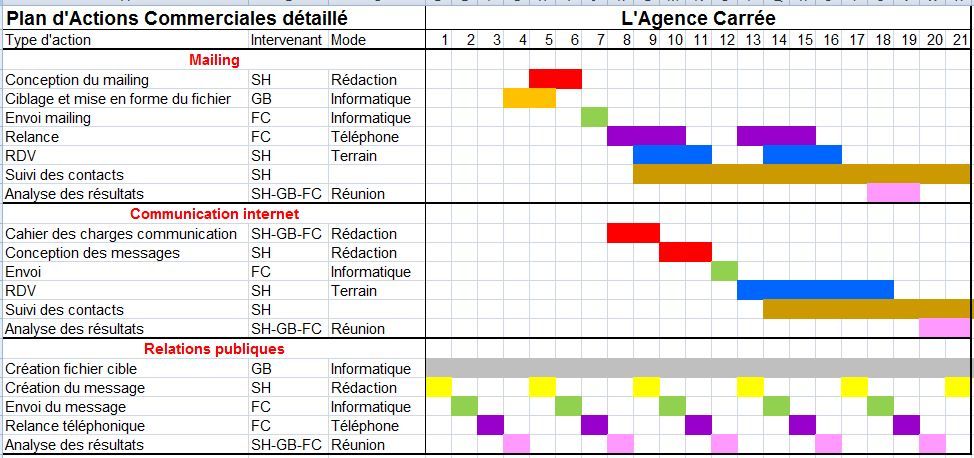
Planning when to conceive
Planning for Pregnancy | Preconception Care
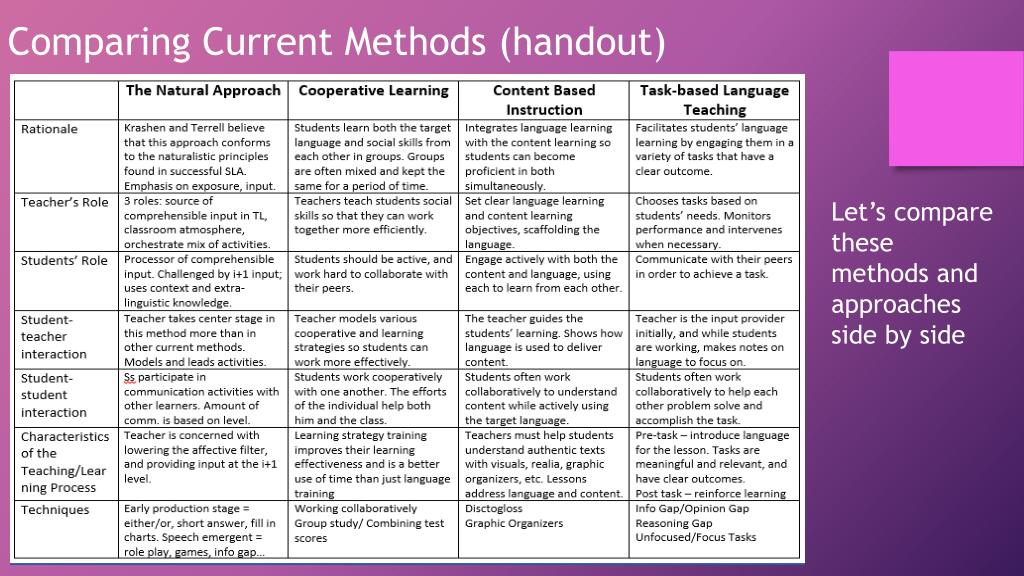
If you are trying to have a baby or are just thinking about it, it is not too early to start getting ready for pregnancy. Preconception health and health care focus on things you can do before and between pregnancies to increase the chances of having a healthy baby. For some people, getting their bodies ready for pregnancy takes a few months. For other people, it might take longer. Whether this is your first, second, or sixth baby, the following are important steps to help you get ready for the healthiest pregnancy possible.
1. Make a Plan and Take Action
Whether or not you’ve written them down, you’ve probably thought about your goals for having or not having children, and how to achieve those goals. For example, when you didn’t want to have a baby, you used effective birth control methods. Now that you’re thinking about getting pregnant, it’s important to take steps to achieve your goal [PDF – 764 KB]—getting pregnant and having a healthy baby!
