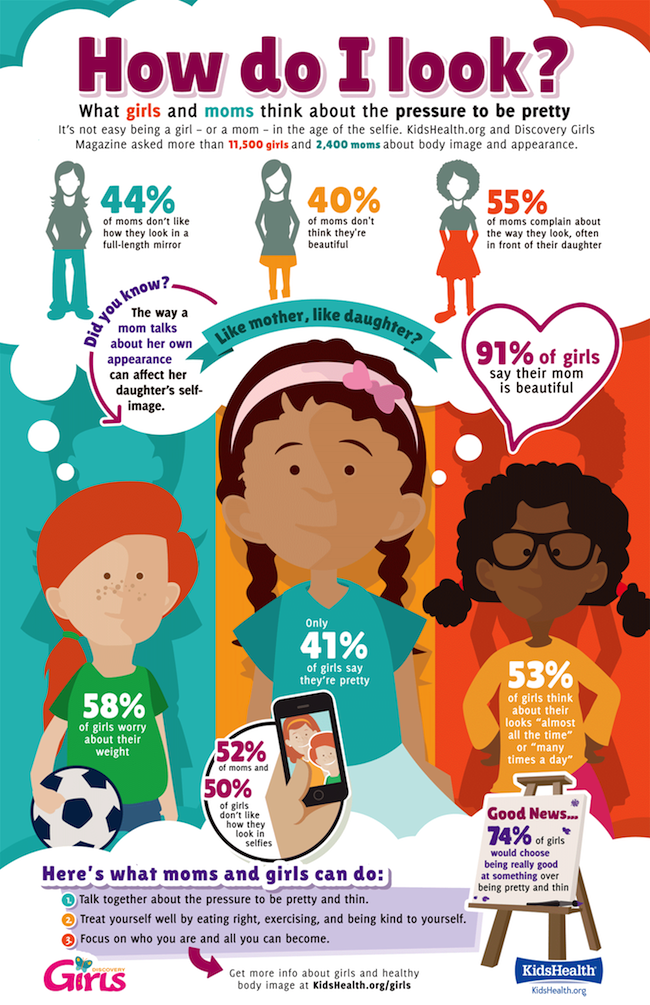
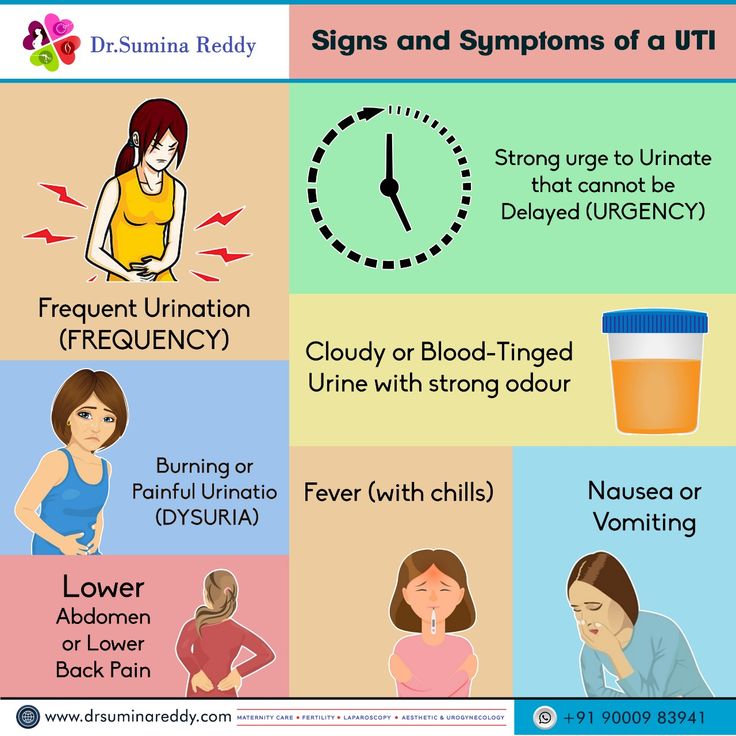
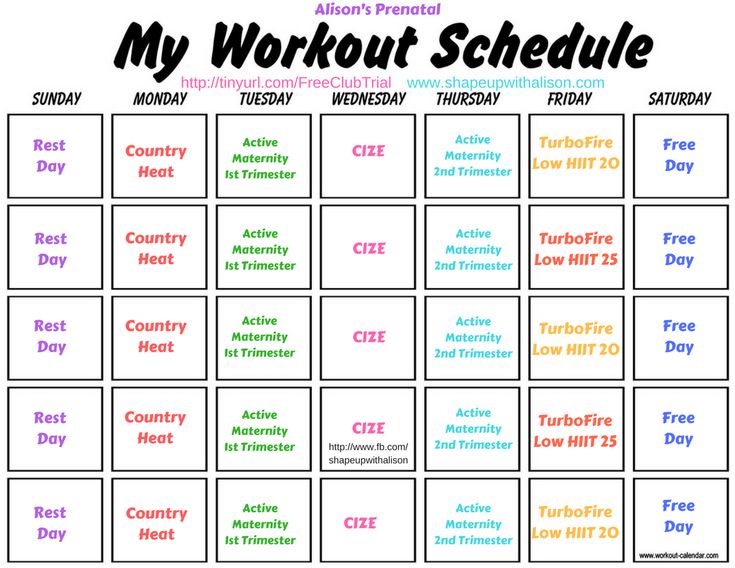
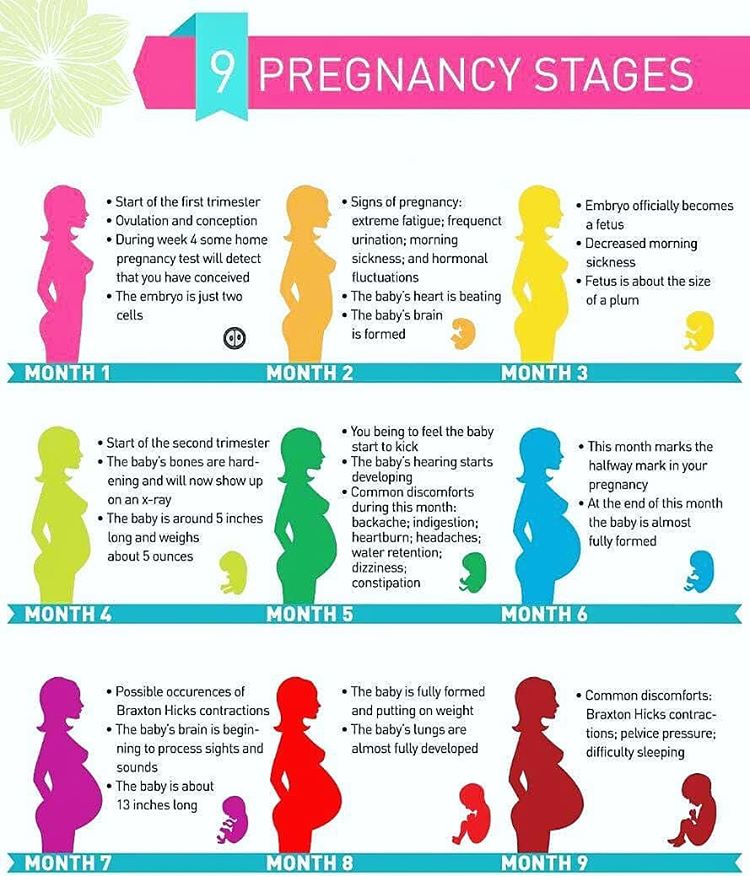
How many weeks are you in second trimester
A Guide for First-Time Parents (for Parents)
Life has changed now that your baby is here, and you might have lots of questions about what to do. These tips can help nervous first-time parents feel confident about caring for a newborn in no time.
