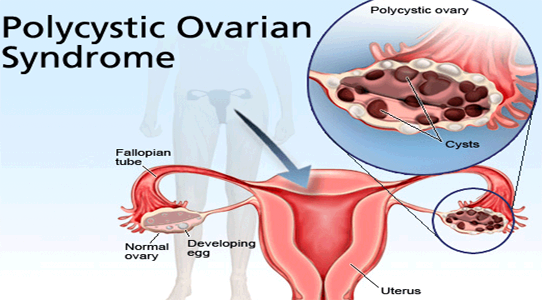
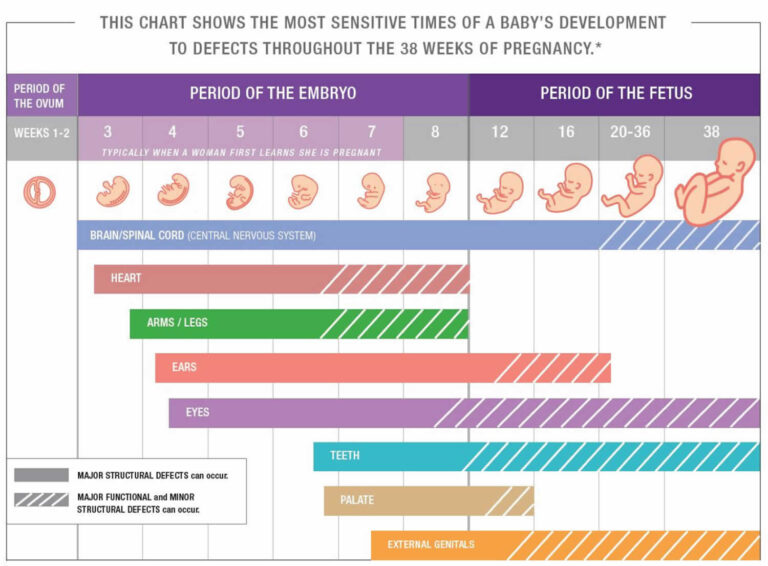
Pregnant women baby delivery
Pregnancy and Childbirth - familydoctor.org
Questions about pregnancy and impending parenthood? familydoctor.org has facts on pregnancy, fetal health, labor, childbirth and caring for your newborn.
All results in Pregnancy and Childbirth
Sort By:
- A-Z
- Z-A
- Recently Updated
-
Adult vaccinations
Adult vaccinations are important for adults for staying healthy as they age.
-
Anemia
Anemia is the most common blood disorder in the U.S. It affects your red blood cells and hemoglobin. Most people…
-
Back Pain During Pregnancy
Back pain during pregnancy is common and varies in severity.
-
Becoming Parents: What It Means for Couples
Having a baby changes many things at home, including your relationship with your partner. Use these tips to help you…
-
Being a Single Parent
Being a single parent can be challenging.
It can also be very rewarding. It’s important to find a way to…
-
Birthing Classes
Birthing classes are an important part of preparing to have a baby. They can help you develop a birth plan…
-
Bleeding During Pregnancy – What‘s Normal?
Having bleeding during pregnancy is not normal and requires a visit to your doctor.
