Red hands white spots
What Is It and What Causes It?
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Medically Reviewed by Dan Brennan, MD on April 19, 2021
In this Article
- Symptoms of Palmar Erythema
- What Causes the Redness?
- Primary Palmar Erythema
- Secondary Palmar Erythema
- How is Palmar Erythema Diagnosed?
- How Is Palmar Erythema Treated?
Palmar erythema is a skin condition that makes the palms of your hands turn red. It can be hereditary but can also be the result of a variety of health conditions. It’s also relatively common during pregnancy.
Palmar erythema is also known as liver palms, red palms, or Lane’s disease.
Symptoms of Palmar Erythema
Here are some ways to know if the redness on your palms is palmar erythema:
- It’s symmetrical — that is, the redness appears on both palms.
- The redness is blanchable, meaning if you press on it, it goes away.
- Your palms feel slightly warm.
- It’s not painful and not itchy.
The redness usually involves the lower part of your palm but may extend to your fingers. In some cases, it may extend over the fingertips to the nail beds.
If there is redness on the soles of your feet, that’s called plantar erythema.
What Causes the Redness?
Your palms have turned red because of dilated capillaries, which are the smallest blood vessels in your body. How red your palms get seems to vary with how severe the underlying disease is. Some researchers believe this has to do with increased hormone levels.
Primary Palmar Erythema
Primary palmar erythema can be hereditary or caused by pregnancy, or it can be the result of an unknown factor.
Pregnancy. Pregnancy is a common cause of palmar erythema. It’s estimated that it occurs in about two-thirds of lighter-skinned pregnant women and up to one-third of darker-skinned pregnant women. This may happen because of changes to your blood vessels related to an increase in estrogen production during pregnancy.
Many of the changes to your blood vessels in pregnancy are temporary and disappear soon after you give birth.
Hereditary. Palmar erythema can be inherited, but it is a very rare condition. The redness of the palms can appear at birth or later in life and remain from then on. This may happen to at least two members of the family, but some individual cases have also been reported.
There are no signs of inflammation, allergic reaction, or other health conditions that have been linked to palmar erythema. Only a few cases of hereditary palmar erythema have been discussed in medical literature since it was first described by John E. Lane in 1929.
Unknown origin. In some cases, palmar erythema may be idiopathic. This means that there’s no known cause and you have no other associated health conditions.
Secondary Palmar Erythema
Secondary palmar erythema can be the result of an underlying medical condition, medication, or environmental causes. There is a large variety of possible underlying conditions that can cause it.
There is a large variety of possible underlying conditions that can cause it.
Liver disease. Palmar erythema is associated with several types of liver diseases. About 23% of those with liver cirrhosis have palmar erythema.
Cirrhosis happens when your liver is severely scarred and your healthy liver tissue is being replaced with scar tissue as it tries to repair itself.
Other liver diseases related to palmar erythema include rare liver diseases like Wilson Disease, an inherited disorder in which excessive amounts of copper build up in your body, and hereditary hemochromatosis, in which your body absorbs too much iron from the food you eat.
Babies and young children with liver disease are less likely to have palmar erythema than teenagers and adults.
Autoimmune diseases.Rheumatoid arthritis is a common autoimmune and inflammatory disease that causes painful swelling in the joints and other parts of the body.
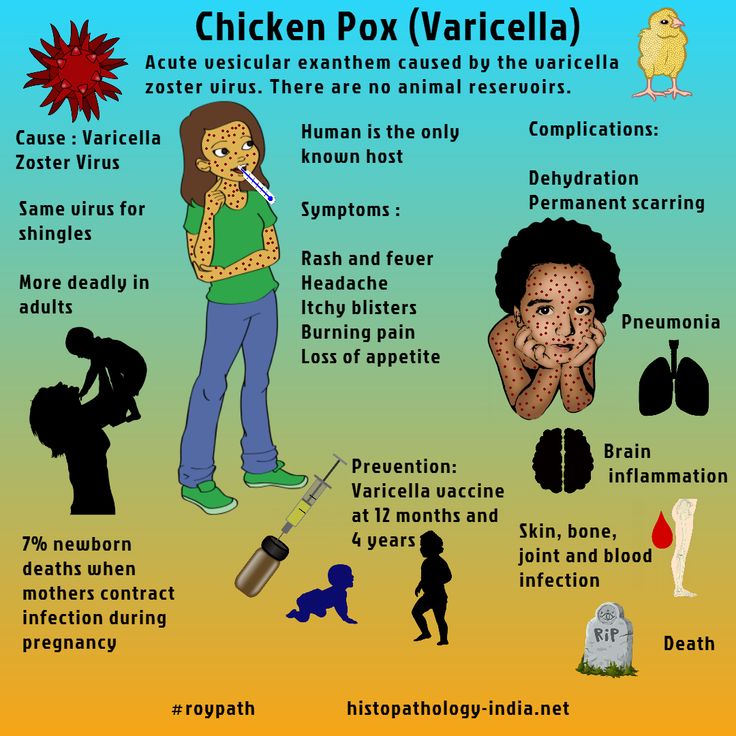
In a study of 152 people with rheumatoid arthritis, 61% were found to have palmar erythema.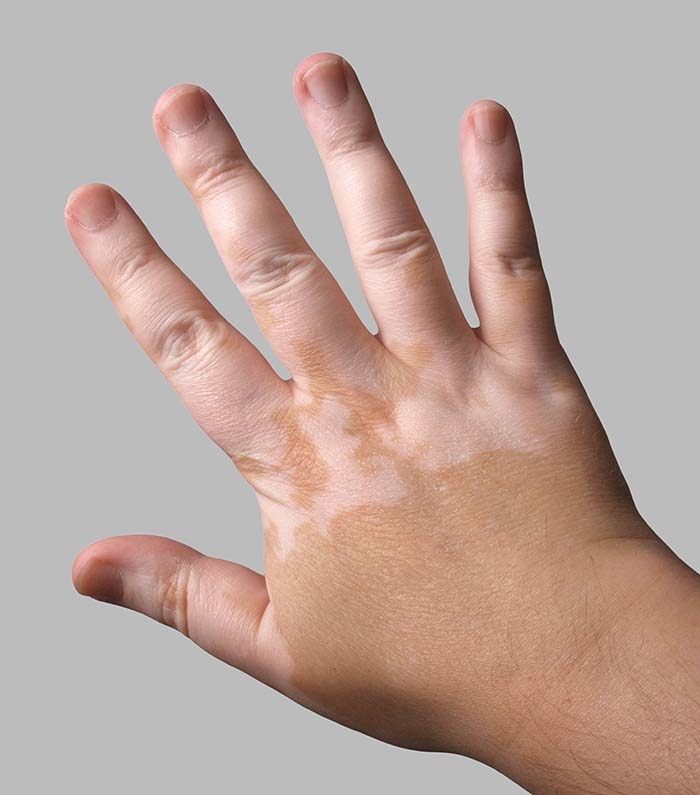 Another study compared patients with rheumatoid arthritis with those who had other internal diseases. Palmar erythema was significantly higher in those with rheumatoid arthritis.
Another study compared patients with rheumatoid arthritis with those who had other internal diseases. Palmar erythema was significantly higher in those with rheumatoid arthritis.
