Pregnancy week 7 weight gain
Weight Gain in First Trimester: How Much Is Normal?
Congratulations — you’re pregnant! Along with what to put on the baby registry, how to set up the nursery, and where to go for preschool (just kidding — it’s a bit too early for that!), many people want to know how much weight they can expect to gain over the next 9 months.
While the majority of the pounds will make their appearance during the second and third trimester, there’s some initial weight gain that will happen in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. In fact, on average, people gain 1 to 4 pounds in the first trimester — but it can vary. Let’s take a look at the factors involved.
“This is one of the most asked questions for patients during their much anticipated first obstetrical visit with their doctor,” says Jamie Lipeles, MD, DO, OB-GYN and founder of Marina OB/GYN.
Despite what you might have heard, you don’t gain too much weight in the first trimester, with the standard recommendation being 1 to 4 pounds. And unlike the second and third trimester (when body mass index, or BMI, may be more of a factor), Lipeles says the weight gain during the first 12 weeks is pretty much the same for all body types.
And if you’re pregnant with twins, Lipeles says the same guidelines apply to weight gain during the first trimester. However, this can change during the second and third trimesters, as twin pregnancies typically result in greater weight gain.
That said, there are occasions when your doctor may have a different recommendation for the first 12 weeks. “For patients with a BMI of more than 35, we often encourage them to maintain their weight for the entire first trimester,” says G. Thomas Ruiz, MD, OB-GYN at MemorialCare Orange Coast Medical Center.
Spending more time tightening your pants than loosening them in the first trimester? You might be wondering if losing or maintaining your weight is a red flag.
The good news? Not gaining any weight during the first trimester doesn’t mean anything’s wrong. In fact, losing a few pounds in the first half of your pregnancy is a common occurrence (hello, morning sickness and food aversions!).
In fact, losing a few pounds in the first half of your pregnancy is a common occurrence (hello, morning sickness and food aversions!).
If you haven’t experienced morning sickness, consider yourself lucky. Feeling nauseous and experiencing occasional vomiting at any time of the day may cause you to maintain your weight or lose a few pounds. Fortunately, this typically subsides in the second and third trimester.
Pursing your lips at the sight of your favorite plate of scrambled eggs and bacon is also common in the first trimester. “I often joke with my patients and tell them that they might have food aversions in the first trimester, but then will overcompensate in the second and third trimester by having food cravings out of character for them outside of pregnancy,” says Lipeles.
If you’re experiencing vomiting or food aversions, make sure to share this information with your OB-GYN at your routine visits. It’s important to keep them in the loop, especially if you’re losing weight. “Weight loss means the body is in a breakdown mode and is stressed, which leads to a deficiency in nutrients,” says Felice Gersh, MD, an OB-GYN at Integrative Medical Group of Irvin, where she’s the founder and director.
“Weight loss means the body is in a breakdown mode and is stressed, which leads to a deficiency in nutrients,” says Felice Gersh, MD, an OB-GYN at Integrative Medical Group of Irvin, where she’s the founder and director.
“Fortunately, an embryo can still acquire the nutrients needed for its development and growth — the mom, however, can lose important lean body mass and supportive fat,” adds Gersh.
And you do need to be cautious of experiencing notable weight loss.
One of the most common causes of significant weight loss is hyperemesis gravidarum, which is the most severe form of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. This occurs in about 3 percent of pregnancies and typically requires treatment.
One of the perks of being pregnant is being able to ditch the diet mentality more easily. (We should likely all ditch it, permanently.) That said, it’s important to be aware of your weight and how it compares to the weight gain recommendations, as gaining too much weight comes with risks to both you and baby, including:
- Weight gain in baby: When mom gains weight, baby is likely to gain more than usual in the womb.
 This can result in a larger baby at birth.
This can result in a larger baby at birth. - Difficult delivery: With a significant weight gain, Lipeles says the anatomy of the birth canal is altered, yielding a more difficult and dangerous vaginal delivery.
- Higher risk of gestational diabetes: Gaining too much weight, especially early on in your pregnancy, can be an early sign of gestational diabetes. If you gain more than recommended in the first trimester, Lipeles says not to be surprised if your doctor gives you a glucose test prior to the standard 27- to 29-week range.
Despite the old saying “you’re eating for two,” the first trimester isn’t the time to load up on calories. In fact, unless your doctor has told you otherwise, you should maintain your pre-pregnancy intake.
