Spot on baby
Nappy rash - NHS
Around 1 in 4 babies and toddlers in nappies have nappy rash at any one time. It doesn't usually develop in newborns, but all babies can get nappy rash.
Nappy rash can be caused by:
- your baby's skin being in contact with wee or poo for a long time
- the nappy rubbing against your baby's skin
- not cleaning the nappy area or changing the nappy often enough
- soap, detergent or bubble bath
- alcohol-based baby wipes
- some types of medicines, such as antibiotics or laxatives (used to make a baby poo more often)
There may be red patches on your baby's bottom, or the whole area may be red. Their skin may look sore and feel hot to touch, and there may be spots, pimples or blisters.
Most babies with mild nappy rash don't feel sore, but if the rash is severe your baby may feel uncomfortable and be distressed.
If your baby gets nappy rash, you can usually treat their skin yourself.
If the rash isn't upsetting your baby, at each nappy change apply a thin layer of a barrier cream to protect their skin. Ask your health visitor or pharmacist to recommend one.
Follow this advice to help look after your baby's skin.
- Change wet or dirty nappies as soon as possible.
- Clean the whole nappy area gently but thoroughly, wiping from front to back. Use water or fragrance-free and alcohol-free baby wipes. Read more about how to clean your baby and change your baby's nappy.
- Bath your baby daily – but avoid bathing them more than twice a day as that may dry out their skin.
- Dry your baby gently after washing them – avoid vigorous rubbing.
- Lie your baby on a towel and leave their nappy off for as long and as often as you can to let fresh air get to their skin.
- Do not use soap, bubble bath, or lotions.
- Do not use talcum powder as it contains ingredients that could irritate your baby's skin.
- Make sure your baby’s nappy fits properly. If it is too tight then it can irritate the skin and if it is too loose, then the nappy will not be able to soak up pee properly.
Nappy rash usually clears up after about 3 days if you follow this advice. You should keep following this advice as this will help prevent nappy rash from coming back.
If the rash is causing your baby discomfort, your health visitor or pharmacist can recommend a nappy rash cream to treat it.
You should apply the cream first and wait a few minutes before you apply the barrier cream.
If the rash doesn't go away or your baby develops a persistent bright red, moist rash with white or red pimples that spreads into the folds of their skin, they may have an infection.
Ask a pharmacist or health visitor for advice. The pharmacist may recommend a cream for you to use.
If the rash is severe, take your baby to the GP who may prescribe cream or medicine. Follow a GP's instructions on whether and when to apply barrier cream as well as the prescribed cream.
It's normal for babies to develop skin rashes, but it's important to know the difference between a minor irritation and a condition that requires attention.
Read more about rashes in babies and children.
Page last reviewed: 17 September 2021
Next review due: 17 September 2024
Slapped cheek syndrome - NHS
Slapped cheek syndrome (also called fifth disease) is common in children and should get better on its own within 3 weeks. It's rarer in adults, but can be more serious.
It's rarer in adults, but can be more serious.
Check if it's slapped cheek syndrome
The first sign of slapped cheek syndrome is usually feeling unwell for a few days.
Symptoms may include:
- a high temperature
- a runny nose and sore throat
- a headache
Credit:
SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/550792/view
A few days later, a spotty rash may appear on the chest, arms and legs. The rash can be raised and itchy. It may be harder to see on brown and black skin.Credit:
John Kaprielian/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://www.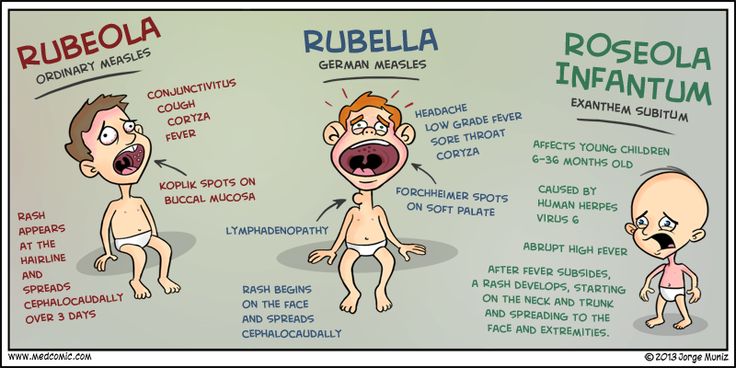 sciencephoto.com/media/618192/view
sciencephoto.com/media/618192/view
How long it lasts
The cheek rash usually fades within 2 weeks.
