Causes of food aversions
Causes and How It Works
Conditioned Taste Aversion: Causes and How It WorksBy Tessa Sawyers on November 21, 2018
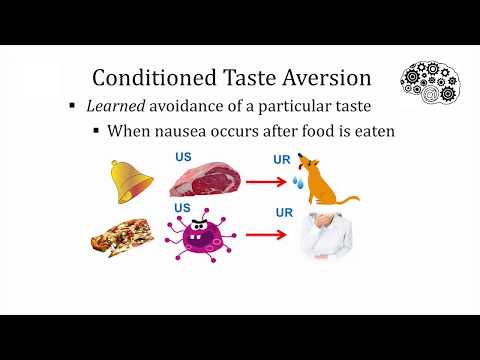
A taste aversion is a tendency to avoid or make negative associations with a food that you ate just before getting sick.
Many people have taste aversions and they’re often the subject of conversations about food. When someone asks, “What food do you dislike?” many people can come up with a story about a run-in with a food that they now refuse to eat.
An example of a conditioned taste aversion is getting the flu after eating a specific food, and then, long past the incident, avoiding the food that you ate prior to getting sick. This can happen even though the food didn’t cause the illness since it isn’t spread this way.
This is called a conditioned taste aversion because you’ve trained yourself to avoid the food even though it wasn’t related to your illness. This is considered a single-trial conditioning since it only took one time for you to be conditioned to avoid the food.
Taste aversions can occur both unconsciously and consciously. Sometimes, you can unconsciously avoid a food without realizing why. The strength of conditioned taste aversion usually depends on how much of the food you consumed and how sick you were.
Typically, taste aversion occurs after you’ve eaten something and then get sick. This sickness usually involves nausea and vomiting. The more intense the sickness, the longer the taste aversion lasts.
Certain conditions or illnesses, unrelated to the food you’re eating, can trigger nausea and vomiting that contribute to your taste aversion:
- chemotherapy
- anorexia
- liver failure
- bulimia
- ear infection
- motion sickness
- rotavirus
- pregnancy and morning sickness
- stomach flu
- drinking too much alcohol
- overeating
Food aversions are, for the most part, psychological. You’re not allergic to the food, your mind is just associating the food with the time you got sick. Here are a few ways to try and combat food aversions:
Here are a few ways to try and combat food aversions:
- Make new associations. You may associate coconut flavor with the time you got ill after eating coconut cream pie, so you associate coconut with vomit. Instead, consciously try associating coconut with tropical islands, vacations, or relaxing on a warm beach.
- Make the food in a new way. If you got sick after eating fried eggs, try to prepare your eggs in a different way — such as an omelet — to avoid associating eggs with sickness.
- Increase your exposure. Slowly increasing your exposure to the taste you have an aversion to can prevent you from feeling sick or disgusted about the taste. Try just smelling it first, then taste a small amount.
Taste aversions can be a sign of a more serious issue such as an eating disorder. If you have taste aversions that affect your ability to eat a balanced diet, talk to your doctor about the possibility of an eating disorder.
Taste aversions usually occur when you get nauseous or vomit after eating something and then associate the food with the sickness. Sometimes, a taste aversion will fade over time. However, some people report having taste aversions many years after the incident occurred.
If you’re experiencing an extreme taste aversion that stops you from getting proper nutrition, make an appointment with your doctor. They can point you in the right direction for specialists or treatments that can help you put your taste aversions behind you.
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Chambers KC. (2018). Conditioned taste aversions. DOI:
1016/j.wjorl.2018.02.003 - Mayo Clinic Staff.
 (2018). Nausea and vomiting: Causes.
(2018). Nausea and vomiting: Causes.
mayoclinic.org/symptoms/nausea/basics/causes/sym-20050736 - Lin J-Y, et al. (2014). Conditioned taste aversion, drugs of abuse and palatability. (2014).
