Stillborn pregnancy symptoms
Stillbirth symptoms and risks | Tommy's
We understand that reading about the symptoms of stillbirth can be very worrying during pregnancy. If you are struggling to manage anxious feelings or thoughts, please talk to your midwife about how you’re feeling. Your healthcare team is there to support you if you have any concerns about your and your baby's health. Please don’t worry about speaking up, asking questions and requesting further investigations.
Even if you do experience some of the symptoms or conditions listed below, please remember that you’re likely to go on to have a healthy pregnancy and baby.
If you’re looking for more information about what causes stillbirth, our information about the causes of stillbirth more helpful.
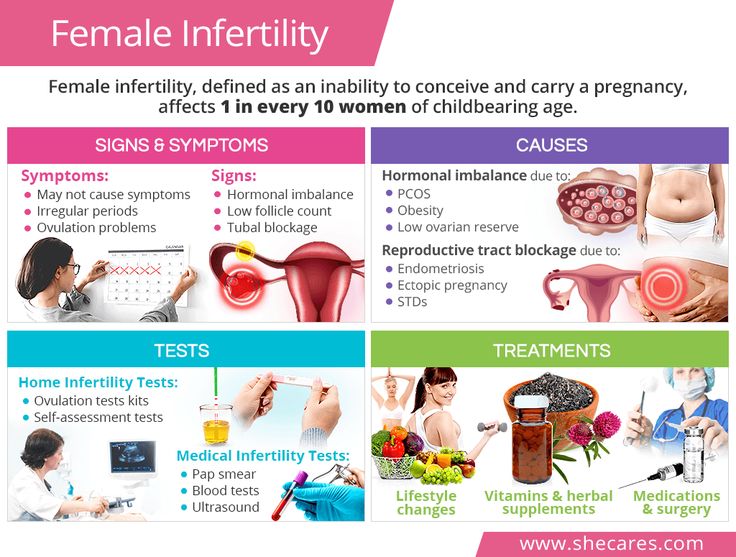
Baby’s movements in pregnancy
You may feel your baby move as early as 16 weeks of pregnancy, but most people usually feel something between 16 and 20 weeks, although it can sometimes be later than this.
If this is your first pregnancy, you may not notice your baby’s movements until you are more than 20 weeks pregnant. Movements feel different to everyone, but you might feel kicking, swirling, fluttering or rolling. It is not true that babies move less towards the end of pregnancy. You should continue to feel your baby move right up to the time you go into labour and during labour.
Every baby has its own pattern of movement – for example your baby may move more in the evenings when you are resting, or before you go to sleep at night. You may also find certain activities like taking a bath, putting your feet up and resting on the sofa, or eating and drinking seem to encourage your baby to move more.
As the weeks go on, you may notice a pattern of movements that becomes familiar to you. The movements usually become fairly regular by 28 weeks. Get to know your baby’s pattern of movements so you can notice any changes.
If a baby is not well, or not receiving enough nutrients and oxygen, they are likely to move less to save energy. Noticing when this happens and contacting your hospital immediately is very important. Studies have shown that around 55% of people who experienced a stillbirth noticed a reduction in baby movements before their baby died.
Studies have shown that around 55% of people who experienced a stillbirth noticed a reduction in baby movements before their baby died.
Read more about your baby’s movements in pregnancy.
If there is a change in your baby’s movements
Contact your midwife or maternity unit immediately if you think your baby’s movements have slowed down, stopped or changed. There are staff on the hospital maternity unit 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Do not wait until the evening or the next day – seek help even if it is the middle of the night or the weekend.
If you think there might be a change in your baby’s movements
If you have any concerns, call your midwife or maternity unit immediately. Trust your instincts.
Who will I talk to if I report a change in my baby's movements?
Unless you have been given alternative numbers to ring during your pregnancy, the best place to ring is usually the labour ward. The labour ward is not just for people in labour but also for emergencies in pregnancy. The ward should be open 24 hours a day and there should always be a midwife there who will be able to listen to your worries and advise you. Midwives often receive calls about reduced baby movements – they would much rather you got in touch than didn’t.
The ward should be open 24 hours a day and there should always be a midwife there who will be able to listen to your worries and advise you. Midwives often receive calls about reduced baby movements – they would much rather you got in touch than didn’t.
What will happen if I go into hospital?
Once at the hospital, they will probably check you over and listen to the baby’s heartbeat. If you are more than 28 weeks pregnant they may attach you to a heart rate monitor which records a trace of the baby’s heartbeat. You may also be given a button to push every time you feel the baby move. This can also be seen on the print out of the baby’s heartbeat.
It's quite common that once you lie down, hear the baby’s heartbeat and relax you start to feel the baby kicking. Don’t feel embarrassed about this – midwives see this every day. It is much better to go and be checked so that any potential problems can be picked up.
Find out more about what should happen if you report a change in fetal movements.