-
Bonding with Baby
Bonding is a special connection you have with your baby. Bonding with your baby is not a one-time event. It…
-
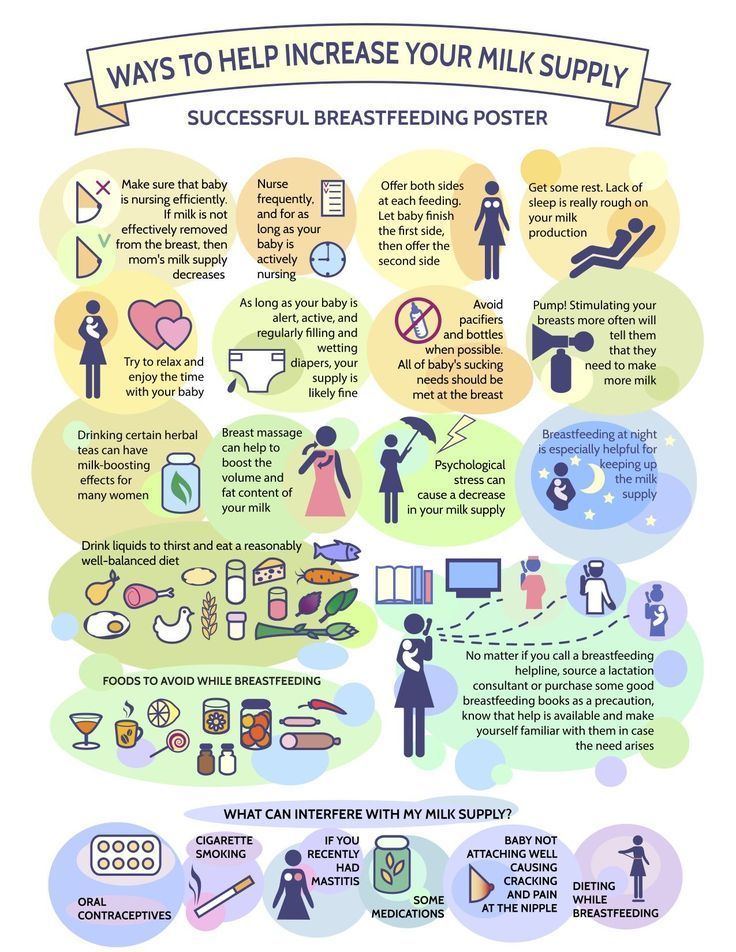
Breastfeeding: Hints to Help You Get Off to a Good Start
Breastfeeding benefits your baby. Breast milk contains nutrients and antibodies your baby needs. Breastfed babies are less likely to develop…
-
Breech Babies: What Can I Do if My Baby is Breech?
A baby is breech when it is in a headfirst position prior to birth. There are several ways to try…
-
Bringing Your Baby Home
Welcoming a baby into your home is a big event.
 It can be scary if it is your first baby…
It can be scary if it is your first baby… -
Car Safety for Pregnant Women
A pregnant woman must take extra precautions when riding in or driving a car.
-
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the muscles in the heart. It causes your heart muscles to become enlarged. This can…
-
Caring for Your Premature Baby
A baby’s birth can be a happy time. However, it can be stressful if your baby is born premature. Premature…
-
Changes in Your Body During Pregnancy: First Trimester
The first trimester of pregnancy can be exciting and scary. A person’s body goes through a lot of changes—physically and…
-
Changes in Your Body During Pregnancy: Second Trimester
Your body continues to change in the second trimester of pregnancy. As your baby continues to grow, so does your…
-
Circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure where the foreskin (the skin that covers the tip of the penis) is removed.
 It’s usually…
It’s usually… -
Common Skin Conditions During Pregnancy
It's important to know what skin conditions are common during pregnancy to help identify uncommon conditions that should be seen…
-
Congenital Heart Disease: How to Care for Your Baby and Yourself
In many ways, babies born with heart defects are cared for just like any other baby. But there are times…
-
COVID-19 Vaccine and Pregnancy
If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant and wondering whether the COVID-19 vaccine is safe for you and your baby, the good news is it is. According to scientific data pregnancy increases your risk of a severe COVID-19 infection and
Close Modal
What happens to your body during childbirth
Childbirth is challenging and complications occur, but women's bodies are designed to give birth. The shape of the pelvis, hormones, powerful muscles and more all work together to help you bring your baby into the world - before, during and after childbirth.
How your body prepares for labour
Here are some of the ways your body will prepare both you and your baby for the birth ahead.
Braxton Hicks contractions
In the weeks or days before you start having proper contractions, you may experience Braxton Hicks contractions. This is your uterus tightening then relaxing. These contractions don't usually hurt and are thought to help your uterus and cervix get ready for labour.
