Does an epidural stay in your back
Epidural - NHS
An epidural is an injection in your back to stop you feeling pain in part of your body.
This page covers epidural anaesthesia, a type of epidural commonly given for pain relief in childbirth and in some types of surgery.
When epidurals are used
Epidurals can be used:
- during labour and childbirth, including caesareans
- during some types of surgery
- after some types of surgery
Steroid medicine can also be given with an epidural injection, to treat pain in your back or leg that's caused by sciatica, or a slipped (prolapsed) disc.
Preparing for an epidural
If you have any concerns or questions about having an epidural, discuss these with your doctor. Let them know about any medicines you're taking.
You may be given specific advice about eating, drinking and medicines before the epidural.
You will not be able to drive for 24 hours after having an epidural, so you'll need to arrange for someone to take you home.
How an epidural is given
Epidurals are given by a specialist doctor called an anaesthetist.
You're usually awake during an epidural, but for some types of surgery you may have it while under general anaesthetic.
- A drip will be placed in your arm so you can be given fluids while you're having the epidural.
- You'll be asked to sit down and lean forwards, or lie on your side with your knees up close your chest.
- You'll be given an injection of local anaesthetic to numb the skin where the epidural will be inserted.
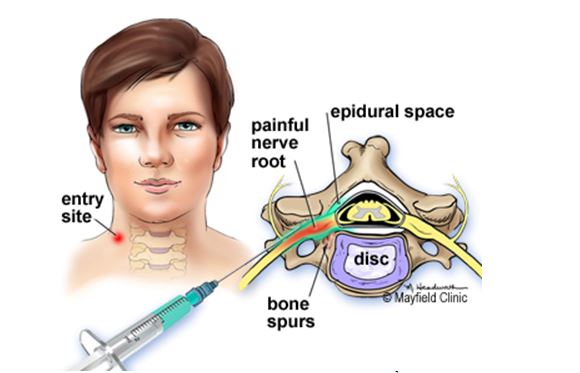
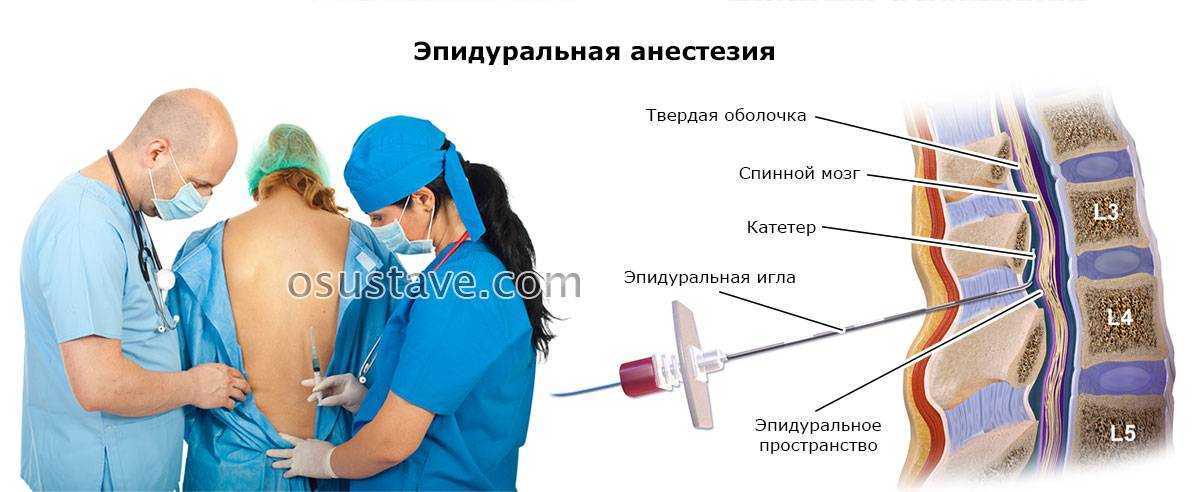
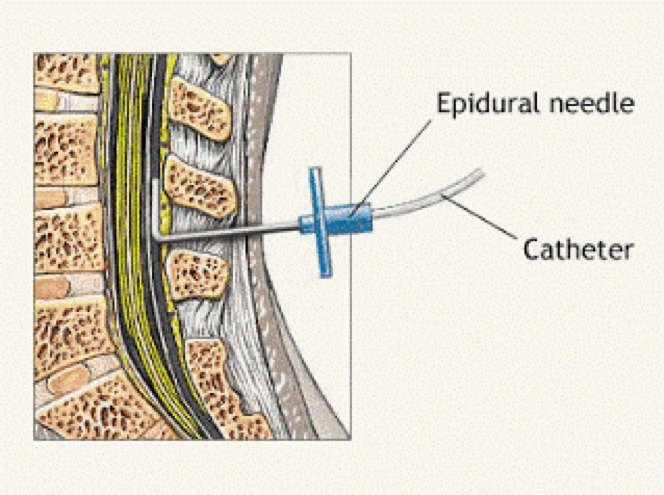
- A needle is used to insert a fine plastic tube called an epidural catheter into your back (spine) near the nerves that carry pain messages to your brain.
- The needle is then removed, leaving just the catheter in your spine.
- You may feel mild discomfort when the epidural needle is positioned and the catheter is inserted.
The epidural can be inserted at different levels of your spine, depending on the area of your body that needs pain relief.
Pain relief medicines are then given through the catheter. These take about 20 to 30 minutes to take full effect.
Your chest, tummy and legs may feel numb while the epidural medicines are being used, and your legs may not feel as strong as usual.
