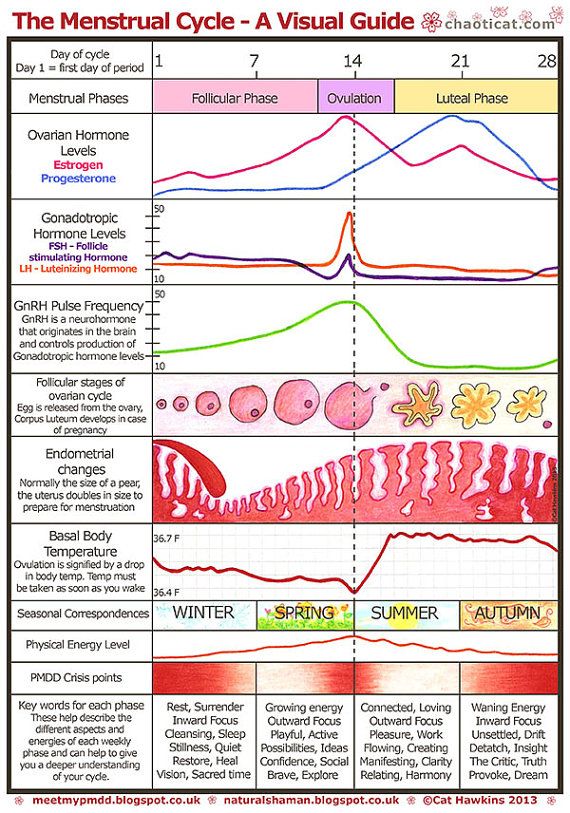
Pregnancy hormones level chart
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone normally produced by the placenta. If you are pregnant, you can detect it in your urine. Blood tests measuring hCG levels can also be used to check how well your pregnancy is progressing.
Confirming pregnancy
After you conceive (when the sperm fertilises the egg), the developing placenta begins to produce and release hCG.
It takes about 2 weeks for your hCG levels to be high enough to be detected in your urine using a home pregnancy test.
A positive home test result is almost certainly correct, but a negative result is less reliable.
If you do a pregnancy test on the first day after your missed period, and it’s negative, wait about a week. If you still think you might be pregnant, do the test again or see your doctor.
hCG blood levels by week
If your doctor needs more information about your hCG levels, they may order a blood test. Low levels of hCG may be detected in your blood around 8 to 11 days after conception. hCG levels are highest towards the end of the first trimester, then gradually decline over the rest of your pregnancy.
The average levels of hCG in a pregnant woman’s blood are:
| 3 weeks | 6 – 70 IU/L |
| 4 weeks | 10 - 750 IU/L |
| 5 weeks | 200 - 7,100 IU/L |
| 6 weeks | 160 - 32,000 IU/L |
| 7 weeks | 3,700 - 160,000 IU/L |
| 8 weeks | 32,000 - 150,000 IU/L |
| 9 weeks | 64,000 - 150,000 IU/L |
| 10 weeks | 47,000 - 190,000 IU/L |
| 12 weeks | 28,000 - 210,000 IU/L |
| 14 weeks | 14,000 - 63,000 IU/L |
| 15 weeks | 12,000 - 71,000 IU/L |
| 16 weeks | 9,000 - 56,000 IU/L |
| 16 - 29 weeks (second trimester) | 1,400 - 53,000 IU/L |
| 29 - 41 weeks (third trimester) | 940 - 60,000 IU/L |
The amount of hCG in your blood can give some information about your pregnancy and the health of your baby.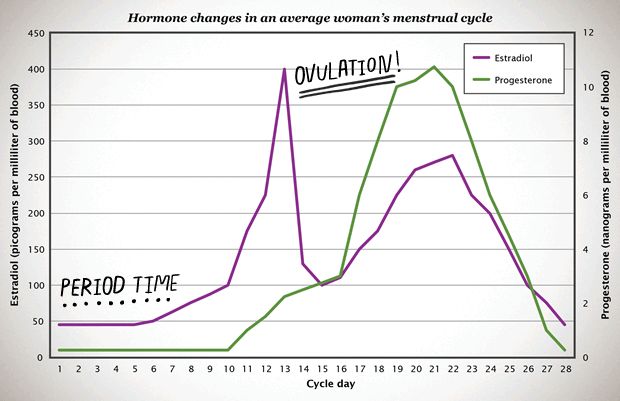
- Higher than expected levels: you may have multiple pregnancies (for example, twins and triplets) or an abnormal growth in the uterus
- Your hCG levels are falling: you may be having a loss of pregnancy (miscarriage) or risk of miscarriage
- Levels that are rising more slowly than expected: you may have an ectopic pregnancy – where the fertilised egg implants in the fallopian tube
hCG levels and multiple pregnancies
One of the ways of diagnosing a multiple pregnancy is by your hCG levels. A high level may indicate you are carrying multiple babies, but it can also be caused by other factors. You will need an ultrasound to confirm that it’s twins or more.
Levels of hCG in your blood don’t provide a diagnosis of anything. They can only suggest that there are issues to look into.
