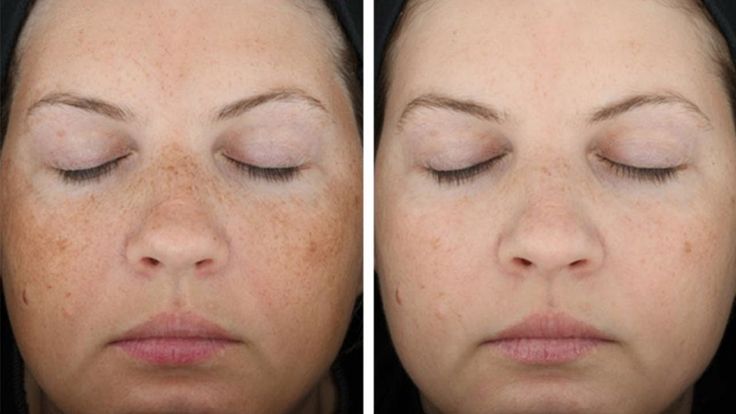
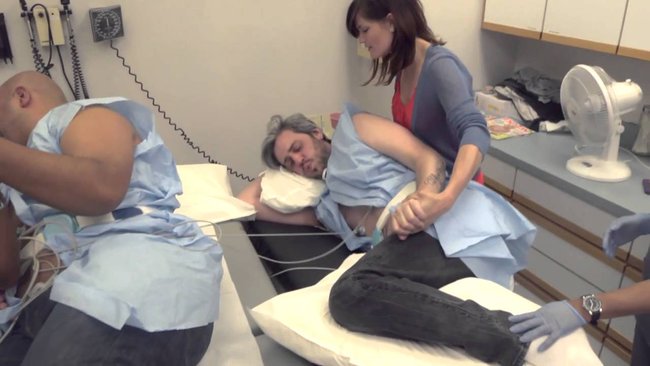
Shot during labor
Epidural block - pregnancy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
An epidural block is a numbing medicine given by injection (shot) in a specific place in the back. It numbs or causes a loss of feeling in the lower half of your body. This lessens the pain of contractions during childbirth. An epidural block may also be used to reduce pain during surgery on the lower extremities. This article focuses on epidural blocks during childbirth.
The block or shot is given into an area over your lower back or spine.
- You may be asked to lie on your side, or you may sit up.
- Either way, you will be asked to pull your stomach inward and hunch your back outward.
Your health care provider will wash the area of your back and inject a little medicine to numb the spot where the epidural needle is placed:
- The provider inserts a needle into your lower back.
- The needle is placed into a small space outside your spinal cord.
- A small soft tube (catheter) is placed into your back, next to your spine.
- The needle is removed.
The numbing medicine is given through the tube for as long as it is needed.
In most cases, you will receive a low dose because it is safer for you and baby. Once the medicine takes effect (10 to 20 minutes), you should have less pain due to labor. You may still feel some back or rectal pressure during contractions.
You may shiver after an epidural, but this is common. Many women shiver during labor even without an epidural.
Many studies have shown that an epidural is a safe way to manage pain during childbirth. While rare, there are some risks.
Your blood pressure may drop for a short while. This might cause the baby's heart rate to slow down.
- To avoid this, you will receive fluids through an intravenous (IV) line to help keep your blood pressure stable.
- If your blood pressure shows a drop, you may need to lie on your side to keep the blood moving throughout your body.
- Your provider may also give you medicine to raise your blood pressure.

An epidural block may change or alter labor and delivery.
- If you are very numb from the block, you may have a harder time bearing down to push your baby through the birth canal.
- Contractions may lessen or slow down for a little while, but labor will still move along as it should. In some cases, it may even go faster. If your labor slows down, your doctor can give you medicine to speed up your contractions. It is best to wait until you are in active labor to have the epidural placed.
Other rare side effects are:
- You may get a headache after your epidural but this is rare.
- Medicine could enter your spinal fluid. For a short while, it could make you feel dizzy, or you might have a hard time breathing. You could also have a seizure. This is also rare.