Leaking fluid or vaginal discharge in pregnancy
If you experience any leaking of fluid from your vagina during your pregnancy, you should contact your hospital immediately and go into be monitored. It could be your waters breaking early or a sign of infection of the womb.
Waters breaking early in pregnancy
Waters can sometimes break early in pregnancy, not just in the last couple of weeks, and this can lead to premature birth. If you feel a gush or trickle of fluid from your vagina, or feel damp, it could be a sign that your waters have broken. Put on a clean sanitary towel (not a tampon) and call the maternity unit straight away. They may ask you to sniff the pad – as it is common to leak urine in pregnancy – or they may ask you to check the pad again in around 20 minutes to see if it is damp.
Amniotic fluid (the fluid from around the baby) smells different to urine and is usually clear, pinkish or can be green or brown. If you think it might be amniotic fluid, it is important to go straight to the hospital to be examined. You may be asked to wear a special panty liner for up to 12 hours to confirm if you are leaking amniotic fluid, and you may need an internal examination (inside the vagina) to look for signs that your cervix is opening or softening for labour.
You may be asked to wear a special panty liner for up to 12 hours to confirm if you are leaking amniotic fluid, and you may need an internal examination (inside the vagina) to look for signs that your cervix is opening or softening for labour.
Infection in pregnancy
You should report any discharge from your vagina which is smelly, and any colour other than white, as it may be a sign of an intrauterine infection. Infections can weaken the bag of membranes around the baby, cause an infection inside the womb or make your waters break.
If you experience an unusual discharge, contact your midwife, GP or hospital and ask for a swab to be taken to look for infection. Other symptoms of an infection include a high temperature or stomach pain.
Diabetes in pregnancy
People with diabetes in pregnancy are more affected by:
- miscarriage
- pre-eclampsia
- preterm labour
- stillbirth
- problems with the baby (while in the womb, at delivery and after the birth).
It’s very important to control your blood sugar levels and get regular monitoring during your pregnancy. Whether you had diabetes already, or develop diabetes during pregnancy (gestational diabetes), you will be closely monitored during your pregnancy. You will need to be aware of how best to care for yourself and your baby during your pregnancy.
What to do if you have diabetes in pregnancy
The best way to reduce the risks to you and your baby is to make sure that your diabetes is well controlled before you get pregnant. Before you start trying for a baby, ask your GP or diabetes specialist for advice. They will be able to give you information about how pregnancy and diabetes may affect you.
If you are pregnant with diabetes, you will probably be regularly seen by a consultant and a specialist diabetes midwife and/or diabetes specalist. Make sure that you attend all your scheduled appointments so your healthcare team can monitor your condition. Seek help immediately from your GP, midwife or hospital doctors if you are concerned about your blood sugar control or any other factors affecting your pregnancy or your diabetes.
Monitoring the growth and movements of your baby is very important. If you’re worried, do not wait until the next day to get help – you can contact the labour ward to speak to a midwife 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
If you have any of the risk factors for developing gestational diabetes, including having a BMI of 30 or over, you should be offered a blood sugar test between 24 and 28 weeks. It is important to go to this blood test.
Pre-eclampsia and stillbirth
Pre-eclampsia is common. It is usually mild and normally has very little effect on pregnancy. However, it is important to know if you have the condition because, in a small number of cases, it can develop into a more serious illness. Severe pre-eclampsia can be life-threatening for both the mum/birthing person and the baby.
Early signs of pre-eclampsia include having high blood pressure (hypertension) and protein in your urine (proteinuria).
Pre-eclampsia is one of the pregnancy conditions your midwife will be testing for at your antenatal appointments, which is why it’s important to attend all of your appointments.
Signs of pre-eclampsia
Look out for any of the warning signs of pre-eclampsia, such as:
- severe headaches
- vision problems, such as blurring or flashing
- sudden swelling, particularly of your feet, ankles, hands and face
- pain just under the ribs
- vomiting.
If you notice any of these, contact your GP, midwife or maternity unit straightaway. Don’t wait until your next scheduled appointment. You should be seen by a healthcare professional the same day.
Read more about risk factors, diagnosis and treatment of pre-eclampsia.
Obstetric cholestasis (intrahepatic cholestasis)
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP), also known as obstetric cholestasis (OC), is a liver disorder that can develop during pregnancy. It has been linked to an increased risk of stillbirth in some cases. The main symptom is itching, usually without a rash. This is often worse at night and more noticeable on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
Itching is very common in pregnancy and only a small number of pregnant will have ICP. But if you are having itching, it’s important to tell your midwife or doctor.
Read more about obstetric cholestasis.
Finding the causes of stillbirth
Sadly, many parents never find out why their baby died. A report of all UK stillbirths showed around 35.5% of stillbirths were unexplained in 2018.
Tommy’s researchers are investigating the causes of stillbirth because unless we know why it happens, we can't find treatments or predict who may be at risk.
Read more about Tommy's research into stillbirth.
Stillbirth - NHS
A stillbirth is when a baby is born dead after 24 completed weeks of pregnancy. It happens in around 1 in every 200 births in England.
