Stomach burns while pregnant
Indigestion and heartburn in pregnancy
Indigestion, also called heartburn or acid reflux, is common in pregnancy. It can be caused by hormonal changes and the growing baby pressing against your stomach.
You can help ease indigestion and heartburn by making changes to your diet and lifestyle, and there are medicines that are safe to take in pregnancy.
Symptoms of indigestion and heartburn
Symptoms of indigestion and heartburn include:
- a burning sensation or pain in the chest
- feeling full, heavy or bloated
- burping or belching
- feeling or being sick
- bringing up food
Symptoms usually come on soon after eating or drinking, but there can sometimes be a delay between eating and developing indigestion.
You can get symptoms at any point during your pregnancy, but they are more common from 27 weeks onwards.
Things you can do to help with indigestion and heartburn
Changes to your diet and lifestyle may be enough to control your symptoms, particularly if they are mild.
Eat healthily
You're more likely to get indigestion if you're very full.
If you're pregnant, it may be tempting to eat more than you would normally, but this may not be good for you or your baby.
Find out more about a healthy diet in pregnancy and foods to avoid.
Change your eating and drinking habits
You may be able to control your indigestion with changes to your eating habits.
It can help to eat small meals often, rather than larger meals 3 times a day, and to not eat within 3 hours of going to bed at night.
Cutting down on drinks containing caffeine, and foods that are rich, spicy or fatty, can also ease symptoms.
Keep upright
Sit up straight when you eat. This will take the pressure off your stomach. Propping your head and shoulders up when you go to bed can stop stomach acid coming up while you sleep.
Stop smoking
Smoking when pregnant can cause indigestion, and can seriously affect the health of you and your unborn baby.
When you smoke, the chemicals you inhale can contribute to your indigestion. These chemicals can cause the ring of muscle at the lower end of your gullet to relax, which allows stomach acid to come back up more easily. This is known as acid reflux.
Smoking also increases the risk of:
- your baby being born prematurely (before week 37 of your pregnancy)
- your baby being born with a low birthweight
- sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), or "cot death"
There's lots of help available to stop smoking. Talk to your midwife or call the NHS Smokefree helpline on 0300 123 1044. Find out more about stopping smoking in pregnancy.
Talk to your midwife or call the NHS Smokefree helpline on 0300 123 1044. Find out more about stopping smoking in pregnancy.
Avoid alcohol
Drinking alcohol can cause indigestion. During pregnancy, it can also lead to long-term harm to the baby. It's safest to not drink alcohol at all in pregnancy.
Find out more about alcohol and pregnancy
When to get medical help
See your midwife or GP if you need help managing your symptoms or if changes to your diet and lifestyle do not work. They may recommend medicine to ease your symptoms.
You should also see your midwife or GP if you have any of the following:
- difficulty eating or keeping food down
- weight loss
- stomach pains
Your midwife or GP may ask about your symptoms and examine you by pressing gently on different areas of your chest and stomach to see whether it's painful.
If you're taking prescription medicines
Speak to your GP if you're taking medicine for another condition, such as antidepressants, and you think it may be making your indigestion worse. They may be able to prescribe an alternative medicine.
Never stop taking a prescribed medicine unless you're advised to do so by your GP or another qualified healthcare professional who's responsible for your care.
Medicines for indigestion and heartburn
Medicines for indigestion and heartburn during pregnancy include:
- antacids – to neutralise the acid in your stomach (some are available over the counter from a pharmacist)
- alginates – to relieve indigestion caused by acid reflux by stopping the acid in your stomach coming back up your gullet
You may only need to take antacids and alginates when you start getting symptoms. However, your GP may recommend taking them before symptoms come on – for example, before a meal or before bed.
However, your GP may recommend taking them before symptoms come on – for example, before a meal or before bed.
If you're taking iron supplements as well as antacids, do not take them at the same time. Antacids can stop iron from being absorbed by your body.
If antacids and alginates do not improve your symptoms, your GP may prescribe a medicine to reduce the amount of acid in your stomach. 2 that are widely used in pregnancy and not known to be harmful to an unborn baby are:
- ranitidine – a tablet you take twice a day
- omeprazole – a tablet you take once a day
Causes of indigestion in pregnancy
Symptoms of indigestion come when the acid in your stomach irritates your stomach lining or your gullet. This causes pain and a burning feeling.
When you're pregnant, you're more likely to have indigestion because of:
- hormonal changes
- the growing baby pressing on your stomach
- the muscles between your stomach and gullet relaxing, allowing stomach acid to come back up
You may be more likely to get indigestion in pregnancy if:
- you had indigestion before you were pregnant
- you've been pregnant before
- you're in the later stages of pregnancy
Video: Eating well on a budget
In this video, a dietitian gives advice on how to eat healthily on a budget.
Media last reviewed: 13 January 2021
Media review due: 13 January 2024
Indigestion and heartburn in pregnancy
Indigestion and heartburn in pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content6-minute read
Listen
Key facts
- Indigestion (dyspepsia) is a feeling of pain or discomfort in your stomach, while heartburn is a burning pain in your stomach and chest caused by stomach acid.
- Heartburn is very common in pregnancy because of hormonal changes and your uterus pressing up against your stomach as your baby grows.
