Sperms for pregnancy
How Long Sperm Live, Sperm Count, and More
Written by Mary Anne Dunkin
You may know it takes one sperm and one egg to make a baby, but if you're like most folks, you might not remember much else about sperm from biology class. If infertility is an issue for you and your partner, it helps to understand the basics.
How long do sperm live?
The answer depends on a number of things, but the most important is where the sperm are located.
On a dry surface, such as clothing or bedding, sperm are dead by the time the semen has dried. In water, such as a warm bath or hot tub, they'll likely live longer because they thrive in warm, wet places. But the odds that sperm in a tub of water will find their way inside a woman's body and cause them to get pregnant are extremely low.
When sperm are inside women's body, they can live for up to 5 days. If you're a man and you have sex even a few days before your partner ovulates, there's chance they may get pregnant.
How many sperm do you need to get pregnant?
It takes just one sperm to fertilize a woman's egg. Keep in mind, though, for each sperm that reaches the egg, there are millions that don't.
On average, each time men ejaculate they release nearly 100 million sperm. Why are so many sperm released if it takes only one to make a baby? To meet the waiting egg, semen must travel from the vagina to the fallopian tubes, a tough journey that few sperm survive. Experts believe this process may be nature's way of allowing only the healthiest sperm to fertilize the egg, to provide the best chances of having a healthy baby.
For those sperm that complete the trip, getting into the egg, which is covered by a thick layer, is far from a sure thing.
Is there anything you can do to improve the health of your sperm?
Many of the things you do to keep yourself healthy can also do the same for sperm. Try some of these tips:
- Don't smoke or use illicit drugs, especially anabolic steroids.
- Avoid contact with toxins such as pesticides and heavy metals.
- Limit how much alcohol you drink.
- Eat a healthy diet and keep your weight under control.
- Keep your scrotum cool, because heat slows down the making of sperm. To do this, avoid hot baths, wear boxers instead of briefs, and try not to wear tight pants.
What does a semen analysis tell?
It's a test that can help your doctor figure out why you and your partner are having trouble having a baby.
Some things you can learn from the analysis:
Amount and thickness of semen. On average, each time men ejaculate they release 2-6 milliliters (mL) of semen, or around a 1/2 teaspoon to 1 teaspoon.
Less than that amount may not contain enough sperm for a woman to get pregnant. On the other hand, more than that could dilute the concentration of sperm.
Semen should be thick to start with and become thinner 10 to 15 minutes after ejaculation. Semen that stays thick may make it difficult for sperm to move.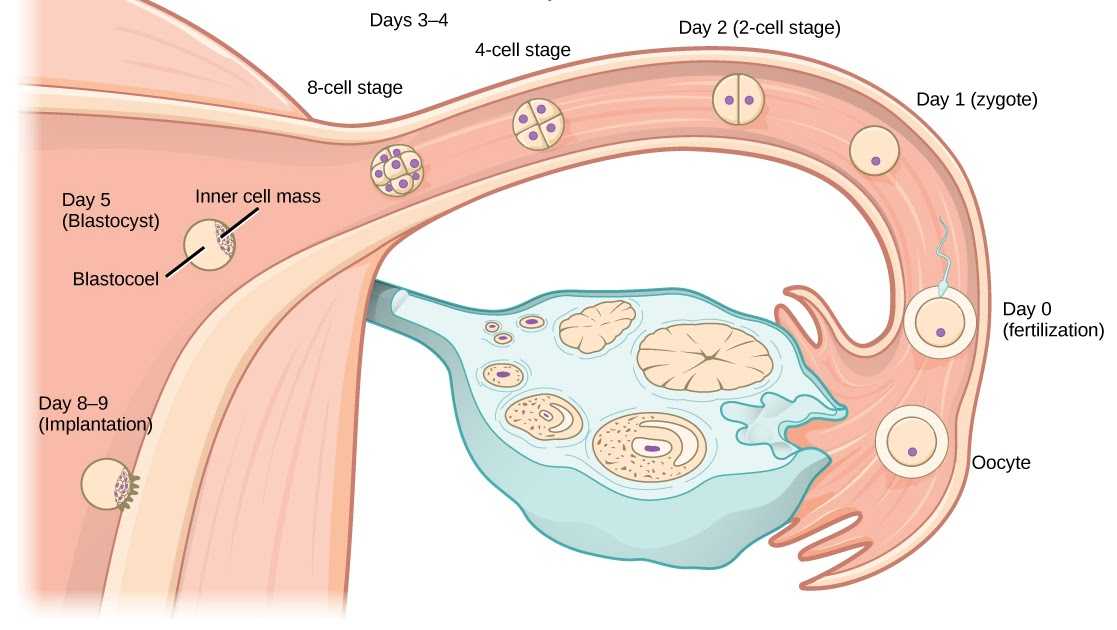
Sperm concentration. Also called sperm density, this is the number of sperm in millions per milliliter of semen. Fifteen million or more sperm per mL is considered normal.
Sperm motility. This is the percentage of sperm in a sample that are moving, as well as an assessment of how they move. One hour after ejaculation, at least 32% of sperm should be moving forward in a straight line.
Morphology. This is an analysis of the size, shape, and appearance of sperm.
Do men stop making sperm when they're older?
Men can continue to be fertile throughout life. The amount of sperm you make goes down as you get older, but even elderly men have fathered children.
Infertility & Reproduction Guide
- Overview
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis & Tests
- Treatment & Care
- Support & Resources
How Does Pregnancy Happen? | Pregnancy Symptoms & Signs
In This Section
- How Pregnancy Happens
- What are some tips for getting pregnant?
How Does Pregnancy Happen | Planned Parenthood Video
How Does Pregnancy Happen | Planned Parenthood VideoHow does pregnancy happen?
In order for pregnancy to happen, sperm needs to meet up with an egg. Pregnancy officially starts when a fertilized egg implants in the lining of the uterus. It takes up to 2-3 weeks after sex for pregnancy to happen.
Pregnancy officially starts when a fertilized egg implants in the lining of the uterus. It takes up to 2-3 weeks after sex for pregnancy to happen.
How do people get pregnant?
Pregnancy is actually a pretty complicated process that has several steps. It all starts with sperm cells and an egg.
