Pictures of babies born at 32 weeks
Premature baby development: 26-36 weeks
Premature baby development: the basics
A premature baby’s development typically happens in the same order as it would have happened in the womb.
But premature babies might have some health challenges along the way. Sometimes premature babies also have delays in growth and development. Very premature babies and premature babies with medical challenges are more likely to have delays.
For example, a premature baby born at 32 weeks is likely to act differently from a baby born at 26 weeks, who has had many medical challenges by the time they get to 32 weeks. The baby born at 26 weeks might take extra time to put on weight, learn to feed and come out into the social world.
Here are the changes you can expect and watch in your premature baby during their time in hospital.
26 weeks
At 26 weeks, a baby in the womb is about 35 cm long and weighs about 760 gm. But premature babies are often small for their age. A baby born at 26 weeks would probably fit snugly into your hand.
At this age your premature baby’s main job is to grow, sleep and become medically stable.
Your baby might open their eyes occasionally, but they can’t focus. Light or other visual stimuli might stress their body’s systems. Your baby’s nurse might place a cover over your baby’s incubator, and some neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) dim the lights at night.
Your baby’s movements are often jerks, twitches or startles. Your baby doesn’t yet have good muscle tone and can’t curl up. Hospital staff will put your baby in a curled-up position, support their body with bedding and keep them warm. This helps your baby keep up their energy.
Your baby might also have apnoea. This is common for very premature babies. The breath triggering part of your baby’s brain hasn’t fully developed yet, so pauses between breaths are common. Your baby will grow out of it.
Your baby’s ears and hearing structures are already fully formed, but your baby might be sensitive to external sounds. Your baby might notice your voice but they can’t respond to you yet.
Your baby might notice your voice but they can’t respond to you yet.
Your baby won’t be able to feed from your breast yet.
Your baby’s skin is fragile and sensitive, and they might get stressed if they’re handled or touched. The nurses will probably encourage you to ‘comfort hold’ your baby but not stroke them.
Our article on touching, holding and massaging your baby has more information on comfort holding and kangaroo care. And our article on premature baby body language explains what your premature baby’s behaviour is telling you.
26-28 weeks
At 26-28 weeks, babies in the womb continue to put on weight and grow longer. But if your premature baby is sick, their weight gain might not keep up with a baby in the womb. Also, hospitals use careful, staged feeding plans to protect your baby’s immature gut from infection, and this might slow weight gain.
At this age, babies start blinking. They also grow eyelashes and eyebrows.
Your baby still has low muscle tone and is likely to have twitches and tremors.
Your baby’s sleep and wake cycles aren’t clear yet, but your baby might have active and quiet periods and very brief alert times.
Your baby might open their eyes, but they probably still can’t focus or get their eyes moving together.
At this age, your baby’s responses to sound might change from hour to hour or day to day. Or they might respond to your voice but get stressed by other noises. Your baby’s responses will start to give you some clues to what they like and dislike.
Your baby might begin sucking, but they still can’t feed from your breast. To breastfeed, they need to know how to suck, swallow and breathe in the right order.
Your baby’s skin is still fragile and sensitive. But if your baby is medically stable, you might be able to start skin-to-skin contact by doing kangaroo care.
28-30 weeks
In the womb a baby keeps getting heavier and longer, starts to move more often, knows the difference between some sounds – for example, voices and music – starts to grasp with their hands, and opens and shuts their eyes.
At this age, your premature baby will still be well supported with bedding and positioning, but they might move and stretch more actively as their muscle tone gets better.
Your baby’s quiet deep sleep (when they don’t move) and light sleep (when they move their limbs and eyes) increase at about 30 weeks. You’ll also start to see short alert, eye-opening periods, but this can be affected by your baby’s health, the environment or the time of day.
Your baby is starting to close their eyelids tightly if it’s bright, but they still can’t move their eyes together very much. Their eyes wouldn’t usually get much stimulation at this age, so it might help to limit what they see.
Your baby keeps responding to pleasant sounds and is still sensitive to other sounds. They might be quiet and attentive to your voice and might even seem to ‘wake up’ when you come in. You can start to talk or sing to your baby during their short alert times. But keep stimulation to one thing at a time – for example, eye contact or talking, but not both at once.
They might be quiet and attentive to your voice and might even seem to ‘wake up’ when you come in. You can start to talk or sing to your baby during their short alert times. But keep stimulation to one thing at a time – for example, eye contact or talking, but not both at once.
Your baby’s rooting reflex – turning to a touch on the cheek – might start around this time. This means they’re getting ready for breastfeeding. Your baby might even start sucking, but they can’t feed at your breast yet.
Your baby might still be sensitive to touch, but they like steady, gentle, hands-on touch or skin-to-skin contact. You might be able to get involved in caring for your baby about now.
30-33 weeks
At this age, a baby’s organs are maturing. A baby born now might not need much medical help.
Your premature baby’s movement is smoother and more controlled, and they’ll start to bend their arms and legs for themselves.
Your baby’s deep sleep increases. Their alert periods come more often, especially if the room is dim. When they’re alert, your baby might focus on your face or another interesting object, and they might show an obvious response to your voice. Your baby might shut their eyes tightly if the room is bright.
Their alert periods come more often, especially if the room is dim. When they’re alert, your baby might focus on your face or another interesting object, and they might show an obvious response to your voice. Your baby might shut their eyes tightly if the room is bright.
Your baby might like eye contact, cuddling or talking during these times – but it’s still a good idea to keep it to one thing at a time. And you can also watch your baby’s body language for signs of stress.
Your baby might start to suck rhythmically and might show that they’re ready to suck to feed. Letting your baby smell and taste breastmilk gets their senses ready for breastfeeding. Gently rubbing around your baby’s lips and inside their mouth before feeds helps your baby get ready for the touch sensations of feeding from your breast.
If you see your baby putting their hands to their mouth, this means that they’re starting to soothe themselves.
