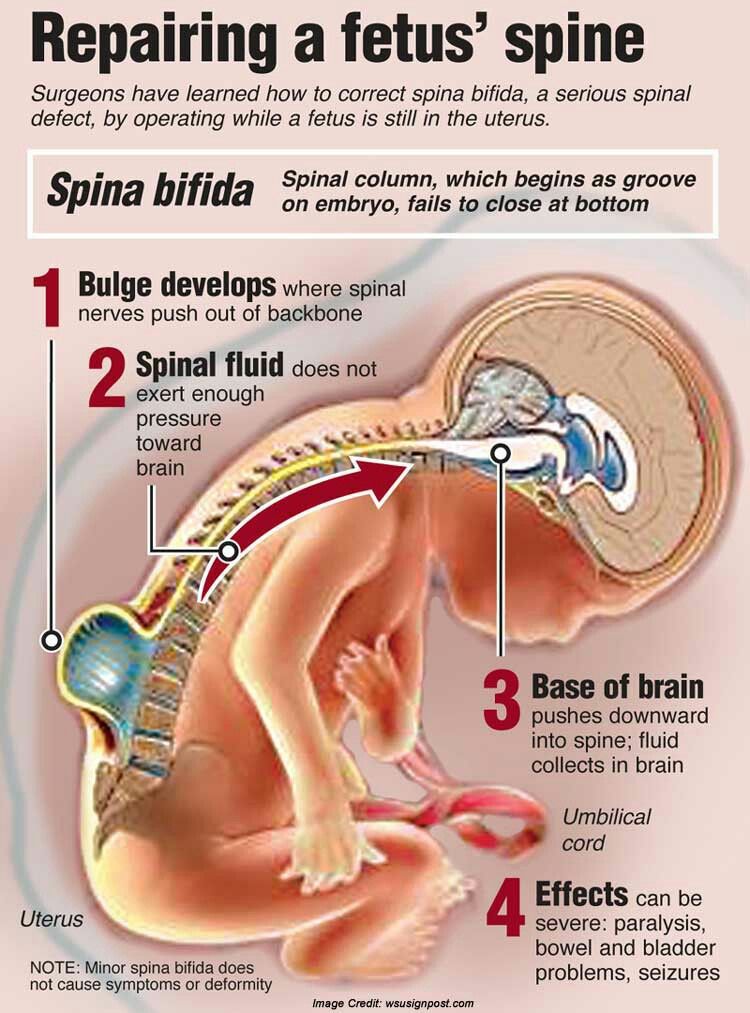
Sharp pains in stomach 35 weeks pregnant
Upper stomach pain during pregnancy: Third trimester
Many people experience pain in the upper part of their stomach or abdomen during pregnancy. This is usually nothing to worry about, but sometimes it might be necessary to see a doctor.
The third trimester is notoriously difficult. From breathing through Braxton–Hicks contractions and wondering whether they are the real thing to stretching skin and crowded organs, people may feel exhausted and ready to give birth by the end of the third trimester.
Stomach pain is a common pregnancy complaint. Some people report pain in the upper stomach or upper abdomen during their third trimester. This pain may be sharp and shooting or a dull ache.
Many of the causes of upper abdominal pain are harmless, but feeling intense pain here can signal a serious problem. Talk to a doctor or midwife about any unusual or very painful sensations.
In this article, we look at the possible causes of upper abdominal pain during pregnancy, how to ease the symptoms, and when to see a doctor about it.
Stomach or abdomen pain is more common during early pregnancy, when hormonal shifts can trigger the nausea and vomiting of morning sickness. In the middle of the second trimester, at around 20 weeks, stomach pain usually goes away.
In the third trimester, abdominal pain can reappear as the uterus begins to crowd the organs. Some women experience heartburn or a sensation that the skin of the stomach is stretching.
