uterus pushes the intestines up and to the sides. If you've had a belly button piercing, you'll want to take your jewelry off because it will be uncomfortable.
Probably, your nipples have grown, and the skin around them - the areola - has darkened. The uterus is growing, and your tummy is already noticeable. The uterus pushes the intestines up and to the sides. If you've had a belly button piercing, you'll want to take your jewelry off because it will be uncomfortable.
The ligaments that hold the uterus are stretched, and you may feel slight pulling pains in the lower abdomen on both sides.
How the body changes, nineteenweek
How your body changes at 18 weeks pregnant
The uterus is already the size of a melon and is growing all the time.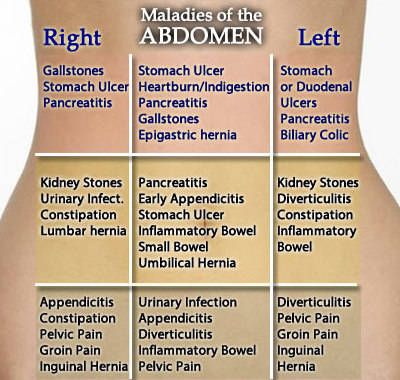 Probably because the center of gravity has shifted, your back sometimes hurts.
Probably because the center of gravity has shifted, your back sometimes hurts.
Among other changes, you will probably note the appearance on the abdomen, from the navel to the pubic bone, of a dark line, which in Latin is called "linea nigra" - "black line", although in fact it is not black, but rather brown. On dark skin it is not visible at all. nine0003
You may have gained some weight. Most women gain weight gradually, but if you're concerned about weight gain, talk to your doctor.
Second trimester, 18-20 week
Changes in a woman's body: 17-20 weeks
Your clothes will now become tight as the bottom of the uterus has reached the level of the navel. Sweating will probably increase, and vaginal discharge will appear. Gum problems can develop due to high blood flow and high levels of the hormone progesterone, which softens the tissues of the body, so you will have to see a dentist. nine0003
Sweating will probably increase, and vaginal discharge will appear. Gum problems can develop due to high blood flow and high levels of the hormone progesterone, which softens the tissues of the body, so you will have to see a dentist. nine0003
How the body changes, 20 week
How your body changes in the 19th week of pregnancy
Your uterine fundus is probably just below your belly button, and if you're expecting twins, it's already higher.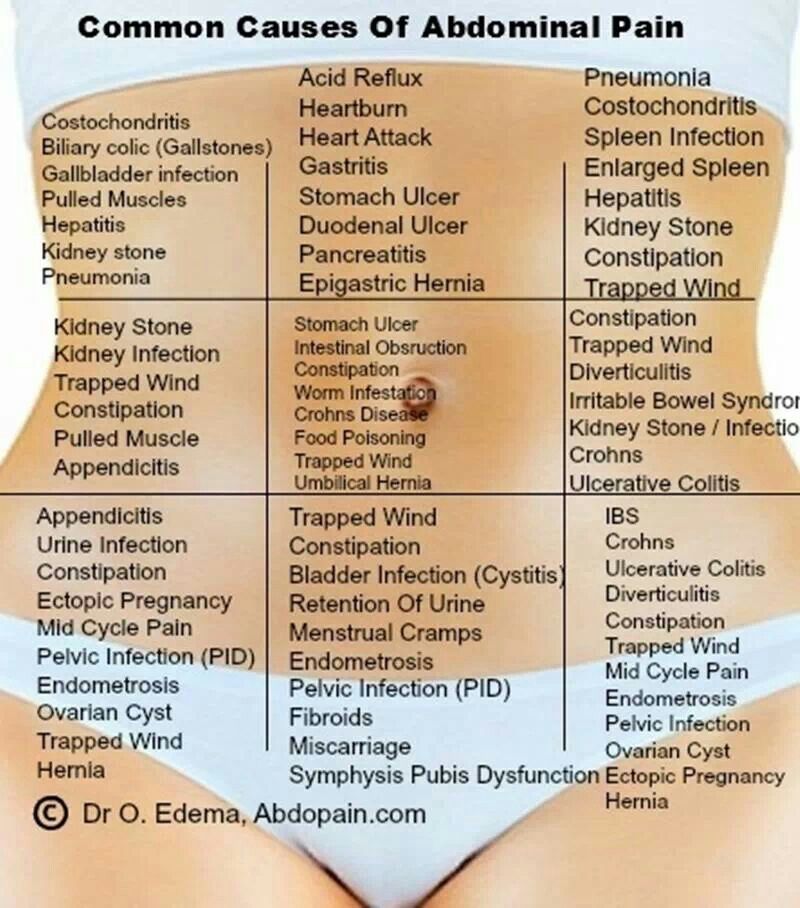 Look at yourself from the side, and you will immediately see how your silhouette has changed.
Look at yourself from the side, and you will immediately see how your silhouette has changed.
Now is the time to find out how childbirth has changed over a couple of generations and what opportunities you have to organize childbirth.
nine0002 Second trimester, 16-20 weekSecond wind during the second trimester of pregnancy
Between 15 and 20 weeks you will start to look really pregnant. You will feel an increase in energy and vitality, you will notice an improvement in the condition of your hair and skin. In many women, due to the rise in hormone levels, sexual desire increases.
You will feel an increase in energy and vitality, you will notice an improvement in the condition of your hair and skin. In many women, due to the rise in hormone levels, sexual desire increases.
How your body changes in the 20th week of pregnancy
The fundus of the uterus is probably already at the level of the umbilicus. From this moment until about the 36th week, the fundus of the uterus will rise all the time. The constancy of this rise is more important than the numbers indicating the height of the uterine fundus. If the bottom of the uterus stops, then the child has problems.
From this moment until about the 36th week, the fundus of the uterus will rise all the time. The constancy of this rise is more important than the numbers indicating the height of the uterine fundus. If the bottom of the uterus stops, then the child has problems.
Increased vaginal discharge. You may feel like you need to empty your bladder more often during this period. The uterus sits just above the bladder and compresses it as the baby grows. nine0003
This is the equator of pregnancy, the boundary between the first and second half of it, which is not entirely true, because the baby has only been developing in the uterus for 18 weeks, and he still has 20.