Sperm are microscopic cells that are made in testicles. Sperm mixes with other fluids to make semen (cum), which comes out of the penis during ejaculation. Millions and millions of sperm come out every time you ejaculate — but it only takes 1 sperm cell to meet with an egg for pregnancy to happen.
Eggs live in ovaries, and the hormones that control your menstrual cycle cause a few eggs to mature every month. When your egg is mature, it means it’s ready to be fertilized by a sperm cell. These hormones also make the lining of your uterus thick and spongy, which gets your body ready for pregnancy.
About halfway through your menstrual cycle, one mature egg leaves the ovary — called ovulation — and travels through the fallopian tube towards your uterus.
The egg hangs out for about 12-24 hours, slowly moving through the fallopian tube, to see if any sperm are around.
If semen gets in your vagina, sperm cells can swim up through the cervix. The sperm and uterus work together to move the sperm towards the fallopian tubes. If an egg is moving through your fallopian tubes at the same time, the sperm and egg can join together. The sperm has up to six days to join with an egg before it dies.
When a sperm cell joins with an egg, it’s called fertilization. Fertilization doesn’t happen right away. Since sperm can hang out in your uterus and fallopian tube for up to 6 days after sex, there’s up to 6 days between sex and fertilization.
If a sperm cell does join up with your egg, the fertilized egg moves down the fallopian tube toward the uterus. It begins to divide into more and more cells, forming a ball as it grows. The ball of cells (called a blastocyst) gets to the uterus about 3–4 days after fertilization.
The ball of cells floats in the uterus for another 2–3 days.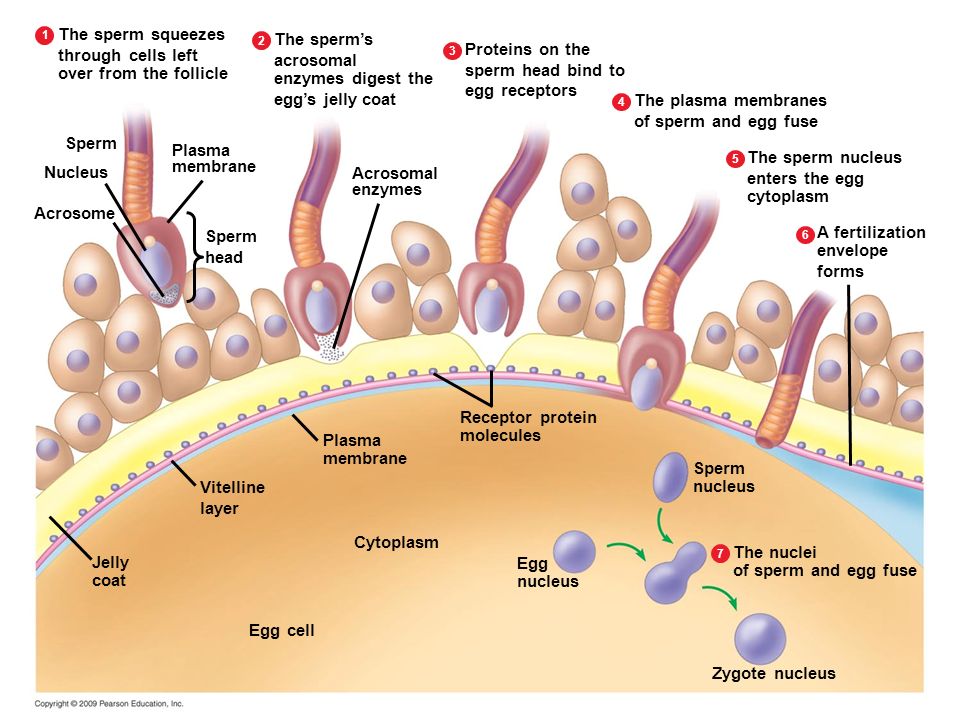 If the ball of cells attaches to the lining of your uterus, it’s called implantation — when pregnancy officially begins.
If the ball of cells attaches to the lining of your uterus, it’s called implantation — when pregnancy officially begins.
Implantation usually starts about 6 days after fertilization, and takes about 3-4 days to complete. The embryo develops from cells on the inside of the ball. The placenta develops from the cells on the outside of the ball.
When a fertilized egg implants in the uterus, it releases pregnancy hormones that prevent the lining of your uterus from shedding — that’s why people don’t get periods when they’re pregnant. If your egg doesn’t meet up with sperm, or a fertilized egg doesn’t implant in your uterus, the thick lining of your uterus isn’t needed and it leaves your body during your period. Up to half of all fertilized eggs naturally don’t implant in the uterus — they pass out of your body during your period.
What are early pregnancy symptoms?
Many people notice symptoms early in their pregnancy, but others may not have any symptoms at all.
Common signs and symptoms of pregnancy can include:
-
Missed period
-
Swollen or tender breasts
-
Nausea and/or vomiting
-
Feeling tired
-
Bloating
-
Constipation
-
Peeing more often than usual
Some early pregnancy symptoms can sometimes feel like other common conditions (like PMS). So the only way to know for sure if you’re pregnant is to take a pregnancy test. You can either take a home pregnancy test (the kind you buy at the drug or grocery store), or get a pregnancy test at your doctor’s office or local Planned Parenthood Health Center.
So the only way to know for sure if you’re pregnant is to take a pregnancy test. You can either take a home pregnancy test (the kind you buy at the drug or grocery store), or get a pregnancy test at your doctor’s office or local Planned Parenthood Health Center.
How do people get pregnant with twins?
There are 2 ways that twins can happen. Identical twins are made when 1 already-fertilized egg splits into 2 separate embryos. Because identical twins come from the same sperm and egg, they have the same genetic material (DNA) and look exactly alike.
Non-identical twins (also called “fraternal” twins), are made when two separate eggs are fertilized by two separate sperm, and both fertilized eggs implant in the uterus. This can happen if your ovaries release more than one egg, or during certain kinds of fertility treatments. Non-identical twins have completely different genetic material (DNA), and usually don’t look alike. They’re the most common type of twin.
What is gestational age?
The term “gestational age” basically means how far along into a pregnancy you are. Gestational age is counted by starting with the first day of your last menstrual period (called LMP).
Gestational age is counted by starting with the first day of your last menstrual period (called LMP).
