Pregnant and don't feel like eating
Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy
Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content6-minute read
Listen
Key facts
- Appetite changes are very common during pregnancy and may affect weight changes.
- A food aversion is an intense dislike of a specific food, together with unpleasant physical symptoms when you see or smell a particular food.
- Eating for 2 during pregnancy is a myth. It is the quality not quantity of food that matters.
- When you are pregnant, your body needs certain vitamins, minerals and nutrients, including iron, folate and iodine.
- If your nausea prevents you from getting enough nutrition, or if you are vomiting, not able to keep food or fluids down or losing weight, see your doctor or maternal health nurse.
What are food aversions, and why does appetite change during pregnancy?
A food aversion is an intense dislike of a specific food, together with unpleasant physical symptoms when you see or smell a particular food. These reactions are usually triggered by emotions associated with food rather than the food itself. You might also experience food cravings (an intense urge to eat a specific food). While these appetite changes are quite common, they can make healthy eating during pregnancy a challenge.
Is it normal for my appetite to change during pregnancy?
It is normal to experience either a loss of appetite or a change in food preferences during pregnancy. This may play a part in how much your weight changes during pregnancy.
Food aversions are common, and around 6 in 10 people experience a food aversion while pregnant.
When are food aversions likely to start and end?
You can experience food aversions resulting from generalised nausea (also known as 'morning sickness') at any time of day, and it tends to peak between week 6 and week 14 of pregnancy.
For this reason, if you've gone off certain foods that are important for your diet, you can try again later in your pregnancy to see if the aversion has passed. If your nausea prevents you from getting enough nutrition, or you are vomiting, not able to keep food or fluids down or losing weight, it's time to see your doctor.
What food aversions are common?
Common food aversions include:
- alcohol
- coffee / tea
- meat
- fatty food
- spicy food
- eggs
What causes food aversions?
While the cause of food aversions during pregnancy isn't clear, hormonal changes could affect the food you enjoy, particularly early in your pregnancy. For example, human gonadotropin (also known as hCG) is a hormone produced during pregnancy. It can cause feelings of nausea, appetite changes and food aversion. Pregnancy can also cause a greater sensitivity to smell and taste, which can influence the foods you prefer to eat.
More research is needed to better understand why food cravings and aversions occur. Some reasons may include hormonal balance or protecting the unborn baby from harmful substances and/or nutritional deficiencies. This is to encourage good nutrition and growth in the pregnancy.
Some reasons may include hormonal balance or protecting the unborn baby from harmful substances and/or nutritional deficiencies. This is to encourage good nutrition and growth in the pregnancy.
How can I eat well and have a healthy diet?
A healthy diet is important for both you and your baby. Eating for 2 during pregnancy is a myth. It is the quality not quantity of food that matters, and there is no need to eat twice as much. It is the quality not the quantity of food that matters most. Your diet should include a variety of the five food groups:
- vegetables and legumes
- breads and cereals
- milk, yoghurt and cheese
- meat, poultry, fish and alternatives
- fruit
During pregnancy, your body also needs plenty of water (8 to 10 glasses each day). You will also need extra vitamins, minerals, and nutrients to help your baby develop, including these:
- Folate (Folic acid) helps build your baby’s brain cells and prevents risk of the baby being born with a birth defect of the brain and/or spinal cord.
 This is especially important in the early stages of pregnancy. Folate-rich foods include green leafy vegetables, broccoli, legumes, oranges, avocado, or fortified breads and cereals.
This is especially important in the early stages of pregnancy. Folate-rich foods include green leafy vegetables, broccoli, legumes, oranges, avocado, or fortified breads and cereals. - Iodine is also important for your baby’s growth and development. Choose foods that are sources of iodine, such as low-fat milk products, eggs, cooked fish and seafood. Foods that contain seaweed, such as sushi, are also a good source of iodine, but if you’re pregnant only eat sushi without raw fish, cold meat or egg, and that is freshly prepared. If you add salt to your food or in cooking, choose iodised salt. If you have a thyroid condition, seek advice from your doctor before taking an iodine supplement.
- Iron-rich foods are recommended during pregnancy. These include red meat, poultry, tofu, and iron-fortified cereals. Eating foods high in vitamin C such as oranges, kiwi fruit, capsicum and broccoli can help iron absorption. Do not take an iron supplement during pregnancy without first checking with your doctor.