How the body changes, 22 week
How your body changes in the 21st week of pregnancy
Now your waist is not the same as it was before pregnancy.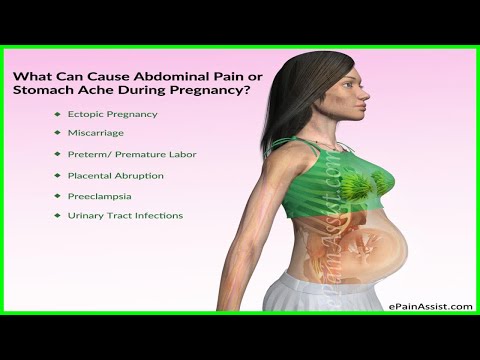 The bottom of the uterus is above the navel, and your pregnancy is visible to everyone you meet. Due to increased blood volume and hormonal changes, you may experience nosebleeds during your term.
The bottom of the uterus is above the navel, and your pregnancy is visible to everyone you meet. Due to increased blood volume and hormonal changes, you may experience nosebleeds during your term.
How the body changes, 23 week
How your body changes at 22 weeks pregnant
At this time you feel great. The inconveniences of the first half of pregnancy are over, and the tummy is still small and does not interfere. By this time, the bottom of the uterus is a few centimeters above the navel. The skin on the abdomen begins to stretch. The uterus has become heavy and presses on the bladder.
The inconveniences of the first half of pregnancy are over, and the tummy is still small and does not interfere. By this time, the bottom of the uterus is a few centimeters above the navel. The skin on the abdomen begins to stretch. The uterus has become heavy and presses on the bladder.
Changes in a woman's body: 21-23 weeks
At 21-23 weeks, you will feel the baby moving (although the baby has been moving in the uterus since the 9th week). Your hair can become thicker and your skin smoother and more elastic. Some women experience heartburn attacks. Very often increases, or, conversely, decreases sexual desire.
Your hair can become thicker and your skin smoother and more elastic. Some women experience heartburn attacks. Very often increases, or, conversely, decreases sexual desire.
How your body changes at 23 weeks pregnant
No one doubts that you are pregnant, and now you can compare your tummy with the tummy of other women who have the same period.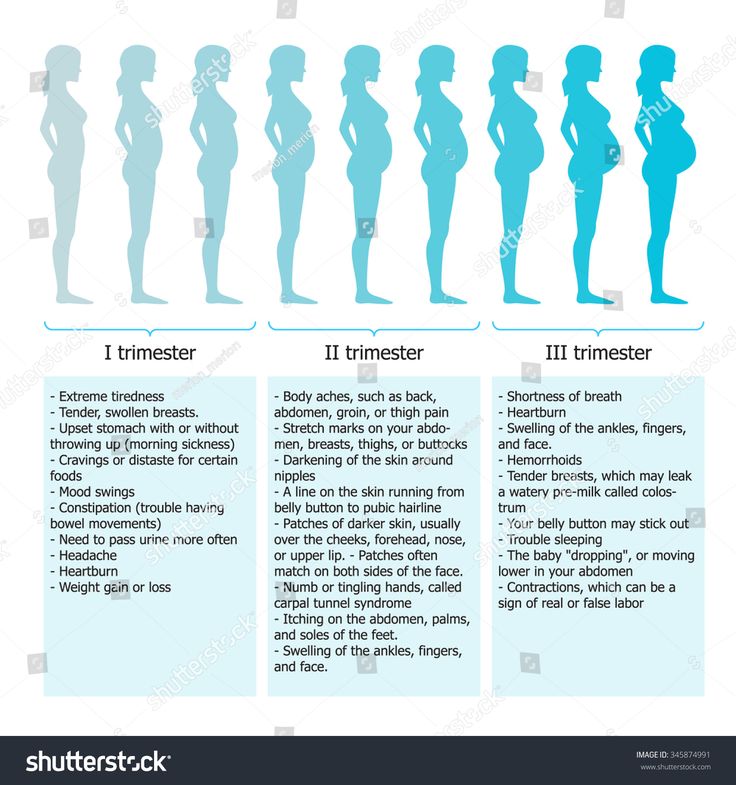 Some tummies are bigger, some are smaller. At this time, it is important that the child grows steadily and gradually, and along with the growth of the baby, the uterus, the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid grow. nine0003
Some tummies are bigger, some are smaller. At this time, it is important that the child grows steadily and gradually, and along with the growth of the baby, the uterus, the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid grow. nine0003
They also wear their tummies differently. Some are lower, others higher. Wise old women say that if your tummy is all forward, then there will be a boy, and if to the sides, then a girl.
You may feel numbness or tingling in your hands, which is a sign of carpal tunnel syndrome. It is caused by swelling of the wrist. Maybe your ankles are swollen too.