Gestational age can be kind of confusing, since it measures pregnancy from your last period — about 3-4 weeks BEFORE you’re actually pregnant. Common knowledge about pregnancy says it lasts 9 months, and it’s true that you’re usually pregnant for about 9 months. But the way pregnancy is measured makes it a little longer. A typical full-term pregnancy ranges from 38-42 weeks LMP — around 10 months.
Many people can’t remember the exact date of their last menstrual period — that’s totally okay. Your nurse or doctor can find out the gestational age using an ultrasound.
More questions from patients:
Can you get pregnant from precum?
Your chances of getting pregnant from precum are pretty low. But it is possible.
Precum (also known as pre-ejaculate) is a small amount of fluid that comes out of the penis when you’re aroused, but before ejaculation happens.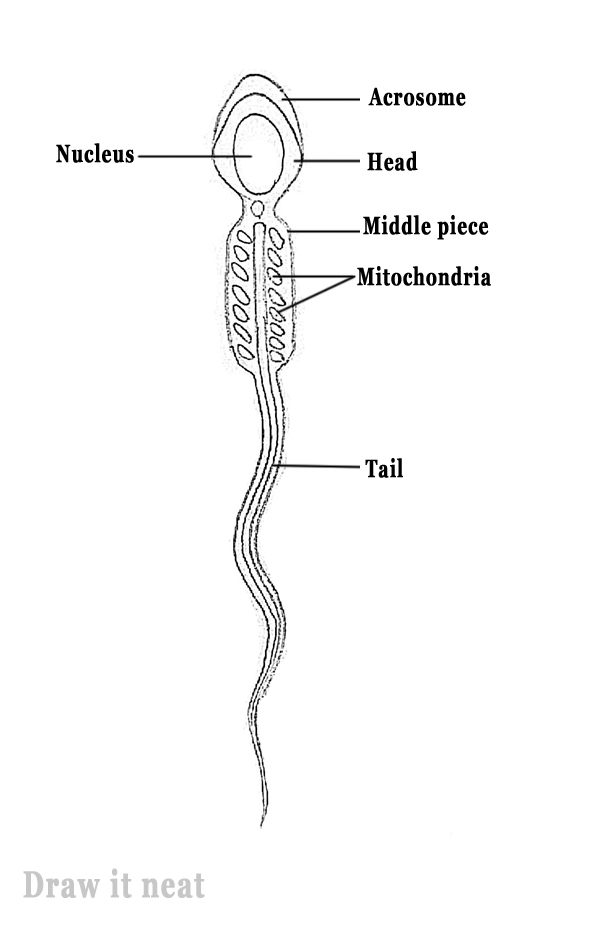 It doesn’t usually have any sperm in it. But some people’s precum does have a small amount of sperm in it sometimes. This means sperm can get into the vagina and possibly fertilize an egg.
It doesn’t usually have any sperm in it. But some people’s precum does have a small amount of sperm in it sometimes. This means sperm can get into the vagina and possibly fertilize an egg.
There’s no way to know who has sperm in their precum and who doesn’t, so that’s one reason why the withdrawal method (pulling out) isn’t the best at preventing pregnancy.
If you don’t want to get pregnant, put on a condom before your genitals touch your partner’s. Even better, use both condoms and another kind of birth control together.
What are the stages of pregnancy?
Pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks. The stages of pregnancy are divided into 3 trimesters. Each trimester is a little longer than 13 weeks.
You’ll go through many changes during each trimester. Some people feel lots of discomfort. Others don’t feel much at all.
During the first trimester, you’ll probably have lots of body changes, including:
-
Tiredness
-
Tender, swollen breasts
-
Morning sickness
-
Cravings or distaste for certain foods
-
Mood swings
-
Constipation
-
Needing to pee more often
-
Headache
-
Heartburn
-
Weight gain or loss
Most of these symptoms go away when you get to the second trimester. This is when your belly gets bigger and you’ll feel the fetus move. You may also notice:
This is when your belly gets bigger and you’ll feel the fetus move. You may also notice:
-
Body aches
-
Stretch marks
-
Darkening of your areolas
-
A line on your skin running from your belly button to pubic bone
-
Patches of darker skin
-
Numb or tingling hands
-
Itching on your abdomen, palms, and feet
-
Swelling of your ankles, fingers, or face
In the third trimester, some of the same symptoms may continue. You may also experience:
-
Shortness of breath
-
Needing to pee even more often
-
Hemorrhoids
-
Your breasts leaking a watery pre-milk called colostrum
-
Your belly button sticking out
-
Trouble sleeping
-
The baby "dropping" or moving lower in your abdomen
-
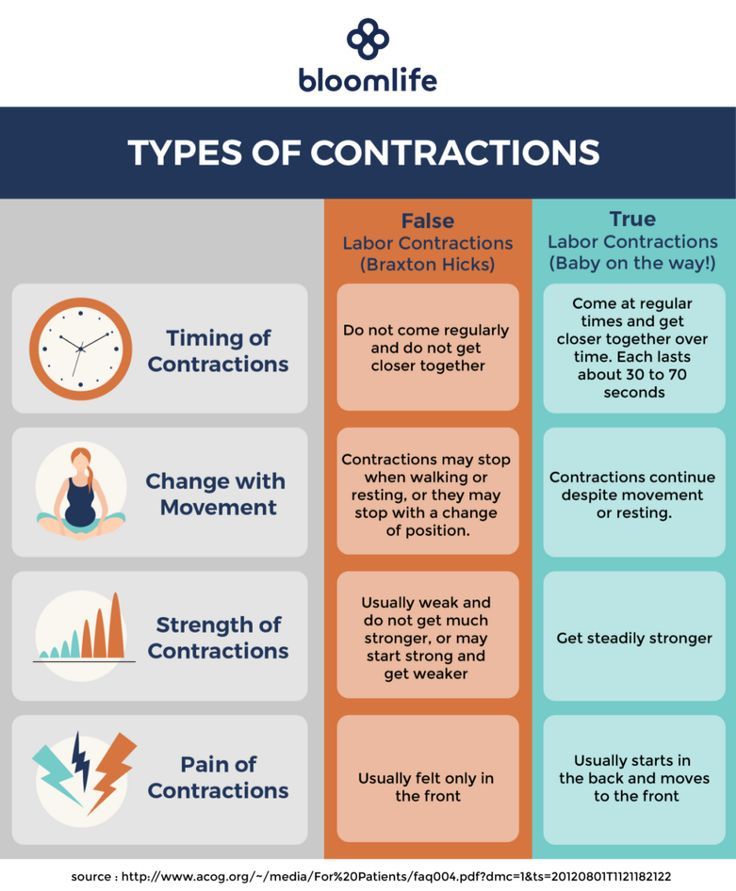
Contractions
If you aren’t sure if your symptoms are normal, call your doctor or midwife or visit your local Planned Parenthood health center.