If the baby dies before 24 completed weeks, it's known as a miscarriage or late foetal loss.
Contact your midwife or doctor straightaway if you're pregnant and worried about your baby – for example, if you've noticed your baby moving less than usual. Don't wait until the next day. If your baby is moving less, it can be a sign that something's wrong and needs to be checked out.
Don't wait until the next day. If your baby is moving less, it can be a sign that something's wrong and needs to be checked out.
Causes of stillbirth
Some stillbirths are linked to complications with the placenta, a birth defect or with the mother's health. For others, no cause is found.
Read more about causes of stillbirth.
When a baby dies before they're born
If your baby has died, you may be able to wait for labour to start naturally or your labour may be induced. If your health is at risk, the baby may need to be delivered as soon as possible. It's rare for a stillborn baby to be delivered by caesarean section.
Read more about what to expect if your baby dies before birth.
After a stillbirth
After a stillbirth, decisions about what to do are very personal. There's no right or wrong way to respond.
There's no right or wrong way to respond.
A specialist midwife will talk with you about what you want to do – for example, holding the baby or taking photographs. They can also discuss the tests you may be offered to find out why your baby died and give you information about registering the birth.
Read more about what happens after a stillbirth, including information about baby-loss support groups.
Preventing stillbirths
Not all stillbirths can be prevented, but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk, such as:
- not smoking
- avoiding alcohol and drugs during pregnancy – these can seriously affect your baby's development, and increase the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth
- not going to sleep on your back after 28 weeks – don't worry if you wake up on your back, just turn onto your side before you go back to sleep
- attending all your antenatal appointments so that midwives can monitor the growth and wellbeing of your baby
- taking folic acid before pregnancy and having a flu vaccine during your pregnancy
- limiting the amount of caffeine you consume during pregnancy
Video: Coping with grief after a stillbirth
In this video Lisa and Jason describe how they coped with a stillbirth
Media last reviewed: 16 April 2021
Media review due: 16 April 2024
Page last reviewed: 16 March 2021
Next review due: 16 March 2024
Stillbirth
Stillbirth- Healthcare issues »
- A
- B
- B
- G
- D
- E
- and
- 9000 About
- P
- P
- With
- T
- in
- F
- x
- 9000.
- Sh.
- B
- S
- B
- E
- S
- I
- Popular Topics
- Air pollution
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Hepatitis
- Data and statistics »
- News bulletin
- The facts are clear
- Publications
- Find a country »
- A
- B
- C
- g
- d
- E
- ё
- С
- and
- th
- to
- L
- N 9000 T
- in
- F
- x
- 9000 WHO in countries »
- Reporting
- Regions »
- Africa
- America
- Southeast Asia
- Europe
- Eastern Mediterranean
- Western Pacific
- Media Center
- Press releases
- Statements
- Media messages
- Comments
- Reporting
- Online Q&A
- Developments
- Photo reports
- Questions and answers
- Update
- Emergencies "
- News "
- Disease Outbreak News
- WHO data »
- Dashboards »
- COVID-19 Monitoring Dashboard
- Basic moments "
- About WHO »
- CEO
- About WHO
- WHO activities
- Where does WHO work?
- Governing Bodies »
- World Health Assembly
- Executive committee
- Main page/
- Health /
- Stillbirth
UNICEF/Ramoneda
© A photo
Our activities
Key events
Why is it important for us to talk about the loss of a child
Read
News
All →Events
Reports
Publications
All → As part of the continuum of reproductive health services, antenatal care (ANC) provides a platform for. ..
..
Over five million cases of perinatal death, making it an important goal of international health efforts...
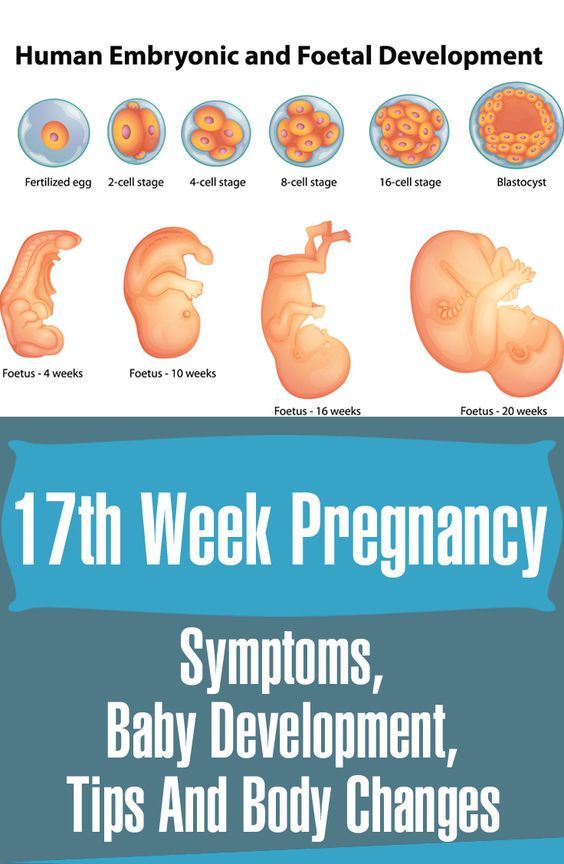
Pregnancy is a time of great expectation for all parents-to-be and their families who dream of raising and loving a healthy baby. 90,000 signs, symptoms and causes. How to determine a frozen pregnancy. Clinic Ak. Grishchenko
03/15/2021
Not always long-awaited and such a desired pregnancy ends with the birth of a baby. Sometimes women find out that the pregnancy has stopped. Unfortunately, this problem is not rare. According to statistics, in about 15% of cases, the planned babies "freeze" in the womb for one reason or another.