The body rash also fades within 2 weeks, but sometimes lasts for up to a month, especially if you're exercising, hot, anxious or stressed.
Adults might also have joint pain and stiffness. This can happen in children too, but it's rare. Joint pain can continue for many weeks, even after the other symptoms have gone.
If you're not sure your child has slapped cheek syndrome
Look at other rashes in babies and children.
Things you can do yourself
You do not usually need to see a GP for slapped cheek syndrome.
There are some things you can do to ease the symptoms.
Do
-
rest
-
drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration – babies should continue their normal feeds
-
take paracetamol or ibuprofen for a high temperature, headaches or joint pain
-
use moisturiser on itchy skin
-
speak to a pharmacist about itchy skin – they can recommend the best antihistamine for children
Important
Tell your midwife or a GP if you're pregnant or have a weakened immune system and have been near someone with slapped cheek syndrome.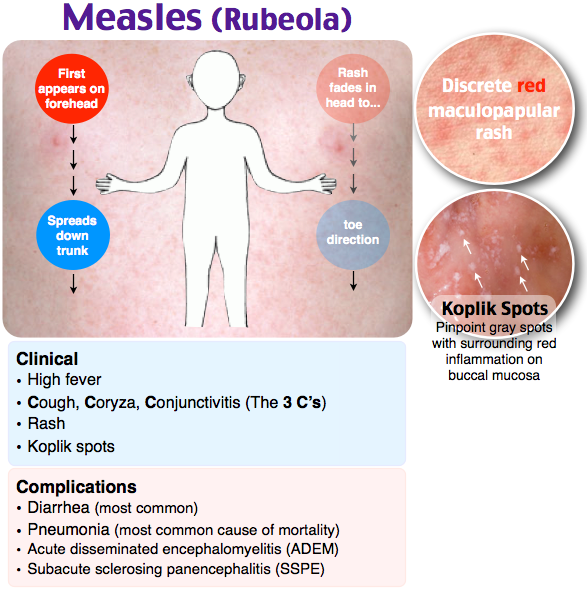
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if:
you think you have slapped cheek syndrome and:
- you're pregnant – there's a very small risk of miscarriage or other complications
- you have a blood disorder, such as sickle cell disease or thalassaemia – there's a risk of severe anaemia
- you have a weakened immune system – for example, because of chemotherapy or diabetes
Ask for an urgent appointment if you have:
- very pale skin
- shortness of breath
- extreme tiredness
- fainting
These can be signs of severe anaemia and you might be sent to hospital for a blood transfusion.
How slapped cheek syndrome is spread
It's hard to avoid spreading slapped cheek syndrome because most people do not know they have it until they get the rash.
You can only spread it to other people before the rash appears.
Slapped cheek syndrome is caused by a virus (parvovirus B19). The virus spreads to other people, surfaces or objects by coughing or sneezing near them.
To reduce the risk of spreading the virus:
- wash your hands often with water and soap
- use tissues to trap germs when you cough or sneeze
- bin used tissues as quickly as possible
Information:
You do not have to stay off work or school after the rash appears.
Let the school or teacher know if your child has slapped cheek syndrome.
Page last reviewed: 18 February 2021
Next review due: 18 February 2024
reasons and what to do about it
Red areas of the skin can be the result of a violation of the rules of care, that is, they can be caused by physiological causes, and also be one of the first symptoms of various dermatological diseases. In order to eliminate redness, you first need to establish the cause of the unpleasant phenomenon.
In order to eliminate redness, you first need to establish the cause of the unpleasant phenomenon.
Pathological redness can be caused by an allergic reaction, a symptom of an infectious or autoimmune disease. nine0003
In a child, redness of the skin of the hands is often a sign of allergic dermatitis. External signs of this disease are usually localized in open areas of the body: face, hands, neck. In addition to redness of the skin, allergic dermatitis is accompanied by symptoms such as:
Severe forms of allergies include diseases such as eczema and Quincke's edema. With eczema, the skin is a reddened, itchy area covered with crusts or blisters. Angioedema usually occurs as an allergic reaction to insect bites or certain allergens. nine0003
Redness of the skin of the hands in a child can be caused by kidney or liver failure, infectious diseases, or be the result of exposure to detergents, care cosmetics.