- Yes
- No
Help us improve - how could this information be more helpful?
How did this information help you?
Please answer below.
Are you human? (Sorry, we have to ask!)
Please don't check this box if you are a human.
You’re the best! Thanks for your feedback.
Thanks for your feedback.
Preparing for pregnancy: what depends on the man? - Assisted reproductive technologies - Departments
The article was published in the magazine 9 months №7 2004.
Author: Bozhedomov Vladimir Alexandrovich, Doctor of Medicine, professor, urologist-andrologist of the highest qualification category.
One of the most pressing questions that worries any person is the question: "What do we live for?". I think truly intelligent life on our planet arose when someone first tried to comprehend the meaning of their own existence. Searches and various interpretations of the meaning of life are the core of religious books and philosophical treatises of all times and peoples, are reflected in the scientific works of biologists and psychologists, the writings of poets and prose writers. Each of us sooner or later asks himself this eternal question, and gives one or another answer to it. But time, lived years, accumulated experience often change even their own ideas. Does this mean there is no correct answer? Probably, yes, there really is no single correct one. But there is one thing that is definitely correct: the meaning of the life of any living being, including humans, is to leave behind offspring, create conditions for children to grow up healthy and also be able to pass on your immortal genes “by inheritance”.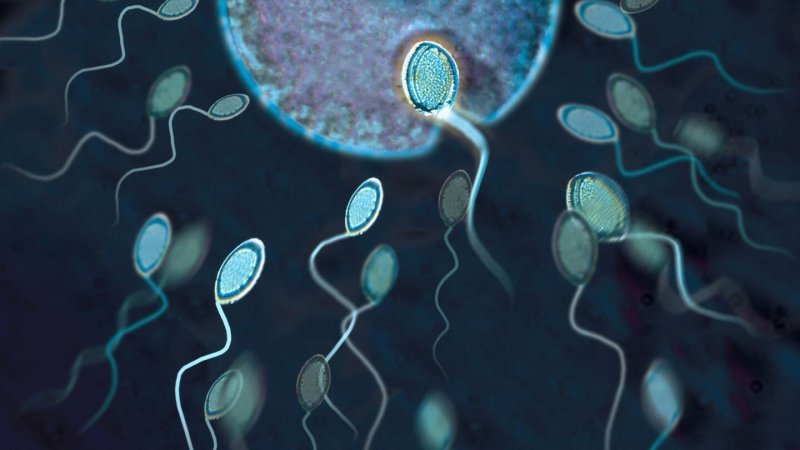 This is the highest law of Life.
This is the highest law of Life.
Unlike animals, in humans, having children is not the only purpose of existence. An important place is occupied by education, professional self-realization, interesting communication, new impressions, for which someone turns to TV, and someone goes on a trip. Human sexuality today includes not so much a procreational function (reproducing offspring), but rather recreational (getting pleasure) and relational (communication with a loved one, knowledge and self-awareness, unity) relationships. The birth of a child in most cases is no longer an unconditional reflex act, but a reasonably planned event in the life of the family. But the biological basis of reproduction remains basically the same as millions of years ago, when the first mammals appeared. And, in fact, little has changed in the sexual, i.e. directed preservation of the genus, behavior: selection and “conquest” of the most promising partner in terms of reproduction, care for the future mother and children, teaching offspring the skills necessary for life.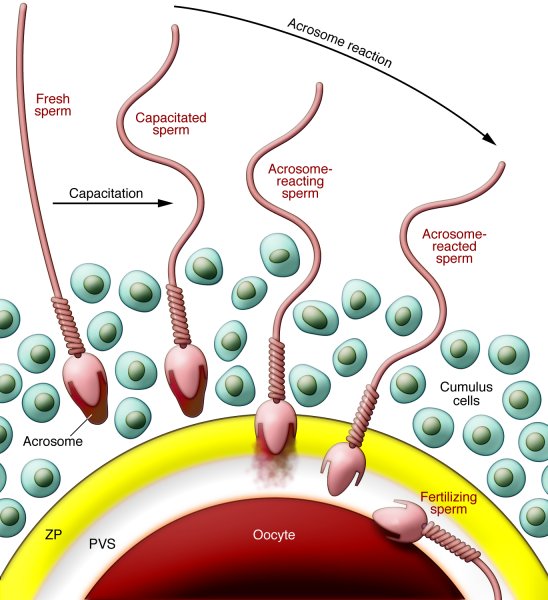 Therefore, it is important to know what depends on the spouses and what does not depend on when the birth of a child is planned.
Therefore, it is important to know what depends on the spouses and what does not depend on when the birth of a child is planned.
Today we will take a brief look at what depends on a man when a couple is preparing for pregnancy.
Most adults know that the gender of the unborn child depends on the man. Unlike women, instead of two X chromosomes of the same size and shape, men have one Y chromosome and one X chromosome. The Y chromosome contains hereditary information that directs the development of indifferent gonads along the male path, turning them into testicles. With the divergence of chromosomes in the process of meiosis - a special cell division that occurs in the testicles during the formation of germ cells, each spermatozoon gets 23 chromosomes out of 46 original ones. At the same time, from a pair of sex chromosomes, a Y-chromosome enters one spermatozoon, an X-chromosome enters the second, therefore half of all spermatozoa contain a Y-chromosome, half contain an X. If the egg is fertilized by a spermatozoon of the first type, a boy will be born, the second - a girl. These processes are random and do not depend in any way on the will and desire of the future father, or his way of life. Therefore, with natural conception, planning the sex of the unborn child is impossible. No diets and predictions of astrologers will help here. It is possible to achieve the birth of a child of the desired sex only after the fertilization of the egg “in vitro”, when the so-called. preimplantation genetic testing, and embryos of the desired sex are transferred into the uterine cavity.