However, as your pregnancy progresses, a gradual increase in calories is recommended. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics suggests a range of 2,200 to 2,900 calories a day, depending on your BMI prior to pregnancy. This equates to the following increase per trimester (use your pre-pregnancy intake as a baseline):
This equates to the following increase per trimester (use your pre-pregnancy intake as a baseline):
- First trimester: no additional calories
- Second trimester: eat an additional 340 calories per day
- Third trimester: eat an additional 450 calories per day
Most of us begin this journey with high hopes of eating healthily, exercising regularly, and avoiding anything with a shelf life longer than our pregnancy.
But then, life happens.
Between managing work, other children, social obligations, and all those trips to the restroom, finding the time — and energy — to maintain your pre-pregnancy exercise schedule or whip up a celebrity-inspired meal is sometimes a real challenge. The good news? You don’t have to get it right every day to grow a healthy human being.
So, what should you aim for? If you’re up for it, keep doing what you were doing before getting pregnant, as long as it doesn’t involve hanging upside down from a trapeze bar.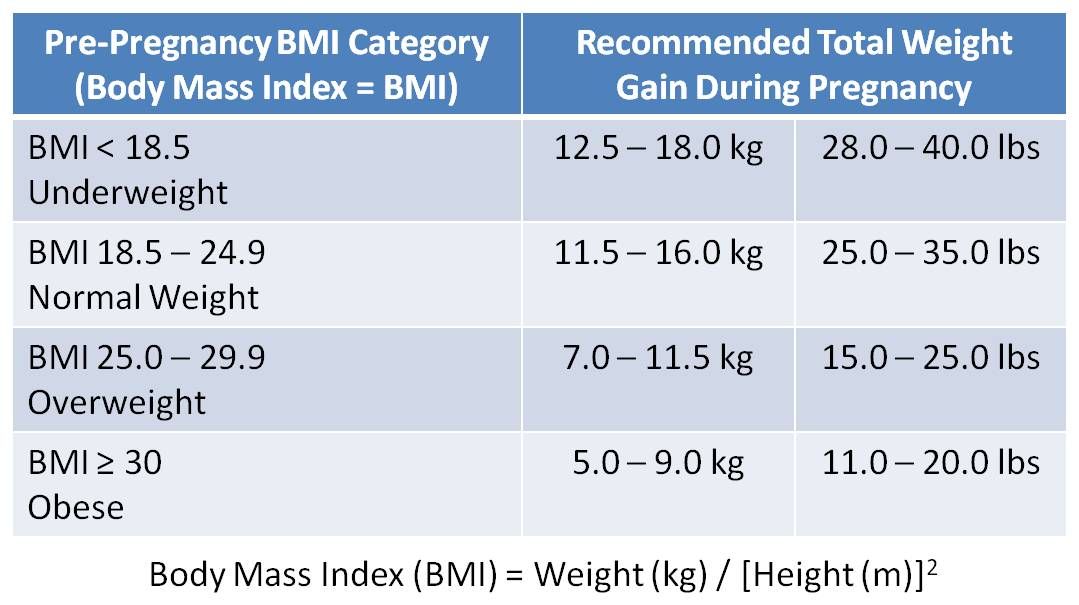 Physical activities that are excellent choices during the first trimester include:
Physical activities that are excellent choices during the first trimester include:
- walking
- swimming
- jogging
- indoor cycling
- resistance training
- yoga
Set a goal to exercise most days of the week, or at least 150 minutes each week. The important thing is to stick to what you know. This is not the time to take up marathon training, especially if you’ve never run before.
As far as nutrition, aim to eat a balanced diet with a variety of foods. This includes:
- whole grains
- fruit
- vegetables
- lean protein
- healthy fats
- low fat dairy products like milk and yogurt
Since your body doesn’t require additional calories during the first trimester, eating as you usually would — provided it’s nutritious — is the goal.
While no two pregnancies are the same, there are some general guidelines to follow when it comes to gaining weight throughout all three trimesters. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), along with the Institute of Medicine (IOM), categorizes weight gain based on your weight at your first appointment.
In general, the range for all 9 months is anywhere between 11 and 40 pounds. Those with more weight or obesity may need to gain less, whereas those with less weight may need to gain more. More specifically, the ACOG and IOM recommend the following ranges:
- BMI less than 18.5: approximately 28–40 pounds
- BMI of 18.5–24.9: approximately 25–35 pounds
- BMI of 25–29.9: approximately 15–25 pounds
- BMI 30 and greater: approximately 11–20 pounds
For twin pregnancies, the IOM recommends a total weight gain of 37 to 54 pounds.
To get a better idea of how many people stay within this range, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) analyzed data from several studies. It found that 21 percent gained less than the recommended amount of weight, whereas 47 percent gained more than the recommended amount.