If you have any concerns about your hCG levels, or wish to know more, speak to your doctor or maternity healthcare professional. You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436.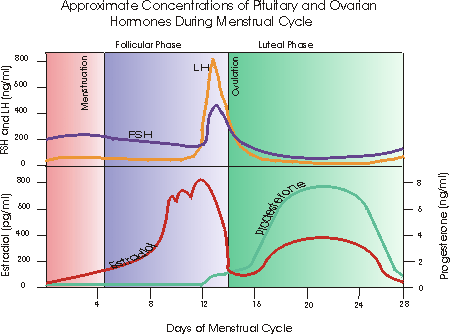
Sources:
UNSW Embryology (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin), Elsevier Patient Education (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin test), SydPath (hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotrophin), Pathology Tests Explained (Human chorionic gonadotropin), NSW Government Health Pathology (hCG factsheet)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: December 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Due date calculator
- Pregnancy tests
- Early signs of pregnancy
Need more information?
Human chorionic gonadotropin - Pathology Tests Explained
Why and when to get tested for hCG
Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website
Pregnancy testing - MyDr.
 com.au
com.au Pregnancy testing can be done from around the time that your period is due, and involves testing your urine for the pregnancy hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Read more on myDr website
Pregnancy tests
Find out how a home pregnancy test works.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy testing - Better Health Channel
Sometimes, a home pregnancy test may be positive when a woman isn’t pregnant.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Molar pregnancy
A molar pregnancy is a type of pregnancy where a baby does not develop. A molar pregnancy can be either complete or partial.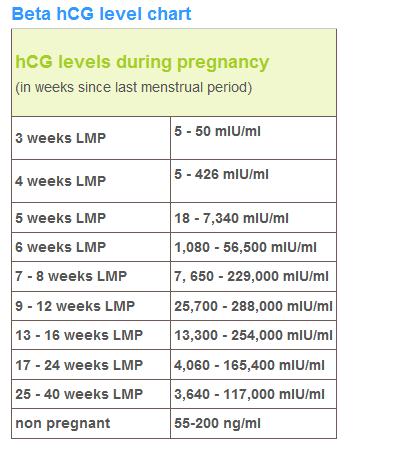
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Beta HCG Test | HealthEngine Blog
A Beta HCG (BHCG or Blood Pregnancy Test) May Be Performed by Your Doctor If They Suspect That You May Be Pregnant, or if You Suspect Pregnancy Yourself!
Read more on HealthEngine website
5 weeks pregnant: Changes for mum
Week 5 of pregnancy is probably when you’ll know that you’re pregnant because your period is missing. There are also subtle changes in your body which are symptoms of pregnancy such as changes to your breasts, and pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and pregnancy heartburn. These changes are caused by pregnancy hormones, like hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, produced by the placenta) which is the hormone detected by a pregnancy test.
Read more on Parenthub website
4 weeks pregnant: Key points
When you are 4 weeks pregnant your body and your new baby are undergoing rapid changes. The placenta forms and begins producing a hormone called human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), which is the substance a pregnancy test detects to confirm you are pregnant. The cells which are growing into your new baby establish membranes which connect them to the placenta and prepare themselves for differentiation into different types of cells, which will occur next week when you are 5 weeks pregnant. These developments may cause you to experience unusual emotions and also cause changes in your body such as darkening of the areolas of your nipples.
Read more on Parenthub website
Week by week pregnancy- 6 weeks pregnant
6 weeks pregnant is a time when embryo development is occurring rapidly and pregnant women often start experiencing pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness. Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Read more on Parenthub website
5 weeks pregnant: Key points
The fifth week of pregnancy begins around the time your menstrual bleeding is due and is a good time to take a pregnancy test to confirm that you are pregnant. You are also likely to begin experiencing pregnancy symptoms like fatigue, morning sickness and changes to your breasts this week. Your baby is still only about 1.5mm long but it is developing rapidly and taking on a more human form. If you have not already visited your doctor the 5th week of pregnancy is a good time to do so.
Read more on Parenthub website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.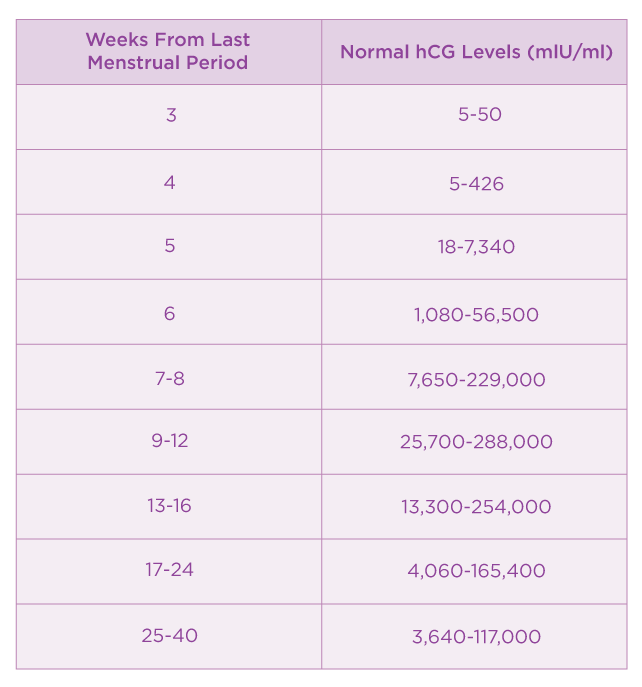
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care.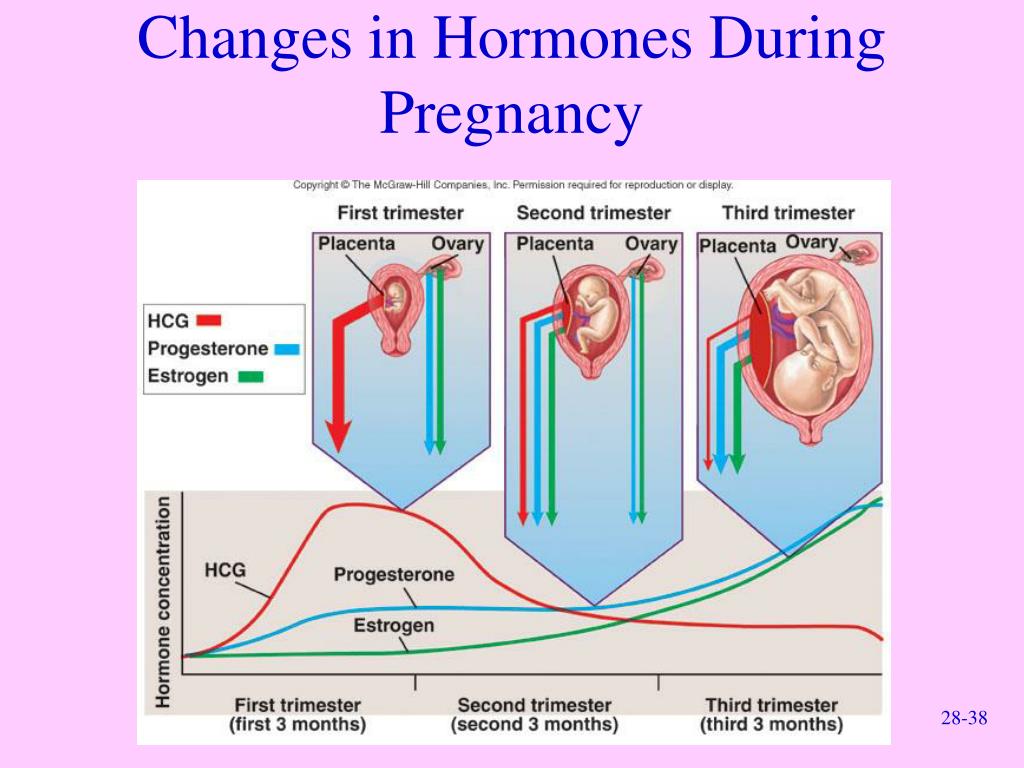 If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