Second trimester, 13-25 week
The importance of iodine for the future baby and his mother
The amount of iodine consumed plays an important role during pregnancy, since the supply of this trace element to the fetus occurs solely at the expense of your body.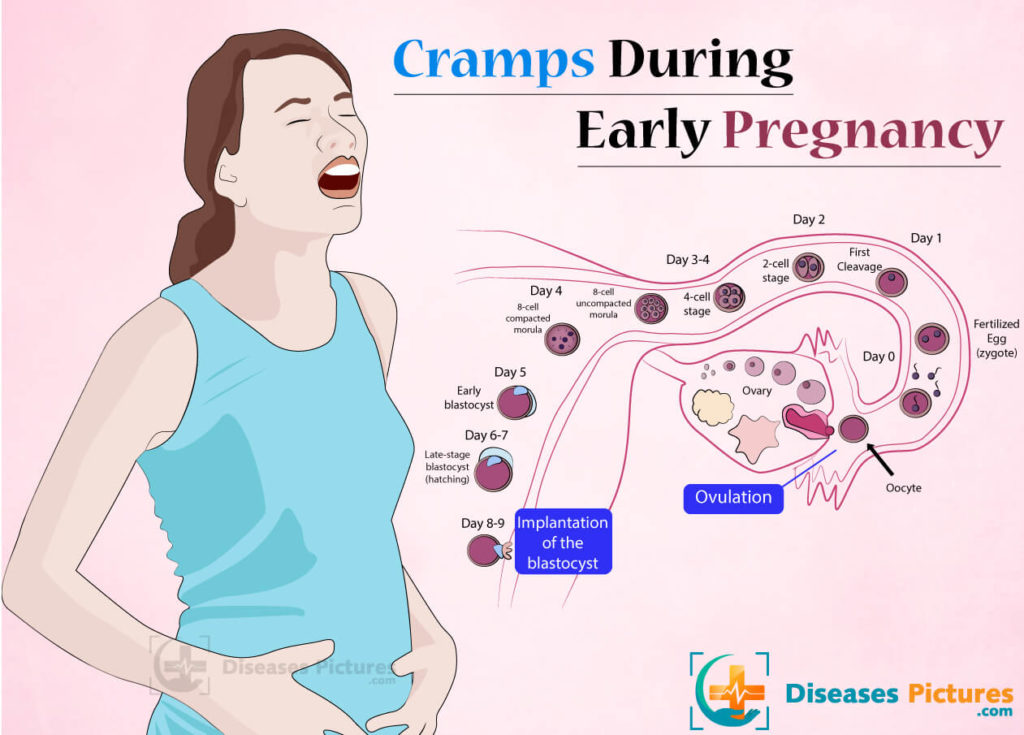 During pregnancy, there are additional losses of iodine. In the 2nd half of pregnancy, part of the mother's iodine supply is spent on the fetoplacental complex, the main function of which is to ensure the normal development of the fetus. Hormonal requirements increase while the iodine content in the mother's thyroid gland decreases. nine0003
During pregnancy, there are additional losses of iodine. In the 2nd half of pregnancy, part of the mother's iodine supply is spent on the fetoplacental complex, the main function of which is to ensure the normal development of the fetus. Hormonal requirements increase while the iodine content in the mother's thyroid gland decreases. nine0003
Against the background of iodine deficiency, endemic goiter and hypothyroidism, disturbances in the formation of the child's brain can occur, this can be expressed - from a mild decrease in intelligence to severe forms of endemic cretinism. There is a clear relationship between the functional state of the thyroid gland and the quality of memory in children. In a number of cases, these deviations in the health of children, not detected during the neonatal period, manifest themselves in subsequent years of life, especially during critical periods, for example, during puberty. Living in iodine-deficient areas is accompanied by a decrease in the reproduction of auditory information, deterioration in visual memory, other mental activity, as well as the adaptive capabilities of the central nervous system.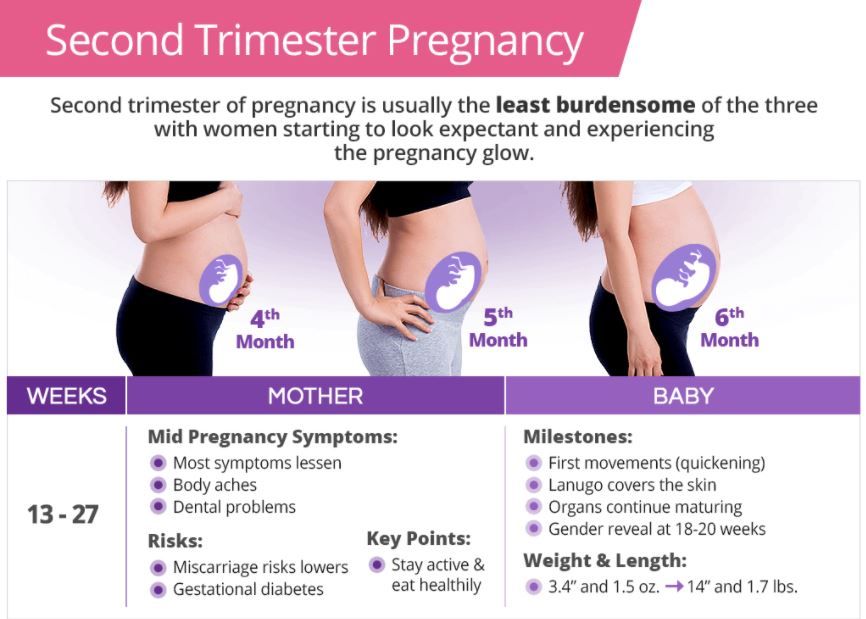 Moreover, it was found that against the background of chronic iodine deficiency, 30-60% of children have behavioral, emotional abnormalities, personality formation disorders. Therefore, it is important to provide the body with a sufficient amount of iodine. nine0003
Moreover, it was found that against the background of chronic iodine deficiency, 30-60% of children have behavioral, emotional abnormalities, personality formation disorders. Therefore, it is important to provide the body with a sufficient amount of iodine. nine0003
How the body changes, 25 week
How your body changes at 24 weeks pregnant
The amount of amniotic fluid is rapidly increasing. At this time, you already have about 500 milliliters of them, and by the 36th week their volume will reach a maximum of 1.2 liters.
At this time, you already have about 500 milliliters of them, and by the 36th week their volume will reach a maximum of 1.2 liters.
You may have noticed that colostrum is produced in the breast.
Treatment of abdominal pain - Network of clinics "OSTEOMED"
Pain in the abdomen during pregnancy can be of different localization and in most cases they do not conceal anything threatening. Basically, this is a normal reaction of the body to the increasing weight and growth of the uterus. The most hectic period of pregnancy is the first trimester, because ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous abortion and the like can take place here. Anxiety contributes to a lot of hormonal failure in the body. After all, during this period they need to quickly reorganize in a new way, which will allow them to endure, give birth to a healthy child without problems, and even set up proper lactation. Moreover, in each of these stages there is a certain hormonal jump, in which the emotional state of the pregnant woman is often changeable. nine0121
nine0121
Quite often, pain in the lower abdomen is felt during pregnancy in the early stages. If they do not bring much discomfort, there is no spotting, as well as other symptoms of a possible pathology or disease, then treatment is not required. At the beginning of pregnancy, such pains can be associated with hormonal changes, in the middle - with the rapid growth of the uterus, and at the end - with the preparation of the uterus for childbirth.
