Pregnancy week progress
2 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Pictures & More
Are you pregnant this week?
You're not pregnant yet, but if you conceive this week, you'll be two weeks pregnant. That's because healthcare providers use your last menstrual period to determine your due date, so technically the first day of your period is also the first day of your pregnancy. Since you ovulate about two weeks into your cycle, conception happens around the time you're two weeks pregnant.
The best time to conceive
You're most fertile during the three days leading up to ovulation. Signs you may be ovulating include changes in your basal body temperature, breast tenderness, mild cramps, and increased vaginal discharge.
Detecting ovulation
To get pregnant faster, use our Ovulation Calculator, which can help you determine your most fertile days. You can also use ovulation test strips to figure out the days when sex (or insemination) is most likely to lead to pregnancy.
2 weeks is how many months?
You're in your first month!
Baby development at 2 weeks
Getting ready to grow a baby
During the past few days, an increase in estrogen and progesterone prompted the lining of your uterus to thicken to support a fertilized egg. At the same time, in your ovaries, eggs have "ripened" in fluid-filled sacs called follicles.
An egg is released
Once you ovulate, an egg erupts from its follicle and is swept from your ovary into a fallopian tube. Ovulation doesn't necessarily occur right in the middle of your cycle. For example, it could happen any time between days 9 and 21 for women with a 28-day cycle.
Your baby at 2 weeks Tap the plus for more details
advertisement | page continues below
Fertilization
Sperm meets egg
During the 24 hours after ovulation, your egg will be fertilized if one healthy sperm manages to swim from your vagina through your cervix, then up through your uterus into your fallopian tube, and penetrate the egg. There are nearly 250 million sperm in an ejaculation, and about 400 sperm survive the 10-hour journey to the egg. But it's usually only one that succeeds in burrowing through its outer membrane.
The genes combine
In the next 10 to 30 hours, the successful sperm's nucleus merges with the egg's and they combine their genetic material. If the sperm carries a Y chromosome, your baby will be a boy. If it has an X chromosome, you'll conceive a girl. The fertilized egg is called a zygote.
If the sperm carries a Y chromosome, your baby will be a boy. If it has an X chromosome, you'll conceive a girl. The fertilized egg is called a zygote.
Implantation
The egg takes three or four days to travel from the fallopian tube to your uterus, dividing into 100 or more identical cells along the way. Once it enters the uterus, it's called a blastocyst. A day or two later, it will begin burrowing into the lush lining of your uterus, where it continues to grow and divide.
Pregnancy symptoms during week 2
Slippery cervical mucus
Cervical mucus is the vaginal discharge you sometimes find in your underwear. In the days around ovulation, it'll be clear, slippery, and stretchy – like raw egg whites.
Mild cramping
Some women notice mild cramps or twinges of pain in their abdomen, or a one-sided backache, around the time of ovulation. This is known as mittelschmerz – German for "middle pain."
Increased sex drive
Your sex drive may rev up and your body odor may be more attractive to men around the time you're fertile.
Heightened sense of smell
Some studies have found that a woman's sense of smell gets stronger near ovulation – and it may be especially sensitive to male pheromones.
Tender breasts
Hormonal changes around ovulation may make your breasts feel a bit full or sore. To learn more about what to expect in the coming weeks, read about how breasts change during pregnancy.
Cervical changes
During ovulation, your cervix is softer, higher, wetter, and more open. You can feel these changes if you reach inside your vagina with a finger to examine your cervix, though you may have to check it daily to recognize the differences.
A boost in your basal body temperature (BBT)
You can use a special thermometer to take your BBT every morning. On the day after you ovulate, it goes up a bit and stays elevated until your next period.
Your body at 2 weeks Tap the plus for more details
Pregnancy checklist at 2 weeks pregnant
Take your vitamins
If you haven't yet, start taking a prenatal vitamin with at least 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid every day. Prenatal vitamins provide essential nutrients for you and your baby, including iron, vitamin D, and calcium. Folic acid reduces your baby's risk of certain birth defects, and it's crucial to get enough – especially very early in pregnancy when your baby's neural tube is developing.
Prenatal vitamins provide essential nutrients for you and your baby, including iron, vitamin D, and calcium. Folic acid reduces your baby's risk of certain birth defects, and it's crucial to get enough – especially very early in pregnancy when your baby's neural tube is developing.
See your healthcare provider
It's a good idea to have a preconception checkup to make sure your body is in the best possible shape for baby-making. Find out whether you should stop taking any prescription or over-the-counter medications or supplements. Also use this time to talk about any problems or concerns you have about pregnancy or parenthood.
Consider this blood test
You and your partner may want to get genetic carrier screening to see whether you carry genes that would put your baby at risk for serious inherited illnesses. Although many of these conditions are rare, a large study found that 24 percent of those tested were carriers for at least one genetic mutation. Talking to a genetic counselor will help you stay informed about your reproductive choices.
Have frequent sex
Wondering how often to have sex to get pregnant? Studies show that the highest pregnancy rates are in couples who have sex daily or every other day. But you don't have to get busy that often: A good rule of thumb is to try at least every two to three days soon after the end of your period. Sperm can live in your body for about 72 hours, so if you have sex in the three-day span before ovulation, there will be sperm waiting to greet your just-released egg.
Make time for self-care
When you take care of your mental health and physical well-being, you're better able to care for others. Start filling your cup now by eating foods that support pregnancy, getting good quality sleep, exercising, and managing your stress. Try massage, yoga, or deep breathing: Reducing your stress levels can increase your odds of conceiving and having a healthy pregnancy.
Prepare your body for pregnancy
Taking the time to strengthen your belly and back before (or while) your body changes will benefit you throughout pregnancy and beyond. A stronger core prevents back problems as your bump grows, and even shortens your recovery time after childbirth. Weight training and yoga are two good activities to help you get stronger.
A stronger core prevents back problems as your bump grows, and even shortens your recovery time after childbirth. Weight training and yoga are two good activities to help you get stronger.
Know what to avoid
When you're trying to conceive and newly pregnant, you'll want to steer clear of tobacco, marijuana, illegal drugs, alcohol, and too much caffeine.
Pregnancy week-by-week | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Pregnancy week-by-week | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of contentPregnancy at weeks 1 to 4
When you conceive, your body’s hormone levels change, but you may not notice any signs that you’re pregnant yet.
Pregnancy at week 5
You may still wonder, at week 5, if you are pregnant, but you can do a pregnancy test the day after you miss a period.
Pregnancy at week 6
By week 6, your baby is growing quickly and you may notice the early signs of your pregnancy, such as feeling nauseous.
Pregnancy at week 7
Your baby is now about 1cm long and if you haven’t seen your doctor yet, now is a good time to start your antenatal care.
Pregnancy at week 8
By week 8, you might be experiencing morning sickness, need frequent trips to the toilet, and feel tired or moody.
Pregnancy at week 9
Your baby is now the size of a peanut. You won't be showing just yet, but you may have put on a little weight.
Pregnancy at week 10
Think about the prenatal screening tests you might have, and whether you want a dating scan to confirm your due date.
Pregnancy at week 11
During week 11, you might have your first ultrasound and see your baby for the first time.
Pregnancy at week 12
By week 12, your baby is the size of a plum but fully formed, with their organs, muscles, limbs and bones in place.
Pregnancy at week 13
At week 13 of pregnancy, you officially enter your second trimester and hopefully any morning sickness has eased off.
Pregnancy at week 14
By week 14, your baby’s organs have formed, their face is becoming more recognisable, and you may be feeling more energetic.
Pregnancy at week 15
By week 15, your baby may be able to respond to sound and light, while you are gaining weight and your skin and hair are changing.
Pregnancy at week 16
At week 16, you might begin to feel your baby moving, while hormonal changes may be affecting your libido.