 Too much iron can pose health risks to you and your baby. A blood test will help your doctor know if you need to take iron tablets.
Too much iron can pose health risks to you and your baby. A blood test will help your doctor know if you need to take iron tablets.
If you develop an aversion to meat or another essential food, consider how you might substitute these for alternatives. For example, substitute meat for nuts.
It is also important to limit foods containing:
- saturated fats (biscuits, cakes, pies, butter and cream)
- added salt (processed meats, pickled fish, fast foods)
- added sugars (confectionary, sugar sweetened soft drinks, fruit juice and cordial)
Alcohol is not safe for developing babies, and not drinking alcohol is the safest option while you’re pregnant.
There are also certain foods you should avoid during pregnancy, so ask your doctor or maternal health nurse for more information.
Appetite changes during pregnancy are unlikely to harm you or your baby or significantly compromise your nutrition. If you are not sure which foods are most important for your diet, or you have no appetite for foods containing important nutrients, seek advice.
More information on changes in appetite
For more advice on food aversions or appetite loss in pregnancy speak to your:
- doctor
- midwife
- obstetrician
- accredited practising dietitian
Sources:
Epworth Hospital (Ask an Epworth midwife Your guide to early pregnancy), Royal Women Hospital Melbourne (Common concerns in early pregnancy), Queensland Health (During pregnancy), ACT Government (Good Nutrition in pregnancy), Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (Food Intolerance), University of Queensland (What the health: Why do women crave certain foods when they are pregnant), Australian Government (Healthy eating during your pregnancy), Science and Education Publishing (Psychological Factors in Food Aversions, Nausea, and Vomiting During Pregnancy), National Health and Medical Research Council (Australian guidelines to reduce health risks from drinking alcohol)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Foods to avoid when pregnant
- Food cravings during pregnancy
- Guide to a healthy pregnancy
Need more information?
Healthy diet during pregnancy
A healthy diet is an important part of a healthy lifestyle at any time, but especially vital if you're pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy health & wellbeing | Raising Children Network
Pregnant? Here’s all you need to stay healthy during pregnancy, including tips for healthy diet and lifestyle and a guide to pregnancy health care.
Read more on raisingchildren. net.au website
net.au website
Pregnancy and Healthy Eating
It’s especially important to eat healthy food during pregnancy and while breast feeding.
Read more on Healthy Eating Active Living NSW website
Healthy eating when you’re pregnant or breastfeeding | Eat For Health
Eating well during pregnancy and while breastfeeding has health benefits for you and your baby.
Read more on NHMRC – National Health and Medical Research Council website
Having a healthy pregnancy
Having a healthy pregnancy means following a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, knowing what to avoid and making sure your vaccinations are up to date. Find out more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Things to avoid during pregnancy
From hair dye to house paints, there are a few products or lifestyle habits pregnant women and their partners should be cautious of during pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy and diet - Better Health Channel
Good nutrition during pregnancy can help to keep you and your developing baby healthy.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Gi and Pregnancy | GI Foundation
Home / Gi Health Benefits / Gi and Pregnancy Gi and Pregnancy Following a healthy low Gi diet during pregnancy helps protect your child’s future health and improves health and wellbeing for lifelong benefits
Read more on Glycemic Index Foundation website
Healthy Weight During Pregnancy
Weight gain is a normal part of pregnancy. The amount of weight you put on partly depends on your weight before pregnancy.
Read more on SA Health website
Losing weight after birth safely
Tips for losing weight after birth, including how to enjoy a healthy lifestyle, setting realistic goals, breastfeeding and weight loss and when to seek help.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Pregnant Not Eating Food? 7 Appetite Loss Tips for Expecting Moms
Share with:
Pregnancy triggers ravenous hunger but not for everyone.
Having a bun in the oven usually leads to cravings and an increased appetite. Yet, some women feel turned off of food completely. Why? And what can you do about it?
In this article, we’re discussing why you might be pregnant, not eating, and experiencing a decreased appetite.
Most people know that pregnancy can make you furiously hungry, have weird cravings, and develop taste aversions. However, it can also impact your appetite in the opposite way. While many women experience a bigger appetite, some don’t change their eating patterns at all. Others feel their appetite has come to a sudden halt.