Ideally, you’ll find a doctor you can trust to answer some seriously awkward questions. But even if this is your first go-around with your OB-GYN, leaning on them for knowledge and support is key to easing anxiety during pregnancy.
But even if this is your first go-around with your OB-GYN, leaning on them for knowledge and support is key to easing anxiety during pregnancy.
Since weight measurements are a part of every prenatal visit, each appointment is an opportunity to address any questions or concerns, especially since your OB is tracking a number of things, including weight changes.
How much weight should I gain while pregnant?
Weight gain is essential for a healthy pregnancy
Learning to eat well and manage your weight gain are key components to a healthy pregnancy. Weight gain helps your baby to grow and develop properly, and allows your body to make physical changes to support pregnancy, such as growth of your uterus, development of the placenta and an increase in blood volume. But how much weight is the right amount to gain? When determining a weight-gain range, some important things to consider are: your pre-pregnancy weight for height, commonly referred to as your Body Mass Index (BMI), your medical history, and whether you're carrying one baby, twins or multiples.
How much weight should I gain?
There is no set amount of weight gain that is right for everyone. Yet over time, some general guidelines have been accepted. For women carrying one baby, the first trimester is typically considered a time of minimal weight gain, regardless of your pre-pregnancy BMI. As you near the end of your first trimester, and begin the second, weight gain is expected to increase. Some providers like to see women with a "healthy" BMI prior to pregnancy, gain 10 pounds by 20 weeks. During the second and third trimester, guidelines often suggest gaining 1/2 to 1 pound per week. Whatever weight-gain range is determined to be right for you, try to gain the weight gradually. Below are some generally accepted total weight-gain guidelines based on pre-pregnancy BMI.
BMI below 19 prior to pregnancy
Of all categories, underweight women are at highest risk for delivering low birth-weight babies. If you were underweight before becoming pregnant, it's especially important to gain an adequate amount of weight during your pregnancy - 28 to 40 pounds is often recommended.
BMI of 19 to 25 prior to pregnancy
Your pregnancy is off to a healthy start if you're in the "recommended" BMI category. It's typically advised that you gain 25 to 35 pounds over the course of your pregnancy.
BMI of 25 to 30 prior to pregnancy
If you start your pregnancy in this BMI group, your weight gain range is slightly less, however, it's still important to gain weight to support a healthy pregnancy and provide your baby with adequate nourishment – 15 to 25 pounds is often recommended.
BMI above 30 prior to pregnancy
If your BMI is above 30 before you become pregnant, strive for a modest weight gain of 15 pounds – and remember that pregnancy is not a time to lose weight!
Pregnant with twins or multiples
Women who are pregnant with more than one baby typically need to gain additional weight to provide adequate nourishment for the babies. It's best to discuss your weight-gain range with your provider.
My baby only weighs 7 pounds – what makes up the rest?
Rest assured – it is not all fat. Most of the weight will go away gradually after delivery. Here's what you're carrying and approximately how it adds up:
Most of the weight will go away gradually after delivery. Here's what you're carrying and approximately how it adds up:
- Amniotic fluid and placenta: 4 pounds
- Increase in blood and other fluids: 8 pounds
- Fat reserves: 7 pounds
- Enlarged uterus and breasts: 4 to 6 pounds
How do the calories add up?
You may have heard the saying, "you're eating for two." Although it is true that the food you eat is nourishing two, your calorie needs only increase by about 300 per day after the first trimester. So if your goal is a healthy weight gain, keep in mind that your calorie needs don't increase that much. Here are three examples of healthy food choices that add up to 300 calories:
- Whole-wheat English muffin with two tablespoons peanut butter
- One cup of yogurt with one cup fresh fruit
- Bowl of high-fiber cereal with reduced-fat or skim milk
How will I lose the weight after delivery?
When you combine healthy eating with regular activity during your pregnancy, you'll feel better and shed those extra pounds easier once your baby is born.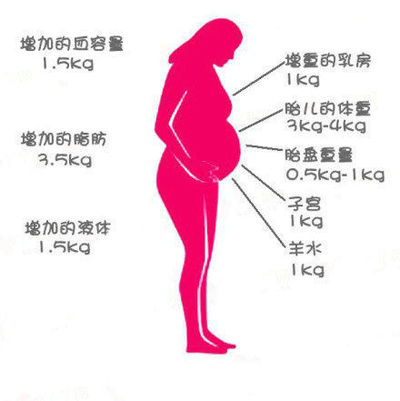 Gaining the recommended amount of weight during pregnancy can actually help you lose it more quickly afterward. If you're gaining at a faster rate, consult with your health care provider. Try these tips to increase activity and eat healthy during your pregnancy:
Gaining the recommended amount of weight during pregnancy can actually help you lose it more quickly afterward. If you're gaining at a faster rate, consult with your health care provider. Try these tips to increase activity and eat healthy during your pregnancy:
- Park further away from buildings; use the stairs instead of elevators.