Having stomach pain in the third trimester may indicate a more serious problem if it:
- occurs with other symptoms, such as itching
- feels sudden or intense
- is constant
- is in a specific location
- appears alongside a fever, nausea, or vomiting
- appears alongside vaginal bleeding
Many causes of upper abdominal pain in the third trimester are harmless. However, because premature labor, placenta issues, and other concerns can endanger the woman and the baby, it is important to be cautious and tell a doctor or midwife about any unusual symptoms.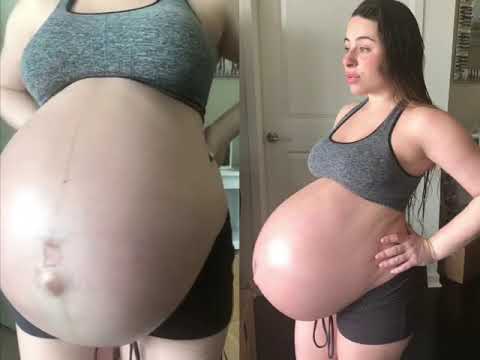
Possible causes of upper abdomen pain during the third trimester include:
Constipation and gas
Constipation is one of the most common pregnancy complaints.
During the first trimester, hormonal shifts may trigger constipation. By the third trimester, the uterus is putting significant pressure on the intestines and making it more difficult for a person to have a bowel movement.
Having a vague feeling of fullness in the upper stomach or abdomen is sometimes a symptom of severe constipation. Other symptoms might include gas, straining to have a bowel movement, and having very hard or small bowel movements.
Eating fiber-rich foods may help. Taking laxatives can also provide relief, but it is important to talk to a doctor or midwife before taking any medication when pregnant.
Acid reflux
Heartburn is a common symptom, affecting an estimated 17–45 percent of women during pregnancy. A pregnancy hormone called progesterone can cause acid reflux and heartburn.
As the uterus grows, pressure on the digestive tract can make this problem more severe. Many pregnant women experience acid reflux when lying down.
Pain in the upper abdomen may be from acid reflux if the pain extends up the chest and into the throat or includes a burning sensation. Some women belch or experience gas.
Taking over-the-counter heartburn medications, eating smaller meals, and opting for a less acidic diet may help.
Stretching skin
Some pregnant people report feeling an intense sensation of stretching skin. As the uterus expands, this sensation can extend to the upper abdomen. If the skin itches and feels tight, and the pain is on the outside of the stomach rather than deep in the abdomen, stretching skin could be the culprit.
Gently massaging the area, applying lotion to it, and taking warm showers can sometimes help relieve the discomfort.
Muscle pain and strain
The abdominal muscles must stretch to accommodate the growing fetus. The pressure of the uterus on the lower body can also change the way a person walks or moves, increasing the likelihood of sustaining an injury.
The pressure of the uterus on the lower body can also change the way a person walks or moves, increasing the likelihood of sustaining an injury.
Feeling pain when bending or lifting may mean an injury to the stomach or chest muscles. Resting and stretching can help with minor injuries. People can see a doctor about injuries that do not go away on their own.
Gallbladder issues
Pain in the upper right part of the abdomen, under or near the ribs, may mean that there is a problem with the liver or gallbladder.
If there is nausea or vomiting, or if the pain comes in waves or attacks, it may be a sign of gallstones. Left untreated, gallstones can block the bile duct and cause liver problems.
If the gallstones do not pass on their own, a doctor might recommend removing the gallbladder.
Liver issues
Pregnancy-related hormone changes can cause a condition called intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (IHP), or cholestasis. For most women, the first symptom is itching. Some also experience pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, vomiting, or yellowing eyes or skin.
Some also experience pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, vomiting, or yellowing eyes or skin.
A doctor must carefully monitor liver health in a person with IHP. In some cases, they will need to deliver the baby early to prevent serious complications, including liver failure and injuries to the developing baby.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation in the pancreas. Infections, injuries, and problems with other organs, including the liver and gallbladder, can cause pancreatitis.
Pancreatitis may cause upper abdomen pain, exhaustion, nausea, or changes in the color of stool.
Depending on the cause of pancreatitis, a woman may need to stay at the hospital. In some cases, a doctor may recommend antibiotics or fluids.
Spleen injury
Pain in the upper abdomen, especially the left side, may mean that there is a problem with the spleen.
A blow to the stomach can bruise or injure the spleen. Infections can cause the spleen to rupture. Rarely, a person’s spleen may rupture for no clear reason.
Spleen injuries cause intense, sudden pain. A woman may feel dizzy or lightheaded, and they must seek emergency treatment. A surgeon may need to remove the spleen.
Contractions
True labor contractions typically start at the top of the uterus, causing an intense tightening sensation that becomes progressively more painful. A woman who feels contractions beginning in the top of the abdomen may be going into labor.