Your baby might still be very sensitive to touch and handling. It’s helpful to tell them what you’re about to do so they can start associating your voice with what you’re doing. For example, ‘We’re going to change your nappy now’.
It’s helpful to tell them what you’re about to do so they can start associating your voice with what you’re doing. For example, ‘We’re going to change your nappy now’.
33-36 weeks
Your baby is now approaching the date they were due to be born. But even when they’ve reached 37 weeks, they aren’t necessarily like a full-term baby.
Your baby can now move more smoothly and bend their arms and legs. They can also move their head from side to side, and their muscle tone is stronger.
Your baby will be much less likely to experience apnoea.
Your baby’s states are clear – quiet sleep, active sleep, drowsy, quiet and alert, awake and fussy, or crying. Their alert states are still quite short, but they’re getting longer and happening more often. Your baby can have longer social times, and they can now turn away or close their eyes when they’ve had enough.
Your baby is more likely to respond to sounds and noises in the same way from day to day.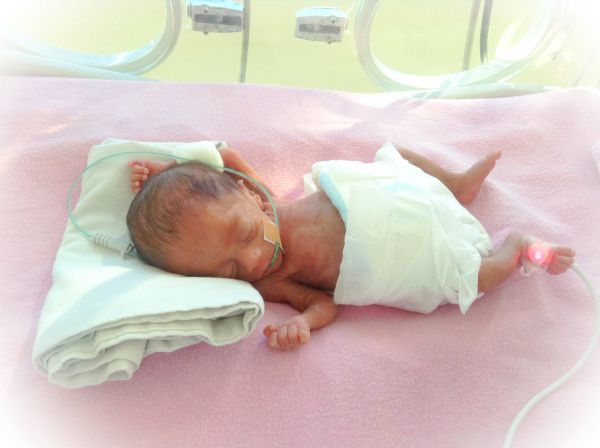 You might even know how they’re going to react when you say something to them.
You might even know how they’re going to react when you say something to them.
Your baby probably still doesn’t cry much. But as your baby gets closer to term, they’ll cry more often to let you know what they want.
Your baby can usually start breastfeeding around this time.
Your baby might still be sensitive to touch and handling, although telling your baby what you’re about to do will help them relax over time.
37 weeks and beyond
Your baby might be ready to go home before their expected birth date. But it might take longer if your baby has had surgery or an illness.
The hospital will have health, growth and development goals for your baby to meet before you can take them home. These might include steadily gaining weight, feeding from your breast or a bottle at all feeds, and having no problems with apnoea.
Our article on going home with your premature baby has more information on how to prepare for your baby’s homecoming.
Survival Rate, Time in Hospital, More
The final months of pregnancy are full of prepping and planning. And, of course, planning is important. But be prepared: Many births don’t go according to plan.
For example, you might end up having a cesarean delivery (C-section) or other interventions that you weren’t planning on. Or you may find yourself with much less time to prepare if your baby decides to show up to the party earlier than expected!
About 11 percent of babies worldwide are born early (premature). This means that they’re born more than 3 weeks before their estimated due date. About 85 percent of these are born between 32 and 36 weeks of pregnancy.
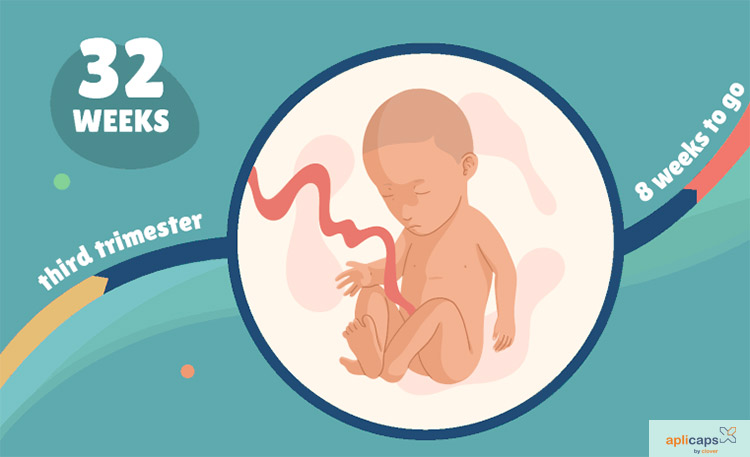
But if your baby is born even more prematurely — say, at 32 weeks — they still have very good odds at being healthy with some supportive medical care. Here’s what you need to know about a baby born at 32 weeks.
Yes, a baby can safely be born at 32 weeks, but they may need specialized care to help support their development as they navigate their early days in the world.
A baby who’s born before week 37 of pregnancy is considered to be premature. However, during pregnancy, every week — and even every day — makes a difference in a baby’s growth and development. This is why premature babies are grouped into four stages:
- late preterm, born between 34 and 36 weeks
- moderate preterm, born between 32 and 34 weeks
- very preterm, born between 25 and 32 weeks
- extremely preterm, born before 25 weeks
If your baby reaches 32 weeks of gestation (time in the womb) and is born at 32 weeks, they’re moderate preterm. Babies born at 32 weeks have a survival rate as high as 95 percent. They also have very good chances of growing into healthy babies and children without any complications.
Babies who are born very preterm and extremely preterm have a higher risk of complications and health problems than a baby born at 32 weeks.
How healthy and developed your baby is at 32 weeks also depends on what kind of pregnancy you have. If you’re carrying twins or other multiples they may be smaller than if you’re carrying a singleton baby.
If you’re carrying twins or other multiples they may be smaller than if you’re carrying a singleton baby.
At 32 weeks, babies still have a couple months to go before reaching their full birth weight, but they’re well developed. Your baby will look almost like a full-term baby, just smaller, thinner, and even more delicate.
They’ll have almost-there toenails and perhaps a few wisps of hair on their head. Most of the soft, downy hair (lanugo) that covered them earlier in the womb will have started falling off, but they’ll still be a little fuzzy.
They probably will not yet have fully formed fingernails. Their eyes, though developed, may be too sensitive to light to open just yet. By 32 weeks most babies are practicing breathing, and their lungs are in the final stages of development. Their skull and all their bones will still be very soft.