Getting Help After Your Baby Comes Home
An important part of caring for a newborn is to also take care of yourself. Consider getting help during this time, which can feel hectic and overwhelming.
Relatives and friends might want to help. Even if you disagree on some things, their own experiences might be helpful. It's reasonable for you to ask anyone handling or helping with your baby to be up to date on vaccines and only help if they are feeling well.
But if you don't feel up to having guests or have other concerns, don't feel guilty about limiting visitors.
Handling Your Newborn
If you haven't spent a lot of time around newborns, they may seem very fragile. Here are a few basics to remember:
- Wash your hands (or use a hand sanitizer) before handling your baby.
Newborns don't have a strong immune system yet, so they're at risk for infections. Make sure that everyone who handles your baby has clean hands.
- Support your baby's head and neck. Cradle the head when carrying your baby and support their head when carrying the baby upright or when you lay your baby down.
- Never shake your newborn, whether in play or in frustration. Shaking can cause bleeding in the brain and even death. If you need to wake your infant, don't do it by shaking — instead, tickle your baby's feet or blow gently on a cheek.
- Make sure your baby is securely fastened into the carrier, stroller, or car seat. Limit any activity that could be too rough or bouncy.
- Remember that your newborn is not ready for rough play, such as being jiggled on the knee or thrown in the air.
Bonding With and Soothing Your Newborn
Bonding is one of the most enjoyable parts of infant care.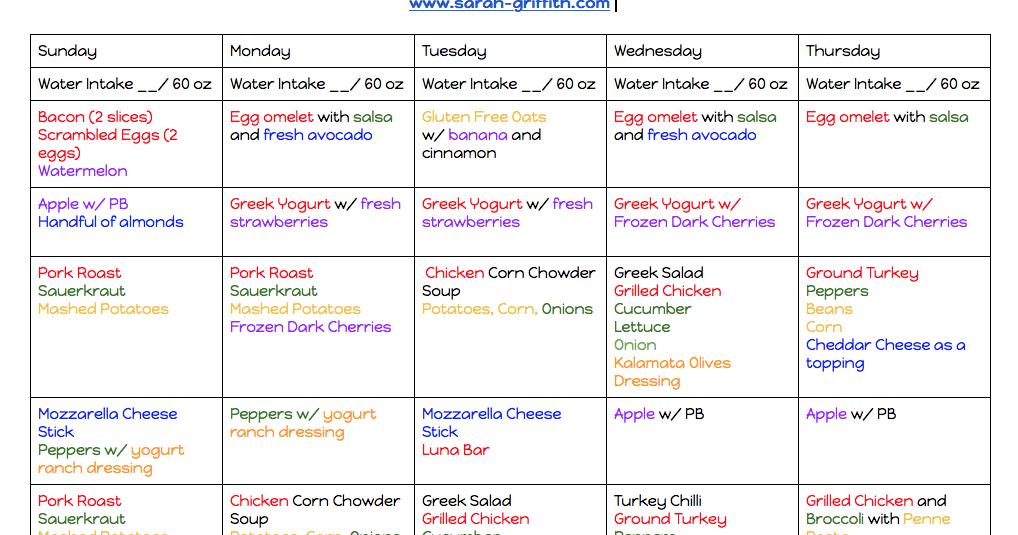 It happens during the sensitive time in the first hours and days after birth when parents make a deep connection with their infant. Physical closeness can promote an emotional connection.
It happens during the sensitive time in the first hours and days after birth when parents make a deep connection with their infant. Physical closeness can promote an emotional connection.
For infants, the attachment contributes to their emotional growth, which also affects their development in other areas, such as physical growth. Another way to think of bonding is "falling in love" with your baby. Children thrive from having a parent or other adult in their life who loves them unconditionally.
Begin bonding by cradling your baby and gently stroking them in different patterns. You and your partner both can be "skin-to-skin" with your baby, holding your newborn against your own skin while feeding or cradling.
Babies, especially premature babies and those with medical problems, may respond to infant massage. Some types of massage may enhance bonding and help with infant growth and development. Many books and videos cover infant massage — ask your doctor for recommendations. Be careful, though — babies are not as strong as adults, so massage your baby gently.
Be careful, though — babies are not as strong as adults, so massage your baby gently.
Babies usually love vocal sounds, such as talking, babbling, singing, and cooing. Your baby will probably love listening to music. Baby rattles and musical mobiles are other good ways to stimulate your infant's hearing. If your little one is being fussy, try singing, reciting poetry and nursery rhymes, or reading aloud as you sway or rock your baby gently in a chair.
Some babies can be unusually sensitive to touch, light, or sound, and might startle and cry easily, sleep less than expected, or turn their faces away when someone speaks or sings to them. If that's the case with your baby, keep noise and light levels low to moderate.
Swaddling, which works well for some babies during their first few weeks, is another soothing technique to learn. Proper swaddling keeps a baby's arms close to their body while letting them move their legs a bit. Not only does swaddling keep a baby warm, but it seems to give most newborns a sense of security and comfort. Swaddling also may help limit the startle reflex, which can wake a baby.
Swaddling also may help limit the startle reflex, which can wake a baby.
Here's how to swaddle a baby:
- Spread out a baby blanket, with one corner folded over slightly.
- Lay the baby face-up on the blanket with their head above the folded corner.