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4134772/ - Lin J-Y, et al. (2017). Conditioned taste aversions: From poisons to pain to drugs of abuse. DOI:
3758/s13423-016-1092-8
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Nov 21, 2018
Written By
Tessa Sawyers
Edited By
Ginger Wojcik
Share this article
By Tessa Sawyers on November 21, 2018
related stories
Everything You Need to Know About Food Aversions During Pregnancy
Nausea and Vomiting
6 Common Types of Eating Disorders (and Their Symptoms)
Is There a Best At-Home Food Sensitivity Test? A Dietitian Explains
Oral Immunotherapy for Food Allergies
Read this next
Everything You Need to Know About Food Aversions During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.
 D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COIYou’ve heard of pregnancy cravings, but what about the opposite, food aversions? Why do some women develop a sudden hatred for foods they used to love?
READ MORE
Nausea and Vomiting
Medically reviewed by Carissa Stephens, R.N., CCRN, CPN
Vomiting is an uncontrollable reflex that expels the contents of the stomach through the mouth. It’s also called "being sick" or "throwing up."
READ MORE
6 Common Types of Eating Disorders (and Their Symptoms)
By Alina Petre, MS, RD (NL)
Eating disorders are characterized by unusual or disturbed eating habits. Learn more here.
READ MORE
Is There a Best At-Home Food Sensitivity Test? A Dietitian Explains
If you suspect you have a food sensitivity, you may be wondering whether it's worth purchasing an at-home test.
 Our dietitian discusses whether food…
Our dietitian discusses whether food…READ MORE
Oral Immunotherapy for Food Allergies
Medically reviewed by Marc Meth, MD, FACAAI, FAAAI
Oral immunotherapy can help treat food allergies by desensitizing your body to the allergenic substance. Learn how it works.
READ MORE
My Allergy Origin Story: A Food Allergy Journey
Medically reviewed by Adrienne Seitz, MS, RD, LDN
Roshay was no stranger to frustrating allergies. Wheat wasn’t the first major allergy, nor the fifth, she’d been diagnosed with in her lifetime.
READ MORE
Malabsorption Syndrome
Medically reviewed by Saurabh Sethi, M.D., MPH
Malabsorption syndrome refers to a number of disorders in which the small intestine is unable to absorb enough nutrients.

READ MORE
The 8 Most Common Food Allergies
By Helen West, RD and Alyssa Northrop, MPH, RD, LMT
Most food allergies are caused by just eight foods. This article explains what they are, what symptoms they cause, and what you can do about it.
READ MORE
What Is the Best Food Sensitivity Test?
By Marsha McCulloch, MS, RD
Certain foods can make you feel unwell, but it can be tricky to figure out which ones are causing your symptoms. Learn the best tests for food…
READ MORE
Poor Feeding in Infants
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D.
"Poor feeding in infants" describes an infant with little interest in feeding or who is not feeding enough to receive the necessary nutrition.
READ MORE
Causes and How It Works
Conditioned Taste Aversion: Causes and How It WorksBy Tessa Sawyers on November 21, 2018
A taste aversion is a tendency to avoid or make negative associations with a food that you ate just before getting sick.
Many people have taste aversions and they’re often the subject of conversations about food. When someone asks, “What food do you dislike?” many people can come up with a story about a run-in with a food that they now refuse to eat.
An example of a conditioned taste aversion is getting the flu after eating a specific food, and then, long past the incident, avoiding the food that you ate prior to getting sick. This can happen even though the food didn’t cause the illness since it isn’t spread this way.
This is called a conditioned taste aversion because you’ve trained yourself to avoid the food even though it wasn’t related to your illness. This is considered a single-trial conditioning since it only took one time for you to be conditioned to avoid the food.
Taste aversions can occur both unconsciously and consciously. Sometimes, you can unconsciously avoid a food without realizing why. The strength of conditioned taste aversion usually depends on how much of the food you consumed and how sick you were.
Typically, taste aversion occurs after you’ve eaten something and then get sick. This sickness usually involves nausea and vomiting. The more intense the sickness, the longer the taste aversion lasts.