While the catheter remains in your back, it can be used to top up your pain relief medicines manually or using an automatic pump.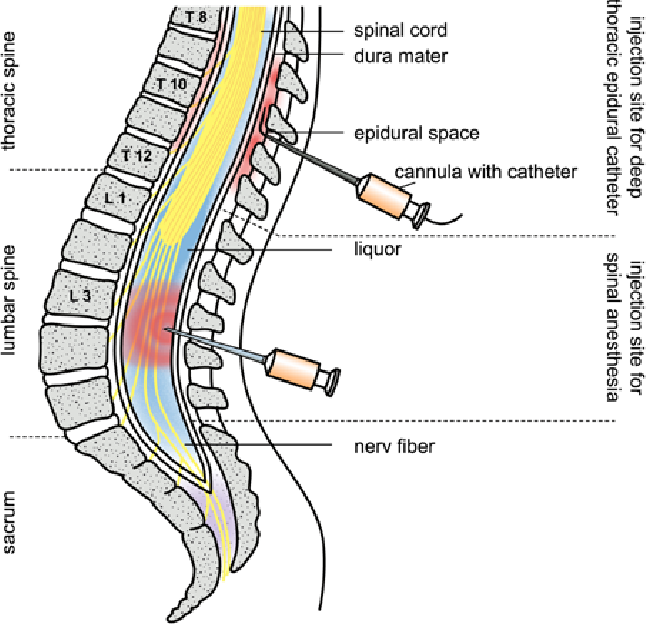
This can be for several hours (during childbirth) or for a few days (after major surgery).
Mobile epidurals, which use a lower dose of pain relief medicines, are sometimes used in childbirth, allowing you to walk around during labour.
Recovering from an epidural
When the epidural is stopped, the numbness usually lasts for a few hours before its effects begin to wear off.
While the medicine wears off, you'll probably be advised to rest in a lying or sitting position until the feeling in your legs returns.
This can take a couple of hours, and you may feel a slight tingling sensation in your skin.
Tell the doctor or nurse if you feel any pain. They can give you medicines to help control it.
Do not drive, operate machinery or drink alcohol for 24 hours after having an epidural.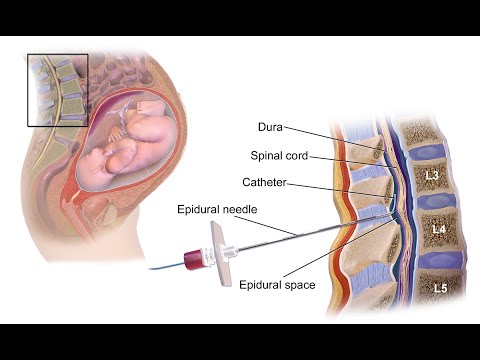
Risks and side effects of an epidural
Epidurals are usually safe, but there's a small risk of side effects and complications, including:
- low blood pressure, which can make you feel lightheaded or nauseous
- temporary loss of bladder control
- itchy skin
- feeling sick
- headaches
- nerve damage
Read more about the side effects and complications of an epidural
Page last reviewed: 01 February 2023
Next review due: 01 February 2026
What It Is, Procedure, Risks & Side Effects
Overview
An epidural injects medication into the space around your spinal nerves known as the epidural space.What is an epidural?
An epidural is a procedure that involves injecting a medication — either an anesthetic or a steroid — into the space around your spinal nerves known as the epidural space.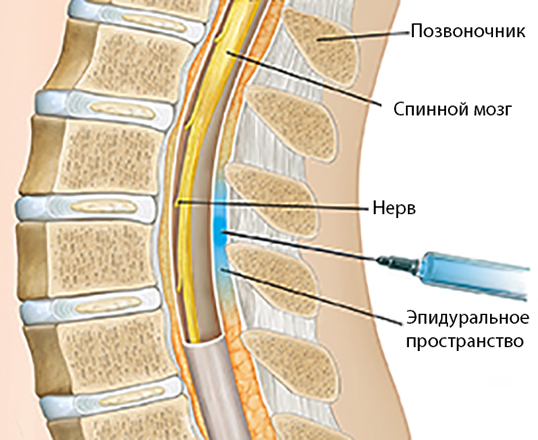 The goal of an epidural procedure is to provide pain relief (analgesia) or a complete lack of feeling (anesthesia) for one region of your body, such as your legs or belly.
The goal of an epidural procedure is to provide pain relief (analgesia) or a complete lack of feeling (anesthesia) for one region of your body, such as your legs or belly.
An epidural is commonly called the following terms:
- Epidural anesthesia.
- Epidural block.
- Epidural steroid injection (ESI).
- Regional anesthesia.
- Neuraxial anesthesia.
How does an epidural work?
An epidural anesthesia injection works by injecting an anesthetic into the epidural space around your spine so that it can stop pain signals from traveling from your spine to your brain. The epidural space is filled with fluid and surrounds your spinal cord. Think of it as a liquid sleeve around your spinal cord.
Your spinal cord acts like a highway that connects the nerves located all over your body to your brain. When you get injured, for example, the nerve in that area of your body sends a pain signal that travels through your spinal cord to your brain and back.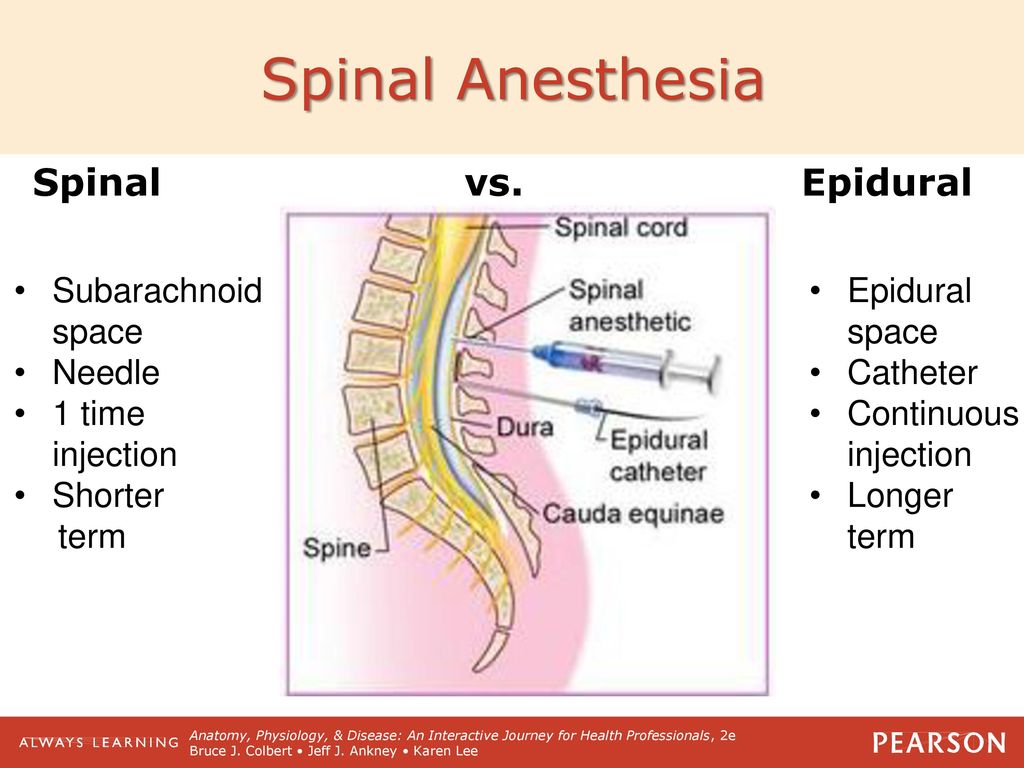 An epidural anesthetic temporarily numbs the spinal nerves, which then blocks pain signals in a certain region of your body depending on where along your spine your provider injected the epidural.