- Wrap the left corner over the baby's body and tuck it beneath the back of the baby, going under the right arm.
- Bring the bottom corner up over the baby's feet and pull it toward their head, folding the fabric down if it gets close to the face. Be sure not to wrap too tightly around the hips. Hips and knees should be slightly bent and turned out. Wrapping your baby too tightly may increase the chance of hip dysplasia.
- Wrap the right corner around the baby, and tuck it under the baby's back on the left side, leaving only the neck and head exposed. To make sure your baby is not wrapped too tight, make sure you can slip a hand between the blanket and your baby's chest, which will allow comfortable breathing.
 But make sure that the blanket is not so loose that it could come undone.
But make sure that the blanket is not so loose that it could come undone. - Babies should not be swaddled after they show signs of starting to roll over. That’s usually when they're 2 months old. At this age, some babies can roll over while swaddled, which increases their risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
All About Diapering
Whether you use cloth or disposable diapers, your little one will dirty them about 10 times a day, or about 70 times a week.
Before diapering your baby, make sure you have all supplies within reach. You'll need:
- a clean diaper
- fasteners (if cloth diapers are used)
- diaper ointment
- diaper wipes (or a container of warm water and a clean washcloth or cotton balls)
After each bowel movement or if the diaper is wet, lay your baby on their back and remove the dirty diaper. Use the water, cotton balls, and washcloth or the wipes to gently wipe your baby's genital area clean. When removing a boy's diaper, do so carefully because exposure to the air can make him pee. When wiping a girl, wipe her bottom from front to back to avoid a urinary tract infection (UTI). To prevent or heal a rash, apply ointment. Always wash your hands after you change a diaper.
When removing a boy's diaper, do so carefully because exposure to the air can make him pee. When wiping a girl, wipe her bottom from front to back to avoid a urinary tract infection (UTI). To prevent or heal a rash, apply ointment. Always wash your hands after you change a diaper.
Diaper rash is a common concern. Typically the rash is red and bumpy and will go away in a few days with warm baths, some diaper cream, and a little time out of the diaper. Most rashes happen because the baby's skin is sensitive and becomes irritated by the wet or poopy diaper.
To prevent or heal diaper rash, try these tips:
- Change your baby's diaper often, and as soon as possible after bowel movements.
- Gently clean the area with mild soap and water (wipes sometimes can be irritating), dry the skin, then apply a very thick layer of diaper rash or “barrier” cream. Creams with zinc oxide are best because they form a barrier against moisture.
- If you use cloth diapers, wash them in dye- and fragrance-free detergents.

- Let your baby go undiapered for part of the day. This gives the skin a chance to air out.
If the diaper rash continues for more than 3 days or seems to be getting worse, call your doctor — it may be caused by a fungal infection that needs treatment with a prescription medicine.
Baby Bathing Basics
Give your baby only sponge baths until after:
- the umbilical cord falls off and the navel heals completely (1–4 weeks)
- the circumcision heals (1–2 weeks)
A bath two or three times a week in the first year is fine. More frequent bathing may be drying to the skin.
Have these items ready before bathing your baby:
- a soft, clean washcloth
- mild, unscented baby soap and shampoo
- a soft brush to stimulate the baby's scalp
- towels or blankets
- a clean diaper
- clean clothes
Sponge baths. For a sponge bath, select a safe, flat surface (such as a changing table, floor, or counter) in a warm room. Fill a sink, if nearby, or bowl with warm (not hot!) water. Undress your baby and wrap them in a towel. Wipe your infant's eyes with a washcloth (or a clean cotton ball) dampened with water only, starting with one eye and wiping from the inner corner to the outer corner. Use a clean corner of the washcloth or another cotton ball to wash the other eye. Clean your baby's nose and ears with the damp washcloth. Then wet the cloth again and, using a little soap, wash their face gently and pat it dry.
Fill a sink, if nearby, or bowl with warm (not hot!) water. Undress your baby and wrap them in a towel. Wipe your infant's eyes with a washcloth (or a clean cotton ball) dampened with water only, starting with one eye and wiping from the inner corner to the outer corner. Use a clean corner of the washcloth or another cotton ball to wash the other eye. Clean your baby's nose and ears with the damp washcloth. Then wet the cloth again and, using a little soap, wash their face gently and pat it dry.
Next, using baby shampoo, create a lather and gently wash your baby's head and rinse. Using a wet cloth and soap, gently wash the rest of the baby, paying special attention to creases under the arms, behind the ears, around the neck, and in the genital area. Once you have washed those areas, make sure they are dry and then diaper and dress your baby.
Tub baths. When your baby is ready for tub baths, the first baths should be gentle and brief. If your baby gets upset, go back to sponge baths for a week or two, then try the bath again.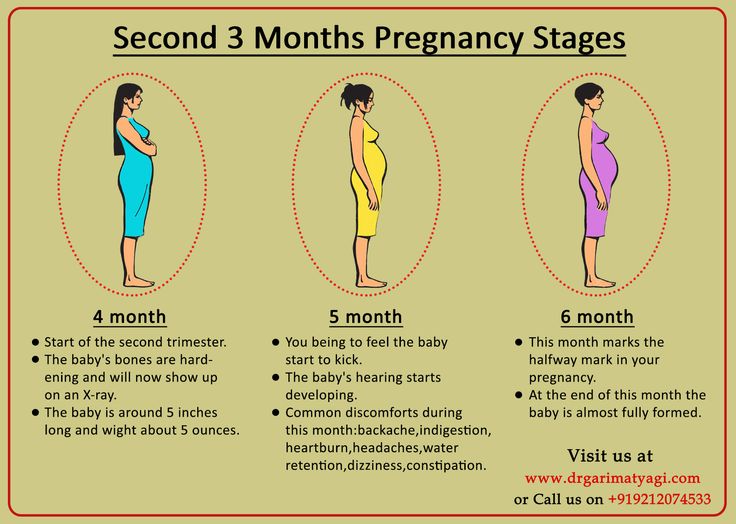
Besides the supplies listed above, add:
- an infant tub with 2 to 3 inches of warm — not hot! — water (to test the water temperature, feel the water with the inside of your elbow or wrist). An infant tub is a plastic tub that can fit in the bathtub; it's a better size for babies and makes bathing easier to manage.
In a warm room, undress your baby and then place them in the water right away to prevent chills. Make sure the water in the tub is no more than 2–3 inches deep, and that water is no longer running in the tub. Use one of your hands to support the head and the other hand to guide the baby in feet-first. Speaking gently, slowly lower your baby up to their chest into the tub.