Pregnancy at week 17
By week 17, you may want to start thinking about antenatal classes to help you and your partner prepare for the birth and beyond.
Pregnancy at week 18
By week 18, you may start to feel light-headed and dizzy, but you may also be able to find out whether you’re having a boy or a girl.
Pregnancy at week 19
By week 19, you will likely look very obviously pregnant, while your baby can now hear sounds from outside your body.
Pregnancy at week 20
By week 20, your baby is very active although you might feel breathless now and then and your back and hips may ache.
Pregnancy at week 21
At week 21, you should consider whether to do any travel since you may not be able to for much longer in your pregnancy.
Pregnancy at week 22
By week 22, some parts of your baby’s body are fully formed, while some women experience Braxton Hicks contractions about now.
Pregnancy at week 23
By week 23, your baby is practising to breathe in the womb and you might be experiencing some incontinence.
Pregnancy at week 24
Your baby is continuing to grow rapidly and might respond to light and sound. You might also find their movements are getting stronger.
You might also find their movements are getting stronger.
Pregnancy at week 25
As you are approaching the end of the second trimester, you might be starting to feel a bit uncomfortable as your baby continues to grow.
Pregnancy at week 26
Your baby is starting to put on fat and muscle and as your baby grows, your centre of gravity will shift, so you might find that you are starting to w...
Pregnancy at week 27
Your baby is growing fast and probably quite active now. You'll also be gaining more weight and might even be getting some stretch marks.
Pregnancy at week 28
You are now in the third trimester and you'll probably be feeling many of the common discomforts of pregnancy, like a sore back, swelling, heartburn o. ..
..
Pregnancy at week 29
Your baby should weigh about 1kg by now and as your uterus pushes against your diaphragm and lungs, you might be feeling quite breathless.
Pregnancy at week 30
Your baby's reflexes are developing, and they may even be sucking their thumb or fingers. You might be tired and sore, but try to exercise and get eno...
Pregnancy at week 31
Feeling tired and emotional during the third trimester is very common, but it's important to discuss these feelings with your doctor or midwife.
Pregnancy at week 32
Your baby doesn't have a lot of room, but they will still be moving. The extra weight might cause you some back and pelvic pain which can make it diff...
The extra weight might cause you some back and pelvic pain which can make it diff...
Pregnancy at week 33
Your baby's brain and nervous system are now fully developed, and the baby is continuing to gain weight. You'll probably also be feeling sore and tire...
Pregnancy at week 34
As at the start of your pregnancy, you’re probably feeling tired and emotional. The baby doesn't have much room to move, but you might feel them kick ...
Pregnancy at week 35
You'll probably be having lots of Braxton Hicks contractions by now. It's your body's way of preparing for the birth. They should stop if you move pos...
Pregnancy at week 36
Your baby will by now be curled up and cramped inside your uterus and weigh about 2. 5kg. Your bump may have moved down, putting pressure on your lower...
5kg. Your bump may have moved down, putting pressure on your lower...
Pregnancy at week 37
By the end of week 37, your baby is considered full-term. You'll probably be very tired because of the extra weight so try and get as much rest as you...
Pregnancy at week 38
Your baby is now ready to be born and you could go into labour at any time. Make sure you have you plan for getting to the hospital and you have every...
Pregnancy at week 39
Your baby's weight gain should slow down since they are now ready to be born. You might soon start to notice the early signs of labour.
Pregnancy at week 40
Your baby will arrive very soon – if it hasn't already. Babies are rarely born on their due date and many go past 40 weeks.
Babies are rarely born on their due date and many go past 40 weeks.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari.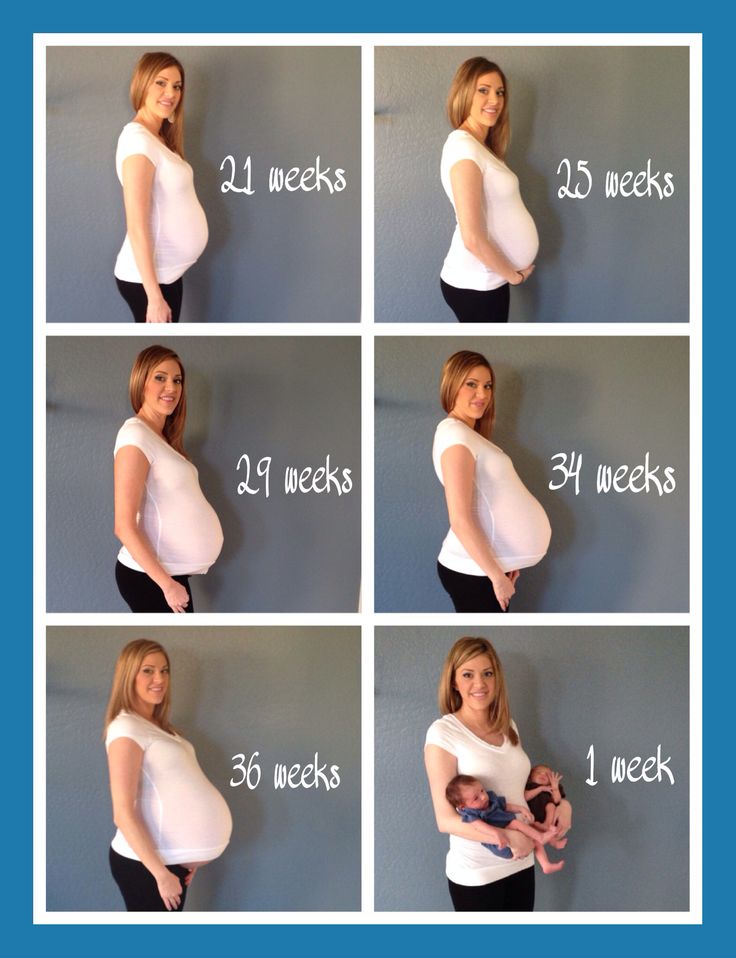 For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Pregnancy calendar
You are pregnant! Your baby will be born in 40 weeks. What changes will occur in your body, how your baby will grow will tell "Calendar of pregnancy".
1-2 weeks
Pregnancy begins at the moment of fertilization or conception.
Fertilization is a complex biological process of the fusion of female and male germ cells (egg and sperm). The resulting cell (zygote) is a new daughter organism.
A mature egg leaves the ovary approximately on the 12-14th day of the menstrual cycle (ovulation) and enters the fallopian tube, where it remains viable for 24 hours. During an orgasm, a man ejects from 200 to 400 million spermatozoa into the woman's vagina. Some of them penetrate through the cervix into the uterine cavity, and from there into the fallopian tubes. Here, spermatozoa retain the ability to fertilize for 48 hours. Thus, within 6-7 days of a woman's menstrual cycle, conception is possible.
During an orgasm, a man ejects from 200 to 400 million spermatozoa into the woman's vagina. Some of them penetrate through the cervix into the uterine cavity, and from there into the fallopian tubes. Here, spermatozoa retain the ability to fertilize for 48 hours. Thus, within 6-7 days of a woman's menstrual cycle, conception is possible.
Fertilization of the female egg is performed by a single sperm in the upper part of the fallopian tube. There are two types of sperm: those containing the Y chromosome (“male”) and the X chromosome (“female”). When an egg cell (containing the X chromosome) fuses with a sperm cell, their genetic material is combined and the sex of the child is determined. If there are two X chromosomes in the child's genetic makeup, it's a girl; if an X chromosome and a Y chromosome, it's a boy. It is impossible to change the sex of the child, so you should not follow the "folk beliefs" that guarantee the birth of a child of a given gender.
The fertilized egg begins to divide with the formation of a multicellular organism and move through the fallopian tube into the uterine cavity. During this period, the nutrition of the embryo is carried out at the expense of those substances that have been accumulated in the egg. If the peristalsis of the tube is slowed down (due to inflammatory diseases), the embryo penetrates the wall of the fallopian tube with the occurrence of an ectopic pregnancy.
