Abnormal nt scan
Nuchal translucency test Information | Mount Sinai
Nuchal translucency screening; NT; Nuchal fold test; Nuchal fold scan; Prenatal genetic screening; Down syndrome - nuchal translucency
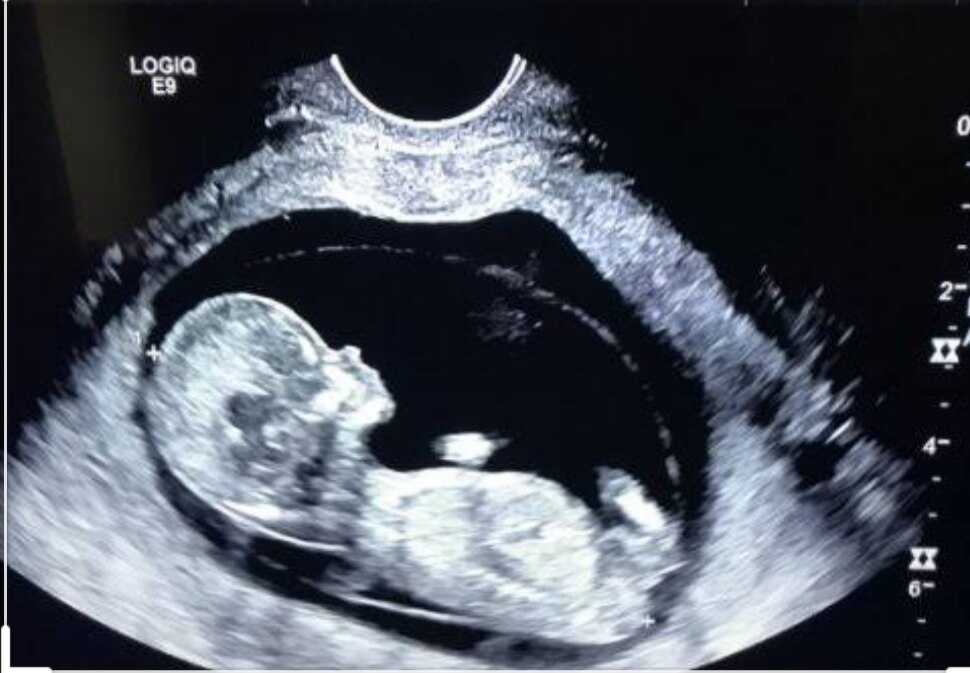
The nuchal translucency test measures the nuchal fold thickness. This is an area of tissue at the back of an unborn baby's neck. Measuring this thickness helps assess the risk for Down syndrome and other genetic problems in the baby.
How the Test is Performed
Your health care provider uses abdominal ultrasound (not vaginal) to measure the nuchal fold. All unborn babies have some fluid at the back of their neck. In a baby with Down syndrome or other genetic disorders, there is more fluid than normal. This makes the space look thicker.
A blood test of the mother is also done. Together, these two tests will tell if the baby could have Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.
How to Prepare for the Test
Having a full bladder will give the best ultrasound picture. You may be asked to drink 2 to 3 glasses of liquid an hour before the test. DO NOT urinate before your ultrasound.
How the Test will Feel
You may have some discomfort from pressure on your bladder during the ultrasound. The gel used during the test may feel slightly cold and wet. You will not feel the ultrasound waves.
The gel used during the test may feel slightly cold and wet. You will not feel the ultrasound waves.
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may advise this test to screen your baby for Down syndrome. Many pregnant women decide to have this test.
Nuchal translucency is usually done between the 11th and 14th week of pregnancy. It can be done earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis. This is another test that checks for birth defects.
Normal Results
A normal amount of fluid in the back of the neck during ultrasound means it is very unlikely your baby has Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.
Nuchal translucency measurement increases with gestational age. This is the period between conception and birth. The higher the measurement compared to babies the same gestational age, the higher the risk is for certain genetic disorders.
The measurements below are considered low risk for genetic disorders:
- At 11 weeks -- up to 2 mm
- At 13 weeks, 6 days -- up to 2.8 mm
What Abnormal Results Mean
More fluid than normal in the back of the neck means there is a higher risk for Down syndrome, trisomy 18, trisomy 13, Turner syndrome, or congenital heart disease. But it does not tell for certain that the baby has Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.