Other conditions that have been associated with palmar erythema include:
Diabetes. People with diabetes tend to get skin infections, and their wounds also heal slower. An estimated 4.1% of people with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes mellitus have palmar erythema.
Thyroid disease. Palmar erythema affects up to 18% of those with thyrotoxicosis, which is when you have too much thyroid hormones in your blood.
Brain tumors. In a study of 107 people with brain tumours, 25% were found to have palmar erythema. The intensity of the redness depended on the type of tumor and its growth.
HIV. There has been one reported case of palmar erythema linked to HIV.
Medications. Some medications may cause palmar erythema. For example, if you take topiramate for treatment of paranoid schizophrenia. In a rare case, a pregnant woman given albuterol to prevent premature labor developed palmar erythema.
For example, if you take topiramate for treatment of paranoid schizophrenia. In a rare case, a pregnant woman given albuterol to prevent premature labor developed palmar erythema.
Other medications that may be linked to palmar erythema include amiodarone, gemfibrozil, and cholestyramine.
Environmental causes. Smoking, alcoholism, and mercury poisoning are some environmental causes of palmar erythema.
There are a few other possible conditions that researchers say may be associated with palmar erythema. These include:
Skin conditions. A recent case of palmar erythema in a three-year-old boy with no other problems had doctors puzzled until they learned that he had been using hand sanitizer every 20 to 30 minutes throughout the day. They determined that it was an unusual presentation of contact dermatitis.
COVID-19. Skin rashes have appeared in some people with COVID-19. In one case of a woman who tested positive for Covid-19, palmar erythema was the only symptom. She didn’t have other typical COVID-19 symptoms, nor did she have other health conditions related to palmar erythema.
She didn’t have other typical COVID-19 symptoms, nor did she have other health conditions related to palmar erythema.
How is Palmar Erythema Diagnosed?
Your doctor will be able to diagnose palmar erythema by inspecting your palms, but they’ll also review your medical history and perform a physical exam.
As there are many possible underlying disorders that can result in the redness of your palms, your doctor may order one or more diagnostic tests. These include tests that measure:
- Liver function
- Blood urea nitrogen or creatinine
- Complete blood count
- Fasting glucose levels
- Iron levels
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis B
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone
Other tests may include:
- Bone marrow biopsy
- Chest X-ray
- CT scan of chest, abdomen, and/or pelvis
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain
- Tests for antibodies
How Is Palmar Erythema Treated?
There’s no standard treatment for palmar erythema. If you have an underlying condition causing the palmar erythema, your doctor will work to treat it. If the cause is related to a medication, it’s advisable to stop it or change to a different class of drug.
If you have an underlying condition causing the palmar erythema, your doctor will work to treat it. If the cause is related to a medication, it’s advisable to stop it or change to a different class of drug.
Palmar erythema: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
Palmar erythema is a rare condition that makes the palms of the hands turn red. There are a few different causes for the condition, such as pregnancy and liver cirrhosis.
Anyone experiencing the symptoms of palmar erythema should contact their doctor for diagnosis and treatment of any underlying conditions.
Share on PinterestPalmar erythema causes red palms, which may feel slightly warm.Palmar erythema, often called liver palms, is reddening in both of the palms. Reddening typically occurs on the lower part of the palm (the heel), but sometimes it may extend all the way up through the fingers. Redness may also show up on the soles of the feet, but this is called plantar erythema.
The redness may resemble a rash, and the skin will turn pale when pressed.