Use a washcloth to wash your baby's face and hair. Gently massage your baby's scalp with the pads of your fingers or a soft baby hairbrush, including the area over the fontanelles (soft spots) on the top of the head. When you rinse the soap or shampoo from your baby's head, cup your hand across their forehead so the suds run toward the sides and soap doesn't get into your baby's eyes. Gently wash the rest of your baby's body with water and a small amount of soap.
Gently wash the rest of your baby's body with water and a small amount of soap.
Throughout the bath, regularly pour water gently over your baby's body so they don't get cold. After the bath, wrap your baby in a towel right away, making sure to cover their head. Baby towels with hoods are great for keeping a freshly washed baby warm.
While bathing your infant, never leave the baby alone. If you need to leave the bathroom, wrap the baby in a towel and take them with you.
Circumcision and Umbilical Cord Care
After a circumcision, the tip of the penis is usually covered with gauze coated with petroleum jelly to keep the wound from sticking to the diaper. Gently wipe the tip clean with warm water after a diaper change, then apply petroleum jelly to the tip so it doesn't stick to the diaper. Redness or irritation of the penis should heal within a few days. Call your baby's doctor right away, though, if the redness or swelling gets worse or if pus-filled blisters form, as these can be signs of an infection.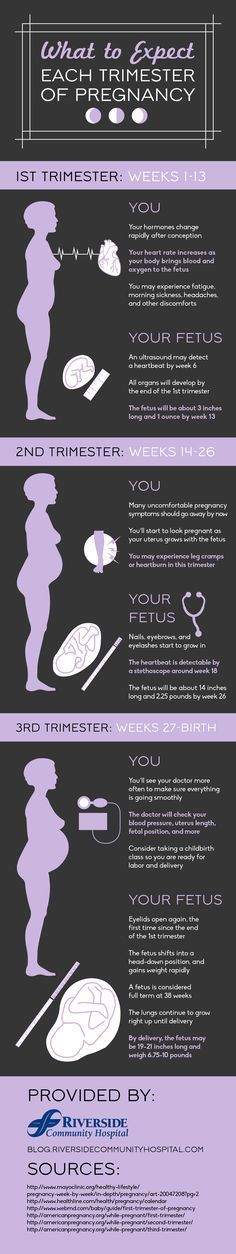
Umbilical cord care in newborns is also important. Clean around the stump with plain water and blot dry until the cord stump dries up and falls off, usually in 10 days to 3 weeks.
An infant's umbilical area shouldn't be submerged in water until the cord stump falls off and the area is healed. Until it falls off, the cord stump will change color from yellow to brown or black — this is normal. Call your doctor if the umbilical area looks red or if a bad odor or discharge develops.
Feeding and Burping Your Baby
Whether feeding your newborn by breast or a bottle, you may wonder how often to do so. Generally, it's recommended that babies be fed on demand — whenever they seem hungry. Your baby may cue you by crying, putting fingers in their mouth, or making sucking noises.
A newborn baby needs to be fed every 2–3 hours. If you breastfeed, give your baby the chance to nurse about 10–15 minutes at each breast. If you formula-feed, your baby probably will take about 2–3 ounces (60–90 milliliters) at each feeding.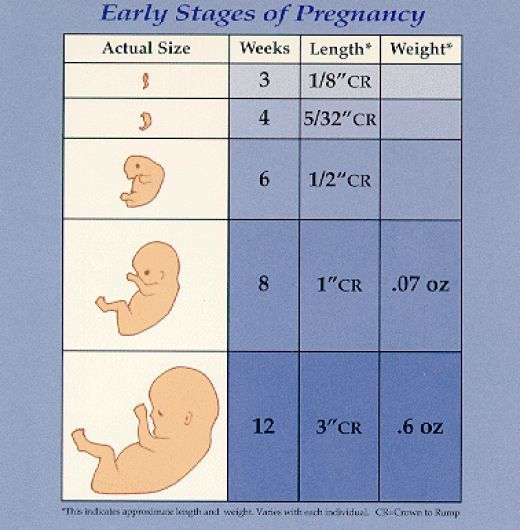
Some newborns may need to be awakened every few hours to make sure they get enough to eat. Call your baby's doctor if you need to wake your newborn often or if your baby doesn't seem interested in eating or sucking.
If you're formula-feeding, you can easily see if your baby is getting enough to eat. But if you're breastfeeding, it can be a little trickier. If your baby seems satisfied, makes about six wet diapers and several poops a day, sleeps well, and is gaining weight regularly, then they're probably eating enough.
Another good way to tell if your baby is getting milk is to notice if your breasts feel full before feeding your baby and less full after feeding. Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about your child's growth or feeding schedule.
Babies often swallow air during feedings, which can make them fussy. To help prevent this, burp your baby often. Try burping your baby after every 2–3 ounces (60–90 milliliters) if you bottle-feed, and each time you switch breasts if you breastfeed.
If your baby tends to be gassy, has gastroesophageal reflux, or seems fussy during feeding, try burping your little one after every ounce during bottle-feeding or every 5 minutes during breastfeeding.
Try these burping tips:
- Hold your baby upright with their head on your shoulder. Support your baby's head and back while gently patting the back with your other hand.
- Sit your baby on your lap. Support your baby's chest and head with one hand by cradling your baby's chin in the palm of your hand and resting the heel of your hand on your baby's chest (be careful to grip your baby's chin — not throat). Use the other hand to gently pat your baby's back.
- Lay your baby face-down on your lap. Support your baby's head, making sure it's higher than their chest, and gently pat or rub your baby's back.