Legs
Redness of the skin of the legs, accompanied by a rash, itching and increased dryness, should not be left out of the attention of parents. There may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
There may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
- urticaria or contact dermatitis - red patches varying in shape and size, may merge with each other, causing irritation, severe itching and discomfort; nine0018
- injuries, bruises and sprains - in addition to redness, the child has noticeable swelling;
- fungal infection - redness accompanied by peeling of the skin, the appearance of cracks and severe itching;
- bacterial infections - often resulting from reinfection through scratching and other skin breaks;
- Coxsackie virus, chicken pox, measles.
The appearance of redness on the skin of the legs requires an immediate visit to a doctor - a pediatrician or dermatologist. nine0003
Face and neck
The appearance of red spots on the cheeks usually indicates an allergic reaction. In infancy, the organs of the digestive system can not always successfully perform their function. In addition to redness, the child has nausea, constipation or diarrhea, abdominal pain, problems with appetite, irritability, sleep disturbances.
Food allergies are most often caused by cow's milk protein, chicken eggs, fish, honey, chocolate, strawberries, citrus fruits. Allergic reactions often occur when a baby tries a new food for the first time, especially when it comes to exotic fruits. nine0003
In the cold season, the child may experience redness around the mouth. The absence of sebaceous glands in the lips provokes drying, irritation and the appearance of painful points and small wounds.
The reasons for this phenomenon may be:
- allergic reactions;
- decreased general immunity;
- adverse weather conditions;
- deficiency of vitamins in the body; nine0018
- bad habits - eg thumb sucking;
- features of digestion.
Redness of the skin on the face also occurs with seborrheic dermatitis. With this disease, increased dryness and peeling are noted in certain parts of the body. The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis has not been established, but it usually develops on oily skin and is not associated with allergic reactions or lack of hygiene.
Peeling crusts are usually localized in the scalp, around the wings of the nose, eyebrows, ears, less often on the child's body. nine0003
Seborrheic dermatitis can appear at any age, this physiological deficiency is often observed in infants. Usually, the crusts do not present discomfort to the child and can be regarded mainly as an aesthetic defect. The scaly growths and redness do not cause pain or irritation and often go away on their own without treatment. It is believed that the cause of their appearance are maternal hormones transmitted to the child.
To eliminate crusts from the baby's head, before washing the affected area is smeared with vegetable oil, and then the hair is washed with a mild baby shampoo. nine0003
In order to eliminate redness and its accompanying symptoms, it is necessary to establish the cause of the phenomenon.
Buttocks
Redness of the skin on the pope in a child is the result of diaper rash (diaper dermatitis). The skin turns red in the perineum or in the folds, where moisture accumulates the most. Usually the baby reacts negatively to touch when changing a diaper, washing after a bowel movement.
The skin turns red in the perineum or in the folds, where moisture accumulates the most. Usually the baby reacts negatively to touch when changing a diaper, washing after a bowel movement.
An increased risk of diaper rash on the buttocks occurs when there are violations in the digestive system. Frequent rare stool irritates the delicate skin of the baby, causing redness of the skin. In this case, a review of the child's nutrition system can help. nine0003
The reasons for the appearance of redness of the buttocks in a baby can be:
- incorrectly fitted diaper;
- increased temperature in the room when the child develops prickly heat;
- taking certain medications;
- transition to a new milk formula;
- incorrect selection of detergents and cosmetics for skin care;
- urticaria;
- fungal diseases. nine0018
If redness is not associated with physiological causes, the child should be shown to the doctor.
Diagnosis of redness and irritation
Since the appearance of red patches of skin can be caused by a huge number of reasons, the diagnosis of this problem is of great importance. Depending on the cause of the disease, a pediatrician, dermatologist or other specialist will choose the most effective treatment methods.