The degree of redness may vary depending on several factors, such as a person’s body temperature, physical activity, and even their emotional state.
Palmar erythema is not a harmful condition. It can be a primary condition with no underlying cause, but it is usually caused by another medical condition. These underlying conditions may be harmful if they are left untreated.
The redness in the palms is caused by dilated capillaries in the hand, which draw more blood to the surface. Many doctors think palmar erythema is linked to hormone changes.
There are a variety of causes and underlying risk factors that may contribute to palmar erythema, and they vary based on the type of erythema.
Primary palmar erythema
Primary palmar erythema is a physical symptom that is not caused by another condition. There are a few risk factors for developing the condition.
Pregnancy is a very common cause of primary palmar erythema. A pregnant woman’s body goes through hormonal changes during pregnancy, causing estrogen levels to rise.
Higher estrogen levels may increase the likelihood of developing palmar erythema. This rise in estrogen is temporary, so redness in the palms will likely disappear after the pregnancy.
In rare cases, genetics may contribute to primary palmar erythema. People who have family members with palmar erythema may be more likely to get the condition themselves.
Palmar erythema may also be idiopathic. This means that there is no known cause and that doctors cannot find any underlying trigger for the symptom.
Secondary palmar erythema
Share on PinterestPalmer erythema may be the first obvious symptom of a medical condition.
As a secondary symptom, palmar erythema is linked to many different conditions and is often the first sign of a medical problem.
Palmar erythema is commonly associated with liver diseases, such as liver cirrhosis, hemochromatosis, and Wilson disease.
Some liver conditions are hereditary, while others may be influenced by diet and lifestyle choices, such as drinking alcohol.
Depending on a person’s liver function, some medications may also cause palmar erythema. During diagnosis, a doctor will often ask about any medicines a person is taking to see if the condition is a side effect of any particular drug.
Other conditions may cause the redness in the palms. These include:
- thyrotoxicosis
- autoimmune conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and HIV
- endocrine conditions, including diabetes
- hepatitis C
- skin conditions, such as atopic dermatitis or eczema
- viral or bacterial infections
- smoking
- metastatic brain cancer
- chronic obstructive lung disease
When palmar erythema shows up in children, it may be linked to different conditions. The most common of these conditions include:
- congenital syphilis
- Wilson disease
- poisoning
- hepatopulmonary hypertension
- Kawasaki disease
Children may also develop palmar erythema due to a genetic predisposition. Symptoms
Symptoms
Palmar erythema is characterized by redness of the palms of the hands. This redness appears on both hands and is not painful or itchy.
Some people may notice that their hands feel slightly warmer but are not irritated or swollen. The condition may spread to the fingers but will not spread to anywhere else on the body.
Other symptoms may show up in the body depending on the underlying condition, but palmar erythema typically causes no additional symptoms.
Share on PinterestIn some cases, MRI or CT scans may be required to diagnose an underlying condition.
Doctors can easily diagnose palmar erythema by inspecting the palms. However, doctors will also perform a thorough examination to determine if there is anything else causing the condition.
To help them with their diagnosis, a doctor will review the person’s medical history and may ask if the symptom has shown up in any blood relatives.
Doctors will typically order one or more tests to help confirm their diagnosis. This can include tests that measure:
This can include tests that measure:
- liver function
- fasting glucose levels
- total blood cell count
- the presence of hepatitis B or C
- thyroid function
- iron or copper levels
- blood urea nitrogen
- blood creatine levels
- levels of various antibodies
Depending on the suspected cause of palmar erythema, a doctor may also order imaging tests, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In some cases, they may order a bone marrow biopsy.
If initial testing does not verify a doctor’s diagnosis, a person may have to return for additional testing. This is important to help identify any underlying issues that could pose significant health risks.
Doctors will typically only conclude that palmar erythema is idiopathic if they have tested all other possibilities.
There is no specific treatment to cure red palms caused by palmar erythema. Treatment involves finding and addressing the underlying cause of the condition. Once the underlying cause is treated, the redness in the palms may go away partially or entirely.
Once the underlying cause is treated, the redness in the palms may go away partially or entirely.
If the redness is a side effect of a medication, doctors may recommend alternative medications. Changing or stopping medications should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Palmar erythema is redness in the palms that may also be a sign of an underlying condition. Anyone with unexplained redness in the palms should contact their doctor for diagnosis and treatment to avoid any complications.
Accurately diagnosing the underlying cause of palmar erythema is crucial but may take some time. Treating the underlying cause of palmar erythema will often reduce symptoms.
In cases where palmar erythema has no underlying cause, symptoms may be persistent but are harmless. It is always good to check in with a doctor periodically if palmar erythema is long-term.
Spots on the skin: red and white spots on the skin - how to treat dark pigment spots
On the skin of any person, you can see spots, wrinkles, scars, and often all kinds of rashes. These spots, nodules and vesicles are called morphological elements of the epidermis. They can not only tell about the condition of the skin, but also indicate the problems of the whole organism.
These spots, nodules and vesicles are called morphological elements of the epidermis. They can not only tell about the condition of the skin, but also indicate the problems of the whole organism.
Brown spots on the skin often worsen the appearance and upset their owners for quite a long time (sometimes permanently), although sometimes they disappear without a trace. What is it and what types of spots on the skin are there?