During this period, the nutrition of the embryo is carried out at the expense of those substances that have been accumulated in the egg. If the peristalsis of the tube is slowed down (due to inflammatory diseases), the embryo penetrates the wall of the fallopian tube with the occurrence of an ectopic pregnancy.
Implantation (introduction) of the embryo into the uterine wall occurs 7-8 days after fertilization.
On the seventh day of pregnancy, the outer layer of the embryo (trophoblast) begins to produce a hormone - chorionic gonadotropin. This hormone gives the mother's body information that pregnancy has occurred, and begins its functional restructuring. Diagnostic test strips detect the chorionic gonadotropin in the urine of a pregnant woman, which makes it possible to diagnose pregnancy at an early stage.
3-4 weeks
You do not have the expected menstruation, nausea in the morning, and frequent urination during the day. You become emotionally labile, irritable, whiny.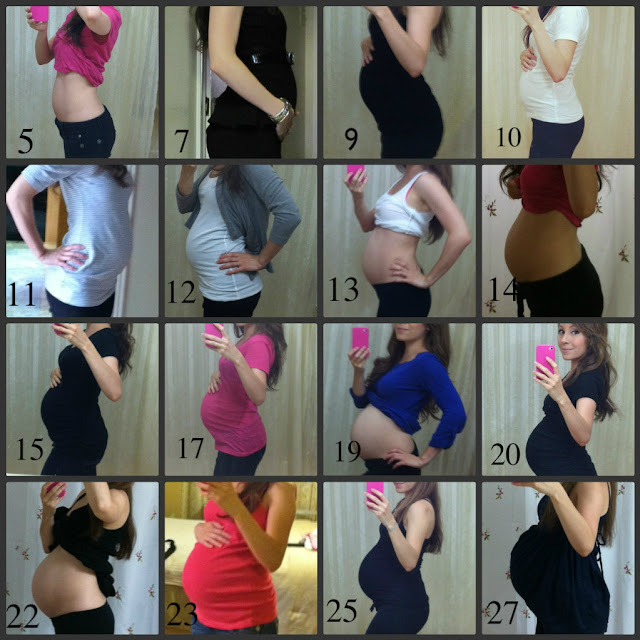 Basal body temperature is above 37°C.
Basal body temperature is above 37°C.
In appearance, your unborn baby resembles a small auricle measuring 4 mm, surrounded by a small amount of amniotic fluid. On the 21st day after conception, the brain and spinal cord are formed. By the end of the first month, the circulation of embryonic blood is established, the umbilical cord has formed - the connection of the embryo with the future placenta. The eye sockets, the rudiments of arms and legs appeared, the laying and development of other internal organs of the fetus is underway: the liver, kidneys, urinary tract, and digestive organs.
5-6 weeks
You no longer doubt that you are pregnant. Regardless of how you feel, all pregnant women need to visit a antenatal clinic and undergo an examination that will allow you to identify and correct existing health problems in time.
Starting from the 5th week, there may be a threat of termination of pregnancy. This will be evidenced by: periodic pain in the lower abdomen and in the lumbar region, a feeling of pressure on the rectum, an increased amount of mucus. If you experience these symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
If you experience these symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
By week 6, the face is formed in the embryo: eyes, nose, jaws and limbs.
7-8 weeks
From the 7th week of pregnancy, the yellow body of pregnancy undergoes reverse development, the production of hormones begins to be carried out by the forming placenta.
The baby develops large blood vessels, the heart becomes four-chambered. Bile ducts appear in the liver. There is a development of the endocrine glands, the brain. The auricles are already formed, fingers have appeared on the limbs. The embryo begins to move. At week 8, under the influence of the Y chromosome, the formation of male gonads (testicles) occurs. They begin to produce testosterone - the male sex hormone, which will lead to the formation of the sexual characteristics of the boy.
9-10 weeks
Your metabolism is changing significantly to provide the growing body with all the necessary "building materials" - amino acids, energy.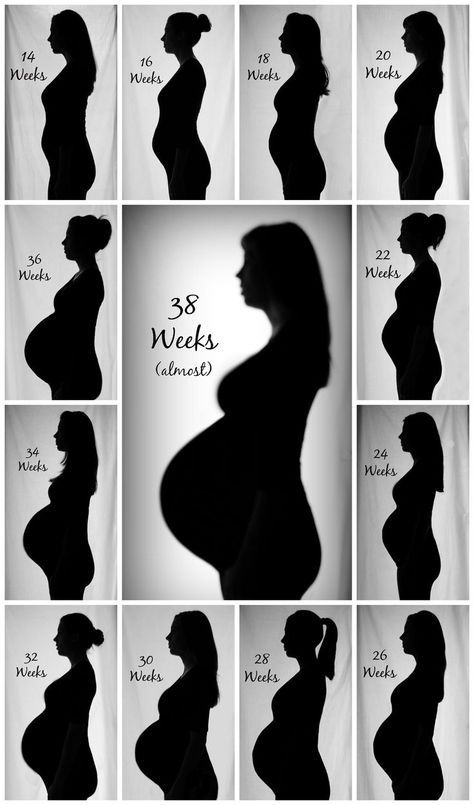 Disadaptation to such a restructuring can result in toxicosis of the 1st half of pregnancy. It is characterized by nausea, vomiting, salivation, weight loss. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Disadaptation to such a restructuring can result in toxicosis of the 1st half of pregnancy. It is characterized by nausea, vomiting, salivation, weight loss. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
At the tenth week, the development of the oral cavity, intestines, rectum, and bile ducts ends in the embryo. The formation of the face and hemispheres of the brain was completed. The development of the cerebellum, the main coordinator of movements, begins.
11-12 weeks
The body has adapted to the new conditions. By this time, nausea, vomiting, salivation practically disappear. You become balanced, calm.
After 12 weeks, the growth of the uterus becomes noticeable
13-14 weeks
By this time, the formation of the main organs of the unborn child is completed. In appearance, the fetus resembles a small person.
15-16 weeks
A change in skin pigmentation is possible - the midline of the abdomen, nipples and the skin around them have darkened. These phenomena should pass soon after childbirth.
These phenomena should pass soon after childbirth.
The formation of the placenta ends. The fetus and placenta represent a single functional system. During this period of pregnancy, the fetus floats freely in the amniotic fluid. The composition of the amniotic fluid can determine the condition of the fetus.
17-18 weeks
These days, your unborn child begins to move. His limbs, ligamentous apparatus, cerebellum have already developed enough. By this time, the formation of the immune system is completed.
19-20 weeks
There have been big changes in your body. The pulse quickened, cardiac output increased significantly (40% higher than the initial level) and the volume of circulating blood (almost 500 ml).
Due to the increased volume of plasma compared to the mass of red blood cells, hemoglobin decreases in blood tests.
Some women during this period experience frequent and painful urination, pain in the lumbar region on the right or left, weakness. A large uterus presses down on the bladder, the mouth of the ureters, disrupting the outflow of urine. Stagnation of urine and incomplete emptying of the renal pelvis create conditions for the development of infection. Bacteriuria develops and pyelonephritis of pregnant women may occur. If there is any suspicion of pyelonephritis, you should immediately consult a doctor, because this disease is not only dangerous for your health, but also for the further growth and development of the fetus.
A large uterus presses down on the bladder, the mouth of the ureters, disrupting the outflow of urine. Stagnation of urine and incomplete emptying of the renal pelvis create conditions for the development of infection. Bacteriuria develops and pyelonephritis of pregnant women may occur. If there is any suspicion of pyelonephritis, you should immediately consult a doctor, because this disease is not only dangerous for your health, but also for the further growth and development of the fetus.
The weight of the baby is 300-350 grams, he often and quite actively moves, swallows amniotic fluid, begins to open his eyes.