HCG Levels in Pregnancy & hCG Levels Chart by Week
Human chorionic gonadotropin, or hCG for short, is often referred to as “the pregnancy hormone” because it’s present in large quantities during pregnancy. And it is, after all, the hormone that many at-home pregnancy tests are designed to detect! Find out more about what hCG is, when it’s detectable by at-home pregnancy tests, and what the typical hCG levels are for each of the early weeks of pregnancy.
And it is, after all, the hormone that many at-home pregnancy tests are designed to detect! Find out more about what hCG is, when it’s detectable by at-home pregnancy tests, and what the typical hCG levels are for each of the early weeks of pregnancy.
What Is hCG and When Does Your Body Start Producing It?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is known as the pregnancy hormone, as your body produces it in large amounts when you’re pregnant.
Although you can have low levels of hCG in your body at any time, the levels of this hormone tend to rise sharply early on in your pregnancy for two reasons:
About 10 days after conception, the fertilized egg attaches to the lining of your uterus and your body starts to make hCG. Over the next week or so, hCG levels will increase.
At about 4 weeks pregnant, the egg—now called an embryo—implants further into the uterus and begins to produce even more hCG, which triggers increased productions of other hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
Together, these hormones help build the lining of the uterus and send signals to the ovaries to stop releasing eggs, ultimately stopping your period.
During these early weeks of pregnancy, you may not show any outward signs of being pregnant and you may not even suspect that you’re pregnant! You may, however, experience implantation bleeding when the fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus (as described above). This is normal and may resemble spotting or a light period.
When Can Pregnancy Tests Detect hCG?
Home pregnancy tests often work by detecting hCG in your urine. All of these over-the-counter pregnancy tests work a little differently, so check the instructions in or on the box. Keep in mind that hCG levels increase over time, so at-home tests are more accurate as your pregnancy progresses. Therefore, a home-pregnancy test that’s taken too early might not detect low levels of hCG and could produce a false negative, meaning the result is negative when you’re actually pregnant. If you’re wondering when to take an at-home pregnancy test, try one of the following timelines:
If you’re wondering when to take an at-home pregnancy test, try one of the following timelines:
You might try taking a pregnancy test about three to four weeks after the first day of your last period, as this is when the levels of hCG in your urine will have increased enough to be detectable.
You could wait until around the time you miss your next period, which could be the initial clue that you may be pregnant anyway! By then, the levels of hCG are detectable.
A blood test is the most accurate way to detect hCG levels, because more of the pregnancy hormone is present in the blood than in the urine. Plus, blood tests need less of the hCG hormone to detect a pregnancy, as explained below:
Blood tests. Pregnancy blood tests can detect hCG hormone levels as low as 5 to 10 mIU/mL.
Urine tests. At-home urine tests require higher levels of hCG to detect a pregnancy, typically at least 20 mIU/mL.

If your home pregnancy test is positive, your healthcare provider may offer a blood test to check your hCG levels. The results can help your provider confirm your pregnancy and determine how far along you are.
If you’ve just found out you’re pregnant, you can get an estimate of your due date with our Due Date Calculator using either the date of conception or the date of the first day of your last menstrual period!
hCG Levels Chart by Week
The week-by-week chart below will give you an idea of how your hCG levels may rise during the first trimester, and then dip slightly during the second trimester. Keep in mind that, if you want your hCG blood test results explained in more detail, your healthcare provider is the best person to ask.