Make sure you are up to date on preventive services. See which screening tests and vaccines you or your loved ones need to stay healthy.
2. See Your Doctor
Before getting pregnant, talk to your healthcare provider about preconception health care. Your provider will want to discuss your health history and any medical conditions you currently have that could affect a pregnancy. They may want to discuss any previous pregnancy problems, medicines you currently are taking, vaccinations you might need, and steps you can take before pregnancy to help prevent certain birth defects.
Take a list of talking points so you don’t forget anything. Be sure to talk to your doctor about:
Medical Conditions
If you currently have any medical conditions, be sure they are under control and being treated. Some of these conditions include: sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), diabetes, thyroid disease, high blood pressure, and other chronic diseases.
Lifestyle and Behaviors
Talk with your healthcare provider if you
- smoke, drink alcohol, or use certain drugs;
- live in a stressful or abusive environment; or
- work with or live around toxic substances.

Health-care professionals can help you with counseling, treatment, and other support services.
Medications
Almost every pregnant person will face a decision about taking medicines before and during pregnancy. Talk to your healthcare providers before starting or stopping any medicines. Be sure to discuss the following with your healthcare providers:
- All medicines you take, including prescriptions, over-the-counter medicines, herbal and dietary supplements, and vitamins
- Best ways to keep any health conditions you have under control
- Your personal goals and preferences for the health of you and your baby
Vaccinations (shots)
Most vaccines are safe during pregnancy and some, such as the flu vaccine and Tdap (adult tetanus, diphtheria and acellular pertussis vaccine), are specifically recommended during pregnancy. Learn about vaccinations during pregnancy and learn more about COVID-19 vaccines while pregnant or breastfeeding.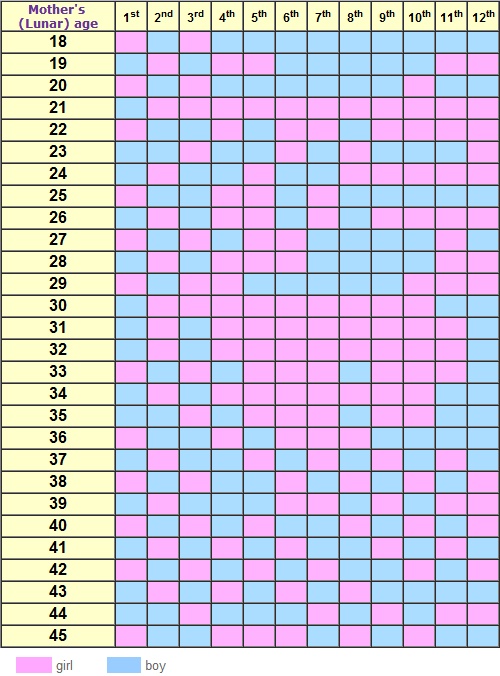 Having the right vaccinations at the right time can help keep you healthy and help protect your baby from some diseases during the first few months of life.
Having the right vaccinations at the right time can help keep you healthy and help protect your baby from some diseases during the first few months of life.
3. Get 400 Micrograms of Folic Acid Every Day
Folic acid is a B vitamin. Having enough folic acid in your body at least 1 month before and during pregnancy can help prevent major birth defects of the developing baby’s brain and spine (anencephaly and spina bifida). CDC urges all people who can become pregnant to get 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid each day, from fortified foods or supplements, or a combination of the two, in addition to a varied diet rich in folate.
Learn more about folic acid »
4. Stop Drinking Alcohol, Smoking, and Using Certain Drugs
Smoking, drinking alcohol, and using certain drugs can cause many problems during pregnancy, such as premature birth, birth defects, and infant death.
If you are trying to get pregnant and cannot stop drinking, smoking, or using drugs, contact your healthcare provider, local Alcoholics Anonymous, or local alcohol treatment center.
Alcohol and Drug Resources
Substance Abuse Treatment Facility Locator
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) has a treatment facility locator. This locator helps people find drug and alcohol treatment programs in their area.
Alcoholics Anonymous (A.A.)
Alcoholics Anonymous® is a fellowship of people who come together to solve their drinking problem. Membership is open to anyone who wants to do something about their drinking problem. A.A.’s primary purpose is to help alcoholics to achieve sobriety. Locate an A.A. program near you.