Call a medical professional straight away. If there is vaginal bleeding, go to the emergency room.
The risk of missing a serious problem far outweighs any benefits of trying home remedies. If the cause of the problem is unclear, call a doctor or midwife first.
If they feel that the pain is not dangerous or does not need medical treatment, some home remedies that may help ease upper abdomen pain during pregnancy include:
- stretching to ease muscle pain and tension
- eating fewer acidic foods
- with a doctor or midwife’s permission, using an antacid to deal with heartburn
- eating smaller, more frequent meals to reduce the pain of a full stomach and heartburn
- massaging the area to ease muscle tension and stress
Call a doctor or midwife within a day for any unusual pain in the stomach or abdomen. At each visit with a provider, talk about any recent symptoms, as well as any symptoms that have changed in severity.
At each visit with a provider, talk about any recent symptoms, as well as any symptoms that have changed in severity.
Go to the emergency room or immediately call a medical professional for:
- intense upper abdominal pain, especially if it is on the right side or if the pain is unbearable
- abdominal pain accompanied by vaginal bleeding
- contractions that come at regular intervals
- abdominal pain and a fever
- symptoms of high blood pressure, such as dizziness, difficulty breathing, a bad headache, or intense fatigue
- itching, yellowing skin or eyes, or vomiting
Most causes of stomach or abdominal pain in the third trimester are not fully preventable. As the fetus grows, the organs must shift. This can cause some aches and pains.
For some women, hormonal shifts trigger serious complications, such as IHP.
The best strategy to prevent serious pregnancy complications is to get regular prenatal care. Talk to a provider about any concerns, and ask about lifestyle strategies to ensure a healthy pregnancy.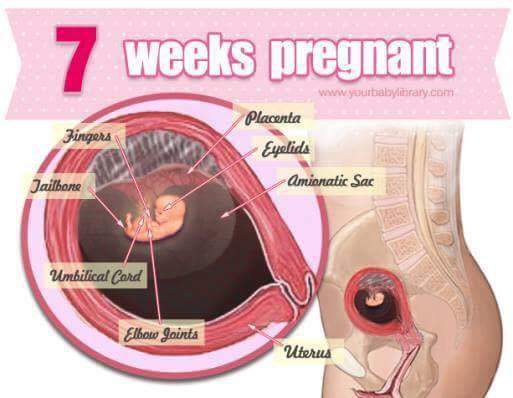
For most women, eating a healthful and balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and devising healthful strategies for managing stress can all help with the aches and pains of pregnancy.
Abdominal pain is one of the most common pregnancy complaints. This does not mean that a woman should ignore it. Only a doctor or midwife can diagnose the problem, so do not hesitate to call them.
They can either reassure a person that there is nothing to worry about or offer medical care to prevent an emerging condition from becoming more serious.
Read the article in Spanish.
Sharp Pregnancy Pain - Causes & Symptoms
It can be stressful, especially for first-time mothers, to discern between normal pregnancy pains and when there is a possible complication from a sharp pain during pregnancy. During pregnancy, your body will undergo many changes as it adapts to the growing life inside of you. You will gain weight and your body will grow to accommodate your new baby. While this is natural and necessary, it can cause some discomfort.
Possible Causes of a Sharp Pain During Pregnancy
One of the most common sharp pains that women report is a stabbing pain in and around the uterus, stomach or groin area. While this can be uncomfortable, in many cases it can be explained by normal changes that occur during pregnancy.
Some common causes include:
- Cramping – You may experience sharp pain due to the cramping that occurs from the uterus expanding
- Gas and Bloating
- Constipation
- Round Ligament Pain – Round ligament pain can occur during the second trimester and can cause a sharp pain in the abdomen on either or both sides. The pain is caused by the stretching of the ligament that supports the uterus as the uterus grows.