Certain conditions or illnesses, unrelated to the food you’re eating, can trigger nausea and vomiting that contribute to your taste aversion:
- chemotherapy
- anorexia
- liver failure
- bulimia
- ear infection
- motion sickness
- rotavirus
- pregnancy and morning sickness
- stomach flu
- drinking too much alcohol
- overeating
Food aversions are, for the most part, psychological. You’re not allergic to the food, your mind is just associating the food with the time you got sick. Here are a few ways to try and combat food aversions:
- Make new associations. You may associate coconut flavor with the time you got ill after eating coconut cream pie, so you associate coconut with vomit.
 Instead, consciously try associating coconut with tropical islands, vacations, or relaxing on a warm beach.
Instead, consciously try associating coconut with tropical islands, vacations, or relaxing on a warm beach. - Make the food in a new way. If you got sick after eating fried eggs, try to prepare your eggs in a different way — such as an omelet — to avoid associating eggs with sickness.
- Increase your exposure. Slowly increasing your exposure to the taste you have an aversion to can prevent you from feeling sick or disgusted about the taste. Try just smelling it first, then taste a small amount.
Taste aversions can be a sign of a more serious issue such as an eating disorder. If you have taste aversions that affect your ability to eat a balanced diet, talk to your doctor about the possibility of an eating disorder.
Taste aversions usually occur when you get nauseous or vomit after eating something and then associate the food with the sickness. Sometimes, a taste aversion will fade over time. However, some people report having taste aversions many years after the incident occurred.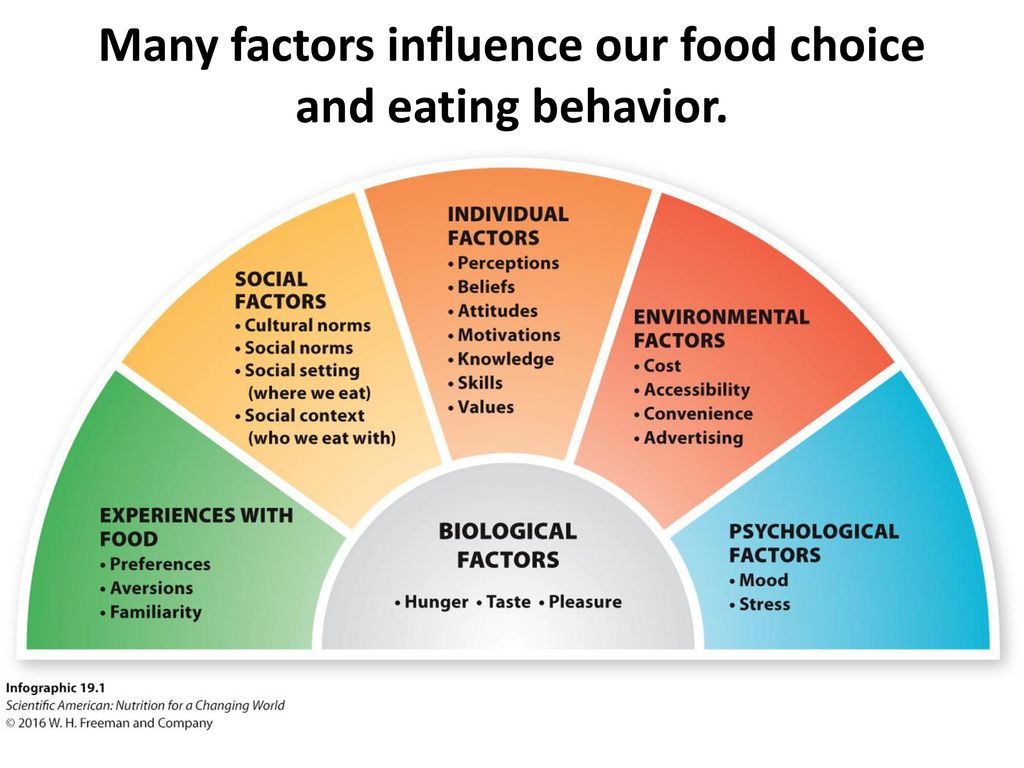
If you’re experiencing an extreme taste aversion that stops you from getting proper nutrition, make an appointment with your doctor. They can point you in the right direction for specialists or treatments that can help you put your taste aversions behind you.