Braxton Hicks contractions may become more regular as you get closer to the time of birth, but unlike labour contractions, they don't change the shape of the cervix and are sometimes referred to as 'false labour'. Your midwife can tell you if you're experiencing Braxton Hicks contractions or if you are in labour by doing a vaginal examination to look at your cervix.
Changes to the cervix
As labour gets closer, your cervix softens and becomes thinner, getting ready for the dilation (widening) that will allow the baby to enter the vagina. You may also see a 'show', which is a pinkish plug of mucus, stained with blood.
You may also see a 'show', which is a pinkish plug of mucus, stained with blood.
Engagement
Your baby may move further down your pelvis as the head engages, or sits in place over your cervix, ready for the birth. Some women feel they have more room to breathe after the baby has moved down. This is called 'lightening'.
Rupture of the membranes, or 'waters breaking'
Some women find the sac of amniotic fluid containing the baby breaks before labour, contractions start and the fluid runs (or gushes) out of the vagina. This is referred to as rupture of the membranes, or 'waters breaking'.
Let your maternity team know when your waters have broken and take notice of the colour of the fluid. It is usually light yellow. If it is green or red, tell your maternity team since this could mean the baby is having problems.
If your waters have broken but you have not started having regular contractions within 24 hours, you may need your labour to be induced because there is a risk of infection. Your midwife or doctor will talk to you about this.
Your midwife or doctor will talk to you about this.
How will you know when labour has started?
Movies often show women suddenly being struck by painful contractions and rushing to hospital. In real life, many women are not sure if they have actually started their labour.
You may feel restless, have back pain or period-like pain, or stomach disturbances such as diarrhoea.
Labour officially begins with contractions, which start working to open up the cervix. You should phone your midwife when your contractions start, although you probably won't be encouraged to come to the hospital or birthing centre until your contractions are closer together.
In preparation for labour, your baby may move further down your pelvis as the head engages, or sits in place over your cervix.How the pelvis is designed for childbirth
Your pelvis is located between your hip bones. Women typically have wider, flatter pelvises than men, as well as a wider pelvic cavity (hole) to allow a baby to pass through.
The organs sitting in a woman's pelvis include the uterus, cervix and vagina, which are held together by a group of muscles. During childbirth, the muscles at the top of your uterus press down on the baby's bottom. Your baby's head then presses on your cervix which, along with the release of the hormone oxytocin (see 'How hormones help you give birth', below), brings on contractions. Your cervix should dilate so your baby can pass through it.
Your pelvis has bones and ligaments that move or stretch as the baby travels into the vagina. Your baby also has spaces between the skull bones called 'sutures', and the gaps where the sutures meet on the skull are called fontanelles. This allows for the baby's head to mould as the skull bones meet or overlap, allowing it to fit more easily as it travels through your pelvis.
How hormones help you give birth
Your body produces hormones that trigger changes in your body before, during and after childbirth. Here's how they work to help you deliver your baby.
- Prostaglandin Before childbirth, a higher level of prostaglandin will help open the cervix and make your body more receptive to another important hormone, oxytocin.
- Oxytocin This hormone causes contractions during labour, as well as the contractions that deliver the placenta after the baby is born. These post-birth contractions, including more that can occur during breastfeeding, help your uterus shrink back to its normal size. Oxytocin and prolactin are the two main hormones that produce and let down breast milk for your baby. Skin-to-skin contact between a mother and baby helps to release more of these hormones.
- Relaxin The hormone relaxin helps soften and stretch the cervix for birth, while helping your waters break and stretching the ligaments in your pelvis to allow the baby to come through.
- Beta-endorphins During childbirth, this type of endorphin helps with pain relief and can cause you to feel joyful or euphoric.

- 'Baby blues' After birth, your hormone balance can change again, and this is believed to cause the ‘baby blues’ in some women. You may feel teary, anxious and irritable and your mood can go up and down.
When childbirth doesn’t go to plan
Sometimes, complications can occur before or during childbirth that mean things don’t go as expected.
