Red dot rash on stomach
Pictures, causes, treatment, and when to seek help
A person may notice pinpoint red dots on their skin for a number of reasons, ranging from allergic reactions to heat exposure.
Many causes of red dots on the skin are harmless and resolve on their own. Others may require at-home or over-the-counter (OTC) treatment.
In this article, we discuss some of the possible causes of red dots on the skin, their treatment options, and when to contact a doctor.
Skin rashes come in a variety of sizes, colors, and textures.
Not all rashes require emergency medical treatment. However, people should seek immediate medical attention if they have a rash and notice any of the following symptoms:
- a rash that covers the entire body
- fever
- blisters or open wounds
- difficulty breathing, speaking, or swallowing
- swelling of the face, eyes, or lips
- stiff neck
- light sensitivity
- seizures
- drowsiness or unresponsiveness
People should also seek immediate attention for any new rashes that are painful and that affect the eyes, inside of the mouth, or genitalia.
When in doubt, a person should seek the opinion of a primary care provider or board-certified dermatologist.
Heat rash, or miliaria, occurs when the sweat glands become blocked, trapping sweat in the deep layers of the skin.
While anyone can have heat rash, this condition is most common among infants and young children with immature sweat glands.
Symptoms of heat rash include:
- clusters of small red bumps called papules
- firm, flesh-colored bumps
- itchy or prickly sensation
- mild or absent sweating in the affected area
- inflammation and soreness
- dizziness
- nausea
Treatment
Heat rash usually goes away within 24 hours.
Treatment typically involves using lotions to soothe the itching, irritation, and swelling.
People can also keep the skin cool and avoid tight-fitting clothing.
Learn more about the treatment options for heat rash here.
Keratosis pilaris (KP) is a common skin condition that causes tiny red, white, or flesh-colored bumps on the skin.
It most often affects the outer parts of the upper arms. It can also affect the forearms and upper back, but this is less common.
Symptoms of KP include:
- skin that feels rough or dry
- patches of small, painless bumps on the skin
- itching
Treatment
People can treat the symptoms of KP with:
- moisturizers containing urea or lactic acid
- alpha hydroxy acid
- glycolic acid
- lactic acid
- retinoids
- salicylic acid
- laser or light therapy
Learn more about home management for KP here.
Contact dermatitis occurs when a person comes into contact with a substance that irritates their skin or triggers an allergic reaction.
Contact dermatitis symptoms vary depending on the trigger and the severity of the reaction.
Symptoms of contact dermatitis include:
- a rash that appears in geometric patterns or shapes
- dry skin that flakes and cracks
- a bright, flushed skin rash
- clusters of small red dots on the skin
- hives, or extremely itchy welts on the skin
- intense itching, tightness, or burning sensation
- fluid-filled blisters that ooze and crust over
- dark, thickened skin
- sensitivity to sunlight
Learn more about contact dermatitis here.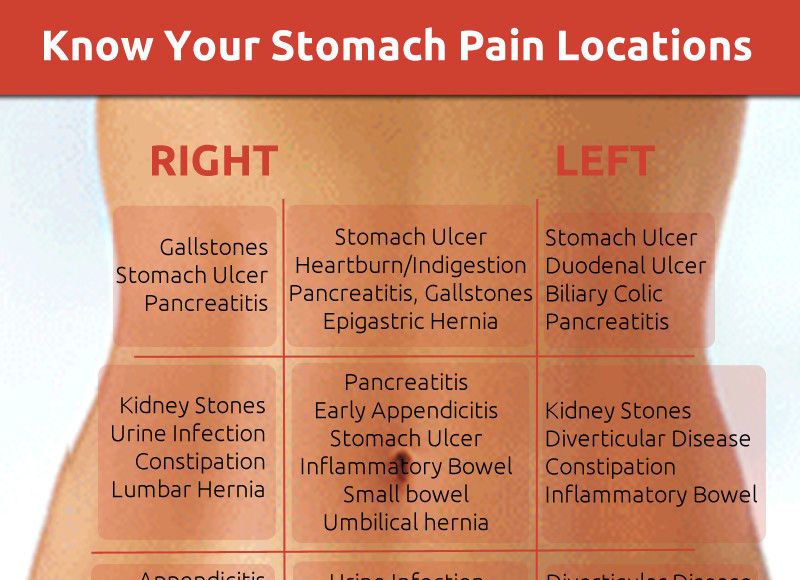
Treatment
Treatment for contact dermatitis depends on the cause and severity of a person’s symptoms.
Mild to moderate symptoms improve when a person avoids contact with the irritant or allergen. If possible, people should:
- avoid skin care products that contain harsh or irritating chemicals
- avoid nickel- or gold-plated jewelry
- avoid foods or medicines that cause allergic reactions
- wear protective clothing in work environments or areas with poisonous plants
If the dermatitis is limited to a small area, a person can apply 1% hydrocortisone cream.
A doctor can prescribe stronger topical or oral antihistamines for people who do not respond to OTC medication.
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition.
There are many different types of eczema, including:
- Follicular eczema: This type of eczema affects the hair follicles.
