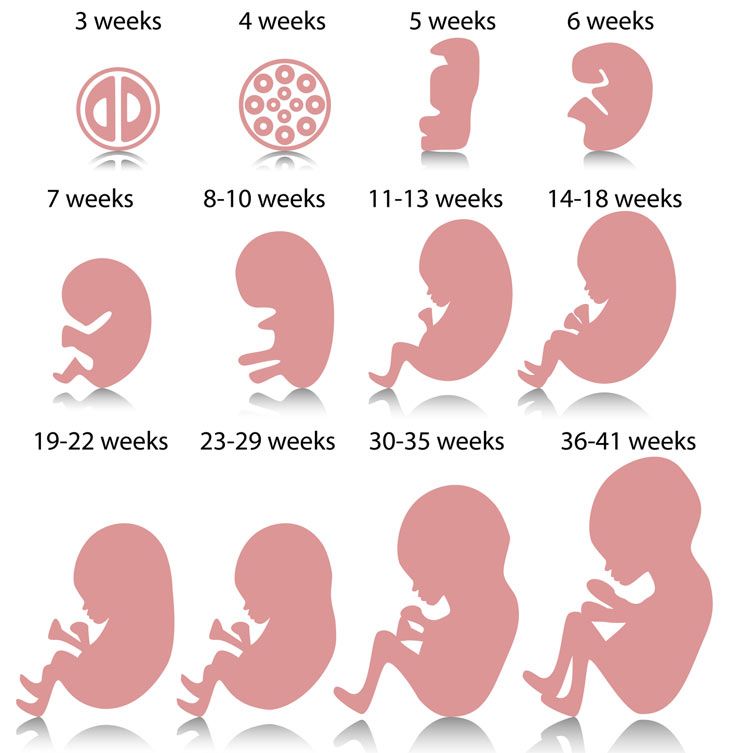
Signs im ovulating
Am I Ovulating? Physical Signs That You Are Fertile
Written by Lisa Fields
In this Article
- What Are Ovulation Symptoms?
- How to Track Ovulation Symptoms
- When Does Ovulation Happen?
- How Long Does Ovulation Last?
- Ask Your Doctor
To boost your chances of getting pregnant, it helps to know when you're ovulating. Then you'll know when you and your partner should be having sex.
Ovulation happens halfway through your cycle. Every woman’s cycle is different, so you have to pay attention to the signs.
There are many ways you can tell if the time is right.
What Are Ovulation Symptoms?
Here are the signs you may have when your body releases an egg:
- Your basal or resting temperature falls slightly, then rises again. You can use a special thermometer to check your temperature every morning before you get out of bed. You’re most fertile 2 or 3 days before your temperature rises.
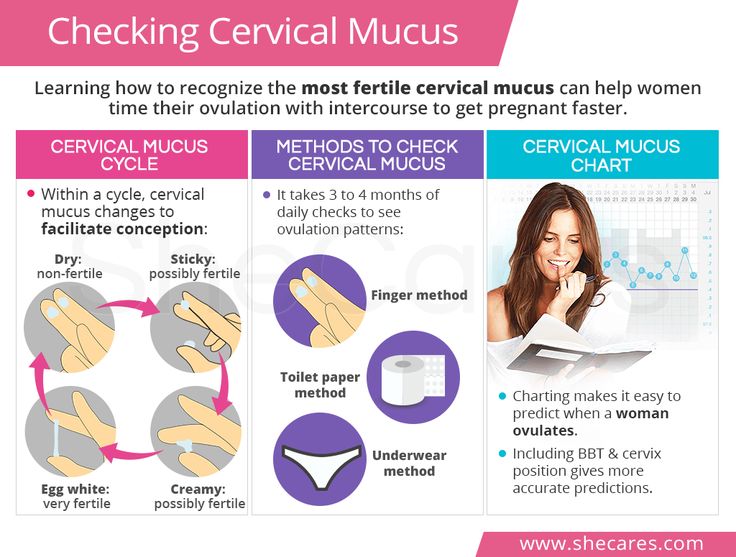
- Your cervical mucus becomes clearer and thinner with a slippery consistency, like egg whites.
You may also notice:
- Tender breasts
- Bloating
- Cramps
But these symptoms don’t always mean you’re ovulating.
How to Track Ovulation Symptoms
Mark your calendar
Take note of when your period begins and ends and know how long your cycle lasts. Doctors say it's best to have sex at least every other day, especially during the 5 days before you ovulate. They call this your "fertile window." Your egg only lives for about 12 to 24 hours. But sperm can survive for a few days inside your body, so it's ideal to have them already there waiting for your egg.