- Avoid sitting for long periods of time – take short walk breaks.
- Snack on yogurt, string cheese, fresh fruit, or whole-grains (like popcorn and high-fiber cereal) instead of chips, candy and high-fat desserts.
- Eat regular meals and snacks.
In addition, women who choose to breastfeed may find it a bit easier to lose weight because of the extra calories (about 500 per day) it takes for their body to produce milk. However, the best approach to losing weight is always through healthy low-fat eating and regular moderate exercise.
Visit our pregnancy page to schedule an appointment and learn more about our services.
Weight during pregnancy. What increase is considered optimal?
Why is excessive weight gain during pregnancy particularly harmful? What should be the calorie content of the diet? How to build your diet so that you can eat varied (and tasty), but at the same time not gain too much? Let's figure it out.
What makes up weight gain during pregnancy?
An increase in the subcutaneous fat layer during pregnancy is a normal and natural process.
While the baby is growing inside you, he needs energy and external protection. But during pregnancy, weight increases not only and not so much due to the adipose tissue of the mother: there is more fluid in the body, the uterus grows, the fetus and placenta develop, and the breasts increase in preparation for the feeding process.
Interestingly, weight loss during the period of toxicosis can later provoke its increase: the body will try to regain what was lost.
Expectant mothers especially actively gain weight in the second trimester and the beginning of the third, but closer to childbirth, a pregnant woman can even lose 1-2 kilograms. nine0004
As long as the weight increases more or less evenly and does not go beyond the upper limit of the norm, there is nothing to worry about. But if your weight is rapidly going up, you should be wary.
How to correctly calculate the weight, and what increase is considered optimal?
In Russian obstetric practice, it is generally accepted that the total gain should not exceed 12 kg. for the entire pregnancy. Of these 12 kg. 5-6 accounts for the fetus, placenta, amniotic fluid, another 1.5-2 - for an increase in the uterus and mammary glands, and only 3-3.5 - for the fat mass of a woman. nine0004
But this is a general indicator, a kind of "average temperature in the hospital." The optimal increase is calculated individually and depends on the initial weight of the pregnant woman, her age, the number of fetuses and the size of the child (children), physical activity.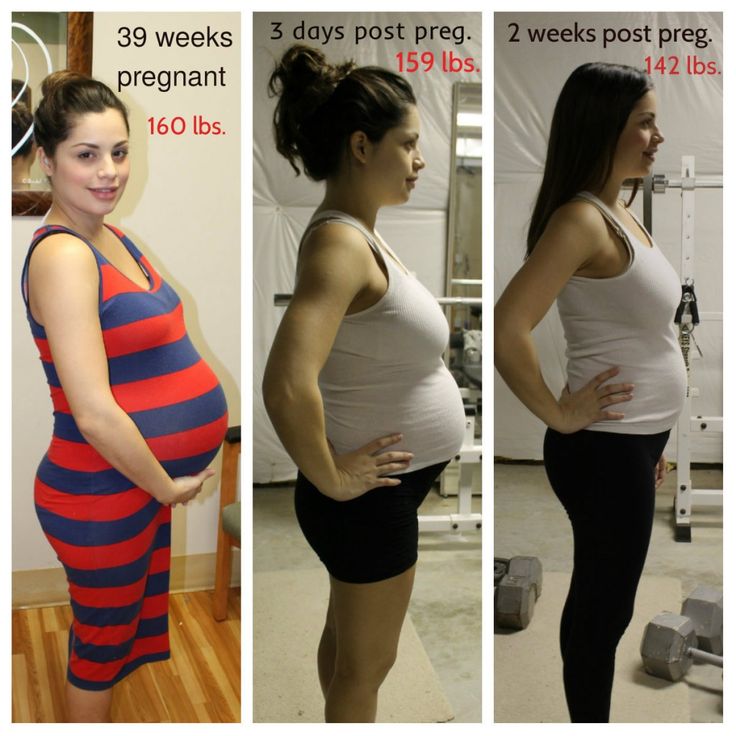
WHO recommends that optimal weight gain be calculated based on Body Mass Index (BMI).