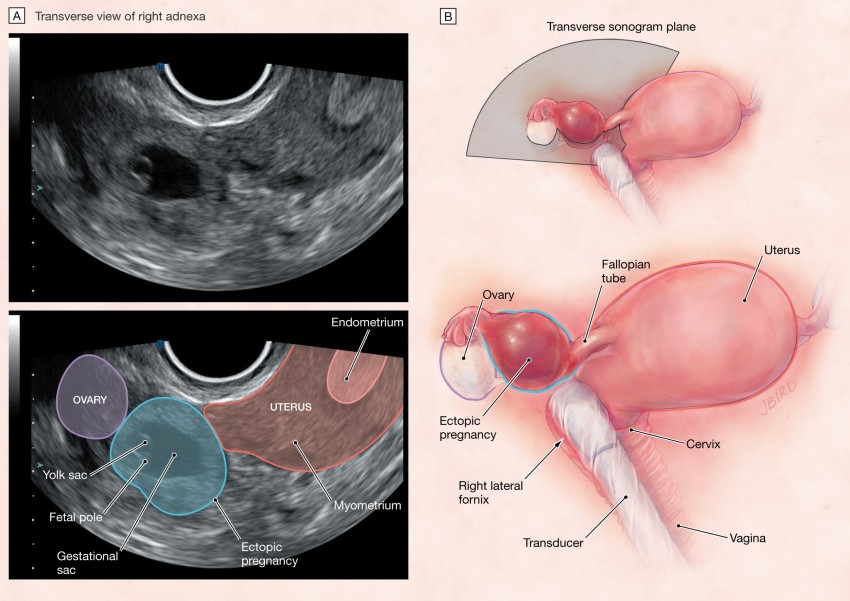
Although the above conditions are part of normal pregnancy, they typically don’t cause sharp pain. If the sharp pain you are experiencing is localized on one side, it could be indicative of an ectopic pregnancy. This is a serious condition and requires urgent medical attention.
A pending miscarriage can also result in a sharp pain from the cramping. This raises concerns for expecting mothers who want to know the difference between normal cramping associated with the expanding uterus and cramping from a pending miscarriage.
Contacting your healthcare provider to discuss your symptoms is always the right choice.
Warning Signs/ Symptoms for a Sharp Pain During Pregnancy
Despite the fact that sharp pain can be the result of normal pregnancy change, there are some warning signs that you need to watch out for in case the sharp pain is the result of a complication.
- If pain is accompanied by vomiting, fever, chills, heavy bleeding/blood flow, or change in vaginal discharge
- If the sharp pain is continual after resting or adjusting (round ligament pain shouldn’t last more than a few minutes)
- If the pain makes it difficult to breathe, walk or speak
If you experience any of the above symptoms contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Coping With Pregnancy Pains
If you are experiencing sharp or stabbing pain during pregnancy, there are some possible solutions that you can try to alleviate the pain:
- Pregnancy safe stretches
- Breathing exercises/controlled breathing
- Experiment with sleeping and sitting positions
- Go on a walk
Again, if the pain becomes too intense or prevents you from doing day-to-day activities, contact your health care provider immediately. Consult with your doctor for more pregnancy-safe pain management ideas.
Want to Know More?
- Medical Terms to Know
- Treating Muscle Cramps Naturally During Pregnancy
- Pregnancy and Leg Cramps
Get the Fetal Life App for Apple and Android endorsed by the American Pregnancy Association. It features meal recommendations, kicks counter, blood glucose tracking, and more.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————–
Gibbs, R.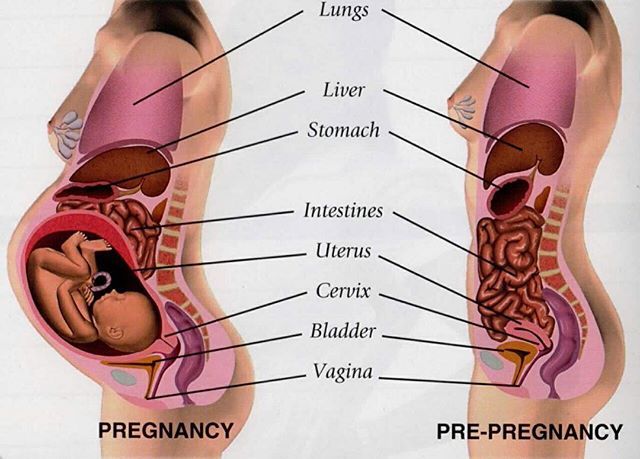 (2008). Prenatal Care. In Danforth’s obstetrics and gynecology (10th ed., p. 18). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
(2008). Prenatal Care. In Danforth’s obstetrics and gynecology (10th ed., p. 18). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Harms, R. (2004). Mayo Clinic guide to a healthy pregnancy (1st ed.). New York: HarperResource.