If you’re pregnant and not eating food, it may be concerning. When you should be eating more for the baby, why are you eating less?
Fortunately, losing your appetite can be normal during pregnancy. Although you need more nutrients for the baby, your body may go through changes while it adapts.
Your appetite will likely return. If it doesn’t or if you’re unable to eat, contact your doctor. Since your baby needs specific nutrients to develop, eating right during pregnancy is important.
Pregnant Not Eating Food: 7 CausesIf you’re pregnant, not eating food and have a reduced appetite, you’re probably wondering why. There’s a variety of reasons you may want to eat less—instead of more—during pregnancy. Scroll the list of possible causes below and see if you can relate to any.
There’s a variety of reasons you may want to eat less—instead of more—during pregnancy. Scroll the list of possible causes below and see if you can relate to any.
Whether triggered by taste or smell, an aversion is a food that completely turns you off. They’re one of the biggest reasons for decreased appetite. Between 50% and 90% of pregnant women experience cravings and aversions.
The most common aversions include:
- Caffeinated drinks
- Meats
- Fish
- Eggs
Research shows that changes to food cravings and aversions usually happen in the first and third trimesters.
You might wonder why you’ve developed an aversion to a specific food. However, the answer isn’t clear. Some women believe their aversions or cravings are nature’s way of altering their diet, making it healthier for pregnancy. There is no evidence that’s true. You shouldn’t assume your diet is healthy just because you’ve listened to your aversions or cravings.
In fact, it’s possible your aversions could weaken your diet and affect your baby. For example, meats and eggs are a common aversion that can lower your protein intake. Low maternal protein can cause embryo loss, restriction of intrauterine growth, and reduced postnatal growth.
Experts say that a combination of factors likely causes your appetite and preferences to change. That could include biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
#2 Morning SicknessA second major reason why you might be pregnant not eating food is because of morning sickness. Up to 80% of women experience nausea and vomiting in the first trimester.
There’s a variety of reasons morning sickness may happen. Some experts believe hormones play a large role. For other women, food aversions can trigger vomiting.
In any case, if you feel sick when you eat, eating can become less appealing. If you’re afraid of vomiting, you might only eat when necessary.
#3 Decreased Food = Adjusted Feelings of FullnessFood aversions and morning sickness are normal. However, if eating less becomes a pattern, it can change your appetite in the long term.
However, if eating less becomes a pattern, it can change your appetite in the long term.
When you eat less food, your body will begin to adjust. Over time, it will take less food to make you feel full. Instead of feeling full after a meal, eating only half may leave you stuffed.
Many people attribute this change in appetite to their “stomach shrinking.” However, your stomach doesn’t actually shrink—it just gets more sensitive to small amounts of food. If this happens, you’ll probably notice a reduced appetite as your body learns to feel full from less food.
It’s important to recognize that even though you feel full, you might not be getting enough nutrients for the baby.
#4 ConstipationConstipation is another common pregnancy symptom that can affect your appetite. If you’re unable to pass stools normally, you might avoid eating in fear that the problem will worsen. You might also be afraid of the gas pains constipation can cause.
Another reason could be that constipation reduces your appetite. If food stays in your system longer, you might feel fuller longer. When there’s not much room for new food, your body won’t send hunger cues.
If food stays in your system longer, you might feel fuller longer. When there’s not much room for new food, your body won’t send hunger cues.
While you’re expecting, the extra acid in your stomach can create numerous problems. Most commonly, women experience heartburn, AKA acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It can also worsen nausea and vomiting. One lesser-known impact is that it can also decrease your appetite. The excess stomach acid could be making you feel full too quickly.
#6 Mental HealthWe’ve covered the physical reasons why you might lose your appetite while expecting. Next, we need to consider that mental health changes could be why you’re pregnant and not eating.