A spot is an area of skin with a change in color. Only the color of the skin changes, while the density and relief remain the same. In dermatology, spots are usually referred to as primary morphological elements, i.e., rashes that occur on intact and intact skin of the face and body, the red border of the lips, and the oral mucosa.
Spots are divided into congenital and acquired , vascular and pigmented , hypo- and hyperpigmented . Their appearance is usually associated with a change in the content of melanin in the skin, sometimes with other pigments and dyes. What are these pigments?
Melanins are dark brown and black spots on the skin that are found in the skin, hair, and retina of the eye. Melanin is produced by melanocytes - epithelial cells located in the basal layer of the epidermis. The more melanin in the skin, the darker it is. All of us, brunettes and blondes, differ in skin, hair and eye color, primarily due to melanin. This pigment is usually (but not always) distributed fairly evenly throughout the skin.
In the spring, with the first rays of the sun, a light tan appears on the skin with normal melanin content. And in areas of skin with a high content of melanin (or its predecessor, promelanin), reddish-brown spots, freckles, appear. They usually appear in red-haired and blond people.
Should I fight freckles? Everyone decides for himself. If necessary, you can use sunscreens: SPF-30, SPF-22, SPF-15, SPF-8 and cosmetics with whitening properties. And if they want to use folk remedies to whiten freckles, then you need to find a cucumber seed, pour vodka (1:10), insist for two weeks, strain, dilute with water before drinking (1:10) and wipe your face daily until the freckles disappear under the influence of tincture. I think that using our cosmetics is still more convenient and effective: SORBENT-PEELING mask WITH GREEN TEA, WHITENING SERUM, ALBINA day cream. Well, quickly and effectively level the complexion of our PLASTICIZING masks.
I think that using our cosmetics is still more convenient and effective: SORBENT-PEELING mask WITH GREEN TEA, WHITENING SERUM, ALBINA day cream. Well, quickly and effectively level the complexion of our PLASTICIZING masks.
Now another example of hyperpigmented patches is chloasma. These are large areas of yellowish-brown pigmentation on the skin of the face. Chloasma occurs when there is an excess of melanin in the skin. But melanin can accumulate in all tissues of the body (the so-called melanosis).
Everyone knows pregnancy chloasma (pregnancy spots) - hyperpigmentation that develops during childbearing and slowly disappears after childbirth. Chloasma can also appear in non-pregnant, healthy women as a result of minor hormonal imbalances, as well as when using hormonal contraceptives. All this points to the great role of the endocrine system in the regulation of the formation of melanin and, consequently, in the development of age spots.
But chloasma can also occur in young men who use scented soaps, some lotions and other perfumes after shaving. What is it - the undesirable effect of impurities, fragrances, other chemical components of this cosmetics and perfumery? Or just a reaction of the skin, which after shaving becomes vulnerable to extraneous influences? Therefore, it is very important that the AFTER SHAVING gel recommended by us not only does not irritate the skin, but also soothes it, removes the tendency to inflammation.
What is it - the undesirable effect of impurities, fragrances, other chemical components of this cosmetics and perfumery? Or just a reaction of the skin, which after shaving becomes vulnerable to extraneous influences? Therefore, it is very important that the AFTER SHAVING gel recommended by us not only does not irritate the skin, but also soothes it, removes the tendency to inflammation.
Among the recommendations for the prevention of age spots are the following: protect areas with age spots from the sun, avoid irritating influences (washcloths, pumice stone, abrasive cleaners, some types of soap). The literature describes cases when creams for removing freckles caused a backlash - increased pigmentation. This has never happened with our products. Nevertheless, the discoloration of age spots is a long process. Here you need to be patient. If they want to remove age spots on the skin quickly, dermatologists can burn them out with an electric needle, phenol or trichloroacetic acid, freeze them with liquid nitrogen, there are a great many ways to do this.
Another pigment, hemosiderin, is an iron-containing pigment with a deep dark yellow color. It is formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin or with intensive absorption of iron in the intestine. With an excess of iron in the body, hemosiderin is deposited not only in the internal organs, but also in the epidermis. Then gray-brown or brown spots appear on the skin (open parts of the body, armpits, genitals and old scars). In older people, these dark spots on the skin are often combined with local subcutaneous hemorrhages and are located in large areas (the so-called senile hemosiderosis). Treatment of patients with hemosiderosis is the work of a specialist doctor. When the disease develops, the liver, lungs, and pancreas suffer. Therefore, when carrying out recreational activities, bioadditives MIRANDA-1, MIRANDA-3, MIRADOL, MIRRASIL-1, MIRRASIL-3 can be used.
Lipofuscin is a pigment scattered in the form of yellow-brown lumps in the cytoplasm of cells of all organs and tissues. The level of lipofuscin increases with aging, with debilitating diseases. It is surprising that this most interesting pigment in cosmetology has not yet received sufficient attention.
The level of lipofuscin increases with aging, with debilitating diseases. It is surprising that this most interesting pigment in cosmetology has not yet received sufficient attention.
Meanwhile, one should not think that you and I are one thing, and lipofuscin is something completely different, which has nothing to do with us. Try eating heavy, fatty foods for a while. Or stay in conditions conducive to excessive intake of various “pollutants” into the body. And soon, especially if you are no longer young, yellow or brown lipofuscin spots will appear on your skin. Lipofuscin is a wear pigment, an aging pigment. A pigment, the accumulation of which directly indicates the slagging of the body.