CONTENT:
- What is it?
- Dangerous timing: when can it happen?
- Why is this happening?
- How do doctors determine missed pregnancy?
- Signs and symptoms
- How to recover from a missed pregnancy?
- What tests to pass after?
- Answers from experts on whether ST cleanup is required.
- Frequently asked questions for which go to the forum.
What is it?
A missed pregnancy is a pregnancy that initially met all medical standards, but suddenly stopped developing in a certain period. The cessation of progress in the development of the fetus leads to its death, but it remains in the uterine cavity. For this reason, such a pathology is called a failed miscarriage.
In fact, at the very beginning, everything happens, as in a normal pregnancy - the egg is fertilized, enters the uterus and is implanted for further development, but it stops at one moment. This pathology also includes the syndrome of "empty fetal egg". It is the development of fetal membranes in which there is no embryo. With this syndrome, a pregnancy test is positive, as well as an analysis for hCG.
Dangerous timing: when can it happen?
Fetal development can stop at any time up to 28 weeks (in rare cases, development can stop later), but the greatest probability of such a pathology occurs in the first trimester. There are also several periods with the highest risk of miscarriage, these include the following periods:
There are also several periods with the highest risk of miscarriage, these include the following periods:
- 3-4 weeks;
- 8-10 weeks;
- 16-18 weeks.
It is these terms that most often become critical for pregnancy.
Causes of miscarriage?
Even doctors are not always able to find out exactly why a miscarriage happened. In modern medicine, there are a number of reasons that can cause such a pathology. All of them are divided into several large groups:
- Genetic pathologies . It is these reasons that most often provoke a halt in fetal development. Pathological genes or the presence of an extra chromosome in the embryo can cause the development of many defects that are incompatible with life, leading to termination of pregnancy. Often, genetic pathologies cause a stop in the development of pregnancy in the eighth to tenth week.
- Infections . A missed pregnancy can also often happen due to the presence of infectious diseases, since during the period of bearing a child, a woman experiences a rather serious decline in immune defenses.
 Especially dangerous for this period are TORCH infections, which include rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes and toxoplasmosis. The greatest danger to the fetus is the first "meeting" of the mother with the infection in an already pregnant state. Therefore, when registering, pregnant women are strongly recommended to be screened for these types of infections. Even seemingly simple and familiar diseases such as influenza or SARS can cause pathology, especially in the early stages, when vital organs are formed in the fetus. The infection can affect the fetus directly, causing various types of anomalies, or on the membranes, resulting in a significant lack of oxygen or nutrients to the fetus.
Especially dangerous for this period are TORCH infections, which include rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes and toxoplasmosis. The greatest danger to the fetus is the first "meeting" of the mother with the infection in an already pregnant state. Therefore, when registering, pregnant women are strongly recommended to be screened for these types of infections. Even seemingly simple and familiar diseases such as influenza or SARS can cause pathology, especially in the early stages, when vital organs are formed in the fetus. The infection can affect the fetus directly, causing various types of anomalies, or on the membranes, resulting in a significant lack of oxygen or nutrients to the fetus. - Hormonal disorders . Hormonal balance is extremely important for the normal bearing of a child. Therefore, with a lack of progesterone or an excess of male hormones (androgens), the likelihood of miscarriage significantly increases. Any hormonal disruptions are recommended to be treated before pregnancy.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome . Because of them, the formation of placental vessels or their blockage may also decrease, which leads to a violation of the fetus receiving the necessary nutrition.
- Teratozoospermia . This cause of a missed pregnancy is associated with pathologies in the seminal fluid of a man. With teratozoospermia, spermatozoa have an irregular structure, so fertilization with such a cell leads to abnormalities in the development of the embryo.
- Lifestyle . The presence of bad habits, as well as lifestyle during childbearing (and the planning period) can also adversely affect the development of the embryo, causing it to freeze. The use of alcoholic beverages, smoking, stress, occupational hazards, daily routine, sedentary lifestyle, unbalanced diet - all this is considered negative factors for pregnancy.
- Other factors. Pregnancy fading can also occur due to a sharp change in climate, a history of abortions (especially if there were several).

In some cases, several causes can be found at once, which could lead to a pregnancy fading.