If the egg is fertilized by a spermatozoon of the first type, a boy will be born, the second - a girl. These processes are random and do not depend in any way on the will and desire of the future father, or his way of life. Therefore, with natural conception, planning the sex of the unborn child is impossible. No diets and predictions of astrologers will help here. It is possible to achieve the birth of a child of the desired sex only after the fertilization of the egg “in vitro”, when the so-called. preimplantation genetic testing, and embryos of the desired sex are transferred into the uterine cavity.
When planning the birth of a child, you need to remember that the onset of pregnancy is a probabilistic process that depends on many factors: the quantity and quality of spermatozoa in the sperm, the presence and timing of ovulation of the female egg, the presence of patency of the fallopian tubes, and many others. It has been shown that the probability of conception depends, among other things, on the frequency of sexual intercourse: in healthy partners with sexual intimacy 2 times a week, the probability of pregnancy during one female cycle is 20-25%, with a frequency of 4-5 times a week it increases to 40 -42%. Repeated sexual intercourse during ovulation days can reduce the chance of conception due to the fact that the second portion of semen contains fewer full-fledged spermatozoa, and excess volume leads to leakage from the vagina. At present, it is assumed that pregnancy should normally occur within a year of regular intercourse without contraception.
Repeated sexual intercourse during ovulation days can reduce the chance of conception due to the fact that the second portion of semen contains fewer full-fledged spermatozoa, and excess volume leads to leakage from the vagina. At present, it is assumed that pregnancy should normally occur within a year of regular intercourse without contraception.
Of course, the likelihood of pregnancy depends on the quality of sperm. The lower the number of spermatozoa, the more immobile "freaks", the less chance that the egg will be fertilized. It is important to remember that male potency is not automatically a confirmation of his fertility, i. ability to have children. It is not uncommon for sexually weak men to have excellent sperm and, conversely, for sexually active men, the content of spermatozoa is reduced or completely absent. The quality and potential fertilizing ability of sperm can be assessed only after special laboratory tests, which include determining the quantity, motility and morphology of spermatozoa, an acrosomal reaction characterizing their functional maturity, the presence of antisperm antibodies, the content of reactive oxygen radicals in the semen, zinc, fructose and other indicators.
In recent years, scientists in many countries, including andrologists in our country, have been seriously concerned about the decline in the reproductive potential of men. In a retrospective analysis of the quantitative indicators of spermograms, it was found that the quality of the sperm of Europeans and North Americans has deteriorated over the past 50 years by almost three times. Obviously, this happened as a result of various man-made factors, environmental pollution and lifestyle changes. It is now generally accepted that men (and males in general), although they are considered the “strong” sex, are more susceptible to negative environmental factors. Evolutionarily, this is due to the peculiarity of their biological role. Males in wildlife are the main material of evolutionary selection, various combinations of genes that nature tries to survive. (it is well known that more boys are born and fewer survive than girls). The appearance of offspring is also a “reward for courage”, which not all males will get in the animal kingdom. Every day, a man produces tens and hundreds of millions of spermatozoa, and all of them are genetically different, while only 1-2 eggs mature in a woman every month. Of these millions of sperm, only one fertilizes this egg. Only one who passes the sieve of natural selection, which first occurs in the genitals of the man himself, and then continues in the genital tract of the woman. The basis of selection is that all spermatozoa are genetically different. As a result of a special cell division - meiosis - there is not only a halving of the number of chromosomes in each cell, but also an exchange of similar sections of chromosomes that a man once inherited from his father and mother. That is why all spermatozoa are genetically different and carry different sets of traits. The selection of spermatozoa begins in the testicles themselves, then continues in the epididymis and seminal vesicles, where the sperm accumulates before ejaculation. It is estimated that about 100 million spermatozoa are formed in a normal man every hour, and when abstinence for several days, sperm contains several tens of millions, i.
Every day, a man produces tens and hundreds of millions of spermatozoa, and all of them are genetically different, while only 1-2 eggs mature in a woman every month. Of these millions of sperm, only one fertilizes this egg. Only one who passes the sieve of natural selection, which first occurs in the genitals of the man himself, and then continues in the genital tract of the woman. The basis of selection is that all spermatozoa are genetically different. As a result of a special cell division - meiosis - there is not only a halving of the number of chromosomes in each cell, but also an exchange of similar sections of chromosomes that a man once inherited from his father and mother. That is why all spermatozoa are genetically different and carry different sets of traits. The selection of spermatozoa begins in the testicles themselves, then continues in the epididymis and seminal vesicles, where the sperm accumulates before ejaculation. It is estimated that about 100 million spermatozoa are formed in a normal man every hour, and when abstinence for several days, sperm contains several tens of millions, i. e. 100 times less. "Defective" spermatozoa are eliminated by special cells-devourers. Of those gametes that entered the vagina, less than 1% of the cells pass through the cervical canal into the uterus, only a few hundred participate in the siege of the “fortress”, which is the egg.
e. 100 times less. "Defective" spermatozoa are eliminated by special cells-devourers. Of those gametes that entered the vagina, less than 1% of the cells pass through the cervical canal into the uterus, only a few hundred participate in the siege of the “fortress”, which is the egg.
The process of maturation of spermatozoa is much faster than that of eggs. In men, the duration of spermatogenesis is about three months. In women, the reproduction of germ cells occurs in the prenatal period, by the time of puberty, female germ cells are at the stage of the primary oocyte, which has entered the prophase of meiosis, and still retain complete, i.e. diploid set of chromosomes. Each cycle, no more than 30 potential eggs enter into further maturation, of which one dominates at the last stage.
We can say that in evolutionary terms a man is a bearer of genetic and behavioral mobility. A woman, on the contrary, is a genetic "conservative", she preserves and passes on to her children what was accumulated by previous generations. Therefore, the causes of female infertility are much more often associated with malfunctions in the work of the female body itself, while external circumstances often have a fatal influence on a man. If conditions are unfavorable, offspring should not appear. Such regulation is ensured by the close relationship between the sexual and all other systems of the body, primarily the nervous system. The formation of spermatozoa is regulated along the axis of the hypothalamus - pituitary gland - testicles and their subsequent maturation and "selection" - with the participation of additional organs of the reproductive tract: appendages, prostate, vesicles, etc. At each stage of this process, violations can occur.