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Chambers KC. (2018). Conditioned taste aversions. DOI:
1016/j.wjorl.2018.02.003 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2018). Nausea and vomiting: Causes.
mayoclinic.org/symptoms/nausea/basics/causes/sym-20050736 - Lin J-Y, et al. (2014). Conditioned taste aversion, drugs of abuse and palatability. (2014).
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4134772/ - Lin J-Y, et al.
 (2017). Conditioned taste aversions: From poisons to pain to drugs of abuse. DOI:
(2017). Conditioned taste aversions: From poisons to pain to drugs of abuse. DOI:
3758/s13423-016-1092-8
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Nov 21, 2018
Written By
Tessa Sawyers
Edited By
Ginger Wojcik
Share this article
By Tessa Sawyers on November 21, 2018
related stories
Everything You Need to Know About Food Aversions During Pregnancy
Nausea and Vomiting
6 Common Types of Eating Disorders (and Their Symptoms)
Is There a Best At-Home Food Sensitivity Test? A Dietitian Explains
Oral Immunotherapy for Food Allergies
Read this next
Everything You Need to Know About Food Aversions During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
You’ve heard of pregnancy cravings, but what about the opposite, food aversions? Why do some women develop a sudden hatred for foods they used to love?
READ MORE
Nausea and Vomiting
Medically reviewed by Carissa Stephens, R.
 N., CCRN, CPN
N., CCRN, CPNVomiting is an uncontrollable reflex that expels the contents of the stomach through the mouth. It’s also called "being sick" or "throwing up."
READ MORE
6 Common Types of Eating Disorders (and Their Symptoms)
By Alina Petre, MS, RD (NL)
Eating disorders are characterized by unusual or disturbed eating habits. Learn more here.
READ MORE
Is There a Best At-Home Food Sensitivity Test? A Dietitian Explains
If you suspect you have a food sensitivity, you may be wondering whether it's worth purchasing an at-home test. Our dietitian discusses whether food…
READ MORE
Oral Immunotherapy for Food Allergies
Medically reviewed by Marc Meth, MD, FACAAI, FAAAI
Oral immunotherapy can help treat food allergies by desensitizing your body to the allergenic substance.
 Learn how it works.
Learn how it works.READ MORE
My Allergy Origin Story: A Food Allergy Journey
Medically reviewed by Adrienne Seitz, MS, RD, LDN
Roshay was no stranger to frustrating allergies. Wheat wasn’t the first major allergy, nor the fifth, she’d been diagnosed with in her lifetime.
READ MORE
Malabsorption Syndrome
Medically reviewed by Saurabh Sethi, M.D., MPH
Malabsorption syndrome refers to a number of disorders in which the small intestine is unable to absorb enough nutrients.
READ MORE
The 8 Most Common Food Allergies
By Helen West, RD and Alyssa Northrop, MPH, RD, LMT
Most food allergies are caused by just eight foods. This article explains what they are, what symptoms they cause, and what you can do about it.
READ MORE
What Is the Best Food Sensitivity Test?
By Marsha McCulloch, MS, RD
Certain foods can make you feel unwell, but it can be tricky to figure out which ones are causing your symptoms.
 Learn the best tests for food…
Learn the best tests for food…READ MORE
Poor Feeding in Infants
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D.
"Poor feeding in infants" describes an infant with little interest in feeding or who is not feeding enough to receive the necessary nutrition.