What Does It Mean if You Have High or Low hCG Levels?
It’s important to remember that every pregnancy is different, and you may have lower or higher levels of hCG hormone than what’s indicated in the week-by-week chart above. Most likely, there’s no cause for concern, but your healthcare provider will help you understand what these levels mean.
Most likely, there’s no cause for concern, but your healthcare provider will help you understand what these levels mean.
Low Levels of hCG
Low levels of hCG are normal for non-pregnant women and men. Normally, hCG levels would be less than 5 mIU/mL and less than 2 mIU/mL, respectively, for these groups. If you’re pregnant and experience low hCG levels, it’s important to look at your entire pregnancy as a whole. Your healthcare provider will consider all the factors of your pregnancy to determine why you might be experiencing lower-than-normal levels of hCG. If your provider suspects anything like an ectopic pregnancy, they may perform additional tests to rule it out.
High Levels of hCG
Likewise, high levels of the hCG hormone might not indicate anything out of the ordinary. However, a higher-than-normal level of hCG may be a sign that you’re having twins or triplets! Again, your healthcare provider will work with you to determine an appropriate course of action, if any is needed.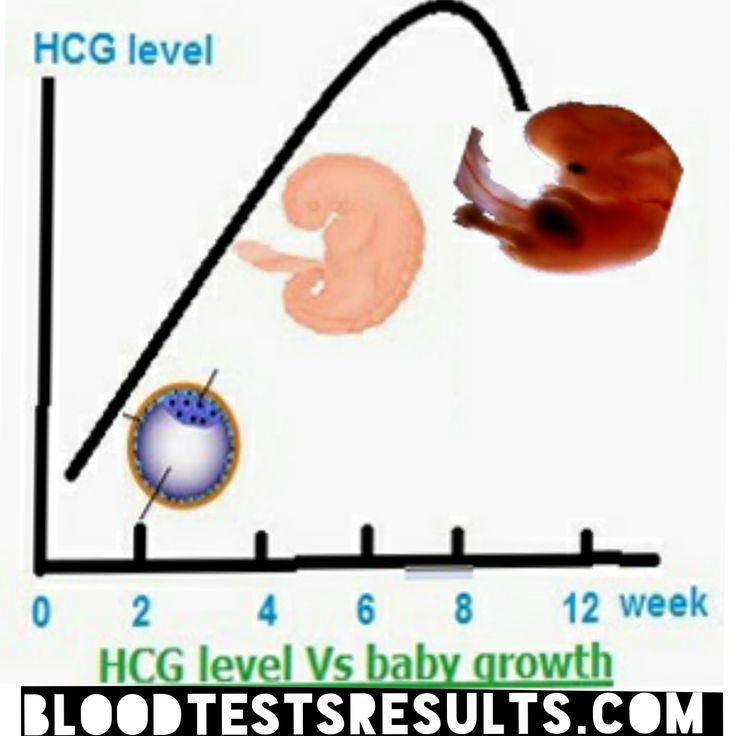 Lower- or higher-than-normal levels of the hCG hormone during your pregnancy might not indicate anything unusual. However, it’s always a good idea to follow up with your healthcare provider as a precaution, regardless of any questions or concerns you have. Read more about other pregnancy symptoms not to ignore.
Lower- or higher-than-normal levels of the hCG hormone during your pregnancy might not indicate anything unusual. However, it’s always a good idea to follow up with your healthcare provider as a precaution, regardless of any questions or concerns you have. Read more about other pregnancy symptoms not to ignore.
The Bottom Line
The hCG hormone plays an important role in your pregnancy, and the changing levels of this hormone are just one of many transformations your body will experience as your baby develops. Although hormonal changes can make you feel a little off from time to time during your pregnancy, try to take these as reassurance that your baby is growing, and you’re getting closer and closer to the day you finally get to meet them. In the meantime, prepare for your baby’s arrival and get rewards on all your diapers and wipes purchases with the Pampers Club app! Ready to share your pregnancy news with friends and family? Get creative pregnancy announcement ideas in the video below!
Physiological changes in a woman's body during pregnancy
A woman's pregnancy lasts an average of 280 days. Starting from the very first days, a woman's body is completely rebuilt in order to prepare for childbirth and the birth of a new person into the world. There is not a single tissue and not a single organ that would not take part in this process of transformation. Each system of the body adapts to a new state according to its own scheme.
Starting from the very first days, a woman's body is completely rebuilt in order to prepare for childbirth and the birth of a new person into the world. There is not a single tissue and not a single organ that would not take part in this process of transformation. Each system of the body adapts to a new state according to its own scheme.