An epidural anesthetic temporarily numbs the spinal nerves, which then blocks pain signals in a certain region of your body depending on where along your spine your provider injected the epidural.
Epidural anesthesia can provide temporary pain relief or a temporary total lack of feeling. The following factors contribute to how much feeling you temporarily lose from an epidural:
- The type of anesthetic drug your provider uses.
- The concentration of the drug (how strong it is).
- The dosage of the drug.
An epidural steroid injection (ESI) works slightly differently and is used for chronic pain management. Instead of anesthetic medication, your provider injects a steroid or corticosteroid medication into the epidural space around your spine. Instead of blocking pain or feeling in a region of your body, the steroid coats the irritated nerve(s) that are causing you pain and works to reduce swelling. The steroid allows the nerve(s) time to heal. Epidural steroid injections can lead to temporary, long-term or permanent pain relief.
Who performs an epidural?
An anesthesiologist or certified registered nurse anesthetist usually performs an epidural procedure. Anesthesiologists have special training in the field of anesthesiology, which is a medical specialty that involves the care of people before, during and after their surgery or procedure. Anesthesiology covers anesthesia, pain medicine, intensive care medicine and critical emergency medicine.
Healthcare providers of other specialties, such as neurology, may also perform an epidural. Again, they’re specially trained to properly and safely perform an epidural procedure.
For epidural procedures that use a catheter, a supporting healthcare provider is usually present to help as needed.
What’s the difference between epidural analgesia and epidural anesthesia?
Analgesia is pain relief without losing consciousness (going to sleep) and without complete loss of feeling or movement. Anesthesiologists use epidural analgesia for people who are in labor and are delivering a baby. They inject the epidural into your lower back to provide pain relief for the lower part of your body due to contractions and childbirth.
They inject the epidural into your lower back to provide pain relief for the lower part of your body due to contractions and childbirth.
Anesthesia is the loss of physical sensation with or without loss of consciousness. Epidural anesthesia itself won’t cause a loss of consciousness, but if you’re having a certain kind of surgery, your anesthesiologist may give you epidural anesthesia so you don’t feel any pain or don’t move during the surgery and a different medication to make you go to sleep (lose consciousness).
What are epidurals used for?
Your healthcare provider may recommend an epidural procedure for the following situations:
- To provide pain relief (analgesia) for labor and childbirth.
- To provide anesthesia for certain surgeries as an alternative to general anesthesia.
- To provide pain relief after certain surgeries.
- To manage certain causes of back pain and other forms of chronic pain (through epidural steroid injections).

What are the different kinds of epidurals?
There are different variations of epidurals based on certain factors. This section will explain different kinds of epidurals grouped into the following categories:
- How the medication is delivered.
- Labor and childbirth epidurals.
- Epidural steroid injections (ESI).
Epidural medication delivery options
There are a few ways your healthcare provider can deliver medication with an epidural, including:
- Single-injection epidural: This type of epidural involves one injection of a medication (an anesthetic or a steroid) into the epidural space around your spine. If you get a single injection of an anesthesia epidural, the feeling in your affected area usually returns within a few hours. A single injection anesthesia epidural is for short-term pain relief. Most epidural steroid injections are single injections.
- Epidural with a catheter: Most epidural procedures involve the use of a catheter in your epidural space so that your healthcare provider can give you a continuous flow of anesthetic medication, multiple separate doses or both.
 A catheter is a small, flexible tube that’s inserted through a narrow opening into a body cavity. In this case, your provider places a catheter that opens into the epidural space in your spinal area. This way, your provider can administer more than just one injection of medication. Providers usually recommend this type of epidural for longer operations, for providing pain relief over several days and for labor and childbirth.
A catheter is a small, flexible tube that’s inserted through a narrow opening into a body cavity. In this case, your provider places a catheter that opens into the epidural space in your spinal area. This way, your provider can administer more than just one injection of medication. Providers usually recommend this type of epidural for longer operations, for providing pain relief over several days and for labor and childbirth. - Epidural with patient-controlled analgesia (PCA): For recovery from certain kinds of surgery, your healthcare provider may allow you to control the amount of pain relief you’re receiving through your epidural catheter. This is called patient-controlled analgesia (PCA). Your healthcare provider sets controls on the PCA pump, which are programmed for the pain-relieving drug your provider orders based on your age, weight and the type of surgery you had. The PCA pump is safe to use because you receive medication by pressing a button when you feel pain, but the pump won’t give you the medication if it’s not time to receive another dose yet.

Labor and delivery epidurals
There are two general kinds of epidurals that you may choose during labor and childbirth. These include:
- Epidural with a catheter: Your provider will administer medicine through a catheter in your lower back that they insert with an epidural injection. The catheter remains in your epidural space so that your provider can give you more medication if needed.
- Combined spinal-epidural (CSE): A CSE is a combination of two injections: a spinal injection (spinal block) and an epidural. A CSE provides pain relief much faster than just an epidural. Because it involves a lower dose of medication, you’ll have a bit more feeling in your lower half. This allows you to move around more easily and change positions. This type of epidural is often called a “walking” epidural, but most people aren’t able to fully walk with this kind of epidural.
Epidural steroid injections (ESI)
An epidural steroid injection (ESI) involves an injection of a steroid or corticosteroid into your epidural space. It can help relieve neck, arm, back and leg pain caused by inflamed spinal nerves due to certain conditions or injuries. Pain relief from an ESI may last for several days or even years.