First trimester abdominal pain
If the stomach hurts during early pregnancy, then this does not always indicate some kind of pathology. With mild, rarely occurring and quickly passing pains, you should not worry. But for greater certainty, as soon as the test showed two strips, it is worth contacting a gynecologist as soon as possible. This will not only relieve the hassle, but also morally set you up for the upcoming event. With frequent aching, intense and cramping pains, it is urgent to find time and be sure to see a doctor.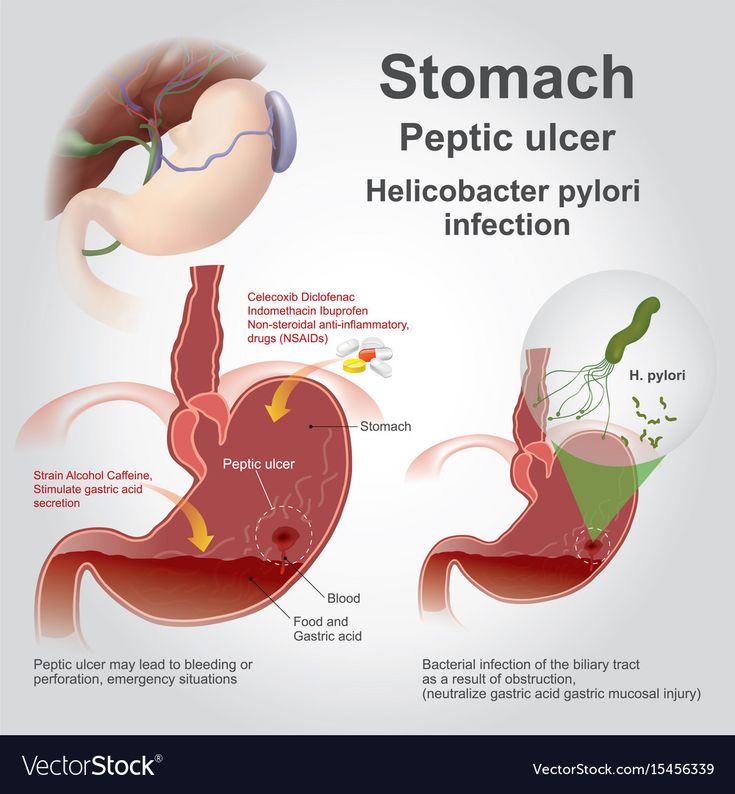 After all, this may indicate an ectopic pregnancy, which will require urgent surgical intervention. In addition, spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) can also be the cause. However, often, but not always, abdominal pain is accompanied by lower back pain and bleeding. If all indicators of pregnancy are normal, but the stomach still aches, this is explained very simply. The body is rebuilt, the tissues supporting the uterus become softer, looser, while the uterus itself grows and shifts, which contributes to tingling and sipping pains in the lower abdomen. nine0121
After all, this may indicate an ectopic pregnancy, which will require urgent surgical intervention. In addition, spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) can also be the cause. However, often, but not always, abdominal pain is accompanied by lower back pain and bleeding. If all indicators of pregnancy are normal, but the stomach still aches, this is explained very simply. The body is rebuilt, the tissues supporting the uterus become softer, looser, while the uterus itself grows and shifts, which contributes to tingling and sipping pains in the lower abdomen. nine0121
Lower abdominal pain
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, and especially in the later stages, is often due to internal pressure, that is, the growing uterus presses on the internal organs, thus disrupting their full-fledged work. The intestine reacts very sensitively to the hormones of "pregnancy" with a decrease in motility, a violation of peristalsis, which is a common cause of constipation, bloating and colic.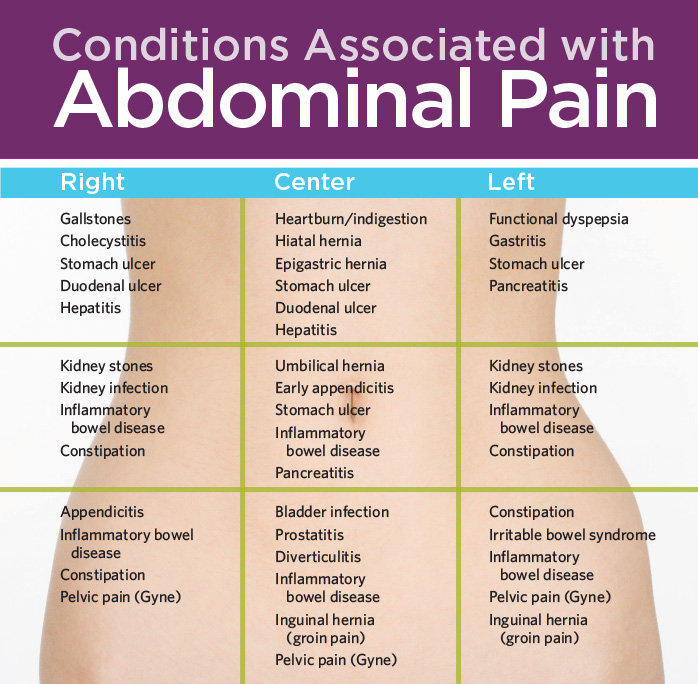 To avoid this, you need to move more often, eat foods rich in fiber (fruits, vegetables, whole grain bread) and, of course, drink more fluids. Also, pain concentrated in the lower abdomen can be caused by a sprain due to the rapid growth of the uterus, or it can be triggered by premature detachment of the placenta. In the latter case, urgent medical attention is needed, because irreparable harm can be done to the mother and child. In this case, rapid delivery and immediate stopping of bleeding are indicated. In addition, during pregnancy, new or exacerbated chronic diseases can develop, which can also give signals in the lower abdomen. These are cholecystitis, intestinal dysbacteriosis and others. In some cases, emergency surgery is indicated, and therefore it is worth paying attention to the slightest changes in the nature of the pain. If there is even the slightest doubt, you should urgently consult a doctor, otherwise it may be too late. In addition, problems with the genitourinary system are quite possible, which can also provoke pain in the lower abdomen.