Learn more about alcohol and pregnancy »
Smoking Resources
1-800-QUIT-NOW (1-800-784-8669)
Learn more about smoking during pregnancy »
5. Avoid Toxic Substances and Environmental Contaminants
Avoid harmful chemicals, environmental contaminants, and other toxic substances such as synthetic chemicals, some metals, fertilizer, bug spray, and cat or rodent feces around the home and in the workplace. These substances can hurt the reproductive systems of men and women. They can make it more difficult to get pregnant. Exposure to even small amounts during pregnancy, infancy, childhood, or puberty can lead to diseases. Learn how to protect yourself and your loved ones from toxic substances at work and at home.
These substances can hurt the reproductive systems of men and women. They can make it more difficult to get pregnant. Exposure to even small amounts during pregnancy, infancy, childhood, or puberty can lead to diseases. Learn how to protect yourself and your loved ones from toxic substances at work and at home.
Learn about the effects of toxic substances on reproductive health »
Learn how CDC tracks Children’s Environmental Health »
6. Reach and Maintain a Healthy Weight
People who are overweight or obese have a higher risk for many serious conditions, including complications during pregnancy, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers (endometrial, breast, and colon).1 People who are underweight are also at risk for serious health problems.2
The key to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight isn’t about short-term dietary changes. It’s about a lifestyle that includes healthy eating and regular physical activity.
If you are underweight, overweight, or obese, talk with your doctor about ways to reach and maintain a healthy weight before you get pregnant.
Learn more about healthy weight »
7. Learn Your Family History
Collecting your family’s health history can help you identify factors that might affect your baby during infancy or childhood or your ability to become pregnant. You might not realize that your sister’s heart defect or your cousin’s sickle cell disease could affect your baby, but sharing this family history information with your doctor can be important.
Based on your family health history, your doctor might refer you for genetic counseling. Other reasons for genetic counseling include having had several miscarriages, infant deaths, or trouble getting pregnant (infertility), or having a genetic condition or birth defect that occurred during a previous pregnancy.
Learn more about family history »
Learn more about genetic counseling »
8. Get Mentally Healthy
Mental health is how we think, feel, and act as we cope with life. To be at your best, you need to feel good about your life and value yourself. Everyone feels worried, anxious, sad, or stressed sometimes. However, if these feelings do not go away and they interfere with your daily life, get help. Talk with your healthcare provider about your feelings and treatment options.
Everyone feels worried, anxious, sad, or stressed sometimes. However, if these feelings do not go away and they interfere with your daily life, get help. Talk with your healthcare provider about your feelings and treatment options.
Learn about mental health »
Learn about depression »
References
- NIH, NHLBI Obesity Education Initiative. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. Available online:
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/obesity/ob_gdlns.pdf (PDF-1.25Mb) - Moos, Merry-K, et al. Healthier women, healthier reproductive outcomes: recommendations for the routine care of all women of reproductive age. AJOG Volume 199, Issue 6, Supplement B , Pages S280-S289, December 2008.
Planning for your pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Planning for your pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
If you are thinking about pregnancy, visit your doctor for a preconception consult.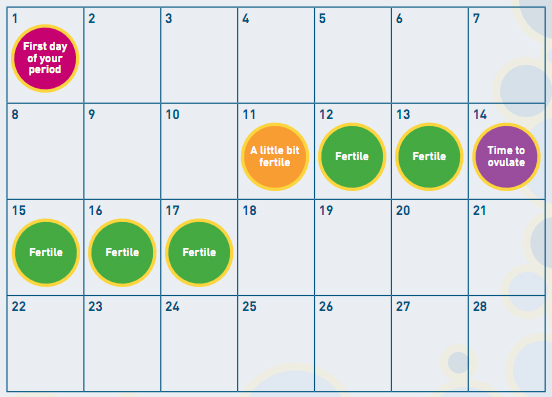 They will provide you with expert advice on planning your pregnancy.
They will provide you with expert advice on planning your pregnancy.
The preconception period (3 to 6 months prior to pregnancy) is the time to make life changes that can help boost fertility, reduce problems during pregnancy and assist in recovery from birth.
Folic acid
If you and your partner are planning to conceive, you should start taking a folic and iodine supplement before you get pregnant. Folic acid helps to provide the best health outcomes for your baby when they are growing. Taking folic acid daily before and during pregnancy also prevents the occurrence of neural tube defects, such as spina bifida, in your baby. Iodine is important for the baby’s brain development.