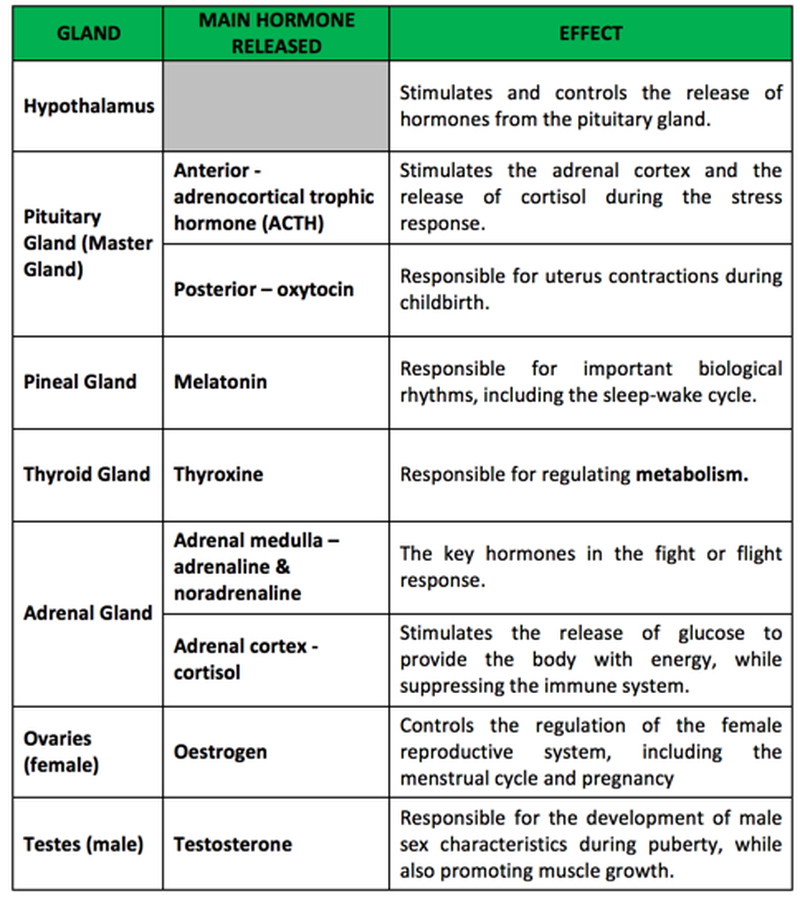
1) The hormonal system comes into action first. Chorionic gonadotropin, or pregnancy hormone, informs the whole body about the new condition already on the 6-8th day. The number of female hormones that previously regulated the menstrual cycle is reduced. The content of prostaglandin, a hormone that preserves pregnancy, increases. Of course, these changes affect behavior and character. Tearfulness and impressionability of pregnant women, whims, mood swings - all these are consequences of hormonal changes.
2) Since hormones are produced in the endocrine glands, the glands themselves also change. The pituitary gland, adrenal glands, ovaries are reorganized into a new mode of operation.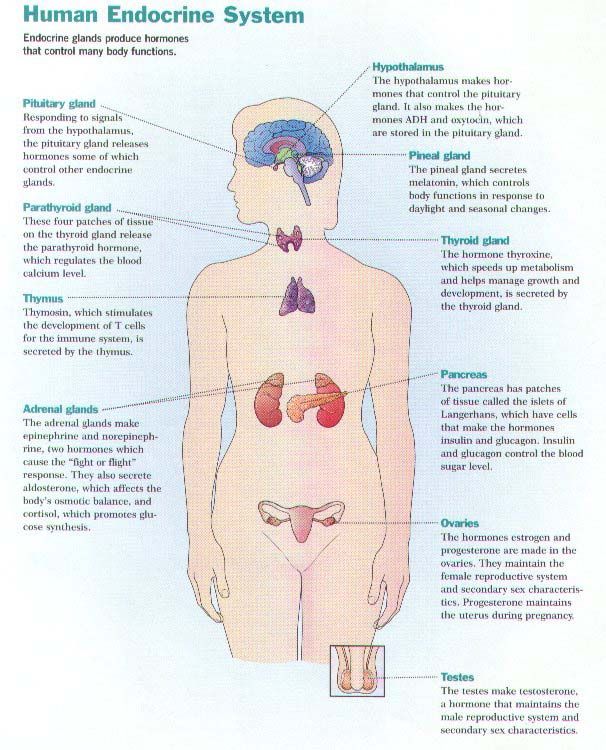 The substances they secrete now contribute to the growth of the uterus and mammary glands.
The substances they secrete now contribute to the growth of the uterus and mammary glands.
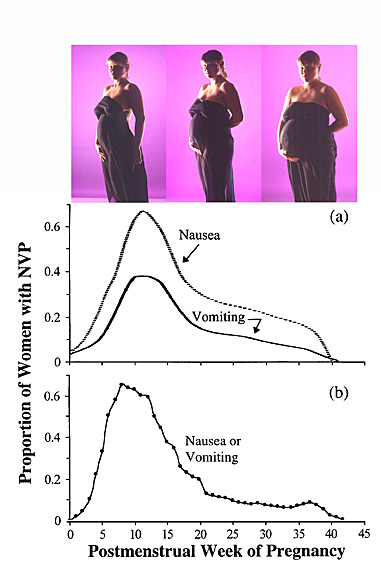
3) The nervous system reacts to changes in hormones and also adapts. It is changes in the nervous system that cause nausea and vomiting in the first half of pregnancy. During this period, the processes of excitation prevail over the processes of inhibition. But in the second half of pregnancy, the processes of inhibition gradually take over - this is associated with drowsiness and a weakening of the cognitive functions of the pregnant woman. The body makes this sacrifice to smooth out the shock of labor activity.