Watch for body changes
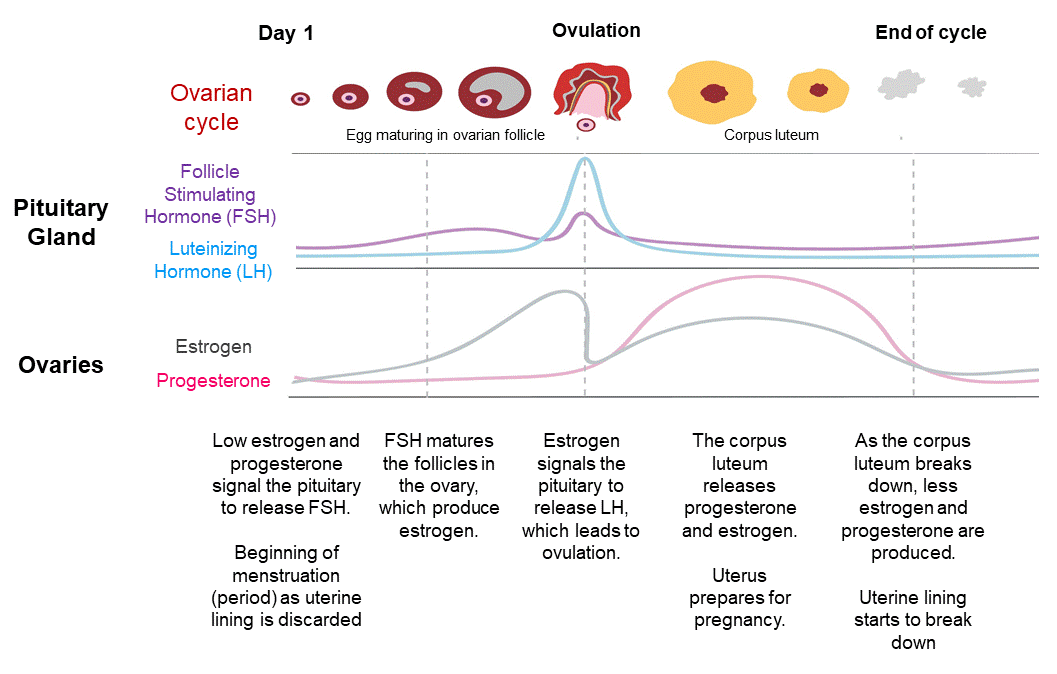
Your hormone levels change throughout your menstrual cycle. During the first half, your ovaries give off the hormone estrogen. When your estrogen levels get high enough, your ovary releases an egg. Then your body starts to make progesterone, another hormone. It makes your body temperature rise slightly.
Your hormones also change the texture of your cervical mucus, the sticky fluid that comes from your cervix, the bottom of your uterus. As your body gets ready to ovulate, you have more of it, and it feels more stretchy and slippery, like raw egg whites. The texture helps sperm swim inside your body. When your mucus feels like this, you should be in your fertile window.
As your body gets ready to ovulate, you have more of it, and it feels more stretchy and slippery, like raw egg whites. The texture helps sperm swim inside your body. When your mucus feels like this, you should be in your fertile window.
Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs)
You can find these at most drugstores. They cost about $25-$75 a month. These kits test the presence or the amount of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine. Some detect both LH and estrogen levels. This indicates ovulation will happen. When the surge is detected, having sex in the next 24-36 hours will improve your chances of getting pregnant. Because sperm will survive for some time inside of you, they'll be ready to join the egg during ovulation.
The kits have enough test strips to let you check your LH levels several times during your menstrual cycle. Start testing a few days before you think you might ovulate, then repeat a few times over the next few days to pinpoint the exact day.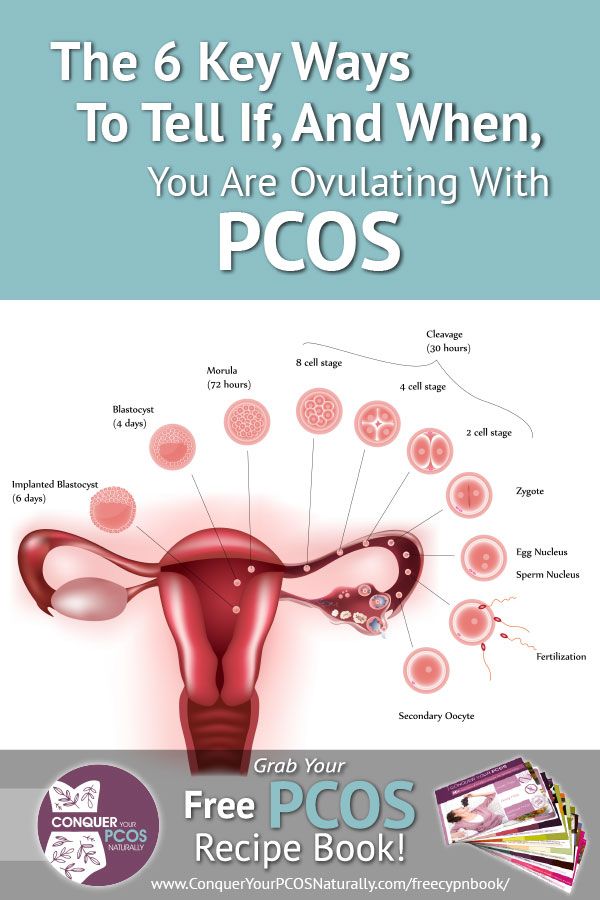 When your LH levels are highest, you're in the fertile window.
When your LH levels are highest, you're in the fertile window.
Fertility monitors
They can be expensive, but they have a significant benefit. While most ovulation predictors only give you a fertile window of up to 2 days, these can show 6-7 days of potential fertility for each cycle.
Fertility monitors give you more days to try to conceive, and they give a more accurate day of ovulation. Fertility monitors collect data from your body and your cycle. They use data and algorithms to help you determine exactly when you're going to ovulate. They're 89%-99% accurate in identifying your fertile window if used correctly. They monitor various signs of fertility, including skin temperature, basal body temperature, and vaginal fluids.
Progesterone ovulation tests
These tests can find out whether you have ovulated. They look at the levels of progesterone metabolite (pregnanediol glucuronide, or PdG) in your urine.