You can buy a supplement at most pharmacies. Check it contains at least 500 micrograms (mcg) of folate and 150mcg of iodine.
For more information see folate and pregnancy.
Watching what you eat
If you and your partner are preparing for pregnancy, you should look at your diet and see where you may be able to make healthier food choices. Eating a well-balanced diet including plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables will help with your chances of conceiving and having a healthy pregnancy.
Eating a well-balanced diet including plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables will help with your chances of conceiving and having a healthy pregnancy.
Learn more about preconception health for women and men.
Alcohol
There is no safe amount of alcohol to drink during pregnancy; therefore, for women who are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, not drinking is the safest option. Alcohol can affect the health and development of an unborn baby for life.
Smoking
Quitting smoking before pregnancy is the single most effective means of protecting your baby and yourself from the development of serious complications during pregnancy. By quitting smoking you are more likely to conceive naturally and without delay, less likely to suffer a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy and less likely to deliver your baby prematurely.
Pre-pregnancy check up
It is a good idea to have a chat with your doctor if you are planning to become pregnant. There may be some investigations to consider doing as well as discussing your general health and family history. This can also include considering vaccinations, pre-pregnancy health checks such as cervical screening, STI screening and dental checks, and discussing lifestyle changes. There is also an option of considering genetic carrier screening for some genetic conditions you may be at risk of passing on to your baby that you were not aware of. Discuss this with your doctor.
This can also include considering vaccinations, pre-pregnancy health checks such as cervical screening, STI screening and dental checks, and discussing lifestyle changes. There is also an option of considering genetic carrier screening for some genetic conditions you may be at risk of passing on to your baby that you were not aware of. Discuss this with your doctor.
The best time to get pregnant
The woman's monthly cycle
Ovulation occurs each month when an egg is released from one of the ovaries.
Occasionally, more than one egg is released, usually within 24 hours of the first egg. At the same time, the lining of the womb begins to thicken and the mucus in the cervix becomes thinner so that sperm can swim through it more easily.
The egg begins to travel slowly down the fallopian tube. If a man and a woman have recently had sex, the egg may be fertilised here by the man's sperm.
The lining of the womb is now thick enough for the egg to be implanted in it after it has been fertilised.
If the egg is not fertilised, it passes out of the body during the woman's monthly period, along with the lining of the womb, which is also shed. The egg is so small that it cannot be seen.
Falling pregnant
You're most likely to get pregnant if you have sex within a day or so of ovulation (releasing an egg from the ovary). Ovulation occurs 14 days before the first day of your next period (not after). The average cycle takes 28 days, but shorter or longer cycles are normal. So a women with a 28 day cycle will ovulate on day 14 but a women with a 30 day cycle will ovulate day 16.
An egg lives for about 12 to 24 hours after it's released. For pregnancy to happen, the egg must be fertilised by a sperm within this time. If you want to get pregnant, having sex every couple of days will mean there's always sperm waiting in the fallopian tubes to meet the egg when it's released.
Sperm can live for about 5 days inside a woman’s body. So if you’ve had sex in the days before ovulation, the sperm will have had time to travel up the fallopian tubes to ‘wait’ for the egg to be released. It’s difficult to know exactly when ovulation happens, unless you are practising natural family planning, or fertility awareness.
It’s difficult to know exactly when ovulation happens, unless you are practising natural family planning, or fertility awareness.
You can find out more about timing sex and calculate your ovulation on the Your Fertility website.
Sources:
Department of Health (Smoking and tobacco and pregnancy), NSW Health (Thinking of having a baby), Family Planning NSW (Pre-pregnancy planning), Your Fertility (Your Fertility right time for sex, ovulation calculator), RANZCOG (Planning for pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Ovulation signs
- Working out your due date
- Due date calculator
- Understanding fertility
Need more information?
Pregnancy planning for dads
A healthy pregnancy takes two and men need to prepare their bodies and their sperm to ensure they are optimally healthy at the time of conception. Many lifestyle measures, including eating a healthy balanced diet, exercising and avoiding drugs and alcohol, can improve a man’s health and the health of his sperm. In many cases these measures not only increase the chances of conception they also ensure the pregnancy gets off to the healthiest start possible.