Now imagine that you have a potential client in front of you who has a lot of these spots. Why there are so many of them, he most likely never thought about it. How to attract this client to the use of our health products? Say he might get sick? People usually are not afraid of diseases or are afraid of them only theoretically, and therefore they are not interested in either their state of health or a healthy lifestyle, much less preventive or health-improving measures.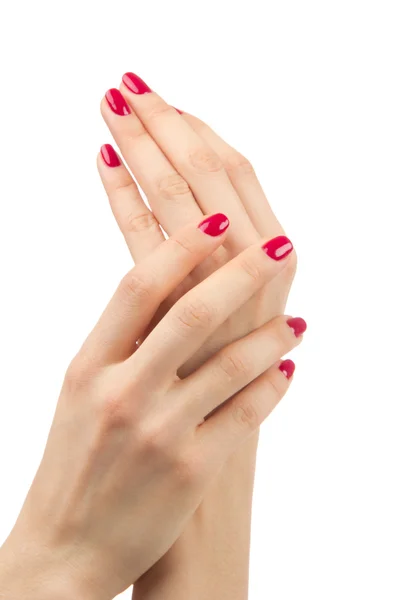
Old age is what people really fear! And the unfavorable condition of the skin in general and lipofuscin "wear spots" in particular are a clear, visible, undoubted sign of accelerated aging of the body.
"Spots of aging" are usually located on the body. Most of them are on the chest, stomach, arms, décolleté and face. It is not difficult to see lipofuscin spots, you just have to take a closer look... This is the subject for a conversation with the client - about the slagging of the body, the need for a health course, the expediency of a sufficiently long and complex use of dietary supplements and other health products of the company.
If a person is interested in the condition of their skin, then it is necessary to explain that the skin is not always “guilty”. Cleansing and drainage measures are needed. Perhaps something is wrong with the liver, with the intestines. Signs of incomplete well-being of the liver are well known - bitterness in the mouth, heaviness in the right hypochondrium, discomfort after fatty foods. Let there be no pronounced pathological changes yet, but the liver is no longer fully able to cope with its cleansing functions. And one of the confirmations of this is skin manifestations (spots, pinpoint hemorrhages).
Let there be no pronounced pathological changes yet, but the liver is no longer fully able to cope with its cleansing functions. And one of the confirmations of this is skin manifestations (spots, pinpoint hemorrhages).
Since the slagging of the body is usually the result of a “defect” of the liver, a course of taking dietary supplements with milk thistle, in particular MIRRASIL-1, is needed. It is rare for any woman to not see dilated superficial veins on the skin. Most often, these are small, initial manifestations of varicose veins. Here, apparently, it is better to start with the dietary supplement MIRRASIL-2, which contains not only milk thistle oil (hepatoprotector), but also a rosehip multivitamin complex, which has an excellent effect on the state of the blood vessel wall.
MIRRASIL-3 can be recommended for concomitant heart problems, with a tendency to high blood pressure. The composition of this dietary supplement, in addition to milk thistle, includes bioactive substances of hawthorn and hops.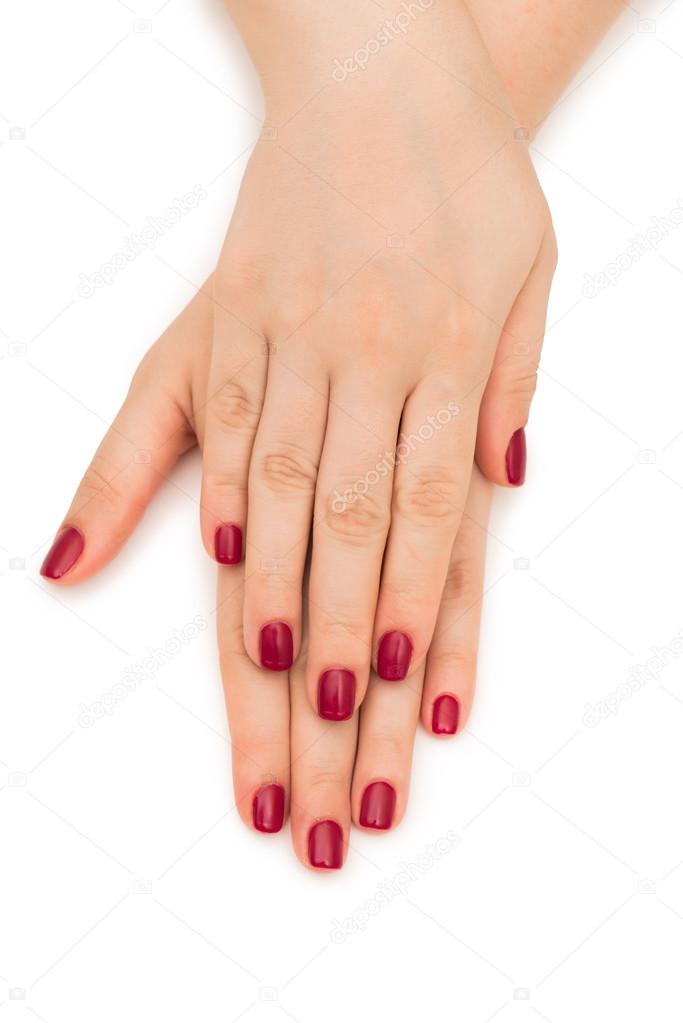 There are many cases when taking this dietary supplement led to the normalization of blood pressure.