There are 2 types:
- "Walking" epidural block. This type of epidural will lessen your pain, but you will still be able to move your legs. Most women are not really able to walk around, but they can move their legs.

- Combined spinal and epidural block. This combines both a spinal and epidural block. It provides pain relief much faster. The combined block is used when women are in very active labor and want relief right away.
Delivery - epidural; Labor - epidural
- Epidural - series
Hawkins JL, Bucklin BA. Obstetric anesthesia. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 16.
Nathan N, Wong CA. Spinal, epidural, and caudal anesthesia: anatomy, physiology, and technique. In: Chestnut DH, Wong CA, Tsen LC, et al, eds. Chestnut's Obstetric Anesthesia: Principles and Practice. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 12.
Sharpe EE, Arendt KW. Anesthesia for obstetrics. In: Gropper MA, ed. Miller's Anesthesia. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 62.
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Browse the Encyclopedia
Epidurals: Meaning and Side Effects of Anesthesia During Labor
An epidural is the most common type of anesthetic used for pain relief during labor. Here’s what you should know before having an epidural, including information that dispels some common myths.
How and when is an epidural for labor pain administered?If you choose to have an epidural, an anesthesiologist will insert a needle and a tiny tube, called a catheter, in the lower part of your back. The needle is removed and the catheter left in place for delivery of the medication through the tube as needed. You can begin an epidural at any time during your labor — in the beginning, in the middle, or even toward the end — in consultation with your physician.
Does it hurt when the epidural is administered?The anesthesiologist will numb the area where the epidural is administered, which may cause a momentary stinging or burning sensation. But because of this numbing, there is very little pain associated with an epidural injection. Instead, most patients will feel some pressure as the needle is inserted.
But because of this numbing, there is very little pain associated with an epidural injection. Instead, most patients will feel some pressure as the needle is inserted.
An epidural provides anesthesia that creates a band of numbness from your bellybutton to your upper legs. It allows you to be awake and alert throughout labor, as well as to feel pressure. The ability to feel second-stage labor pressure enables you to push when it’s time to give birth to your baby. It can take about 15 minutes for the pain medication to work.
How long does the pain relief last?You can continue to receive pain relief through an epidural for as long as you need it. The amount of medication you receive through the epidural can be increased or decreased as necessary.
Can an epidural slow labor or lead to a cesarean delivery (C-section)?There is no credible evidence that it does either. When a woman needs a C-section, other factors usually are at play, including the size or position of the baby or slow progression of labor due to other issues. With an epidural, you might be able to feel contractions — they just won’t hurt — and you’ll be able to push effectively. There is some evidence that epidurals can speed the first stage of labor by allowing the mother to relax.
When a woman needs a C-section, other factors usually are at play, including the size or position of the baby or slow progression of labor due to other issues. With an epidural, you might be able to feel contractions — they just won’t hurt — and you’ll be able to push effectively. There is some evidence that epidurals can speed the first stage of labor by allowing the mother to relax.
The amount of medication that reaches the baby from the epidural is very small, and there is no evidence that it causes any harm.
Are there risks and side effects?Epidurals are very safe; serious complications are extremely rare. However, as with all medications and medical procedures, there are potential side effects:
- Decrease in blood pressure – The medication may lower your blood pressure, which may slow your baby’s heart rate. To make this less likely, you will be given extra fluids through a tube in your arm (IV), and you may need to lie on your side.
 Sometimes, your anesthesiologist will give you a medication to maintain your blood pressure.
Sometimes, your anesthesiologist will give you a medication to maintain your blood pressure. - Sore back – Your lower back may be sore where the needle was inserted to deliver the medication. This soreness should last no more than a few days. There is no evidence that an epidural can cause permanent back pain.
- Headache – On rare occasions, the needle pierces the covering of the spinal cord, which can cause a headache that may last for a few days if left untreated. If this situation arises, discuss the treatment options with your anesthesiologist.