Many lifestyle measures, including eating a healthy balanced diet, exercising and avoiding drugs and alcohol, can improve a man’s health and the health of his sperm. In many cases these measures not only increase the chances of conception they also ensure the pregnancy gets off to the healthiest start possible.
Read more on Parenthub website
Pregnancy | Family Planning NSW
Read more on Family Planning Australia website
Know Your Health: Pregnancy options | Family Planning NSW
This booklet is for people who are pregnant and are not sure what to do.
Read more on Family Planning Australia website
Making decisions about unplanned pregnancies
Having an unplanned pregnancy can be an emotional experience. There will be decisions you will need to make, but there are services available to help you through this time.
There will be decisions you will need to make, but there are services available to help you through this time.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Contraception: natural family planning - MyDr.com.au
What is natural family planning? Is it effective? Find out about the different methods and the advantages and disadvantages of natural family planning.
Read more on myDr website
Fertility awareness (natural family planning)
Fertility awareness means not having sex during the fertile times in a woman’s menstrual cycle.
Read more on WA Health website
Right Time For Sex , When Do You Ovulate ? | Your Fertility
Apart from being healthy, what else can help you get pregnant?
Read more on Your Fertility website
Natural Family Planning | Fertility Awareness | Natural Contraception | Rhythm Method - Sexual Health Victoria
Natural family planning (or fertility awareness) is avoiding sex around the time of the month where you are fertile (most likely to get pregnant).
Read more on Sexual Health Victoria website
Episode #28: Abortion - Sexual Health Victoria
Sexual Health Victoria (formally Family Planning Victoria) focuses on reproductive and sexual health care, education and advocacy. Our vision is to improve ever
Read more on Sexual Health Victoria website
Episode #33: Early Years - Sexual Health Victoria
Sexual Health Victoria (formally Family Planning Victoria) focuses on reproductive and sexual health care, education and advocacy. Our vision is to improve ever
Read more on Sexual Health Victoria website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
How to prepare for conception?
Pregnancy planning is really necessary, especially in our time, when a healthy woman is the exception rather than the rule. Not to mention the fact that pregnancy is a serious test for the body of even a perfectly healthy woman.
It can be said that entering into a pregnancy without prior preparation for it is the same as flying on an airplane that has not been checked in advance: maybe it will cost, or maybe not. Of course, aircraft are tested before each flight. So why does a woman, ready to give birth to a new human being, not always conduct a similar check of her body? After all, the price of her neglect of herself and her health can be the life of the unborn child.
Of course, aircraft are tested before each flight. So why does a woman, ready to give birth to a new human being, not always conduct a similar check of her body? After all, the price of her neglect of herself and her health can be the life of the unborn child.
The process of preparing for pregnancy is quite complex and includes several stages. It is worth starting planning a few months (at least three) before the time when the couple intends to conceive a baby.
And at the stage of pregnancy planning , it is necessary to understand that the bearing and birth of a baby is not a woman's business, but a married couple's. Therefore, the active participation of the father in planning pregnancy is extremely necessary and important for himself, and for his wife, and for the unborn baby.
Without the help of doctors, it will not be possible to manage even at this stage. A visit to the gynecologist will allow you to identify possible diseases and treat them in a timely manner. After the first appeal, future parents undergo several examinations and pass certain tests in order to find out how ready their bodies are for conceiving a baby, as well as to prevent possible problems when carrying a child. The gynecologist will tell you what to do if, before planning a pregnancy, a woman was protected with hormonal contraceptives. It is necessary to stop taking hormonal contraceptives 3 months before the planned pregnancy.
After the first appeal, future parents undergo several examinations and pass certain tests in order to find out how ready their bodies are for conceiving a baby, as well as to prevent possible problems when carrying a child. The gynecologist will tell you what to do if, before planning a pregnancy, a woman was protected with hormonal contraceptives. It is necessary to stop taking hormonal contraceptives 3 months before the planned pregnancy.
It is important for a future mother to understand that only a healthy woman can bear and give birth to a healthy baby. In this regard, you need to start taking care of your own health long before conception. Good physical shape, the absence of diseases, proper nutrition and the rejection of bad habits, hygiene and a measured lifestyle - all this has a beneficial effect on the female body and subsequently makes it easier to endure pregnancy. However, not all vitamins can be obtained from food. For example, the body can only obtain folic acid in an artificial form, since its counterpart (folate), found in green vegetables, beans, asparagus, and citrus fruits, is much less absorbed. Folic acid is very important for the development of the baby to take place correctly, and the need for its intake exists throughout pregnancy. If the mother's body during the bearing of the child receives a sufficient amount of this substance, then the risk of pathology from the nervous system is minimized.