- Papular eczema: This presents as small red bumps on the skin that healthcare professionals refer to as papules.

Alongside red bumps on the skin, eczema can cause:
- extremely itchy skin
- warmth and swelling of the skin
- dry, flaky skin
- clusters of small, fluid-filled blisters
- blisters that leak fluid and crust over
Treatment
People can manage atopic dermatitis symptoms and even prevent flare-ups with the following treatments:
- taking prescription medications, such as steroids and antihistamines
- undergoing phototherapy or light therapy
- applying a moisturizer to treat dry, cracking skin
- using unscented, nonirritating laundry detergent
- avoiding triggers, such as dry air, stress, and allergens
For severe atopic dermatitis that does not respond to the above treatment options, a person should see a board-certified dermatologist.
Taking bleach baths, which require using half a cup of bleach per 40-gallon tub, 1–2 times per week may also help.
Learn more about the treatment options for eczema here.
Rosacea is a skin condition that causes skin irritation, redness, and small pimples.
Although anyone can develop rosacea at any point in their lives, this condition most often occurs among adults aged 30–60 years, people with fair skin, and those going through menopause.
Symptoms of rosacea include:
- irritated or red skin on the forehead, nose, cheeks, and chin
- blood vessels that are visible under the skin
- clusters of small bumps or pimples
- thick skin on the face
- red, itchy, or watery eyes
- inflammation of the eyelids
- blurred vision
Treatment
People can treat rosacea with various strategies and medication. Some strategies that can help relieve rosacea include:
- avoiding triggers, such as ultraviolet light, alcohol, and harsh chemicals
- washing the face with pH-balanced cleansers
- frequently using moisturizers
- wearing a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher
People should also avoid caffeinated products and spicy foods, as these can also trigger rosacea.
Medical treatments for rosacea include:
- brimonidine tartrate
- azelaic acid
- metronidazole
- electrosurgery
- light therapy
- topical ivermectin
- oral tetracyclines
Learn more about the treatment options for rosacea here.
Certain infections can also lead to red dots on the skin.
If a person suspects an infection of the skin, they should consult a doctor.
Examples of these include:
Chickenpox or shingles
The varicella-zoster virus causes these infections, which produce red, itchy, fluid-filled blisters that can appear anywhere on the body.
Chickenpox usually occurs in infants and young children. However, adolescents and adults can also develop chickenpox.
Shingles occurs in adults who have already had chickenpox. According to the National Institute on Aging, shingles usually affects one area on one side of the body.
Rubella
This contagious viral infection causes a distinctive rash of small red or pink dots.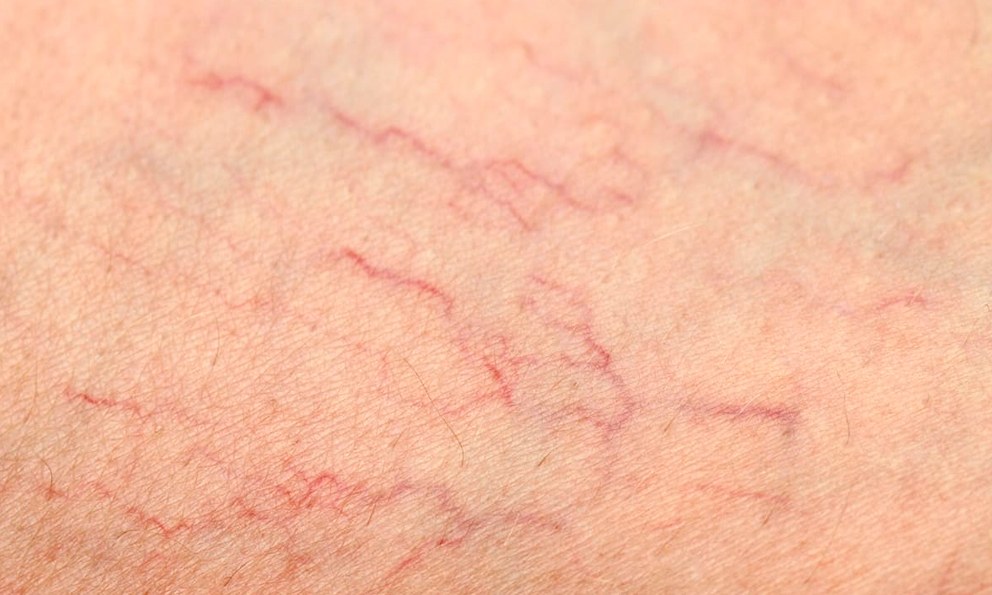
The rash usually starts on the face before spreading to the trunk, arms, and legs. Rubella infections also cause a fever, a headache, and swollen lymph nodes.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) note that rubella is a relatively rare infection in the United States due to the widespread use of the MMR vaccine. The vaccine is available for infants and children aged between 9 months and 6 years.
Meningitis
Meningitis is a medical emergency. It is the inflammation of the membranes that cover the spinal cord and brain. It typically occurs due to a bacterial or viral infection.