There are many cases when taking this dietary supplement led to the normalization of blood pressure.
Schemes for taking bioadditives of the MIRRASIL series can be different depending on the severity of certain disorders, the individual characteristics of the client. In my practice, I recommend taking two capsules twice a day for 20 days. After a week break, the course is repeated.
It is good to combine the intake of one of the MIRRASIL series dietary supplements or the MIRANDA-1 supplement with other supplements - MIRRA-YOD, MIRADOL. Two additives of the MIRRASIL series should not be recommended at the same time.
The client may have symptoms that indicate a bowel problem. This is bloating after eating, grumbling, discomfort, constipation. Then it is better to start the course with the MIRANDA-4 supplement, use other supplements (MIRRA-YOD, MIRANDA-1).
In addition to internal agents - bioadditives, external agents are also needed. After all, slags linger in the skin not only because of the “flaws” of the liver or intestines, but also because the metabolism is disturbed in the skin itself. A bath course is useful here (WELLNESS SPA-complex, DERMATOLOGICAL SPA-complex), which is best carried out together with the intake of dietary supplements.
A bath course is useful here (WELLNESS SPA-complex, DERMATOLOGICAL SPA-complex), which is best carried out together with the intake of dietary supplements.
Yellow-brown lipofuscin spots usually appear on dry, aging skin. Hence the recommendations for the use of our cosmetics. Look at the programs for the use of products for dry skin care, for the care of fading, aging skin. Recommend our moisturizers for blemish areas, especially on the face, hands and décolleté. Try FOOT CREAM, REPAIRING balm and REVENTON. These cosmeceuticals improve microcirculation and metabolism in skin tissues. Naturally, you should not forget about other means: SORBENT-PEELING mask WITH GREEN TEA, WHITENING SERUM, ALBINA day cream.
Another important point. We must not forget that the spots in question are dynamic and reversible. If liver function improves, metabolism normalizes, including in the skin, these spots may become less colored or disappear altogether. Most of our clients are middle-aged or transitional people. At this time, many more disorders in the body are functional, incomplete. Much more can be influenced. And it's a sin not to use it.
At this time, many more disorders in the body are functional, incomplete. Much more can be influenced. And it's a sin not to use it.
Now about vascular, congenital, hypochromic and other age spots.
How can we treat vitiligo, eczema, psoriasis with our cosmetics? What to do if white spots appear on the skin? How to smear it, what supplements to take orally? These and similar questions continue to come in from distributors and customers. Apparently, it is worth continuing the conversation about the skin and related problems.
Above it was said about the pigments - melanin, lipofuscin, hemosiderin, which give the skin one or another shade (color). The color of the so-called acquired spots - freckles, chloasma - also depends on these pigments.
But spots can also be congenital - these are well-known nevi or moles. Nevi are intensely colored (hyperpigmented) red, burgundy, brown spots on the skin that can have different sizes and shapes. Sometimes nevi are very noticeable, especially if these spots are located on the face.
Most birthmarks do not change over the years and do not pose any danger. Nevuses are very different in their structure. Sometimes you can see a pigmented hair nevus - a birthmark with excess hair growth on it. For a warty nevus, characteristic growths are characteristic. A vascular nevus (or hemangioma), which is red spots on the skin, is already a tumor, usually benign.
How to treat skin spots, namely nevi, with the products of our company? But no way. The correct advice is not to touch birthmarks, this is not our business with you. Let cosmetologists deal with nevi. But, if the spots become “active” (their size or color changes, any unusual sensations or bleeding appear), you should immediately contact a dermatologist. And already the specialist will decide on the presence or absence of tumor growth, on the need to remove the spot, on surgical and other types of treatment.
Unlike nevi, in depigmented spots, the content of melanin is reduced, and sometimes this pigment is completely absent.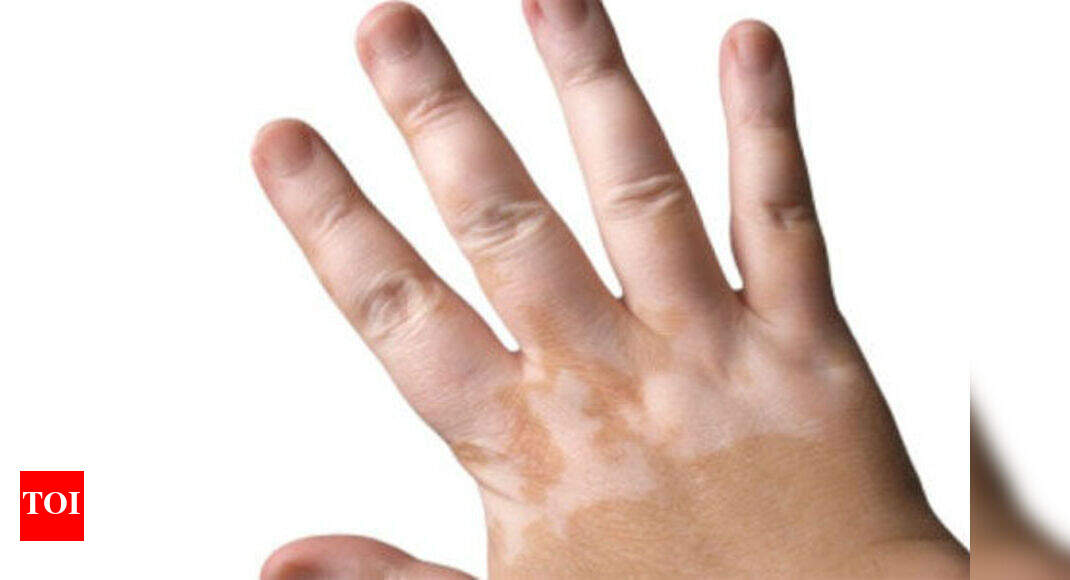 Typically, such spots are areas of white skin, of various sizes and shapes, with a hyperpigmentation zone surrounding them. These white patches on the skin tend to increase, which is very worrying for their owners. This is what vitiligo looks like.