At 32 weeks, a baby may:
- weigh almost 4 pounds
- be between 16 and 17 inches long
- have a head size (circumference) between 11 and 12 inches
How long your baby needs to stay in the hospital after they’re born at 32 weeks depends on several things.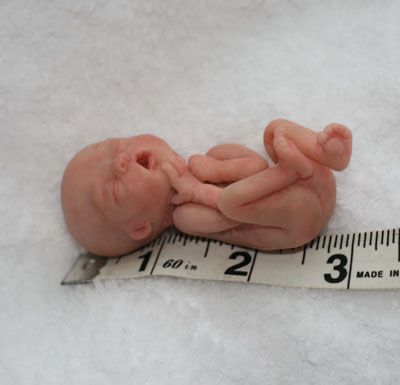
After birth, your premature baby will be taken to a special care nursery or the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) in the hospital where you gave birth.
Most babies born at 32 weeks of pregnancy have only a few temporary health issues and need to stay in the NICU for only a few days to a few weeks. After birth, your baby may need extra help learning and developing the skills needed for feeding, staying warm, and breathing on their own.
Babies born at 32 weeks will generally not yet be strong enough to breastfeed because their sucking muscles are still weak and uncoordinated. They’ll likely need to be tube-fed for a few weeks.
That said, receiving breast milk is especially important for preterm babies. Compared to preterm babies who receive formula, those who receive human milk typically have higher survival rates, shorter NICU stays, and fewer serious health complications.
Even if you weren’t planning to breastfeed, you may consider expressing milk to help nourish your premature baby. You may also consider donor milk.
You may also consider donor milk.
Most babies born at 32 weeks don’t have breathing problems, but your doctors and nurses will make sure they’re breathing properly.
Before your baby can safely go home with you, your doctor will make sure they don’t have any other health problems and are growing and developing enough to do well without NICU care.
Before they’re discharged, your baby will be evaluated on their:
- weight gain
- ability to suck and swallow milk on their own
- temperature regulation
- eye development and sensitivity
Babies born at 32 weeks might have some temporary health problems such as:
- low birth weight
- jaundice
- hypothermia
- feeding difficulties
Some long-term issues in babies born at 32 weeks might show up months to years later. These are not common, but can include slower development. In most cases, babies with learning or developmental delays catch up later in childhood with a little bit of extra help.
A 2017 medical study in France that followed 5,170 babies who were born between 22 to 34 weeks of pregnancy found that babies born at 32 to 34 weeks had very low risks of long-term health problems.
The researchers found that about 1 percent of babies born at 32 to 34 weeks had the neuromotor disorder cerebral palsy.
The same study tested 2,506 2-year-olds who were born prematurely. In the group born at 32 to 34 weeks of pregnancy, 36.2 percent scored slightly lower than average on a questionnaire that was used to test brain development.
While this means that some babies born at 32 weeks may have delayed learning development and skills in early childhood, and early intervention can have a significant impact in improving skills.
If your baby is born at 32 weeks, they have very good chances of being born healthy and developing just fine.
They’ll be considered premature, specifically moderately preterm, and will need extra medical care to make sure they’re healthy and growing normally before they can go home. Your baby may be in the hospital or NICU for several days to weeks.
Your baby may be in the hospital or NICU for several days to weeks.
In rare cases, a baby born at 32 weeks may have neurodevelopmental (brain and learning) delays. In most cases, they’ll catch up with some extra help during early childhood.
Your baby was born prematurely | Regional Perinatal Center
Premature babies
If your baby is born too early, the joy of having a baby can be overshadowed by health concerns and thoughts about the possible consequences.
Instead of returning home with the baby, holding him and caressing him, you will have to stay in the department, learn to cope with the fear of touching the baby, realize the need for treatment and various manipulations, get used to the complex equipment that surrounds him. nine0005
In this situation, not only your baby needs help, you need it too! The best assistants are your loved ones, their love and care, as well as professional advice and recommendations from doctors and psychologists.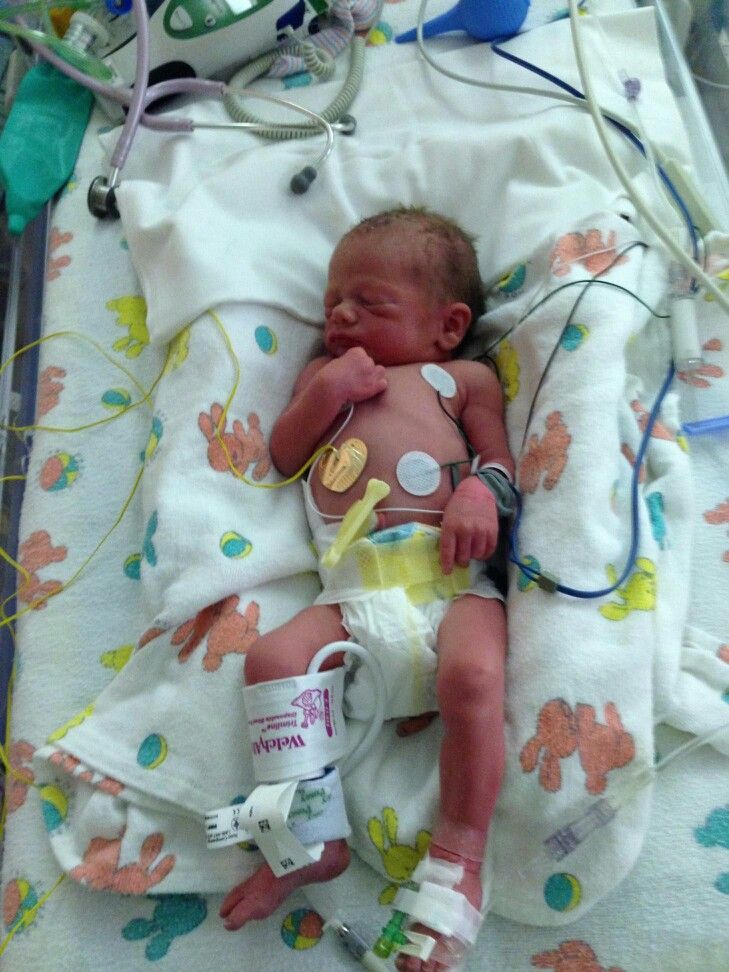 This section of articles will help you improve your knowledge of preterm infant care, development and nutrition.