To avoid this, you need to move more often, eat foods rich in fiber (fruits, vegetables, whole grain bread) and, of course, drink more fluids. Also, pain concentrated in the lower abdomen can be caused by a sprain due to the rapid growth of the uterus, or it can be triggered by premature detachment of the placenta. In the latter case, urgent medical attention is needed, because irreparable harm can be done to the mother and child. In this case, rapid delivery and immediate stopping of bleeding are indicated. In addition, during pregnancy, new or exacerbated chronic diseases can develop, which can also give signals in the lower abdomen. These are cholecystitis, intestinal dysbacteriosis and others. In some cases, emergency surgery is indicated, and therefore it is worth paying attention to the slightest changes in the nature of the pain. If there is even the slightest doubt, you should urgently consult a doctor, otherwise it may be too late. In addition, problems with the genitourinary system are quite possible, which can also provoke pain in the lower abdomen. nine0003
nine0003
Uterine tone
Uterine tone is painless or slightly painful uterine contractions. If a pregnant woman feels a spasm in the lower abdomen, the stomach becomes like a stone (this is especially noticeable in the second half of pregnancy) - this is a tone. The tone is diagnosed by a gynecologist during an external examination. The fact that the tone was recorded on the ultrasound, contrary to popular belief, is not an indication for treatment and hospitalization. The uterus is a muscular organ, and it is quite normal that it contracts periodically. The key word here is periodically, and, of course, painlessly and for a short time. With uterine tone, doctors recommend taking a horizontal position, lying on your side, you can take an antispasmodic pill and use a Papaverine suppository. nine0003
Preliminaries
As a rule, there are minor pains in the lower abdomen during late pregnancy - these are preparatory contractions. Thus, the uterus prepares for the upcoming birth. In some women, the uterus begins to “prepare” like this at 32 weeks, in others for 1-2 weeks, and someone either does not notice these weak contractions, or considers this the norm, and therefore does not pay attention. It is very important to learn to distinguish between preliminary contractions and true ones, those that begin already in childbirth. Preliminary contractions last for several seconds, and they are not regular, unlike true ones, and do not intensify. It has been observed that nulliparous women are more likely to experience pre-contractions than multiparous women. This kind of pain is removed very easily by non-drug methods - you can just take a deep breath, lie down and relax. In many cases, taking a warm (not hot!) bath helps. nine0003
Thus, the uterus prepares for the upcoming birth. In some women, the uterus begins to “prepare” like this at 32 weeks, in others for 1-2 weeks, and someone either does not notice these weak contractions, or considers this the norm, and therefore does not pay attention. It is very important to learn to distinguish between preliminary contractions and true ones, those that begin already in childbirth. Preliminary contractions last for several seconds, and they are not regular, unlike true ones, and do not intensify. It has been observed that nulliparous women are more likely to experience pre-contractions than multiparous women. This kind of pain is removed very easily by non-drug methods - you can just take a deep breath, lie down and relax. In many cases, taking a warm (not hot!) bath helps. nine0003
Gynecological pathologies
Those 4 reasons that we described above are variants of the norm. However, it is urgent to consult a doctor if these conditions are accompanied by bloody or brown vaginal discharge, clear or greenish vaginal discharge (they may turn out to be amniotic fluid), if the pain lasts for several minutes, is not relieved by antispasmodics and only increases when weakness appears, dizziness, flies before the eyes, etc.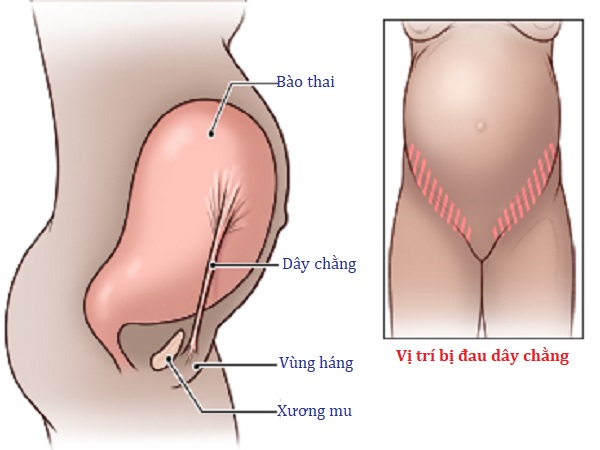 In a word, if the condition worsens. Such symptoms may indicate a threat or a spontaneous miscarriage, a frozen or ectopic pregnancy (when an early pregnancy, pain in the lower abdomen), premature or term birth, etc. nine0003
In a word, if the condition worsens. Such symptoms may indicate a threat or a spontaneous miscarriage, a frozen or ectopic pregnancy (when an early pregnancy, pain in the lower abdomen), premature or term birth, etc. nine0003
Other reasons
However, not always abdominal pain in expectant mothers occurs precisely because of gynecological problems and is a consequence of pregnancy. Here are some other possible reasons.
1. Cystitis and other diseases of the female excretory system. The ureter is located next to the internal genital organs, because this pain is often confused with "gynecological". Usually the pain occurs in such cases suddenly, has a "stabbing" character. Pain in the lower abdomen is accompanied by frequent and painful urination. The urologist treats the genitourinary system. You should not start the disease, because it is caused by an infection that is unsafe for the child. Folk remedies, like bearberry, do not help well, but the doctor can prescribe effective medications that are approved for use by pregnant women.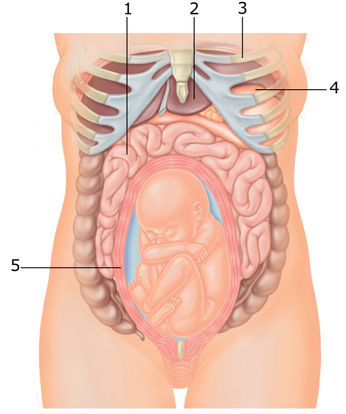 nine0003
nine0003
2. Problems with the intestines: diarrhea, constipation, bloating. It should be noted that the last 2 are frequent occurrences in expectant mothers. Constipation is caused by a decrease in physical activity, displacement of internal organs due to the growth of the uterus, malnutrition, and insufficient fluid intake. Bloating is caused by the consumption of appropriate foods, as well as soda. Sometimes it is enough to go to the toilet for the pain in the abdomen to go away if it's constipation.