Sometimes, labour needs to be induced or started. There are a few ways to induce labour, including the mother being offered synthetic prostaglandin. This is inserted into the vagina to soften the cervix and start contractions.
If contractions slow down or stop during labour, the mother may be offered synthetic oxytocin from a drip to increase the contractions. In both these cases contractions can come on strongly and more pain relief may be needed. Your maternity team should explain the benefits and risks of this with you before you agree to it.
The baby could be in a posterior or breech position, not ideally placed above the cervix before the birth. Your maternity team may need to use forceps or a vacuum to help turn the baby or help the baby travel out of the vagina. Sometimes a caesarean is needed.
Your maternity team may need to use forceps or a vacuum to help turn the baby or help the baby travel out of the vagina. Sometimes a caesarean is needed.
In rare cases, a mother may experience cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD), which is when the baby’s head is too big to fit through the pelvis. A diagnosis of CPD is usually made when labour hasn’t progressed and synthetic oxytocin has not helped. A caesarean is usually the next step.
More information
If you have any questions about childbirth or pregnancy, you can call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436, 7 days a week, to speak to a maternal health nurse.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Ways to help pregnant women avoid preterm labor
What is the problem?
Preterm birth, or birth before 37 weeks of gestation, is the leading cause of newborn death and can also lead to long-term disability in surviving infants. There are many ways health professionals try to prevent preterm labor in women. Pregnant women may be asked to take vitamins, limit smoking, take medicines to treat infections, or attend regular checkups with specialists. Our review looks at different ways (or interventions) to prevent preterm birth. We searched the Cochrane Library for relevant documents on November 2, 2017.
Pregnant women may be asked to take vitamins, limit smoking, take medicines to treat infections, or attend regular checkups with specialists. Our review looks at different ways (or interventions) to prevent preterm birth. We searched the Cochrane Library for relevant documents on November 2, 2017.
Why is this important?
Premature births have devastating and costly consequences for women, families and health systems. We wanted to summarize relevant information for pregnant women, healthcare professionals and researchers.
What evidence did we find?
We included 83 systematic reviews of evidence of whether certain interventions reduced the chance of preterm birth or death in children. Seventy reviews contained information on preterm birth. We categorized the evidence we found as follows: clear benefit or harm; no effect; possible benefit or harm; unknown effect.
Outcome: preterm birth
Clear Benefit
We were confident that the following interventions helped specific groups of pregnant women avoid preterm labor: continuous obstetric care models versus other models of care for all women; screening for lower genital tract infections; zinc supplements for pregnant women without systemic diseases. Cervical suturing (cerclage) was only useful for women at high risk of preterm birth and singleton pregnancies.
Cervical suturing (cerclage) was only useful for women at high risk of preterm birth and singleton pregnancies.
Clear harm
We did not find any interventions that increased the chance of preterm birth in women.
Potential benefits
The following interventions may have helped some groups of pregnant women avoid preterm birth, but we are less certain about these results: group antenatal care for all pregnant women; antibiotics for pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria; pharmacological interventions for smoking cessation; vitamin D supplements for women without health problems.
Potential harm
We found two interventions that may worsen some pregnant women: intramuscular progesterone for women at high risk of preterm birth and multiple pregnancies; supplementation of vitamin D, calcium and other minerals by pregnant women without health problems.
Exodus: perinatal death
Clear benefit
We were confident in the evidence for the continuous obstetric monitoring model for all pregnancies and fetal and umbilical cord Doppler for high-risk pregnant women; these interventions appear to reduce a woman's chance of child death.
Overt harm
We did not find any interventions that increased the woman's risk of child death.
Potential benefits
We have found a possible benefit of cervical sutures (cerclage) for women with singleton pregnancies at high risk of preterm birth.
Possible harms
One review reported possible harms associated with fewer antenatal visits, even for pregnant women at low risk of pregnancy problems. The pregnant women in this review already received limited antenatal care.