This section of articles will help you improve your knowledge of preterm infant care, development and nutrition.
Your help for the baby
Previously, parents were often not allowed into the neonatal unit and, especially, into the intensive care unit because of the fear of infection of the baby, but now the contact of the parent with the child is recognized as desirable and is prohibited only in exceptional cases (for example, if parents have acute infections)
Close communication between you and your baby is very important from the first days of his life. Even very immature premature babies recognize the voices and feel the touch of their parents.
The newborn needs this contact. Studies have shown that it greatly contributes to the faster adaptation of an immature child to new conditions and the stabilization of his condition. The baby's resistance to therapy increases, he absorbs large amounts of food and quickly begins to suck on his own. Contact with the child is important for parents. Taking part in the care of the baby, they feel their involvement in what is happening and quickly get used to a new role, especially when they see how he reacts to their presence. nine0005
Contact with the child is important for parents. Taking part in the care of the baby, they feel their involvement in what is happening and quickly get used to a new role, especially when they see how he reacts to their presence. nine0005
By constantly and attentively observing the baby, parents can notice the smallest changes in his condition before others. In addition, communication in the hospital is a good practice that will undoubtedly come in handy after discharge. For parents, early physical contact with the baby is very valuable, because it allows them to feel him, despite the incubator and other obstacles, and show him their love.
Treatment in the neonatal intensive care unit requires parents to have full confidence in all medical staff. nine0005
Nursing premature babies in the hospital
Many premature babies cannot breathe, suckle and regulate their body temperature sufficiently after birth. Only in the last weeks of pregnancy is the maturation of the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, brain, which regulates and coordinates the work of all organs and systems.
Fluid loss due to the immaturity of the skin of premature babies and the insufficiency of thermoregulation processes require constant attention. Modern approaches focused on nursing premature babies help to cope with these problems. nine0005
Heat regulation incubator
Premature babies are very susceptible to temperature fluctuations. At the same time, clothing can interfere with the monitoring of the baby's condition and its treatment. That is why an incubator is used to provide the conditions necessary for premature babies. It maintains a certain temperature and humidity, which change as the child grows. When the body weight of a premature infant reaches 1500-1700 g, he can be transferred to a heated bed, and after reaching a weight of 2000, most premature babies can do without this support. There are no strict rules here: when nursing children with low body weight, doctors are guided by the severity of the condition of each premature baby and its degree of maturity. nine0005
nine0005
In incubators, very young premature babies are placed in special "nests" - soft hemispheres in which the baby feels comfortable and assumes a position close to intrauterine. It must be protected from bright lights and loud noises. For this purpose, special screens and coatings are used.
Critical treatments during the first days of life of premature babies with low and very low birth weight:
Use of an incubator or heated bed. nine0005
Oxygen supply for respiratory support.
If necessary, artificial ventilation of the lungs or breathing using the CPAP system.
Intravenous administration of various drugs and fluids.
Carrying out parenteral nutrition with solutions of amino acids, glucose and fat emulsions.
Don't worry: not all premature babies need such extensive treatment!
Mechanical ventilation and CPAP for respiratory support
When it comes to nursing, oxygen supply is of the utmost importance for premature babies. In a child born before the 34-35th week of pregnancy, the ability of the lungs to work independently is not yet sufficiently developed. The use of a constant flow of air with oxygen, which maintains a positive airway pressure (CPAP), leads to an increase in blood oxygen saturation.
In a child born before the 34-35th week of pregnancy, the ability of the lungs to work independently is not yet sufficiently developed. The use of a constant flow of air with oxygen, which maintains a positive airway pressure (CPAP), leads to an increase in blood oxygen saturation.
This new method made it possible for the majority of even very immature children to do without mechanical ventilation. The need for intubation of children has disappeared: during treatment with CPAP, oxygen is supplied through short tubes - cannulas that are inserted into the nasal passages. CPAP or mechanical ventilation is continued until the lungs can function at full capacity on their own. nine0005
In order for the lungs to expand and remain in such a state in the future, a surfactant is needed - a substance that lines the alveoli from the inside and reduces surface tension. Surfactant is produced in sufficient quantities starting from the 34-35th week of pregnancy. Basically, it is by this time that the formation of the lungs is completed. If the baby was born earlier, modern technologies allow the introduction of surfactant into the lungs of premature babies immediately after their birth.
If the baby was born earlier, modern technologies allow the introduction of surfactant into the lungs of premature babies immediately after their birth.
Parenteral nutrition - administering nutrient solutions by vein
Premature babies, especially those born weighing less than 1500 g, are not able to get and absorb enough nutrients, even when fed through a tube. For the rapid growth of the baby, a large amount of nutrition is needed, and the size of the stomach is still very small, and the activity of digestive enzymes is also reduced. Therefore, such children are given parenteral nutrition.
Special nutrients are injected into a vein using infusion pumps that deliver solutions slowly at a predetermined rate. In this case, amino acids necessary for building proteins, fat emulsions and glucose, which are sources of energy, are used. These substances are also used for the synthesis of a number of hormones, enzymes and other biologically active substances. Additionally, minerals and vitamins are introduced. nine0005
Additionally, minerals and vitamins are introduced. nine0005
Gradually, the volume of enteral nutrition increases, and parenteral nutrition decreases until it is completely canceled.
Premature infants with gastrointestinal disease require parenteral nutrition for a longer period of time.
By the time your grown baby is discharged from the hospital, everything should be well prepared at home. And this applies not only to the environment, clothes and means of caring for the child.