21-22 weeks
In these weeks, the fetus already has a mass of 400-500 grams, and it develops very intensively bones and muscles, which require calcium from your body. Therefore, if you do not want to lose your white-toothed smile, then, on the advice of your obstetrician-gynecologist, start taking calcium supplements regularly. This will help save your teeth and get rid of leg cramps. They appear for the same reason of calcium deficiency.
They appear for the same reason of calcium deficiency.
23-24 weeks
At this time, the weight of the fetus is 500-600 g. It already has all the organs and systems fully formed. Until that time, only his lungs remained immature. And now, by 24 weeks, they begin to ripen. And the cells lining the lung alveoli produce surfactant, a substance that, by lubricating the alveoli, prevents them from sticking together during breathing. However, the amount of surfactant is so small that a child born at this time will not be able to breathe on its own. To survive outside the uterus, he needs sophisticated breathing equipment, incubators, a control system, infusors for nutrition, infusion media, artificial surfactant.
There are perinatal centers where children born during these terms of pregnancy are nursed. It is very difficult. And therefore, the longer the pregnancy is prolonged, the more likely the birth of a healthy and viable child. Therefore, try to do everything so that the child is born on time, full-term and healthy.
By this gestational age, the uterus is at a height of about 24 cm above the pubic bone, and now it not only builds up muscles, but is also stretched by the fetus that completely filled its cavity.
25-26 weeks
The fetus already has a mass of 700-750 g. Due to the improvement of the brain structures in his body, a connection is established with the adrenal cortex and they begin to produce corticoids - hormones necessary for adaptation. The pituitary gland of the fetus reaches such a degree of maturity that the production of adrenocorticotropic hormone begins, which also stimulates hormonal production by the adrenal glands. In short, all forces are thrown to the upcoming "publication". But the most obvious changes in these weeks occur in the lungs - there is an increased maturation of cells that produce surfactant. However, a fetus born during this period can only survive in incubators with artificial lung ventilation, artificial feeding with special infusion media. Therefore, try to keep both him and yourself from rash steps.
Therefore, try to keep both him and yourself from rash steps.
At this time, it's time to start preparing for the future feeding of the child. Under the influence of placental lactogen, your breasts, that is, the mammary glands, are growing rapidly. From time to time, droplets of colostrum may appear on the nipples. Daily air baths, washing with cool water, rubbing the nipples with a rough towel will help prepare the nipples for feeding. If the nipples are flat, start to stretch them little by little.
27-28 weeks
This period completes the second trimester of pregnancy. By this time, the fetus weighs up to 1000 g and has a height of up to 35 cm. However, he still cannot live on his own, because. his lungs are not mature enough and special equipment is still needed to nurse him. During these periods of pregnancy, there is an intensive growth of the fetus, the formation of muscles. His movements become more active. Periods of movement alternate with its relatively calm state when the fetus is sleeping. With an ultrasound, you can see that he already knows how to suck his thumb and even smile!
The fundus of the uterus stands on average at a height of 27-28 cm above the womb.
29-30 weeks
The third trimester of pregnancy begins. The uterus stands at a height of 29-30 cm, it becomes more difficult for you to breathe. Now one of the most serious complications can develop - toxicosis of the second half of pregnancy, which is characterized by the appearance of edema, increased blood pressure and the appearance of protein in the urine. For early diagnosis of this complication, it is necessary to carefully observe an obstetrician-gynecologist and follow all his recommendations, incl. strict weight control. In the III trimester of pregnancy, the daily weight gain should be no more than 50 g, i.e. no more than 300 g per week. You should also monitor the ratio of drunk and secreted fluid.
31-32 weeks
Have you asked your doctor how the fetus is? Find out now it's very important. Its position can be longitudinal, transverse, oblique. Correct, normal is the longitudinal position of the fetus. Childbirth is safer with cephalic presentation. From this period of pregnancy, it is necessary to wear a prenatal bandage that will support the anterior abdominal wall and help maintain the correct position and presentation of the fetus. If the presentation of the fetus is breech, i.e. above the entrance to the pelvis is the pelvic end of the fetus, then the bandage should not be worn yet. There is gymnastics to correct the presentation of the fetus.
In the morning and evening for 1 hour, do the following: lie down on the bed on your left side and lie quietly for 15 minutes, then turn over to your right side and lie for the next 15 minutes, and then repeat these turns 2 more times.
Pregnant women with Rh-negative blood and with O (I) blood type need blood tests for Rh - or group immune antibodies. Immunization of pregnant women with Rh-negative blood is carried out from 28 weeks and within 72 hours after childbirth according to the indications, which will be discussed by the doctor observing you in the antenatal clinic.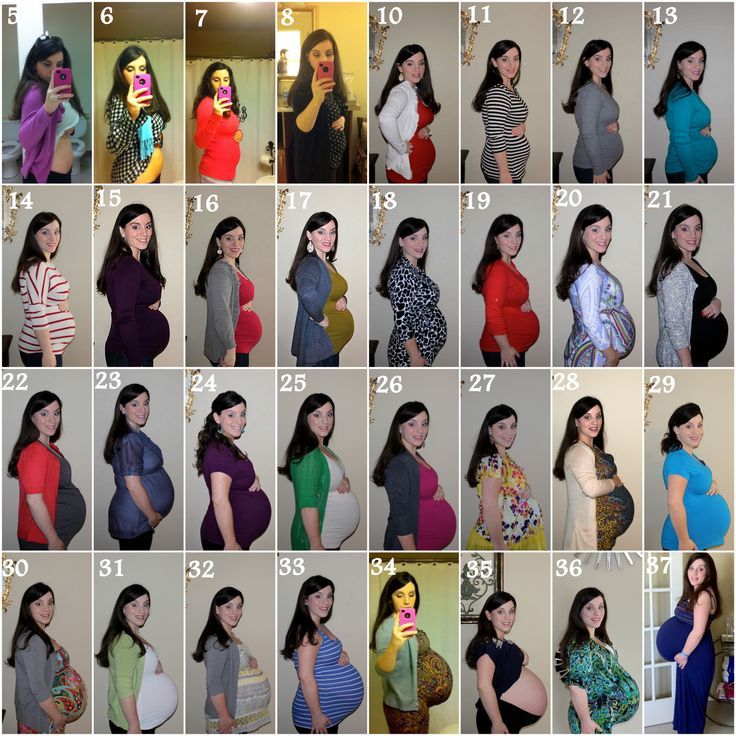
33-34 weeks
The fetus already has a mass of 1800-2100 g, a height of 40-41 cm. By the end of this period, its lungs will begin to produce surfactant in full and will be able to breathe without special equipment. The fetus is fully developed, its chances of surviving in case of preterm birth are greatly increased. However, there is still extremely little subcutaneous fat, so his skin is thin and has a red color. Such a newborn retains heat very poorly and at birth needs an incubator or a heating pad. His body is still covered with fluff and cheese-like grease, the auricles are still very small, but they are already beginning to straighten out, the boy's testicles descend into the scrotum.
Caring for a premature baby is the hardest work for the whole family, associated with high material costs, physical overload of parents, and this work is not always rewarded, since a child can be born and remain sick. Therefore, up to 37 weeks of pregnancy, a woman should be especially attentive to her condition and, at the slightest suspicion of an increase in the tone of the uterus, starting frequent and regular contractions, immediately consult a doctor.
Doctors know that women, in anticipation of the arrival of a new person in the house, begin to glue walls and paint ceilings during this period. Don't take unnecessary risks. For this, prenatal leave is provided from 30 weeks, so that you can avoid overwork, do not push in transport, and have the opportunity to sleep. So repairs, stuffy shops, queues are no longer for you.
35-36 weeks
The fetus already has a mass of 2100-2700 g and a height of 44-45 cm. It is advisable to see a doctor during this period of pregnancy at least once every 10 days.