- Heartburn is often triggered by fatty or spicy foods, caffeine, chocolate or citrus fruit juice.
- You can try to avoid heartburn by eating small meals more often, eating slowly, not lying down or exercising after meals and sleeping on several pillows.

- There are medicines you can use to control indigestion and heartburn, so see your doctor if your symptoms don’t settle down on their own.
What are indigestion and heartburn?
Indigestion and heartburn are symptoms that are very common in pregnancy. If you’re pregnant, you have an 8 in 10 chance you will experience these symptoms at some point in your pregnancy.
Indigestion, also called 'dyspepsia', is a feeling of pain or discomfort in your stomach . This mostly occurs after eating or drinking.
Heartburn, also known as reflux, is a burning pain in your stomach or chest going up towards your throat. It’s caused by stomach acid coming up your oesophagus (the tube that connects your mouth to your stomach). The acid irritates the lining of your oesophagus.
Sometimes food might come back up from your stomach into your mouth. You might also notice a bitter taste in your mouth.
Why might I get heartburn when I’m pregnant?
Heartburn may be caused by changes in your hormone levels. One of the pregnancy hormones, called progesterone, can relax the muscle that usually holds your oesophagus closed where it meets your stomach. This allows food and acid from your stomach to go back up your oesophagus.
One of the pregnancy hormones, called progesterone, can relax the muscle that usually holds your oesophagus closed where it meets your stomach. This allows food and acid from your stomach to go back up your oesophagus.
Heartburn becomes more common as your pregnancy progresses. This can happen when your uterus (womb) pushes up against your stomach as your baby grows. This also pushes the contents of your stomach up into your oesophagus.
You’re more likely to get heartburn during pregnancy if you’ve had a baby before or if you get heartburn when you’re not pregnant.
What kinds of things will give me heartburn?
Heartburn can be triggered by what you eat and drink, such as:
- a big meal
- high-fat foods
- spicy foods
- chocolate
- citrus fruit juices
- drinks containing caffeine, including coffee, tea and cola
- alcohol (which is not recommended in pregnancy)
Other things that may trigger heartburn include:
- doing exercise soon after eating
- lying down after eating
- feeling anxious
Because everyone is different, it's a good idea to take note of the particular foods, drinks or activities that give you heartburn while you are pregnant.
Can heartburn hurt my baby?
Heartburn usually won’t cause any problems for your baby, but it’s uncomfortable for you.
A healthy diet is important for both your and your baby’s health. If heartburn is making it hard to eat healthy food, it’s best to treat it.
How can I avoid getting heartburn?
If your symptoms are mild, changing how you eat may help prevent heartburn. You could try:
- eating smaller meals more often and eating slowly
- avoiding eating for 2 or 3 hours before exercise or going to bed
- avoiding foods and drinks that give you heartburn
- avoiding eating and drinking at the same time, which can make your stomach more full
- sitting up straight while eating and not lying down after a meal
- raising the head of your bed or sleeping on at least 2 pillows
- sleeping on your left side
You might find it helpful to chew gum, which makes you produce more saliva to help neutralise the acid from your stomach. Drinking milk can also help neutralise acid.
Drinking milk can also help neutralise acid.
Is there any medicine I can take?
If your heartburn doesn’t improve by changing how you eat, your doctor or midwife may suggest that you take medicine for it.
Antacids are the first type of medicine to try. They can relieve your symptoms quickly. Antacids are safe in pregnancy as long as you don’t take more than the recommended dose. There are many different types — talk to your pharmacist to find one that’s most suitable for you.
If antacids don’t control your symptoms, speak to your doctor about other medicines you can take.
When should I see a doctor?
If your heartburn symptoms don't go away with medicine, it's important to see your doctor. A serious pregnancy condition called pre-eclampsia can cause pain under your ribs and a feeling of heartburn.
You should also see your doctor immediately if:
- you are vomiting up blood
- you are losing weight
- swallowing is painful or difficult
CHECK YOUR SYMPTOMS — Use the Symptom Checker and find out if you need to seek medical help.![]()
FIND A HEALTH SERVICE — The Service Finder can help you find doctors, pharmacies, hospitals and other health services.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care (Pregnancy care guidelines – reflux (heartburn)), NSW Health (Heartburn in pregnancy and breastfeeding), NSW Government (Having a baby), King Edward Memorial Hospital (Minor symptoms or disorders in pregnancy), Mater Mothers (Managing pregnancy discomforts), Pharmaceutical Society of Australia (Heartburn and indigestion), MSD Manual (Dyspepsia), RANZCOG (Pre-eclampsia and high blood pressure during pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: September 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Common discomforts during pregnancy
- Pre-eclampsia
Need more information?
Heartburn in pregnancy | Parenthub
Pregnancy might be a beautiful miracle but it can also be an uncomfortable one, especially when you are experiencing the worst heartburn of your life. And though we may not be able to help you with arguments over baby names or even 'cankles', we can help you with ins and outs of heartburn ... pun intended.
Read more on Parenthub website
Heartburn in Pregnancy | HealthEngine Blog
Heartburn is a symptom commonly experienced by pregnant women such that some women and obstetricians even consider it to be a normal occurrence in a healthy pregnancy.