Symptoms of meningitis include:
- fever
- stiff neck
- headache
- nausea
- light sensitivity
- confusion
- vomiting
A rash does not always appear. However, if it does, a person might notice small pink, red, brown, or purple pinpricks on the skin. Also, it will not fade when a person rolls a glass over it.
MRSA (staph) infection
The CDC define Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) as “a type of bacteria that is resistant to several antibiotics. ”
”
MRSA often infects the skin, leading to painful areas of inflamed skin. People may also experience pus drainage from the affected skin and fever.
Other bacterial infections of the skin may also cause painful and inflamed areas of the skin. If a person suspects that they are experiencing a skin infection, they should consult a doctor.
Scarlet fever
Streptococcus bacteria cause this infection.
These bacteria naturally inhabit the nose and throat. They cause a red rash on the neck, under the armpit, and on the groin. The rash consists of small red dots that are rough to the touch.
If a person suspects an infection of the skin, they should always consult a doctor.
People should also speak with a doctor if their rash does not improve despite using OTC or at-home treatments.
People should also seek medical attention if they have a skin rash accompanied by the following symptoms:
- fever
- severe head or neck pain
- joint pain or stiffness
- difficulty breathing
- frequent vomiting or diarrhea
- confusion
- dizziness
If a person suspects a skin infection, they should contact a healthcare professional before trying any home remedies.
To relieve and manage skin rashes, people can try the following home treatments:
- using mild, unscented soaps, body washes, and cleansers
- avoiding bathing or showering in hot water
- keeping the affected skin dry and clean
- wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing
- avoiding rubbing or scratching the skin rash
- applying a cold compress to relieve swelling and pain
- applying aloe vera to the affected skin to reduce swelling and soothe pain
- using moisturizers to hydrate dry, flaky skin
There are several possible causes for red dots on the skin, including heat rash, KP, contact dermatitis, and atopic dermatitis.
Red dots on the skin may also occur due to more serious conditions, such as a viral or bacterial infection.
If people suspect that they have a skin infection, they should contact a doctor rather than use home remedies.
People can treat some skin rashes and their accompanying symptoms with home remedies and OTC treatments. These include avoiding the source of irritation and using OTC anti-itch ointments.
These include avoiding the source of irritation and using OTC anti-itch ointments.
People can contact a doctor or dermatologist if their symptoms persist despite using at-home or OTC treatments. A doctor or dermatologist can diagnose the underlying cause and make appropriate treatment recommendations.
Read this article in Spanish.
Pictures, causes, treatment, and when to seek help
A person may notice pinpoint red dots on their skin for a number of reasons, ranging from allergic reactions to heat exposure.
Many causes of red dots on the skin are harmless and resolve on their own. Others may require at-home or over-the-counter (OTC) treatment.
In this article, we discuss some of the possible causes of red dots on the skin, their treatment options, and when to contact a doctor.
Skin rashes come in a variety of sizes, colors, and textures.
Not all rashes require emergency medical treatment. However, people should seek immediate medical attention if they have a rash and notice any of the following symptoms:
- a rash that covers the entire body
- fever
- blisters or open wounds
- difficulty breathing, speaking, or swallowing
- swelling of the face, eyes, or lips
- stiff neck
- light sensitivity
- seizures
- drowsiness or unresponsiveness
People should also seek immediate attention for any new rashes that are painful and that affect the eyes, inside of the mouth, or genitalia.
When in doubt, a person should seek the opinion of a primary care provider or board-certified dermatologist.
Heat rash, or miliaria, occurs when the sweat glands become blocked, trapping sweat in the deep layers of the skin.
While anyone can have heat rash, this condition is most common among infants and young children with immature sweat glands.
Symptoms of heat rash include:
- clusters of small red bumps called papules
- firm, flesh-colored bumps
- itchy or prickly sensation
- mild or absent sweating in the affected area
- inflammation and soreness
- dizziness
- nausea
Treatment
Heat rash usually goes away within 24 hours.
Treatment typically involves using lotions to soothe the itching, irritation, and swelling.
People can also keep the skin cool and avoid tight-fitting clothing.
Learn more about the treatment options for heat rash here.
Keratosis pilaris (KP) is a common skin condition that causes tiny red, white, or flesh-colored bumps on the skin.
It most often affects the outer parts of the upper arms. It can also affect the forearms and upper back, but this is less common.
Symptoms of KP include:
- skin that feels rough or dry
- patches of small, painless bumps on the skin
- itching
Treatment
People can treat the symptoms of KP with:
- moisturizers containing urea or lactic acid
- alpha hydroxy acid
- glycolic acid
- lactic acid
- retinoids
- salicylic acid
- laser or light therapy
Learn more about home management for KP here.
Contact dermatitis occurs when a person comes into contact with a substance that irritates their skin or triggers an allergic reaction.
Contact dermatitis symptoms vary depending on the trigger and the severity of the reaction.