Outcome: preterm birth and perinatal death
Unknown benefit or harm
It is not known whether home monitoring of uterine activity was helpful or harmful for pregnant women at high risk of preterm birth for any reason, including multiple pregnancies. The benefits or harms of the following interventions for high-risk pregnant women with multiple pregnancies have not been established: bed rest, prophylactic oral beta-mimetics, vaginal progesterone, and cervical cerclage.
What does this mean?
The Cochrane Library contains valuable information for women, clinicians, midwives and researchers interested in preventing preterm birth. We summarized the results of systematic reviews to describe how well different strategies for preventing early birth and death of children work. We have organized the information we found in a clear graphical way to show our confidence in the results and point readers to promising interventions for certain groups of pregnant women.
In preparing the review, we did not find up-to-date information in the Cochrane Library on such important tools as a cervical pessary, vaginal progesterone, or cervical ultrasound assessment. We did not find high-quality evidence for women at high risk of preterm birth due to multiple pregnancies. It is important that pregnant women and health care providers carefully consider whether certain strategies to prevent preterm birth would be beneficial for individual women or specific groups.
Translation notes:
Translation: Ivanyuk Alina Viktorovna. Editing: Kukushkin Mikhail Evgenievich. Project coordination for translation into Russian: Cochrane Russia - Cochrane Russia (branch of the Northern Cochrane Center on the basis of Kazan Federal University). For questions related to this translation, please contact us at: [email protected]; [email protected]
Pregnancy Questions and Answers - Useful Articles
What to expect? How to eat? How to deal with difficulties? How to do everything right? These and many questions will be answered by Irina Alexandrovna Soleeva, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the Sadko clinic.
- How is due date calculated?
From the first day of the last menstruation. To determine the due date, 280 days are added to the first day of the last menstruation, i.e. 10 obstetric, or 9 calendar months.
Usually, the calculation of the due date is simpler: from the date of the first day of the last menstruation, count back 3 calendar months and add 7 days. So, if the last menstruation began on October 2, then, counting back 3 months (September 2, August 2 and July 2) and adding 7 days, determine the expected date of birth - 9July; if the last menstruation began on May 20, then the expected due date is February 27, etc.
So, if the last menstruation began on October 2, then, counting back 3 months (September 2, August 2 and July 2) and adding 7 days, determine the expected date of birth - 9July; if the last menstruation began on May 20, then the expected due date is February 27, etc.
Expected due date can be calculated by ovulation: 14-16 days are counted back from the first day of the expected but not arrived menstruation and 273-274 days are added to the found date.
- And if you know the exact date of conception, how many days to add?
A large-scale study was conducted with a large number of pregnant women, according to various indicators, the gestational age and, accordingly, the date of birth were determined. It turned out that the woman most often remembers the date of the last menstruation. And from this fixed date, as the study showed, childbirth occurs at the 40th week ± a couple of weeks. Obstetrician-gynecologists are guided precisely by this system of calculations.
- Should I change my diet, if so, how?
4 meals a day are recommended in the first half of pregnancy, 5-6 meals a day in the second. It is better to eat often, but little by little. For healthy women, there are no forbidden foods (except alcoholic beverages), only more or less preferred ones.
So, the body absorbs easily digestible milk fats and vegetable oils better. The latter are not only a source of essential linoleic acid, but also vitamin E, which has a positive effect on the course of pregnancy.
To eliminate constipation, it is worth enriching the diet with sources of dietary fiber (fiber, pectins) - vegetables and fruits, buckwheat and oatmeal.
In the second half of pregnancy, sugar, confectionery and flour products, rice should be eaten in very small quantities. Do not get carried away with fried, spicy, salty foods, because. during this period, the liver and kidneys of a pregnant woman function with tension. It is better to prefer boiled and steamed dishes.
The main thing is to include a variety of foods in your diet: vegetables, fruits, juices - and you will provide yourself and your unborn child with everything necessary for normal development.
- I really want olives, but they are canned. Can?
It depends on the gestational age. After 20 weeks, I would not recommend eating too salty foods, including olives. And in general, any canned food is not the most suitable food for a pregnant woman. Although olives, in themselves, the product is very useful. Therefore, within reasonable limits, say, a jar can be eaten in two days.