Read more on HealthEngine website
5 weeks pregnant: Changes for mum
Week 5 of pregnancy is probably when you’ll know that you’re pregnant because your period is missing. There are also subtle changes in your body which are symptoms of pregnancy such as changes to your breasts, and pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and pregnancy heartburn. These changes are caused by pregnancy hormones, like hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, produced by the placenta) which is the hormone detected by a pregnancy test.
Read more on Parenthub website
Pregnancy at week 28
You are now in the third trimester and you'll probably be feeling many of the common discomforts of pregnancy, like a sore back, swelling, heartburn or cramps.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 21
At week 21, you should consider whether to do any travel since you may not be able to for much longer in your pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 13
At week 13 of pregnancy, you officially enter your second trimester and hopefully any morning sickness has eased off.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy nausea and morning sickness remedies
Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy are common and affect women differently. Dr Joe discusses the causes and morning sickness remedies in this video.
Read more on Parenthub website
Pregnancy at week 25
As you are approaching the end of the second trimester, you might be starting to feel a bit uncomfortable as your baby continues to grow.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pre-eclampsia and High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, very high blood pressure (severe hypertension) can cause complications for both you and your baby
Read more on RANZCOG - Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists website
Pregnancy - signs and symptoms - Better Health Channel
All women experience pregnancy differently, and you will experience different symptoms at different stages of your pregnancy.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
5th week of pregnancy burning belly. Pleasant Breast Transformation
In some women, the initial symptoms appear almost immediately after conception. But usually, toxicosis begins to torment expectant mothers when pregnancy reaches 5 weeks. What happens to the body of the mother and the embryo at such an early stage?
5 weeks of pregnancy what happens
At a period of five weeks, all organs are laid in the embryo, which will only develop later. Therefore, the initial weeks of pregnancy are considered very important.
At the fifth week of pregnancy, the fertilized egg completes its movement and is firmly attached to the wall of the uterus. But the embryo is still too small. It weighs no more than a gram, and its length is only three millimeters. A groove runs along the body of the embryo, which will later become the neural tube. Seals are noticeable next to it, which will then turn into muscles. In the early stages, the spinal cord and brain are formed, the nervous system gradually begins to develop. At week 5, the cardiovascular system begins to form in the embryo. The heart first looks like a tube, which then develops into a four-chambered organ. During the 5th week of pregnancy, the embryo's heart begins to beat.
But the heart is not the only organ that is formed at this time. The kidneys and lungs begin to form. The liver is also formed, such glands as the thyroid and pancreas. The first rudiments of the intestine appear, and the trachea gradually begins to separate from the esophagus.
The fifth week of pregnancy is a very short period, but even at this time you can see the rudiments of hands, ears and eyes. It is said that during intrauterine development, the future man goes through all the stages of embryonic development of animals. While the arms of the embryo are more like fins.
Changes in the body of the expectant mother
Although the belly remains the same size during the 5th week of pregnancy, global changes occur inside the body of the expectant mother. The entire hormonal system is rebuilt. The pregnancy hormone hCG, or human chorionic gonadotropin, enters the bloodstream. Progesterone and estrogen are also actively produced.
Despite the fact that the expectant mother does not yet feel an increase in the abdomen, the uterus becomes larger. One of the first signs that indicate the imminent appearance of a child is swollen breasts. Women notice that she begins to hurt like before the onset of menstruation. The nipples become extremely sensitive, and a halo appears around them in the form of a brown circle. Such changes in the breast are associated with its restructuring for future lactation.
Drawing pains in the abdomen can also cause discomfort. They also appear due to hormonal changes, and there is no need to worry about this. In addition, abdominal pain is associated with the fact that the uterus begins to gradually stretch.
What else can appear at this time, but is not an obligatory sign? Often, the expectant mother complains of swelling and constipation. Toxicosis is a frequent companion of pregnancy at this time. Urination may become more frequent as the bladder is under pressure from the uterus. Body temperature may rise, but slightly - up to 37 degrees. Heartburn and problems with the gastrointestinal tract also appear due to the activity of hormones. The latter are also reflected in the mood of a woman. She can become extremely irritable. The first signs that marks the 5th week of pregnancy are very similar to the premenstrual state.
Abdominal pain may be accompanied by discharge that gets worse. This is the norm, but only if they have neither color nor smell. If all this is present, the likelihood of intrauterine infection is high.
If the discharge during the 5th week of pregnancy is brown and accompanied by a small amount of blood, you should immediately consult a doctor. Most often, this is due to increased uterine tone, which can lead to miscarriage. In the first trimester, a woman may also have her usual menstrual flow, but, as a rule, they are scarce and end earlier than usual.
If the pain in the lower abdomen is very severe, this may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. In this case, it is also necessary to urgently consult a doctor, as this case can be fatal.
5th week of pregnancy and nutrition
Since this period is very important for the proper laying of the organs of the embryo, you need to eat accordingly.
It is very important to consume a lot of protein, which helps to form the body of the embryo. But protein should be useful. A pregnant woman should pay attention to cottage cheese, egg white, white poultry meat. As for legumes, which are also high in protein, they should be consumed in minimal quantities. They can lead to excessive gas formation, which will cause additional discomfort.
A pregnant woman should pay attention to cottage cheese, egg white, white poultry meat. As for legumes, which are also high in protein, they should be consumed in minimal quantities. They can lead to excessive gas formation, which will cause additional discomfort.