37-38 weeks
From this point on, your pregnancy is considered full-term. And if you have a baby in these weeks, he will live. Its development is complete. Now he has a mass of approximately 2700-3000 g. Height is 49-50 cm. The remaining two weeks he will add a little in weight and height.
It becomes easier for you to breathe, as the fetal head is pressed tightly against the entrance to the pelvis, the uterus pulls the anterior abdominal wall more, and therefore its bottom sank lower. Tension of the uterus; small sharp pulling pains in the lumbar region.
With an exacerbation of extragenital diseases, the appearance of signs of toxicosis in the second half of pregnancy, with an incorrect position of the fetus, with some gynecological diseases, against which pregnancy develops, a scar on the uterus, etc., early prenatal hospitalization is required. Do not forget to take an exchange card, passport, medical insurance policy and birth certificate to the hospital.
39-40 weeks
You can find out the approximate day of delivery by the date of the last normal menstruation - count back three months and add 7 days. The resulting number will be the estimated date of birth. More precisely, according to many parameters, ultrasound data, additional studies, the date of the first fetal movement, the date of the first visit to the obstetrician-gynecologist, especially if the visit was before 11-12 weeks of pregnancy.
The child already has all the signs of maturity. His weight is more than 3000 g, and his height is more than 50 cm, he has fair skin, a sufficient amount of subcutaneous fat, he retains heat and does not need special heating. He will scream loudly, breathe, suck. There is a very small amount of lubricant on the skin, which will no longer be able to protect it from the effects of amniotic fluid.
For you, regular contractions (1 contraction every 10 minutes) will become an indicator of the beginning of the birth process, or you will feel the outflow of amniotic fluid, you will see scanty bloody discharge - do not panic, call an ambulance, the telephone number for transportation for pregnant women is written on the margins of your exchange card. While she is driving, change your clothes, prepare your passport, exchange card, medical insurance policy and birth certificate.
Weekly pregnancy calendar | Fetal development, trimesters
- Fetal development by week: what happens
- 1-2 weeks
- 3-4 weeks
- 5-6 weeks
- 7-8 weeks
- 9-10 weeks
- 11-12 weeks
- 13-14 weeks
- 15-16 weeks
- 17-18 weeks
- 19-20 weeks
- 21-22 weeks
- 23-24 weeks
- 25-26 weeks
- 27-28 weeks
- 29-30 weeks
- 31-32 weeks
- 33-34 weeks
- 35-36 weeks
- 37-38 weeks
- 39-40 weeks
- What problems might a future mother face
- Advice for pregnant women
Pregnancy is one of the most beautiful and exciting periods in a woman's life, when the expectant mother begins to change her usual way of life, feels responsible not only for herself, but also for her unborn baby. To bear and give birth to a healthy child, it is useful to know what happens in the body at all stages of pregnancy, how the fetus develops, what sensations and changes to expect. A weekly pregnancy calendar will help with this. This is a kind of guide for the expectant mother, who will accompany her for 40 weeks. It will contain interesting answers to questions, which will allow you to properly prepare for the upcoming birth and meeting with the baby.
To bear and give birth to a healthy child, it is useful to know what happens in the body at all stages of pregnancy, how the fetus develops, what sensations and changes to expect. A weekly pregnancy calendar will help with this. This is a kind of guide for the expectant mother, who will accompany her for 40 weeks. It will contain interesting answers to questions, which will allow you to properly prepare for the upcoming birth and meeting with the baby.
Fetal development by week: what happens
A normal pregnancy lasts from 37 to 41 weeks. From the moment of conception to the birth of a child, a number of physiological changes occur in a woman's body, which can affect her well-being, appearance, and lifestyle. Many are accustomed to considering pregnancy in trimesters, but if the expectant mother wants to know everything about the development of the unborn child, here you will need a weekly pregnancy calendar.
The terms of gestation are divided into obstetric - counted from the first day of the last menstruation and embryonic - more than the true one by 2 weeks. Doctors, with the correct calculation and date of the last menstruation, can determine the expected date of birth.
Doctors, with the correct calculation and date of the last menstruation, can determine the expected date of birth.
Keeping and knowing the pregnancy calendar is not only useful, but also convenient. In it, the expectant mother will find answers to such questions:
- what happens in the body during each week of pregnancy;
- how the fetus develops and forms;
- when to undergo scheduled examinations;
- what sensations to expect, what to prepare for;
- when the belly starts to grow;
- when to wait for the first fetal movements;
- how to prepare for childbirth;
- what are the signs that you need to go to the hospital.
The information in the manual will allow you to avoid unnecessary worries, consult a doctor if necessary, carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
Weeks 1–2
Pregnancy starts from the moment of fertilization. This is a complex process in which the fusion of the egg and sperm takes place. This leads to the formation of a zygote. If it contains two X chromosomes, it is a girl; if it contains an X chromosome and a Y chromosome, it is a boy. There is no way to influence the gender of the child. After fertilization of the egg, a multicellular embryo is formed - the blastocyst.
This leads to the formation of a zygote. If it contains two X chromosomes, it is a girl; if it contains an X chromosome and a Y chromosome, it is a boy. There is no way to influence the gender of the child. After fertilization of the egg, a multicellular embryo is formed - the blastocyst.
Throughout the first week after conception, the villi of the fallopian tube move the blastocyst to the uterus, by the second week the embryo sinks into the endometrium, attaches to the wall.
If the peristalsis of the fallopian tube is slow, inflammatory processes are present, or the woman suffers from other gynecological diseases, the embryo may attach to the fallopian tube, leading to an ectopic pregnancy that cannot be saved.
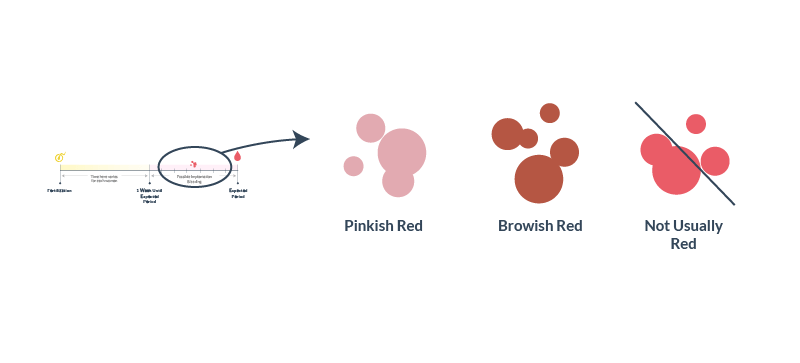
Normal embryo implantation occurs within 7-8 days after conception. During this period, the hormone chorionic gonadotropin is produced, which gives the woman the first signals of a possible pregnancy. To determine its presence in the body, a test or analysis for hCG will help.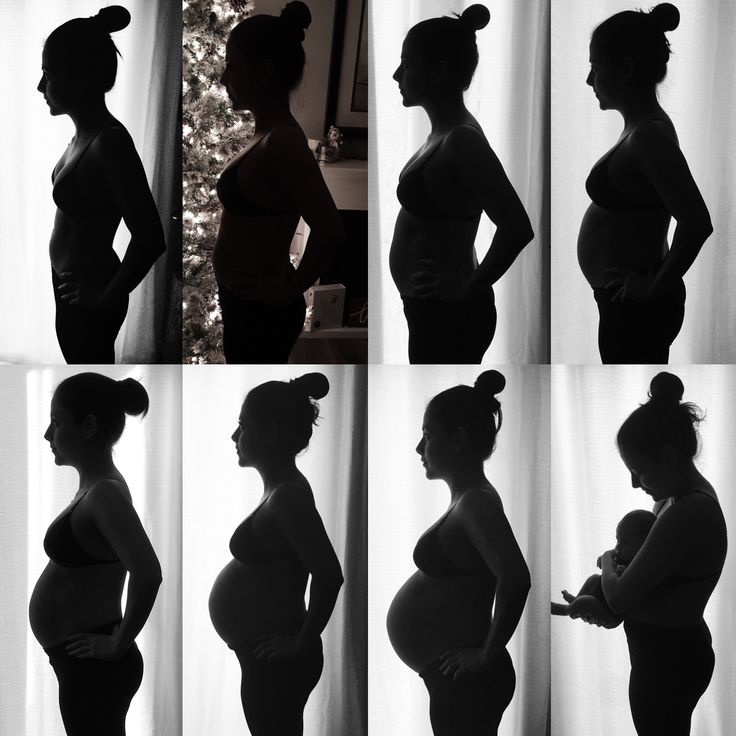 In some cases, during the implantation of the egg, a woman may have small spotting, which she takes for menstruation, so if there is a suspicion of a frowning conception, it is better to buy a test.