All family members must be ready to receive the baby. Of course, the main care will fall on the shoulders of the parents. Although you have already gained some experience in the hospital, it is important to feel the support of others, especially in the early days.
Older children can also help. The discharge of your baby is a great joy that you want to share with all your relatives.
While you are getting used to your new role, it is important that nothing distracts you from communicating with your child. Now all the care and responsibility for the baby lies entirely with you. Everything you need to take care of him should be at hand. nine0005
Now all the care and responsibility for the baby lies entirely with you. Everything you need to take care of him should be at hand. nine0005
Preparing for discharge from the hospital
Before discharge, you must make sure that:
- Prepared the crib, bath for bathing and a place for changing clothes, preferably a changing table. A crib should be placed in the parents' bedroom, the child should not be left alone even at night. A stroller is also required. you have baby milk that was recommended by the doctor before discharge (if the child is on mixed or artificial feeding). As a rule, this is a specialized medical product. You need a certain number of small bottles and teats of the appropriate size, as well as a sterilizer. All premature babies will need pacifiers. nine0126
- You have fully mastered breastfeeding or bottle feeding.
- If your baby is not suckling all the required amount of milk from the breast and is supplementing from a bottle, you have purchased a breast pump that you have learned to use; you may also need it if you have a lot of breast milk.

- You have asked your doctor how often your child's weight should be monitored.
- If your baby still needs medication, you have the required amount at home. And you know exactly how and when to give them to your child. nine0126
- You know which warning signs to look out for.
- After the baby is discharged, a pediatrician and a neonatologist will look after the baby, to whom you will give the discharge summary from the hospital.
- You know how the hospital from which your child is being discharged will provide follow-up care after discharge.
- You know which specialists and how often should examine your baby (oculist, neuropathologist, etc.). nine0126
- All the emergency phone numbers you need are at your fingertips.
When can a child go home
This question is very difficult to answer because all children are different. The stay in the hospital can last from 6 days to 6 months, depending on the degree of prematurity of the child, the severity of his condition, as well as the presence of certain complications.
Of course, all parents look forward to the moment when the baby can be brought home. Long-term nursing of a premature baby is often a difficult test for you. But we must not forget that safety comes first, and the baby can be discharged home only when the doctors are confident in the stability of his condition. It is certainly in your interest as well. nine0005
The rate of increase in body weight and length
Weight gain is the main indicator of the growth of the baby and the adequacy of the treatment. The weight of the child, especially in the first days and weeks of life, is influenced by a number of factors: the presence of milk in the stomach (immediately after feeding), the time of bowel movement, the degree of filling of the bladder, the presence of edema. Therefore, if an edematous child does not gain weight for several days, and perhaps even loses it, do not worry. It should be remembered that children grow unevenly and periods of high weight gain alternate with lower ones. It is better to focus not on weight gain per day, but on the dynamics of this indicator over several days or a week. nine0005
It is better to focus not on weight gain per day, but on the dynamics of this indicator over several days or a week. nine0005
It is currently accepted that in the interval corresponding to 28-34 weeks of pregnancy, the normal weight gain of the child is 16-20 g/kg per day. Then it is reduced to 15 g/kg.
It is also important to take into account the rate of increase in body length. With malnutrition, at first the child gains less weight (or even loses it), and with a more pronounced deficiency of nutrients, his growth is also disturbed.
The weight must not only increase at a certain rate, but must also correspond to the length of the baby. An important parameter characterizing the development of the baby is an increase in the circumference of the head. The brain most actively increases in size during the first 12–18 months of life. But an excessively rapid increase in head circumference, as well as a slowdown in its increase, indicate neurological disorders. nine0005
A premature baby can be discharged from the hospital if:
- he is able to independently maintain the required body temperature;
- does not need breathing support and constant monitoring of the work of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems;
- can suck out the required amount of nutrition on its own;
- does not need round-the-clock monitoring and frequent determination of biochemical or other indicators; nine0126
- supportive care can be provided at home;
- he will be under the supervision of a local pediatrician and neonatologist at the place of residence.

The decision to discharge home is made for each patient individually. In addition to the state of health of the baby, the degree of preparedness of parents, their ability to provide high-level care for a premature baby is also taken into account.
Feeding a premature baby after discharge
Breastfeeding is the ideal way to feed premature babies.
However, if the baby was born much prematurely and his birth weight did not exceed 1800-2000 g, his high nutritional requirements cannot be met by breastfeeding. The growth rate will be insufficient. Moreover, over time, the content of many nutrients, including protein, in milk decreases. And it is the main material for building organs, and primarily brain tissue. Therefore, proteins must be supplied to the body of a premature infant in the optimal amount. nine0005
In addition, premature babies have a significantly increased need for calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for bone formation.