It can help relieve neck, arm, back and leg pain caused by inflamed spinal nerves due to certain conditions or injuries. Pain relief from an ESI may last for several days or even years.
People who have pain in their neck, arm, lower back or leg due to the following conditions may benefit from epidural steroid injections:
- Spinal stenosis.
- Spondylolisthesis.
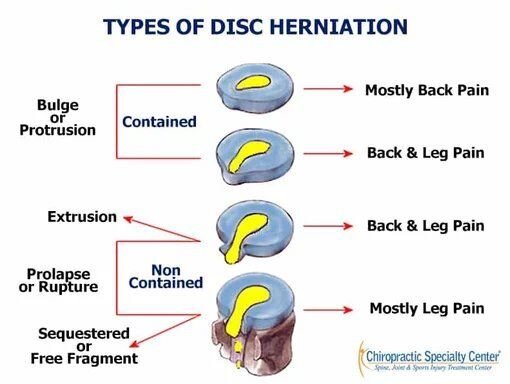
- Herniated disk (slipped, ruptured or bulging disk).
- Degenerative disk disease.
- Sciatica.
How common are epidurals?
Epidurals are a common procedure. An epidural is the most popular method of pain relief during labor and childbirth. More than 50% of people who give birth at a hospital choose to receive epidural analgesia. Epidural steroid injections (ESI) are one of the most commonly performed pain relief procedures.
Who shouldn’t get an epidural?
Due to certain medical conditions, not everyone can have an epidural. Because of this, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about your medical history and any questions you have. If you have any of the following conditions, you may not be able to get an epidural:
If you have any of the following conditions, you may not be able to get an epidural:
- Anesthetic drug allergies.
- Blood clotting issues.
- An infection.
- Poorly managed diabetes (for epidural steroid injections).
If you’re unable to undergo an epidural procedure, your healthcare provider may recommend another type of pain relief or anesthesia for you, or they may have you wait until a better time to have your surgery, if possible.
Procedure Details
How do I prepare for an epidural?
Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions about what you need to do to prepare for your epidural. Be sure to follow their instructions. Your provider may:
- Have you not eat or drink for a certain amount of time before your epidural.
- Adjust certain medications you’re taking, especially blood thinner medications.
- Make sure you have someone with you to drive you home after your epidural.
Questions that may be helpful to ask your healthcare provider before you get an epidural include:
- How often do you perform epidurals?
- What do I need to do to prepare for my epidural?
- What are the risks of getting an epidural?
- What will my epidural feel like?
- How long will my epidural last?
- How long will it take to recover from my epidural?
What happens during the epidural procedure?
This section will explain the general procedure for two kinds of epidurals: epidurals that use a catheter and epidural steroid injections.
Single-injection epidurals are similar in procedure to epidurals that use a catheter except there’s no catheter placement. Your provider will inject one dose of medication when they insert the needle into your epidural space.
Epidural with a catheter procedure
The steps involved in an epidural procedure that uses a catheter include:
- Before your epidural procedure, a healthcare provider will likely insert a cannula into a vein in your arm so that a medical drip can be attached to it if needed. This is a safety precaution in case your blood pressure drops during the epidural. If this happens, your provider can access the cannula very quickly to give you medication to help stabilize your blood pressure.
- You will likely have to lie on your side or sit up — either way, you’ll need to tuck in your chin to your chest and hunch your back so that your provider can more easily see and access the area where they’ll insert the epidural.
- Your provider will thoroughly clean the area of your back where they’ll insert the epidural to minimize the risk of infection.

- They will then inject local anesthesia with a small needle near the area where they’ll insert the epidural. This is so you won’t feel as much pain when they insert the epidural needle, which is larger than a standard shot needle, such as a vaccine shot needle.
- Your provider will then insert the epidural needle into your back in the epidural space just outside of your spinal cord. If you’re getting an epidural for labor and childbirth, it’ll be in your lower back.
- They’ll then thread a small, soft tube called a catheter through the needle and into your back where the needle went in
- They’ll remove the epidural needle, and the catheter will remain in your back.
- Now your provider can give you anesthetic medicine through the catheter for as long as it’s needed.
- Once you no longer need the epidural, your provider will remove the catheter, clean the area again with an antiseptic and apply a dressing over the site.
Epidural steroid injection procedure
Epidural steroid injections are often used to manage or treat chronic pain.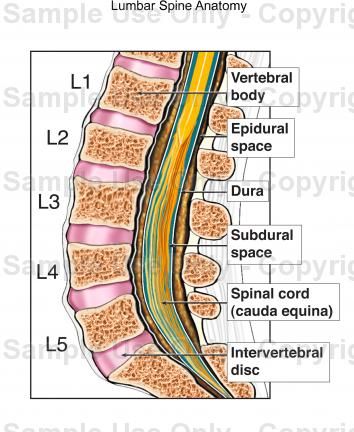 Depending on what’s causing your pain, your healthcare provider will inject the epidural somewhere along your spine. Here are the general steps of an epidural steroid injection procedure:
Depending on what’s causing your pain, your healthcare provider will inject the epidural somewhere along your spine. Here are the general steps of an epidural steroid injection procedure:
- You will lie on a comfortable table on your stomach or side.
- Your healthcare provider will thoroughly clean the area of your back where they’ll insert the epidural to minimize the risk of infection.
- Your provider will inject local anesthesia with a small needle near the area where they’ll insert the epidural. This is so you won’t feel as much pain when they insert the epidural needle, which is larger than a standard shot needle.
- Once the area is numb, your provider will most likely use an imaging machine, such as fluoroscopy equipment or a CT scanner (both are radiology imaging) to help guide the epidural needle to exactly the right position.
- When the epidural needle is in place in the epidural space around your spinal cord, your provider will inject the contrast material.
 The contrast material will make it easier for your provider to see the area they’re targeting on the screen of the imaging machine. This helps to make sure that the medication will reach the inflamed nerves they are targeting.
The contrast material will make it easier for your provider to see the area they’re targeting on the screen of the imaging machine. This helps to make sure that the medication will reach the inflamed nerves they are targeting. - Your provider will then slowly inject the medication, which is usually an anti-inflammatory medication, such as a steroid or corticosteroid. Some providers may inject a mixture of a corticosteroid and a long-acting anesthetic.