A spinal block is sometimes used in combination with an epidural during labor to provide immediate pain relief. A spinal block, like an epidural, involves an injection in the lower back. While you sit or lie on your side in bed, a small amount of medication is injected into the spinal fluid to numb the lower half of the body. It brings good relief from pain and starts working quickly, but it lasts only an hour or two and is usually given only once during labor. The epidural provides continued pain relief after the spinal block wears off.
It brings good relief from pain and starts working quickly, but it lasts only an hour or two and is usually given only once during labor. The epidural provides continued pain relief after the spinal block wears off.
Anesthesiologists are committed to patient safety and high-quality care, and have the necessary knowledge to understand and treat the entire human body.
The waitress who was injured during the assassination attempt on Ded Khasan became worse
January 18, 2013 09:32
The condition of a 30-year-old woman who was wounded in Moscow during an assassination attempt on crime boss Aslan Usoyan, known as Ded Khasan, has worsened. Miryat Bikchurina is in the surgical intensive care unit. The condition of the victim is assessed as extremely serious.
The condition of a 30-year-old woman who was wounded in Moscow during an attempt on crime boss Aslan Usoyan, known as Ded Khasan, has worsened. Miryat Bikchurina is in the surgical intensive care unit. The condition of the victim is assessed as extremely serious. nine0003
Miryat Bikchurina is in the surgical intensive care unit. The condition of the victim is assessed as extremely serious. nine0003
Aslan Usoyan was shot dead by a professional killer, who accurately hit the target from a distance of about 100-120 meters, reminds "Interfax". The offender used a silent automatic machine "Val". This weapon is used by fighters of special forces of the Russian army and special services.
A 30-year-old waitress at the Old Phaeton restaurant was in the line of fire. The killer calmly fired several shots at the woman. The woman, wounded during the attack, is now in the Botkin hospital, doctors are fighting for her life. The victim has a lot of blood loss, her spinal cord is damaged, her lung is pierced, her thigh is shot through. She is currently in intensive care on a ventilator. nine0003
75-year-old Usoyan was killed the day before in the area of Povarskaya street near the restaurant "Old Phaeton".
This is the second serious attempt on Ded Khasan's life.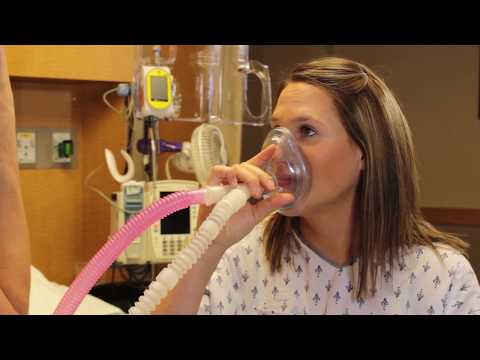 On September 16, 2010, an unidentified person shot him with a firearm in the entrance of a house at 12/7 Tverskaya Street. Then Usoyan managed to survive. Experts do not exclude that both assassination attempts on Usoyan were organized and prepared by the same people.
On September 16, 2010, an unidentified person shot him with a firearm in the entrance of a house at 12/7 Tverskaya Street. Then Usoyan managed to survive. Experts do not exclude that both assassination attempts on Usoyan were organized and prepared by the same people.
Ded Khasan was an "ally" of another crime boss - Vyacheslav Ivankov (Yaponchik), who was shot dead in Moscow in 2009year.
society news
Previously related
-
The media reported another murder of the main enemy Ded Khasan
-
Ded Khasan's nephew was left under arrest
-
In Rome, the alleged killers of Ded Hasan were detained
-
The Ural police continue to catch people from the clan of Ded Khasan
-
A bandit from the clan of Grandfather Hassan was taken for the murder of Abbas
-
Russian police officers will help Italians fight the Georgian mafia
How does the baby feel during childbirth?
Children, unlike mothers, cannot share their birth stories…maybe it is not in vain that this is provided by nature?