Symptoms of contact dermatitis include:
- a rash that appears in geometric patterns or shapes
- dry skin that flakes and cracks
- a bright, flushed skin rash
- clusters of small red dots on the skin
- hives, or extremely itchy welts on the skin
- intense itching, tightness, or burning sensation
- fluid-filled blisters that ooze and crust over
- dark, thickened skin
- sensitivity to sunlight
Learn more about contact dermatitis here.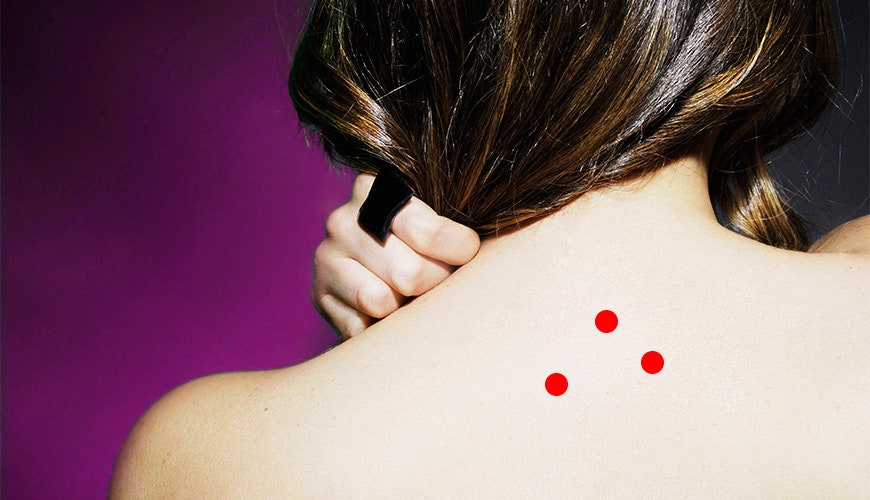
Treatment
Treatment for contact dermatitis depends on the cause and severity of a person’s symptoms.
Mild to moderate symptoms improve when a person avoids contact with the irritant or allergen. If possible, people should:
- avoid skin care products that contain harsh or irritating chemicals
- avoid nickel- or gold-plated jewelry
- avoid foods or medicines that cause allergic reactions
- wear protective clothing in work environments or areas with poisonous plants
If the dermatitis is limited to a small area, a person can apply 1% hydrocortisone cream.
A doctor can prescribe stronger topical or oral antihistamines for people who do not respond to OTC medication.
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition.
There are many different types of eczema, including:
- Follicular eczema: This type of eczema affects the hair follicles.
- Papular eczema: This presents as small red bumps on the skin that healthcare professionals refer to as papules.
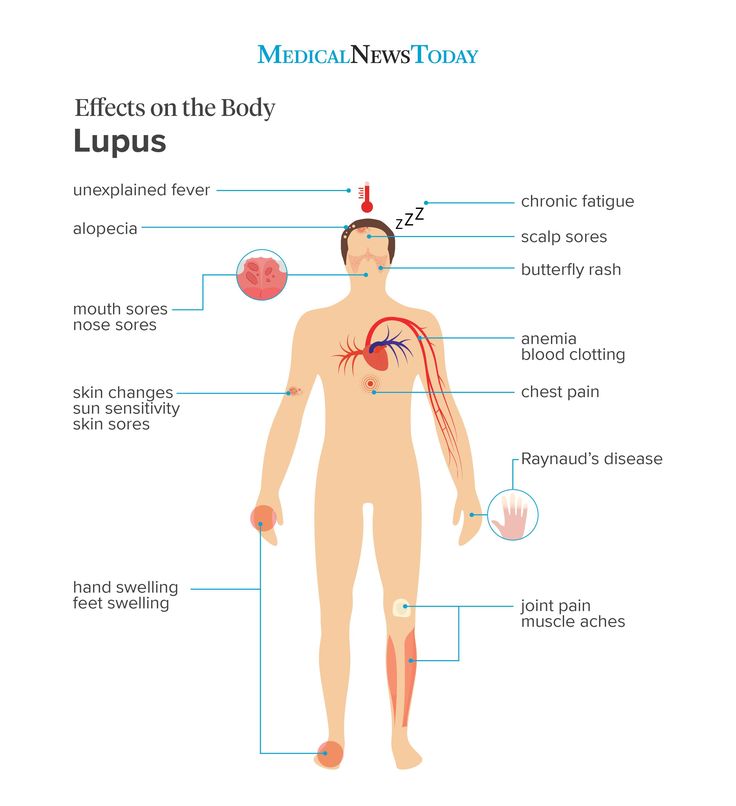
Alongside red bumps on the skin, eczema can cause:
- extremely itchy skin
- warmth and swelling of the skin
- dry, flaky skin
- clusters of small, fluid-filled blisters
- blisters that leak fluid and crust over
Treatment
People can manage atopic dermatitis symptoms and even prevent flare-ups with the following treatments:
- taking prescription medications, such as steroids and antihistamines
- undergoing phototherapy or light therapy
- applying a moisturizer to treat dry, cracking skin
- using unscented, nonirritating laundry detergent
- avoiding triggers, such as dry air, stress, and allergens
For severe atopic dermatitis that does not respond to the above treatment options, a person should see a board-certified dermatologist.
Taking bleach baths, which require using half a cup of bleach per 40-gallon tub, 1–2 times per week may also help.