Research has shown that anxiety and depression can lead to appetite changes. Pregnancy can bring about a slew of new emotions. You might experience anxiety about your health, the baby, or upcoming life changes.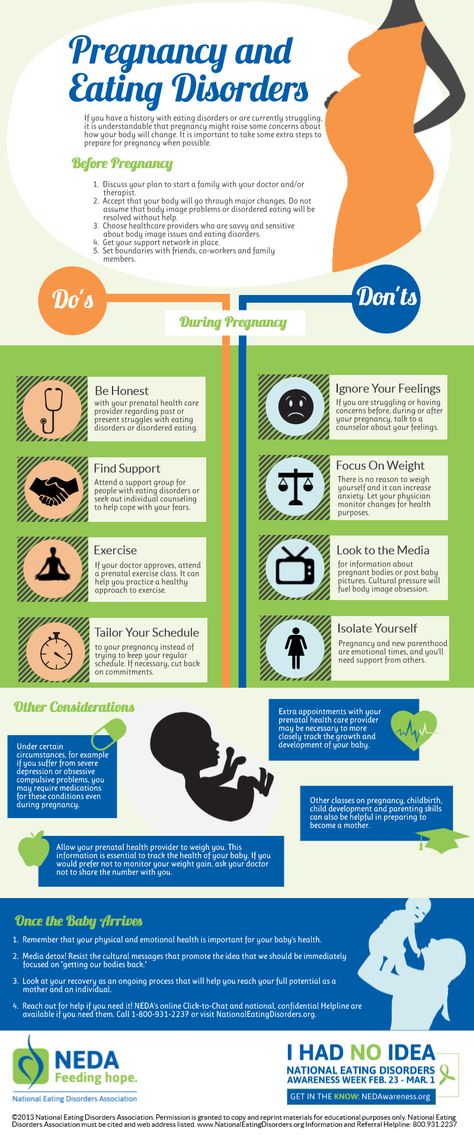 Pregnancy depression can also reduce your appetite.
Pregnancy depression can also reduce your appetite.
Another psychological reason why you might be pregnant and not eating is because of body image concerns.
Most women gain weight during pregnancy; however, it might be difficult to accept. If you’ve experienced body image issues or disordered eating before, pregnancy can trigger these concerns or make them worse.
Knowingly or unknowingly, you may be reducing your food intake to try to limit weight gain.
7 Tips for Those Pregnant Not Eating FoodIf you’re pregnant and not eating food, try to pinpoint the cause. When you understand why your appetite has decreased, you can brainstorm possible solutions. Consider the suggestions below.
#1 Pinpoint Your AversionIf aversions are the reason you’re pregnant and not eating, get specific about the foods you don’t like. For example, maybe you loved spicy foods before but now anything with a kick kills your hunger. Pay attention to other types of aversions too. Perhaps a specific scent or the temperature of food is throwing you off.
Pay attention to other types of aversions too. Perhaps a specific scent or the temperature of food is throwing you off.
If the reason you’re pregnant and not eating food is because of morning sickness, explore your options.
After you’ve pinpointed your aversions using the tip above, brainstorm new snack ideas. When you discover foods that don’t turn you off, add them to your daily staples. Make sure to stock up and keep snacks in your purse to ensure you’re frequently eating.
Need ideas? Read 33 Satisfying Pregnancy Snacks Perfect for Morning Sickness
#3 Eat Frequent, Smaller MealsInstead of eating big meals, break it up into more frequent, smaller meals. This trick is helpful for those experiencing morning sickness or acid reflux.
#4 Take Steps to Reduce NauseaYou probably can’t fully rid yourself of nausea—but you can take steps to reduce the intensity of it. Try a few anti-morning sickness tricks and see what works for you:
Try a few anti-morning sickness tricks and see what works for you:
- Carry a pleasant scent to sniff when you smell something nauseating
- Stay hydrated
- Take B6 vitamin
- Reduce cybersickness before eating (scrolling through your phone or on the computer)
- Use deep breathing
- Take your prenatal vitamin at a different time of day
Read: 16 Best Morning Sickness Relievers to Ban Nausea
Try Our Acupressure Anti-Nausea Wristband to Alleviate Morning Sickness!
#5 Improve Your DigestionIf you think constipation is affecting your appetite, take steps to get things moving again. You can free up space in your stomach and alleviate constipation by:
- Slowly increasing your fiber intake
- Drinking more water
- Exercising
- Using a poop stool (AKA squatty potty)
- Choosing the right iron supplement (or prenatal with iron)
For more tips on improving constipation, read Constipation in Pregnancy: 7 Fixes
#6 Address Your Mental Health
Pregnancy can be overwhelming and you don’t have to go through it alone. If you suspect you’re pregnant and not eating because of anxiety or depression, reach out for help. Your doctor can recommend a therapist, free community resources, or coping mechanisms.