It is determined by the formula: body weight (kg) / height squared (m).
| BMI | Recommended weight gain |
|---|---|
| 19.8-26 (normal body weight) | 12.5-15 kg |
| 26.1-29 (overweight) | 11.5 - 14 kg |
| over 29 (obese) | 7-9 kg |
How to calculate the optimal weight gain?
To do this, use the following chart:
- Calculate your BMI: divide your initial weight in kg. for height in meters squared. nine0072
For example, your "pre-pregnancy" weight was 60 kg with a height of 170 cm.
BMI = 60: (170 x 170) = 20.76.
- A BMI of less than 18.5 indicates underweight. Indicators from 18.
 5 to 25 are within the norm, from 25 to 30 are above the norm, and a figure greater than 30 indicates obesity.
5 to 25 are within the norm, from 25 to 30 are above the norm, and a figure greater than 30 indicates obesity. - Now that you know your BMI, find the optimal weekly increase in the table and compare it with yours.
| Week of pregnancy | nine0033 Underweight before pregnancy (BMI less than 18.5)Normal pre-pregnancy weight (BMI 18.5 to 24.9) | Overweight before pregnancy (BMI over 30) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0-0.9 kg | 0-0.7 kg | 0-0.5 kg |
| 6 | 0-1.4 kg | 0-1 kg | 0-0.6 kg |
| 8 | 0-1.6 kg | 0-1.2 kg | 0-0.7 kg |
| 10 | 0-1.8 kg | 0-1.3 kg | 0-0.8 kg |
| 12 | 0-2 kg | 0-1.5 kg | 0-1 kg |
| 14 | 0.5-2.7 kg | 0. 5-2 kg 5-2 kg | 0.5-1.2 kg |
| 16 | up to 3.6 kg | up to 3 kg | up to 1.4 kg |
| 18 | up to 4.6 kg | up to 4 kg | up to 2.3 kg | nine0039
| 20 | up to 6 kg | up to 5.9 kg | up to 2.9 kg |
| 22 | up to 7.2 kg | up to 7 kg | up to 3.4 kg |
| 24 | up to 8.6 kg | up to 8.5 kg | up to 3.9 kg |
| 26 | up to 10 kg | up to 10 kg | up to 5 kg |
| 28 | up to 13 kg | up to 11 kg | up to 5.4 kg |
| 30 | up to 14 kg | up to 12 kg | up to 5.9 kg |
| 32 | up to 15 kg | up to 13 kg | up to 6.4 kg |
| 34 | up to 16 kg | up to 14 kg | up to 7. 3 kg 3 kg |
| 36 | up to 17 kg | up to 15 kg | up to 7.9 kg |
| 38 | up to 18 kg | up to 16 kg | up to 8.6 kg |
| 40 | up to 18 kg | up to 16 kg | up to 9.1 kg |
Recently, doctors are increasingly talking about an individual approach and urge not to panic if the increase is slightly beyond the normal range. When assessing the state of health of a pregnant woman, the doctor focuses not only on weight, but also takes into account the results of tests and examinations and other important indicators.
Why is excessive weight gain dangerous?
Gaining extra pounds can lead to gestational diabetes, hypertension, preeclampsia, or cause a caesarean section.
In addition, excessive weight gain during pregnancy may increase the risk of obesity and associated cardiovascular disease.
What can I do to keep my weight within normal limits during pregnancy?
First of all, consult a nutritionist. If there is no such doctor in the antenatal clinic, it makes sense to contact a specialist on a commercial basis. He will develop an individual diet, which will contain all the useful elements, and will offer to keep a food diary. It will also tell you how to eat right and weigh yourself. nine0003 To prevent excessive weight gain during pregnancy, it is enough to follow simple rules of a healthy diet:
If there is no such doctor in the antenatal clinic, it makes sense to contact a specialist on a commercial basis. He will develop an individual diet, which will contain all the useful elements, and will offer to keep a food diary. It will also tell you how to eat right and weigh yourself. nine0003 To prevent excessive weight gain during pregnancy, it is enough to follow simple rules of a healthy diet:
- Eat often and in small portions;
- Always keep a “healthy snack” on hand: fresh apple wedges, unsweetened crackers, dried fruit, or sugar-free yogurt;
- Refuse soda, chips, sausages and sausages;
- Minimize sweets;
- Avoid fast food;
- Limit the use of condiments, especially salt, which retains water in the body; nine0072
- Choose steamed dishes;
- Eat more fiber-rich foods such as whole grain bread, bran, vegetables;
The diet of a pregnant woman should be varied. Include grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy products, meat and fish, legumes, or nuts.