If your baby doesn't burp after a few minutes, change the baby's position and try burping for another few minutes before feeding again. Always burp your baby when feeding time is over, then keep your little one in an upright position for at least 10–15 minutes to help prevent them from spitting up.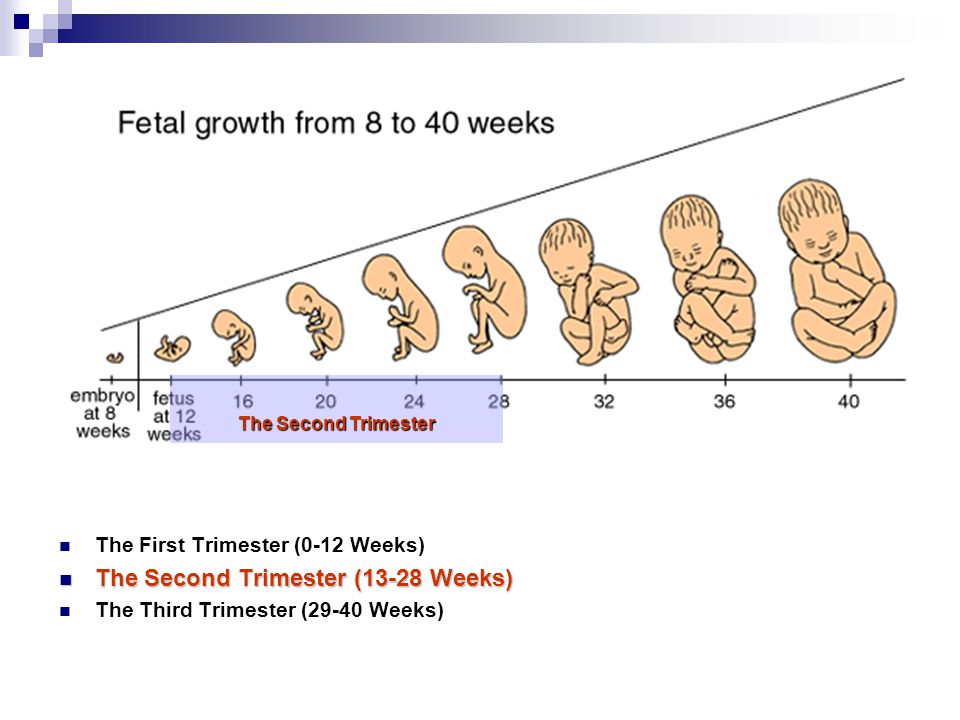
Newborn Sleeping Basics
As a new parent, you may be surprised to learn that your newborn, who seems to need you every minute of the day, actually sleeps about 16 hours or more!
Newborns typically sleep for periods of 2–4 hours. Don't expect yours to sleep through the night — the digestive system of babies is so small that they need nourishment every few hours and should be awakened if they haven't been fed for 4 hours (or more often if your doctor is concerned about weight gain).
When can you expect your baby to sleep through the night? Many babies sleep through the night (between 6–8 hours) at 3 months of age, but if yours doesn't, it's not a cause for concern. Like adults, babies must develop their own sleep patterns and cycles. So if your newborn is gaining weight and appears healthy, don't despair if they're not sleeping through the night at 3 months.
It's important to always place babies on their backs to sleep to reduce the risk of SIDS. Other safe sleeping practices include:
Other safe sleeping practices include:
- not using blankets, quilts, sheepskins, stuffed animals, and pillows in the crib or bassinet (these can suffocate a baby)
- parents sharing a bedroom (but not a bed) with the baby for the first 6 months to 1 year
Also be sure to change the position of your baby's head from night to night (first right, then left, and so on) to prevent the development of a flat spot on one side of the head.
Many newborns have their days and nights "mixed up." They tend to be more awake and alert at night, and sleepier during the day. One way to help them is to keep stimulation at night to a minimum. Keep the lights low, such as by using a nightlight. Save talking and playing with your baby for the daytime. When your baby wakes up during the day, try to keep them awake a little longer by talking and playing.
Even if you feel a little nervous about handling a newborn, in a few weeks you'll have a routine and be parenting like a pro! If you have questions or concerns, talk to your doctor. They can recommend resources that can help you and your baby grow together.
They can recommend resources that can help you and your baby grow together.
What To Expect, Development & Tests
What is the second trimester of pregnancy?
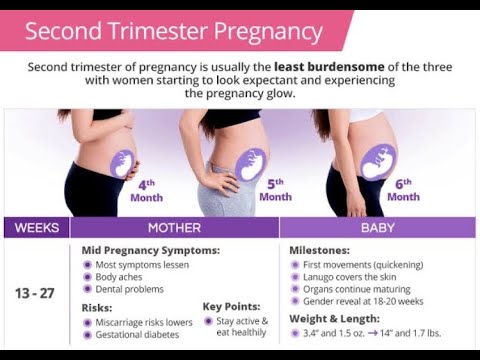
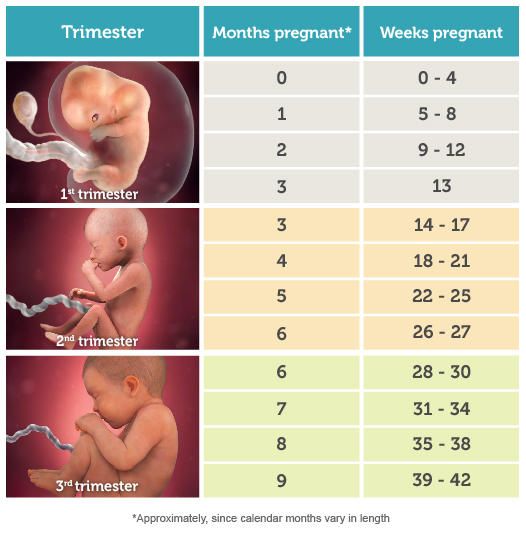
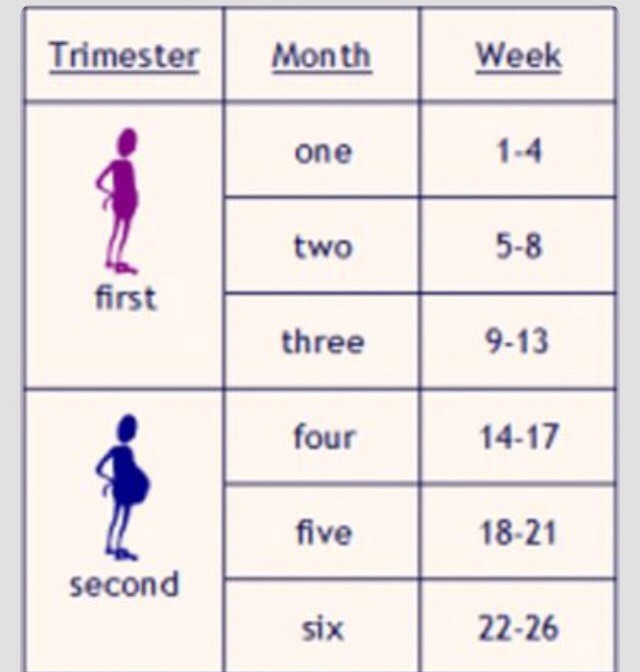
The typical pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks. It’s divided into three periods of time — the first, second and third trimester. Each trimester is roughly 14 weeks long. When you enter your second trimester, you are around 14 weeks pregnant. This middle trimester will last from week 14 to the end of week 27.