If the result is abnormal, other tests can be done. Most of the time, the other test done is amniocentesis.
Risks
There are no known risks from ultrasound.
Driscoll DA, Simpson JL. Genetic screening and diagnosis. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 10.
Walsh JM, D'Alton ME. Nuchal translucency. In: Copel JA, D'Alton ME, Feltovich H, et al, eds. Obstetric Imaging: Fetal Diagnosis and Care. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 45.
2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 45.
Last reviewed on: 3/31/2020
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Pregnancy Outcome of Abnormal Nuchal Translucency: A Systematic Review
[1] Nicolaides KH. Nuchal translucency and other first-trimester sonographic markers of chromosomal abnormalities. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;191(1):45–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[2] Snijders R, Noble P, Sebire N, Souka A, Nicolaides K. UK multicentre project on assessment of risk of trisomy 21 by maternal age and fetal nuchal-translucency thickness at 10–14 weeks of gestation. The Lancet. 1998;352(9125):343–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[3] Grandjean H, Sarramon MF. Sonographic measurement of nuchal skinfold thickness for detection of Down syndrome in the second-trimester fetus: a multicenter prospective study.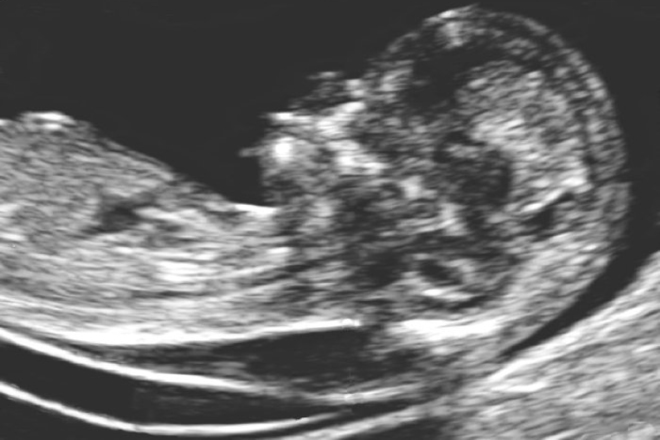 J Obstetet Gynecol. 1995;85(1):103–06. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
J Obstetet Gynecol. 1995;85(1):103–06. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[4] Watson WJ, Miller RC, Menard MK, Chescheir NC, Katz VL, Hansen WF, et al. Ultrasonographic measurement of fetal nuchal skin to screen for chromosomal abnormalities. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;170(2):583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[5] Michailidis GD, Economides DL. Nuchal translucency measurement and pregnancy outcome in karyotypically normal fetuses. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001;17(2):102–05. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[6] Sepulveda W, Wong AE, Casasbuenas A, Solari A, Alcalde JL. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia in a first-trimester ultrasound aneuploidy screening program. Prenat Diagn. 2008;28(6):531–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[7] Sotiriadis A, Papatheodorou S, Makrydimas G. Neurodevelopmental outcome of fetuses with increased nuchal translucency and apparently normal prenatal and/or postnatal assessment: a systematic review. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2012;39(1):10–09. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[8] Bilardo C, Timmerman E, Pajkrt E, van Maarle M. Increased nuchal translucency in euploid fetuses what should we be telling the parents? Prenat Diagn. 2010;30(2):93–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Increased nuchal translucency in euploid fetuses what should we be telling the parents? Prenat Diagn. 2010;30(2):93–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[9] Von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP. STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(4):344–49. PMID: 18313558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[10] Abdi F, Kazemi F, Ramezani Tehrani F, Roozbeh N. Protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis: hop (Humuluslupulus L.) for menopausal vasomotor symptoms. BMJ Open. 2016;6(4):e010734. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[11] Ghi T, Huggon IC, Zosmer N, Nicolides KH. Incidence of major structural cardiac defects associated with increased nuchal translucency but normal karyotype. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001;18:610–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[12] Zosmer N, Souter VL, han CSYC, Huggon IC, Nicolaides KH. Early diagnosis of major cardiac defects in chromosomally normal fetuses with increased nuchal translucency. Br J Obstetet Gynaecol. 1999;06:829–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Early diagnosis of major cardiac defects in chromosomally normal fetuses with increased nuchal translucency. Br J Obstetet Gynaecol. 1999;06:829–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[13] Hiippala A, Eronen M, Taipale P, Salonen R, Hiilesmaa V. Fetal nuchal translucency and normal chromosomes: a long-term follow-up study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001;18:18–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[14] Vieira LA, Silva SV, de Faria RB, Lippi UG, Lopes RG. Perinatal and pediatric follow up of children with increased nuchal translucency and normal karyotype. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2013;35(6):274–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[15] Matias A, Gomes C, Flack N, Montenegro N, Nicolaides KH. Screening for chromosomal abnormalities at 10–14 weeks: the role of ductusvenosus blood flow. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1998;12:380–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[16] Jauniaux E, Gavrill P, Khun P, Kurdi W, Hyett J, Nicolaides KH. Fetal heart rate and umbilico-placental Doppler flow velocity waveforms in early pregnancies with a chromosomal abnormality and/or an increased nuchal translucency thickness. Human Repro. 1996;11(2):435–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Human Repro. 1996;11(2):435–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[17] Maymon R, Jauniaux E, Cohen O, Dreazen E, Weinraub Z, Herman A. Pregnancy outcome and infant follow-up of fetuses with abnormally increased first trimester nuchal translucency. Human Reproduction. 2000;15(9):2023–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[18] Schwarzler P, Carvalho tJS, Senat MV, Masroor T, Campbell Professor S. Screening for fetal aneuploidies and fetal cardiac abnormalities by nuchal translucency thickness measurement at 10-14 weeks of gestation as part of routine antenatal care in an unselected population. Br J Obstetet Gynaecol. 1999;106:1029–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[19] Westin M, Saltvedt S, Bergman G, Almström H, Grunewald C, Valentin L. Is measurement of nuchal translucency thickness a useful screening tool for heart defects? A study of 16,383 fetuses. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2006;27:632–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[20] Zoppi MA, Ibba RM, Floris M, Monni G. Fetal nuchal translucency screening in 12 495 pregnancies in Sardinia. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001;18:649–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001;18:649–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[21] Nicolides KH, Spencer K, Avgidou K, Faiola S, Falcon O. Multicenter study of first trimester screening for trisomy 21 in 75, 821 pregnancies: results and estimation of the potential impact of individual risk-orientated two-stage first-trimester screening. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2005;25:221–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[22] Taipale P, Hiilesmaa V, Salonen R, Ylöstalo P. Increased Nuchal Translucency as a Marker for Fetal Chromosomal Defects. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1654–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[23] Bijok J, Ziora-Jakutowicz K, Ilnicka A, Pawłowska B, Jóźwiak A, Dangel J, et al. Increased nuchal translucency in chromosomally normal fetuses and pregnancy outcomes-a retrospective study. Ginekol Pol. 2013;84(3):172–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[24] Äyräs O, Tikkanen M, Eronen M, Paavonen J, Stefanovic V. Increased nuchal translucency and pregnancy outcome: a retrospective study of 1063 consecutive singleton pregnancies in a single referral institution. Prenatal Diagnosis. 2013;33(9):856–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Prenatal Diagnosis. 2013;33(9):856–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[25] Dane B, Dane C, Cetin A, Kiray M, Sivri D, Yayla M. Pregnancy outcome in fetuses with increased nuchal translucency. J Perinatol. 2008;28:400–04. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[26] Lithner CU, Kublickas M, Sverker Ek. Pregnancy outcome for fetuses with increased nuchal translucency but normal karyotype. J Med Screen. 2016;23(1):01–06. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[27] Brady AF, Pandya PP, Yuksel B, Greenough A, Patton MA, Nicolaides KH. Outcome of normal with chromosomally livebirths increased fetal nuchal translucency at 10-14 weeks’ gestation. J Med Genet. 1998;35:222–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[28] Souka AP, Krampl E, Bakalis S, Heath V, Nicolides KH. Outcome of pregnancy in chromosomally normal fetuses with increased nuchal translucency in the first trimester. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001;18:9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[29] Tahmasebpour A, BaradaranRafiee N, Ghaffari S, Jamal A. Increased Nuchal Translucency and Pregnancy Outcome. IJPH. 2012;41(11):92–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Increased Nuchal Translucency and Pregnancy Outcome. IJPH. 2012;41(11):92–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[30] Mula R, Goncé A, Bennásar M, Arigita M, Meler E, Nadal A, et al. Increased nuchal translucency and normal karyotype: perinatal and pediatric outcomes at 2 years of age. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2012;39(1):34–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[31] Scholl J, Durfee SM, Russell MA, Heard AJ, Iyer C, Alammari R, et al. First-Trimester Cystic Hygroma: Relationship of Nuchal Translucency Thickness and Outcomes. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120(3):551–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
[32] Muru K, Vals M-A, Sitska M, Asser K, Tammur P, Zilina O. Outcome of Children with Marked Changes in Maternal Screening Tests and Normal Karyotype. Genetics. 2013;3:1. [Google Scholar]
[33] Czuba B, Borowski D, Cnota W, Sieroszewski P, Grettka K, Pietryga M, et al. Ultrasonographic assessment of fetal nuchal translucency (NT) at 11th and 14th week of gestation–Polish multicentre study. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2007;28(2):175–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2007;28(2):175–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
When should I do an NT Scan?
nt screening is usually performed between weeks 11 1/2 and 13 1/2, but must be performed between 10 and 13 weeks of pregnancy . After that, the fabric becomes thicker and is no longer translucent, so the test results become inconclusive.
What is the best week for NT?
This data suggests that when only the last menstrual period is known, the optimal time to schedule a Nuchal translucency measurement is 12 to 13 weeks .
Can I get a scan after 15 weeks?
nt-scan is considered safe . It does not harm your child. But make sure you only get an NT scan in the first trimester. The reason why NT scans in the first trimester is because the space behind the neck may disappear by the 15th week of pregnancy.
Do you see any abnormalities on the 12 week scan?
Some major abnormalities may be visible after 12 weeks, but it is much better to have an ultrasound at 20-22 weeks to rule out structural abnormalities as much as possible. Assess the risk of Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities.
Assess the risk of Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities.
13 weeks late for NT scan?
Too late to do NT Scan at 14 weeks as any excess Nuchal fluid may be absorbed by your baby's developing body. You will be offered a verified second trimester test if for any reason your scan does not occur before 14 weeks.
What is the normal NT scan range?
The normal NT range for this age is 1.6-2.4 mm . Nuchal skin (NF) skin measurements and prenatal follow-up ultrasound findings were normal.
Is the transparency of Nuchal going away?
Studies have shown that in normal fetuses, fluid collection, known as NT, increases with gestational age until about 13 weeks of gestation3 and usually disappears after 14 weeks3 , 4.
What is an abnormal NT measurement?
Fetal NT increases with gestational age/crown - tear length. Because of this, the NT measurement may be considered abnormal when it is above 3. 0 mm or above the 99th percentile for gestational age. In pooled data from 30 studies, only NT screen has a sensitivity for trisomy 21 of 77% with a 6% false positive rate.
0 mm or above the 99th percentile for gestational age. In pooled data from 30 studies, only NT screen has a sensitivity for trisomy 21 of 77% with a 6% false positive rate.
What makes you at high risk for Down syndrome, baby?
One of the factors that increases the risk of having a child with Down syndrome is the age of the mother . Women who are 35 or older when they become pregnant are more likely to be affected by Down syndrome than women who become pregnant at a younger age.
When is it too late for a NIPT test?
NIPT is performed with one blood test in the first or second trimester. This can be done any time after the 10th week of pregnancy . What can NIPT tell me? The NIPT can tell you if your pregnancy is at low or high risk for common chromosome disorders including: Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Trisomy 18, Trisomy 13.
What happens if you test positive for Down syndrome?