It must be remembered that expectant mothers should never starve and adhere to extreme diets.
How many calories per day do you need during pregnancy? nine0006
It is difficult to calculate the energy value per day on your own, and then strictly adhere to a certain number of calories, and it is not necessary, unless it is recommended by a nutritionist or endocrinologist. On average, you can aim for 2000-2500 calories per day, but it is important to understand that the need for calories depends on many factors: age, initial weight, health status and level of physical activity.
When should I be on the alert?
Strictly speaking, it is better for a pregnant woman not to worry and entrust her condition to a doctor who will control the development of pregnancy, analyzes and monitor weight. It is important to take tests to determine the level of fasting blood glucose once a trimester. The appearance of glucosuria, an increase in fasting blood glucose (more than 5. 5 mmol / l) or an hour after a meal (more than 7.7 mmol / l) indicate the possible development of "diabetes in pregnancy", in connection with which the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment . In addition, a sharp increase in body weight can cause preeclampsia. nine0004
5 mmol / l) or an hour after a meal (more than 7.7 mmol / l) indicate the possible development of "diabetes in pregnancy", in connection with which the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment . In addition, a sharp increase in body weight can cause preeclampsia. nine0004
These and other diseases can be dangerous, which is why you need to carefully monitor the body weight during the gestation period, but remember that pregnancy is not the time for strict diets.
When using any materials from the site nutriclub.ru, a link to the site is required.
© Nutriclub, 2020
You will also be interested
- Nutriclub - healthy nutrition and child development nine0072
- Pregnancy
- Mom's health and well-being
- weight during pregnancy. What increase is considered optimal? - Nutriclub
Weekly weight gain during pregnancy: calculator
What does the weight of a pregnant woman consist of
The total weight of the expectant mother increases due to various factors. This is both the intrauterine growth of the child and the changes taking place in her body (enlargement of the uterus, accumulation of adipose tissue, an increase in the volume of circulating blood and tissue fluid, an increase in the size of the mammary glands). After childbirth, the parameters of a woman do not immediately return to their original values. nine0004
This is both the intrauterine growth of the child and the changes taking place in her body (enlargement of the uterus, accumulation of adipose tissue, an increase in the volume of circulating blood and tissue fluid, an increase in the size of the mammary glands). After childbirth, the parameters of a woman do not immediately return to their original values. nine0004