In the course of diagnosis, data from an external examination of the child are used. At the same time, attention is paid to the localization of redness, spots and rashes, their size, shape and severity of manifestation. nine0003
Based on the results of the examination, it is recommended to conduct laboratory and instrumental studies. The patient is prescribed general and biochemical blood tests, allergy tests are performed to determine the allergen. If the reddening of the skin in a child is caused by infectious diseases, diagnostic measures are aimed at identifying the causative agent of the infection for the purpose of surgical treatment.
If a fungal infection is suspected, a skin scraping is taken for further examination under a microscope. nine0003
If redness is caused by physiological causes, parents are given recommendations on how to organize the child's nutrition and care procedures. These measures will minimize not only redness, but also other negative reactions from the skin, such as excessive dryness, irritation and roughness.
The treatment of redness as part of the symptoms of various diseases, first of all, is aimed at eliminating the cause that causes this phenomenon. It also aims to ensure that negative skin reactions that cause discomfort to the child are eliminated as soon as possible. nine0003
Prevention of redness and skin irritation
Negative reactions from the skin in childhood are rarely caused by serious diseases and in most cases this problem can be solved by timely treatment and preventive measures.
Prevention of atopic dermatitis:
- adjust the child's diet, exclude foods that cause negative reactions in the body; nine0017 moisturize the skin with hypoallergenic cosmetics;
- eliminate or minimize environmental allergens - pets, synthetic clothing, certain foods, harsh detergents;
- regularly carry out wet cleaning of the premises;
- for washing clothes and baby diapers, use special products.

In order to prevent the severe course of diseases caused by viral, bacterial or fungal infections, it is necessary to detect diseases in a timely manner and carry out appropriate treatment. nine0003
It is possible to prevent the appearance of redness and irritation of the baby's skin caused by diaper rash, subject to the following recommendations:
- bed linen and clothing of the child must be made of natural, breathable fabrics only;
- regularly change the baby's diapers or swaddling clothes, do not allow the baby to stay wet for a long time;
- after each bowel movement, the baby should be washed with warm water; nine0017 while bathing, it is recommended to add decoctions of string or chamomile to the bath;
- from time to time the baby should be left undressed on the changing table for air baths;
- only products intended for sensitive skin can be used while bathing;
- use soft towels to dry the body after washing, do not rub the skin;
- powders and care oils are used separately; nine0018
- ensure that the child is not deficient in vitamins.

To prevent allergic reactions, in which redness and irritation of the skin occurs, care must be taken when introducing new complementary foods. You can not introduce several products into the baby's diet at once, you need to start with vegetable or fruit purees. A new product is given in a limited amount (for example, a teaspoon) and the body's reaction is monitored. In the absence of allergies, the amount of the product is increased. nine0003
Of great importance in prevention belongs to walks in the fresh air. With the child you need to walk daily for 2-3 hours. During the heating period in the room, it is important to prevent the air from drying out. To do this, it is recommended to use special humidifiers or at least put a container of water in the room.
If redness, itching, skin irritation still occur, in addition to general treatment, it is necessary to use special cosmetics with effective local action. Their use is aimed at the rapid elimination of external manifestations of allergies and other diseases. nine0003
nine0003
Anti-irritants
You can quickly eliminate redness and irritation of the skin in a child with the help of emollients. The active substances in these cosmetic products help to soften, moisturize, relieve inflammation and regenerate the skin.
Emollients that are suitable for sensitive and delicate skin at any age are presented in the Emolium cosmetic series. Their regular use allows you to successfully deal with such phenomena as excessive dryness, roughness, inflammation and redness of the skin. Leading dermatologists and pediatricians took part in the development of the Emolium series. nine0003
Emolium products are successfully used in skin care prone to such diseases as atopic dermatitis, urticaria, seborrheic dermatitis. They can be recommended for children whose skin is prone to rashes, blisters and crusts.
Moisturizing the skin and maintaining its water-lipid barrier is of great importance. To do this, use the bathing emulsion of the Emolium series. The remedy can be prescribed from the first days of a baby's life in order to soften hard water and prevent dryness and irritation. nine0003
The remedy can be prescribed from the first days of a baby's life in order to soften hard water and prevent dryness and irritation. nine0003
"Emolium" is represented by three types of funds: basic, special and triactive series. You can learn more about the products by clicking on the link.
Baby birthmarks, medical supervision recommended. Lakhta Junior in St. Petersburg
Let's talk about children's birthmarks, their possible and most common options.