In some cases, during the implantation of the egg, a woman may have small spotting, which she takes for menstruation, so if there is a suspicion of a frowning conception, it is better to buy a test.
3–4 weeks
At this stage, the first changes begin to occur in the woman's body, which affect her well-being. The first signs of pregnancy appear:
- no menstruation;
- frequent mood swings;
- frequent urination;
- nausea, urge to vomit;
- restructuring of taste preferences;
- basal temperature above 37°C.
All these symptoms indicate the initial development of toxicosis, which appears against the background of hormonal changes in the body.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, it is important for a woman to register, undergo the necessary examinations, and follow all medical recommendations.
Changes also occur in the development of the fetus, which outwardly resembles a small shell, 4 mm in size.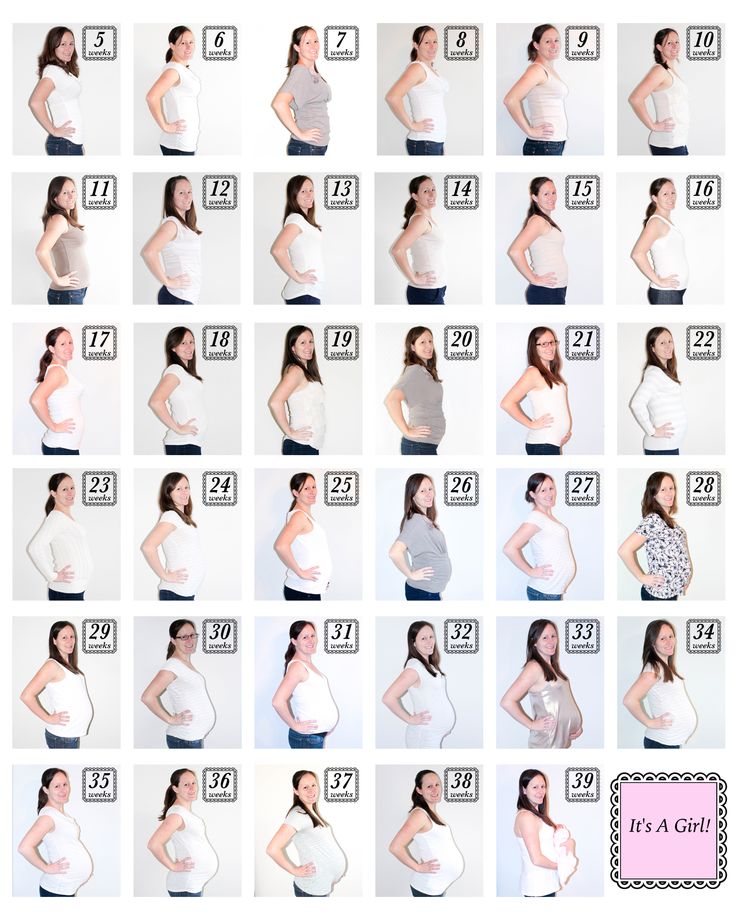 Starting from the 21st day, the formation of the brain and spinal cord takes place, and by the end of the first month, the umbilical cord appears, which holds the connection of the embryo with the future placenta.
Starting from the 21st day, the formation of the brain and spinal cord takes place, and by the end of the first month, the umbilical cord appears, which holds the connection of the embryo with the future placenta.
During this period, other rudiments of organs begin to form: eye sockets, arms and legs, liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract. The neural tube is laid - the future brain, the cardiovascular system. It is during this period that folic acid should be present in the woman's body in sufficient quantities, since its deficiency can lead to neural tube defects, intrauterine pathologies. With the choice of vitamins for pregnant women, a gynecologist who leads the expectant mother will help.
5-6 weeks
During this period, there is no doubt that pregnancy has occurred. A woman should undergo the necessary tests:
- general clinical urine and blood tests to determine the blood type and Rh factor;
- coagulogram;
- TORCH analysis - detects herpes viruses, toxoplasmosis.

- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
If the woman has a history of chronic illness, the doctor may prescribe additional tests.
At 5 weeks, there is a high risk of abortion, so a woman should be very careful about her health. Eliminate heavy physical labor, stress, it is forbidden to lift weights. A possible miscarriage is evidenced by symptoms such as pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, a feeling of pressure in the rectal area, and spotting vaginal discharge. Such symptoms should be a reason for immediate medical attention.
In the normal course of pregnancy, a woman is worried about toxicosis: nausea, heartburn, urge to vomit. A cervical plug is formed, which isolates the uterus from the external environment. Breasts increase in size, frequent urination worries.
The fetus increases in size. An umbilical cord appears, through which he receives all the nutrients from his mother. Visually, the embryo looks like a tadpole. By week 6, the face begins to form: eyes, nose, upper and lower limbs. The cartilaginous tissue is already formed, the skeletal system begins to develop, and the retina is formed in the eyes.
The cartilaginous tissue is already formed, the skeletal system begins to develop, and the retina is formed in the eyes.
The size of the embryo is up to 20 mm. It begins to grow rapidly, vital organs and systems are formed, so it is important for a woman to take vitamins for pregnant women, to exclude factors that can harm the unborn child.
7–8 weeks
Starting from the 7th week, the formation of the placenta ends, which passes only the necessary substances for the fetus, protects it from potentially dangerous compounds that are present in the mother's blood. To provide the unborn child with nutrients, the mother's body begins to work in an enhanced mode, which puts a strain on the heart. Toxicosis worries, the expectant mother gets tired quickly, so it is recommended to rest more.
The fetus still looks like a tadpole, but at the same time it loses its “tail”, increases to 30 mm. Fingers and toes appear, and eyelids appear in front of the eyes. The heart already has 4 chambers, the genitourinary and excretory systems are being formed, the bile ducts are appearing. Large blood vessels, endocrine glands and the brain begin to develop. The embryo begins to move. By the 8th week, under the influence of the Y chromosome, the male gonads (testicles) are formed in the fetus, testosterone begins to be produced, which in the future will make it possible to determine the sex characteristics of the baby.
Large blood vessels, endocrine glands and the brain begin to develop. The embryo begins to move. By the 8th week, under the influence of the Y chromosome, the male gonads (testicles) are formed in the fetus, testosterone begins to be produced, which in the future will make it possible to determine the sex characteristics of the baby.
9–10 weeks
In a woman's body, metabolic processes work more intensively, so the symptoms of toxicosis may increase. The change in metabolism allows you to provide the baby's body with "building materials" - amino acids, energy. Of the symptoms that were not there before, there is heaviness and fatigue in the legs. It is important to adhere to proper nutrition, do not skip meals. If the body does not have enough essential minerals, this can lead to growth retardation in the fetus or the development of anemia in the expectant mother.
During this period, the embryo has already formed all the organs, some of which are already working, and the other will start working after birth. The fetus is actively growing, its weight can reach 10 g. Its brain is divided into hemispheres, the Rh factor and blood type are formed. By the 10th week of pregnancy, the formation of the oral cavity, rectum ends, the cerebellum develops.