weight gain during pregnancy includes such components:
Fruit
2500-4000 g
Placenta
400-600 g
uterus
900–1000 g
Amniotic liquid
~ 1–1, 5 liters
Blood volume increase
~ 1.5 liters
Tissue fluid reserves
~ 2.5 liters
Subcutaneous fat
2000-3000 g
Breast enlargement 0004500-700 g
Good to know
The average weight gain during pregnancy is 11-15 kg.
What should be the weight gain during pregnancy
On average, the expectant mother gains 300-400 g per week.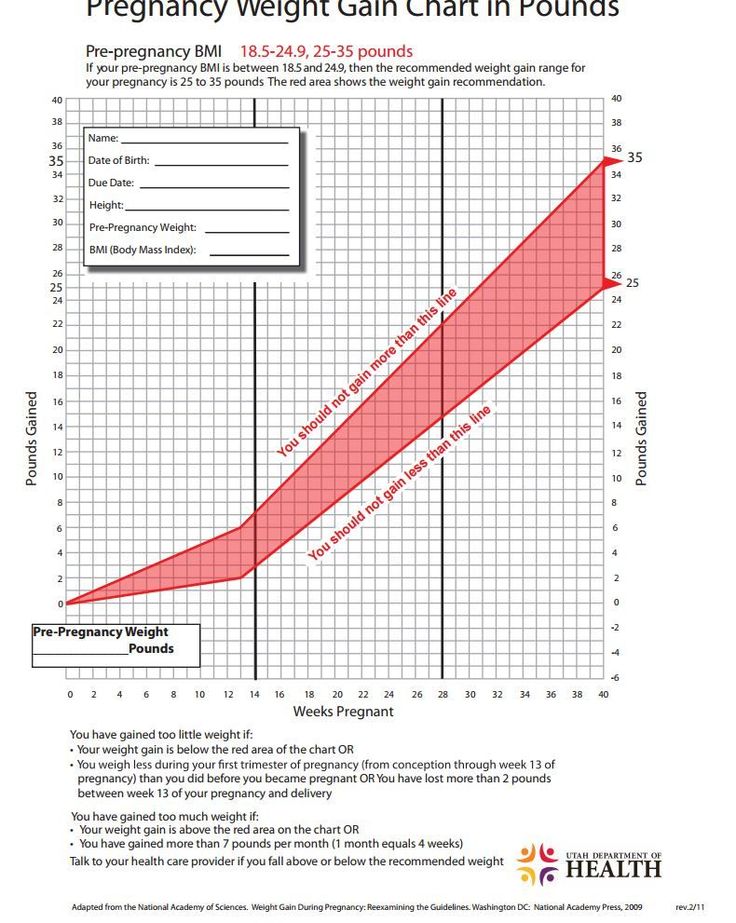 But the weight of a pregnant woman increases unevenly over the weeks. First, the mother's body adapts to a new state. It lasts about two months, and during this period body weight does not change significantly. By the end of the first trimester, a woman adds about 1.5–2 kg. At this time, the expectant mother can even lose weight due to early toxicosis, which prevents her from fully eating, accompanied by nausea and vomiting. nine0004
But the weight of a pregnant woman increases unevenly over the weeks. First, the mother's body adapts to a new state. It lasts about two months, and during this period body weight does not change significantly. By the end of the first trimester, a woman adds about 1.5–2 kg. At this time, the expectant mother can even lose weight due to early toxicosis, which prevents her from fully eating, accompanied by nausea and vomiting. nine0004
During the second trimester of pregnancy, the baby is actively growing, and the weight of the pregnant woman increases rapidly. The average weekly increase after 12-14 weeks is 250-300 grams. Exceeding these values may indicate emerging edema: first hidden, then obvious. Therefore, if the weight is growing, it is imperative to inform the doctor about it - in order to exclude complications that are dangerous for the mother and fetus. But if a woman has toxicosis, weight gain may be less or even absent. nine0004
In the third trimester, the weight of a pregnant woman increases faster week by week.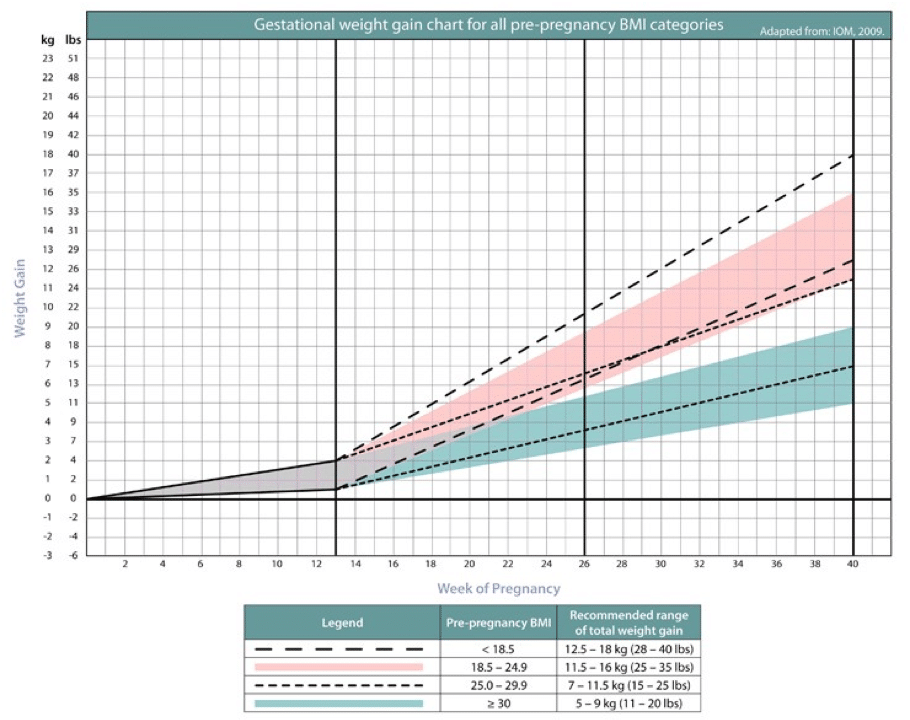 The expectant mother is gaining about 300–400 g per week. A rapid increase in body weight at this time may be associated with edema. They are not always visible to you on examination, but a doctor can detect them. Therefore, if the weight grows too fast, it is necessary to inform the doctor about this in order to exclude complications that are dangerous for the mother and fetus.
The expectant mother is gaining about 300–400 g per week. A rapid increase in body weight at this time may be associated with edema. They are not always visible to you on examination, but a doctor can detect them. Therefore, if the weight grows too fast, it is necessary to inform the doctor about this in order to exclude complications that are dangerous for the mother and fetus.