READ MORE
Aversion to certain foods may warn of cancer | 74.ru
All newsYou can’t take your eyes off: wonderful babies that appeared in the Chelyabinsk zoo in 2022
The last chairman of the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR Ruslan Khasbulatov died
The Federation Council proposed to deprive Valery Meladze of Russian citizenship for supporting Ukraine. What the artist replied to this
A two-month-old girl died in the Chelyabinsk region, who was admitted to the hospital with a temperature of
Putin called the girl whose card he chose at the Wishing Tree
There were no drivers willing to help: the traffic police pulled the car stuck in the snow in the Southern Urals kids will become happy and rich
Beautiful, hot, healthy: we publish recipes for ideal winter drinks (they are easy to make at home)
“The wheels get stuck, they drag on the road”: the mayor’s office reports on road cleaning, and Chelyabinsk residents publish photos of snow porridge
“They rest for three days, and then they don’t know what to do”: the State Duma proposed to shorten the New Year holidays for Russians
In Magnitogorsk, a pensioner fell into a snow-covered well
“Thongs are uncomfortable”: the story of a tire shop owner who works as a stripper at night
The plane flying from Moscow to Magnitogorsk made an emergency landing in Koltsovo
Andryukha, we have a corpse! What do you remember from the main (and favorite) series about cops
Two popular skating rinks were closed in Chelyabinsk
“Aries will succeed”: why we believe in horoscopes, but they come true — we talk with a psychologist
Snowdrifts and more than 30 cars in an accident on the highway: watching the consequences of a snowstorm that hit the South Urals
“We will go to a low level and sit there”: economists talk about what will happen to the economy and the ruble in 2023
“Newbies do not know that there is a crisis in public catering »: a restaurant boom began in Chelyabinsk
"There is a shortage. " Pilot Lekha - about who we will fly with next and how passengers have changed
" Pilot Lekha - about who we will fly with next and how passengers have changed
Out of town, to the capital or abroad: what trends await the real estate market in the new year
Per square meter - with square eyes: summing up the unexpected results of the year in the housing market in Chelyabinsk
A multi-kilometer traffic jam has gathered on the M-5 highway due to massive traffic accidents
The Ministry of Defense announced the number of Russian military dead in Makeyevka
Chelyabinsk resident beat his mother and her random defender in the courtyard of a high-rise building
“He doesn't leave the door even at -30”: the story of Hachiko, who has been sitting on the porch of the hospital for a year and a half
Drivers will be tested for alcohol according to the new rules
Even schoolchildren can do better! 10 questions that will prove that you have forgotten the Russian language
Chelyabinsk residents have been warned about worsening weather: snowfalls and a blizzard are approaching the region
They speak a strange language and do not drink alcohol. How the disappearing Mennonite community lives on the edge of Russia
How the disappearing Mennonite community lives on the edge of Russia
Due to snowfalls, buses linking Chelyabinsk and Ufa turn around on the M-5 highway
“Let women have animal rights”: how virgin men become extremists
Traffic restrictions were introduced on the M-5 highway due to snowfall and blizzard
In the Chelyabinsk region, an eight-year-old boy's fingers were torn off by a firecracker explosion
Eat and watch: 13 cool films for all the holidays0003
“I’m not naked, I’m very heavily dressed”: a Russian teacher makes cosplays for Japanese anime that cancer patients could not eat eggs. But after recovery, normal tastes returned to them
Photo: Timofey Kalmakov / 59.RU
Share
Sweet becomes salty, sour becomes bitter. All patients who have experienced cancer treatment know this. Until now, this was considered a side effect of the treatment. But now there is evidence that the disease itself can cause food aversion, says Dr. Peter. nine0089
Peter. nine0089
This is the conclusion of the scientist Turstan Bruin, who devoted his life to studying alcohol intolerance and taste changes in people with cancer. In one of his studies, published in the Journal of Clinical Radiology, he noted that one in four of the patients he examined had an aversion to certain foods.
“I had two male patients with lung cancer,” recalls Dr. Bruin. Both at some point stopped eating sausages. For one, they have become tasteless and like leather, for the other, on the contrary, they are too flavored. nine0089
At the same time, one of the patients had an aversion to sausages 2 years before the diagnosis, and the other - 3 years.
The doctor recalls patients with cervical cancer: by the time the disease was diagnosed, one could not eat eggs for four months, the other had been sick of them for six years. At the same time, a few months after treatment, normal tastes returned to them.