Typically, such spots are areas of white skin, of various sizes and shapes, with a hyperpigmentation zone surrounding them. These white patches on the skin tend to increase, which is very worrying for their owners. This is what vitiligo looks like.
Vitiligo is a very common disease (occurs on average in one in every hundred people). Vitiligo is classified as idiopathic dyschromia. Translated into ordinary language, this means "a violation of the color of the skin for unknown reasons."
Vitiligo is called a mysterious and unpredictable disease. Indeed, it is often impossible to determine the cause of rapid (but less often gradual) skin discoloration. The disease can begin as a result of a stressful situation, after intense sunburn, and often without any apparent reason. Spots usually appear in exposed areas, but they can appear anywhere on the body. Sometimes one family member is sick, but sometimes the whole family is sick. In half of the cases, the first symptoms of the disease appear in childhood and adolescence, but the disease can begin at any age.
The prognosis for vitiligo is often unfavorable - the disease progresses, it can reach partial albinism. This term refers to the discoloration of the skin (and hair) on a significant part of the body. Albinism is also called a congenital disease, which is manifested by a complete or partial absence of skin and hair pigmentation. As for vitiligo, a temporary improvement occurs in no more than 20% of patients.
For the treatment of vitiligo, modern medicine offers skin irradiation with ultraviolet light (solar and UV radiation). In addition, medications are used to increase the sensitivity of the skin to UV rays. Irradiation of areas of the skin affected by vitiligo can give a favorable result, but exposure to sunlight on undamaged areas of the skin can provoke the onset of discoloration in these areas as well.
Some "light at the end of the tunnel" regarding the prevention and treatment of vitiligo has appeared only very recently. During mass examinations of the population for the content of vital bioelements (trace elements) in the body, it was found that the development of vitiligo is often associated with a lack of copper in the body (A. V. Skalny, I. A. Rudakov, 2004). The mechanism of influence of copper deficiency on the condition of the skin is also known. The fact is that the amino acid tyrosine, which is very necessary for the body, is converted into the pigment melanin under the action of the enzyme tyrosinase. Copper is necessary for the activation of this enzyme. Roughly speaking, little copper - little melanin.
V. Skalny, I. A. Rudakov, 2004). The mechanism of influence of copper deficiency on the condition of the skin is also known. The fact is that the amino acid tyrosine, which is very necessary for the body, is converted into the pigment melanin under the action of the enzyme tyrosinase. Copper is necessary for the activation of this enzyme. Roughly speaking, little copper - little melanin.
These studies have allowed for a more meaningful approach to the etiology (causes) and treatment of vitiligo. Recently, I have been sending patients with vitiligo for a bioelemental analysis (the level of copper in the body is judged by the content of this bioelement in the hair, blood or urine). As for the causes of copper deficiency, among them are insufficient intake of copper from outside, long-term use of certain drugs (corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics), impaired copper metabolism in the body.
If it's only a matter of insufficient intake of copper from food, you need to increase the amount of foods rich in copper in the diet: seafood, carrots, cabbage, spinach, chocolate, it's also good to remember the healthy and almost forgotten drink - cocoa.
If copper deficiency has developed as a result of prolonged use of antibiotics or other drugs with severe side effects, then you should try to avoid such situations in the future, consult an experienced doctor, and in no case self-medicate.
If the progression of the disease is associated with a disorder of copper metabolism in the body, then the problem is more complicated, because the normal functioning of many organs and systems depends on this bioelement. In addition, a vicious circle often occurs in the body - a deficiency of a factor (for example, a bioelement) leads to a deterioration in any function (for example, inhibition of hematopoiesis) and vice versa.
This, in particular, explains the different frequency of relapses of vitiligo in different people (in "generally healthier people" - relapses less often, in "generally less healthy people" - relapses more often). All this is understandable from the standpoint of common sense.
Therefore, returning to the question of whether our products can be used to treat vitiligo, the answer should be: it is possible, of course, it is possible. You just need to keep in mind that this is a non-drug treatment, that treatment means helping the body with our health-improving means, which enhance energy, have a drainage effect, and improve the functioning of organs. It is imperative to find out which systems and organs, along with the skin, are the weak link and suffer the most in a person with copper-deficient vitiligo.
You just need to keep in mind that this is a non-drug treatment, that treatment means helping the body with our health-improving means, which enhance energy, have a drainage effect, and improve the functioning of organs. It is imperative to find out which systems and organs, along with the skin, are the weak link and suffer the most in a person with copper-deficient vitiligo.