Vitamin E is very important for a successful pregnancy at any stage. Therefore, doctors prescribe it without fail. But if you can find a synthetic element on sale, then some products contain natural vitamin E, which, of course, is better for its absorption by the body. It is abundant in fish and oil. Olive and flaxseed oils will be very useful, because in addition to a large number of trace elements they contain Omega 3.
The most important for the proper course of pregnancy is folic acid, which helps in the formation of DNA. If there is not enough of it in the woman's body, then the central nervous system may not form correctly in the embryo. With a planned pregnancy, her appointment is prescribed three weeks before the intended conception. In foods, it is abundant in greens, any cabbage, nuts, whole grains, cod liver, eggs and cereals.
In foods, it is abundant in greens, any cabbage, nuts, whole grains, cod liver, eggs and cereals.
Ascorbic acid will help fight infections by supporting the immune system. And she should work for two in a woman's body during pregnancy.
A pregnant woman's diet should contain a lot of vegetables and fruits, which are a source of natural vitamins and microelements. In addition to this, it is necessary to take vitamins prescribed by the doctor.
Of course, toxicosis in the early stages can correct your diet. The body of the expectant mother may reject this or that product. Often, expectant mothers cannot eat anything at all due to toxicosis. In this case, you should consult a doctor, as this has an extremely negative effect on pregnancy and the development of the embryo.
Can I drink coffee at this time? This drink is undesirable for those who are expecting a baby. If you love coffee, you can have one cup a day. But it is better to gradually change your habits and switch to purified water or green tea. Naturally, you should give up alcohol and carbonated drinks.
Naturally, you should give up alcohol and carbonated drinks.
As far as diet is concerned, it is not required at this early date. Subsequently, if a woman does not gain weight heavily, she may not change her diet. But if in the fifth month she can gain about one and a half kilograms in a week, then everything fatty and floury should be abandoned. Indeed, there are cases when women, consoling themselves with the thought that the body eats for two, gain 30 kilograms each.
Tests at 5 weeks
Routine screening is done from 10 to 13 weeks. It consists of a biochemical blood test and the first ultrasound. But even in the fifth week, you may be prescribed tests. Most often this is done to confirm pregnancy, because the test is often wrong, and an increase in the uterus can be associated not only with the bearing of the fetus. Elevated levels of hCG in the blood can indicate pregnancy accurately and determine its duration.
- Early ultrasound is not recommended, but if the doctor sees the need, he may refer the woman for an ultrasound.

Dangers in the fifth week of pregnancy
The first trimester is a rather dangerous time for the embryo. Indeed, during the first weeks, a miscarriage occurs very often. Why do spontaneous abortions sometimes happen in women? This is largely due to the fact that the body is trying to get rid of the embryo with a defect. A miscarriage can also indicate that a woman's body is not yet ready for full bearing.
Other possible causes include hormonal disorders. If a woman's body produces an excessive amount of male hormones, then the pregnancy cannot proceed normally.
The second reason is the Rhesus conflict between the blood of the father and mother. With its existence, the body of the expectant mother will try to get rid of the fetus, as from a foreign body.
All kinds of sexually transmitted infections are common. That is why pregnancy is ideally planned to check the body of both women and men.
If a woman has diseases of the genital organs, this can also cause spontaneous abortion.
Medications and various foods can also cause miscarriage. Therefore, women are forbidden to drink infusions of St. John's wort or tansy.
Trauma and other outside influences can lead to miscarriage. If a woman accidentally slips and inaccurately falls, then this is also fraught with miscarriage.
Another risk is miscarriage. She has many reasons, ranging from inflammation of the female genital organs to too old for childbirth. The most common miscarriage in the first trimester occurs in women over 40 years of age. At the fifth week, it is very difficult to identify it on your own; only a doctor can fix the death of the embryo. However, if your toxicosis suddenly ended, then this is the first sign.
In fact, there are many risks that are identified early. They also include various pathologies of the child, including trisomy syndromes, heart defects and central nervous system. But this will be revealed with the help of the first screening tests for the level of hormones from the blood and the data of the first ultrasound.
At the 5th week of pregnancy, the baby inside the mother's womb is the size of a sesame seed. Its weight already reaches 1 g, and its height is 1.5 mm. In general, the 5th week of a woman's pregnancy proceeds favorably. Note that, according to obstetric calculations, the 5th week of pregnancy corresponds to a three-week period from the moment of conception. And if the pregnancy was planned in advance, and the woman already knows about the existence of a baby inside the womb, then from now on she should be especially careful about her own health. From the five-week gestation period, all the vital organs and systems of a small child are formed.
Feelings at 5 weeks
If the expectant mother has no idea that a new life is developing inside her, then at a five-week period the first signs appear, announcing the onset of conception. This period is characterized by the appearance of initial signs that make it possible to reveal a new status.
The first and most significant symptom of a five-week pregnancy is a delay in menstruation. At this stage, in addition to the cessation of menstruation, a woman may experience changes in her state of health and some ailments due to the onset of hormonal changes in the female body.
At this stage, in addition to the cessation of menstruation, a woman may experience changes in her state of health and some ailments due to the onset of hormonal changes in the female body.