Therefore, the causes of female infertility are much more often associated with malfunctions in the work of the female body itself, while external circumstances often have a fatal influence on a man. If conditions are unfavorable, offspring should not appear. Such regulation is ensured by the close relationship between the sexual and all other systems of the body, primarily the nervous system. The formation of spermatozoa is regulated along the axis of the hypothalamus - pituitary gland - testicles and their subsequent maturation and "selection" - with the participation of additional organs of the reproductive tract: appendages, prostate, vesicles, etc. At each stage of this process, violations can occur.
What diseases and what factors reduce a man's reproductive potential?
Some factors are congenital, caused by genetic or developmental abnormalities. These include the genetic syndromes of Klinefelter, Reifinstein, Kalman, and others, as well as the absence of some elements of the genitourinary system. In this case, there is very little or no spermatozoa in the semen, which makes pregnancy in the natural cycle almost impossible.
In this case, there is very little or no spermatozoa in the semen, which makes pregnancy in the natural cycle almost impossible.
Many of the risk factors are "man-made" and depend on a person's lifestyle. Among them, the most massive should be considered: smoking, alcohol abuse, malnutrition, physical inactivity, psycho-emotional stress, lack of sleep. Of the specific - primarily sexually transmitted infections.
Inflammatory processes in the genitals or even asymptomatic carriage of infections such as chlamydia and mycoplasmas are one of the most common causes of infertility. This pathology is often observed in half of the cases. The infectious process leads to damage to spermatozoa by active radicals and other factors of inflammatory reactions, obstruction of the genital tract, disorders of the endocrine function of the gonads, and the development of autoimmune reactions against one's own spermatozoa. If adequate antibiotic treatment is started in a timely manner, sperm quality disorders are usually reversible. If the process has acquired a chronic course and led to organic changes in the organs of the reproductive tract, the prognosis is less favorable.
If the process has acquired a chronic course and led to organic changes in the organs of the reproductive tract, the prognosis is less favorable.
Low physical activity, sedentary work, passive rest, too tight jeans and thick underwear, overweight, lipid deposits in the vessels disturb the blood circulation in the pelvic region and lead to stagnation of blood in the vessels. Where there is stagnation, there is a lack of oxygen, an increased content of metabolic products, and inflammation. The pathogenesis of varicocele, a male disease in which the veins of the spermatic cord are dilated, is associated with overheating and the accumulation of harmful metabolites. This is usually seen in the left side of the scrotum. Circulatory disorders are exacerbated by overheating and vibration, so taxi drivers and professional drivers who drive more than four hours a day, infertility is more common than in men of other professions. The problem of the effect of hyperthermia on fertility is purely male. It is no coincidence that the place of formation of spermatozoa - the testicles - has been removed from the body. The temperature in the scrotum is normally several degrees lower than body temperature. Therefore, trousers that are too warm, especially synthetic ones, thick blankets or electrically heated blankets, constant baths, saunas and hot baths adversely affect the quality of sperm. Finnish researchers have found that those who visit the sauna twice a week have a statistically higher risk of developing male infertility compared to those who take a steam bath once a week. Any febrile conditions with influenza, measles and other diseases lead to a deterioration in the quality of sperm, and such a decrease in quality can be observed up to 3 months. - this is how long the maturation of each spermatozoon in the testicle and appendages continues. Fortunately, mild overheating disorders are usually reversible.
It is no coincidence that the place of formation of spermatozoa - the testicles - has been removed from the body. The temperature in the scrotum is normally several degrees lower than body temperature. Therefore, trousers that are too warm, especially synthetic ones, thick blankets or electrically heated blankets, constant baths, saunas and hot baths adversely affect the quality of sperm. Finnish researchers have found that those who visit the sauna twice a week have a statistically higher risk of developing male infertility compared to those who take a steam bath once a week. Any febrile conditions with influenza, measles and other diseases lead to a deterioration in the quality of sperm, and such a decrease in quality can be observed up to 3 months. - this is how long the maturation of each spermatozoon in the testicle and appendages continues. Fortunately, mild overheating disorders are usually reversible.
All men know that the groin area is very sensitive to any blows. Bruises, ruptures, cuts of the testicles in the vast majority of cases lead to infertility.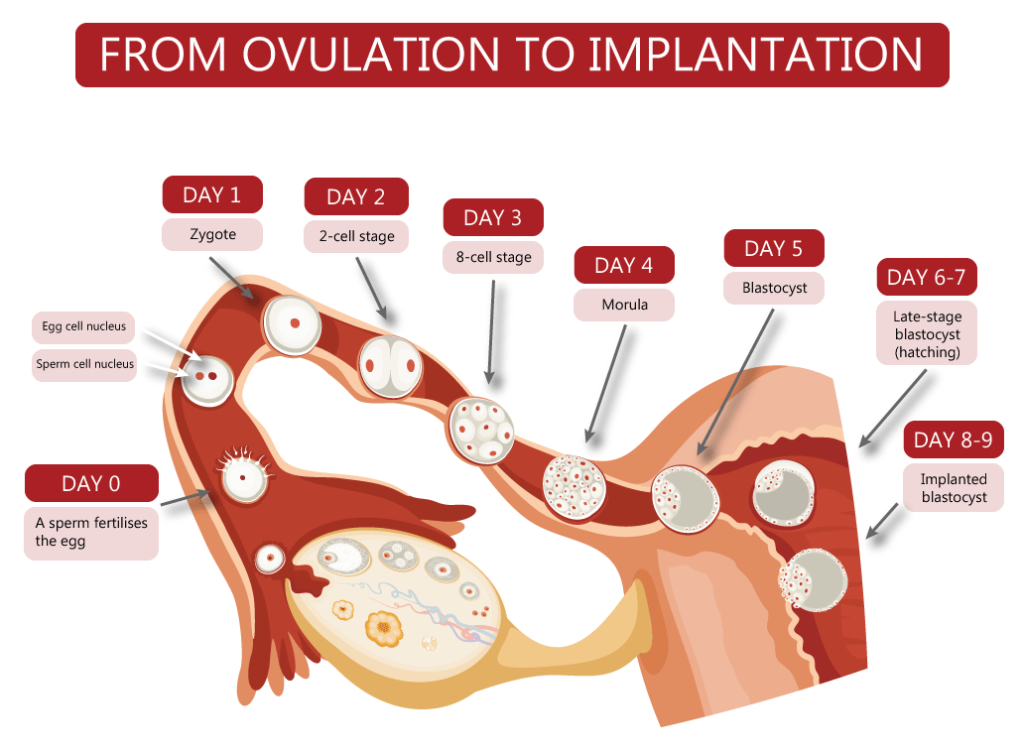 But recently, including our research, it has been convincingly shown that even minor injuries that do not immediately cause serious consequences, which the patient hardly remembers, trigger an invisible mechanism of autoimmune warfare, when the immune system “attacks” its own cells. Many years after such an injury, it turns out that the body has long since taken up arms against the spermatozoa produced by itself, and the man has immune infertility. The risk groups here are martial arts athletes, wrestlers, cyclists.