Jordan, R. (2014). Exercise, Recreational and occupational issues, and intimate relationships in pregnancy. In Prenatal and postnatal care: A woman-centered approach (pp. 274-279). Oxford: Wiley Blackwell.
33-36 weeks of pregnancy
33 weeks of pregnancy
How does the baby develop?
This week, the baby continues to actively grow and gain weight, his height is already about 44 cm, and the weight of a tiny body is approximately 1800-1900 g. During this period, the baby is no longer so easy to turn around, it takes up more space, which is why and his movements. This week, the baby sleeps a lot and therefore moves less, and the amplitude of his movements also decreases. The muscles become stronger, so the pushes, although rare, are quite strong and more concentrated. For a mother, baby movements can be very sensitive and painful, causing internal organs to suffer. The blood vessels of the baby are already expanding and contracting, their walls are becoming thicker, and the tone is higher. Brain cells undergo a process of adhesion. The skin of the crumbs turns pink, and due to the increase in subcutaneous fat, all wrinkles on the body are smoothed out. On the head of the crumbs, the hairs become darker and thicker, and the hairs covering the body become less and less. This fluffy hairiness is called lanugo. At 33 weeks, the baby's skin is covered with a special lubricant that protects it and ensures an easier delivery. Lubrication most of all covers the face, back, folds under the arms, groin and neck.
For a mother, baby movements can be very sensitive and painful, causing internal organs to suffer. The blood vessels of the baby are already expanding and contracting, their walls are becoming thicker, and the tone is higher. Brain cells undergo a process of adhesion. The skin of the crumbs turns pink, and due to the increase in subcutaneous fat, all wrinkles on the body are smoothed out. On the head of the crumbs, the hairs become darker and thicker, and the hairs covering the body become less and less. This fluffy hairiness is called lanugo. At 33 weeks, the baby's skin is covered with a special lubricant that protects it and ensures an easier delivery. Lubrication most of all covers the face, back, folds under the arms, groin and neck.
How does mother feel?
The uterus of the expectant mother rises higher and higher, at a distance of up to 34 cm from the pubis, and the tummy grows significantly. This is due to the large weight of the crumbs, amniotic fluid and placenta.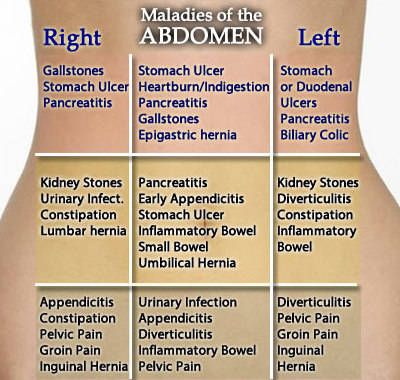 At the same time, it is harder for the mother to squat and make other movements. Strong and sharp jolts of the baby, as well as an enlarged uterus, can cause pain. But the expectant mother can already determine what exactly pushed her baby: with her knee or fist. If the tremors are light, this may indicate that the baby is hiccuping. At this time, a woman is recommended light physical activity, which allows you to take frequent breaks. Walking or fitness is best. Due to the fact that the enlarged uterus puts pressure on many organs, the mother may experience temporary discomfort, which is not related to any diseases. A high load is placed on the spine, causing pain in the sacrum, lower back and pelvis. In a pregnant woman, the volume of circulating blood increases by a liter, which has a strong effect on the functioning of the kidneys, oppressing the bladder and causing frequent urination. Sometimes mom can get up to six times a night. The cause of heaviness in the stomach, heartburn and nausea is the pressure of the uterus on the stomach.
At the same time, it is harder for the mother to squat and make other movements. Strong and sharp jolts of the baby, as well as an enlarged uterus, can cause pain. But the expectant mother can already determine what exactly pushed her baby: with her knee or fist. If the tremors are light, this may indicate that the baby is hiccuping. At this time, a woman is recommended light physical activity, which allows you to take frequent breaks. Walking or fitness is best. Due to the fact that the enlarged uterus puts pressure on many organs, the mother may experience temporary discomfort, which is not related to any diseases. A high load is placed on the spine, causing pain in the sacrum, lower back and pelvis. In a pregnant woman, the volume of circulating blood increases by a liter, which has a strong effect on the functioning of the kidneys, oppressing the bladder and causing frequent urination. Sometimes mom can get up to six times a night. The cause of heaviness in the stomach, heartburn and nausea is the pressure of the uterus on the stomach. In this case, frequent meals in small portions will help to alleviate the condition.