PdG levels typically rise 24-36 hours after you ovulate, so the tests are highly accurate.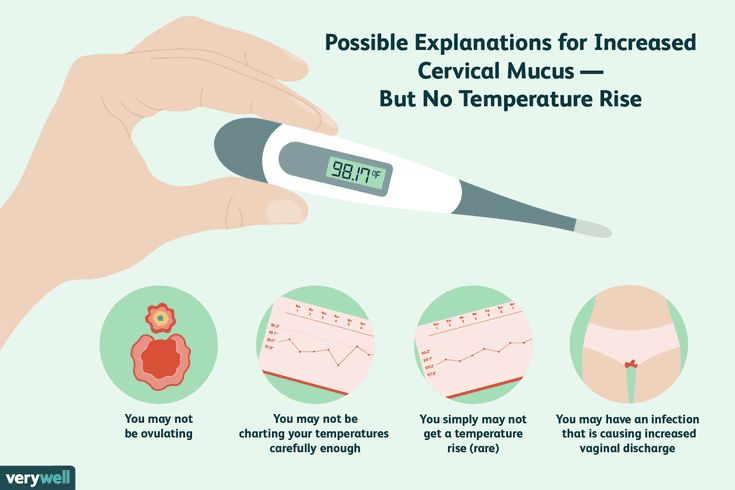 Start testing your levels before your anticipated menstrual cycle. These tests also have several strips to allow you to check your progesterone levels throughout your cycle.
Start testing your levels before your anticipated menstrual cycle. These tests also have several strips to allow you to check your progesterone levels throughout your cycle.
A twinge of pain
It's possible to feel yourself ovulate, but many women don't notice it. You might notice a slight pain in your side about halfway through your menstrual cycle. But if you're trying to get pregnant, don't wait for the twinge. That means your fertile window is soon closing.
When Does Ovulation Happen?
If your menstrual cycle lasts 28 days and your period arrives like clockwork, it's likely that you'll ovulate on day 14. That's halfway through your cycle. Your fertile window begins on day 10. You're more likely to get pregnant if you have sex at least every other day between days 10 and 14 of a 28-day cycle.
How Long Does Ovulation Last?
Your fertile window typically lasts 4-5 days. These are the days leading up to when you ovulate.
Ask Your Doctor
Some women don't ovulate on a set schedule. If you can't figure out when it happens or if your menstrual cycle isn't regular, ask your doctor for help.
Am I Ovulating? Physical Signs That You Are Fertile
Written by Lisa Fields
In this Article
- What Are Ovulation Symptoms?
- How to Track Ovulation Symptoms
- When Does Ovulation Happen?
- How Long Does Ovulation Last?
- Ask Your Doctor
To boost your chances of getting pregnant, it helps to know when you're ovulating. Then you'll know when you and your partner should be having sex.
Ovulation happens halfway through your cycle. Every woman’s cycle is different, so you have to pay attention to the signs.
There are many ways you can tell if the time is right.
What Are Ovulation Symptoms?
Here are the signs you may have when your body releases an egg:
- Your basal or resting temperature falls slightly, then rises again.
 You can use a special thermometer to check your temperature every morning before you get out of bed. You’re most fertile 2 or 3 days before your temperature rises.
You can use a special thermometer to check your temperature every morning before you get out of bed. You’re most fertile 2 or 3 days before your temperature rises. - Your cervical mucus becomes clearer and thinner with a slippery consistency, like egg whites.
You may also notice:
- Tender breasts
- Bloating
- Cramps
But these symptoms don’t always mean you’re ovulating.
How to Track Ovulation Symptoms
Mark your calendar
Take note of when your period begins and ends and know how long your cycle lasts. Doctors say it's best to have sex at least every other day, especially during the 5 days before you ovulate. They call this your "fertile window." Your egg only lives for about 12 to 24 hours. But sperm can survive for a few days inside your body, so it's ideal to have them already there waiting for your egg.
Watch for body changes
Your hormone levels change throughout your menstrual cycle. During the first half, your ovaries give off the hormone estrogen. When your estrogen levels get high enough, your ovary releases an egg. Then your body starts to make progesterone, another hormone. It makes your body temperature rise slightly.
During the first half, your ovaries give off the hormone estrogen. When your estrogen levels get high enough, your ovary releases an egg. Then your body starts to make progesterone, another hormone. It makes your body temperature rise slightly.
Your hormones also change the texture of your cervical mucus, the sticky fluid that comes from your cervix, the bottom of your uterus. As your body gets ready to ovulate, you have more of it, and it feels more stretchy and slippery, like raw egg whites. The texture helps sperm swim inside your body. When your mucus feels like this, you should be in your fertile window.
Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs)
You can find these at most drugstores. They cost about $25-$75 a month. These kits test the presence or the amount of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine. Some detect both LH and estrogen levels. This indicates ovulation will happen. When the surge is detected, having sex in the next 24-36 hours will improve your chances of getting pregnant. Because sperm will survive for some time inside of you, they'll be ready to join the egg during ovulation.
Because sperm will survive for some time inside of you, they'll be ready to join the egg during ovulation.
The kits have enough test strips to let you check your LH levels several times during your menstrual cycle. Start testing a few days before you think you might ovulate, then repeat a few times over the next few days to pinpoint the exact day. When your LH levels are highest, you're in the fertile window.
Fertility monitors
They can be expensive, but they have a significant benefit. While most ovulation predictors only give you a fertile window of up to 2 days, these can show 6-7 days of potential fertility for each cycle.