Folic acid is very important for the development of the baby to take place correctly, and the need for its intake exists throughout pregnancy. If the mother's body during the bearing of the child receives a sufficient amount of this substance, then the risk of pathology from the nervous system is minimized.
What tests should a married couple undergo
before planning a pregnancy?
- Gynecological examination, colposcopy for women.
- Blood type, Rh factor for both spouses. If a woman has a positive Rh factor, there is no problem. If a woman has a negative Rh factor - antibodies to the Rh factor (even if a man is also negative). If they are positive, pregnancy is not currently possible and needs to be corrected. If negative - repeat this analysis once a month, starting from 8 weeks of pregnancy. If a woman has 1 group, and a man has any other group, incompatibility by blood types is possible. An analysis for group antibodies, as well as an analysis for antibodies to the Rh factor, is carried out once a month, starting from 8 weeks of pregnancy.

- Tests for infections: routine smear, PCR for latent infections - both spouses.
- Blood test for TORCH-complex. Antibodies to rubella, toxoplasma, herpes, CMV, chlamydia - quantitative analysis (with titer). The presence of IgG antibodies means immunity to these infections, and is not an obstacle to pregnancy. The presence of IgM means an acute stage, planning in this case must be postponed until recovery. If there are no IgG antibodies to rubella, it is necessary to be vaccinated and protected for another 3 months after it.
- A trip to the dentist, a therapist, chest x-ray is a must for both spouses. By appointment of the therapist - consultation of narrow specialists (ENT doctor, urologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist).
- Spermogram. Desirable, but not required. It is done to determine the quality of spermatozoa and identify a hidden inflammatory process (a much more informative analysis than any smears and PCR).
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs - at least 2 times per cycle: after menstruation and before menstruation.
 For the first time, the general condition of the pelvic organs is assessed, in the second, the presence of a corpus luteum and endometrial transformation, indicating that ovulation has occurred. Ideally, an intermediate third ultrasound on the eve of the expected ovulation is to detect the dominant follicle.
For the first time, the general condition of the pelvic organs is assessed, in the second, the presence of a corpus luteum and endometrial transformation, indicating that ovulation has occurred. Ideally, an intermediate third ultrasound on the eve of the expected ovulation is to detect the dominant follicle. - Blood test for hormones of the reproductive system, thyroid gland, adrenal glands - according to indications.
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, mammary glands - according to indications.
- Hemostasiogram, coagulogram. - according to indications.
- General clinical blood test (hemoglobin, erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets, ESR, color index, leukocyte formula). Finger blood. General urinalysis (morning portion of urine - completely collected, it is important that the analysis does not include discharge from neighboring organs).
- Blood tests for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis B and C - for both spouses.
- If there was a case of hereditary diseases in the family, miscarriages, spontaneous miscarriages, seek advice from a medical genetic consultation (Krasnoyarsk Regional Consultative and Diagnostic Center for Medical Genetics, Krasnoyarsk, Molokova St.
 7, t. 55-99-20).
7, t. 55-99-20).
Pregnancy planning
From the physiological data of expectant mothers and fathers, as well as their tendency to certain diseases, not only how quickly and safely the conception occurs, but also the nature of the course of pregnancy and the development of the fetus and, of course, the health of the born baby. It is important not only to eat right and get rid of harmful attachments, it is necessary to minimize all possible risks, therefore, preparation for pregnancy should begin from the first and most important stage - the passage of a full-fledged study by potential parents, which includes laboratory tests and diagnostics.
This approach will allow to obtain a general clinical picture and, if necessary, will make it possible to establish the true cause of infertility and systematic miscarriages, as well as to select the most effective therapy and minimize the risks of complications and pathologies. Moreover, both expectant mothers and fathers should be examined, even if they are very young and have never felt unwell.
General tests
A feature of the female body is the ability to quickly adapt to any physiological changes and therefore many diseases often cannot be diagnosed by primary signs and symptoms. Laboratory studies will help to take an anamnesis and establish the true causes of dysfunction of various organs that affect childbearing.