In order for the baby's nutrition to be complete even after being discharged from the hospital, special additives - "enrichers" are introduced into breast milk in a certain amount, already less than in the hospital. They make up for the lack of protein in it, as well as some vitamins and minerals. As a result, the child receives them in the optimal amount. The duration of their use will be determined by your doctor. If there is not enough milk or it does not exist at all, children born prematurely should be transferred to artificial feeding. Complementary feeding of premature babies is carried out with special children's dairy products designed for children with low birth weight. This baby milk is ideally suited to both the ability of immature children to digest and assimilate nutrients, and their needs. nine0005
Premature infant milk contains more protein, fat and carbohydrates than term infant milk, resulting in a higher calorie content. In specialized baby milk, the concentration of many minerals is higher, especially iron, zinc, calcium, phosphorus, as well as vitamins, including vitamin D. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids of the Omega-3 and Omega-6 classes are introduced into such products, which are necessary for proper development of the brain and organ of vision, as well as nucleotides that contribute to the optimal development of immunity. However, when the child reaches a certain weight (2000-2500 g), you should gradually switch to feeding with standard baby milk, but not completely. Specialized baby milk can be present in the diet of a premature baby for several months. This time, as well as the volume of the product, will be determined by the doctor. He will answer all your questions about how to feed your baby. nine0005
Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids of the Omega-3 and Omega-6 classes are introduced into such products, which are necessary for proper development of the brain and organ of vision, as well as nucleotides that contribute to the optimal development of immunity. However, when the child reaches a certain weight (2000-2500 g), you should gradually switch to feeding with standard baby milk, but not completely. Specialized baby milk can be present in the diet of a premature baby for several months. This time, as well as the volume of the product, will be determined by the doctor. He will answer all your questions about how to feed your baby. nine0005
At present, specialized children's dairy products have been developed and are being used to feed premature babies after discharge from the hospital. In its composition, it occupies an intermediate position between a specialized product for premature babies and regular baby milk. Your baby will be transferred to such baby milk while still in the hospital.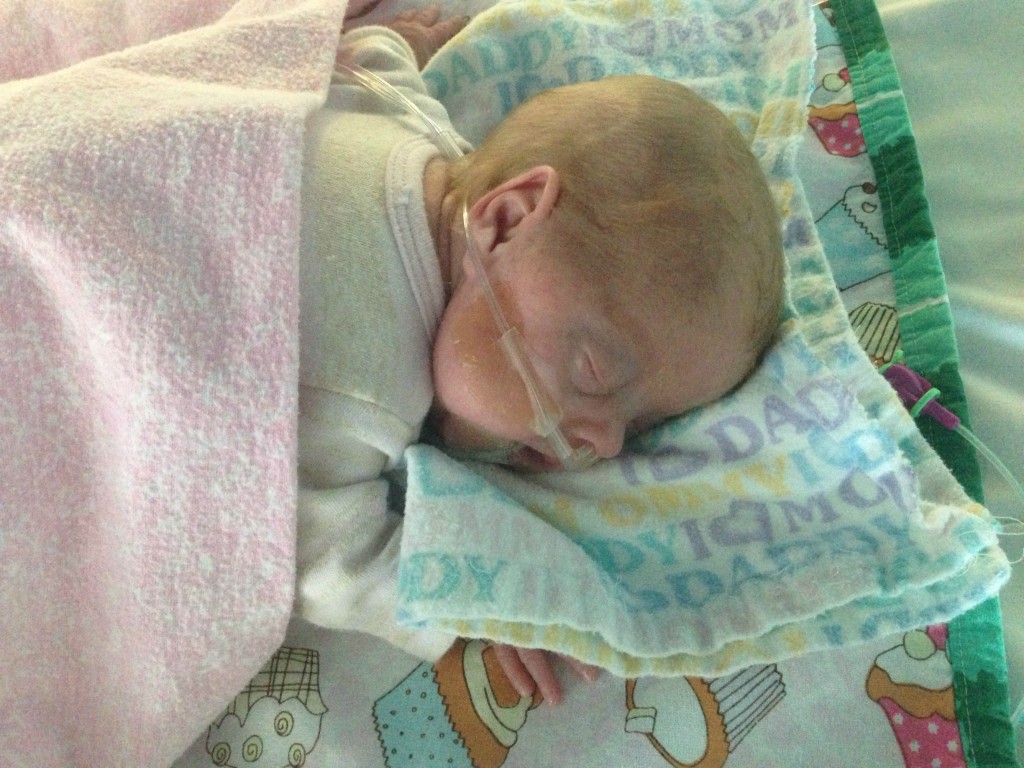 You will continue to give it to your child at home, and the doctor, watching him, will tell you when it will be possible to switch to regular standard baby milk. If the baby was born with a very low body weight or is not gaining weight well, special baby milk can be used for a long time - up to 4 months, 6 or even 9months. The beneficial effect of such children's dairy products on the growth and development of the child has been proven in scientific studies.
You will continue to give it to your child at home, and the doctor, watching him, will tell you when it will be possible to switch to regular standard baby milk. If the baby was born with a very low body weight or is not gaining weight well, special baby milk can be used for a long time - up to 4 months, 6 or even 9months. The beneficial effect of such children's dairy products on the growth and development of the child has been proven in scientific studies.
Feeding needs for premature babies
Higher caloric intake because they need to gain weight faster than term babies.
More protein as premature babies grow faster.
More calcium and phosphorus for bone building.
More trace elements and vitamins for growth and development. nine0005
A premature baby grows faster than a term baby. Nutrition for such children is calculated taking into account body weight at birth, the age of the baby and its growth rate. As a rule, the calorie content of the daily diet is about 120-130 calories per 1 kg of body weight.
It is very important that your baby continues to gain weight quickly and grow in length after discharge. To do this, feeding premature babies must be carried out using a specialized fortified diet prescribed by a doctor. nine0005
The first weeks of a premature baby: what to prepare for
What is the difference between caring for a newborn if he was born prematurely and how to help him "catch up" with other babies
You were not ready for the fact that the baby will be born ahead of schedule? No one, unfortunately, is immune from preterm birth. The reasons are varied, from multiple pregnancy to infection and severe stress. Fortunately, modern medicine is able to nurse most premature babies. Neonatologist Milana Basargina talks about special care rules. nine0236
A baby is considered premature if he was born at a gestational age of 36 weeks or less. Most premature babies are born with a body weight of less than 2500 g and a height of less than 45 cm. According to the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation, the frequency of birth of children with low body weight in Russia is 4.0-7.3% in relation to the number of births. Among premature babies, about 80% are children born at a gestational age of 32–36 weeks. Babies born less than 32 weeks of age and weighing less than 1500 g are considered profoundly preterm.
According to the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation, the frequency of birth of children with low body weight in Russia is 4.0-7.3% in relation to the number of births. Among premature babies, about 80% are children born at a gestational age of 32–36 weeks. Babies born less than 32 weeks of age and weighing less than 1500 g are considered profoundly preterm.
The birth of a premature baby is always a cause for special worries and worries for parents. Doctors, relatives and the child himself have a lot of work to make up for lost weeks or even months of intrauterine development.