There are no external changes in the female body yet. However, if the future mother carefully looks at her own body, she will see that the nipple halo becomes darker, and in addition, her favorite bra becomes tight. Sometimes women show such a symptom as a darkening of the strip going down from the navel. Of course, these signs are relevant for late pregnancy, but sometimes they also manifest themselves at a five-week period.
Ultrasound photo
Ultrasound at the 5th week of pregnancy is not a mandatory examination, however, for many women, for various reasons, it may be necessary to undergo such a diagnostic examination. Some expectant mothers want to make sure of the diagnosis of pregnancy as soon as possible, while for others, ultrasound is performed in accordance with the appointment of a medical specialist.
At the fifth obstetric week, the embryo passes into the embryo stage, and its outlines are already visible on the monitor of the ultrasound scanner. It is impossible to see the subtleties of the development of the baby on the ultrasound of the five-week gestation period. But special equipment allows you to recognize the baby's heart, the beating of which begins already in the next, sixth, week of pregnancy.
Ultrasound at the 5th week of pregnancy is the only way for doctors to know if the embryo has reached the uterine cavity or not. The main tasks pursued by ultrasound at the five-week gestation period are:
- Denial or confirmation of the patient's pregnancy.
- Clarification on the coccyx-parietal size of the baby's age.
- Establishment of the place of fixation of the embryo (in the uterus or outside it).
- Determination of the number of embryos in the uterine cavity.
- Determination of the state of amniotic fluid and uterine placenta.

- Assess how viable the fetus is (according to the existing heartbeat).
Ultrasound examination at the 5th week of pregnancy is not one of the mandatory procedures, and therefore the controversy never subsides around the need for its implementation. Many women believe that ultrasound in early pregnancy has a negative impact on the health of the baby. However, from a medical point of view, an ultrasound examination of a pregnant woman is one of the safest procedures. And if it is carried out in the first trimester (the first few weeks after conception), then with its help you can see the pathology of the fetus and take the necessary medical measures in a timely manner.
Main symptoms
At the 5th week of pregnancy, the test does not always show reliable information. The level of the hormone signaling conception during this period of time is still too low, however, a woman also recognizes the presence of an embryo inside the womb by other symptoms that already appear by this time.
- Nausea occurs in the morning;
- The sensitivity of the breast increases, it swells;
- Some of the pregnant women complain of a pulling pain in the lower abdomen;
- Pregnant women at the 5th week of pregnancy note the appearance of drowsiness, fatigue, lethargy;
- Increased sensitivity to a variety of smells and aromas.
Starting to look for symptoms of pregnancy at the fifth week, a woman should understand that her body is individual, so you may not feel any changes in yourself at all, and this state of affairs is considered quite normal, because the gestational age is still short. It is impossible to consider the absence of symptoms for a five-week period as a pathological condition.
At the 5th week of pregnancy, a woman experiences unusual and new sensations. These include emotional outbursts, the emergence of inspiration and enthusiasm, a high degree of vulnerability. If your movements are too abrupt, then after them there will be severe dizziness. The same symptom occurs with sudden changes in body position. All the described conditions will quickly replace each other in the 5th week of pregnancy. Sometimes during this period there is pain inside the abdomen, there may be scant discharge from the vagina. If they are not too abundant, and do not provoke too uncomfortable and painful sensations in a woman, then such processes can be considered normal and natural.
The same symptom occurs with sudden changes in body position. All the described conditions will quickly replace each other in the 5th week of pregnancy. Sometimes during this period there is pain inside the abdomen, there may be scant discharge from the vagina. If they are not too abundant, and do not provoke too uncomfortable and painful sensations in a woman, then such processes can be considered normal and natural.
Belly at 5 weeks
The tummy of a woman at the 5th week of pregnancy is not too big, almost invisible. For others, pregnancy at the 5th week will be almost imperceptible, but the woman may already feel some swelling inside the abdomen, which makes it difficult to lie comfortably on it. such sensations are caused by an increase in blood supply in the uterine cavity, the size of which on the 5th week is already increasing so much that a qualified gynecologist can already accurately tell about the presence of pregnancy during a diagnostic examination.
During this period, in addition to the abdomen, the breasts also increase in size, they swell and become very sensitive. All these symptoms already greatly annoy a woman in the first weeks of pregnancy, preventing her from sleeping on her stomach.
What happens in the body
The size of the fetus at the 5th week of pregnancy is still small, but when undergoing ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor will already be able to discern the presence of the embryo in the uterine cavity. True, at such an early date, only the amniotic egg is often visible there. During this period of time, the rudiments of internal organs and systems are already beginning to form in the future baby.
On the 5th week, the active laying of the respiratory system takes place, the baby's nervous system is formed. At this stage, it is represented only by the neural tube, the end of which is nothing more than the rudiment of the brain. Active cell division of the organism developing inside the womb continues. At the 5th week of pregnancy, the heart and circulatory system begin to form. Another week, and the embryo's heart will begin to beat. The length of the fetus at the 5th week of pregnancy is only 2 mm.
At the 5th week of pregnancy, the heart and circulatory system begin to form. Another week, and the embryo's heart will begin to beat. The length of the fetus at the 5th week of pregnancy is only 2 mm.
The risk of miscarriage at this time is still very high, and therefore gynecologists advise avoiding serious and strenuous sports, as well as active pastime. In the next 9 months, it is worth giving up strenuous physical activity to prevent the likelihood of harm to the baby inside the womb and minimize the risk of miscarriage.