On average, a woman gains 35-40% of the total increase in the first half of pregnancy and another 60-65% in the second. nine0004
Good to know
Excess weight during pregnancy can be associated with carrying a large baby (more than 4 kg) or twins. In this case, there is a slight excess of the norm of body weight gain.
To calculate normal weight during pregnancy, you can use special tables or a calculator. However, it must be remembered that such schemes do not take into account the individual characteristics of the expectant mother and baby and give only average values. A calculator and tables will be useless if a woman is expecting twins, a large fetus, or suffers from diseases that affect metabolism. nine0004
nine0004
What affects the weight gain during pregnancy
The weight gain of the future mother depends on many factors, and first of all it is the initial body weight. The less a woman weighs before conceiving a child, the more she is likely to gain weight. So the body compensates for the initial weight deficit and increases the supply of nutrients necessary for the development of the fetus. Conversely, overweight women tend to gain fewer pounds during pregnancy.
Below is a table that allows you to calculate the approximate weight gain, taking into account BMI (body mass index) in a singleton pregnancy. nine0004
BMI before pregnancy
Expected weight gain during pregnancy
less than 18.5 (weight deficit)
13–18 kg
18.5–24.9 (normal weight)
10–15 kg
25.0–29.9 (overweight)
8–10 kg
30 or more (obese)
6–9 kg
To calculate BMI, divide weight in kilograms by height in square meters.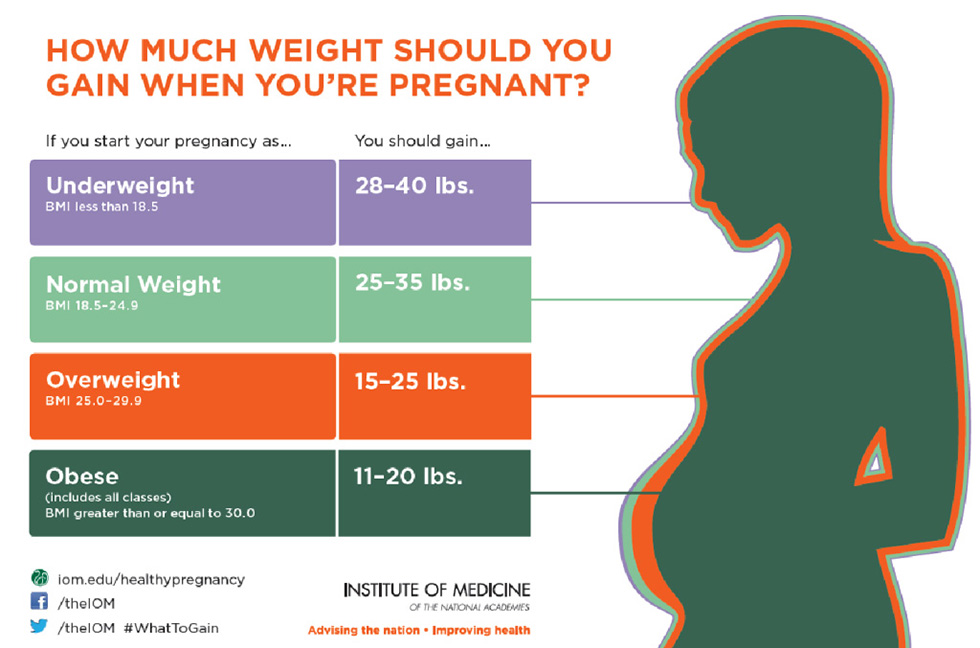 For example, if a woman is 175 cm tall and weighs 70 kg, her BMI would be 70/1.752 = 22.8, which is normal weight. During pregnancy, she will gain weight in the range of 10-15 kg. nine0004
For example, if a woman is 175 cm tall and weighs 70 kg, her BMI would be 70/1.752 = 22.8, which is normal weight. During pregnancy, she will gain weight in the range of 10-15 kg. nine0004
Weight gain during pregnancy also depends on age. The older the woman, the more kilograms she can gain while carrying a child.
Height also matters. It is noticed that tall women gain more weight during pregnancy.
Another important aspect is the number of previous pregnancies and births. Re-pregnancy within 5 years is a risk factor for rapid weight gain.
What threatens rapid weight gain during pregnancy
A significant weight gain in a future mother is dangerous for the development of complications. Here are some possible negative consequences:
- preeclampsia is a complication of pregnancy in which blood pressure rises and protein appears in the urine;
- gestational diabetes mellitus;
- premature birth.
Excess weight during pregnancy can adversely affect the health of the expectant mother and fetus.