In this case, frequent meals in small portions will help to alleviate the condition.
34 weeks pregnant. How does the baby develop?
At this time, the baby has grown significantly, the weight of his small body reaches 2100 g, and the length is 45 cm. The body of the baby is already proportional and it is difficult to distinguish it from a newborn child. There are no wrinkles and folds on the face, the skin is smooth and even. The baby already often sucks his finger, developing a sucking reflex, so his cheeks are already formed and visible. Bones become denser, muscle mass also grows significantly. You can already see even the facial muscles on the face. By this time, the baby has already finally settled down in his mother's tummy and he is unlikely to be able to change the position of the body now. The bones of the skull, which are filled with connective tissue, remain very soft.
The baby's internal organs continue to develop. He swallows amniotic fluid many times throughout the day.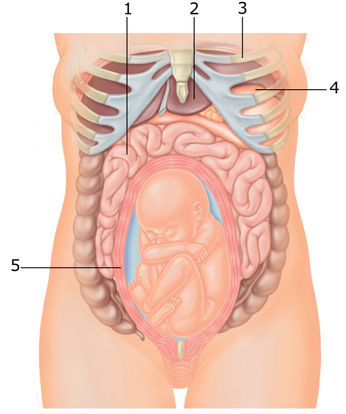 Water passes through the digestive tract and stimulates the muscles. The pancreas and liver process the dense part of the amniotic fluid, which consists of vellus hairs, lubrication, and small skin flakes. The liquid component of the water is excreted by the kidneys. The body thus processes about half a liter of water. Bile continues to accumulate in the gallbladder, providing preparation for the activities of the organs after birth. There is an intensive preparation for the appearance of the crumbs into the world, his head shape may change. With the onset of childbirth during this period, the lungs of the baby are able to provide the body with the necessary amount of oxygen.
Water passes through the digestive tract and stimulates the muscles. The pancreas and liver process the dense part of the amniotic fluid, which consists of vellus hairs, lubrication, and small skin flakes. The liquid component of the water is excreted by the kidneys. The body thus processes about half a liter of water. Bile continues to accumulate in the gallbladder, providing preparation for the activities of the organs after birth. There is an intensive preparation for the appearance of the crumbs into the world, his head shape may change. With the onset of childbirth during this period, the lungs of the baby are able to provide the body with the necessary amount of oxygen.
How does mother feel?
This week of pregnancy requires conscientious control of the condition of the expectant mother. This is just the period when a woman can feel false contractions. Painful sensations appear in the upper part of the uterus and gradually subside. With the increase in the duration of pregnancy, contractions become more pronounced. They resemble short muscle contractions lasting from a few seconds to five minutes. Thus, the body prepares for the upcoming birth. This process with varying intensity accompanies the pregnancy of every woman. Experts call it Braxton-Hicks contractions. How can a future mother distinguish labor pains from precursors, especially if she is expecting a baby for the first time?
They resemble short muscle contractions lasting from a few seconds to five minutes. Thus, the body prepares for the upcoming birth. This process with varying intensity accompanies the pregnancy of every woman. Experts call it Braxton-Hicks contractions. How can a future mother distinguish labor pains from precursors, especially if she is expecting a baby for the first time?
Consider the main differences:
- Preparatory contractions are characterized by a high interval between them, which varies in duration. And prenatal contractions are regular, with a gradually decreasing interval.
- Preparatory contractions may stop immediately after rest or a change in the position of the expectant mother's body, and labor gradually intensifies regardless of the change in position.
- Pain is also different. Labor pains are accompanied by severe pains that become more and more noticeable. Preparatory contractions are characterized by either sharp pain, or they can be completely painless.

- False contractions may stop with the use of medically approved antispasmodics. While such drugs will not have any effect on labor pains or it will be minimized.
- A woman can feel false contractions in various places. This may be the lower abdomen, the side walls of the uterus, the entire abdomen. Pain during labor pains can resemble premenstrual pain. Also, pain can begin in the lower back, gradually covering the front of the abdomen.
It is very important for a woman with such symptoms to ensure a sense of security, in case of any contractions, it is necessary to inform the gynecologist of the pregnant woman.