How do doctors determine a miscarriage?
At each examination of a pregnant woman, the gynecologist determines the size of the uterus, so if they do not correspond to the current period, the specialist may suspect the fetus will freeze. But such a diagnosis is made only after an ultrasound examination. In rare cases, ultrasound is not performed - if the woman turned to the doctor late and intoxication of the body has already occurred due to the death of the fetus.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of a miscarriage are the same in any trimester. The main signs that may indicate such a pathology are:
- vaginal discharge with blood impurities;
- general weakness, chills, fever;
- drawing pains in the lower part of the abdomen;
- cessation of swelling and soreness of the mammary glands;
- abrupt disappearance of manifestations of toxicosis;
- absence of fetal movements (with pathology in the second trimester).
Despite the presence of characteristic symptoms of pathology, often the cessation of fetal development goes unnoticed, since the basal temperature can remain within 37 degrees, and the hCG level remains high for several more weeks. In this case, the woman learns about the problem only at the next appointment with the doctor or a planned ultrasound.
How to recover from a missed pregnancy?
If this pathology occurs, it is imperative to remove the dead embryo from the uterine cavity, if this did not happen naturally. For this, a cleaning is carried out, with the help of which all particles of the fetal membranes are removed from the uterus. Both scraping and vacuum can be used. If the fading occurred at a very early date, doctors may suggest a medical abortion, which is somewhat more gentle for the woman, including psychologically.
Doctors recommend to refrain from the next pregnancy for six months (according to the recommendation of the World Health Organization). This time is enough for the body to recover after what happened. Therefore, during this time, women are advised to take oral contraceptives, which minimize the likelihood of conception, and also allow you to normalize hormonal levels.
This time is enough for the body to recover after what happened. Therefore, during this time, women are advised to take oral contraceptives, which minimize the likelihood of conception, and also allow you to normalize hormonal levels.
During recovery, it is also recommended to lead the most healthy and active lifestyle, take care of a balanced diet and take vitamin complexes. A woman definitely needs psychological support, and if she endured the incident especially hard, she may need the help of specialists - a psychologist or psychiatrist. This will help you get back to normal and prepare for your next pregnancy.
What tests to take after?
Before becoming pregnant after a missed pregnancy, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of a recurrence of what happened. Treatment should be appropriate to the problem that caused the pathology. Therefore, it is extremely important to undergo a complete examination, which will help determine the cause of the fetal development fading.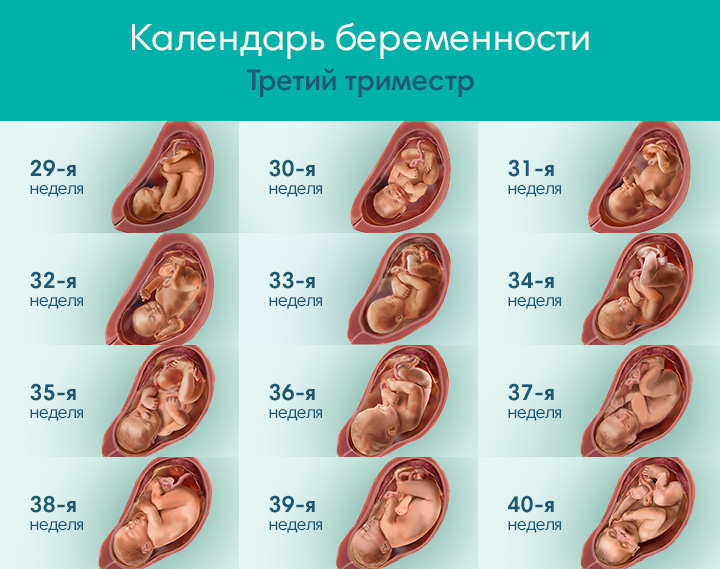 According to the results of the examination, doctors prescribe treatment in accordance with the detected diseases.
According to the results of the examination, doctors prescribe treatment in accordance with the detected diseases.
It is recommended to undergo an examination after the restoration of the woman's menstrual cycle (usually takes about 30 days after cleansing). But both spouses should be tested. The full examination includes:
- genetic testing of spouses;
- tests for TORCH infections;
- study of hormonal levels;
- blood coagulogram;
- Gynecological ultrasound;
- spermogram;
- immunogram.
This examination is usually enough to determine the causes of miscarriage, both early and late. The attending physician may prescribe additional studies if necessary. All these examinations can be done at the IVF and infertility treatment clinic of Academician V.I. Grishchenko.
Frozen pregnancy is not a sentence - in 90% of cases, after the occurrence of such a pathology, spouses become happy parents of healthy babies in the near future. The main thing is to undergo a complete examination and eliminate the cause of the pathology. And if necessary, you can go through the procedure of artificial insemination (IVF).
The main thing is to undergo a complete examination and eliminate the cause of the pathology. And if necessary, you can go through the procedure of artificial insemination (IVF).