Fertility monitors give you more days to try to conceive, and they give a more accurate day of ovulation. Fertility monitors collect data from your body and your cycle. They use data and algorithms to help you determine exactly when you're going to ovulate. They're 89%-99% accurate in identifying your fertile window if used correctly. They monitor various signs of fertility, including skin temperature, basal body temperature, and vaginal fluids.
They monitor various signs of fertility, including skin temperature, basal body temperature, and vaginal fluids.
Progesterone ovulation tests
These tests can find out whether you have ovulated. They look at the levels of progesterone metabolite (pregnanediol glucuronide, or PdG) in your urine.
PdG levels typically rise 24-36 hours after you ovulate, so the tests are highly accurate. Start testing your levels before your anticipated menstrual cycle. These tests also have several strips to allow you to check your progesterone levels throughout your cycle.
A twinge of pain
It's possible to feel yourself ovulate, but many women don't notice it. You might notice a slight pain in your side about halfway through your menstrual cycle. But if you're trying to get pregnant, don't wait for the twinge. That means your fertile window is soon closing.
When Does Ovulation Happen?
If your menstrual cycle lasts 28 days and your period arrives like clockwork, it's likely that you'll ovulate on day 14. That's halfway through your cycle. Your fertile window begins on day 10. You're more likely to get pregnant if you have sex at least every other day between days 10 and 14 of a 28-day cycle.
That's halfway through your cycle. Your fertile window begins on day 10. You're more likely to get pregnant if you have sex at least every other day between days 10 and 14 of a 28-day cycle.
How Long Does Ovulation Last?
Your fertile window typically lasts 4-5 days. These are the days leading up to when you ovulate.
Ask Your Doctor
Some women don't ovulate on a set schedule. If you can't figure out when it happens or if your menstrual cycle isn't regular, ask your doctor for help.
Signs of ovulation | Clinic MEdel
OVULATION (from lat. ovum - egg) - release of a mature egg capable of fertilization from the ovarian follicle into the abdominal cavity; stage of the menstrual cycle (ovarian cycle). Ovulation in women of childbearing age occurs periodically (every 21-35 days). The frequency of ovulation is regulated by neurohumoral mechanisms, mainly gonadotropic hormones of the anterior pituitary gland and ovarian follicular hormone. nine0003 Ovulation contributes to the accumulation of follicular fluid and thinning of the ovarian tissue located above the protruding pole of the follicle. The rhythm of ovulation , which is constant for every woman, undergoes changes within 3 months after an abortion, within a year after childbirth, and also after 40 years, when the body is preparing for the premenopausal period. Stops ovulation with the onset of pregnancy and after the extinction of menstrual function. Setting a deadline ovulation is important when choosing the most effective time for fertilization, artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization.
nine0003 Ovulation contributes to the accumulation of follicular fluid and thinning of the ovarian tissue located above the protruding pole of the follicle. The rhythm of ovulation , which is constant for every woman, undergoes changes within 3 months after an abortion, within a year after childbirth, and also after 40 years, when the body is preparing for the premenopausal period. Stops ovulation with the onset of pregnancy and after the extinction of menstrual function. Setting a deadline ovulation is important when choosing the most effective time for fertilization, artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization.
Signs of ovulation
Subjective signs of ovulation may be short-term pain in the lower abdomen. objective signs of ovulation are an increase in mucous discharge from the vagina and a decrease in rectal (basal) temperature on the day of ovulation with an increase in it the next day, an increase in the content of progesterone in the blood plasma, etc.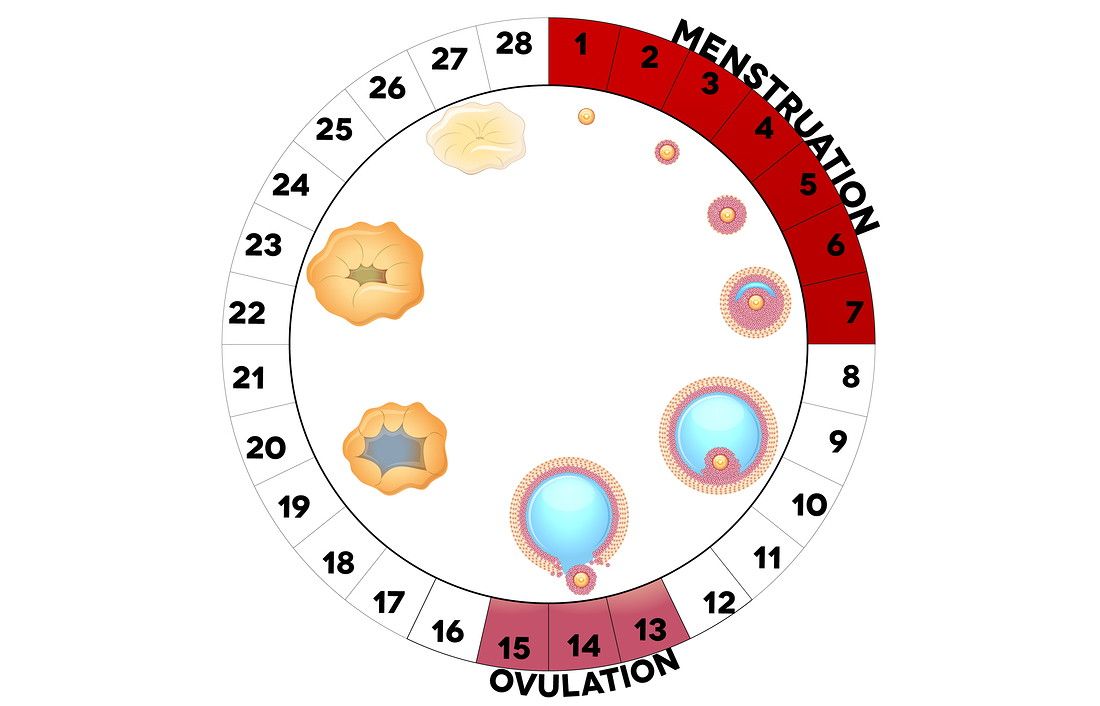 Violation of ovulation is due to dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system and can be caused by inflammation of the genitals, dysfunction of the adrenal cortex or thyroid gland, systemic diseases, tumors of the pituitary and hypothalamus , stressful situations. Lack of ovulation at childbearing age (anovulation) is manifested by a violation of the rhythm of menstruation by the type of oligomenorrhea (menstruation lasting 1-2 days), amenorrhea, dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Absence ovulation (anovulation) is always the cause of a woman's infertility. Methods for restoring ovulation are determined by the cause that caused anovulation, and require an appointment with a gynecologist and special treatment.