If you suspect you’re pregnant and not eating because of anxiety or depression, reach out for help. Your doctor can recommend a therapist, free community resources, or coping mechanisms.
Also look at science-backed ways to improve your mental health, including:
- Exercise
- Journaling
- Meditation
- Self-guided workbooks
Read:
- 7 Actionable Tips to Manage Panic Attacks in Pregnancy
- What’s The Difference Between Postpartum Depression and Baby Blues?
- Pregnancy Worry: 10 Practical Remedies for Anxiety During Pregnancy
- How to Prevent Postpartum Depression Before Delivery: 8 Ways
- Pregnancy Mood Swings: 9 Powerful Remedies
Thoughts about your weight and body image may be affecting your appetite. Whether these are new or old patterns of thinking, pregnancy is a good time to tackle them.
If you’re pregnant and think you may be struggling with disordered eating, talk to your doctor. They can put you in touch with a counselor, nutritionist, and/or community resources.
They can put you in touch with a counselor, nutritionist, and/or community resources.
Talking about body image is difficult and being pregnant can double the shame. Try to remember that other women struggle with disordered eating when pregnant. Along with advice from your healthcare provider, consider joining a support group for moms-to-be with eating disorders.
Summary: Pregnant Not Eating FoodIf you’re pregnant, not eating food, and wondering why, there’s a few possible causes. Nausea, constipation, extra stomach acid, and mental health problems can all contribute to changes. To increase your appetite, use the tips above. If your appetite doesn’t go back to normal, contact your doctor. Remember that your baby needs nutrients to develop properly, so eating right is extra important during pregnancy.
P.S. If nausea is causing a lack of appetite, try an acupressure wristband. They’re designed to press your P6 acupressure point, alleviating feelings of sickness.
Is Morning Sickness Wrecking Your Appetite? Try Our Anti-Nausea Wristband!
Share with:
The cause of pregnancy whimsical nutrition: it's not because their body lacks something
- Veronica Greenwood
- BBC Future
Subscribe to our newsletter: it will help you understand the context events.
Image copyright Getty Images
What's behind pregnancy's weird eating habits? Most likely, not at all what we are used to thinking about.
We have all heard stories a thousand times about a pregnant woman who, in the middle of the night, wanted a pickled cucumber with ice cream so much that she sent her husband in search of the desired products. Or who passionately wants chocolate - but not any, namely one that cannot be found in stores nearby. nine0011
nine0011
However, why "heard"? Perhaps you yourself experienced an inexplicable desire to eat something special when you were pregnant.
Often they try to explain this by saying that the food whims of pregnant women occur due to the fact that their body (or the body of a developing fetus) suddenly needed certain nutrients, and there is even something attractive, touching in such an explanation.
In the end, bearing a child is a difficult, long, not always pleasant and sometimes mysterious process. And if a burning desire to urgently eat a burger, or even two, has such a good reason - well, so be it. nine0011
However, if you look at the scientific studies of this phenomenon, everything turns out to be much more complex and fascinating.
Researchers have found that the food whims of pregnancy (as a concept) did not exist in all cultures.
And in those non-English speaking countries where pregnant women sometimes report their sudden food cravings, they want something completely different than, for example, women in the US and the UK. For example, in Japan, most often they want such a prosaic thing as rice. nine0011
For example, in Japan, most often they want such a prosaic thing as rice. nine0011
- Why you shouldn't trust your craving to eat
- Why you want to eat land
- Three Pregnancy Myths: Food, Pain, and Airplanes
Skip the Podcast and continue reading.
Podcast
What was that?
We quickly, simply and clearly explain what happened, why it's important and what's next.
episodes
End of Story Podcast
Going further, studies that have tried to find out whether the body gets the special nutrients it needs from the foods that pregnant women most often want to eat have found no evidence of this. nine0011
In fact, women who reported cravings for food ended up gaining much more weight than is considered healthy during pregnancy as a result, which could lead to more complications.