Answers from specialists in the field of reproduction, fertility, women's health about whether cleaning is mandatory during a missed pregnancy.
On the Internet, the question is often asked: “Is it necessary to do curettage during a missed pregnancy (ZB)?”
We asked this question to our doctors:
Parashchuk Valentin Yurievich
Chief Physician of Academician Grishchenko Clinic, obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist.
Good afternoon. If the pregnancy froze at an early stage and there are no signs that it is going to resolve itself, that is, there is no bleeding, then it is advisable to evacuate the contents of the uterine cavity, that is, to do curettage. If the pregnancy seeks to resolve itself, then it can come out on its own. And then curettage is not required, you can just look at the ultrasound as soon as the discharge ends, that there are no inclusions in the uterine cavity, that there are no elements of the ovum left in the uterine cavity.
If the pregnancy seeks to resolve itself, then it can come out on its own. And then curettage is not required, you can just look at the ultrasound as soon as the discharge ends, that there are no inclusions in the uterine cavity, that there are no elements of the ovum left in the uterine cavity.
Another situation is when the pregnancy has stalled and you really need to evacuate the contents, and then there are alternative methods, sometimes they offer the so-called "medical abortion", this is such a term. And it is more correct to do a scraping, or a vacuum, if the time permits. Because, sometimes, after these very medical abortions, you have to do scraping, but already in fact of complications. Because the entire contents of the uterine cavity does not always come out completely, and then inflammation joins, this is a big trauma for the uterus, this is already a conditionally urgent condition, and it is better not to allow it. Therefore, it is better to do a moderate, without severe injury and without complications, curettage on time than to do it as a necessary measure. When it is already clear that this is a frozen pregnancy, tactics can be discussed, but it is important to really understand when it is, which are such dangerous or alarming calls.
When it is already clear that this is a frozen pregnancy, tactics can be discussed, but it is important to really understand when it is, which are such dangerous or alarming calls.
The main complaint is if the uterus is already frozen and the uterus is trying to get rid of the pregnancy, then this is bloody discharge, that is, the pregnancy is already rejected. But it happens that she freezes and the patient knows absolutely nothing about it, and they become a godsend at a later date, when she is told that the fetal egg does not match in size, that she stopped earlier, and this cannot be suspected in any way. Therefore, if there are pains, pulling pains in the lower abdomen, spotting, you should definitely consult a doctor. Firstly, because it is not a fact that it is frozen. Or maybe it’s a threat of pregnancy fading, and you can turn in time, respond in time, stop the process and save the pregnancy. And if she really froze, then react in time and get rid of the fetal egg that has already stopped in development, without allowing any complications.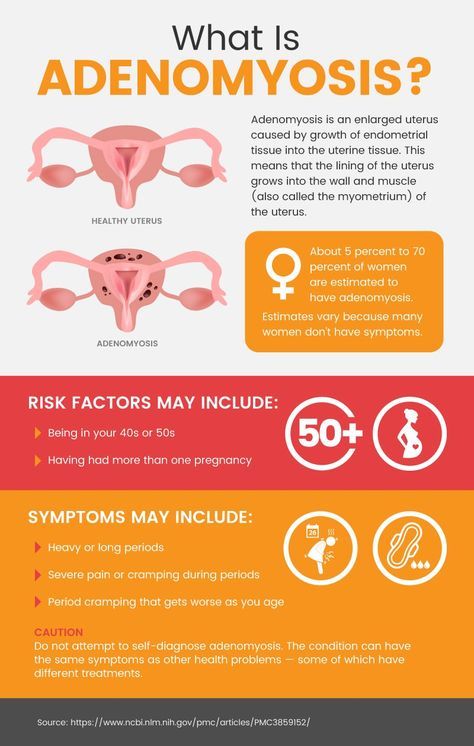 In any case, if pain or spotting occurs during pregnancy, at any time, this is an indication to consult a doctor. There should be no pain, there should be no blood.
In any case, if pain or spotting occurs during pregnancy, at any time, this is an indication to consult a doctor. There should be no pain, there should be no blood.
Alipova Elena Konstantinovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist, ultrasound specialist.
The question is unconditional that the miscarriage must be removed from the uterus. That is, non-developing tissues, they are the source of the inflammatory process in the first place, and these tissues should be removed as soon as possible. The best method is still scraping.
As for not deleting at all, this is not even discussed. You can talk a little about medical abortion, but in my opinion, he also has no right to exist with a missed pregnancy. First, because everything needs to be done:
- fast;
- as carefully as possible.
And most the main thing is that scraping products, concept products, as they say now, can be sent in this case for genetic testing . And this, with a frozen pregnancy, is very important because, well, what happened, it happened, and everyone is interested in the question of why it happened. A genetic study of abortive material helps in about 80% of cases to answer the question of what happened after all. If genetics is to blame, this is one conversation, if everything is in order from a genetic point of view, additional examinations will be directed in another direction.
Lutsky Andrey Sergeevich
Obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist.