Related articles:
Of course, any woman will be wary if it is the 5th week of pregnancy and the lower abdomen hurts. But this will not always mean a threat or a reason to sound the alarm. Therefore, do not wind yourself up ahead of time.
Drawing pain in the abdomen below or on the sides is one of the signs of pregnancy. A woman feels similar to premenstrual sensations - the stomach begins to pull, there is tension and discomfort. All these pain sensations are considered quite normal symptoms of pregnancy when the 5th week goes.
All these pain sensations are considered quite normal symptoms of pregnancy when the 5th week goes.
What is worth fearing and what is not?
After the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus, the uterus itself becomes larger and stretches. Many women do not even notice these sensations. But if the pains are sharp and quite strong, you should not consider them normal, but immediately visit a doctor.
Although mild convulsions and spasms of the ovaries are possible, in which hormones are directly to blame. Uterine cramps in early pregnancy can occur during movement, sports, and even orgasm.
If a woman has more than one fetus, then she may be visited by a sharp pain in the groin area, which decreases during walking.
Discomfort that appears in the lower abdomen, as a rule, manifests itself in women who complained of painful menstruation before pregnancy. Such pains will pass by themselves, they cannot be prevented or warned in advance.
But if the lower abdomen hurts, and bloody discharge appears, then you need to urgently visit a doctor.
What is really dangerous
At the 5th week of pregnancy, the supporting ligaments and discs soften, and the level of progesterone increases. All this causes painful spasms in the lower back. Slight pulling pain in a pregnant woman does not mean at all that something bad is happening. But if this worries you, then it is better to visit a doctor who will accurately determine the source of pain and give the necessary advice.
Pain in early pregnancy may indicate an ectopic pregnancy or inflammation of the fallopian tubes. Moreover, pain in the lower abdomen may be signs of spontaneous abortion. Therefore, if the doctor notices you have uterine hypertonicity, he will refer you for treatment.
In other cases, one should calmly treat the pulling pain in the lower abdomen. It is necessary to completely relax, continuing to breathe calmly in the stomach.
New sensations at the 5th week
In the second month of pregnancy, a woman is visited by new feelings - subjective manifestations. There is a selective approach to food. A woman can start eating those foods that she did not like at all before. In addition, a woman can attend headaches, nausea and vomiting, dizziness. There may also be problems with the stool, there is heartburn, frequent urination, bloating. Moreover, a pregnant woman may feel tired, even with the slightest exertion.
There is a selective approach to food. A woman can start eating those foods that she did not like at all before. In addition, a woman can attend headaches, nausea and vomiting, dizziness. There may also be problems with the stool, there is heartburn, frequent urination, bloating. Moreover, a pregnant woman may feel tired, even with the slightest exertion.
Emotional changes are observed - irritability, resentment, tearfulness, abrupt mood changes, anxiety. But it is at this time that the feeling of happiness that pregnancy brings appears. All these changes are quite natural and are caused by hormones in the blood.
Toxemia, Intestinal Problems & Heartburn
Find out how pregnancy affects the digestive tract, which trimesters are more likely to cause bowel symptoms and nausea, and what to do to manage them.
During pregnancy, the burden on the mother's body increases. The body needs more nutrients, the body produces additional hormones. And the growing fetus puts pressure on neighboring organs, including the stomach and intestines. We tell you what symptoms are observed in each trimester, how to cope with toxicosis and get rid of heartburn.
We tell you what symptoms are observed in each trimester, how to cope with toxicosis and get rid of heartburn.
Contents:
- 2. Toxicosis and pregnancy
- 3. Causes, risks and treatment of diarrhea during pregnancy
- 4. Heartburn and stomach pain during pregnancy
- 5. Bloating, constipation and microbiota during pregnancy
- 6. Note
Changes in the work of the gastrointestinal tract by trimesters of pregnancy
The average duration of pregnancy is 40 weeks, which are usually divided into trimesters in accordance with the stages of intrauterine development of the child.
Each trimester is accompanied by a number of changes in the body, including in the gastrointestinal tract:
Causes of gastrointestinal problems during pregnancy
Every pregnancy is accompanied by inevitable changes in the functioning of the digestive system. They are more often caused by hormonal changes and increased stress on the organs, but they can also be associated with lifestyle and health conditions, for example:
- Sedentary lifestyle and unbalanced diet;
- Certain drugs, including calcium or aluminum antacids;
- Viral and bacterial infections;
- Intolerance to certain nutrients and allergic reactions;
- Stress;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
If you have chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and you are planning a pregnancy, try to consult your doctor in advance. Symptoms of conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or acid reflux are more likely to get worse during pregnancy. Your doctor will help prepare your body and create a prevention plan to help relieve symptoms during this time.
Irritable bowel syndrome, or IBS, is a functional bowel disease that causes frequent abdominal pain, impaired peristalsis, bloating, constipation, or diarrhea.