“Like a baby,” we envy about the most healthy, satiny, velvety, uniform skin. But the idea that any spot on the skin of a baby is obviously a pathology is nothing more than a myth. nine0003
Birthmarks are called so because they are often visible already in a newborn, although sometimes they appear at later stages of development. The color, size, shape of a birthmark can be very different. Some of these marks disappear over time, others become brighter and/or remain permanently.
Much and completely justified attention is being paid today to the dangers that moles carry in themselves in adulthood and old age. On the contrary, most children's moles do not pose any danger. nine0003
On the contrary, most children's moles do not pose any danger. nine0003
Vascular ("stork mark", "angel's kiss", hemangiomas, venous malformations, etc.). The cause of such spots are problems with small blood vessels, usually transient. Vascular spots are distinguished by a red-violet color in one shade or another; may rise slightly above the surface of the skin or be flat.
Brown spots (“café au lait”, melanocystosis, Mongolian spots, etc.). Formed by various skin cells; look, as a rule, brown-gray, usually do not rise above the skin. nine0168 Again, in most cases, both main varieties of birthmarks are quite safe and harmless. And yet, only a doctor can judge whether it is possible to confine oneself to observation or whether the stain is to be removed for medical reasons. This type of consultation is strictly required.
Let's take a closer look at the most common types of birthmarks.
Stork Mark (stork peck, stork mark, etc. ).
).
So in many countries they call specks of a reddish-pink color that a newborn may have on the back of the head or back of the neck. As a rule, such spots do not rise above the surface and have an uneven shape. Most often, the stork mark occurs in children with fair skin. nine0168 The explanation that this is a trace of the "transportation" of the baby by the stork, older brothers and sisters, as a rule, is accepted unconditionally, and even with delight. "Stork peck" usually disappears without a trace by 18 months of age. Otherwise, especially if the stain causes noticeable discomfort, it is removed (for example, using minimally invasive laser technology).
"Port-wine stain"
Port-wine stain or, in medical terminology, flaming nevus - flat capillary moles, outwardly and really resembling a puddle of spilled purple-red wine. They occur with a frequency of 3-5 cases per 1000 newborns. With age, they can increase and acquire a darker shade. nine0168 Treatment is not usually required, but the skin in this area tends to dry out and become irritated. Sometimes they resort to the method of laser removal, which, however, does not always completely eliminate the cosmetic defect.
Sometimes they resort to the method of laser removal, which, however, does not always completely eliminate the cosmetic defect.
"Strawberry hemangioma"
Obsolete name for infantile hemangioma, a bright red congenital benign vascular tumor that rises above the surface of the skin and has a characteristic surface texture. It occurs in about 5% of newborns, more often in girls, twins and premature babies. nine0168 Usually localized on the face, head or chest; as a rule, decreases with age and finally disappears in the preschool period. It is possible to remove a hemangioma, especially if it is large and / or located near the eyes, nose, mouth. Both minimally invasive surgical and conservative methods of removal are practiced.
Venous malformations
These are blue-purple spots that can sometimes appear on the skin, especially during moments of intense crying. Venous malformations (lit. "malformations") are always congenital in nature, but sometimes remain almost invisible until adolescence. They can be located on any part of the body. Compared to other types of birthmarks, they are rare - in one case in about five thousand. nine0003
They can be located on any part of the body. Compared to other types of birthmarks, they are rare - in one case in about five thousand. nine0003
Coffee with milk
Localized abnormal pigmentation that occurs in 30% of people. The color of such a spot is usually light brown or beige, which is reflected in the name. The edges are usually even, the perimeter is sometimes darker than the inner area. In most cases, a café au lait pigment spot is quite harmless, but it can enlarge and/or darken with age. Such spots are subject to observation in dynamics, in some cases they can be removed.
Moles proper
Well-known round or oval freckle-like growths. The color varies from light brown or pink-red to almost black. Sizes in individual cases also vary widely. They can be both flat and protruding above the surface.
Moles should be inspected regularly to prevent any damage (mechanical, chemical, etc.). If a mole begins to bleed, change color, shape, appearance and any other characteristics, you should see a specialist as soon as possible - a dermatologist or oncologist at the Lakhta Junior Children's Clinic in St.