Often a prematurely born child causes parents to feel fear, guilt and hopelessness - and then there is increased overprotection, anxiety, disappointment. But modern medicine copes well with such situations, and with proper home care and a properly selected rehabilitation course (specialists will take care of this!) Even very premature babies not only survive, but by the age of 1. 5–3 years they catch up with their peers. nine0005
5–3 years they catch up with their peers. nine0005
An object of increased attention
Every newborn needs the attention of visiting nurses and pediatricians, but in case of premature birth, the baby is constantly monitored by several specialists: a pediatrician, a cardiologist, a neurologist, an ophthalmologist, and, if indicated, a pulmonologist, an orthopedist, an immunologist. Such children can be registered at the dispensary for up to 7 years. This does not mean that all premature babies will necessarily have health problems, but since the risk is high, it is better for parents to be on the lookout and remember that any little things can matter. Do not be afraid to ask the doctor absolutely any questions, no matter how ridiculous they may seem to you! nine0005
The first weeks in the maternity hospital are a very difficult period, when in no case should you let feelings of guilt, anxiety and fear take over all your thoughts. It is necessary to maintain a positive attitude in order to convey your calmness to the baby. For support, you can contact a psychologist who is in the perinatal center or maternity hospital.
For support, you can contact a psychologist who is in the perinatal center or maternity hospital.
It is very dangerous for a premature baby to meet with infections. Therefore, after the child is discharged home, it is better to ask strangers to refrain from visiting for the time being. But it’s better for a child to get to know all the pets better so that he can get used to their microflora and develop immunity. nine0005
Sleep and temperature
In the first month, a premature baby will sleep a lot. Some of these babies sleep up to 22 hours a day. In a dream, they gain strength. Many parents worry, but this amount of sleep is nothing to worry about. In a month, the baby will get stronger, will be more awake, will, like all other babies, worry about colic, be capricious and behave more actively.
Watch the temperature! A premature baby has poorly developed subcutaneous tissue and a completely immature thermoregulation system, so he needs more heat. The air in the room should be warmed up to 22-25ºС.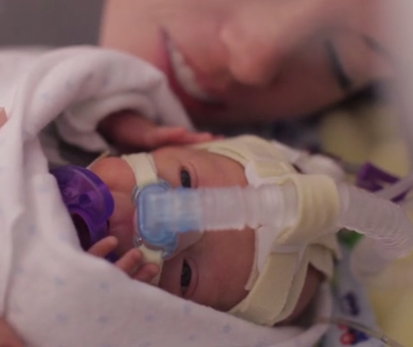 The baby himself is additionally heated with heating pads with water at 60-65ºС. You can use from one to three heating pads, depending on the degree of prematurity of the child and the temperature in the room. Warmers should be wrapped in towels or diapers and placed under the blanket at the feet, as well as on top of the blanket on the sides of the child, at a palm's distance from him. No direct contact of heating pads with the baby's skin! To constantly monitor the temperature under the blanket next to the baby, you can put a thermometer. You need to change the heating pads every one and a half to two hours, alternately, in order to maintain constant heating. But the face of a newborn must be left open (without covering it with a blanket). nine0005
The baby himself is additionally heated with heating pads with water at 60-65ºС. You can use from one to three heating pads, depending on the degree of prematurity of the child and the temperature in the room. Warmers should be wrapped in towels or diapers and placed under the blanket at the feet, as well as on top of the blanket on the sides of the child, at a palm's distance from him. No direct contact of heating pads with the baby's skin! To constantly monitor the temperature under the blanket next to the baby, you can put a thermometer. You need to change the heating pads every one and a half to two hours, alternately, in order to maintain constant heating. But the face of a newborn must be left open (without covering it with a blanket). nine0005
By the end of the first month, the baby will begin to “keep” body temperature on his own and gradually it will be possible to refuse artificial heating. The body temperature of a premature baby should be measured in the morning and in the evening. According to the doctor's recommendations - more often, sometimes with each swaddling. This must be done without undressing the baby.
According to the doctor's recommendations - more often, sometimes with each swaddling. This must be done without undressing the baby.
Meals by the hour
A child, even a sleeping one, also needs food, so at first it is better to feed not on demand, but at the frequency indicated by the doctor. nine0005
The only person who definitely needs breastfeeding is a baby in a hurry to be born. Breast milk prevents a number of neurological problems, improves immunity. Breast milk is living tissue in the body that adapts to the needs of the baby. There are no analogues of such food!