If the test is positive, you will be offered a diagnostic test, usually CVS or possibly an amniocentesis.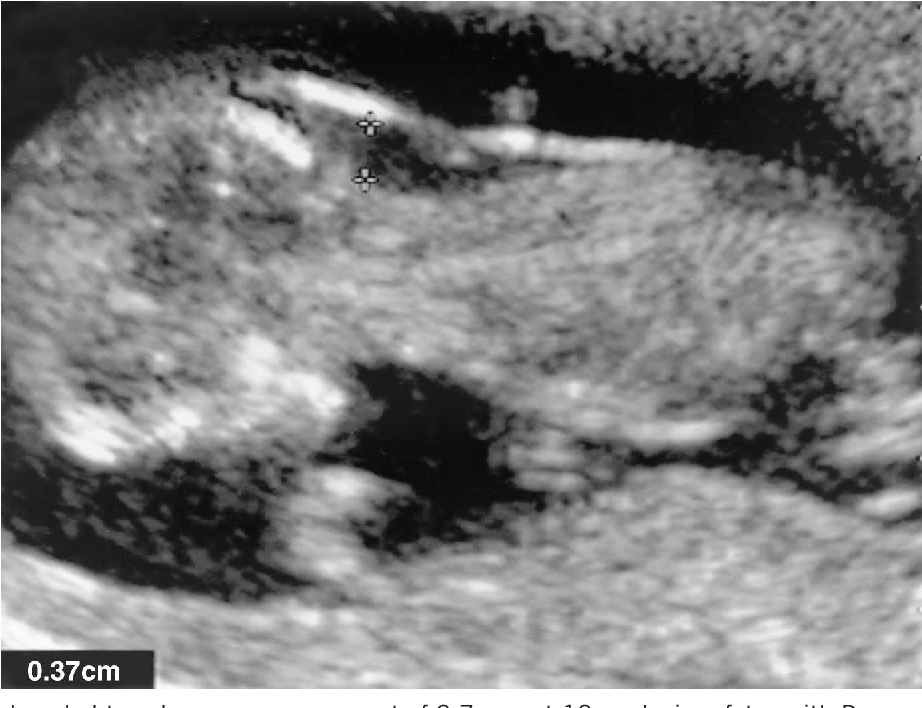 A diagnostic test will determine if the pregnancy is actually affected. CVS is offered early in pregnancy (usually 10 to 13 weeks).
A diagnostic test will determine if the pregnancy is actually affected. CVS is offered early in pregnancy (usually 10 to 13 weeks).
How accurate is the 12-week scan for Down syndrome?
First trimester screening results are given as positive or negative and as a probability, eg 1 in 250 risk of transporting a child with Down syndrome. Proper first trimester screening will identify 90,007 about 85 percent of women who are carrying a baby with Down syndrome.
Do I need to drink water before an NT scan?
You must have a full bladder. You must drink 600-800 ml of water two hours before the scan and refrain from going to the toilet before the scan.
How often is NT wrong?
This test is not perfect. There is 5% false crease . In other words, 5 percent of the women tested get positive results, but the baby is fine. After a positive result, your doctor may suggest another blood test called a cell-free prenatal DNA screen.
can a thick nuchal fold be normal?
Many healthy children have thick folds with the knife. However, there is a higher chance of Down syndrome or other chromosome conditions when the Nuchal fold is thick. There may also be a higher chance for rare genetic conditions.
can increased translucency be normal?
Our study shows that increased NT thickness in first trimester ultrasound screening is associated with poor pregnancy outcome even when the karyotype is normal. However, in euploid pregnancies with normal second trimester ultrasound results, a beneficial outcome occurs in 74.1% of cases.
What happens if the translucency is too high?
Elevated NT has also been associated with a high risk of miscarriage or fetal death. This risk increases with increasing NT thickness, and miscarriage or fetal death may be preceded by symptoms of heart failure such as fetal hydrops.
2 mm Translucency OK?
Conclusion. In euploid, anatomically normal fruits.
In euploid, anatomically normal fruits.
What is Nuchal translucency off?
Objectives: Link between isolated, elevated translucency thickness (NT) and pathogenic data by chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA). A recent meta-analysis reported that most studies use a limited NT value of 3.5 mm .
What causes extra fluid behind the neck in the fetus?
In fetal fluid, collects behind the neck, just as it does in dependent ankle edema later in life. This is partly due to the tendency of the fetus to lie on its back and partly due to laxity of the neck skin.