- And the grapes?
Grapes are very well digestible. It's fructose. It is immediately absorbed and quickly raises blood sugar. But if you are overweight, it is either not recommended at all, or it is allowed in small quantities. It is allowed to eat a small brush, or you can treat yourself to something else.
For some reason, it is customary for us to believe that if you are pregnant, you have to eat for three or whatever you want. As a result, pregnant women buy grapes in boxes and eat them in kilograms. Such a diet does not lead to anything good: sugar appears in the urine, blood sugar rises, babies are born large. Moreover, a large load falls not only on the mother's pancreas, but also on the child's pancreas - the baby from birth will be predisposed to being overweight.
As a result, pregnant women buy grapes in boxes and eat them in kilograms. Such a diet does not lead to anything good: sugar appears in the urine, blood sugar rises, babies are born large. Moreover, a large load falls not only on the mother's pancreas, but also on the child's pancreas - the baby from birth will be predisposed to being overweight.
- Is it possible to reduce excess weight during pregnancy and cleanse your body with the help of special teas?
All cleansing teas are contraindicated during pregnancy. We have drugs that improve the functions of the liver and kidneys, which have a diuretic effect. We assign everything individually. There are no special cleansing procedures during pregnancy. However, we have fasting days - here is the best cleansing procedure for you.
- Which vitamins are best for pregnancy?
Now there is a huge selection of various vitamin complexes for pregnant women. Of course, they are all close to each other in composition. One or two components or the dosage of some vitamin differ. In order not to harm yourself and the baby, to achieve the maximum effect, each patient needs to select vitamins, based on the advice of her doctor, who controls the course of pregnancy.
One or two components or the dosage of some vitamin differ. In order not to harm yourself and the baby, to achieve the maximum effect, each patient needs to select vitamins, based on the advice of her doctor, who controls the course of pregnancy.
- How long should I take them?
Do not take multivitamin preparations continuously. The necessary course can be selected only by a doctor, taking into account the state of your body. We have different periods when it is better to stop taking vitamins altogether. In certain weather seasons, when there is enough sun, fresh vegetables and fruits, there is no need to take vitamin complexes.
- Can I continue playing sports?
Not only possible, but necessary. From the first months of pregnancy. They will help to maintain good physical shape, and this will definitely help during childbirth, relieve excessive tension and improve mood. The main thing that you should not forget is that the training program should be specially adapted for pregnant women and should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor or an experienced instructor.
- Do I really have to push in prenatal classes? Will not diligence create the danger of premature birth?
No, there is no danger in this exercise. If there is anything to beware of, it is cycling, horseback riding, roller skating - all sports with an increased risk of injury.
- Can I take a contrast shower?
Possible. If a woman used this procedure before pregnancy. But during pregnancy, the water should not be too hot. By the way, hot baths and a bath should also be excluded.
- Can I continue to have sex during pregnancy?
Each couple decides for themselves. If it gives pleasure to both, if the woman is comfortable, then you can keep your sex life almost until childbirth. Of course, too active sex will have to be excluded, and completely stopped 2-3 weeks before the birth: too vigorous sexual intercourse: it can provoke premature birth.
If earlier it was very strict: from 30-32 weeks, sexual life stops, now sex life is excluded by the doctor only if there are any deviations. After a while, he may allow you to resume intimacy. There are cases when sexual life is excluded for all 40 weeks.
After a while, he may allow you to resume intimacy. There are cases when sexual life is excluded for all 40 weeks.
- Do I need to use protection during pregnancy in order not to get pregnant again?
Very funny question. If one pregnancy has already occurred, re-conception during this period can no longer occur. The need for protection is therefore eliminated.