4) Changes in the cardiovascular system are associated with the fact that a pregnant woman has a third circle of blood circulation - uteroplacental, through which the fetus is supplied with maternal blood. Increases body weight and volume of circulating blood - from 4000 to 5200 ml on average; metabolism is enhanced. This increases cardiac output, that is, the amount of blood the heart ejects during contraction.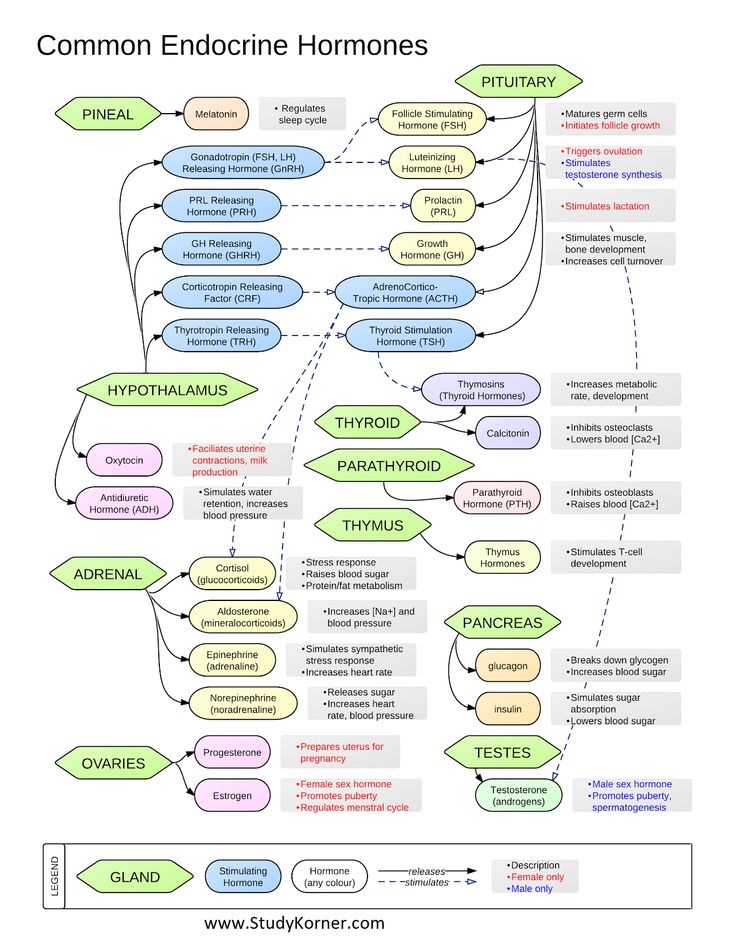 In a healthy woman, the heart quickly adapts to additional loads, but in some cases complications are possible.
In a healthy woman, the heart quickly adapts to additional loads, but in some cases complications are possible.
5) An increased load falls on the digestive system. First, the secretion of gastric juice is inhibited, which slows down the digestion process. Secondly, the blood supply to the digestive system does not increase - blood is needed for the baby. Therefore, intestinal motility weakens, because of this, pregnant women often complain of constipation. In addition, the fetus presses on the stomach, due to which part of the food mass can return to the esophagus and cause heartburn. Therefore, pregnant women in the last weeks are recommended fractional meals - frequent meals in small portions.
6) The lungs and other organs of the respiratory system also adapt to increased stress. More oxygen is required, but at the same time, the growing belly props up the chest and presses on the diaphragm. The lungs expand in width, the respiratory rate quickens.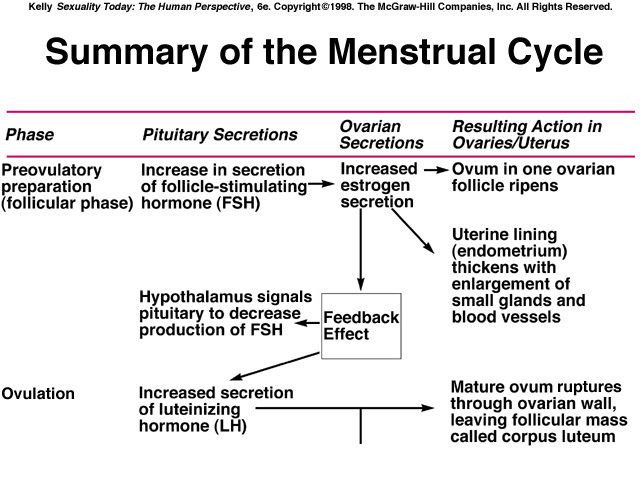
7) The excretory system also works for two, removing toxins from the blood produced by two organisms, mother and child. Therefore, the daily volume of urine may increase. In this case, the bladder is in hypotonia due to the hormone prostaglandin.
8) Musculoskeletal system. Major changes in the spine occur under the weight of the growing belly. The lumbar lordosis becomes deeper, and the woman may suffer from back pain from the unaccustomed bending. Shortly before childbirth, hormones begin to be released in the body that help soften the joints. This is necessary so that the baby's head passes through the mother's pelvis without injury. Because of these hormones, the joints of the limbs can also become slightly loose, and then the woman develops a characteristic duck gait.