35 weeks pregnant. How does the baby develop?
Every baby reaches their weight and height this week. Approximately, his body weight is approximately 2,300 g, and his height is up to 47 cm. Starting this week, the height and weight of the crumbs will gradually increase by 250 g. But these parameters depend on genetics and individual characteristics of the organism. By this period, the formation of all systems and organs of the baby is already ending, and cardinal changes in the body are not expected. The amount of mucus that covers the baby's skin gradually decreases. The hair fluff practically disappears from the body, and even if it remains, it completely disappears after birth. The body becomes pink, the muscles are stronger, and the shoulders become rounded. The baby already almost completely occupies the uterine cavity, its arms and legs are in a bent state. The baby is already very crowded and the mother can feel his every movement. The baby often changes his facial expression, closing his eyelids and contracting facial muscles. Small nails appear on the fingers. This week, the formation of the genitourinary and nervous system ends. The fact that the bones of the skull have not yet fused will make it easier to pass through the birth canal. It is important during this period to control the number of movements of the baby. For half a day, approximately 10 movements should be recorded.
By this period, the formation of all systems and organs of the baby is already ending, and cardinal changes in the body are not expected. The amount of mucus that covers the baby's skin gradually decreases. The hair fluff practically disappears from the body, and even if it remains, it completely disappears after birth. The body becomes pink, the muscles are stronger, and the shoulders become rounded. The baby already almost completely occupies the uterine cavity, its arms and legs are in a bent state. The baby is already very crowded and the mother can feel his every movement. The baby often changes his facial expression, closing his eyelids and contracting facial muscles. Small nails appear on the fingers. This week, the formation of the genitourinary and nervous system ends. The fact that the bones of the skull have not yet fused will make it easier to pass through the birth canal. It is important during this period to control the number of movements of the baby. For half a day, approximately 10 movements should be recorded. If the movements are much more or less, the mother should consult a doctor.
If the movements are much more or less, the mother should consult a doctor.
How does mother feel?
Mom has difficulty breathing during this period. This is caused by the growing uterus, which pushes the lungs first. The lungs cannot fully expand, making breathing difficult. Also, an enlarged uterus pushes the bladder and intestines aside. This week, almost every pregnant woman feels short of breath, she has shallow and rapid breathing and a constant desire to take a deep breath. The cause of shortness of breath during this period can be a long walk or climbing stairs, as well as a long stay in the supine position. Proper alternation of rest and physical activity will help to alleviate the condition. The bottom of the uterus rises 35 cm from the pubis and 15 cm from the navel, this is the highest point for the entire period of bearing a baby. It feels like one of the hardest weeks of pregnancy. The body of the expectant mother is actively preparing for the upcoming birth, all ligaments become more extensible and elastic. It can also lead to an increased risk of injury and falls. During this period, doctors do not recommend flights and long trips. If you need to go somewhere, the presence of a loved one and a mandatory change of position approximately every 15 minutes is important. Mom needs to rest more often this week. Special physical exercises that will help reduce back pain will be useful.
It can also lead to an increased risk of injury and falls. During this period, doctors do not recommend flights and long trips. If you need to go somewhere, the presence of a loved one and a mandatory change of position approximately every 15 minutes is important. Mom needs to rest more often this week. Special physical exercises that will help reduce back pain will be useful.
36 weeks pregnant. How does the baby develop?
This week the baby begins to actively prepare for the birth. All organs of the baby are already almost completely mature and can function independently. The weight of the baby reaches 2,500 g, and its height is approximately 46 cm. This period is preparatory for the birth of the baby. By the beginning of this week, the baby is already in its final position in the uterus. In the vast majority of cases, it is located facing the back of the mother and head down. This position is the safest during the passage of the birth canal and the most convenient. If there is a breech presentation of the baby, a caesarean section is possible. In this case, it all depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. But this week, it is possible to change the position of the body only from the pelvic to the head, since the baby's head is heavier and this part of the body outweighs. The baby constantly sucks his finger and his cheeks become chubby. The baby also receives oxygen through the umbilical cord and also makes respiratory and swallowing movements. The baby at this time looks the way it is born, and the bones of the skull still remain pliable and soft to facilitate passage through the birth canal.
How does mother feel?