Hello. Today we will talk about missed pregnancy. There are surgical methods, such as curettage, vacuum aspiration and hysteroscopic removal of the ovum, and medical methods, the so-called "medical abortion" . Medical methods of abortion are indicated for women who have already had pregnancies in the past and had natural childbirth. This is due to the fact that the cervix of the uterus in such women is ajar and during induction, artificial induction of uterine contractions, a complete spontaneous abortion occurs, no residues remain in the uterine cavity. If the girl is nulliparous, then medical abortion often gives complications. Not everything comes out of the uterine cavity. Parts of the membranes remain, clots, and, let's say, a delay of these parts occurs and there may be an inflammatory process, as a result of which, subsequently, surgical intervention is required - curettage or vacuum aspiration. The method of terminating a missed pregnancy is chosen by the attending physician based on these data. In our clinic, we often encounter missed pregnancy in those women who want to give birth to their child. And to understand the genetics of the fetus, we often recommend hysteroscopic removal or vacuum aspiration of the ovum.
Medical methods of abortion are indicated for women who have already had pregnancies in the past and had natural childbirth. This is due to the fact that the cervix of the uterus in such women is ajar and during induction, artificial induction of uterine contractions, a complete spontaneous abortion occurs, no residues remain in the uterine cavity. If the girl is nulliparous, then medical abortion often gives complications. Not everything comes out of the uterine cavity. Parts of the membranes remain, clots, and, let's say, a delay of these parts occurs and there may be an inflammatory process, as a result of which, subsequently, surgical intervention is required - curettage or vacuum aspiration. The method of terminating a missed pregnancy is chosen by the attending physician based on these data. In our clinic, we often encounter missed pregnancy in those women who want to give birth to their child. And to understand the genetics of the fetus, we often recommend hysteroscopic removal or vacuum aspiration of the ovum.
Yuliya Vladimirovna Labuznaya
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the department of operative gynecology, doctor of the cervical pathology office
Hello. Today I will try to answer the most frequently asked questions regarding non-developing pregnancy. Perhaps I’ll start with such a rink: “Is it necessary to do vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterine cavity, that is, the evacuation of a missed pregnancy, if a non-developing pregnancy is diagnosed?” And so let's deal with the concept. A non-developing pregnancy is a pathological condition in which pregnancy fades, but spontaneous expulsion from the uterine cavity does not occur. At the same time, the woman herself does not immediately understand what happened to her. The first signs of a missed pregnancy can appear 2-3 weeks after the incident. The fetal egg, which is located in the uterine cavity, undergoes various pathological changes, adversely affecting the endometrium, thereby causing an inflammatory process called "endometritis".
The fetal egg, which is located in the uterine cavity, undergoes various pathological changes, adversely affecting the endometrium, thereby causing an inflammatory process called "endometritis".
If a woman decides to wait for the spontaneous expulsion of a frozen pregnancy from the uterine cavity, what happens? The endometrium tries to reject the frozen fetal egg, but the inflammatory processes taking place in this endometrium slow down this process, and the process can last from several days to several weeks. Which absolutely negatively affects the endometrium and contributes to the development of the inflammatory process further. There is an act that the fetal egg from the uterine cavity, as it were, came out, but not completely. There is a part of him left. From this part, often, a placental polyp is formed. The presence of a placental polyp in the uterine cavity contributes to the prevention of a subsequent pregnancy. Before the onset, planning a subsequent pregnancy, such a pali must be removed. In addition, the presence of a fetal egg in the uterine cavity for four weeks or more significantly increases the risk of bleeding. Therefore, the best solution to such an issue, in the presence of a missed pregnancy in a patient, is vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterine cavity with the appointment of subsequent anti-inflammatory therapy.
In addition, the presence of a fetal egg in the uterine cavity for four weeks or more significantly increases the risk of bleeding. Therefore, the best solution to such an issue, in the presence of a missed pregnancy in a patient, is vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterine cavity with the appointment of subsequent anti-inflammatory therapy.