The fetus is actively growing, its weight can reach 10 g. Its brain is divided into hemispheres, the Rh factor and blood type are formed. By the 10th week of pregnancy, the formation of the oral cavity, rectum ends, the cerebellum develops.
11–12 weeks
The first trimester is over, the future mother's condition improves, toxicosis no longer worries. The fetus touches the walls of the uterus, moves in the amniotic fluid. A woman can detect skin pigmentation, but this condition will pass and not everyone appears. A slight roundness of the abdomen may appear. A woman is recommended moderate physical activity, proper and healthy nutrition.
The size of the fetus is about 6 cm. Its skin is covered with small villi, it begins to actively move its limbs, and white blood cells are formed.
The body of the expectant mother slowly adapts to new conditions, the general condition normalizes, strength and confidence appear. A second scheduled ultrasound is scheduled.
13-14 weeks
Due to the growth of the fetus, the load on the heart increases, blood flow changes. In such cases, the doctor may prescribe iron supplements. The unborn child puts pressure on the intestines, constipation may disturb, a dark stripe appears on the abdomen, the chest enlarges, and a small amount of colostrum can be observed. In the abdomen, slight flutters are sometimes felt.
At this stage it is worth thinking about special clothes for pregnant women. The fetus has completed the formation of the main organs and systems. On ultrasound, he already looks like a little man. The final stage of face formation takes place, eyebrows appear. The length of the fetus is from 7 to 10 cm.
15–16 weeks
In the body of the future mother, the volume of blood increases, the need for iron increases. There may be increased weakness, dizziness. For many, due to sprains, discomfort appears in the abdomen, the nipples darken, there is a pronounced line on the abdomen.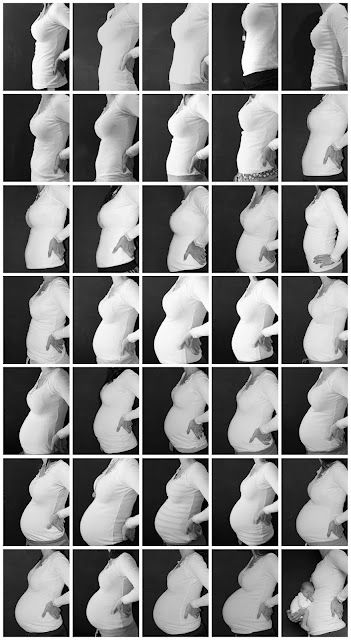 After childbirth, these symptoms will disappear.
After childbirth, these symptoms will disappear.
The fetus continues to grow actively, its proportions become harmonious. The intestines produce the first portions of stool, but it does not consist of digested food, but of amniotic fluid. The rudiments of nails appear on the fingers. The formation of the placenta ends, which makes it and the fetus one. According to the composition of the amniotic fluid, the doctor can determine the condition of the child.
17–18 weeks
The expectant mother gains weight, legs often swell, spider veins appear. The doctor recommends resting more, walking less, wearing compression stockings or stockings. It is important to avoid high heels. Due to increased load and weight gain, shortness of breath, increased sweating may occur. The abdomen acquires roundness, becomes noticeable.
The development of adipose tissue occurs in the fetus, the first rudiments of teeth appear - milk and molars. The skin is covered with a special lubricant that protects the baby from contact with the amniotic fluid. The child is actively growing and developing, begins to recognize sounds.
The child is actively growing and developing, begins to recognize sounds.
19-20 weeks
A growing fetus often causes digestive problems due to pressure on the diaphragm, heartburn, nausea, constipation. The doctor often advises using a special support pillow during rest and after meals.
At this stage, there is a risk of preeclampsia, which is dangerous for both the fetus and the expectant mother. Its symptoms include increased blood pressure, swelling throughout the body, severe nausea, and protein is found in the urine. Treatment is carried out in a hospital under medical supervision.
The endocrine glands are active in the fetus, the formation of blood cells ends, but the nervous system continues to develop. The baby reaches a weight of 300 g, knows how to sleep and stay awake. The expectant mother clearly feels his movements, which are sometimes so strong that they cause discomfort. The belly is quite prominent.
Screening ultrasound is recommended at this stage of pregnancy.
21–22 weeks
A pregnant woman gets tired quickly, often complains of pain in her legs and back. These symptoms appear due to the active growth of the fetus.
The fetus continues to grow, its weight reaches 450 g, its height is about 20 cm. Its lungs and respiratory system are actively developing, but they will work only after birth. There is a rapid heartbeat that can be easily heard through a stethoscope. Joints and bones develop, therefore, to strengthen them, the doctor may advise the expectant mother to take calcium supplements.
23-24 weeks
Increased stress on the pelvic muscles, which can cause frequent urination, up to urinary incontinence. The first stretch marks may appear on the skin, so the doctor will advise you to use a special cream. Occasionally, primary non-birth contractions are disturbing, which should not cause alarm and are the norm.
The swallowing and grasping reflexes appear and increase in the fetus, he can squeeze and unclench his hands, imitate sucking movements.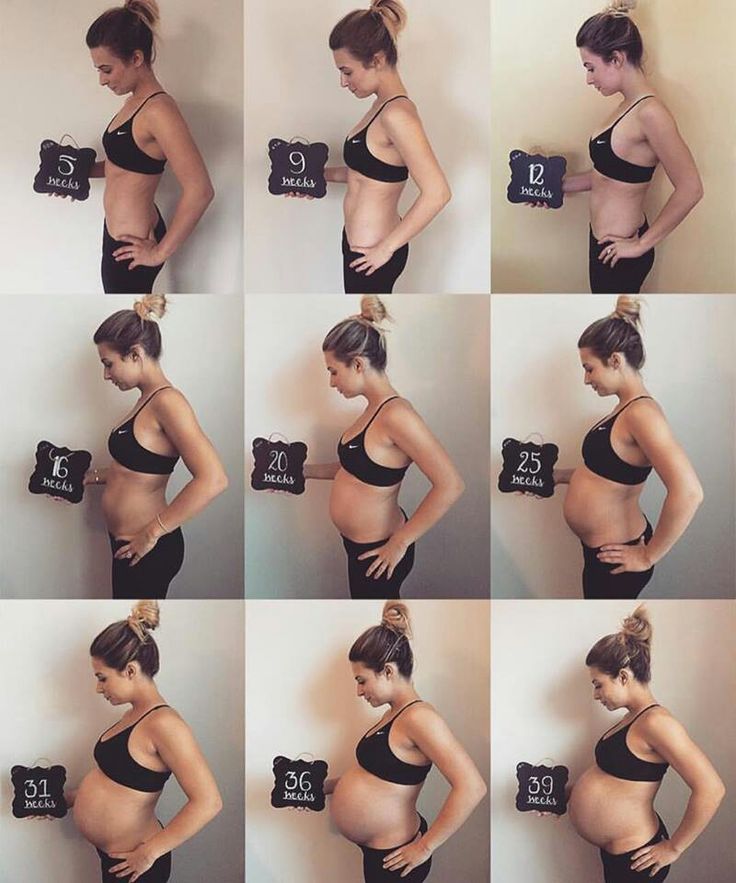 There is an increase in muscle and subcutaneous tissue. All internal organs and systems are almost completely formed. Only the lungs are immature, but by the beginning of the 24th week, the lung cells begin to produce a surfactant that lubricates the alveoli and prevents them from sticking together during inhalation and exhalation. But it is too small, so a child born during this period cannot breathe on its own. With deep prematurity, the baby will need breathing equipment, incubators, and artificial surfactant. Such children are nursed in perinatal centers. Their weight is 600–800 g, their height is about 25–30 cm.