Morning sickness, vomiting and general malaise during pregnancy
Morning sickness and morning sickness during early pregnancy are common, because the body undergoes important changes necessary for the development of the child.
up to 90%
women experience nausea during pregnancy
Doctors find it difficult to say with certainty why pregnant women feel sick in the morning. The main theory is hormonal changes. But there are some patterns associated with an increased risk of morning sickness:
The main theory is hormonal changes. But there are some patterns associated with an increased risk of morning sickness:
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Toxicosis during previous pregnancy;
- History of morning sickness during pregnancy in close relatives;
- Tendency to motion sickness;
- Use of oral contraceptives containing estrogen before pregnancy;
- Frequent migraines;
- BMI 30 and above;
- Increased levels of stress hormones
Risks of severe morning sickness and how to reduce nausea
Nausea and vomiting are usually not associated with a risk to mother and child and will disappear by 16-20 weeks of pregnancy, but it is not necessary to wait that long - there are ways that can help reduce nausea and enjoy the process of waiting for a new person:
- Get plenty of rest - fatigue increases toxicosis;
- Avoid smells and foods that cause nausea;
- Eat something right after waking up.
 A toast or a slice of bread will help reduce nausea;
A toast or a slice of bread will help reduce nausea; - Avoid hunger - empty stomach increases nausea. Eat small meals often, prefer low-fat, high-carbohydrate foods;
- Try ginger - studies show it helps with nausea;
- Sip as often as possible and prefer still water.
In rare cases, pregnant women may develop hyperemesis gestationis or excessive vomiting. This is a serious condition that can lead to dehydration, kidney damage, seizures, abnormal heart rhythms, and even death.
Signs of dehydration include: dry mouth, dizziness, dark urine, infrequent urination and/or dizziness.
Symptoms of excessive pregnancy vomiting:
- frequent nausea for a long time and regular vomiting after meals;
- dry skin and lips;
- sudden weight loss;
- low blood pressure (below 90/60).
If symptoms of excessive pregnancy vomiting occur, do not wait until the condition resolves on its own.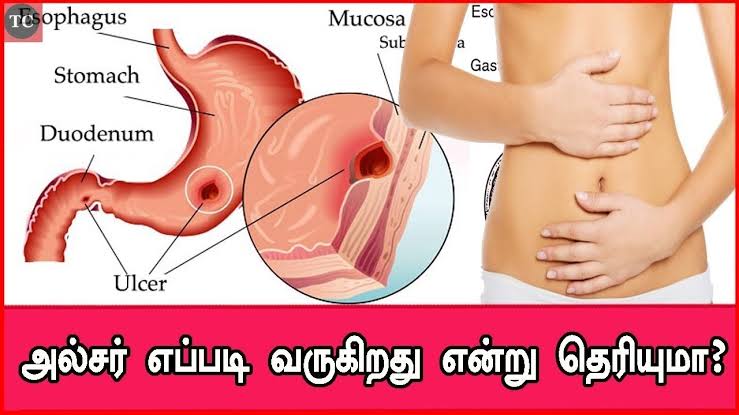 It is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible - the doctor will prescribe treatment, help adjust the diet and lifestyle of the expectant mother.
It is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible - the doctor will prescribe treatment, help adjust the diet and lifestyle of the expectant mother.
0.5–2%
pregnant women experience excessive vomiting
Diarrhea in pregnancy
The word "diarrhea" comes from the Greek language and literally means "to flow through". This is a condition during which bowel movements or bowel movements occur three times a day or more often. This phenomenon is especially typical for the third trimester of pregnancy, but it can also occur earlier.
Symptoms of diarrhea:
- Three or more bowel movements per day
- Urgent urge to have a bowel movement
- Abdominal pain and cramps
- Bloating
Causes of diarrhea during pregnancy poisoning, dysbacteriosis, bacterial and viral infections:
| Gastroenteritis | Use of lactose and gluten in case of intolerance to these nutrients |
| Bacterial infections: listeriosis or salmonella | Chronic gastrointestinal diseases: Crohn's disease, IBS, ulcerative colitis |
| Some antibiotics and antacids to reduce acidity | Laxatives |
| Sugar substitutes such as sorbitol | Overconsumption of certain foods |
Tip: If you have recently returned from a holiday in an exotic country with nausea and diarrhea and find out you are pregnant, see your doctor as soon as possible.
Gastroenteritis
One common cause of diarrhea during pregnancy is gastroenteritis, or stomach flu. It is caused by bacterial or viral infections: norovirus, rotavirus, E. coli, salmonella, which enter the body through contact with contaminated surfaces, dishes, food and water.
Gastroenteritis usually lasts about three days. However, a severe form of the disease is dangerous to health, especially during pregnancy, as it can cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and lead to premature birth.
The main symptoms of gastroenteritis are diarrhea without blood, nausea and vomiting, stomach cramps and pain, slight fever, headache and muscle pain.
Take extra precautions to reduce your risk of getting sick: frequent handwashing and surface disinfection. If the expectant mother has small children, they are not recommended to use the same cutlery.
Risks of diarrhea during pregnancy
Usually diarrhea during pregnancy is not a cause for concern. However, you should consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur during this period:
However, you should consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur during this period:
- Diarrhea for more than two days;
- Blood or mucus stools;
- Sudden weight loss;
- Abdominal pain;
- Dehydration.
How to treat diarrhea during pregnancy
If you have diarrhea during pregnancy, drink plenty of fluids, avoid foods high in fat and sugar, avoid dairy products, and caffeinated drinks.