Learn more about the treatment options for eczema here.
Rosacea is a skin condition that causes skin irritation, redness, and small pimples.
Although anyone can develop rosacea at any point in their lives, this condition most often occurs among adults aged 30–60 years, people with fair skin, and those going through menopause.
Symptoms of rosacea include:
- irritated or red skin on the forehead, nose, cheeks, and chin
- blood vessels that are visible under the skin
- clusters of small bumps or pimples
- thick skin on the face
- red, itchy, or watery eyes
- inflammation of the eyelids
- blurred vision
Treatment
People can treat rosacea with various strategies and medication. Some strategies that can help relieve rosacea include:
- avoiding triggers, such as ultraviolet light, alcohol, and harsh chemicals
- washing the face with pH-balanced cleansers
- frequently using moisturizers
- wearing a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher
People should also avoid caffeinated products and spicy foods, as these can also trigger rosacea.
Medical treatments for rosacea include:
- brimonidine tartrate
- azelaic acid
- metronidazole
- electrosurgery
- light therapy
- topical ivermectin
- oral tetracyclines
Learn more about the treatment options for rosacea here.
Certain infections can also lead to red dots on the skin.
If a person suspects an infection of the skin, they should consult a doctor.
Examples of these include:
Chickenpox or shingles
The varicella-zoster virus causes these infections, which produce red, itchy, fluid-filled blisters that can appear anywhere on the body.
Chickenpox usually occurs in infants and young children. However, adolescents and adults can also develop chickenpox.
Shingles occurs in adults who have already had chickenpox. According to the National Institute on Aging, shingles usually affects one area on one side of the body.
Rubella
This contagious viral infection causes a distinctive rash of small red or pink dots.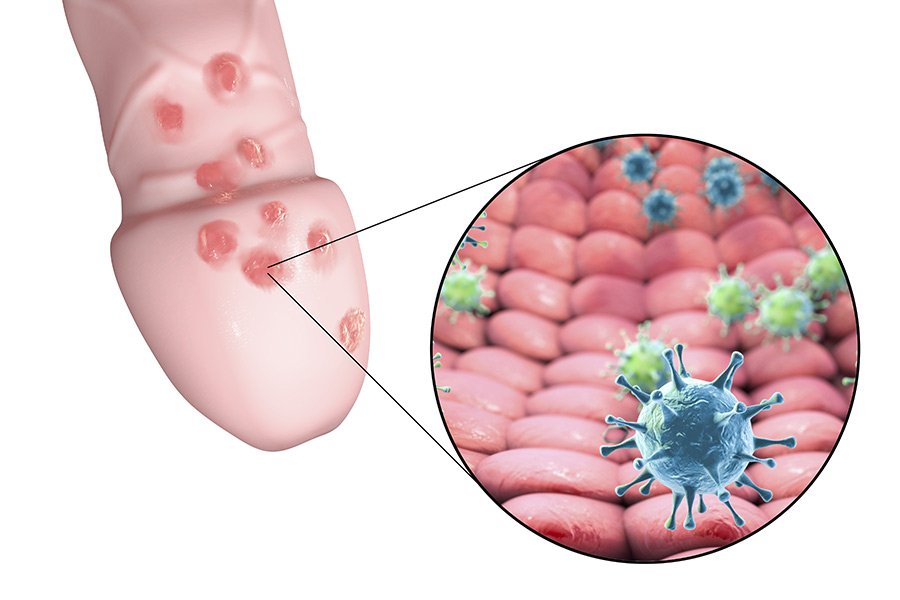
The rash usually starts on the face before spreading to the trunk, arms, and legs. Rubella infections also cause a fever, a headache, and swollen lymph nodes.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) note that rubella is a relatively rare infection in the United States due to the widespread use of the MMR vaccine. The vaccine is available for infants and children aged between 9 months and 6 years.
Meningitis
Meningitis is a medical emergency. It is the inflammation of the membranes that cover the spinal cord and brain. It typically occurs due to a bacterial or viral infection.
Symptoms of meningitis include:
- fever
- stiff neck
- headache
- nausea
- light sensitivity
- confusion
- vomiting
A rash does not always appear. However, if it does, a person might notice small pink, red, brown, or purple pinpricks on the skin. Also, it will not fade when a person rolls a glass over it.
MRSA (staph) infection
The CDC define Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) as “a type of bacteria that is resistant to several antibiotics. ”
”
MRSA often infects the skin, leading to painful areas of inflamed skin. People may also experience pus drainage from the affected skin and fever.
Other bacterial infections of the skin may also cause painful and inflamed areas of the skin. If a person suspects that they are experiencing a skin infection, they should consult a doctor.
Scarlet fever
Streptococcus bacteria cause this infection.
These bacteria naturally inhabit the nose and throat. They cause a red rash on the neck, under the armpit, and on the groin. The rash consists of small red dots that are rough to the touch.
If a person suspects an infection of the skin, they should always consult a doctor.
People should also speak with a doctor if their rash does not improve despite using OTC or at-home treatments.