3. Poisoning or rotovirus infection. Their symptoms are very similar. Usually it all starts with cramping pains in the lower abdomen, sometimes the pain goes to the navel. Then comes diarrhea and/or vomiting. nine0003
4. Appendicitis. If you have pregnancy, pulling pains in the lower abdomen do not always indicate tone or minor ailments, this may be a symptom of appendicitis, especially if the pain is right-sided, accompanied by fever. The correct diagnosis can be made by the surgeon.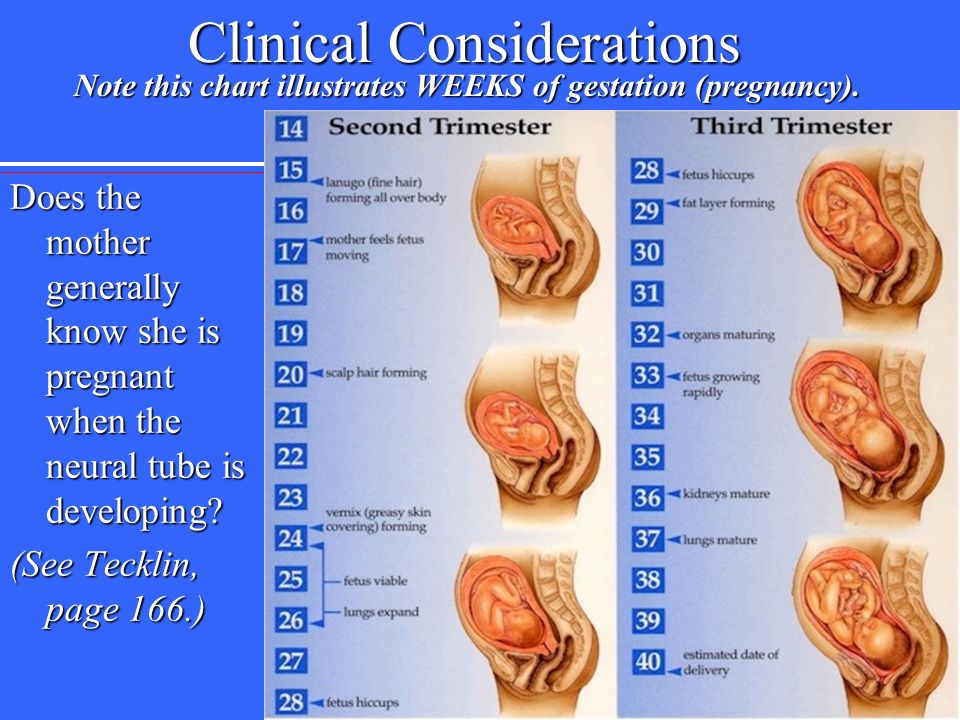 If the pain does not go away within an hour or two, but only increases, you should not attribute everything to an intestinal disorder and drink drugs like "smecta", this is very dangerous. If surgery is not carried out in time, it can lead to peritonitis. nine0003
If the pain does not go away within an hour or two, but only increases, you should not attribute everything to an intestinal disorder and drink drugs like "smecta", this is very dangerous. If surgery is not carried out in time, it can lead to peritonitis. nine0003
And this is not all the reasons. Pregnant women, not for the first time, can quite easily distinguish the pain caused by uterine spasm from other types of pain. But in any case, it does not hurt to see a doctor.
Upper abdominal pain
Pain at the top of the abdomen during pregnancy mainly occurs in the later stages. Their cause is the same uterus, which is constantly growing, slowly begins to reach the upper organs of the peritoneum. This primarily affects the liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, disturbances in which lead to symptoms such as belching, bitterness in the mouth. In addition, very often in the last trimester of pregnancy, the stomach throws gastric juice up the esophagus, causing considerable discomfort.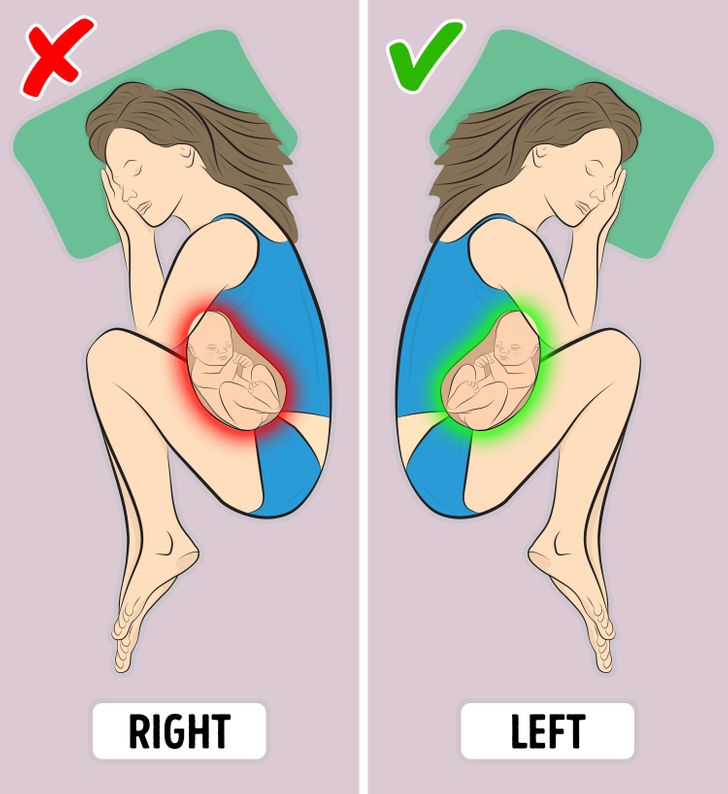 To avoid these unpleasant moments, you need to eat a balanced diet, which should be eaten in small portions. It is desirable, of course, to exclude fried, spicy, too salty and too sweet. nine0003
To avoid these unpleasant moments, you need to eat a balanced diet, which should be eaten in small portions. It is desirable, of course, to exclude fried, spicy, too salty and too sweet. nine0003
Stitches
Stinging abdominal pain during pregnancy occurs for many reasons. This may be stagnation of feces in the intestines, which also provokes flatulence and constipation. By the way, the latter, in the future, can become one of the causes of hemorrhoids. It is also necessary to pay attention to the intensity of pain. If it is weak, rarely occurring, then you should not dwell on it. But if the pain is severe, especially sharp, you need to consult a doctor. Acute pain may be due to the development of appendicitis, inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), pancreas. Often, during the filling of the bladder, expectant mothers complain of pains of a pulling nature in this area, which turn into stitches, and become more painful when urinating, which indicates cystitis. In addition, stabbing pains may indicate the presence of infectious diseases, which are most often sexually transmitted. nine0003
In addition, stabbing pains may indicate the presence of infectious diseases, which are most often sexually transmitted. nine0003
Abdominal pain on the left
Abdominal pain on the left during pregnancy can be caused by various diseases of the internal organs. They can signal various lesions of the stomach and pancreas, the splenic flexure of the colon and, in fact, the spleen itself, as well as the left kidney. In addition, pain localized in the left side of the abdomen is possible when a hiatal hernia occurs.