But recently, including our research, it has been convincingly shown that even minor injuries that do not immediately cause serious consequences, which the patient hardly remembers, trigger an invisible mechanism of autoimmune warfare, when the immune system “attacks” its own cells. Many years after such an injury, it turns out that the body has long since taken up arms against the spermatozoa produced by itself, and the man has immune infertility. The risk groups here are martial arts athletes, wrestlers, cyclists.
The use of alcohol is worth mentioning separately. In small quantities, alcohol is not dangerous, it even improves blood circulation, and today it is considered as a universal preventive measure for diseases of the vascular system, namely, they often affect the quality of sperm. But the "therapeutic" dose of alcohol is about 50 milliliters of alcohol per day, that is, 300-500 grams of "dry" wine or 125 grams of vodka. Exceeding this dose turns alcohol from a "medicine" into a poison. Are there many Russian men capable of limiting themselves to a glass or two of wine? Alcohol and the norm is a problem as old as the world, especially acute in our country. In situations when it comes to planning a pregnancy, it is better not to drink at all than to drink too much.
Are there many Russian men capable of limiting themselves to a glass or two of wine? Alcohol and the norm is a problem as old as the world, especially acute in our country. In situations when it comes to planning a pregnancy, it is better not to drink at all than to drink too much.
It is well known that smoking not only has a direct toxic effect on the body, but also leads to prolonged vasospasm, causing all the same vascular disorders that are detrimental to spermatozoa. It is especially bad when smoking is combined with other risk factors: excessive alcohol consumption, sedentary lifestyle, overheating, stress. And when risk factors combine, their negative impact is multiplied and intensified tenfold. In my opinion, a healthy lifestyle is incompatible with smoking.
Chronic stress is a common and rather dangerous risk factor for infertility in men. The function of producing sperm is not necessary to sustain the life of an individual. This sexual gland product is addressed to the future. But it is obvious that from a biological point of view, offspring should be born in the most favorable environmental conditions, which will allow still helpless creatures to survive. Therefore, any stress - a reaction to threatening situations - is a signal to the body about unfavorable conditions and the need to stop childbearing. As a result of the interaction of the nervous, endocrine and reproductive systems, this leads to the suppression of the process of sperm formation and the development of temporary sterility.
But it is obvious that from a biological point of view, offspring should be born in the most favorable environmental conditions, which will allow still helpless creatures to survive. Therefore, any stress - a reaction to threatening situations - is a signal to the body about unfavorable conditions and the need to stop childbearing. As a result of the interaction of the nervous, endocrine and reproductive systems, this leads to the suppression of the process of sperm formation and the development of temporary sterility.
So, if you plan to expand your family, both spouses should prepare for this joyful event. The minimum training period for a man is 3 months, this is how much spermatozoa mature in the body. During this time, in addition to natural restrictions on smoking and alcohol, the future dad should refuse to visit baths and saunas, as well as work with various varnishes, paints and hydrocarbon-based solvents. Heavy metals, contact with sources of ionizing radiation and powerful microwave electromagnetic radiation also pose a potential hazard.
As for dietary advice, there is only one advice from doctors: adhere to a balanced healthy diet - during Christian fasting periods, the number of male complaints about reproductive problems increases markedly.
And more importantly, and perhaps most importantly, you must love the women from whom you want to have children.
doctor of medical sciences, professor, urologist-andrologist Bozhedomov V.A.
In an interesting position. Why sex during pregnancy is good.
magazine "I want a child", May, 2008
(Elena Smirnova
Immunologist at the Center for Immunology and Reproduction)
I'll start by saying that a pregnant woman is also a person who has the right to a normal human life. And pregnancy is not a disease, but an unusual physiological condition. Therefore, pregnancy is not a hindrance to sexual relations. But! There are some nuances, features, sometimes difficulties, and sometimes limitations. I will tell you about them as a doctor, as well as a woman who has given birth three times.
I will tell you about them as a doctor, as well as a woman who has given birth three times.
Main question
So, is it possible to have sex during pregnancy? Yes, if you feel well and the pregnancy is going well, then you can have sex from the very beginning until delivery. And some sources recommend continuing during those! This recipe is recommended to improve the quality of cervical dilation during childbirth - as an alternative to medications. Of course, for such an extreme method of delivery, you need to have an appropriate temperament and receive special psychological training ...
Of course, an orgasm - if there is not much time left before childbirth - can serve as an impetus for their onset. (Sexual intercourse immediately before delivery will cause or intensify contractions all the more.) But if the birth canal, especially the cervix, is not ready for childbirth, and the child is not yet mature, then uterine contractions during orgasm cannot cause labor (i. e. premature birth).
e. premature birth).
The unborn child is not harmed by the sexual relations of the parents. The child is protected by a thick muscular wall of the uterus, an amniotic bladder and a mucous plug that literally clogs the cervix. And although you may feel it move immediately after orgasm, it is caused more by uterine contractions than by the fact that the child “knows” what is happening or feels pain. And the pleasure that the expectant mother receives has a positive effect on the child.
Time for change
Most often, a woman's sexual desire changes during pregnancy. For some, it rises sharply, in which case the couple enthusiastically recalls nine months as a time of delightful sexual relations. For some, libido, on the contrary, decreases or completely disappears. All this depends on the individual characteristics of the course of pregnancy, the psychological and sexual constitution of the woman, the mood of the partner and the trimester of pregnancy.
In the first trimester, sexual desire most often weakens, especially when it comes to the first pregnancy. This is facilitated by the worries and fears associated with a new unknown condition, as well as poor health, fatigue, nausea, engorgement of the mammary glands, and emotional instability associated with the hormonal changes in the woman's body, which are not uncommon during this period.