This, however, does not mean that women invent all their desires. And the fact that the reasons for their whims are completely different, they are not dictated by biochemical need.
Understanding why people suddenly crave certain foods in the first place can help, says Julia Hormes, a professor of psychology at the State University of New York at Albany, who studies food cravings in a variety of ways. nine0011
For example, she says that about 50% of women in the US report craving chocolate during the week leading up to their period.
The scientists decided to investigate whether this craving is due to certain nutrients in chocolate that are important for menstruation, or whether it reflects hormonal changes.
Image copyright, Getty Images
Image caption,Food cravings may be related to the psychology or cultural traditions of a particular society
In one experiment, a psychologist gave women a box and asked them to eat its contents when they suddenly felt like eating something . nine0011
nine0011
Some of the boxes contained milk chocolate, which had all the usual chocolate ingredients and also had a nice melt-in-the-mouth sweetness.
In others, white chocolate that does not contain cocoa solids (which give milk and dark chocolate its dark color) but still has a pleasant texture.
Third, cocoa candies with all the nutrients of cocoa, but without the mouthfeel that chocolate does. nine0011
It turned out that white chocolate had the greatest success in satisfying desires, which suggests that whims are not spurred on by any particularly useful cocoa ingredients.
Other studies of "chocolate whims" have not found an association with hormone levels.
In fact, even during menopause, women continued to feel the desire to eat chocolate, Horms emphasizes, they simply began to attribute it to other reasons.
All this brings us to the conclusion that the source of food vagaries is in psychology or in cultural traditions. A craving for a cookie, a chocolate bar, or a bag of chips can start as a simple thought and then grow bigger and bigger, becoming an obsession that is hard to resist. nine0011
A craving for a cookie, a chocolate bar, or a bag of chips can start as a simple thought and then grow bigger and bigger, becoming an obsession that is hard to resist. nine0011
At the same time, thoughts of something delicious can coexist with feelings of guilt.
- Coronavirus and pregnancy: what are the risks for expectant mothers?
- "During my pregnancy I lost 20 kg - the doctors didn't understand what was going on"
- Why pregnancy is not a hindrance to sports by definition, and on the other hand, the culture in which I live tells me that I should not eat it. I really want it, but I can’t ... "And this has its consequences. nine0011
In particular, if you hold yourself back for a long time and a barrier has already formed in your head (you are not allowed to eat this food!), it will be extremely difficult to resist and not lose control of your desires when you reach for a forbidden treat.

And then, after eating a piece of cake, instead of feeling satisfied and doing something else, you eat three more pieces.
Adding fuel to the fire is the fact that women during pregnancy can limit themselves to certain foods - either by following a healthier diet or following the recommendations of a doctor. nine0011
Image copyright, Getty Images
Image caption,Eating a piece of chocolate regularly can keep you from falling into uncontrollable devouring of tiles
All of these circumstances give rise - at least in some countries of the world - to situations in which food cravings are more frequent and more likely to occur and are harder to control, which can lead to, say, weight gain.
In addition, during pregnancy, a woman's whims in eating are not customary to condemn. nine0011
"There are certain moments and situations in our culture where women are not judged for eating foods that are normally supposed to be avoided," says Horms.
 "PMS and pregnancy are considered such situations in society."
"PMS and pregnancy are considered such situations in society." - What if women had complete control over when and from whom to get pregnant?
- Medical myths about childbirth: the exact date, spicy food, and the waste of water
Understanding what leads to a craving to eat something can prevent the transition from just thinking about cake to eating cake, Hormes emphasizes. nine0011
One way is to use distractions, both visual and, for example, olfactory. The other is, with the help of self-contemplation and awareness achieved in meditation, to recognize the presence of desire and let it go, let it go.
Professor Hormes also recommends that if you have a craving for chocolate, for example, buy a very high quality bar and eat a couple of pieces every day, thus preventing the food whim from turning into an obsession and subjugating you.
As for food whims during pregnancy, the cultural factor can play an additional role here: pregnancy for a woman is a very stressful time, and it can be difficult to go through it without someone's help.

A study of Tanzanian women who reported their cravings for meat, fish, grains, fruits and vegetables to scientists showed that when a woman got what she wanted, she perceived it as a sign of support from her husband and family. nine0011
Indeed, it takes a lot of dedication to bring pickles to your pregnant wife at two in the morning, which proves that a person really cares about his wife.