Abdominal pain on the right
Abdominal pain on the right during pregnancy most often occurs with diseases of the gallbladder, liver, duodenum, and right kidney. If the pain is accompanied by other symptoms, you should consult a doctor. For example, the symptoms of inflammation of the gallbladder include not only pain in the right side of the abdomen, but also nausea and vomiting (which are often confused with toxicosis). As a rule, following a salt-free diet with the complete exclusion of fatty, fried and spicy foods helps to cope with this problem. Possible formation of sand or kidney stones. Basically, during pregnancy, they try not to affect this organ, because it is of great importance when carrying a child. But if the doctor sees some kind of pathology or the hopelessness of the current situation, which can affect the further course of pregnancy, then measures will be taken to eliminate the cause of pain, with the maximum benefit for the fetus and woman. nine0003
As a rule, following a salt-free diet with the complete exclusion of fatty, fried and spicy foods helps to cope with this problem. Possible formation of sand or kidney stones. Basically, during pregnancy, they try not to affect this organ, because it is of great importance when carrying a child. But if the doctor sees some kind of pathology or the hopelessness of the current situation, which can affect the further course of pregnancy, then measures will be taken to eliminate the cause of pain, with the maximum benefit for the fetus and woman. nine0003
Pain in the abdomen when walking
Often, the stomach hurts when walking in a pregnant woman, causing some discomfort. Basically, this problem concerns the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, that is, those periods when the uterus begins to actively grow, thereby causing a change in the center of balance. This is one of the reasons for the so-called duck walk. Many pregnant women are ashamed of this and try hard to walk the same way as they used to walk, which causes pain.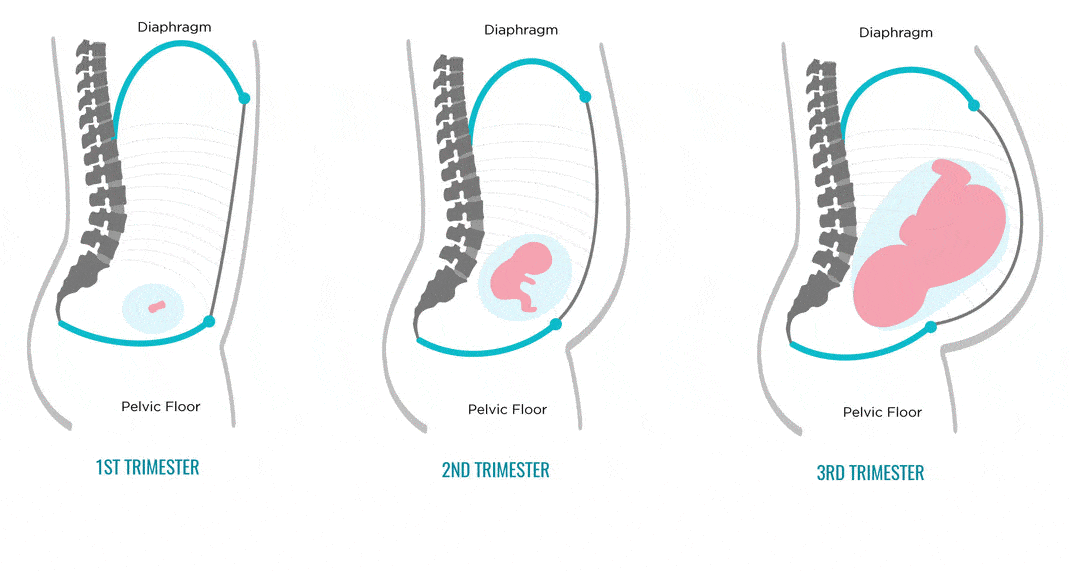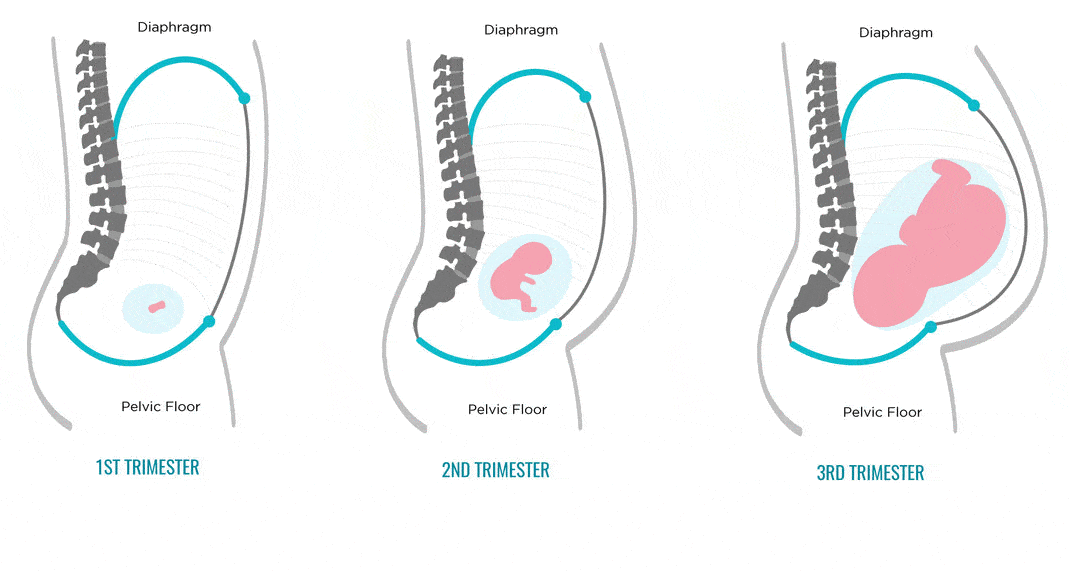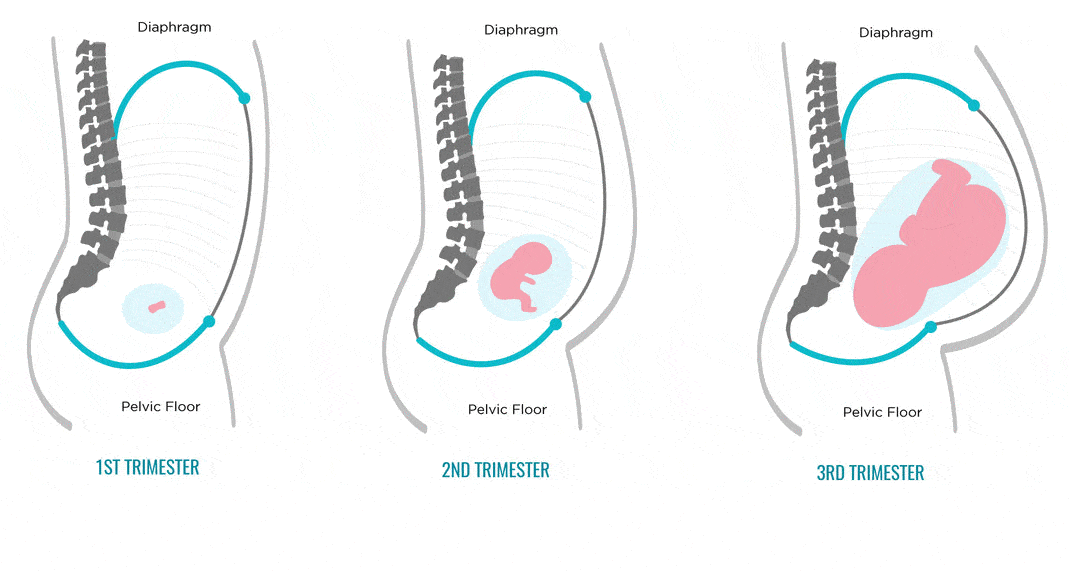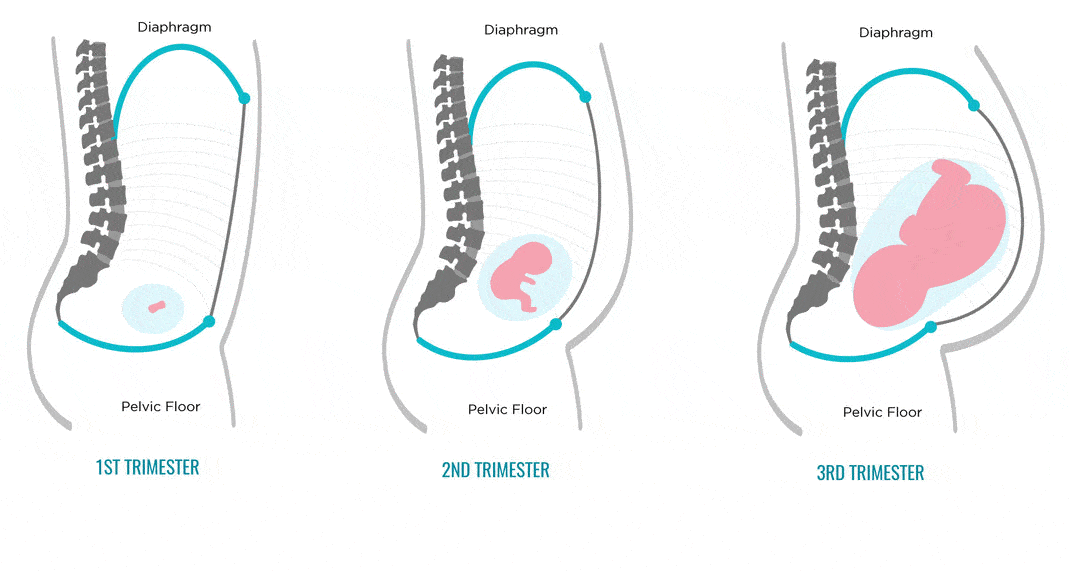 The second reason is the softening of the joints located between the pelvic bones. Thus, the body prepares for the passage of the baby through the birth canal. To reduce or even get rid of pain, you should pay attention to the position of your body when walking. The correct position of the torso during pregnancy is to take the shoulders back, shifting the center of gravity from the toe to the heel, and the use of a special bandage for pregnant women will also bring invaluable help, which will not only reduce the load from the abdomen, but also remove tension from the spine. nine0003