Aversion to it can be a harbinger of several types of cancer at once, such as cervical or lung cancer. In the practice of Dr. Bruin, there were patients who could not eat cheese for several years, but did not even suspect that they had oncology. nine0089
In the practice of Dr. Bruin, there were patients who could not eat cheese for several years, but did not even suspect that they had oncology. nine0089
“One 44-year-old patient admitted that when he ate cheese, he felt like he was chewing gum,” the scientist writes. “After radiation therapy, everyone regained normal tastes.”
Its taste for cancer patients became the most unpleasant, and these complaints were the most frequent. Many of them have given up their favorite drink for years.
According to doctors, changes in taste are associated with tumors growing in the head and neck, as well as with a violation of the intestinal microbiota. According to researchers, aversion to previously loved food may indicate advanced cancer and is the fourth most common symptom among gastrointestinal disorders after dry mouth, weight loss and rapid satiety. nine0089
"Clinicians routinely ignore altered taste perception in cancer patients because it is not a life-threatening aspect," the scientists wrote in a report published in the journal Frontiers in Physiology. “But it's a worrying early sign of tumor growth. Therefore, it is important to identify such a symptom as a manifestation of cancer.”
“But it's a worrying early sign of tumor growth. Therefore, it is important to identify such a symptom as a manifestation of cancer.”
Related
-
August 24, 2022, 18:00
Half of the patients do not know about the diagnosis: how to recognize diabetes in yourself - symptoms and simple ways -
November 22, 2022, 18:00
Attacks in the dark: a new "night" omicron symptom that many people miss - check yourself -
November 25, 2022, 17:00
After what age you can not think about extra pounds. Scientists have named the ideal weight for longevity is there really a link between sugar consumption and the growth of malignant tumors
Irina Sebeleva
Oncology of therassician
- Laik5
- Laughter0
- Surprise3
- Anges 2
- Sorrows 6
saw a nipple? Select a fragment and press Ctrl+Enter
COMMENTS20
Read all comments
What can I do if I log in?
Media news2
Media news2
Why you don’t feel like eating and what to do about it
July 21, 2021 Likbez Health nine0003
You may need to stay cool for a couple of hours.
Why I don't want to eat
Loss of appetite is not a diagnosis. But this can be a sign of serious health problems or just a misunderstanding. Here are a few common factors that can affect appetite.
1. Age
Appetite often decreases with age. Perhaps this is due to the fact that with age, the metabolism slows down and people simply need fewer calories than in their youth. nine0003
But other reasons are not excluded. Scientists suspect that the elderly may not produce enough ghrelin, a hormone responsible for appetite. Or the work of the sense organs is changing, and people do not get the pleasure from food that in their youth (and if so, why eat?).
Research is still ongoing. But it is unambiguously established: the older we get, the less we eat.
2. High physical or mental stress
If you feel like a squirrel in a wheel all day long, rush somewhere, worry about something, and in the evening you fall exhausted from your feet, you should not be surprised at a decrease in appetite. nine0003
nine0003
When you are extremely exhausted, the body is forced to choose what to spend energy on: running around or energy-intensive digestion. If you can’t get out of business, the brain reduces the activity of the gastrointestinal tract. You just don't want to eat.
3. Pregnancy in women
Many mothers-to-be face nausea and loss of appetite. Most often this happens in the first trimester.
Kesha Gaither
MD, obstetrician-gynecologist, in a comment to Parents. nine0003
Approximately one in two pregnant women in the United States experiences periods of aversion to some familiar food.
The exact cause of decreased appetite during pregnancy is not known. But experts suggest that the matter is in the hormonal restructuring of the body and increased sensitivity to tastes and smells. Perhaps the refusal of a favorite food is an evolutionary mechanism: in this way, the mother’s body tries to protect the fetus from substances that are potentially harmful to its development.
4. Weather
In the heat of summer, you want to eat much less than on cold autumn or winter evenings. The fact is that food is part of the body's thermoregulation system. When we are cool, we tend to consume more calories in order to convert them into heat. In the heat, the body does not need additional heating, and therefore neglects food.