People should also seek medical attention if they have a skin rash accompanied by the following symptoms:
- fever
- severe head or neck pain
- joint pain or stiffness
- difficulty breathing
- frequent vomiting or diarrhea
- confusion
- dizziness
If a person suspects a skin infection, they should contact a healthcare professional before trying any home remedies.
To relieve and manage skin rashes, people can try the following home treatments:
- using mild, unscented soaps, body washes, and cleansers
- avoiding bathing or showering in hot water
- keeping the affected skin dry and clean
- wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing
- avoiding rubbing or scratching the skin rash
- applying a cold compress to relieve swelling and pain
- applying aloe vera to the affected skin to reduce swelling and soothe pain
- using moisturizers to hydrate dry, flaky skin
There are several possible causes for red dots on the skin, including heat rash, KP, contact dermatitis, and atopic dermatitis.
Red dots on the skin may also occur due to more serious conditions, such as a viral or bacterial infection.
If people suspect that they have a skin infection, they should contact a doctor rather than use home remedies.
People can treat some skin rashes and their accompanying symptoms with home remedies and OTC treatments. These include avoiding the source of irritation and using OTC anti-itch ointments.
These include avoiding the source of irritation and using OTC anti-itch ointments.
People can contact a doctor or dermatologist if their symptoms persist despite using at-home or OTC treatments. A doctor or dermatologist can diagnose the underlying cause and make appropriate treatment recommendations.
Read this article in Spanish.
symptoms and causes, what to do, prognosis
Rash on the abdomen in an adult: what could it be?
Eruptions on the abdomen can be very annoying, especially when accompanied by symptoms such as itching or burning. There can be many reasons for this ailment, we will consider the most common of them.
Types of rashes in adults
Urticaria
Reddening of the skin is accompanied by the appearance of small blisters, slightly elevated above the level of the skin, similar to those that appear after contact with nettles.
Spotted rash
Spots of indeterminate form appear on the body, usually red. They can merge with each other into small islands or be at a distance from each other. Do not rise above the surface of the skin or rise almost imperceptibly. Such a rash may disappear when the skin is stretched or pressed against it.
They can merge with each other into small islands or be at a distance from each other. Do not rise above the surface of the skin or rise almost imperceptibly. Such a rash may disappear when the skin is stretched or pressed against it.
Papular rash
Papules are small hard blisters filled with solid contents. They feel like solid masses, look like small, firm pustules that are not filled with fluid. Their diameter can reach from 1-3 mm to 1-3 cm.
Bubble (vesicular) rash
Blisters on the skin can be filled with either clear or purulent fluid (then called pustules), tend to merge with each other [1].
Probable causes of rashes on the abdomen in adults
Skin changes on the abdomen or other parts of the body can occur for many reasons. Among the most common are allergies and some infectious diseases.
Skin diseases
This is a large group of diseases, the main manifestations of which are changes in the skin. They can be acute and chronic, infectious and non-infectious. A dermatologist deals with the treatment of skin diseases.
They can be acute and chronic, infectious and non-infectious. A dermatologist deals with the treatment of skin diseases.
Skin diseases that can cause a small red rash on the abdomen include: neurodermatitis, Gibert's pink lichen, eczema, polymorphic photodermatosis, psoriasis, acne and others. Each of these pathologies has its own characteristic symptoms and features of skin manifestations [1].
Diseases of a viral nature
Chickenpox
Chickenpox causes a rash to appear on the abdomen, back, arms, legs and face. At the beginning of the disease, these are small redness in the form of spots, which eventually transform into larger vesicles that dry out after opening. In adults, chickenpox may leave small scars [2].
Shingles
Another disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus is shingles. Before the appearance of skin changes, patients feel pain, burning and itching along the course of the nerve that was attacked by the virus.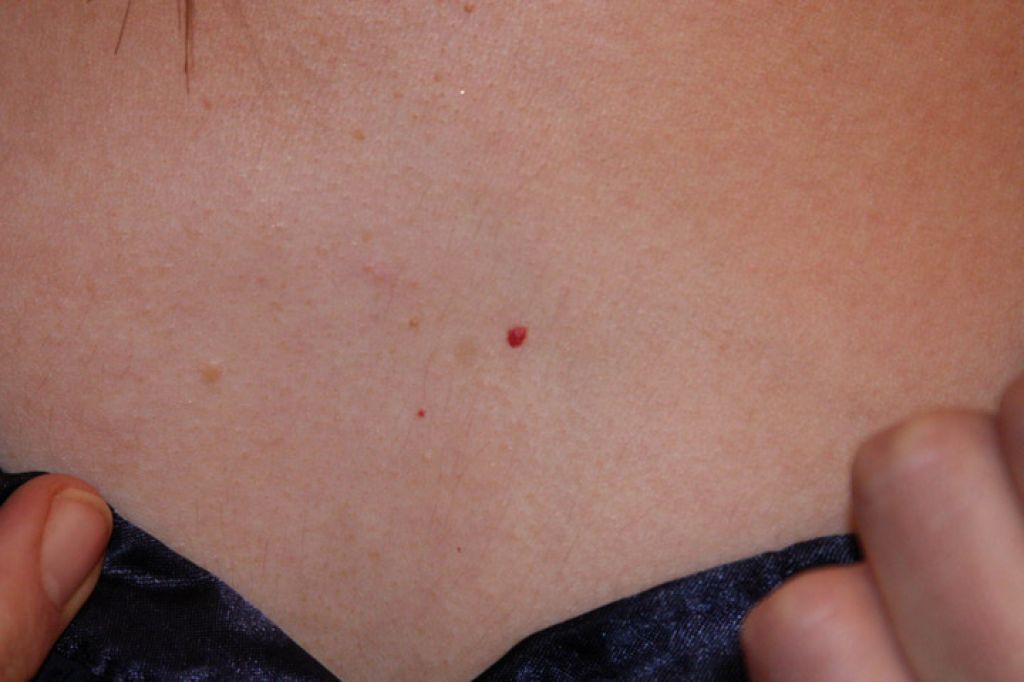 The rash is grouped into characteristic stripes along the body along the intercostal spaces. Skin lesions look the same as with chicken pox, that is, they go through stages in the form of spots, vesicles and drying of the vesicles. [3].