PRESSURE for uterine contractions.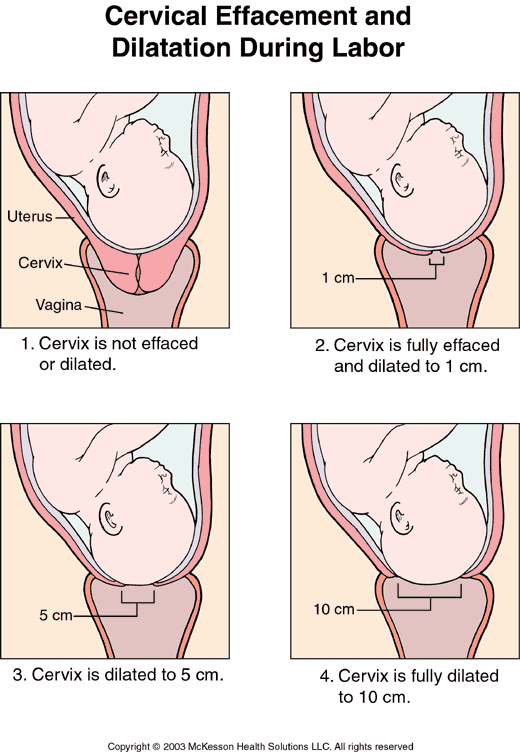 The child is not endangered; during normal childbirth, it is protected by amniotic fluid. When passing through the birth canal, the anatomy (bone mobility) helps to compensate for pressure and prevent injuries to the child. nine0003
The child is not endangered; during normal childbirth, it is protected by amniotic fluid. When passing through the birth canal, the anatomy (bone mobility) helps to compensate for pressure and prevent injuries to the child. nine0003
STRESS , in a good way. During childbirth, the mother's body produces a hormone that helps to cope with pain. It stimulates the production of the stress hormone in the baby, which mobilizes the body to “eliminate the threat” and prepares it for life outside the womb.
SON . The baby can maintain the sleep cycle it is used to in the womb and sleep up to 50 minutes every hour.
DISTRESS fetus. If the pregnancy did not go very smoothly, the condition of the child during childbirth may worsen. For example, oxygen delivery may decrease, and the heartbeat will worsen. Therefore, during childbirth, KTG . If so, the doctors take the necessary measures.
PAIN during the period of exile. With a normal birth, it is not very strong. If, for example, a child is born with a birth tumor, it is logical that he was not well. But the sensations experienced by the child are not comparable with the sensations of the mother. This is due to the fact that the pain receptors in the newborn are not yet fully developed.
With a normal birth, it is not very strong. If, for example, a child is born with a birth tumor, it is logical that he was not well. But the sensations experienced by the child are not comparable with the sensations of the mother. This is due to the fact that the pain receptors in the newborn are not yet fully developed.
MOOD mother. It is necessary to remain calm and positive not only during pregnancy, but also during childbirth. It has been proven that the baby's heartbeat slows down, and he calms down when he hears the mother's voice. No matter how the birth goes, the child understands that “something is wrong”, so it is important for him to hear his mother. There are also studies that prove the positive effect of mother's laughter on the child. Women in childbirth don't often laugh, but having a partner help create the right atmosphere would be great! nine0003
EFFECTS OF DRUGS . Much that enters the mother's body crosses the placental barrier. With general anesthesia, the child may fall asleep or even stop breathing. Therefore, the preferred method of pain relief is epidural anesthesia. The absorption of its components is minimal, so we can say that it practically does not enter the bloodstream of the fetus and does not have a systemic effect on its body.
With general anesthesia, the child may fall asleep or even stop breathing. Therefore, the preferred method of pain relief is epidural anesthesia. The absorption of its components is minimal, so we can say that it practically does not enter the bloodstream of the fetus and does not have a systemic effect on its body.
FIRST BREATH . The crying of a baby after birth speaks of the health of his lungs. During the first breath, the lungs begin to expand, and this mechanism is accompanied by a cry. At the same time, the first breath and cry allow you to clear the lungs of amniotic fluid. nine0003
SENSOR OVERLOAD . After giving birth, everything around becomes colder, noisier and brighter.
TEMPERATURE CHANGE . Amniotic fluid facilitates the transition from uterine temperature to ambient temperature, and the physiology of the newborn compensates for temperature changes. Moreover, in rodboxes we maintain a comfortable temperature for mother and child, and we put newborns on special heated tables.