Vaginal smear for flora
Bacterioscopy of vaginal smear is a routine gynecological research method that allows assessing the condition of the mucous membrane of the walls of the vagina and cervix and identifying pathogenic microflora. Screening with a high degree of certainty confirms inflammatory processes in the vagina and hormonal disorders, also shows the presence of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, yeasts and other pathogens, and the level of apathetic cells.
General and biochemical blood tests
An invasive laboratory method that provides information about the health status of potential parents, advanced screening of basic blood parameters and primary data on metabolism and lack of vital trace elements.
Test results include level data:
- glucose and urea;
- total lipids and non-protein nitrogen;
- cholesterol, phospholipids and triglycerides;
- bilirubin and protein.
Also, the study will help determine the ESR, hemoglobin and the number of leukocytes, platelets and red blood cells. Patients can donate venous or capillary blood for general and biochemical analysis. Biomaterial sampling is carried out using modern materials and eliminates the risk of cross-infection.
Urinalysis
Laboratory research, widely demanded in clinical gynecological practice. The parameters obtained during the analysis allow specialists to judge with high certainty the state of the urinary system and the usefulness of the kidneys. The study is aimed at studying the physicochemical, organoleptic and biochemical parameters, as well as the color of morning urine. Necessarily involves microscopic and microbiological screening of urinary sediment.
PCR scraping from the cervix
Modern invasive polymerase chain reaction method based on molecular biology and detecting multiple diseases even at an early stage. The versatility of the technology makes it possible to recognize a huge number of various infections: from ureplasmosis and chlamydia to tuberculosis and herpes.
A minimal amount of biological material is sufficient for the study. This allows you to make the scraping procedure as painless and comfortable as possible for the patient.
Scraping cytology
Biomaterial for research is taken from the outside of the cervix, the walls of the vagina and from the cervical canal. Cytology involves microscopic examination of scrapings and allows you to establish changes in the tissues of the epithelium, which in the future can provoke the development of neoplasms. Additional preparation of the patient is not required.
Thyroid hormones
As an endocrine organ, the thyroid gland produces numerous thyroid hormones. Its insufficient or increased activity causes numerous disorders that provoke changes in metabolism, negatively affect the reproductive function and the nervous system. At the same time, clinical signs of hormonal imbalance do not have pronounced symptoms. As a rule, this is:
Its insufficient or increased activity causes numerous disorders that provoke changes in metabolism, negatively affect the reproductive function and the nervous system. At the same time, clinical signs of hormonal imbalance do not have pronounced symptoms. As a rule, this is:
- underweight or overweight;
- sleep disturbance and increased nervousness;
- aggression, abruptly replaced by apathy and depression;
- unstable menstrual cycle, infertility, frequent miscarriages.
But these symptoms are also characteristic of other diseases. A blood test for thyroid hormones will allow you to accurately confirm or refute the primary diagnosis and select the most effective medication course.
For analysis, a venous blood sample is taken. If the patient uses hormonal drugs, the study will not be reliable.
Breast and thyroid ultrasound, pelvic organs
Unfortunately, in the modern world, women of childbearing age are increasingly showing fibrotic processes, impaired blood supply to organs, hormonal imbalances and oncological diseases. Ultrasound diagnostics, being a non-invasive and highly informative method, will allow:
Ultrasound diagnostics, being a non-invasive and highly informative method, will allow:
- timely detection of various pathologies;
- monitor the effectiveness of drug therapy;
- confirm or refute the pre-diagnosis.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs - diagnostics that provides reliable and objective information about obstruction of the tubes, adnexitis, fibromas, cysts and other neoplasms. Considering that gynecological problems are associated with a hormonal background and can have mixed symptoms, it is advisable for expectant mothers to undergo a comprehensive examination, which also includes ultrasound diagnostics of the thyroid and mammary glands. This will allow you to get an objective clinical picture, identify neoplasms larger than 2 mm and prescribe the most effective drug or hormonal therapy to your doctor.
Ultrasound of the thyroid and mammary glands, as well as the pelvic organs is absolutely painless and harmless. Therefore, even if it is carried out at a very short gestational age, you can not worry that it will cause any abnormalities in the fetus.
Therefore, even if it is carried out at a very short gestational age, you can not worry that it will cause any abnormalities in the fetus.