The immature intestine perceives food very poorly, but iron, for example, from breast milk is absorbed by the child by 70% (from mixtures - only 10%). The mother of a premature baby needs to make every effort to maintain lactation by the time the baby is discharged from the hospital. If this fails, you can seek help from a lactation consultant. If the baby does not have the strength to suck, milk must be expressed and given from a pipette or from a nipple.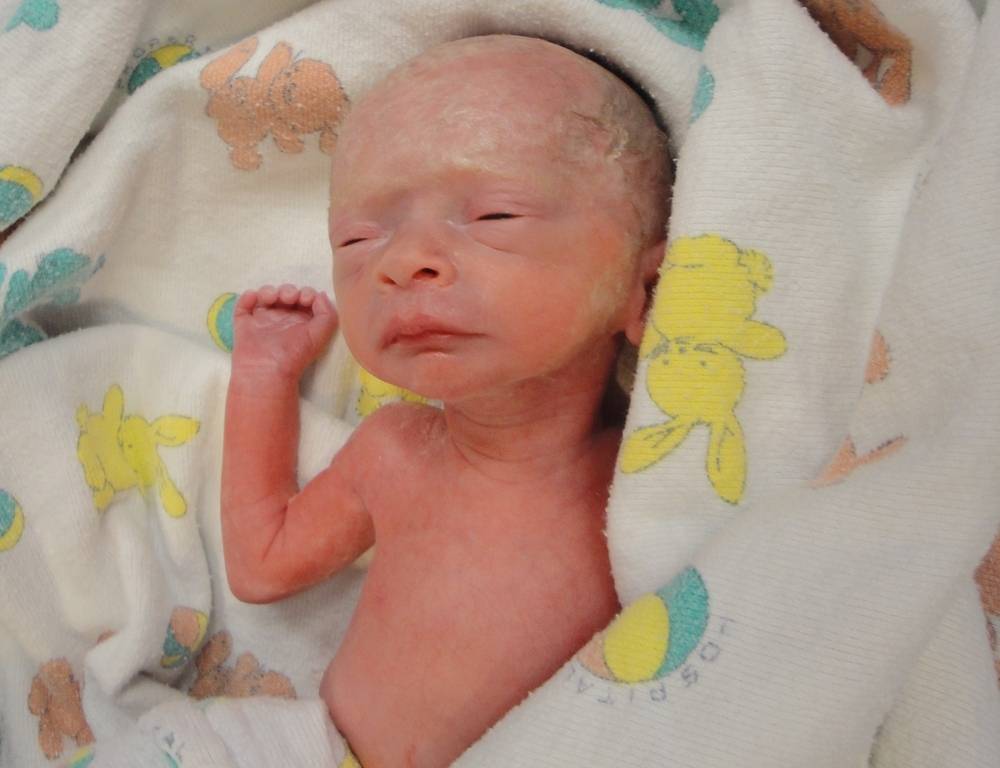 nine0005
nine0005
Daily care
Clothes
If the baby is born weighing more than 2 kg, it does not need to be wrapped up. He will fit the same clothes as other (term) babies. Another thing is crumbs weighing less than 2 kg. They need a lot more things. The wardrobe should have a knitted cap, a knitted blouse with a hood and sewn-in sleeves, and sliders. A child dressed in this way can be wrapped in a flannel blanket or put in a woolen envelope, and covered with a flannel blanket on top. Only the face remains open! By the way, there are special sliders with natural wool lining in the area of the feet, which stimulates reflex zones, providing not only a warming, but also a tonic and restorative effect. nine0005
By the end of the first month, you can gradually give up the envelope and blanket. Since in such babies special attention should be paid to the development of the respiratory system, they should not be constrained by tight swaddling. In order for all parts of the lungs of a newborn to breathe evenly, it must be regularly shifted from one side to the other.
Bathing…by weight
Babies under 1500g do not need daily bathing for the first 2-3 weeks. For the rest of the newborns with low body weight, it is enough to wait 7-10 days with a bath. The temperature of the water in the bath should be 38ºС, and in the room where bathing takes place - at least 25ºС. nine0005
Short walks
Be very careful with walks: a sudden change in temperature can adversely affect your baby's health. Premature babies born with a body weight of more than 1500 g can be taken out for walks for 10–15 minutes, starting from the age of two weeks (during the warm season at an air temperature of 25–26ºС). The time spent outdoors can be gradually increased to 1–1.5 hours.
In autumn and spring (at air temperatures up to 10ºС), you can only walk with babies aged 1–1.5 months weighing at least 2500 g. At air temperatures below 8–10ºС, you can walk with premature babies only from 2 months when they reach a body weight of 2800–3000 g.
Life under observation
Premature babies are observed by doctors at the place of residence. Periodic consultations of specialists, primarily a neurologist, are mandatory. At the age of 1-2 weeks and beyond, to prevent rickets, vitamin D is added to food as prescribed by a doctor, massage and hardening are prescribed.
Periodic consultations of specialists, primarily a neurologist, are mandatory. At the age of 1-2 weeks and beyond, to prevent rickets, vitamin D is added to food as prescribed by a doctor, massage and hardening are prescribed.
Vaccinations for premature babies require an individual approach. Each of them has their own vaccination schedule. For those who are healthy and were born with a body weight of more than 2000 g, the vaccination schedule will not differ from full-term children. Babies born weighing less than 2000 g are not vaccinated with BCG at the maternity hospital. It will be done when the baby weighs at least 2500 g within the time frame individually determined by the doctor. nine0005
During the first two years, a premature baby is under the supervision of a cardiologist. At 2, 4, 6 and 12 months of a child's life, electrocardiography (ECG) is necessary to assess the work of the heart muscle. At 2, 6, 12 and 24 months, it is advisable to conduct an ultrasound examination of the heart (echocardiography - ECHO-KG).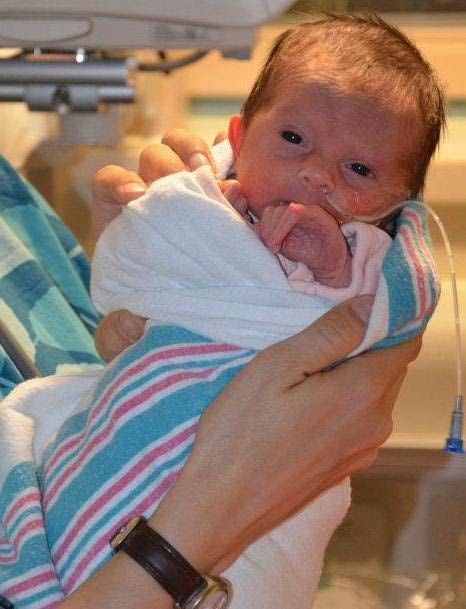
Although all these procedures may take a long time, do not refuse such services. The most difficult thing for families with premature babies is to admit that some problems still remain, because you really want to forget all the difficulties of the first weeks. But regular monitoring is the surest way to avoid complications. nine0005
Warm environment
Not only the ambient temperature is important for the baby. He just needs your warmth. Try to press the baby to your own body as much as possible - skin-to-skin contact is very important for him now. A sling is very good for these purposes. After all, a premature baby needs to be conveyed in the literal sense! In one American hospital, a volunteer named David Deutschman has been helping to nurse newborns in the intensive care unit for more than 12 years. He is exactly what "nourishes" babies. He just holds and wears it on his hands. David comes to the hospital and spends time with premature babies whose parents cannot always be near them.