.
Is NT Scan Painful?
You should not feel pain during the procedure. You may feel some discomfort as the doctor or ultrasound technician draws into your abdomen. This feeling usually passes quickly. If you are having a blood test as part of your first trimester, you may feel a small pinch from the needle.
Where is the baby in your belly in 12 weeks?
Your body at 12 weeks pregnant
it rises to the abdomen as shown in the image. The glans, the upper part of the uterus, is just above the apex of the symphysis, where the pubic bones come together.
The glans, the upper part of the uterus, is just above the apex of the symphysis, where the pubic bones come together.
How long does it take for 12-week scan results?
Normal results will be confirmed in writing within 7 business days. If the result determines pregnancy as a higher risk for any of the conditions, you will be contacted by phone within three days from the midwife.
Raw Crawler】 Pit detected during scanning
Tags: reptile
1. Error: HTTP error 403: Forbidden problem
The above exception occurs because if you open the URL with urllib.request. urlopen, the server will only receive a simple request to access the page, but the server does not know the browser used to make that request. The operating system, hardware platform, and other information, and requests that lack this information, often have abnormal access, such as scanners.
The operating system, hardware platform, and other information, and requests that lack this information, often have abnormal access, such as scanners.
In order to prevent such abnormal access, some websites will check the UserAgent (its information package including the hardware platform, system, software, application, and user's personal preferences), if the UserAgent is abnormal or does not exist, then this request will be rejected (as shown in the error message above).
Solution:
# If you don't add the following line urllib.HTTPError: HTTP Error 403: Forbidden error will appear # Mainly because the site doesn't allow crawling, you can add header information to the request and pretend to be a browser to access the User-Agent headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:23.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/23.0'} req = urllib.request.Request(url=chaper_url, headers=headers) urllib.request.urlopen(req).read() link: https://blog.csdn. net/eric_sunah/article/details/11301873
net/eric_sunah/article/details/11301873
Smart recommendation
PTA-Valentine's Day
The sound of the cello is like the sound of a river. The left bank is my unforgettable memory, and the right bank is the light years that I deserve to capture. The middle current is my weak sentimental h...
SpringMVC Design Summary (to be continued)
Last weekend I was talking to a friend about building a Spring MVC framework. During the day, I tried my best to help him understand the initial design of the Spring framework. After the structure would...
Play with CocoaPods post_install and pre_install
In day to day iOS development, the longest form of using CocoaPods is as follows: But sometimes we want to do something other than install a third party library during install/update...
mvn deploy download jar package to remote warehouse
Use the idea deploy command Configure pom.xml Configure setting.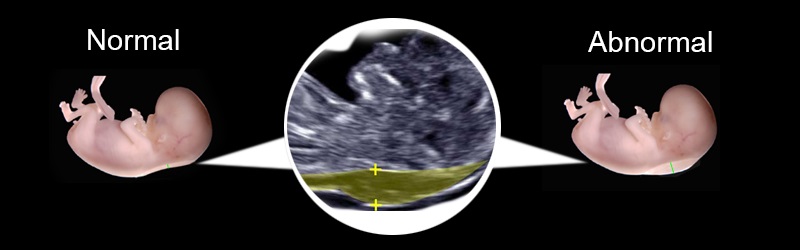 xml
xml
96. Various binary search trees (dynamic scheduling)
96. Different Binary Search Trees Topic Problem Solving Code Topic Given an integer n and how many binary search trees consisting of 1 ... n as a node? Problem Solving When You Collide...
You May Also Like
Java software developers often misunderstand
2019 Unicorn Enterprise Heavy Glour Repringment Python Engineer Standard >>> Array converted to Collection (ArrayList) Error: If this is often treated List ... Resolve Transient Dependency Conflicts Gradle gradle 1 Problem Today I suddenly found that Light Realm can't output logs and the console throws the following warning ⚠️: Seems to be h... Summary Hashmap is an important data structure in Java and hashmap is used to store key-value objects. SDUT -3663 Summary Table 4-2: Reverse Algorithm for Elementary Exchange (Data Enhancement)
No SLF4J providers were found.
Combined with Java8 source code, HASHMAP exploratory principle