During your second trimester of pregnancy, you’ll start looking and feeling more pregnant. For many people, this is the best part of pregnancy because the morning sickness and fatigue of their first trimester fade into the past. Often, any anxiety that went with your first trimester also starts to diminish at this point. You’ll start to feel your fetus move by the end of this trimester, and you might begin to settle into your pregnancy and enjoy it more. Of course, it’s important to remember that pregnancy is different for everyone.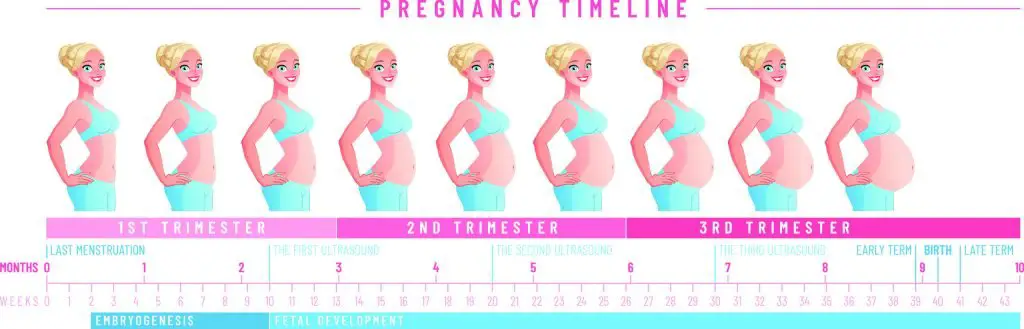 Some people never experience negative symptoms like morning sickness in their first trimester. Others might continue to feel sick well into their second trimester of pregnancy.
Some people never experience negative symptoms like morning sickness in their first trimester. Others might continue to feel sick well into their second trimester of pregnancy.
How does my baby develop during the second trimester of pregnancy?
Your fetus will go through many changes during your second trimester of pregnancy. During this trimester, the fetus starts to look more like a child — with its facial features aligning, and its fingers and toes becoming well-defined. By month four, the fetus will actually have eyelids, eyebrows, eyelashes, nails and hair. The fetus will also be able to stretch, make faces and even suck on its thumb. You’ll soon be able to determine the sex of the fetus on an ultrasound — often around 20 weeks.
At this point, you might also start feeling the fetus move. The movement is often described as a flutter or similar to the feeling of having butterflies in your stomach. The fetus will be doing flips and movements throughout your second trimester.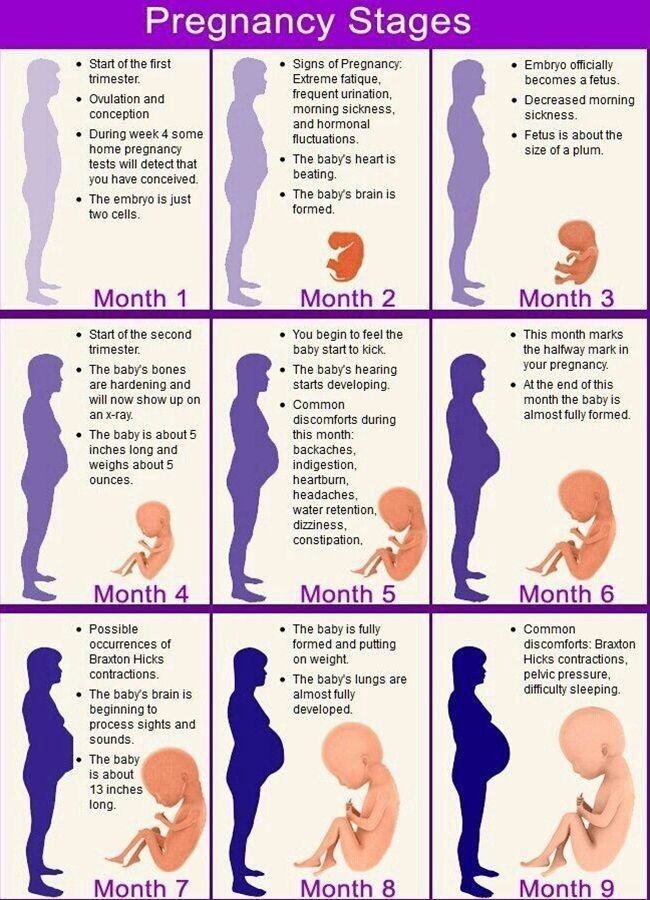 This first movement is called the quickening. If this isn’t your first pregnancy, you might feel the fetus move sooner.
This first movement is called the quickening. If this isn’t your first pregnancy, you might feel the fetus move sooner.
In the last few weeks of the second trimester, the fetus can also hear you. If you talk to your growing belly, you might notice movement in response.
If your baby was born at the end of your second trimester (premature birth), they would be likely to survive with intensive care.
What happens to my body during the second trimester of pregnancy?
The fetus isn’t the only one growing and changing during your second trimester. You'll notice several changes in your own body during this time. Your uterus — the place where the fetus grows during pregnancy — continues to stretch. This organ will expand throughout your pregnancy as the fetus gets larger. After pregnancy, your uterus will return to its pre-pregnancy size (picture an upside-down pear).
However, your uterus isn’t the only thing growing during the second trimester either. You’ll start gaining weight and might start developing the tell-tale enlarged belly of a pregnant person. Don’t worry if this takes time to develop. Everyone is different, and no two bodies will look exactly the same during pregnancy.
Don’t worry if this takes time to develop. Everyone is different, and no two bodies will look exactly the same during pregnancy.
You might also feel or develop a few new symptoms of pregnancy during your second trimester, including:
- An increased appetite.
- An achy body.
- Some swelling in your hands, feet and ankles.
- Some stretch marks.
If you experienced morning sickness during your first trimester, it’s likely fading away now. The uncomfortable symptoms of early pregnancy (nausea and extreme fatigue, for example) don’t typically continue into your second trimester. This is one reason why many people consider their second trimester of pregnancy to be the best part of pregnancy.
What tests will I have during the second trimester of pregnancy?
Throughout your pregnancy, your healthcare provider will order various tests to check on your health and the health of your developing fetus. During your second trimester, you’ll typically be screened for a few different things, including the Rh factor of your blood and the condition gestational diabetes. You'll also have an ultrasound during your second trimester. This ultrasound is probably best known for telling new parents the sex of the fetus, but it’s mainly used to look at their anatomy.
You'll also have an ultrasound during your second trimester. This ultrasound is probably best known for telling new parents the sex of the fetus, but it’s mainly used to look at their anatomy.