The rash is grouped into characteristic stripes along the body along the intercostal spaces. Skin lesions look the same as with chicken pox, that is, they go through stages in the form of spots, vesicles and drying of the vesicles. [3].
Measles
The main symptoms of measles are cough, fever, redness and small spots on the face. As the disease progresses, papules may appear all over the body, but they do not require serious treatment, as they disappear on their own after a few days. As a treatment, dry ointments, for example, with zinc oxide, can be used. Remember that measles should always be diagnosed by a doctor, as it can have serious complications [4].
Allergy
We are surrounded by a huge number of allergens, so one of the most common causes of a rash on the stomach is an allergic reaction. It can be caused by chemicals used for washing, the material from which clothes are made, food, pets, cosmetics, and medicines. A rash on the abdomen caused by an allergy usually presents with redness, small spots, hives, itching, or dry, flaky skin.
Allergy treatments include antihistamines and ointments or creams that moisturize and soothe itchy skin. To avoid such a rash in the future, it is recommended to consult an allergist and carry out allergy tests. In people prone to frequent allergic rashes, it is recommended to use hypoallergenic cosmetics, emollients specifically designed for allergic skin, and limit the consumption of highly allergenic products during daily care [5].
Rash in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Skin manifestations often accompany diseases of the intestines and stomach. Violation of the absorption of vitamins, minerals and nutrients affects the condition of the skin and mucous membranes [6]. Congenital deficiencies usually appear at an early age.
In adults, the rash is associated with atopic reactions of the digestive system - such as irritable bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, colon polyposis, Helicobacter pylori infection (gastritis, duodenitis).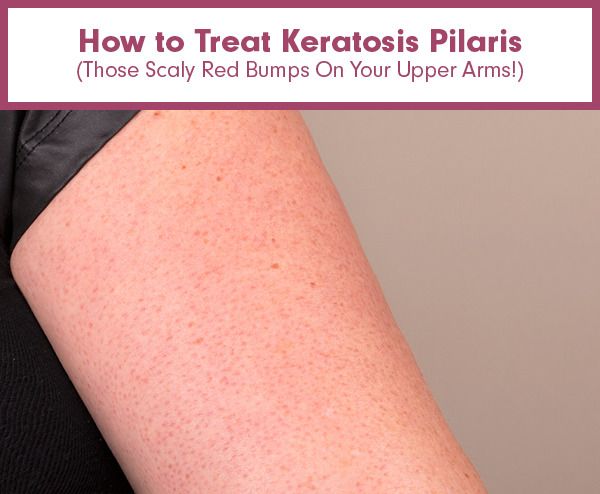 There is an assumption that Helicobacter can provoke the development of psoriasis [7].
There is an assumption that Helicobacter can provoke the development of psoriasis [7].
A bright rash is one of the important symptoms of typhoid fever [8].
Sexual infections
A small red rash on the abdomen is manifested in the following sexually transmitted diseases:
- second stage of syphilis;
- pubic pediculosis [9].
Rash on the abdomen with scabies
The scabies mite causes an itchy rash on the abdomen, the infection spreads by self-infection during scratching of the scabies in the thickness of the skin. The sooner scabies is diagnosed, the sooner you can get rid of it. It is very important not to scratch the lesions on the skin, and wash clothes and bedding at high temperatures [10].
Infectious skin rash
Rash should not be taken as an isolated symptom. Infectious diseases also have the following signs:
- fever, chills, aches, general malaise;
- enlarged regional lymph nodes;
- the presence of an entrance gate of infection;
- history of contact with infected people;
- specific changes in blood tests and biochemical analysis, characteristic of the infectious process (increased ESR, shift of the leukoformula, the appearance of C-reactive protein, etc.
 ).
).
Infections with skin manifestations include herpes, typhus, leptospirosis, rubella, hemorrhagic fevers of various origins, infectious mononucleosis, meningococcal infection, measles, typhoid fever, chickenpox, Rosenberg's erythema, paratyphoid fever, Lyme disease, pseudotuberculosis, salmonellosis , scarlet fever, enterovirus infection, Chamer's infectious erythema, erythema nodosum, etc.