While pickles are great on their own, the fact that your loved one brought them to you and was thinking of you adds value to them.
--
You can read the original English version of this article at BBC Future .
description, features, recommendations, contraindications, what you need to know organism. Because of what this happens, how it affects the child and how to fix it, we will tell in this article.
Contents of the article
Why don't you want to eat?
In the early stages, the reason lies primarily in toxicosis - due to frequent nausea and vomiting, the desire to even look at food simply disappears.
 And this, in turn, is due to hormonal changes in the body, in particular, a sharp increase in the hormone chorionic gonadotropin. A high level of progesterone and fluid retention slows down the work of the digestive tract, which has the same effect. nine0011
And this, in turn, is due to hormonal changes in the body, in particular, a sharp increase in the hormone chorionic gonadotropin. A high level of progesterone and fluid retention slows down the work of the digestive tract, which has the same effect. nine0011 In the second trimester, there is no desire to eat because of the pressure of the uterus on the intestines, which provokes constipation. Lack of appetite during pregnancy in the third trimester is primarily due to the pressure of the fetus on the stomach. Among other reasons:
- increased sense of smell and, as a result, aversion to food due to smells;
- psychological factors: depression, stress, long stay in a bad mood;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys; nine0004
- iron deficiency anemia, in which the need for the fetus in the construction of the circulatory system with insufficient intake of iron-containing products by the mother is replenished from the reserves of her body.

Should I be worried?
At the initial stages of gestation, the laying of organs and systems occurs, the fetus practically does not gain weight. If during this period the numbers on the scales do not increase, there is no need to worry, the main thing is a complete and balanced diet, which is necessary in the first months. nine0011
In the future, the number of calories consumed should increase. A short decrease in appetite is not dangerous, but if it lasts for a long time, it is fraught with consequences. Very rarely (approximately 1 time in 1000 cases) there is indomitable vomiting - the body throws up food eaten in the later stages for a long time. The female body is subjected to dehydration and disruption of the functioning of the liver, and the fetus does not receive vital nutrients, which threatens its death. In order to avoid such an outcome, the expectant mother is hospitalized, glucose, water and electrolytes are administered intravenously. nine0011
Important: pregnant women should gain, not lose weight.
 If the second option is observed, it is necessary to inform the doctor about it. He will prescribe blood and urine tests, ultrasound diagnostics to study the danger of possible risks. You have to keep your finger on the pulse and take action.
If the second option is observed, it is necessary to inform the doctor about it. He will prescribe blood and urine tests, ultrasound diagnostics to study the danger of possible risks. You have to keep your finger on the pulse and take action. How to return the normal feeling of hunger?
In most cases, appetite can be restored during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester without drugs. To get rid of nausea, it is necessary to follow the normal diet of pregnant women with fractional meals: eat little, but often - up to 7 times a day, moreover, at the same time. This develops a habit, which means that the body itself will give the necessary signal. The first time you should have breakfast without getting out of bed: 15 minutes before getting up, have a snack with biscuit cookies or fruit. The daily menu should be dominated by foods high in protein and green vegetables. nine0011
The second rule is water. You need to drink a lot, especially when vomiting. The temperature of the liquid is also important: cool drinks prevent nausea, while warm and hot, on the contrary, aggravate the condition.
 If you feel sick for a long time, resorption of lemon and ginger will help.
If you feel sick for a long time, resorption of lemon and ginger will help. In general, you need to spend more time in the open air, ventilate the room more often, devote more time to sleep and daytime rest, avoid emotional upheavals and stress. When there is no appetite during pregnancy in the third trimester, yoga classes and visiting the pool have a beneficial effect, because physical activity requires energy, and therefore, there is a need to replenish the reserves of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and amino acids. In addition, sport is a guarantee of excellent mood and well-being. nine0011
Psychologists also recommend changing the emotional background in case of such problems, this can be achieved by wearing bright colors and light make-up. And nutritionists say that the desire to eat is stimulated by warm colors, such as orange, beautiful table setting and delicious food. During pregnancy, it is a good habit to eat “for company”, so meet friends more often, actively communicate with other expectant mothers.