- When your provider is done with the injection they’ll clean the area again and apply a dressing to the site. You’ll move into a chair or bed to rest for a few minutes to an hour. This is so your provider can make sure you don’t have any reactions to the medication before you go home.
What will I experience during my epidural procedure?
You’ll likely experience a minor pinch when your provider injects the local anesthetic to numb the area before the epidural procedure.
You may feel pressure, tingling, a burning sensation or momentary shooting pain when your provider injects the epidural.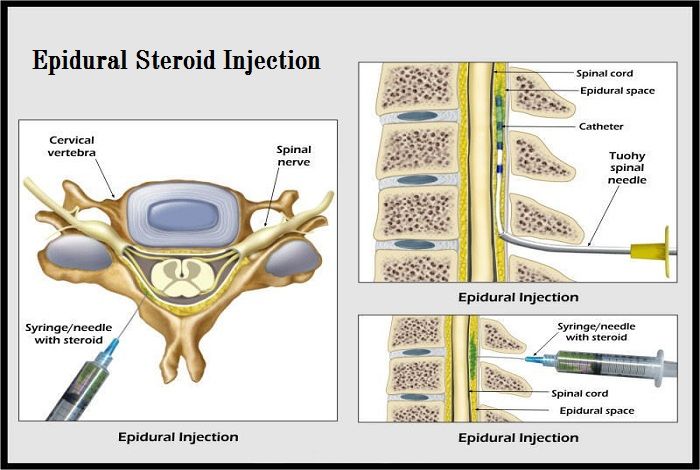 Or you may not feel anything. If you have any discomfort during the injection, it usually disappears once the injection is finished.
Or you may not feel anything. If you have any discomfort during the injection, it usually disappears once the injection is finished.
If you feel intense sharp pain during or after your epidural procedure, tell your provider immediately.
What happens after the epidural procedure?
If you’ve had an epidural with anesthetic medication, it’ll take 20 to 30 minutes for your pain relief and/or loss of feeling to take full effect.
Epidural steroid injections start working within two to seven days, and the pain relief can last several days or longer.
Risks / Benefits
What are the advantages of getting an epidural?
There are different advantages of getting an epidural depending on why you’re getting it.
The advantages of getting epidural analgesia during labor and childbirth include:
- They are usually very effective in minimizing pain felt during labor and delivery.
- They are generally very safe.
- You can often still move around in your bed and push when you need to.

- If you’re experiencing prolonged labor, having an epidural helps you to sleep and recover your strength.
- If you're undergoing a cesarean birth (C-section), you can stay awake during the birth, and your partner can be there as well.
- You can usually get an epidural at any time during your labor.
The advantages of epidural anesthesia injections for surgery include:
- You’ll likely experience less nausea and vomiting than you might with general anesthesia.
- You’ll have a quicker recovery after the surgery than you would with general anesthesia.
- You may have a lower risk of developing a blood clot in one of your leg veins (deep vein thrombosis, or DVT) than you would if you had general anesthesia.
The advantages of epidural steroid injections include:
- You’ll likely experience temporary or long-term pain relief.
- You’ll likely have a better quality of life and an improved ability to do daily activities without the restrictions previously caused by pain.
- Epidural steroid injections may help confirm the origin of your pain. This is often a problem in people who have more than one possible cause of pain.
- Epidural steroid injections may reduce the need for more invasive procedures for pain management.
What are the risks or complications of getting an epidural?
Epidurals are usually safe, but there are risks of certain side effects and complications. Although rare, risks and complications that apply to all types of epidural procedures include:
- Having low blood pressure, which can make you feel lightheaded.
- Experiencing a severe headache caused by spinal fluid leakage. Less than 1% of people experience this side effect.
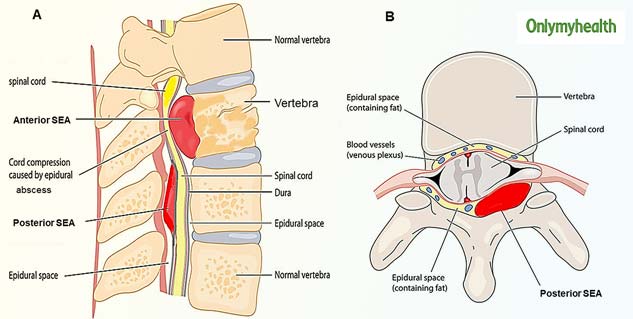
- Getting an infection from the epidural procedure, such as an epidural abscess, discitis, osteomyelitis or meningitis.
- Having a negative reaction to the medications, such as hot flashes or a rash.
- Experiencing bleeding if a blood vessel is accidentally damaged during the injection, which could cause a hematoma or a blood clot to form.
- Having damage to the nerves at the injection site.
- Temporarily losing control of your bladder and bowels. You might need a catheter (a small tube) in your bladder to help you pee.
Disadvantages and risks that apply to epidural analgesia for labor and delivery specifically include:
- You might lose feeling in your legs for a few hours.
- It might slow down the second stage of labor.
- You might not be able to push and need help to give birth. Your provider may need to use forceps or a vacuum to help deliver your baby.
- Your baby will need to be closely monitored during your labor.
Risks and complications that apply to epidural steroid injections specifically include:
- Experiencing a temporary increase in pain.
- If your provider uses fluoroscopy or a CT scan for imaging guidance, there will be minimal low-level radiation exposure due to the X-rays.
- If you have diabetes, a steroid injection will likely cause high blood sugar (hyperglycemia).
 This could last for several hours or even days.
This could last for several hours or even days.
Can getting an epidural cause back problems?
There’s a common belief that getting an epidural will lead to back pain, but it’s very rare for an epidural to cause long-term or chronic back problems.
It’s normal to experience temporary back pain or tenderness at the site of your epidural. This usually goes away within a few days.
This belief likely stems from the fact that many people who go through childbirth experience back pain after labor and delivery — whether they’ve had an epidural or not. This is because the bones and ligaments in your pelvis are shifting back into their original positions from before your pregnancy, which can cause back pain and discomfort.
Can getting an epidural cause long-term side effects?
While it’s very rare, having an epidural procedure can lead to some long-term complications, including:
- Permanent neurologic deficit due to spinal cord or nerve root damage from the epidural injection.