The second issue is errors in the diagnosis of non-developing pregnancy. For example, at 5-6 weeks, an ultrasound examination, in order to avoid such errors, is carried out by at least two specialists. If there are no clear criteria for non-developing pregnancy, it is recommended for the patient to repeat this study after 3-7 days. Again, to avoid mistakes. In addition, in parallel, the task of such an analysis as an analysis of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood is mandatory. If the pregnancy develops, the hCG will increase accordingly, if the pregnancy is still frozen, then the hCG will either fall or not grow at all. If the gestational age is 7-8 weeks, then according to the ultrasound examination, the heart rate of the embryo will be absent.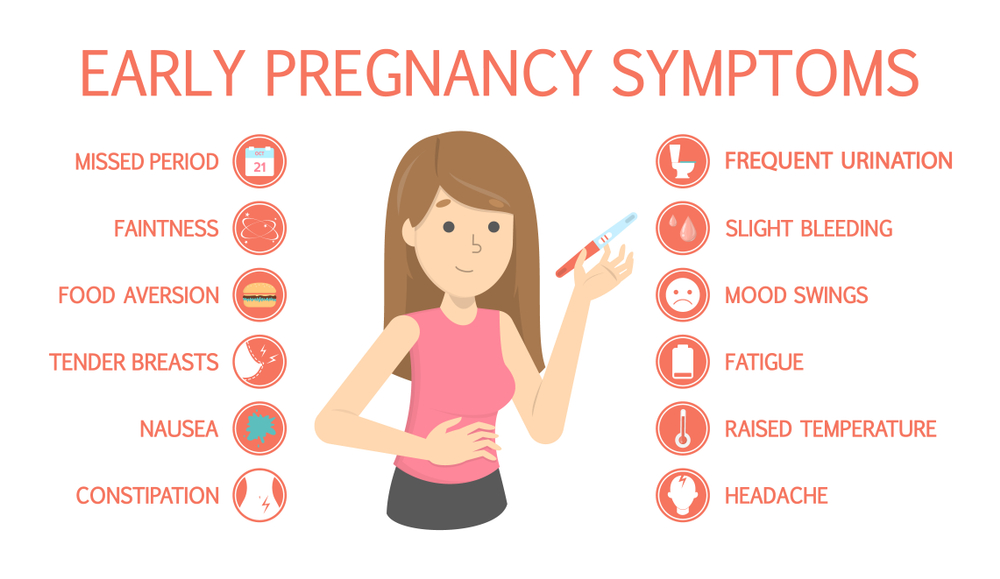 In addition, there will be a discrepancy between the size of the fetal egg and the gestational age. At gestational age 9-12 weeks, in addition to the lack of heart rate and the discrepancy between the gestational age and the size of the fetal egg, there will also be no movement of the embryo. It should always be remembered that every woman has the right to take a closer look at the ultrasound in a few days for an accurate diagnosis, to control the human chorionic gonadotropin, in fact, in order to avoid errors in the diagnosis of "non-developing pregnancy".
In addition, there will be a discrepancy between the size of the fetal egg and the gestational age. At gestational age 9-12 weeks, in addition to the lack of heart rate and the discrepancy between the gestational age and the size of the fetal egg, there will also be no movement of the embryo. It should always be remembered that every woman has the right to take a closer look at the ultrasound in a few days for an accurate diagnosis, to control the human chorionic gonadotropin, in fact, in order to avoid errors in the diagnosis of "non-developing pregnancy".
Answers to frequently asked and discussed questions on the forums:
✅ Can an ultrasound erroneously show a miscarriage?
Misdiagnosis of non-developing pregnancy occurs in the early stages. In our clinic, in order to avoid such errors, ultrasound at 5-6 weeks is performed by at least two specialists. If there are no clear criteria for non-developing pregnancy, then the patient is recommended to do a second study after 3-7 days. And on re-examination, it may turn out that the frozen pregnancy turned out to be normal.
And on re-examination, it may turn out that the frozen pregnancy turned out to be normal.
✅ With a missed pregnancy, is it possible to do without cleaning?
If a frozen pregnancy tends to resolve itself, then it can come out on its own, and then curettage (cleansing) is not required. As soon as the discharge ends, it is necessary to check on an ultrasound scan that there are no elements of the ovum left in the uterine cavity. If the pregnancy froze at an early stage and there are no signs that it is going to resolve itself, that is, there is no bleeding, then it is advisable to do a curettage.
✅ Frozen pregnancy - cleaning or pills?
Medical termination of pregnancy is indicated for women who have had pregnancies in the past and had natural childbirth. But it is more correct to do a scraping, or a vacuum, if the time permits. Because, sometimes, after medical abortions, you also have to do scraping, but already in fact of complications. Because the contents of the uterine cavity do not always come out completely, and inflammation is added, and this is a big trauma for the uterus and it is better not to allow this. Therefore, it is better to do a moderate, without severe injury and without complications, curettage on time than to do it as a necessary measure. And most importantly, scraping products can be sent for genetic testing to identify the causes of fetal development fading.
Therefore, it is better to do a moderate, without severe injury and without complications, curettage on time than to do it as a necessary measure. And most importantly, scraping products can be sent for genetic testing to identify the causes of fetal development fading.
✅ Can there be a miscarriage without symptoms?
It happens that the pregnancy stops, and the patient knows absolutely nothing about it, and this is discovered at a later date, when she is told that the fetal egg does not correspond in size, that the pregnancy stopped earlier, but this, unfortunately, it is impossible to suspect in advance. The first signs of a non-developing pregnancy can appear 2-3 weeks after the incident. These are spotting or pulling pains in the lower abdomen. With these symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor.
✅ How long to wait for a miscarriage with a missed pregnancy?
If a woman decides to wait for the spontaneous expulsion of an undeveloped pregnancy, what happens? The endometrium tries to reject the frozen fetal egg, but the inflammatory processes taking place in this endometrium slow down this process, and the process can last from several days to several weeks.