Violation of ovulation is due to dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system and can be caused by inflammation of the genitals, dysfunction of the adrenal cortex or thyroid gland, systemic diseases, tumors of the pituitary and hypothalamus , stressful situations. Lack of ovulation at childbearing age (anovulation) is manifested by a violation of the rhythm of menstruation by the type of oligomenorrhea (menstruation lasting 1-2 days), amenorrhea, dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Absence ovulation (anovulation) is always the cause of a woman's infertility. Methods for restoring ovulation are determined by the cause that caused anovulation, and require an appointment with a gynecologist and special treatment.
Some women experience peak sexual arousal on days 90,003 of ovulation 90,004. However, the use of a physiological method of contraception against pregnancy, based on sexual abstinence during ovulation , is especially difficult for young spouses, whose frequency of sexual intercourse reaches a fairly high level.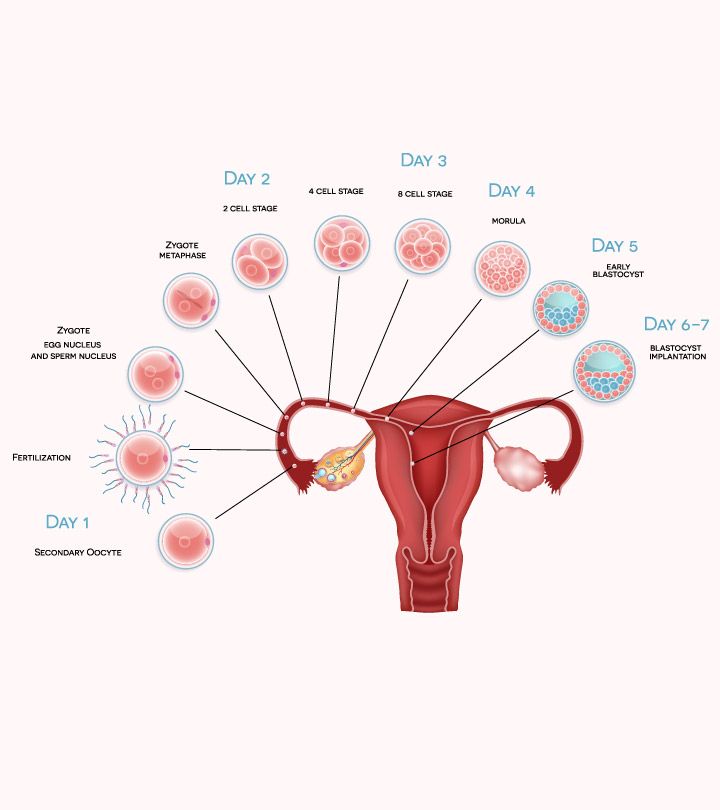 In addition, with strong love excitement and nervous stress, additional ovulation can occur (especially with episodic, irregular intercourse), and then not one, but two eggs mature in one menstrual cycle. This should be remembered when choosing one or another method of contraception. nine0017
In addition, with strong love excitement and nervous stress, additional ovulation can occur (especially with episodic, irregular intercourse), and then not one, but two eggs mature in one menstrual cycle. This should be remembered when choosing one or another method of contraception. nine0017
As soon as every healthy girl at the age of 11-15 begins to menstruate, which is an indicator of her body's readiness for childbearing, then there are problems associated with counting the days of the menstrual cycle and the legitimate question why menstruation does not occur, or vice versa, why the long-awaited pregnancy does not occur. . This makes a woman think and wait all the time, be in the dark about what happens to her every month. And so every month for decades. nine0017
Length of menstruation and cycle
Ideal menstruation lasts 3-5 days and repeats every 28 days. However, for some women, this cycle takes 19 days or even less, while for others it lasts from 35 to 45 days, which is a feature of their body, and not a violation of menstrual function. The duration of menstruation also, depending on the organism, can vary within a week. All this should not cause alarm in a woman, but a delay of more than two months, called opsometry or more than six months - amenorrhea, should alert the woman and make sure to find out the cause with a gynecologist. nine0017
The duration of menstruation also, depending on the organism, can vary within a week. All this should not cause alarm in a woman, but a delay of more than two months, called opsometry or more than six months - amenorrhea, should alert the woman and make sure to find out the cause with a gynecologist. nine0017
Length of menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a complex physiological process that continues in women up to 45-55 years. It is regulated by the so-called sex centers located in the middle part of the diencephalon - the hypothalamus. The changes that occur during the menstrual cycle are most pronounced in the uterus and ovaries. In the ovary, under the influence of hormones produced by the ovarian follicles, partly by the adrenal cortex and testes, the main follicle, which contains the egg, grows and matures. The mature follicle ruptures and the egg, together with the follicular fluid, enters the abdominal cavity, and then into the fallopian tube. The process of rupture of the follicle and the release of a mature (suitable for fertilization) egg from its cavity is called ovulation , which, with a 28-day cycle, occurs most often between the 13th and 15th days.