First of all, with a lack of copper in the body, the work of the heart and the state of blood vessels worsens, lipid metabolism is disturbed. All this leads to an increased risk of developing coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis, and obesity. Therefore, persons suffering from vitiligo, for prophylactic purposes and with the initial signs of the listed diseases, should be recommended course intake of dietary supplements MIRANDA-2, MIRRASIL-2, all means of programs for overweight, etc. It must also be remembered that vitiligo and often associated with this disease predisposition to bronchial asthma and other manifestations of allergies are the consequences of the same cause. Finally, vitiligo often occurs against the background of a decrease in antioxidant protection, suppression of immunity and accelerated aging of the body.
Finally, vitiligo often occurs against the background of a decrease in antioxidant protection, suppression of immunity and accelerated aging of the body.
Cases of significant copper deficiency in the body of patients and rapidly progressing diseases require, of course, the intervention of a doctor. But even in these cases, general health measures, procedures and non-drug support for the body are necessary. And our products meet these challenges in the best possible way.
L. Conde, doctor of the highest category, Ph.D.
*When using the materials of the article, a hyperlink to the source is required.
What do white spots on the face mean?
Many people at some point in their life may develop white spots of varying sizes on their face, arms or chest. Below are the top 5 causes of white spots on the face.
- Milia
Milia are small, round, hard white dots on the face that are often mistaken for whiteheads. They develop when the protein keratin found in the top layer of the skin and other components of dead skin cells build up under the surface of the skin. The most common areas for milia to appear are around the eyes, cheeks, and nose. Milia can be noted in all age groups in both men and women. It is also common among very young children and is then called milk spots.
They develop when the protein keratin found in the top layer of the skin and other components of dead skin cells build up under the surface of the skin. The most common areas for milia to appear are around the eyes, cheeks, and nose. Milia can be noted in all age groups in both men and women. It is also common among very young children and is then called milk spots.
Milia can be caused by an allergic reaction to face cream or sun damage.
A person usually gets better without treatment within a few weeks. Dermatologists recommend not squeezing or punching rashes at home. Changing the face cream or other products that may have caused the allergic reaction may help.
If the condition does not improve on its own, a doctor or dermatologist can treat milia in a variety of ways: opening the capsules (to extract keratin with a medical needle), applying a retinoid cream (on the face, but not around the eyes), microdermabrasion (a procedure that removes the most upper layers of the affected area).
- Seborrheic eczema
The disease looks like pale pink or red scaly inflammations on the skin. They often appear on the face and hands. Seborrheic eczema is more noticeable in dark-skinned individuals or after sun exposure. The condition is mainly noted in children and adolescents. The causes of the disease are unknown.
Spots usually disappear within a few months, but may last up to several years. There is no specific treatment for seborrheic eczema, but a doctor can treat any symptoms of itching or discomfort with steroid or nonsteroidal creams, as well as treat dry skin.
- Vitiligo
Vitiligo appears as spots on the skin that have lost their color pigment. They can appear anywhere, including the face. The disease occurs in about 1% of people worldwide. White spots can be small and remain so, and sometimes gradually increase and cover almost the entire body. Vitiligo can occur at any age, but about half of people develop the disease before age 20.
Heredity is a risk factor for the development of the disease. Vitiligo occurs in people with various skin tones, but is most noticeable on dark skin. The disease is not contagious. Some scientists believe that vitiligo patches develop when the body produces an antibody against melanin and breaks it down.
There are several possible treatments for vitiligo. The choice of method depends on the severity of the condition. Individuals with vitiligo should always wear sunscreen and avoid sun exposure as the affected skin will burn more easily. You can also use special creams to hide the difference in skin color. Your doctor may recommend anti-inflammatory creams, such as corticosteroids. However, long-term use of corticosteroids can cause unwanted side effects, such as thinning of the skin, so doctors may prescribe other types of anti-inflammatory creams.
Vitiligo is sometimes treated with artificial ultraviolet (UV) light therapy or phototherapy, often for several months. Laser treatment can also be used to treat certain areas of the skin. Surgical therapy has been developed, but is not yet a common practice.
Laser treatment can also be used to treat certain areas of the skin. Surgical therapy has been developed, but is not yet a common practice.
- Pityriasis versicolor ( Pityriasis versicolor)
Pityriasis versicolor is a common disease caused by a yeast infection. In this case, spots of various shades of any localization appear on the skin and are accompanied by dry skin and itching. Sometimes the spots are small, and sometimes they become noticeable only when the skin is tanned. Pityriasis multicolor is more common in adolescents and young adults, and is more common in the tropics and subtropical regions. In temperate climates, discolored patches may disappear during the cooler months.
More than 90% of adults have a yeast called Malassezia on their skin. This is a natural phenomenon and usually does not cause any problems. However, sometimes they provoke the development of multi-colored lichen. This may be due to several factors such as:
This may be due to several factors such as:
- hot and humid weather;
- oily skin;
- weak immune system;
- hormonal changes.
Pityriasis versicolor can occur during pregnancy but is not dangerous.
There are many different ways to successfully treat tinea versicolor with antifungal creams and lotions, cleansers, and antifungal tablets.
- Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis, also known as white sunspots, is characterized by the appearance of flat white spots 1 to 10 mm in diameter. These spots can occur on the face, arms, upper back, and lower legs. Although they most commonly develop in fair-skinned individuals, they can also occur in dark-skinned individuals.
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis occurs due to prolonged exposure to the sun on the skin. This skin condition appears more often in people over the age of 40, which may be due to the fact that the disease takes a long time to develop.