- Chronic pain due to due to spinal cord or nerve root damage from the epidural injection.
- Permanent paralysis from a hematoma that occurs when there’s a buildup of blood between the dura mater and the spinal cord.
Recovery and Outlook
How long does an epidural last?
How long an epidural lasts depends on what kind of epidural you got and what kind of medicine your healthcare provider injected. Your provider will let you know what to expect. In general, here’s how long certain types of epidurals last:
- Epidural with a catheter: If you have an epidural with a catheter, your provider can give you a continuous flow of anesthetic medicine or multiple separate doses, depending on your situation and pain level. Once your provider has stopped the medication, you’ll likely experience numbness for a few hours before the effect of the medicine begins to wear off. You’ll likely have to rest in a lying or sitting position until you have full feeling in your legs again.
 You may feel a slight tingling sensation while you’re waiting.
You may feel a slight tingling sensation while you’re waiting. - Single-injection epidural: Single injection epidurals usually last a few hours before you begin to regain feeling in the area that was numb.
- Epidural steroid injection: The length of time an epidural steroid injection can provide pain relief varies. Some people experience permanent pain relief if they have a new disk herniation. For people who have chronic pain, epidural steroid injections usually last 3 to 6 months or more.
When can I return to my normal activities after an epidural?
If you’ve had an epidural, do not drive, operate machinery or drink alcohol for at least 24 hours after. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions about when you can return to your normal activities depending on your type of epidural and your situation. Be sure to follow them.
When to Call the Doctor
When should I see my healthcare provider?
If you experience any of the following symptoms after you’ve returned home from your epidural procedure, be sure to contact your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital as soon as possible:
- Experiencing a severe headache while you’re standing up or sitting that feels better after lying down.
 This could be a sign of a dural puncture.
This could be a sign of a dural puncture. - Having a fever, which could be a sign of an infection.
- Having a reduced or complete loss of bladder or bowel control.
- Feeling numbness and/or weakness in your legs, which could be a sign of nerve injury.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between an epidural and a spinal block?
An epidural and a spinal block both provide pain relief through an injection in the area around your spine. The differences are the placement and the effect.
With an epidural, your healthcare provider injects anesthesia into the epidural space around your spinal nerves. With a spinal block, your provider injects the anesthesia into the dural sac around your spinal nerves that contains cerebrospinal fluid. This placement of a spinal block injection means that it gives immediate relief. Epidural injections usually take 20 to 30 minutes before you feel the full effect of pain relief or lack of feeling.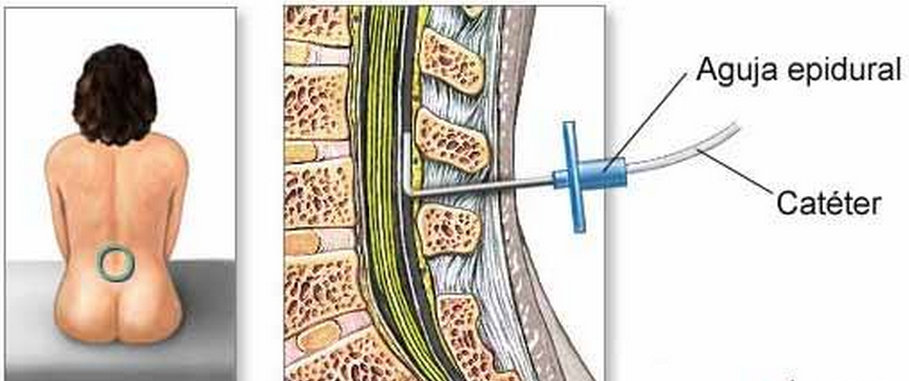
What are the side effects of an epidural after childbirth?
If you get an epidural for labor and childbirth, you may experience the following side effects, which aren’t very common, after delivery:
- Severe headache.
- Temporary difficulty with peeing.
- Temporary difficulty with walking.
- Fever.
You will likely have a small bruise and some tenderness at the site of the epidural after delivery. This should get better in one to two days.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Epidurals are a common, effective and generally safe procedure to deliver quick pain relief and/or a temporary lack of feeling. If you’re feeling anxious about the possibility of receiving an epidural, don’t be afraid to ask your healthcare provider about it and the procedure. They can answer any questions you may have.
Back pain after epidural anesthesia: what to do, treatment
Discomfort in the back can be of a different nature and appear for various reasons. In any case, health problems cannot be ignored, this can lead to more serious consequences and complex treatment. For any discomfort, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
In any case, health problems cannot be ignored, this can lead to more serious consequences and complex treatment. For any discomfort, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
What is epidural anesthesia?
In the treatment of patients, various medications are prescribed. These include painkillers of varying degrees of action. Epidural anesthesia, or epidural, is one of the methods of anesthesia in order to exclude any sensitivity of the patient's body below the waist. Despite the fact that this method has its obvious and undeniable advantages, some of the patients complain that they have back pain after epidural anesthesia. Accordingly, questions arise about why this happens, and what should and can be done to make the discomfort go away faster?
When is it prescribed?
Before answering the question of what to do if your back hurts after epidural anesthesia, you need to understand what this procedure implies and when it is prescribed. Medications are administered by catheterization (through catheters into the cavities in the human body) into the space of the spinal cord. The puncture site is also anesthetized so that the patient does not receive any pain at the time of injection of the painkiller. The effect after the introduction of medicines occurs within 10-15 minutes. Most often, an epidural is prescribed to women in labor - during childbirth or when prescribing a caesarean section. In such cases, it is important not to harm the fetus, and this method is safe for the baby. In addition to obstetrics, an epidural is prescribed in urology, gynecology, during surgical intervention in the peritoneal cavity or on the pelvic organs.
The puncture site is also anesthetized so that the patient does not receive any pain at the time of injection of the painkiller. The effect after the introduction of medicines occurs within 10-15 minutes. Most often, an epidural is prescribed to women in labor - during childbirth or when prescribing a caesarean section. In such cases, it is important not to harm the fetus, and this method is safe for the baby. In addition to obstetrics, an epidural is prescribed in urology, gynecology, during surgical intervention in the peritoneal cavity or on the pelvic organs.
Why does my back hurt after an epidural?