The second reason is the softening of the joints located between the pelvic bones. Thus, the body prepares for the passage of the baby through the birth canal. To reduce or even get rid of pain, you should pay attention to the position of your body when walking. The correct position of the torso during pregnancy is to take the shoulders back, shifting the center of gravity from the toe to the heel, and the use of a special bandage for pregnant women will also bring invaluable help, which will not only reduce the load from the abdomen, but also remove tension from the spine. nine0003
Severe pain
The stomach hurts a lot during pregnancy during the course of some, at least not very good changes. Normally, there should be no severe pain. But if they have already arisen, then you should not endure them, it is imperative to consult with the local gynecologist. Severe pain can be the result of ectopic pregnancy, placental abruption, miscarriage, premature birth, as well as diseases associated with inflammation and chronic diseases of the internal organs. In principle, in any of these cases, it is necessary to call an ambulance as soon as possible, because untimely assistance can lead to disastrous consequences. The most important thing in this matter is not to miss the precious time that can give life to a small miracle, and maybe more than one. nine0003
In principle, in any of these cases, it is necessary to call an ambulance as soon as possible, because untimely assistance can lead to disastrous consequences. The most important thing in this matter is not to miss the precious time that can give life to a small miracle, and maybe more than one. nine0003
Abdominal pain can be of different localization, intensity and etiology. If you have any doubts about this, you should immediately consult a doctor. If other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, loss of consciousness, and the like, join pain in the abdomen, you should urgently, without delay, call an ambulance.
OSTEOPATHICS AND ABDOMINAL PAIN
We recommend that you use our services and prevent abdominal pain without the use of medicines that are harmful to the expectant mother. Osteopathy will help you not only get rid of pain, but also prevent their occurrence. Our specialists, absolutely safely, will carry out the treatment very carefully and efficiently.