There is an increase in muscle and subcutaneous tissue. All internal organs and systems are almost completely formed. Only the lungs are immature, but by the beginning of the 24th week, the lung cells begin to produce a surfactant that lubricates the alveoli and prevents them from sticking together during inhalation and exhalation. But it is too small, so a child born during this period cannot breathe on its own. With deep prematurity, the baby will need breathing equipment, incubators, and artificial surfactant. Such children are nursed in perinatal centers. Their weight is 600–800 g, their height is about 25–30 cm.
25-26 weeks
A pregnant woman often complains of swelling of her legs, so she is advised to reduce the load, avoid wearing tight clothing, reduce fluid intake. The fruit puts pressure on the intestines, so you should eat small portions, but often, avoid foods that irritate the mucous membrane or increase gas formation. At week 25, a scheduled visit to the doctor, a blood test is recommended.
The child quickly gains weight, subcutaneous tissue gives the skin elasticity, it is not translucent. Body weight is about 0.8–1 kg. The sense organs are sharpened, the production of surfactant is enhanced. The brain is improved, which communicates with the adrenal cortex and stimulates the production of corticoids. The pituitary gland, which begins to produce hormones, also acquires maturity.
27-28 weeks
The baby is noticeably enlarged, which makes it difficult to live a normal life, disturbs sleep. Doctors recommend maintaining physical activity, attending water aerobics and yoga groups.
The child's brain continues to develop actively, the first convolutions appear. On ultrasound, you can see that he reacts to sounds and noise. The expectant mother is recommended to include foods high in iodine, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the diet. The child is active, often pushes. The hair on his skin is gone.
At this stage, the second trimester of pregnancy ends. The fetus weighs up to 1000 g, its height is about 35 cm. It cannot live on its own due to the immaturity of the lungs, so it still needs time. The movements of the baby are more active, and periods of wakefulness alternate with sleep. On ultrasound, you can clearly see the sex of the child, his movements and even a smile.
The fetus weighs up to 1000 g, its height is about 35 cm. It cannot live on its own due to the immaturity of the lungs, so it still needs time. The movements of the baby are more active, and periods of wakefulness alternate with sleep. On ultrasound, you can clearly see the sex of the child, his movements and even a smile.
29-30 weeks
Beginning of the third trimester of pregnancy. The abdomen is large enough, the height of the uterus is 29–30 cm. Women often complain of shortness of breath. During this period, it is important to undergo an ultrasound scan, which will help assess the condition of the fetus, measure blood flow, and examine the maturity of the placenta. At 29-30 weeks, some women may develop preeclampsia, in which there is protein in the urine, severe edema throughout the body, and increased blood pressure.
If no abnormalities are found, the doctor may advise the expectant mother to do breathing exercises to help manage shortness of breath.
Due to the large size of the fetus, its movements become less active. He already opens his eyes during wakefulness and closes during sleep. The iris is well formed, but the final eye color will be known after birth.
He already opens his eyes during wakefulness and closes during sleep. The iris is well formed, but the final eye color will be known after birth.
31-32 weeks
At this stage of pregnancy, the baby gains 300-400 g per week. From this point on, the risk of preterm birth increases. There is increased blood flow, which increases the load on the mother's heart. The doctor may recommend not to go far from home, to eat easily digestible food.
The child is fully formed, the skin turns pink, the amount of subcutaneous fat increases. Often he takes a position upside down. During this period, it is important to determine the presentation of the fetus: longitudinal, transverse, oblique. The best option would be the longitudinal position of the fetus. A woman is advised to wear a prenatal bandage that can support the anterior wall of the abdomen. Before delivery, the position of the fetus may change, so do not worry if it is in a different position.
33–34 weeks
The load on the heart increases, which can cause swelling of not only the extremities, but also the face in a pregnant woman.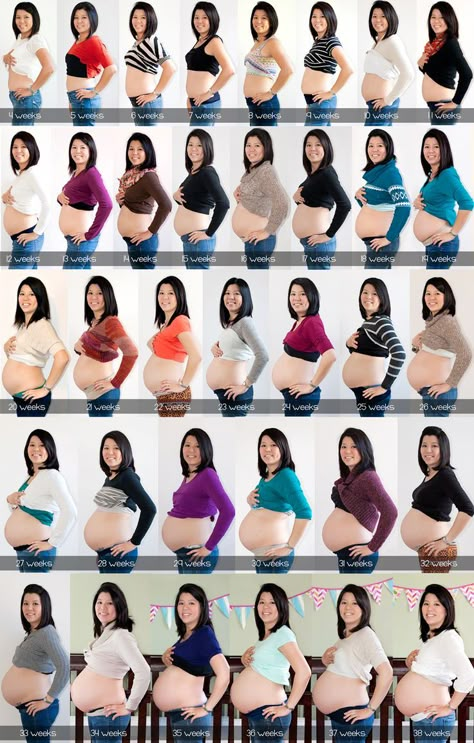 There is an increased risk of developing hemorrhoids, so it is important to avoid foods that can cause constipation. During this period, you can prepare for a trip to the hospital, collect the necessary things and in no case go far from home.
There is an increased risk of developing hemorrhoids, so it is important to avoid foods that can cause constipation. During this period, you can prepare for a trip to the hospital, collect the necessary things and in no case go far from home.
All tissues of the child continue to form, approaching normal values. The baby already looks like after birth. It begins to move into the small pelvis, this can reduce the load on the mother's respiratory centers. His digestive system is formed, he is ready for birth and independent intake of breast milk. All reflexes are well developed. The weight of the baby is about 1800-2100 g, height - 40 cm.
35-36 weeks
Women should prepare for childbirth. Thick discharge from the vagina indicates the discharge of the cervical plug. In such cases, it is necessary to visit a doctor, as this is a sign of an approaching birth. Often worried about prenatal contractions.
The fetus weighs about 2100-2700 g, height - 44-45 cm. At this stage, it is recommended to visit a doctor at least once every 7-10 days. The child in utero begins to lose lubrication, the placenta ages.
The child in utero begins to lose lubrication, the placenta ages.
37-38 weeks
At this stage, the pregnancy is considered full-term, childbirth can occur at any time. The fetus is fully formed, slightly gaining weight and height. Considering that the baby is approaching the birth canal, a woman may be disturbed by minor pains in the lower abdomen, prenatal contractions.
39-40 weeks
Time to give birth. You can find out the approximate day of birth by the date of the last menstruation. The child is completely ready for birth, has all the signs of maturity. After birth, the detachment of the umbilical cord deprives him of nutrition and oxygen, but given that the baby is fully formed, he is able to scream, breathe and suck on his mother's breast.
What problems might a future mother face
During pregnancy, every woman faces certain difficulties, unpleasant symptoms that cause anxiety and make her feel worse. In the early stages of pregnancy, these may be:
- toxicosis;
- frequent urination;
- chest pains;
- increased drowsiness, fatigue;
- vaginal discharge;
- edema.

Late:
- Difficulty walking due to weight gain;
- swelling of the legs;
- discomfort in the lumbar region;
- high blood pressure;
- urge to urinate frequently;
- hemorrhoids;
- stool problems.
All of these symptoms are normal for every woman and will pass fairly quickly. A little discomfort for 9 months cannot be compared with the fact that a long-awaited baby will be born, which will allow you to feel the joy of motherhood.
Advice for pregnant women
Pregnancy is not a disease, so you should not restrict yourself from your usual, but healthy lifestyle. To endure and give birth to a healthy baby, some advice will help:
- in the first trimester, register with the antenatal clinic;
- strictly follow all medical recommendations;
- undergo routine examinations;
- avoid smoking and alcohol;
- eat healthy and proper food;
- take frequent walks in the fresh air;
- avoid large crowds;
- attend swimming pool, yoga and other activities for pregnant women;
- to go on maternity leave on time;
- exclude physical labor in the 1st and 3rd trimesters;
- do not hesitate to visit a doctor if something is bothering you;
- avoid long trips before giving birth.