During this period, a pregnant woman feels very tired. The tummy becomes heavier, making it difficult to choose the position of the body. The baby begins to sink lower, preparing for childbirth, and it becomes easier for the mother to breathe. But this increases the pressure on the bladder, causing more frequent urination. The uterus is located at a distance of 36 cm from the pubis. This is the highest point throughout the entire period of pregnancy. The body of the expectant mother is being rebuilt, leading intensive preparation for childbirth. Hormonal changes cause an increase in hormone levels. The pelvic bones soften under the influence of hormones, trying to make it as easy as possible for the baby to pass through the birth canal. At the same time, contractions intensify and more abundant vaginal discharge appears. A pregnant woman needs to listen more to her body this week and carefully monitor it. With pulling pain in the lower abdomen, as well as pain in the lower back, attention should be paid to its duration and frequency. If you have all the indicators, you should immediately contact a gynecologist: premature birth this week is not uncommon, so it is important to respond to body signals in time. Mom should be very careful: do not make sudden movements, control posture, moderate walks and sitting time.
The uterus is located at a distance of 36 cm from the pubis. This is the highest point throughout the entire period of pregnancy. The body of the expectant mother is being rebuilt, leading intensive preparation for childbirth. Hormonal changes cause an increase in hormone levels. The pelvic bones soften under the influence of hormones, trying to make it as easy as possible for the baby to pass through the birth canal. At the same time, contractions intensify and more abundant vaginal discharge appears. A pregnant woman needs to listen more to her body this week and carefully monitor it. With pulling pain in the lower abdomen, as well as pain in the lower back, attention should be paid to its duration and frequency. If you have all the indicators, you should immediately contact a gynecologist: premature birth this week is not uncommon, so it is important to respond to body signals in time. Mom should be very careful: do not make sudden movements, control posture, moderate walks and sitting time. During this period, sleep is disturbed, so the body is also preparing for the night feeding of the baby. This week, mom can fully feel what puffiness is. It is necessary to control edema, which can cause disruption of the organs.
how to cure, causes, symptoms, prevention, doctor's advice, consequences
When you are 35 weeks pregnant, your stomach may hurt for various reasons. This is normal at this time. The stomach is heavy, it causes great inconvenience. You can only sleep on your side, when you try to lie on your back, the insides are squeezed. The child already weighs about 2.5 kg, do not forget to take into account the weight of the uterus, amniotic fluid, placenta. In this case, it is necessary to inform the doctor about pain, as they may indicate a problem.
Contents of the article
Causes of pain:
- Dysfunction of the symphysis pubis . The ligaments soften, stretch, which causes sharp pain in the lower abdominal cavity due to increased pressure on the fetal head in the pubic part of the mother.
 This problem occurs in about half of pregnant women.
This problem occurs in about half of pregnant women. - Braxton Higgs contractions . At the same time, the stomach hurts like during menstruation. These are practice fights. The mother's body is preparing for the process of childbirth. False contractions do not last long, about a minute, and may stop if the woman lies down or takes a bath. If the contractions become more frequent, become more intense, you need to notify the obstetrician, childbirth is likely to begin.
- Priexlampsia . If the pain in the abdominal region is accompanied by dizziness, severe headache, nausea, increased blood pressure, it is urgent to seek medical help. Most likely, this is late toxicosis. This serious condition poses a threat to the life of the child, do not postpone the trip to the hospital.
- Placental abruption . If there is a sharp pain in the lower abdominal cavity and bleeding begins, you need to call an ambulance.
 Such symptoms are characteristic of placental abruption. This can lead to the death of the baby. Only emergency measures will save the pregnancy, or a caesarean section will be performed.
Such symptoms are characteristic of placental abruption. This can lead to the death of the baby. Only emergency measures will save the pregnancy, or a caesarean section will be performed. - Musculoskeletal disorders . In late pregnancy, the center of gravity shifts, while walking, the woman in labor instinctively leans back, which causes pain in the lower back, clicks when moving. Report this to the obstetrician-gynecologist, you may need to use a special bandage.
- The baby can touch the internal organs of the mother with its legs, for example, in a breech presentation.
- Toned uterus . At the same time, the stomach seems to become stony, hardens, which can cause pain in the lower peritoneum. It is recommended to lie down and rest. When the condition returns to normal, you can take a walk in the fresh air. If the tone has not decreased, inform the specialist, hospitalization will be required.
A woman should listen to herself, her condition.