Tests for infections
For anatomically correct and healthy development of the fetus, it is important to identify antibodies to various infections in a potential mother long before pregnancy. This is due to the fact that an adult organism can have stable immunity to pathogenic pathogens, but the developing fetus is very sensitive, and due to latent infection of the mother's body, a miscarriage may occur or various pathologies may appear in the child. It is extremely important to identify the fact of potential carriage before pregnancy and undergo full treatment.
Antibodies to toxoplasmosis, herpes virus, rubella, cytomegalovirus, human papillomavirus
TORCH infections, which include herpes, cytomegalovirus and other peritonally transmitted diseases, are diagnosed exclusively by laboratory methods. For analysis, venous blood is used.
Screening of plasma protein compounds provides the most objective information about the presence of TORCH infections in the body of a future mother. Therefore, this study is mandatory and is included in the course of analyzes of general preparation for pregnancy.
Antibodies to hepatitis B and C, HIV, syphilis, gonococcus, mycoplasma, gardnerellosis
The causative agents of these infections have a significant incubation period or may pass into asymptomatic chronic conditions. Antibodies to these viral infections are also detected clinically in the SZTSDM research laboratory based on a venous blood test.
A positive immune response is interpreted as the actual carriage of a particular virus. But in some cases, the fact of complex infection is revealed, for example, HCV + HIV.
Antibodies to Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus
Once in the blood or reproductive organs, strains of Escherichia and Staphylococcus provoke intrauterine infection of the fetus, dysbacteriosis and other diseases. By detecting antibodies to Escherichia coli and staphylococcus in a timely manner, you can undergo effective therapy and protect yourself and your unborn child from health problems.
By detecting antibodies to Escherichia coli and staphylococcus in a timely manner, you can undergo effective therapy and protect yourself and your unborn child from health problems.
Enzyme immunoassay of blood serum is the most commonly used method for the detection of antibodies to Escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus. But the analysis can also be carried out by bakpasev in a smear, urine and feces. The study is not carried out if the patient is taking antibacterial drugs, as a false answer is likely.
Blood clotting test
Given that pregnancy and childbirth are potentially associated with possible blood loss, expectant mothers must definitely do a blood clotting test - a coagulogram. This will allow her personally and the attending physician to have complete information, and, therefore, to objectively assess the risks, timely undergo an optimizing course of treatment and, if necessary, prevent or minimize open and internal bleeding.
Which tests should be done for a man
In general, the list of laboratory tests and functional examinations that are recommended for potential fathers when planning a pregnancy is also aimed at assessing the general physical condition, identifying pathogenic and pathogenic infections and inflammatory processes. But if there is a problem of conception, experts recommend undergoing an examination for infertility and spermatogenesis.
But if there is a problem of conception, experts recommend undergoing an examination for infertility and spermatogenesis.
In the Northwestern Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, as part of the pre-pregnancy course, men are offered the opportunity to undergo all the necessary examinations and ultrasound diagnostics. In JSC "SZTsDM" you can do:
- hormone tests;
- spermogram and MAR test;
- general urine and blood tests;
- study of the secret of the prostate gland;
- biochemical screening of blood and Rh factor;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, scrotum and prostate.
And, of course, in order to fully minimize the risks, we recommend future fathers to consider testing for antibodies to TORCH infections (toxoplasmosis, herpes virus, rubella, cytomegalovirus, papillomavirus), sexually transmitted diseases, HCV and HIV. This will completely eliminate the likelihood of intrauterine infection of the fetus, minimize the risk of miscarriage and the development of pathologies. Please note that it is better to complete all studies four, or even six or more months before the planned conception, because drug therapy may be required.
Please note that it is better to complete all studies four, or even six or more months before the planned conception, because drug therapy may be required.
Cost of services in JSC "NWDM"
Our center has implemented a management system in accordance with ISO 9001 and ISO 15189, uses high-quality materials and the most effective methodologies for laboratory and functional diagnostics. This allows us to maintain a high quality of service, guarantee the reliability of surveys and form competitive market prices.
Where to get tested
We have an extensive network of branches and terminals, so contacting the Northwestern Center for Evidence-Based Medicine will allow you to quickly and comprehensively undergo all the necessary examinations and get an absolutely reliable result of laboratory tests and functional diagnostics in the shortest possible time. At the same time, you can call a health worker to your home to collect biological material or receive only one of the above services.