One thing your provider will test for during your second trimester is your Rh factor. Rh factor is an antigen protein found on most people’s red blood cells. If you don’t have the protein, then you are Rh- (negative). You’ll be given an injection of Rh immune globulin (called Rhogam®) during the 28th week of your pregnancy to prevent the development of antibodies that could be harmful to the fetus. You’ll also be given an injection of Rhogam® after delivery if your fetus has Rh+ (positive) blood.
If you are Rh-, you may also receive this injection if you:
- Are having an invasive procedure (such as amniocentesis).
- Had an abdominal trauma.
- Had any significant bleeding during pregnancy.
- Need to have the fetus turned in your uterus (due to breech presentation).
Your provider will also order a test called the oral glucose screening test. This is usually done at the end of your second trimester — often between weeks 24 and 28. The purpose of the glucose screening test is to see if you are developing gestational diabetes. During the test, you’ll be given a syrup-like drink. The healthcare provider administering this test will give you a set amount of time to drink the entire bottle, then you'll be asked to wait nearby for one hour. After the hour is over, you’ll have your blood drawn. Your healthcare provider will then go over your test results with you.
What do I need to prepare or plan for during the second trimester of pregnancy?
There are many things you can start thinking about during your second trimester of pregnancy to prepare for your new family member. Many of these things will center around conversations that you should start having at this point in your pregnancy. It’s good to discuss the type of birth you hope to have and learn about the different ways your child might be born.
A few ways your baby could be born can include:
- Vaginal birth (this could be medicated so that your pain is decreased, or unmedicated).
- Assisted birth (you might need tools like forceps or a vacuum to help with your delivery).
- Cesarean section (C-section).
You can learn more about these types of birth through your own research or in a birth class. This is the time for you to look into educational classes about birth, breastfeeding and parenting of your newborn. These classes can help prepare you for your new role as a parent. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on classes and groups you can join at this point in your pregnancy.
This might also be a good time to take a tour of the hospital where you’ll give birth. A hospital tour is a great way to get familiar with the place where your baby will be born. During the tour, you’ll learn where you should go when you first get to the hospital during labor and what will happen afterward. You’ll typically get to see hospital rooms and learn more about the hospital staff, as well.
You’ll typically get to see hospital rooms and learn more about the hospital staff, as well.
What should I be doing during the second trimester of pregnancy to stay healthy?
Throughout your second trimester, you should continue maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Try to exercise for about 20 minutes a day. Regular exercise is good for you and your developing fetus. Some of the safest types of exercise include walking and swimming; though, there are many other options you can try. Talk to your healthcare provider about the type of exercise you'd like to do beforehand just to be safe. You’ll want to avoid contact sports and activities where you could fall, as these could endanger your pregnancy.
It’s also a good idea to do kegel exercises throughout your entire pregnancy. These exercises will help strengthen your pelvic floor muscles.
Apart from exercise, you should continue eating a healthy diet, taking your prenatal vitamins and attending each of your appointments.
When should I call my doctor during the second trimester of pregnancy?
You’re the person who knows your body the best. If you ever feel like something is wrong, it’s completely OK to reach out to your healthcare provider. It’s also a good idea to call your healthcare provider right away if you have:
- Unusual or severe cramping or abdominal pain.
- Noticeable changes in how much the fetus moves (after 28 weeks of gestation). If you don’t count six to 10 movements in one hour or less, call your provider.
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath that seems to be getting worse over time.
You should also reach out to your provider right away if you start having any signs of premature labor. Talk with your provider if you have any of the following signs of premature labor:
- Regular tightening or pain in your lower abdomen or back that occurs more than four times in an hour.
- Any bleeding in your second or third trimester of pregnancy.
- Any fluid leakage. Vaginal discharge often increases as part of the hormonal changes in pregnancy.
- Pressure in your pelvis or vagina.
Second trimester of pregnancy (from 13 to 28 weeks)
The beginning of the second trimester is traditionally considered one of the calmest. Walk more. Walking is very helpful. Sit down to rest only when you are tired. Movement in the fresh air improves the supply of oxygen to the fetus, which is very necessary for its normal development.
Nausea disappears, appetite improves. Do not eat a lot of salty, refuse marinades, smoked meats, if you have not done this before. The increased need of the child's body for proteins and vitamins begins. The daily diet should include meat or fish (boiled or stewed), dairy products, especially cottage cheese, eggs. Do not forget about vegetables, fruits, greens. An excellent source of vitamin C is sauerkraut (rather than salted) cabbage. Salads from carrots, cabbage, beets, apples, green radish should be on your table every day.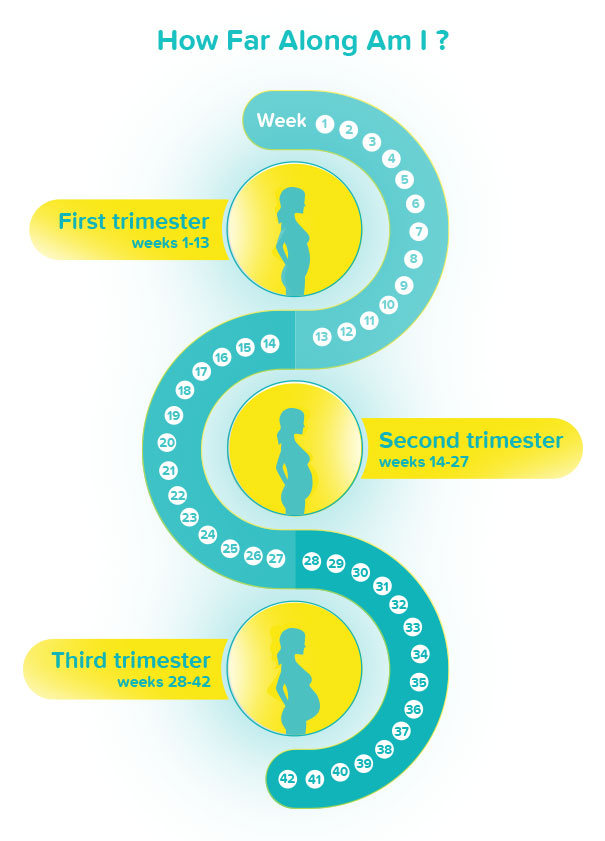
At 17-20 weeks you will feel your baby's first kicks. From them you can determine how comfortable the baby feels. Intense tremors are a signal of lack of oxygen. Maybe you haven’t walked for a long time or, on the contrary, you are engaged in hard physical labor. Get out into the fresh air or lie down to rest and you will immediately feel how the child has calmed down.
But the lack of movement is an alarm. See a doctor immediately!