The process of rupture of the follicle and the release of a mature (suitable for fertilization) egg from its cavity is called ovulation , which, with a 28-day cycle, occurs most often between the 13th and 15th days.
Corpus luteum, estrogen, progesterone
A corpus luteum forms at the site of the ruptured follicle. These morphological changes in the ovary are accompanied by the release of sex steroid hormones - estrogens and progesterone. Estrogens are secreted by the maturing follicle, and progesterone by the corpus luteum.
The release of estrogen has two maxima - during ovulation and during the period of maximum activity of the corpus luteum. So, for example, if the normal estrogen content is about 10 µg/l, then during ovulation it is about 50 µg/l, and during pregnancy, especially towards the end of it, the estrogen content in the blood increases to 70-80 µg/l per due to a sharp increase in the biosynthesis of estrogens in the placenta.
Together with progesterone, estrogens promote the implantation (introduction) of a fertilized egg, maintain pregnancy and promote childbirth. Estrogens play an important role in the regulation of many biochemical processes, are involved in carbohydrate metabolism, lipid distribution, stimulate the synthesis of amino acids, nucleic acids and proteins. Estrogens contribute to the deposition of calcium in bone tissue, delay the release of sodium, potassium, phosphorus and water from the body, that is, increase their concentration both in the blood and in electrolytes (urine, saliva, nasal secretions, tears) of the body. nine0017
The secretion of estrogens is controlled by the anterior pituitary gland and its genadotropic hormones: follicle-stimulating (FSH) and luteinizing (LH).
Under the influence of estrogens in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, called folliculin, regeneration occurs in the uterus, that is, the restoration and growth of its mucous membrane - the endometrium, the growth of glands that stretch in length and become convoluted.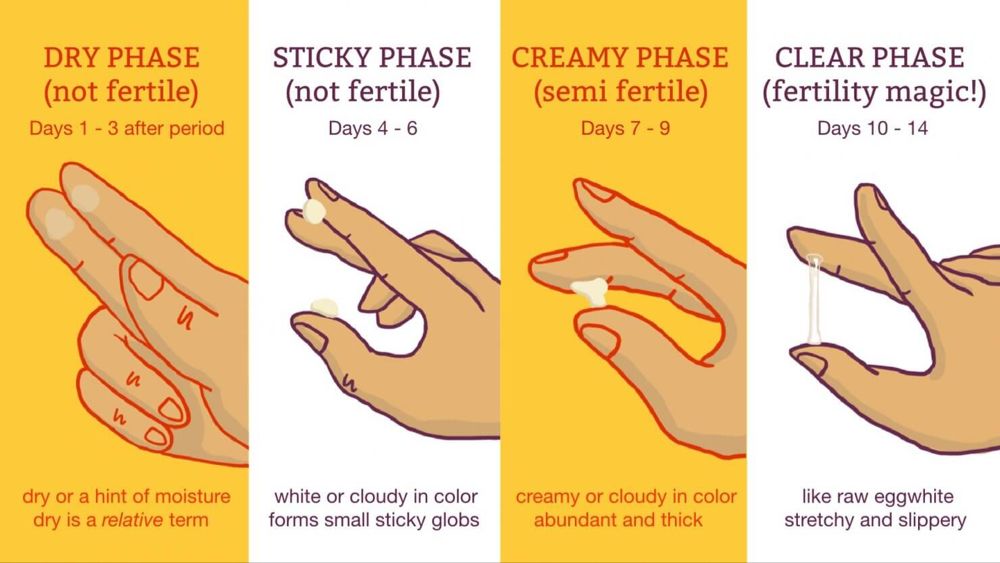 The mucous membrane of the uterus thickens 4-5 times. In the glands of the cervix, the secretion of mucous secretion increases, the cervical canal expands, and becomes easily passable for spermatozoa. In the mammary glands, the epithelium grows inside the milk ducts. nine0017
The mucous membrane of the uterus thickens 4-5 times. In the glands of the cervix, the secretion of mucous secretion increases, the cervical canal expands, and becomes easily passable for spermatozoa. In the mammary glands, the epithelium grows inside the milk ducts. nine0017
In the second phase, called luteal (from the Latin word luteus - yellow), under the influence of progesterone, the intensity of metabolic processes in the body decreases. The growth of the mucous membrane of the body of the uterus stops, it becomes loose, edematous, a secret appears in the glands, which creates favorable conditions for attaching a fertilized egg to the mucous membrane and developing the embryo. The glands stop secreting mucus, the cervical canal closes. In the mammary glands, from the overgrown epithelium of the end sections of the milk ducts, alveoli arise, capable of producing and secreting milk. nine0017
If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum dies, the functional layer of the endometrium is rejected, and menstruation occurs. Monthly bleeding varies from three to seven days, the amount of blood lost is from 40 to 150 g.
Monthly bleeding varies from three to seven days, the amount of blood lost is from 40 to 150 g.