5. Mood
Someone's appetite disappears because of nervousness, someone, on the contrary, gets stressed out. Scientists have not yet discovered any common algorithm for all that connects emotions and eating behavior. But it was quite clearly established that the desire to eat largely depends on mood. And for each person, this connection is individual. nine0003
6. Smoking
Nicotine has a side effect: it reduces the need for food.
7. SARS and other diseases in the acute phase
Leptin is a hormone that causes satiety. But at the same time, this substance takes an active part in the immune response to infection.
With a cold, flu, exacerbation of other infectious diseases, the level of leptin increases - this allows the body to repel a pathogenic attack. But once the hormone becomes more, there is a feeling of satiety. Therefore, sick people often refuse to eat. nine0003
8. Certain medications
Reduced appetite may be one of the side effects of antibiotics. But other drugs sometimes discourage the desire to eat. Painkillers based on codeine and morphine, as well as diuretics, for example, lead to such a reaction.
9. Psychiatric disorders
Loss of appetite may be caused by depression.
Another common mental disorder that is directly related to the reluctance to eat is anorexia nervosa. So doctors call an eating disorder caused by a desperate fear of gaining weight. nine0003
10. Diseases of the digestive system
Changes in appetite may be one of the first symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome and Crohn's disease.
11. Viral hepatitis and other damage to the liver
One of the most important elements in the digestive system is the liver: it is here that blood enters with nutrients processed by the stomach and intestines. The body sorts the substances received, cleanses them of toxins and only then passes them into the general bloodstream. With viral hepatitis and other liver diseases, it ceases to cope with its functions. nine0003
The body sorts the substances received, cleanses them of toxins and only then passes them into the general bloodstream. With viral hepatitis and other liver diseases, it ceases to cope with its functions. nine0003
In order not to overload the suffering liver and give it a chance to recover, the body reduces the production of hormones, enzymes and other substances responsible for the manifestation of appetite.
12. Cardiovascular diseases
Loss of appetite is one of the symptoms of chronic heart failure. In addition, reluctance to eat may be associated with a developing heart attack and heart defects.
13. Endocrine Disorders
If the thyroid gland produces less hormones than necessary (a condition called hypothyroidism), appetite is greatly reduced. However, the weight may increase. nine0003
14. Iron deficiency anemia
Loss of appetite along with weight loss, especially if all this is accompanied by fatigue, a feeling of lack of strength, is one of the most characteristic symptoms of iron deficiency in the body.
15. Cancer
Loss of appetite often accompanies oncological diseases such as:
- stomach cancer;
- pancreatic cancer;
- colon cancer;
- ovarian cancer.
Food aversion can also be a side effect of tumor treatment.
Is it necessary to restore appetite
On the one hand, reducing appetite is a convenient thing. Someone suffers on diets, and you reduce the caloric content of the diet by itself.
On the other hand, one should not rejoice at the lack of appetite. At least because with a limited diet, you get fewer nutrients. And this can lead to hypovitaminosis (and even beriberi), a decrease in hemoglobin levels, anemia and more serious problems - with the liver and other internal organs, vision, joints, teeth. nine0003
What exactly will be the long-term consequences of a decrease in appetite depends on the reasons that caused such a condition. It's one thing if you don't feel like eating just because you're sad or too hot. And it is quite another if the loss of appetite is associated with damage to the liver, heart, and even more so cancer.
And it is quite another if the loss of appetite is associated with damage to the liver, heart, and even more so cancer.
What to do if you don't feel like eating
First, take care of yourself, your well-being, and life circumstances. Perhaps your appetite has decreased for external reasons, for example, due to heat, fatigue, worries. In this case, the desire to eat will return as soon as stress factors disappear. nine0003
But if everything is calm in your life, and your appetite has disappeared, or if indifference to food lasts for weeks, try to see a therapist.
See your doctor as soon as possible if you notice that your reluctance to eat is accompanied by sudden weight loss.
The doctor will examine you and ask you about your symptoms. He will definitely ask what medications you take, what lifestyle you lead, whether the loss of appetite is due to stressful events, such as divorce, the loss of a family member or friend.