Dehydration is a serious risk, especially during pregnancy, so electrolyte balance should be restored first with fluids and simple foods:
| Moderate fruit juices | Drinks without alcohol and caffeine |
| Bananas | Potatoes |
| Rice | Toast |
| Rusks | Light soups and broths |
| Pasta | Applesauce |
Find out about your body's ability to break down lactose and gluten with the Atlas Microbiota Test.
Stomach pain and heartburn during pregnancy
Many women experience stomach pain during pregnancy, especially the upper part of the stomach, as well as heartburn - a burning sensation in the chest and esophagus.
This is more common in the third trimester, after about 27 weeks. This is an unpleasant but natural phenomenon during pregnancy: the baby grows inside the uterus and presses on other organs, including the stomach. And hormones cause the muscles to relax, which causes acid from the stomach to enter the esophagus and irritate it. In addition, pain can be caused by problems with certain organs such as the gallbladder, or inflammation of the pancreas.
Symptoms of heartburn during pregnancy:
- Burning in chest and esophagus;
- Feeling of overeating, heaviness or bloating;
- Belching, including with acid and/or food particles;
- Nausea.
Avoid cramps and heartburn during pregnancy is unlikely. However, some tips can help reduce their frequency:
However, some tips can help reduce their frequency:
Nutrition : try to avoid overeating - eat easily digestible food in small portions; do not eat three hours before bedtime; watch your posture while eating - so the pressure on your stomach will be less.
Smoking and alcohol: In addition to known harms to mothers and babies, tobacco smoke also relaxes the muscles in the lower esophagus, allowing acid to enter the esophagus. And alcohol provokes heartburn and acid reflux.
Although stomach pain and heartburn often accompany pregnancy, abdominal pain, especially in the third trimester, should be taken seriously. It can be a sign of preterm labor or placental abruption, and puts mother and baby at risk.
If you experience severe abdominal pain during pregnancy that is accompanied by the following symptoms, seek medical attention as soon as possible:
| Abdominal pain and fever | Bleeding |
| Regular convulsions | Unusual vaginal discharge/ spotting |
| Vomiting | Low back pain |
| Pain or burning when urinating | Severe pain that lasts 30-60 minutes |
Bloating, constipation and microbiota during pregnancy
Excessive gas and constipation during pregnancy can be caused by hormonal changes, such as increased production of progesterone. This hormone, essential for nourishing the uterus and fetus, relaxes the muscles of the body, including the muscles in the intestines, which slows down digestion and increases flatulence. A similar reaction of the body can be observed before each menstruation, when the production of progesterone increases.
This hormone, essential for nourishing the uterus and fetus, relaxes the muscles of the body, including the muscles in the intestines, which slows down digestion and increases flatulence. A similar reaction of the body can be observed before each menstruation, when the production of progesterone increases.
Flatulence - bloating of the abdomen due to the accumulation of gases.
Here are a few simple rules that will help improve intestinal motility and avoid constipation and bloating:
- If you do not usually eat a lot of fiber and indigestible foods like legumes, try to gradually introduce them into your diet;
- Avoid carbonated drinks and fatty foods;
- Move more;
- Drink plenty of fluids.
If bloating and constipation are accompanied by severe pain that lasts more than 30 minutes, or if you have been constipated for two or more weeks, see your doctor.
Gut microbiota and bacteria during pregnancy
A woman's body goes through many changes during pregnancy, and this can affect the microbiota, the bacterial ecosystem that lives in the gut. Trillions of microorganisms do important work for the whole body: they synthesize vitamins and essential acids, keep your intestines working and protect it from disease and inflammation.
Trillions of microorganisms do important work for the whole body: they synthesize vitamins and essential acids, keep your intestines working and protect it from disease and inflammation.
The additional influx of female hormones that accompanies pregnancy alters gut function and affects the microbiota. This is good, because the bacterial community is constantly adjusting to external and internal conditions in order to keep up with the needs of the body.
To keep your gut bacteria running smoothly, they need your help. Provide them with healthy foods and plant fibers. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds contain prebiotics, special substances that beneficial bacteria feed on. When properly balanced, the bacteria even increase your body's defenses against harmful microorganisms that can cause gastroenteritis during pregnancy.
The Atlas Microbiota Test helps you understand how to prepare your gut for future pregnancies and reduce the risk of digestive problems.
☝️ Take note
Now you have all the necessary knowledge and tools to help you deal with digestive problems during pregnancy. They are quite varied and quite natural, but in some cases it is necessary to immediately seek medical help:
- Vomiting blood;
- Blood in stool;
- Diarrhea for more than two days;
- Constipation for more than two weeks;
- Sudden weight loss;
- Severe pain interfering with daily activities;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Pain when swallowing or difficulty swallowing;
- Excessive fatigue.
More articles on the causes of digestive problems on the blog:
- 7 foods that cause gas and bloating
- Lindsey J Wegrzyniak, Treatment of Hyperemesis Gravidarum, 2012
- Edwards A. et al., The Maternal Gut Microbiome During Pregnancy, 2018
- National Health and Safety (NHS), Vomiting and morning sickness in pregnancy
- Kudzai Kanhutu, Travel and pregnancy: an infectious diseases perspective, 2011
- CDC, Pregnant travelers
- U.