When the medications stop working, the patient begins a recovery period, which is accompanied by various sensations. Sometimes patients start to have back pain after an epidural, and how much it hurts and whether any treatment is needed depends on the type and complexity of the surgery and the consequences that have arisen. The occurrence of pain of varying degrees and localization happens for various reasons.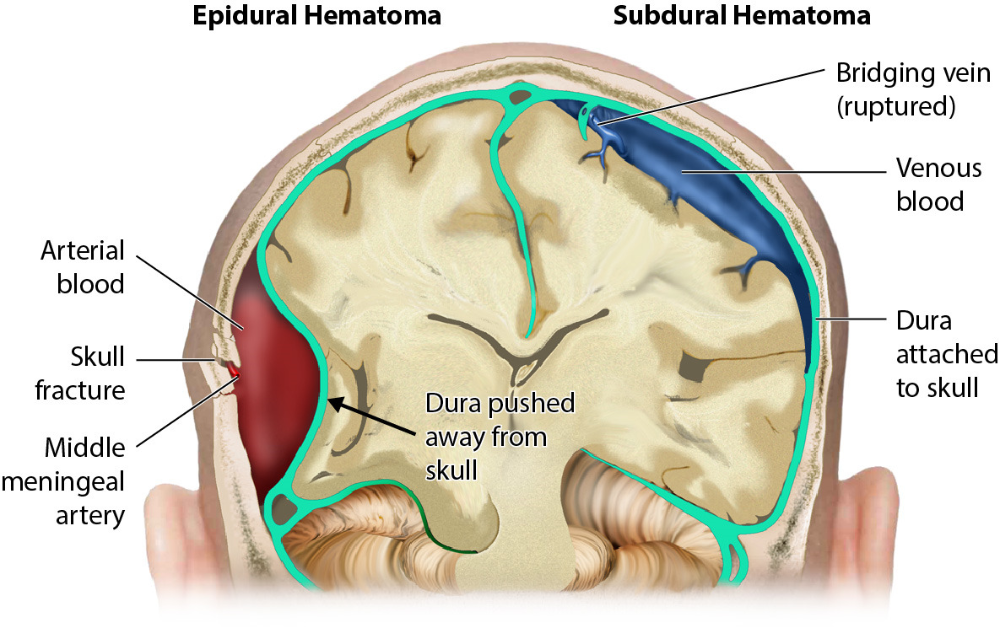 How quickly does a patient recover after an epidural, and what can happen? Timing and response are individual indicators. The causes of pain are also varied.
How quickly does a patient recover after an epidural, and what can happen? Timing and response are individual indicators. The causes of pain are also varied.
Infection
The infection develops where the needle was inserted, for example, due to the fact that mistakes were made during disinfection. In some cases, a problem arises if the catheter is kept in the patient's body when additional and longer pain relief is required.
Herniated disc
If the pain persists for several months or longer, then most likely the patient has an intervertebral hernia. It is not a contraindication to an epidural, but it can become an individual feature that should be taken into account when prescribing this method of anesthesia; in any case, careful monitoring of the patient's condition is required.
Medical errors
Back pain after epidural anesthesia can also be due to medical error. This happens if, when installing a catheter and inserting a needle, the doctor touched a bundle of veins. This is rare, but at risk are patients who take drugs to improve blood circulation (this should be noted in the anamnesis). Also, when carrying out the necessary manipulations (in the absence of sufficient experience from the doctor), a hernia or ligaments, as well as the roots of nerve fibers, can be damaged. The back can also hurt after an epidural anesthesia for a caesarean section. This happens because the center of gravity shifts in a woman in labor, and the body needs time to adjust to a new state and cope with the stress.
This is rare, but at risk are patients who take drugs to improve blood circulation (this should be noted in the anamnesis). Also, when carrying out the necessary manipulations (in the absence of sufficient experience from the doctor), a hernia or ligaments, as well as the roots of nerve fibers, can be damaged. The back can also hurt after an epidural anesthesia for a caesarean section. This happens because the center of gravity shifts in a woman in labor, and the body needs time to adjust to a new state and cope with the stress.
How much does your back hurt after an epidural?
This is an individual indicator that depends on the characteristics of a particular patient and the reaction of his body to the procedure itself and the treatment for which anesthesia was required. For some people, pain or discomfort in the injection area disappears after a couple of days, sometimes discomfort remains for several weeks, and sometimes even for a year or longer.
Pain management after treatment
Normally, the body and the sensitivity of the body are restored after a short time after the procedure. If this does not happen, it is recommended to contact a neurologist who will find out why the back hurts after epidural anesthesia, what to do in this case in order to remove discomfort.
If this does not happen, it is recommended to contact a neurologist who will find out why the back hurts after epidural anesthesia, what to do in this case in order to remove discomfort.
Painkillers
In the normal course of recovery, no painkillers or other medications are required. But if the intensity of pain is high enough and lasts a long time, only a doctor will help you choose the right painkillers, depending on what the epidural was for and why the pain arose.
Seeing a doctor
If there is inflammation or irritation, then for treatment it will be necessary to take antibiotics prescribed by a doctor, and for an abscess and severe suppuration, treatment by a surgeon is necessary. Also, the doctor can give valuable advice on nutrition - especially for overweight patients or women after childbirth, as well as on physical activity to strengthen the muscle corset. Additionally, a course of vitamins may be prescribed.
Prophylaxis
To avoid complications after the procedure, it is recommended to follow the diet and not gain extra pounds.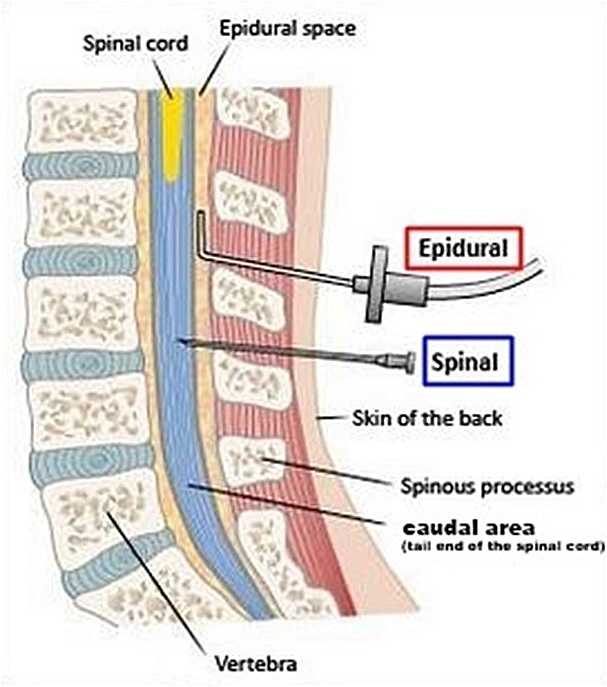 You should also engage in feasible physical education in order to strengthen the muscles of the trunk and the body as a whole.