It should be noted that different women have a noticeable difference in the timing of ovulation . And even for the same woman, the exact timing of the onset fluctuates in different months. In some women, cycles are characterized by exceptional irregularity. In other cases, cycles may be longer or shorter than the average - 14 days. In rare cases, it happens that in women with a very short cycle ovulation occurs around the end of the period of menstrual bleeding, but still, in most cases, ovulation occurs quite regularly.
If, for one reason or another, ovulation does not occur , the endometrial layer in the uterus is thrown out during menstruation. If the fusion of the egg and sperm has occurred, then the cytoplasm of the egg begins to vibrate very strongly, as if the egg is experiencing an orgasm. Sperm penetration is the final stages of egg maturation. All that remains of a spermatozoon is its nucleus, where 23 chromosomes are densely packed (half the set of a normal cell). The sperm nucleus is now rapidly approaching the egg nucleus, which also contains 23 chromosomes. The two cores are slowly touching. Their shells dissolve and they merge, as a result of which they are divided into pairs and form 46 chromosomes. Of the 23 chromosomes of the sperm, 22 are completely analogous to the chromosomes of the egg. They determine all the physical characteristics of a person except gender. In the remaining pair from the egg there is always an X chromosome, and from the sperm there can be an X or Y chromosome. Thus, if there are 2 XX chromosomes in this set, then a girl will be born, if XY, then a boy. nine0017
All that remains of a spermatozoon is its nucleus, where 23 chromosomes are densely packed (half the set of a normal cell). The sperm nucleus is now rapidly approaching the egg nucleus, which also contains 23 chromosomes. The two cores are slowly touching. Their shells dissolve and they merge, as a result of which they are divided into pairs and form 46 chromosomes. Of the 23 chromosomes of the sperm, 22 are completely analogous to the chromosomes of the egg. They determine all the physical characteristics of a person except gender. In the remaining pair from the egg there is always an X chromosome, and from the sperm there can be an X or Y chromosome. Thus, if there are 2 XX chromosomes in this set, then a girl will be born, if XY, then a boy. nine0017
Studies conducted at the National Institute of Environmental Medical Problems (North Carolina) showed that the time of conception in relation to the time of onset of ovulation depends not only on the actual conception of a child, but also on its gender.
The probability of conception is maximum on day of ovulation and is estimated at about 33%. A high probability is also noted on the day before ovulation - 31%, two days before it - 27%. Five days before ovulation the probability of conception is estimated to be 10% four days before ovulation - 14% and three days - 16%. Six days before ovulation and the day after ovulation, the probability of conception during sexual intercourse is very small.
Considering that the average “lifespan” of spermatozoa is 2-3 days (in rare cases it reaches 5-7 days), and the female egg remains viable for about 12-24 hours, then the maximum duration of the “dangerous” period is 6- ninedays and the “dangerous” period corresponds to the phase of slow rise (6-7 days) and rapid decline (1-2 days) before and after the day of ovulation , respectively. Ovulation , as noted above, divides the menstrual cycle into two phases: the follicle maturation phase, which, with an average cycle duration of 10-16 days, and the luteal phase (corpus luteum phase), which is stable, independent of the duration of the menstrual cycle and is 12-16 days. The phase of the corpus luteum is referred to as the period of absolute infertility, it begins 1-2 days after ovulation and ends with the onset of a new menstruation.
The phase of the corpus luteum is referred to as the period of absolute infertility, it begins 1-2 days after ovulation and ends with the onset of a new menstruation.
How to independently determine the beginning of ovulation and not make a mistake
Ovulation is the release of an egg from the follicle. It can be tracked with an ultrasound. Or you can do an ovulation test. But some women claim that they feel it without any auxiliary means. Are you one of those?
Ovulation formula
Knowing when ovulation occurs is important for two things: if a woman wants to get pregnant or if a woman chooses a calendar method of contraception. The fertile period - the period when fertilization can occur - lasts approximately six days: five days before ovulation and the day of ovulation. The highest probability of conception is within two days before and on the day of ovulation. nine0017
Calculating the day of ovulation mathematically makes sense if you have a very clear and stable menstrual cycle.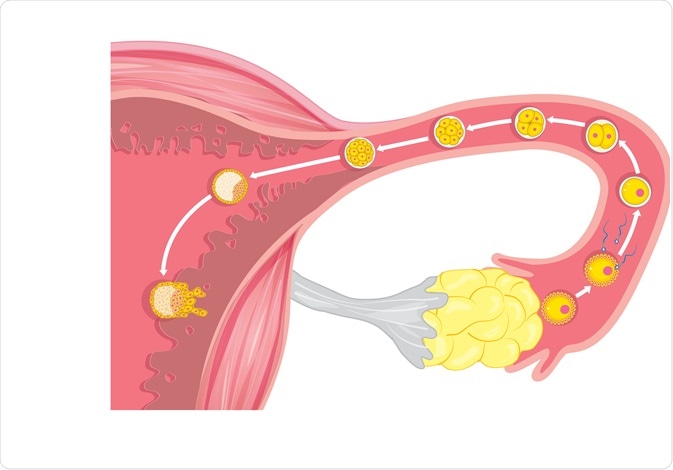 The length of the first phase of the cycle varies. The second phase is more stable and lasts 14 days. Accordingly, to calculate the day of ovulation, it is necessary to subtract 14 from the cycle length. In an ideal 28-day cycle, ovulation occurs exactly in the middle: 28-14 = 14. In a short cycle, it will occur earlier: for example, with a cycle length of 24 days, ovulation will have to around day 10. In the long - later: 33-14 \u003d 19. For women whose menstrual cycle fluctuates by several days, the formula becomes more complicated: you need to take into account the duration of both the shortest and longest cycles, calculate the average. Still, the figure will only be approximate.