This is facilitated by the worries and fears associated with a new unknown condition, as well as poor health, fatigue, nausea, engorgement of the mammary glands, and emotional instability associated with the hormonal changes in the woman's body, which are not uncommon during this period.
The second trimester is usually marked by the restoration of sexual desire and harmonious partnerships.
In the third trimester, the expectation of childbirth, a large belly, which sometimes makes a woman feel unattractive, problems associated with late toxicosis (nephropathy of pregnancy), often again reduce sexual desire.
Benefits of the case
Around the fourth month of pregnancy, the vascular system in the pelvic region of a woman's body begins to constantly increase. As a result, most women's genitals swell. They acquire a dark shade, the lips of the vagina become more fleshy, the vagina and clitoris become more sensitive, lubricant begins to stand out abundantly. Which, as a rule, adds pleasant sensations during intercourse. Sometimes a woman experiences more intense and longer orgasms than before pregnancy, and often multiple orgasms. In addition, during pregnancy there is no need to protect yourself and the woman becomes more free in the manifestations of love for her partner. That is why many women in the position experience strong sexual arousal, and their sexual activity increases.
Which, as a rule, adds pleasant sensations during intercourse. Sometimes a woman experiences more intense and longer orgasms than before pregnancy, and often multiple orgasms. In addition, during pregnancy there is no need to protect yourself and the woman becomes more free in the manifestations of love for her partner. That is why many women in the position experience strong sexual arousal, and their sexual activity increases.
At the same time, sex for a pregnant woman is the best exercise for the muscles of the uterus, which prepares them for the upcoming birth. Sperm, entering the body of a pregnant woman, contributes to the softening of the cervix and its better opening during childbirth, as it contains enzymes, male hormones. And during orgasm, the female body produces oxytocin, a hormone that causes the muscles of the uterus to contract, which in fact causes very pleasant sensations. The same hormone directs the process of preparing a woman's body for childbirth. In addition, sexual discharge is accompanied by the production of endorphins - hormones of joy and pleasure, in childbirth, these same hormones are a natural pain reliever. From which it follows that sex for pregnant women is not only pleasant, but important and useful: it contributes to the successful course of natural childbirth. And in the previous nine months, it helps to fight dysphoria - mood variability (including sexual), which affects most pregnant women.
From which it follows that sex for pregnant women is not only pleasant, but important and useful: it contributes to the successful course of natural childbirth. And in the previous nine months, it helps to fight dysphoria - mood variability (including sexual), which affects most pregnant women.
A smart precaution
It is quite normal for a pregnant woman to feel contractions and uterine contractions during orgasm. Such contractions can last for about half an hour, or even longer. This happens for a number of reasons: because of the extra rush of blood to their genitals; due to the presence of prostaglandins (they act as a vasodilator) in male semen. Sometimes contractions can be caused by great emotional stress. Some experts believe that such contractions help a pregnant woman maintain the muscle tone of the uterus. One way or another, if these contractions begin to give a woman discomfort, use a condom. And see if this situation changes in a couple of weeks. Another way that can help a woman to endure contractions more easily is to massage her back or feet.
Women who experience a decrease in sexual desire during pregnancy may experience an increased need for caress and tenderness from the future father of the child. These caresses and tendernesses can lead him into a state of intense sexual arousal. To help the father-to-be cope with these difficulties, his pregnant partner should lie next to him and caress his thighs, testicles and breasts, allowing him to masturbate and bring herself to orgasm at the same time.
Everything under control
In the middle and later stages of sex should be the most gentle, the main guideline in their choice - the convenience of women. In case of disagreement, you should go towards her wishes.
At any stage of pregnancy, it is convenient and easy for the expectant mother to lie on her side when the man is behind.
The position when a woman sits on her partner's lap with her back to him is especially good in the middle of pregnancy. It not only eliminates pressure on the abdomen and the risk to the child, but also allows the woman to control the depth of penetration. This position is also good because a man can freely caress his partner's breasts and clitoris during intercourse.
This position is also good because a man can freely caress his partner's breasts and clitoris during intercourse.
Some top positions also allow her to control the speed of her movements and the depth of penis penetration, and are great even for late pregnancy.
Many women find it comfortable to sit on all fours.
At different stages of pregnancy, women may experience very different sexual desires and tend to try different approaches. However, swelling of the cervix and the uterus itself in some cases makes vaginal intercourse not particularly pleasant. The woman should be given the opportunity to control the depth of penetration of the penis.
Some couples first try new positions in their clothes. This helps them focus their collective energies on purely technical aspects and allows them to enjoy the funny side of the situation. At the same time, they are not at all worried about issues such as the need to rush and the problem of an erection that cannot wait long.
Change position
During vaginal intercourse at certain stages of pregnancy, women may experience various ailments. For example, bouts of dizziness and nausea - lying on your back. Symptoms in this case will disappear if you roll over on your side or get on all fours. The position on all fours will also help to alleviate or relieve pain in the lower back (sometimes they can occur due to the fact that the hypochondrium muscles of a pregnant woman are somewhat moved apart and begin to put pressure on the pelvic region).
If the discomfort is caused by severe swelling of the genitals, it is recommended to try positions in which the woman's legs are wide apart.
By the last trimester of pregnancy, the cartilage of the pelvic region of a woman becomes softer, as for several months they have been under the influence of special hormones that are produced by the body only during pregnancy. It is the preparation of a woman's body for the birth of a child. This is why the pressure exerted on a woman's hip bones at this stage of pregnancy can make her feel strange or even uncomfortable - change position!
The period of pregnancy is a great time for caresses, as well as a great opportunity to show your feelings, to show evidence of love and tender devotion. Let's hope they are mutual.
Let's hope they are mutual.
Undercoats :
If you are worried about something, for example, bloody discharge or increased myometrial tone, about be sure to consult your doctor!
In addition, for sex during pregnancy, there are the following CONTRAINDICATIONS:
- threatened miscarriage due to mechanical causes;
- recurrent miscarriage (or previous miscarriages) - indirect, since the cause of miscarriage may be different and have nothing to do with intimacy. The final decision can only be made by the supervising doctor;
- presentation or low insertion of placenta;
- multiple pregnancy ;
- signs of infection of the genital tract in one of the partners;
- strong pain ;
- acute unwillingness of a woman, the causes of which may lie in the sphere of ignorance of the issue and fears.