You should also engage in feasible physical education in order to strengthen the muscles of the trunk and the body as a whole.
pregnancy bronchi abdomen vagina genitals pituitary eyes eye orbits shin head brain throat larynx rib cage thoracic region diaphragm for children glands stomach gallbladder stomach retroperitoneum back of the head teeth brush intestines collarbone knee limbs contrast agent coccyx bone sacrum lungs lymph node facial skeleton elbow scapula small pelvis uterus period breast bladder scrotum soft tissues adrenal glands leg nose nasopharynx finger groin liver esophagus pancreas spine penis kidneys small of the back lumbosacral region forearms appendages prostate calcaneus ribs hand sciatic nerve spleen heart vessels joints back foot joints tendon pelvis hip joint trachea Turkish saddle ear jaw scull cervical cervical region neck thyroid ovaries
Sign up for a consultation or diagnostic today!
You can make an appointment by phone: +7 (812) 901-03-03
Or leave a request
full name
Phone number
By clicking the "Make an appointment" button, I accept the terms of the Personal Data Processing and Security Policy and consent to the processing of my personal data.
Our medical centers
Making an appointment
Patient's last name *
Incorrect first name
Name *
Middle name
Contact phone *
E-mail *
By clicking the "Make an appointment" button, I accept the terms of the Personal Data Processing and Security Policy and consent to the processing of my personal data.
Registration and payment for repeated online appointment
Patient's last name *
Incorrect first name
Name *
Middle name *
Contact phone *
E-mail *
By clicking the "Submit request" button, I accept the terms of the Personal Data Processing and Security Policy and consent to the processing of my personal data.
About cookies on this website
We use cookies, IP addresses and device data for analytics to make your visit to the site convenient and personalized. You can disable cookies in your browser settings. By continuing to use our site, you consent to the processing of the listed data and accept the terms of the Privacy Policy.
Spinal anesthesia | orto.lv
Pain medication is injected into the spinal canal (where the anatomical end of the spinal cord). As a general rule, for the spinal anesthesia procedure, the patient should be in a sitting position with a round back arched and the chin pressed to the chest.
"ORTO" clinic performs spinal anesthesia for operations on the cross-ligaments, ankle and foot area, as well as hip prosthetics. When prosthetics of the knee joint, spinal anesthesia is combined with epidural.
Spinal anesthesia begins to work almost immediately after insertion. The maximum effect is achieved after 20 minutes and lasts from 4 to 6 hours.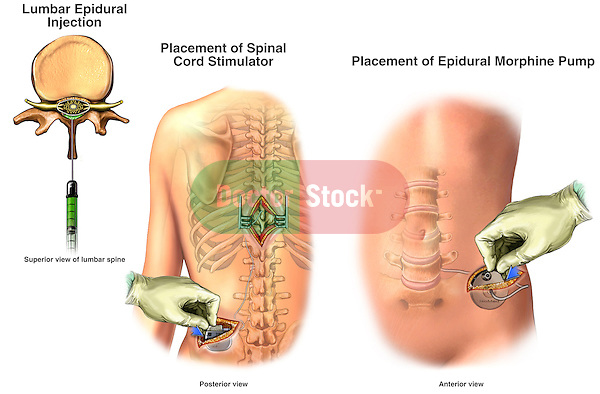
How will I feel after anesthesia is given?
Immediately after injection, you may feel warm, slightly numb and feel heavy in your legs. After about 10-15 minutes, you will not be able to raise your legs, they will become numb, become heavy, lose sensitivity.
How will I feel during the operation?
If a long operation and a monotonous posture are planned, discomfort may occur over time, despite the fact that you will not feel pain. Discomfort can be created, for example, by stretching the leg, strong touch, ambient noise. If you do not want to stay awake, the anesthesiologist will ensure that you get some light sleep during the operation. In addition, the anesthetist monitors your pulse, blood pressure, breathing and consciousness.
How will I feel after the operation?
Within six hours after the operation, you will feel a slight numbness in the legs, there may be slight pain in the wound area, and the mobility of the limbs will be restored.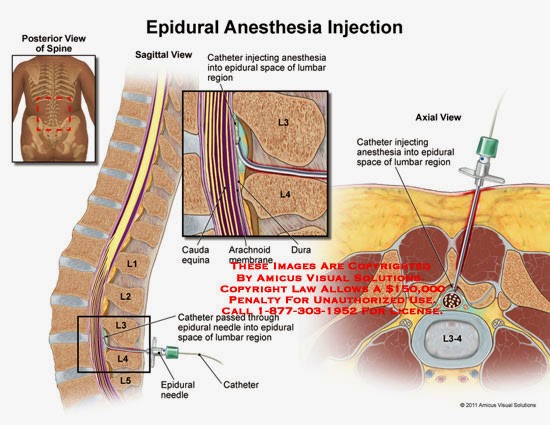 After the operation until the morning of the next day, it is necessary to observe bed rest.
After the operation until the morning of the next day, it is necessary to observe bed rest.
Spinal anesthesia is considered safe, but in rare cases, side effects may occur:
- in 20% of cases there may be nausea or vomiting;
- in 20-30% of cases, urinary retention occurs, since spinal anesthesia also affects the functioning of the muscles of the bladder. As a rule, with the introduction of a drug that relaxes the smooth muscles, the normal functioning of the bladder is restored. If necessary, a catheter is inserted into the bladder;
- may itch and itch the skin. For this purpose, special drugs are provided that reduce the manifestation of this side effect;
- less than 5% of people experience a headache. Most often, this phenomenon affects young and slender people within three to seven days after spinal anesthesia. Sometimes nausea and vomiting can be added to the headache. The pain is more pronounced in an upright position and when the head is tilted down.