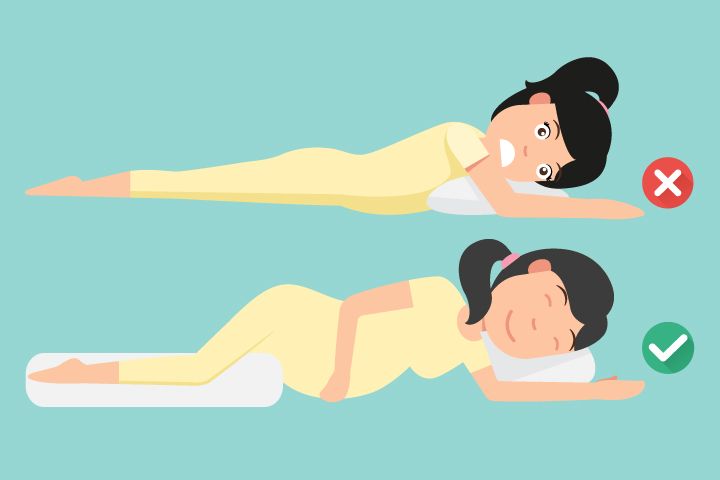
- Can I sleep on my stomach?
On short terms it is possible. The uterus comes out of the pelvic cavity after 12-13 weeks. Before that, it is protected by the pelvic bones, which means that we will not cause any harm to the fetus.
- So, the work of the expectant mother. Is it worth revising your working day, taking into account the new state?
Work during pregnancy is perfectly acceptable if there are no abnormalities. It is important to remember that pregnant women should not lift weights, work in heat and high humidity. Contact with harmful substances and prolonged standing should be avoided.
- Can motorists continue to drive?
You can drive a car if there are no contraindications from the doctor who monitors you during pregnancy. And it is not desirable in the later stages after 30 weeks, because there is a very strong load on the muscles of the pelvic floor, legs and arms work, concentration of attention is required - this is an additional stressful situation for your body. And of course, do not neglect the seat belt. He will not pull your stomach, but will pass under it and under your arm obliquely.
- How to deal with the symptoms of varicose veins?
It depends on the degree of varicose veins, its severity. Despite the rich selection of various drugs for internal and local action - tablets, drops, ointments - the most effective method of struggle is, nevertheless, wearing compression underwear. By the way, those who spend most of their working time sitting at a table, or vice versa, standing on their feet, should also think about the prevention of varicose veins.
It is better to stop your choice on tights: an elastic band or a stocking squeezes the leg too much, and when bandaging the legs, it is difficult to determine the necessary compression.
Tights should be selected by a doctor. A phlebologist works in our clinic. He will be able to choose the desired degree of compression.
Do not be afraid that underwear will be too tight on both legs and stomach: there are special tights for pregnant women. A special insert on the stomach fits him, supporting him, without squeezing at all.
- How to be smokers: won't quitting a bad habit cause stress for the body if the smoking experience before pregnancy was quite long?
Smoking during pregnancy is very bad. This applies equally to active and passive smokers. The fetus develops chronic hypoxia - a constant lack of oxygen. And it primarily affects the development of brain structures. The result is deviations from the norm in mental development. Even if the violations are minor at first, in infancy, most likely, they will manifest themselves in kindergarten or school, when the maximum load falls on the child's intellect. It will be difficult for the baby to learn, to perceive some information.
Even if the violations are minor at first, in infancy, most likely, they will manifest themselves in kindergarten or school, when the maximum load falls on the child's intellect. It will be difficult for the baby to learn, to perceive some information.
Moreover, there is a growing risk of premature births, miscarriages at different stages of pregnancy. Babies are often born small.
Stories that giving up habitual smoking will become a strong stress for the body are far from the truth. Our expectant patients break this bad habit without much difficulty. Even if you regularly inhaled tobacco smoke both before and after conception, you should not think that it is still too late to quit. The harm you will do to your baby if you continue to smoke is incomparable to the reluctance to part with a cigarette.
- Where and how to find a qualified doctor who can be trusted to take care of yourself and your unborn child?
The women's health center of the "SADKO" clinic gathered the best specialists of the city: obstetricians-gynecologists, mammologists, ultrasound doctors, therapists, psychologists, exercise therapy doctors.