9) Metabolism. The body of a pregnant woman accumulates nutrients and water. But normally, weight gain should not exceed 12-15% of the woman's initial weight. In addition, the need for vitamins increases, especially for those substances that the body cannot synthesize on its own.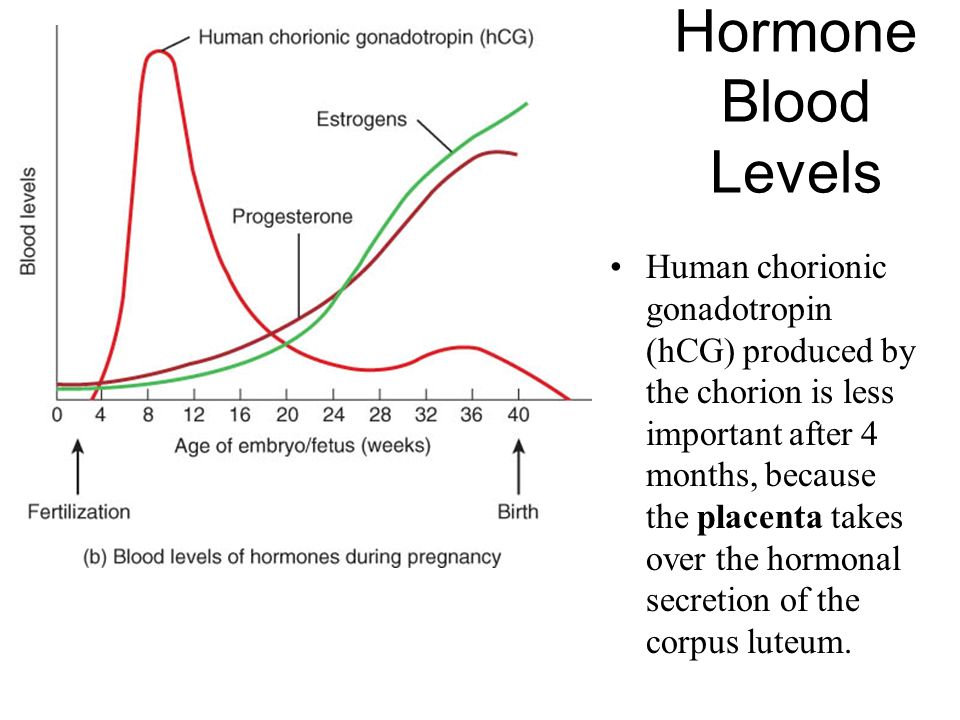
During pregnancy, each of the systems of a woman's body is transformed before childbirth. Both the woman and the supervising doctor must monitor the condition of all systems in order to notice possible problems in time.
Citizens | Ministry of Health of the Kaliningrad Region
| Gestational age | Analyzes | Events (registration, medical examinations, doctor visit schedule) |
| Up to 12 weeks | Early registration in the antenatal clinic Taking medications: folic acid throughout the first trimester, no more than 400 mcg / day; potassium iodide 200-250 mcg/day (in the absence of thyroid disease) | |
| At first appearance | An obstetrician-gynecologist collects anamnesis, conducts a general physical examination of the respiratory, circulatory, digestive, urinary system, mammary glands, anthropometry (measuring height, body weight, determining body mass index), measuring the size of the pelvis, examining the cervix in the mirrors, bimanual vaginal study | |
| Not later than 7-10 days after the initial visit to the antenatal clinic | Inspections and consultations: - general practitioner; - a dentist; - an otolaryngologist; - an ophthalmologist; - other medical specialists - according to indications, taking into account concomitant pathology | |
| First trimester (up to 13 weeks) (and at first visit) | 1. 2. Biochemical blood test (total protein, urea, creatinine, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, alanine transaminase (hereinafter - ALT), aspartate transaminase (hereinafter - AST), glucose, total cholesterol. 3. Coagulogram - platelet count, clotting time, bleeding time, platelet aggregation, activated partial thromboplastin time (hereinafter referred to as APTT), fibrinogen, determination of prothrombin (thromboplastin) time. 4. Determination of antibodies of classes M, G (IgM, IgG) to the rubella virus in the blood, to the herpes simplex virus (HSV), to cytomegalovirus (CMV), determination of antibodies to toxoplasma in the blood. 5. General analysis of urine. 6. Determination of the main blood groups (A, B, 0) and Rh-affiliation. In Rh-negative women: a) examination of the father of the child for group and Rh-affiliation. 7. Determination of antibodies to pale treponema (Treponema pallidum) in the blood, determination of antibodies of classes M, G to the human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1 and HIV-2 in the blood, determination of antibodies of classes M, G to the antigen of viral hepatitis B and viral hepatitis C in blood. 8. Microscopic examination of the discharge of female genital organs for gonococcus, microscopic examination of the vaginal discharge for fungi of the genus Candida. 9. PCR chlamydial infection, PCR gonococcal infection, PCR mycoplasma infection, PCR trichomoniasis. | Visiting an obstetrician-gynecologist every 3-4 weeks (with the physiological course of pregnancy). Electrocardiography (hereinafter - ECG) as prescribed by a general practitioner (cardiologist). Up to 13 weeks of pregnancy are accepted: - folic acid no more than 400 mcg / day; - potassium iodide 200-250 mcg / day (in the absence of thyroid disease) |
| 1 time per month (up to 28 weeks) | Blood test for Rh antibodies (in Rh-negative women with Rh-positive affiliation of the father of the child) | |
| 11-14 weeks | Biochemical screening for serum marker levels: - pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A), - free beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (hereinafter - beta-CG) | In the office of prenatal diagnostics, an ultrasound examination (hereinafter referred to as ultrasound) of the pelvic organs is performed. According to the results of complex prenatal diagnostics, a conclusion of a geneticist is issued. |
| After 14 weeks - once | Culture of midstream urine | To exclude asymptomatic bacteriuria (the presence of bacterial colonies more than 105 in 1 ml of an average portion of urine, determined by a culture method without clinical symptoms) to all pregnant women. |
| In the second trimester (14-26 weeks) | General (clinical) analysis of blood and urine. | Visiting an obstetrician-gynecologist every 2-3 weeks (with the physiological course of pregnancy). At each visit to the doctor of the antenatal clinic - determination of the circumference of the abdomen, the height of the fundus of the uterus (hereinafter referred to as VDM), uterine tone, palpation of the fetus, auscultation of the fetus with a stethoscope. Potassium iodide 200-250 mcg/day |