The length of the first phase of the cycle varies. The second phase is more stable and lasts 14 days. Accordingly, to calculate the day of ovulation, it is necessary to subtract 14 from the cycle length. In an ideal 28-day cycle, ovulation occurs exactly in the middle: 28-14 = 14. In a short cycle, it will occur earlier: for example, with a cycle length of 24 days, ovulation will have to around day 10. In the long - later: 33-14 \u003d 19. For women whose menstrual cycle fluctuates by several days, the formula becomes more complicated: you need to take into account the duration of both the shortest and longest cycles, calculate the average. Still, the figure will only be approximate.
A woman can determine the days favorable for conception if she pays attention to the changes that occur to her on certain days of the cycle. These changes are most noticeable in the uterine mucosa and cervix.
Mucus
Cervical glands produce mucus. Usually it is thick: a real cork that closes the cervical canal and prevents infections from passing into the uterus. In such thick mucus, sperm cells quickly lose their mobility, and it is difficult for them to rise into the uterine cavity. But the main (dominant) follicle growing in the ovary, from which the egg will be released, produces the hormone estradiol. The more estradiol, the more cervical mucus becomes and the thinner it is. On the eve of ovulation, it becomes extensible, like egg white. In some women, this viscous transparent discharge in the middle of the cycle is very noticeable. For some - a few days before ovulation, for others - only on the day of ovulation itself. This is individual. nine0017
In such thick mucus, sperm cells quickly lose their mobility, and it is difficult for them to rise into the uterine cavity. But the main (dominant) follicle growing in the ovary, from which the egg will be released, produces the hormone estradiol. The more estradiol, the more cervical mucus becomes and the thinner it is. On the eve of ovulation, it becomes extensible, like egg white. In some women, this viscous transparent discharge in the middle of the cycle is very noticeable. For some - a few days before ovulation, for others - only on the day of ovulation itself. This is individual. nine0017
Pain
Ovulation may be indicated by pain in the lower abdomen on the days of the cycle, not associated with menstrual bleeding. The pain can be in the lower abdomen in the center or on the right / left - depending on which ovary the dominant follicle matures. The pain is often of a pulling nature. It may be accompanied by slight bloating or a feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen. At first, the pain is slight, but within a couple of days it can intensify. These pains are associated with an increase in the level of biologically active substances in the body of a woman before ovulation - prostaglandins. Prostaglandins dissolve the wall of the follicle and ovarian tissue so that the egg can be released into the abdominal cavity, and from there into the fallopian tube. The "side effect" of prostaglandins is pain. Just like a change in the nature of cervical mucus, pain associated with ovulation may occur only on the day of ovulation itself or be noted on the eve of ovulation and even a day or two after it. nine0017
At first, the pain is slight, but within a couple of days it can intensify. These pains are associated with an increase in the level of biologically active substances in the body of a woman before ovulation - prostaglandins. Prostaglandins dissolve the wall of the follicle and ovarian tissue so that the egg can be released into the abdominal cavity, and from there into the fallopian tube. The "side effect" of prostaglandins is pain. Just like a change in the nature of cervical mucus, pain associated with ovulation may occur only on the day of ovulation itself or be noted on the eve of ovulation and even a day or two after it. nine0017
How to understand that pain is associated with ovulation
It is important to understand that pain in the lower abdomen can be associated with much less pleasant causes than ovulation.
How to understand that this is exactly “it”.
- The pain lasts 1-3 days and goes away on its own.
- Pain recurs in several cycles.

- Approximately 14 days after such pain comes the next menstruation.
Ovulation pain is moderate and does not require pain medication. Severe pain indicates a health problem. If the pain on the days of the alleged ovulation is severe, you need to contact a gynecologist. Other alarming symptoms accompanying pain in the lower abdomen and which may indicate a problem with the uterus and appendages: fever, increased discharge (leucorrhoea) from the genital tract, discoloration of the leucorrhoea from transparent or white to yellow-green, spotting. By the way, taking painkillers and NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) on the days of expected ovulation or shortly before ovulation can reduce the chances of conception. nine0017
Technical aids
Home test
Ovulation can be determined with a home test available from a pharmacy. The principle of the study is based on determining the concentration of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the urine. The level of LH in women fluctuates depending on the period of the menstrual cycle. Just before ovulation, it reaches its maximum values. The ovulation test makes it possible to register the peak of LH release into the blood. After the maximum LH surge, ovulation occurs within the next 36 hours. Therefore, with a positive ovulation test, this and the following days are the most favorable for conception. nine0017
The level of LH in women fluctuates depending on the period of the menstrual cycle. Just before ovulation, it reaches its maximum values. The ovulation test makes it possible to register the peak of LH release into the blood. After the maximum LH surge, ovulation occurs within the next 36 hours. Therefore, with a positive ovulation test, this and the following days are the most favorable for conception. nine0017
Folliculometry
This is a series of ultrasound examinations carried out during one or more menstrual cycles. During folliculometry, the growth of follicles and changes in the endometrium are assessed according to the day of the menstrual cycle, and the fact of ovulation is also ascertained. The average size of the dominant follicle, at which ovulation can occur, is 18-25 mm. If the size of the dominant follicle is 18 mm during folliculometry, this and the next few days are most favorable for pregnancy. The next folliculometry to confirm the fact of ovulation, it is desirable to do in 3-4 days.