Only a doctor can understand this variety. Therefore, if there are signs of an infectious disease, you should not self-medicate [11].
Skin changes in Fabry disease
Fabry disease is a congenital disease of a genetic nature, which is accompanied by a variety of clinical manifestations. One of the characteristic symptoms of Fabry disease is angiokeratomas on the abdomen - small dark red (up to purple) rashes. They can also appear on the face, in the anus, on the fingers and toes. The elements of the rash slightly rise above the surface of the skin, inside there is a dense content.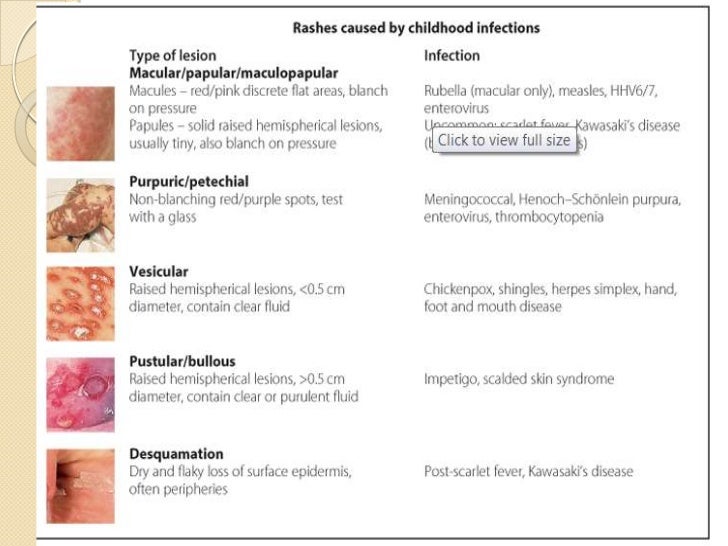
In addition to the rash, patients complain of burning pain in the arms and legs, visual and hearing impairment, and abdominal pain. But, since the rash immediately attracts attention, this is often the first reason to see a doctor. With timely early diagnosis, the progression of Fabry disease can be slowed down with the help of modern enzyme replacement therapy [12].
Diagnosis of rashes on the abdomen
If a rash appears on the abdomen, you should consult a general practitioner or therapist who can make a diagnosis or refer you to a specialist (allergist, dermatologist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, etc.).
After questioning, examination and palpation of the elements of the rash, the doctor may prescribe additional methods of examination:
 ;
; Abdominal rash, causes and treatment
Abdominal rash is a common phenomenon that occurs at least once in every second person. The causes of rashes are varied: from an allergic reaction to hormonal changes during pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases. It is noteworthy that in children, rashes are provoked by specific causes that are uncharacteristic of adults. You should not ignore this symptom: if the rash does not go away for 1-2 days, consult a therapist or dermatologist.
Share:
Causes of rash on the abdomen
- In pregnant women. Most often, rashes are associated with hormonal changes, when hormones negatively affect the skin. A rash in the form of red plaques with a white rim indicates dermatosis, reddish vesicles with liquid inside indicate an allergy.
- For men. Causes of rashes range from harmless prickly heat to malfunctions of the internal organs and infectious diseases.
 If grayish-red bumps appear in the lower abdomen, it is worth suspecting syphilis, gonorrhea, or other sexually transmitted infections. Large red spots with scabs often accompany chronic skin diseases such as psoriasis and eczema.
If grayish-red bumps appear in the lower abdomen, it is worth suspecting syphilis, gonorrhea, or other sexually transmitted infections. Large red spots with scabs often accompany chronic skin diseases such as psoriasis and eczema. - In children. A rash can appear with prickly heat or infectious diseases - scarlet fever, measles, rubella, chickenpox and others. The same reasons can provoke rashes in adults, but children are much more prone to them.
Article checked
Konovalova G. N. Neurologist • 44 years of experience
Publication date: March 24, 2021
Review date: January 20, 2023
Contents of the article
Associated symptoms of a rash on the abdomen
Quote from CMRT specialist
Ulyanova Daria Gennadievna Neurologist • Chiropractor • Experience 24 years
Quote from a CMRT specialist
A rash on the abdomen may indicate an allergic reaction, hormonal disorders, sexually transmitted diseases, and less often neurological pathologies. In order to understand the true cause and prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to visit a specialized specialist, pass current laboratory tests, and undergo diagnostics. Do not self-medicate and postpone a visit to the doctor.
Ulyanova Daria Gennadievna Neurologist • Chiropractor • Experience 24 years
Diagnostic methods
To make a diagnosis, the CMRT conducts an examination, assesses the nature of the rashes and recommends the following examinations and tests:
Where to see a doctor
If your stomach is covered, see a general practitioner or dermatologist first. If a child has a symptom, write it down to the pediatrician. Depending on the results of the initial diagnosis, the doctor will involve a specialist in further treatment, for example, an allergist or an endocrinologist.
How to treat a rash on the stomach
The strategy for treating rashes depends on the cause that provoked it.