| 1 time per month (up to 28 weeks) | Blood for Rh antibodies (in Rh-negative women with Rh-positive affiliation of the father of the child) | |
| 16-18 weeks | Blood test for estriol, alpha-fetoprotein, beta-hCG | Only at late turnout unless biochemical screening for serum marker levels at 11-14 weeks |
| 18-21 weeks | The second screening ultrasound of the fetus is performed in the antenatal clinic | |
| In the third trimester (27-40 weeks) | 1. 2. Biochemical blood test (total protein, urea, creatinine, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, alanine transaminase (hereinafter - ALT), aspartate transaminase (hereinafter - AST), glucose, total cholesterol). 3. Coagulogram - platelet count, clotting time, bleeding time, platelet aggregation, activated partial thromboplastin time (hereinafter referred to as APTT), fibrinogen, determination of prothrombin (thromboplastin) time. 4. Determination of antibodies of classes M, G (IgM, IgG) to the rubella virus in the blood, determination of antibodies to toxoplasma in the blood. 5. General analysis of urine. 6. Determination of antibodies to pale treponema (Treponema pallidum) in the blood, determination of antibodies of classes M, G to the human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1 and HIV-2 in the blood, determination of antibodies of classes M, G to the antigen of viral hepatitis B and viral hepatitis C in blood. 7. | A visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist every 2 weeks, after 36 weeks - weekly (with the physiological course of pregnancy). At each visit to the doctor of the antenatal clinic - determination of the circumference of the abdomen, VDM, uterine tone, fetal palpation, auscultation of the fetus with a stethoscope. Potassium iodide 200-250 mcg/day |
| 24-28 weeks | Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) | |
| 28-30weeks | In Rh-negative women with Rh-positive blood of the child's father and the absence of Rh antibodies in the mother's blood | Administration of human immunoglobulin antirhesus RHO[D] |
| 30 weeks | A certificate of incapacity for work is issued for maternity leave | |
| 30-34 weeks | The third screening ultrasound of the fetus with dopplerometry in the antenatal clinic. - general practitioner; - a dentist. | |
| After 32 weeks | At each visit to the doctor of the antenatal clinic, in addition to determining the circumference of the abdomen, the height of the fundus of the uterus (hereinafter referred to as VDM), the tone of the uterus, determine the position of the fetus, the presenting part, the doctor auscultates the fetus with a stethoscope. | |
| After 33 weeks | Cardiotocography (hereinafter referred to as CTG) of the fetus is performed | |
| Throughout pregnancy | In antenatal clinics there are schools for pregnant women, which are attended by expectant mothers along with fathers. In the process of learning, there is an acquaintance with the changes in the body of a woman during physiological pregnancy, acquaintance with the process of childbirth, the correct behavior in childbirth, the basics of breastfeeding. | |
| Over 37 weeks | Hospitalization with the onset of labor. According to indications - planned antenatal hospitalization. | |
| 41 weeks | Planned hospitalization for delivery | |
| No later than 72 hours after delivery | All women with an Rh-negative blood group who gave birth to a child with a positive Rh-belonging, or a child whose Rh-belonging is not possible to determine, regardless of their compatibility according to the AB0 system | Re-introduction of human immunoglobulin anti-rhesus RHO[D] |
| postpartum period | 1. Early breastfeeding 2. Recommendations for breastfeeding. 3. Consultation of medical specialists on concomitant extragenital disease (if indicated). 4. Toilet of the external genital organs. 5. Dry processing of seams (if any). |
 General (clinical) blood test.
General (clinical) blood test. 
 General (clinical) blood test.
General (clinical) blood test. 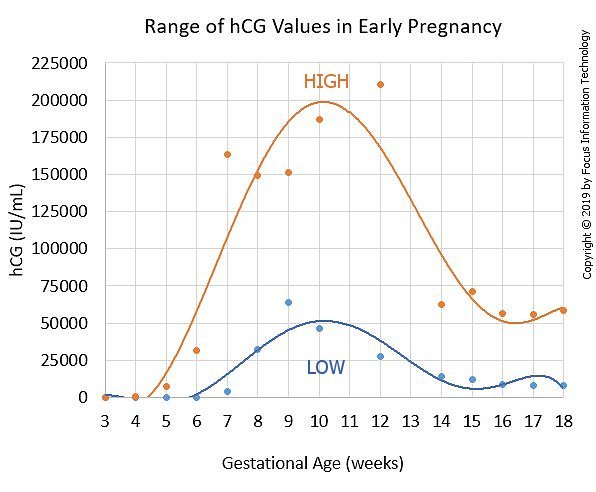 Microscopic examination of the discharge of female genital organs for gonococcus, microscopic examination of the vaginal discharge for fungi of the genus Candida.
Microscopic examination of the discharge of female genital organs for gonococcus, microscopic examination of the vaginal discharge for fungi of the genus Candida. 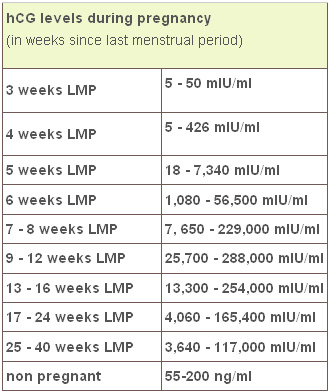 Inspections and consultations:
Inspections and consultations: .jpg)