The fetal need for calcium sharply increases - intensive growth of the skeleton has begun. If you don't have enough free calcium in your body right now, you could lose your teeth. To prevent this from happening, start taking calcium supplements in consultation with your doctor.
At this time, toxicosis of the second half of pregnancy may occur, the child suffers greatly from it. Therefore, if the doctor suggests hospitalization, do not refuse. Toxicosis can, if not be avoided, then at least reduce its manifestations. Be sure to follow your diet.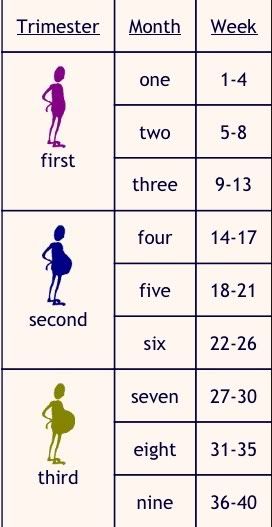 Completely exclude salty, smoked, fried, spicy, canned food, chocolate. Do not eat a lot of grapes and drink fresh milk. Limit flour and rich products. As before, your diet should include boiled meat and fish, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, vegetables and fruits
Completely exclude salty, smoked, fried, spicy, canned food, chocolate. Do not eat a lot of grapes and drink fresh milk. Limit flour and rich products. As before, your diet should include boiled meat and fish, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, vegetables and fruits
Periodically, once a week, check for fluid retention in the body. It is allowed to release liquid 200-300 ml less than what was drunk. If little urine is released, this is a signal of latent edema and the onset of toxicosis.
It is very good if you can measure your blood pressure at home. Show the results of measurements at the next visit to the doctor. Both high and too low pressure should alert. With low pressure, blood sluggishly crosses the placenta, and the baby does not receive enough nutrients.
Do not neglect blood tests - it is important not to miss the development of anemia. In this case, you will be prescribed iron supplements and multivitamins. The diet should include beef liver, tomato juice, buckwheat porridge, apples, preferably Antonovskie (they contain more iron than other varieties).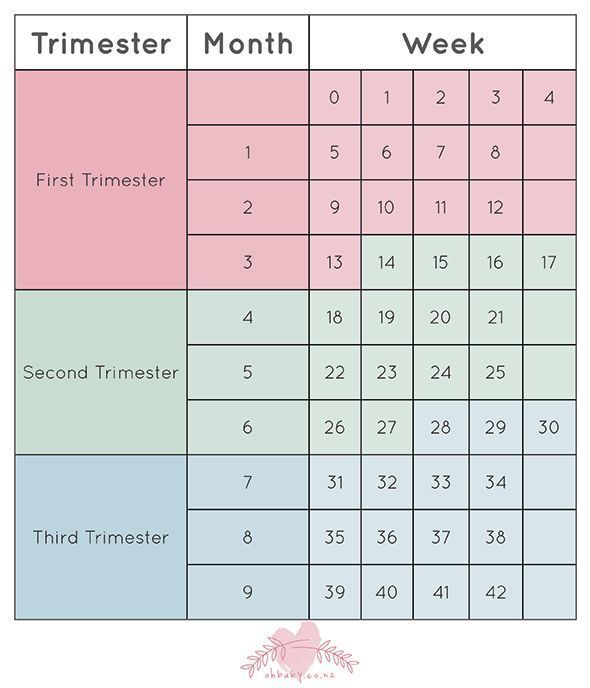
Women who are at risk of giving birth to a child with a genetic pathology (those who have severe hereditary ailments in their families), as well as women over 35 years old (they have an increased likelihood of having a child with Down syndrome) are referred for a consultation by a geneticist.
In case of a normal pregnancy at 20-22 weeks of pregnancy, a second scheduled ultrasound examination is prescribed.
2nd trimester of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus
2nd trimester of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus - Private maternity hospital Ekaterininskaya ClinicsMost women enjoy the 2nd trimester of pregnancy more than the first, with the disappearance of morning sickness, breast tenderness and fatigue. But be prepared for some other symptoms to appear!
- Pain. As a result of stretching of the tissues of the body, you may experience pain in the sides and under the abdomen.
 Weight gain can cause back pain and leg cramps. The doctor will advise you on simple exercises for such cases.
Weight gain can cause back pain and leg cramps. The doctor will advise you on simple exercises for such cases. - Stuffy nose. Increased hormone levels can lead to nasal congestion and nosebleeds.
- Soft gums. Your gums tend to bleed, so oral hygiene requires special attention and careful brushing.
- Skin itching. The skin of the abdomen may itch as a result of stretching associated with the growth of the child. Try to use a moisturizer daily to avoid stretch marks.
- Varicose veins and hemorrhoids. During pregnancy, you will be more susceptible to varicose veins and hemorrhoids. Try not to stand or sit for too long, and avoid crossing your legs while sitting. If discomfort or pain occurs in the anus, the doctor may prescribe a remedy for hemorrhoids.
- Vaginal discharge. White, thin vaginal discharge, called leucorrhea, is normal during this period of pregnancy.
 These secretions help keep the vagina healthy. If you find discharge of a different type or color, contact your doctor for advice.
These secretions help keep the vagina healthy. If you find discharge of a different type or color, contact your doctor for advice. - Impaired skin pigmentation. Pregnancy hormones may contribute to the appearance of dark spots on the face and abdomen. The sun can exacerbate the appearance of spots, so use sunscreen when you go outside. Sun exposure without skin protection is contraindicated!
- Shortness of breath. As your lungs allow more oxygen to meet your baby's needs, you may experience shortness of breath or a faster rate of breathing.
- Increased appetite. As your child grows, you may feel hungry all the time, but there is no need to "eat for two". If you need to snack, choose healthy foods like fruit or yogurt.
2nd trimester milestones
- You may feel your baby move for the first time between 18 and 20 weeks of pregnancy. This phenomenon is called "revival" and is initially felt as a flutter in the abdomen.
- As your baby grows, your belly will grow.
2nd trimester baby development
End of 2nd trimester:
- Your baby moves and responds to touch and sound.
- Eyelids begin to open, eyebrows and eyelashes are visible.
- The skin is covered with fine, downy hairs and a creamy white substance called primordial lubrication.
- Swallowing and sucking reflexes develop.
- Hair began to grow on the head.
- The lines of the fingerprint pattern on the fingers have formed.
- Baby measures about 23 cm from head to lower torso.
Mobile application of the clinic
You can make an appointment with a doctor, get tests
and more...
Fill out the form to make an appointment or order a call back
I agree with personal data processing policy and user agreement I also give my consent to the processing of personal data.